Chapter 19 - Viruses / CRISPR / Animal Viruses
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
What is a virus?
An infectious particles that consists of nucleic acid that’ll be packaged in a protein coat. They can’t reproduce or carry out metabolism out of a host cell. Viruses are also much simpler in structure.
What are three basic categories of classification for Viruses?
Type of protein shell, type of nucleic acid, and whether they have a membrane envelope or not
Capsids are made up of…
capsomeres
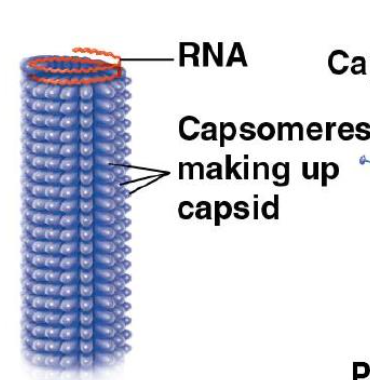
How can you characterize a caspid?
The shape of a viral capsid, rod-shaped, polyhedral, or complexity in shape.
What kind of forms can viral genomes come in?
DNA or RNA
Does the presence of a viral envelope impact a viruses' form?
Yes
What is Host Range?
A limited range of host cells that can be infected.
What are the types of host ranges?
Broad Host Range and Narrow Host Range
What is Broad Host Range?
When a virus can Infect multiple species.
Examples: West Nile and Eastern Equine Encephalitis (EEE) which infect mosquitoes, birds horses, and humans
What is Narrow Host Range?
When viruses can only Infect a single species.
Examples: measlses and polio only infect humans
Viruses can transition between having a broad and ________________?
Narrow Host Range
Viruses are tissue specific.
True.
What are some examples of tissue specific viruses?
Human cold virus - infect only the cells lining the upper respiratory tract
HIV (AIDS virus) - binds to specific receptors on certain types of white blood (immune) cells
What’s the general process of viruses infecting individuals
The viral genome enters the host cell in a variety of ways.
Once the viral genome is in the cell, the cell begins to manufacture viral proteins
The virus uses host enzymes (RNA polymerases), ribosomes, tRNAs, amino acids, ATP, and other molecules to perform replication and transcription.
Once everything is copied and assembled, they will spontaneously self-assemble into new viruses and exit the cell.
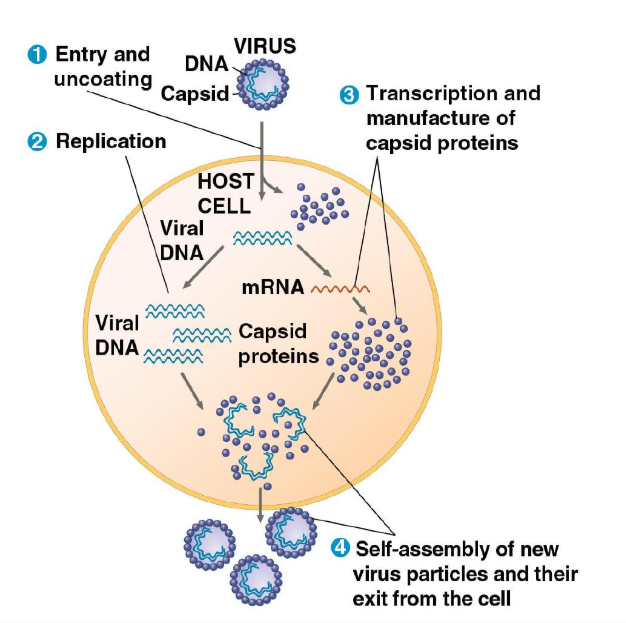
What is the step “recognition of host”?
Viruses reocgnize host by “matching” proteins on their surface,
It’ll be brought into the cell and the viral genome can take over.
Bacterphases will use the tail to pierce the cell wall and inject the cell.
What are the general types of viruses?
Viruses that only attack bacteria, fungi, plants, and animals. All organisms are susceptible to viruses of some kind.
What are bacteriophages?
Viruses that infect bacteria.
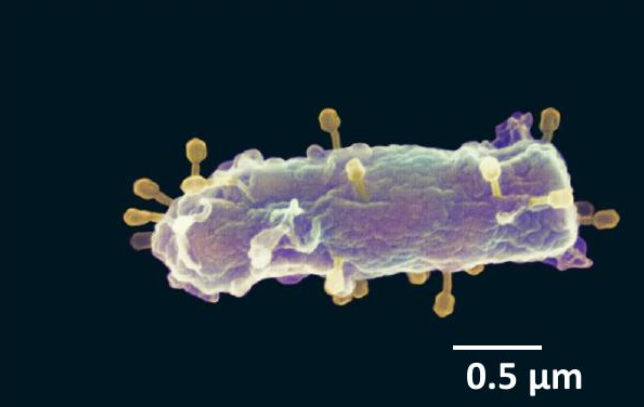
What are the two categories of Bacteriophages?
Virulent phages and temperate phages.
Virulent Phages are…
Bacteriophages that can only produce via lytic cycle.
Temperate phages are…
Bacteriophages that are capable of both lytic and lysogenic cycle.
What is the Lytic Cycle?
(We have an infection, replication, and new phages. The new phages lyse open the cell and begin to infect other bacteria)
A phage replicative cycle that culminates in the death of the host cell.
The lytic cycle produces new phages and lyses (breaks open) the host’s cell wall, releasing the progeny viruses.
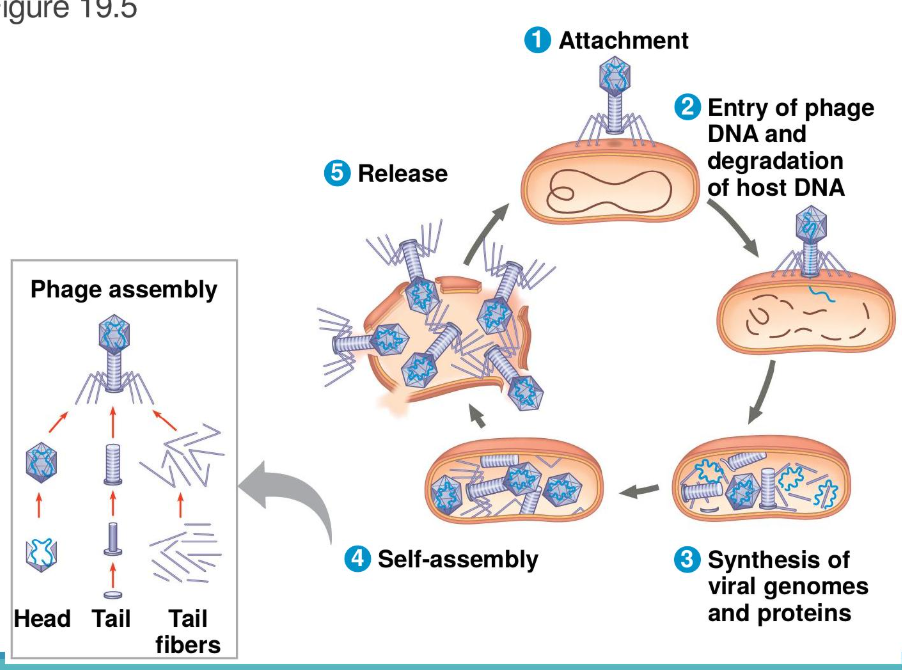
What is the Lysogenic cycle?
General: Replicates the phage genome without destroying the host.
Phage will be incorporated into the host cell’s chromosome every time the cell replicates and divides, now called a Prophage. (Passing onto the daughter cells) It’ll save it’s time until it’s environmental conditions are good, so it can trigger the virus genome, exiting the bacterial chromosome and inducing Lytic cycle.
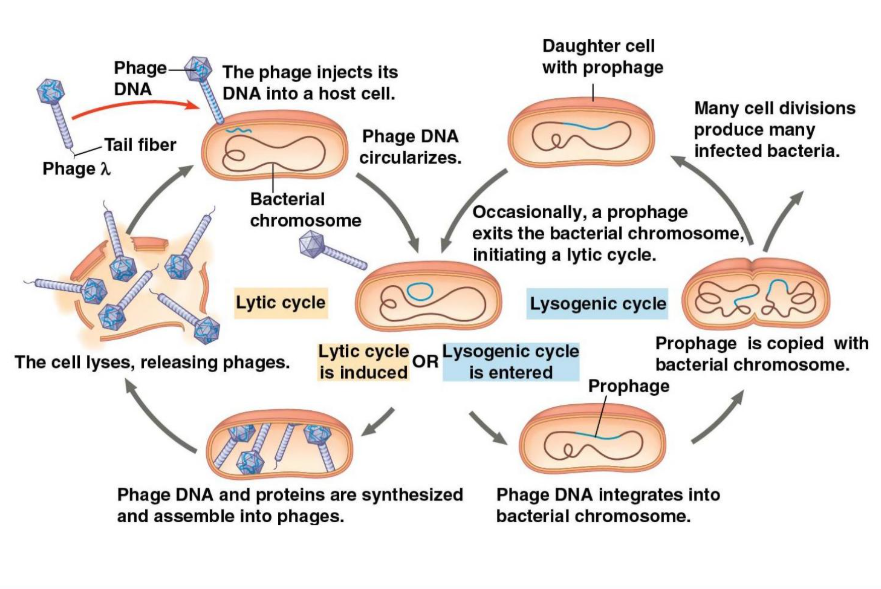
In some cases, prophages can cause the host bacteria to ___________.
make toxins.
What are some ways to defend against the phage?
Natural selection favors bacteria mutants where receptor proteins no longer recognize viral surface proteins.
Restriction enzymes in bacteria chop up phage DNA.
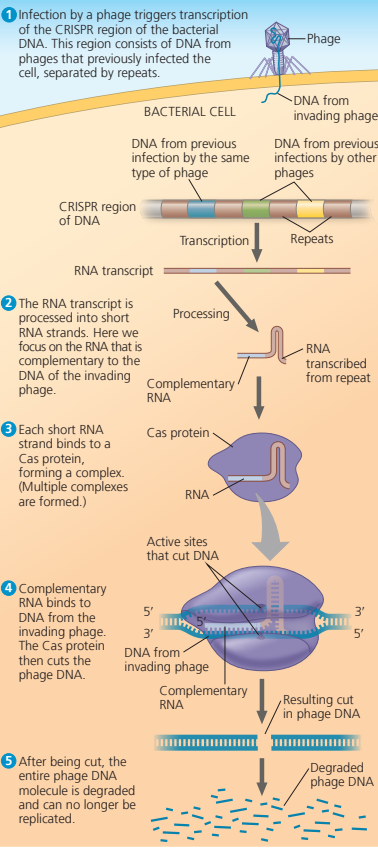
CRISPR-Cas system (clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) is a type of “immune” system for bacteria
How does the CRISPR-Cas system work?
Recognizes and lyse the cell before it can replicate.
A system in prokaryotes, bacteria, and archaea
Is CRISPR universal?
Yes, it’s universal.
What are the steps to using CRISPR in others?
Design a guide RNA that’s complementary to the sequence you wanna target
Insert guide RNA and Cas protein in the cell
Cas9 cuts at specific place in DNA
Cell’s own mechanisms repairs the double stranded break
Re
Non-homologous End Joining:
Homology Directed Repair:
What are key characteristics to classify viruses that infect animals?
RNA or DNA genome
What are the different classes of animal viruses?
Double-Stranded DNA
Single-Stranded DNA
Double-Stranded RNA
Single-Stranded RNA; Serves as mRNA
ssRNA: Serves as a template for mRNA Synthesis
ssRNA: Servers as a template for DNA synthesis
Many viruses that infect animals have a _________________.
membranous envelope.
