11: GT tract and oral cavity and oesophagus
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Learn componenets
learn components
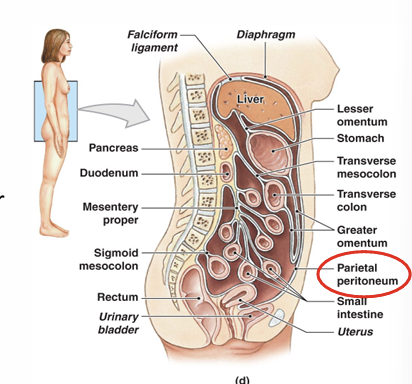
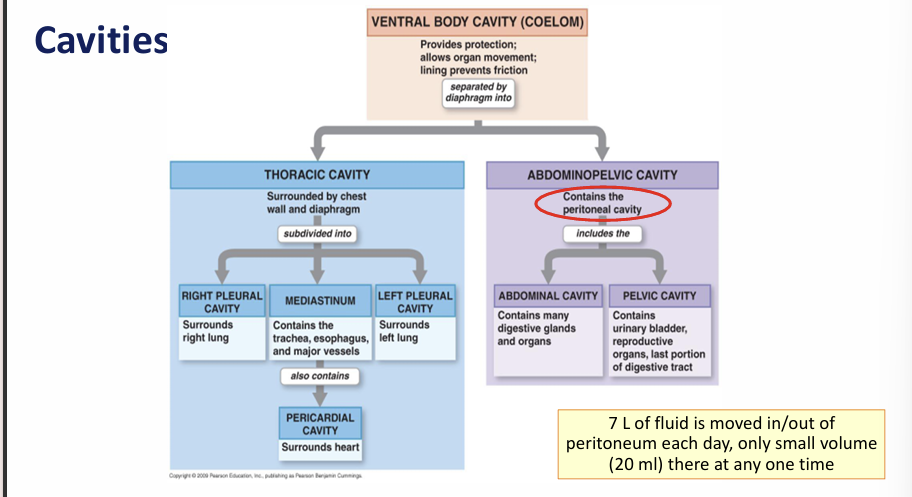
What is the peritoneum?
What is peritonitis?
Disease of the peritoneum- accumulation of peritoneal fluid
Abdominal swelling+pain
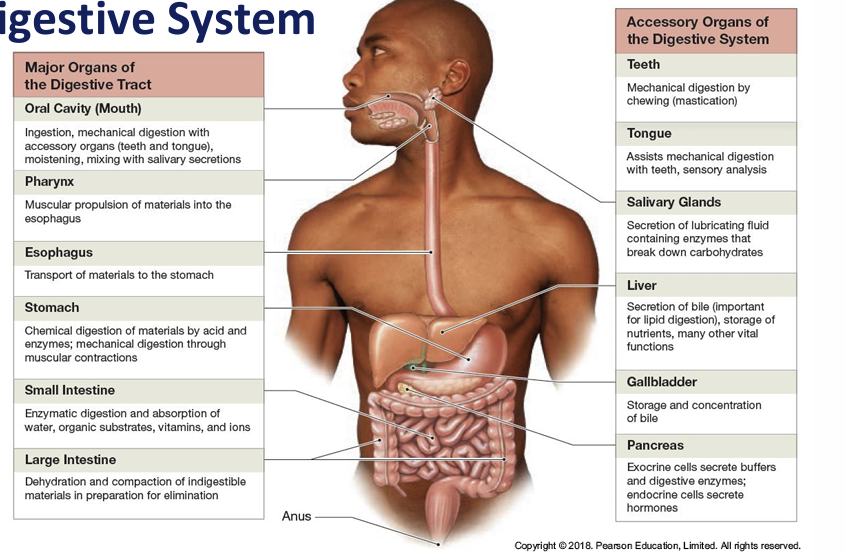
Name 6 functions of the digestive system
Ingestion, mechanical processing, digestion, secretion, absorption and excretion
Function mesentery proper?
Access route for blood/ lymph vessles
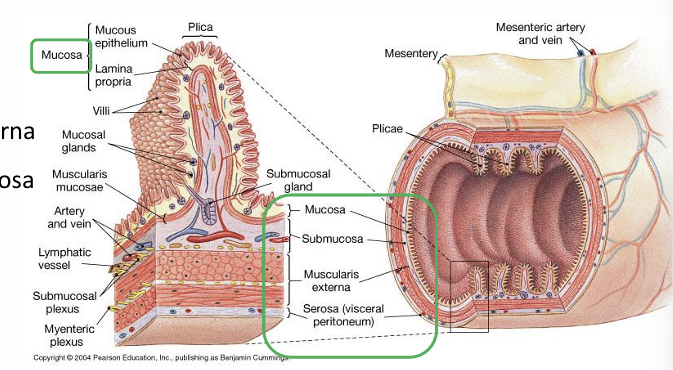
Layers of the gastrointestinal tract- alimentary canal?
Mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, adventitia
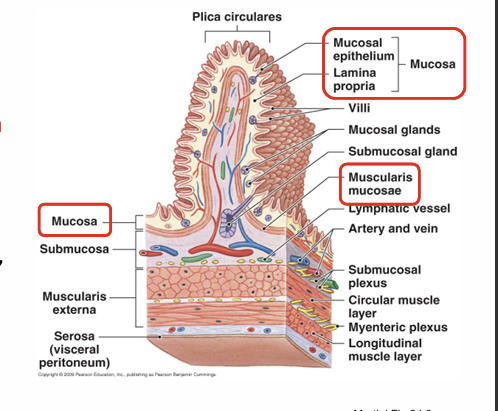
Composition mucosa?
Epithelium and lamina propria
Lamina propria=loose irregulal CT, blood/lymph vessles+ muscularis mucosa
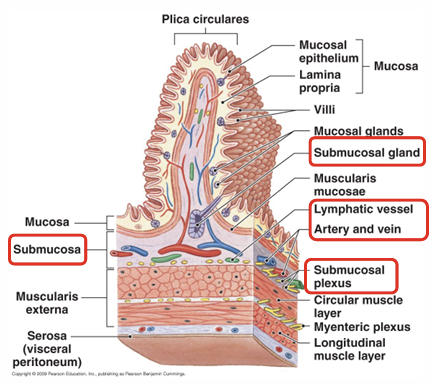
Submucosa composition?
Dense irregular connective tissue
Exocrine glands
Larger blood/lymph vessles
Muscularis externa composition and function function?
Contains circular and longitudinal smooth muscle for peristalsis and segmentation (movement of ingesta).
Controlled by the myenteric nerve plexus; structure and function vary by region.
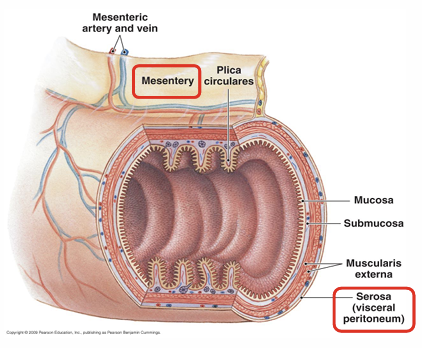
Serosa composition and function?
Loose irregular CT covered by simple squamous epithelia- outermost layer- found in oesophagus
contains vascular and nervous supplies for GIT
SUMMARY
Mucosa lines digestive tract– Moistened by glandular secretions– Lamina propria and epithelium form mucosa
Submucosa – Layer of dense irregular connective tissue
Muscularis externa – Smooth muscle arranged in circular and longitudinal layers – Adventitia
Serosa – Serous membrane covering most of the muscularis externa
Control of digestive function?
Motility
Rate of digestion/absorption
How are digestive functions controlled?
Enteric nervous system
Enterogasterones- hormones
Name 3 ways food is moves in GIT
Peristalsis
Segmentation
Haustral
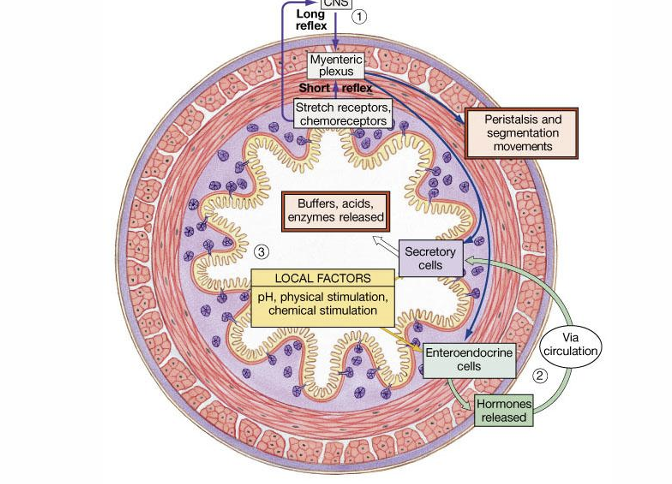
Name 3 ways food is moved along the digestive tract
Local mechanisms- response to pH changes
Neural mechanisms- nervous reflexes
Hormonal mechanisms- enhance/inhibit muscle contraction
Control of digestive system?
Control of Digestive Function:
Short reflexes: Local responses within the GI tract; triggered by local stimuli and act on smooth muscle and glands.
Regulated by enterogasterones
Long reflexes: Involve the CNS; include cephalic reflexes (triggered by sight, smell, thought of food) / afferent signals from the GIT (chemo-, mechano-, and osmoreceptors).
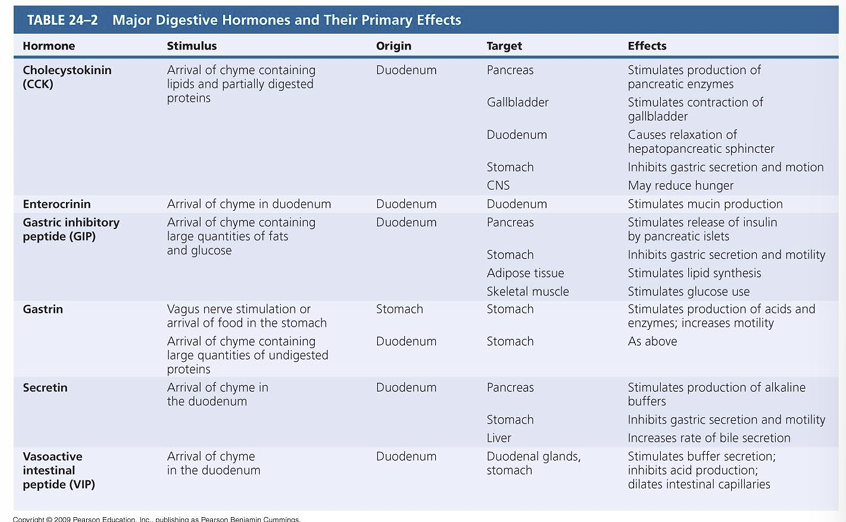
Learn table of gastric hormones
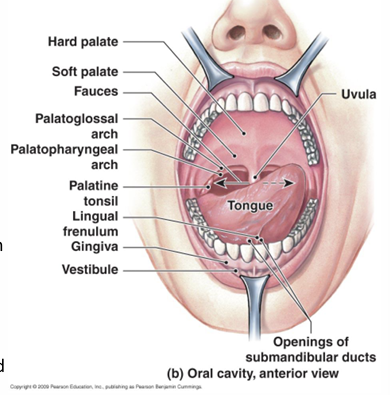
Function of the oral cavity in the GIT
Analysis of food
Mechanical digestion-teeth
Lubrication- mixing mucus+ saliva with food
Limited digestion- chemical digestion
Function oesophagus?
Transport food from pharynx to dtomach
Composition oesophagus?
Walls contain mucosal, submucosal and muscularis layers
Composed of non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Has both smooth and skeletal muscle portions
Muscular layers of oesophagus?
Upper third- skeletal muscle
Lower two thirds- smooth muscle
Upper muscle?
Upper esophageal sphincter- skeletal muscle
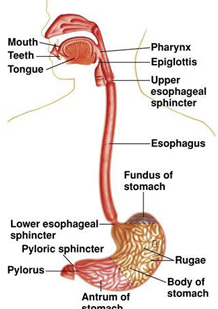
Lower muscle?
Lower esophageal sphincter- smooth muscle
Mucosa, submucosa muscularis externa and adventitia
Learn histology of oesophagus
Name the 3 phases of swallowing
Buccal phase
Pharyngeal phase
Oesophageal phase
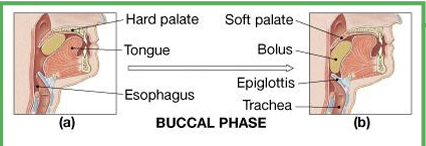
Buccal phase?
Bolus is pressed against the hard palate; tongue pushes it into the oropharynx, raising the soft palate to block the nasopharynx. Reflexes then move the bolus toward the stomach.
Pharyngeal phase?
Begins when the bolus touches the palatal arches and pharyngeal wall.
The larynx elevates and the epiglottis folds to direct the bolus past the closed glottis, while the uvula and soft palate block the nasopharynx.
Oesphageal phase?
The esophogeal phase begins as the contraction of pharyngeal muscles forces the bolus through the entrance to the oesophagus
Once in the oesophagus the bolus is pushed toward the stomach by a peristaltic wave
Dysphagia?
Difficulty swallowing
Barretts oesophagus?
Barrett’s Oesophagus:
A complication of GERD- gastroesophageal reflux disease, caused by acid exposure- reflux. The normal mucosa is replaced by metaplastic columnar epithelium, increasing the risk of oesophageal cancer.