Bio 006 - 7LA: Cell Respiration & Plant Tissues
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Cell Respiration
Process of converting glucose into energy.
Metabolism
Chemical processes for maintaining life.
Tissue
Collection of cells with common structure and function in an organism.
Indeterminate Growth
Continuous growth throughout an organism's life.
Meristematic Tissue
Embryonic tissue responsible for plant growth (forever young)
Permanent Tissue
Mature tissue that has fully differentiated (mature/ evolved)
Simple tissues: made of 1 cell type
Complex tissues: made of multiple cell types
Apical Meristem
Tip of stem and root
Responsible for primary growth
Increases length
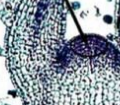
Lateral Meristem
Sides of stems and roots
Responsible for secondary growth
Increases width
Primary Growth
Growth that increases length of plant; develops first
Secondary Growth
Growth that increases width of plant; develops second/later
Protoderm
Forms the epidermis from apical meristem.

Ground Meristem
Inside protoderm; forms ground tissue from apical meristem.

Procambium
Forms primary vascular tissue from apical meristem.

Vascular Tissue
Transport system for water and nutrients. (bundle cap, phloem, xylem, fascicular cambium)
Phloem
Transports sugars and food throughout the plant.

Xylem
Transports water and minerals from roots.
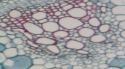
Parenchyma
Big, thin-walled cells used for storage.
(Simple Permanent Tissue)
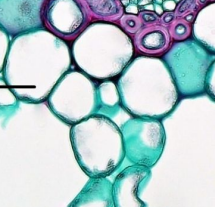
Collenchyma
Cells providing support with irregular walls, used for support/protection
(Simple Permanent Tissue)
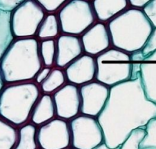
Sclerenchyma
Thick-walled cells for structural support/protection
Fibers: long and narrow
Sclereids: clumped
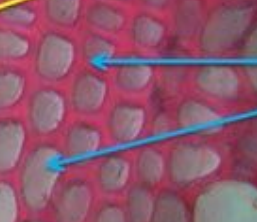
Sieve Tube Element
Main component of phloem for transport.
big tube
forms sieve tube
Vessel Elements
Main component of xylem for water transport.
Tracheids
Xylem cells with pores for horizontal transport.
Control Group
Group without treatment for comparison.
Anaerobic Respiration
Energy production without oxygen, like fermentation.
Vascular cambium
Secondary vascular tissue secondary xylem (inside) & phloem (outside)
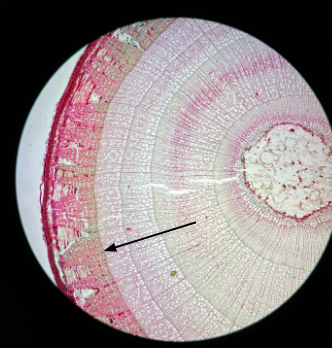
Cork cambium
Replaces epidermis with periderm/cork (bark)
companion cells
Edge of sieve tube, control flow
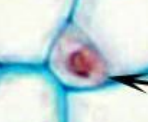
Sieve plate
Looks like a sieve, sits between cells in tube
5
How many cells are participating in Phloem?
4
How many cells are participating in Xylem?
xylem vessel
one-way only
water and minerals
no end walls between cells
thick walls stiffened with lignin
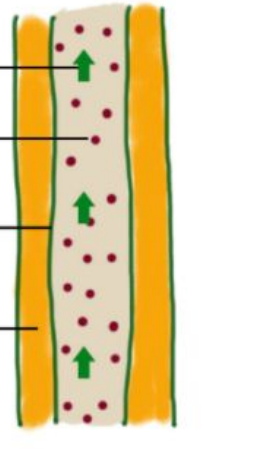
phloem vessel
two-way flow
water and food
cells have end walls with perforations
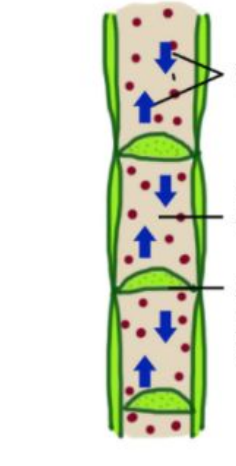
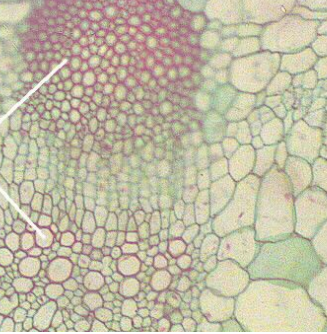
Vascular bundles
identify image
(hint: looks like a candy corn)
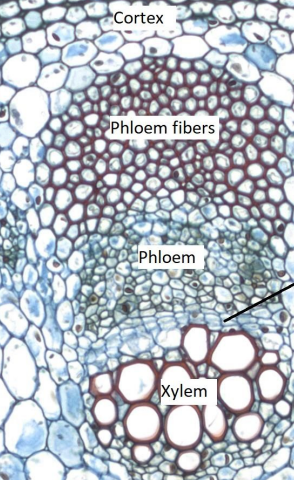
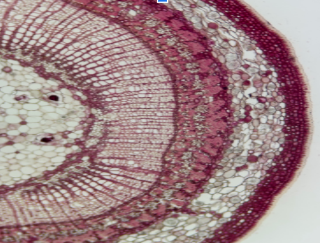
Helianthus Stem
Primary, Simple Permanent:
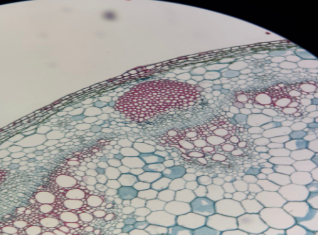
Coleus Stem Tip
Meristematic Tissue:
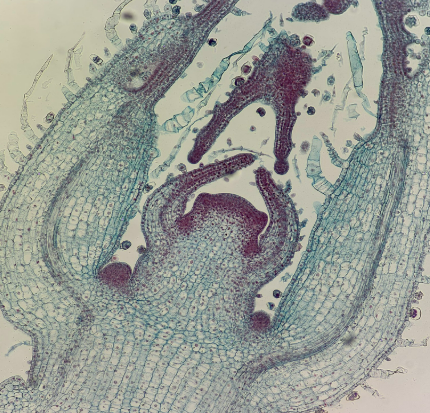
Tilia Stem
Secondary Growth: