GEOG Exam #2
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
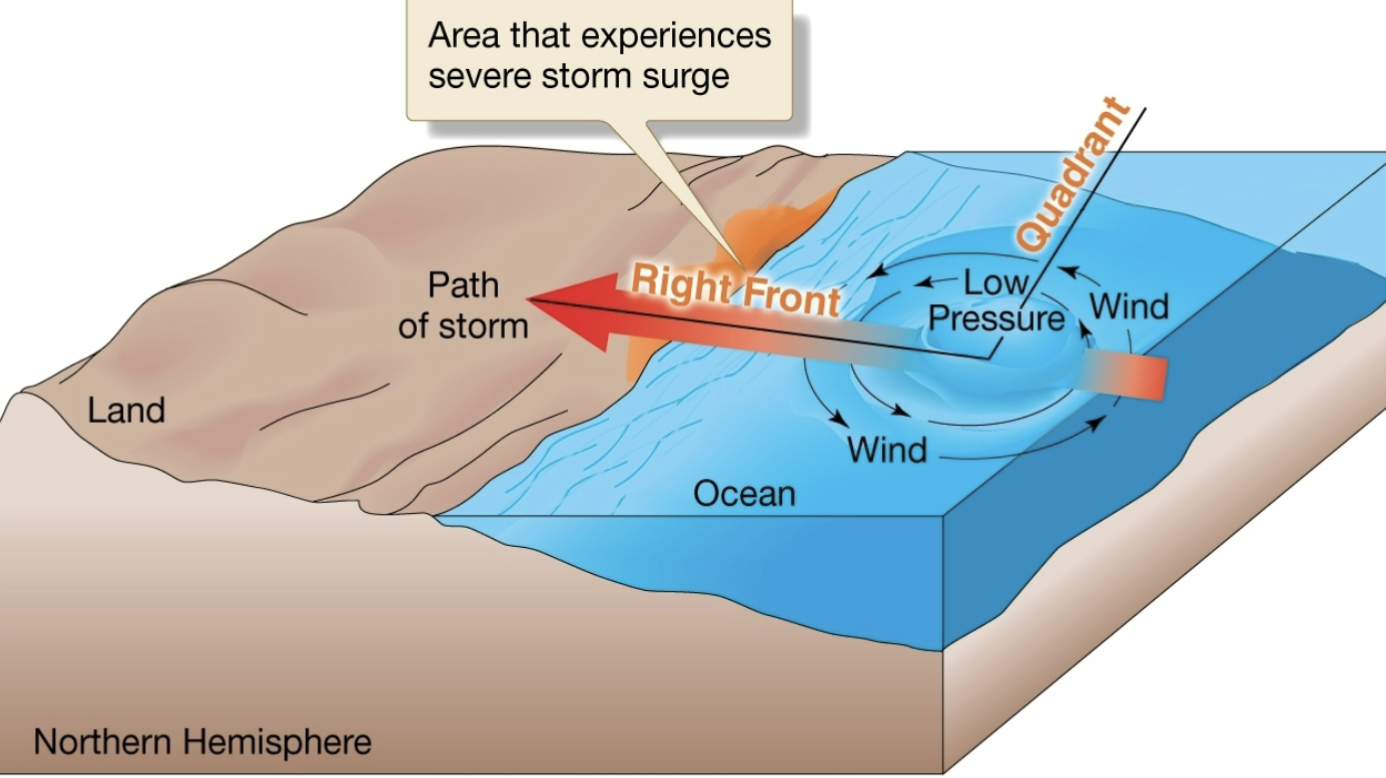
Cyclone
Low pressure air rises and moves in a counterclockwise direction, fueled by warm and moist air.
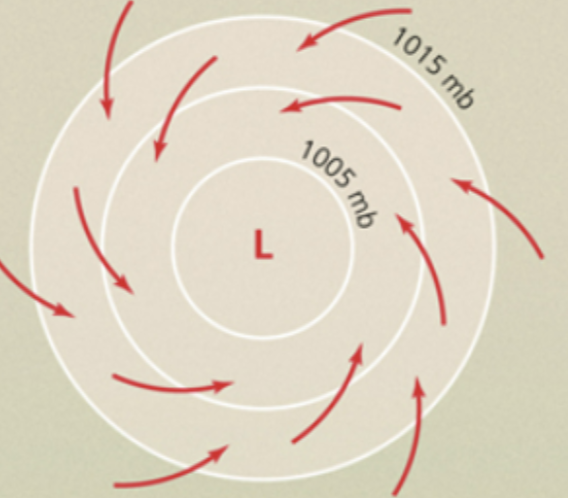
Coriolis Effect
result of Earth's rotation, causing particles in motion to deflect, with high pressure air moving towards low pressure air and being deflected to the right.
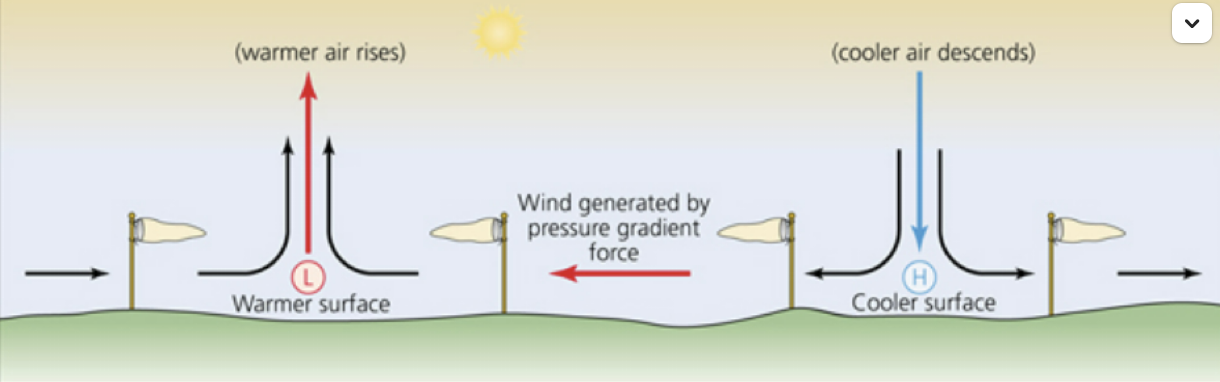
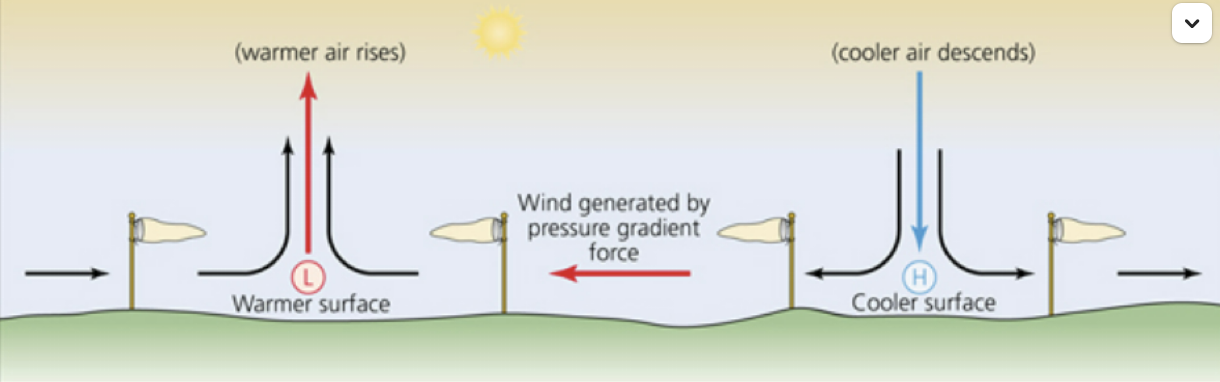
Sea Breeze
occurs due to the differential heating of land and sea surfaces, with land heating up more quickly than the sea, creating a pressure gradient that drives the sea breeze.