What is the viral envelope derived from?
The host cell’s plasma membrane as the viral capsids exit.
What is Hemagglutinin?
“H”; a viral surface protein that helps the virus attach to host cell
What is Neuraminidase?
“N”; an enzyme that helps release new viruses from infected cells.
What is another name for “stomach flu?”
Gastroenteritis.
Examples: Norovirus - ssRNA, positive sense, non-enveloped
Rotavirus - Class III double-stranded RNA, non-enveloped
Retroviruses use ___________ (their own enzyme) to copy their rNA genome in DNA.
reverse transcriptase
What is the host genome called in a Retrovirus?
Provirus
How much of the human genome is made up of viral DNA from retroviruses?
8%.
What are the characteristics of a Class 1 animal virus?
Double-Stranded DNA
What are the characteristics of a Class 2 animal virus?
Single-Stranded DNA
What are the characteristics of a Class 3 animal virus?
Double-Stranded RNA
What are the characteristics of a Class 4 animal virus?
Single-Stranded RNA; Serves as mRNA + Positive Sense
What are the characteristics of a Class 5 animal virus?
Single-Stranded RNA; Serves as a template for mRNA Synthesis + Negative Sense
What are the characteristics of a Class 6 animal virus?
ssRNA; Serves as a Template for DNA Synthesis + Positive Sense
What are some older vaccine platforms?
“Live attenuated vaccines” and “Inactivated pathogen vaccines.”
Taking natural viruses but changing them in some way so that you don’t get sick.
What are some Newer vaccine platforms?
“Adenovirus-vector vaccines”: Actually using a natural virus as a means to get DNA into cells…
mRNA Vaccines
What does the newer methods of vaccination do?
Both adenovirus-vector vaccines are used to insert genetic information on how to build SARS-coV-2 spike proteins.
Where do glycoproteins bind to on a viral envelope?
Specific Receptor Molecules on the surface of a host cell.
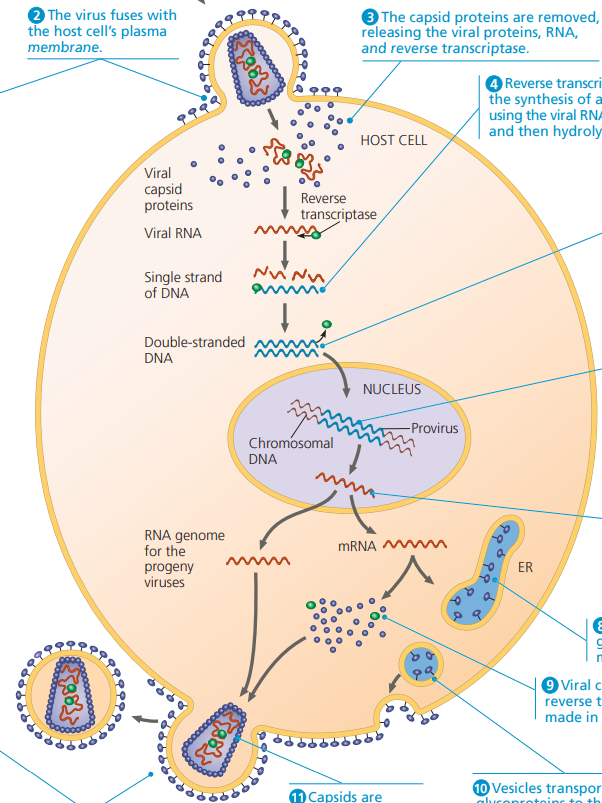
How does the replicative cycle function in Retroviruses?
Viruses are fused with the host cell’s plasma membrane, releasing the viral proteins: RNA and reverse transcriptase.
Reverse transcriptase catalyzes the synthesis of the second DNA strand complementary to the first, copying their RNA genome into DNA.