Wind directions
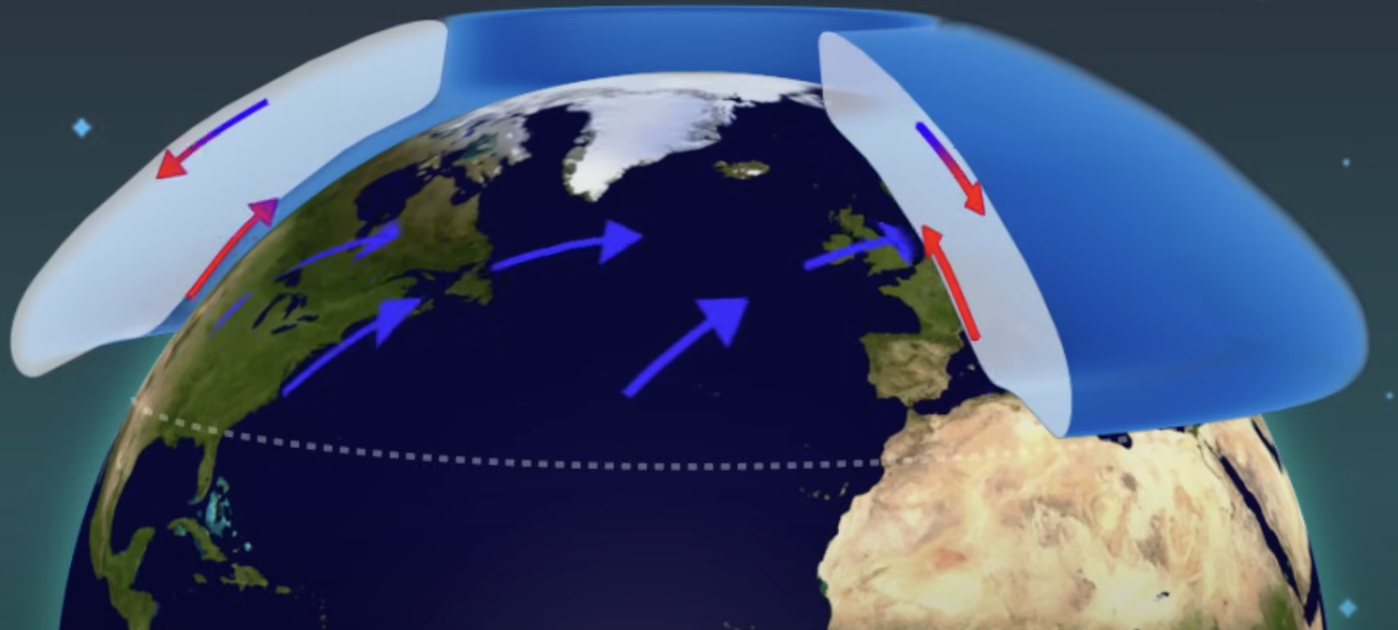
The trade winds, westerlies, and polar easterlies are created by the Earth's rotation, pressure gradient, and Coriolis effect, resulting in prevailing wind directions.
Trade Winds
move from east to west between 0 to 30 latitude,
Jet streams
fast-moving winds that play a crucial role in the weather experience, with speeds over 200 miles per hour and widths of hundreds of kilometers.
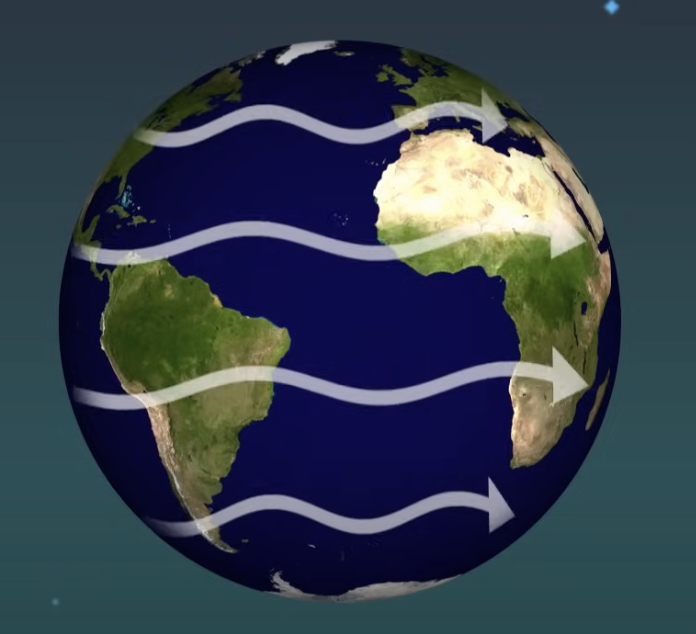

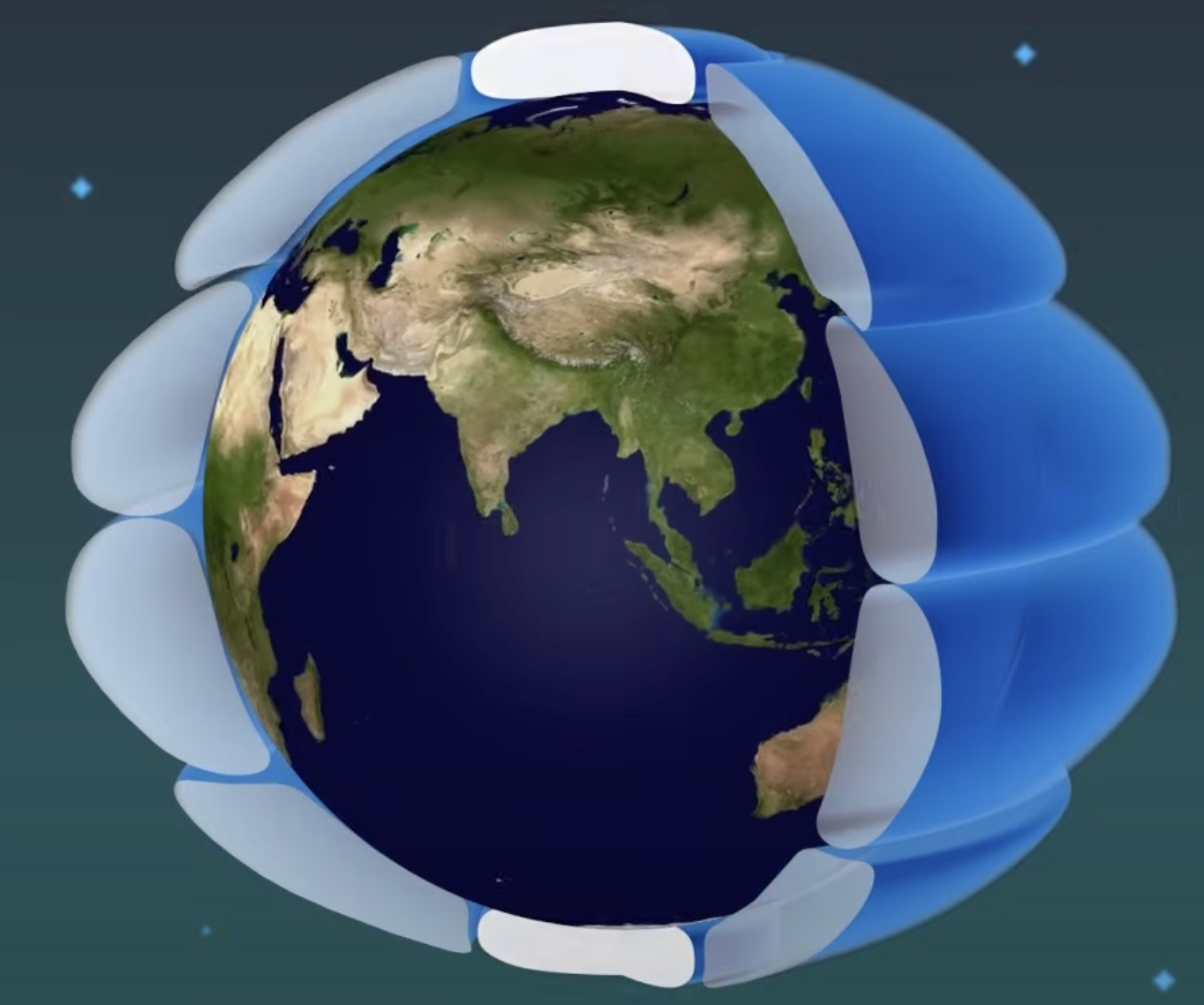
Circulating Cells
transport heat from the equator to the poles, creating areas of high and low pressure.
Rising air = low pressure
creates low pressure, resulting in areas with high rainfall, such as near the equator and the United Kingdom.
Descending Air = High Pressure
creates high pressure, resulting in areas with little rainfall, such as desert regions, including Antarctica, which is the largest and driest desert.
Hadley Cell
large-scale atmospheric circulation cell, warm air rises at the equator and sinks at about 30° latitude, creating trade winds and subtropical highs.
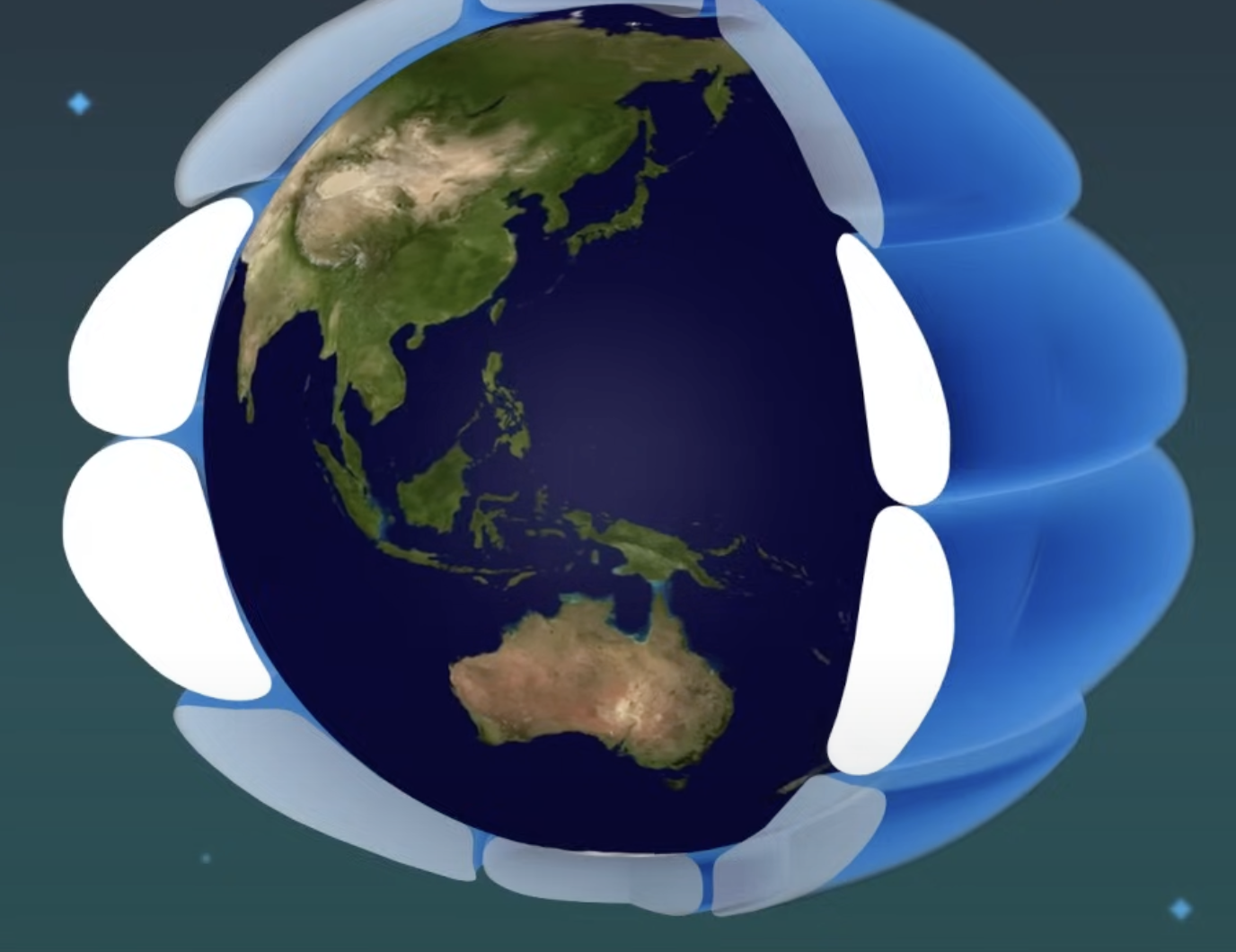

Ferrel Cell
The mid-latitude atmospheric circulation cell between 30° and 60° latitude, with air flowing opposite to Hadley and Polar cells.