The viral DNA is the integrated into the host genome, and remains a permanent resident of the host cell.
RNA polymerase transcribes the proviral DNA into RNA molecules for progeny viruses and as mRNAs for translation into viral protein.
The RNA molecules function both as mRNA for synthesis of viral proteins and as genomes for new virus particles.
Glycoproteins are made in the ER whereas Viral capsid proteins and reverse transcriptase are made in the cytosol.
These molecules are transported via vesicles, and are assembled alongside Capsids to form new viruses… budding off from the host cell.
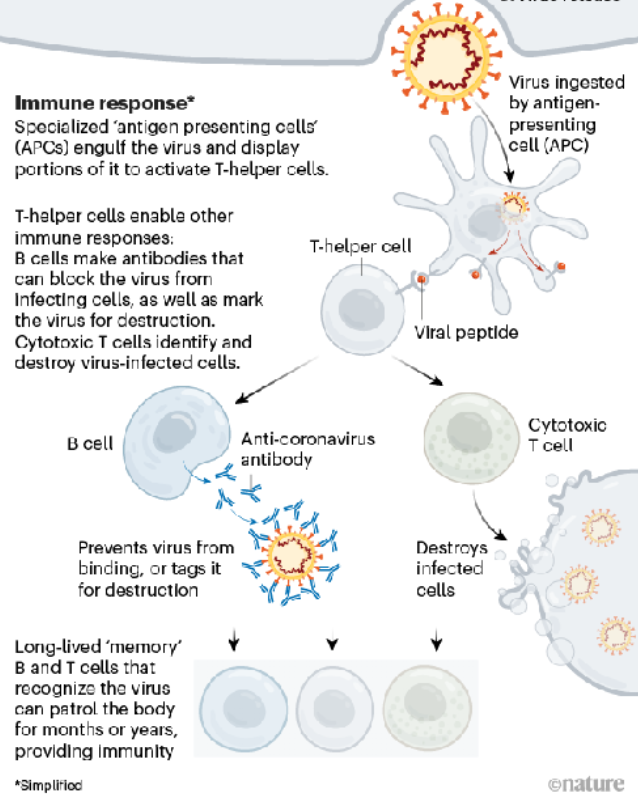
Immune Response: What do antigen-presenting cells (APCs) do?
They ingest and process pathogens, and display antigens to activate T-helper cells.
Immune Response: What is the main function of T-helper cells?
Identify and destroy virus-infected cells.
Immune Response: What do antibodies do?
They either prevent viruses from binding or tag them for destruction.
Immune Response: What is the purpose in exposing T-cells and B cells to virsus?
So that’ll they’ll remember the virus and patrol the body, either preventing it from binding or destroying it on sight… offering months or years of immunity.
Describe the general process of Immune Response
Image.
Describe the general process of Viral Infection
The virus will attach itself to specific receptors on the surface of the human cell, entering by either fusing with the cell membrane or taken in by Endocytosis (via vesicles).
Once inside: the initial virus will begin to break down and it’s RNA is released. This released viral RNA will be translated into viral proteins… eventually assembling new viral proteins and genomes to create a newly replicated virus, soon releasing from the human cell via budding (wrapping itself in a piece of the host’s cell membrane), lysis (exploding the host cell), or exocytosis (merging the virus with the host’s cell membrane, releasing it’s materials outside).
How does the CRISPR-Cas system function?
When a phage infects a bacterial cell that has the CRISPR-Cas system, the DNA of the invading phage is stored, integrated into the genome between two repeat sequences.
Any further attempts by the same type of phage infecting the cell triggers Transcription of the CRISPR region into an RNA molecule that's complementary to the DNA of the invading Phage
These RNAs are cut into pieces and then bound by Cas proteins, such as the Cas9 protein. The Cas protein uses a portion of the phage-related RNA as a homing device to identify the invading phage DNA and cut it, leading to its destruction.
The invading phage DNA is degraded and can no longer be replicated.