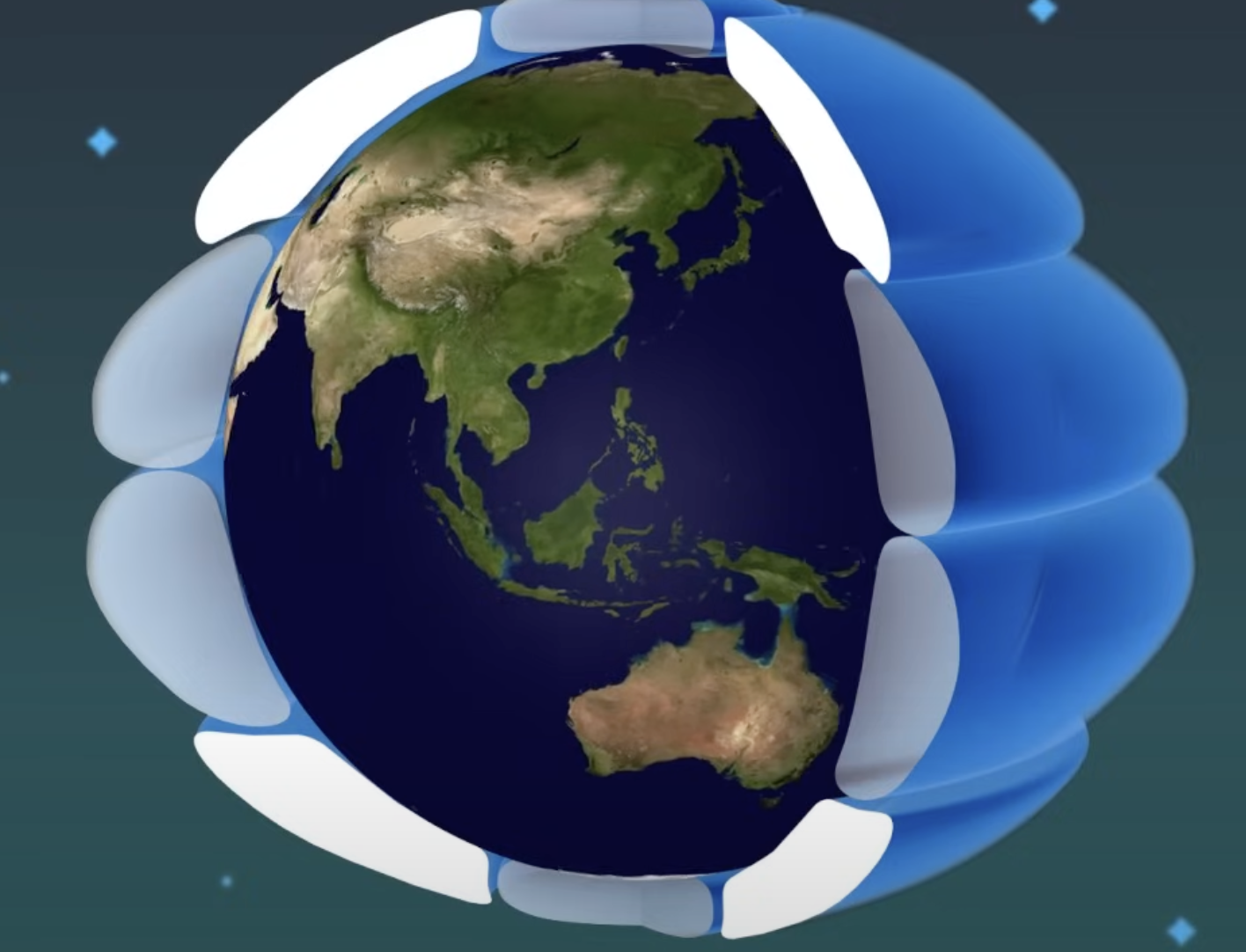

Polar Cell
The circulation cell near the poles where cold, dense air sinks and flows toward lower latitudes.
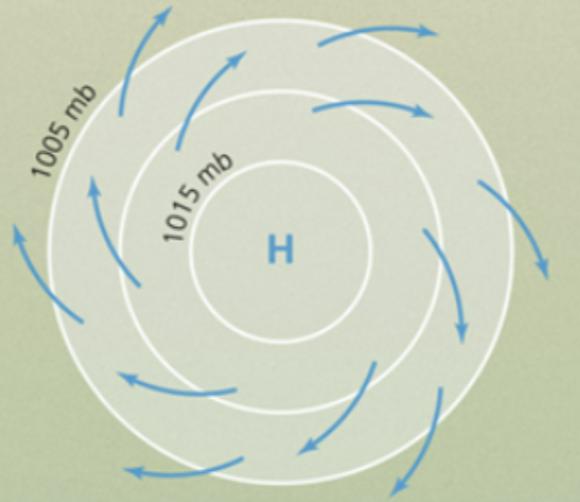
Anticyclone
A high-pressure system characterized by diverging, sinking air and clockwise rotation in the Northern Hemisphere.
Pressure Gradient Force
causes air to move from areas of HIGH pressure —> LOW pressure, driving wind movement.
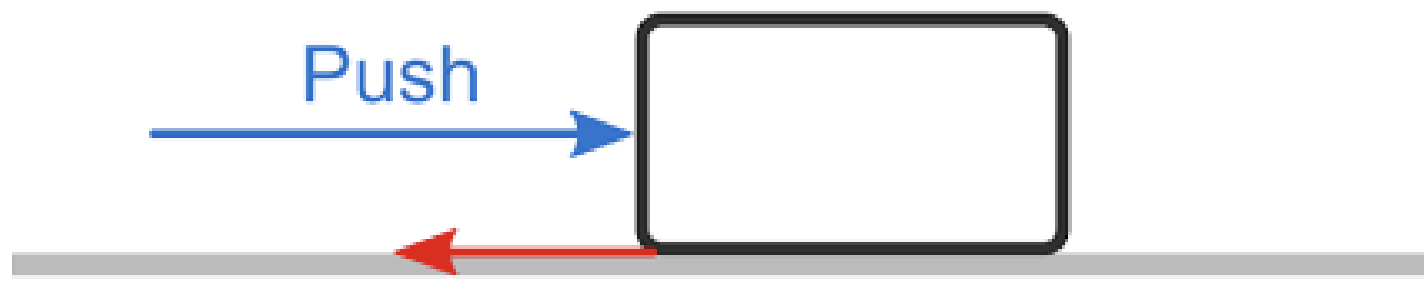
Frictional Force
Cause surface winds to SLOW DOWN and deflect across isobars rather than flow parallel to them.
Air pressure
Gravitational forces and weight of air molecules.
Sea Water Density
Temp differences, salt water dense →sinks
Ekman Transpot
process by which wind directions push water away from the coast, resulting in the replacement of that water with deep ocean water, leading to upwelling and downwelling of water.
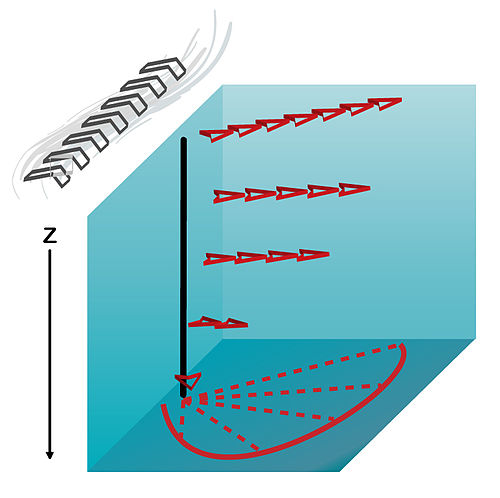
What drives atmospheric circulation?
Uneven solar heating creating pressure differences.
What are ocean currents?
large-scale water movements driven by wind, Coriolis effect, and temperature/salinity differences.
Thermal Circulation
Air movement caused by temperature differences, such as sea breezes.
Atmospheric Pressure Gradient
Change in atmospheric pressure over distance, driving wind flow.
How does Coriolis affect winds?
Deflects winds, shaping global wind patterns (trade winds, westerlies).
vapor pressure
As temperature increases, _____ increases because particles have more energy.
Lifting Mechanisms that produce precipitation
Convergent, frontal, convectional, orographic
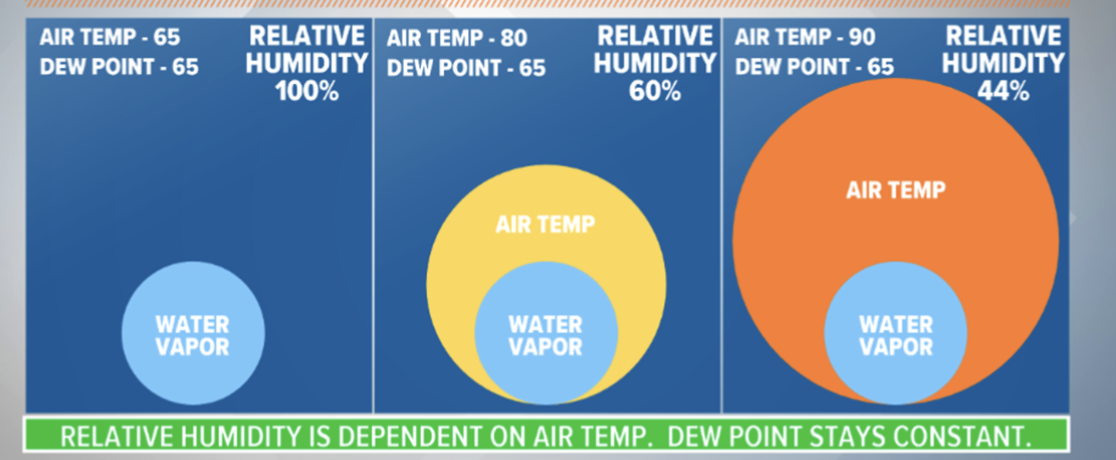
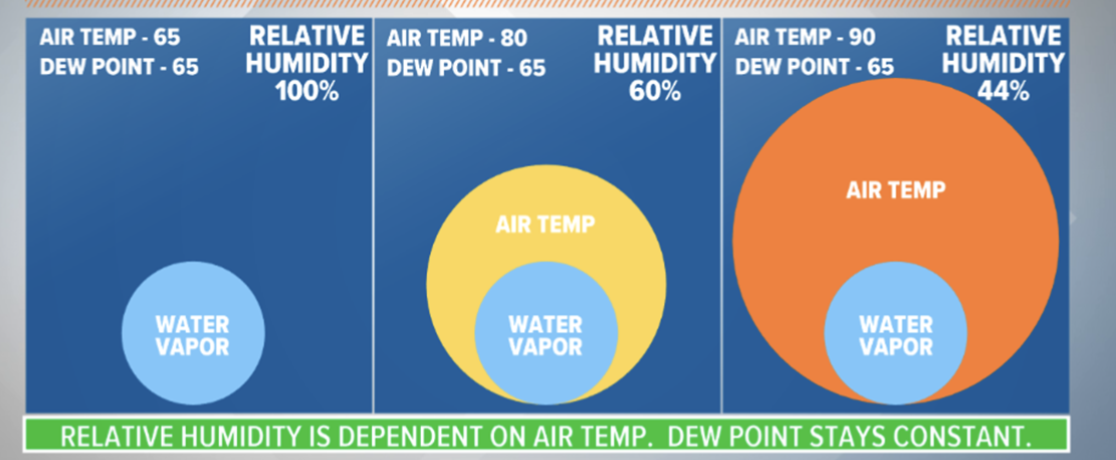
Dew-Point temp.
temperature to which air must COOL for it to become completely saturated with water.
specific humidity
ratio of mass of water vapor to the total mass of air system
relative humidity
water vapor present in air expressed as a % relative to max it could hold at a specific temp.
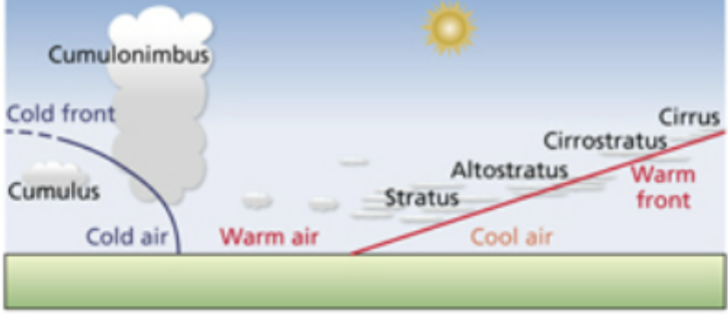
Type of clouds
stratus: layed appearance, cumulus: thick puffy appearance, cirrus: thin wispy streak-like
air masses
large bodies of air w/relatively uniform properties come from specific source regions.
Convergent Lifting
Low pressure at the surface produces converging air that then rises. Ex. hurriences
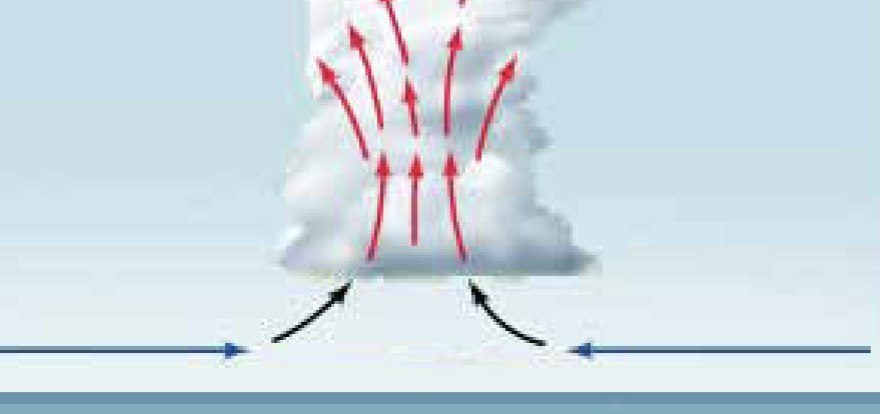
Frontal lifting
collision of large air masses of significantly different temperatures.
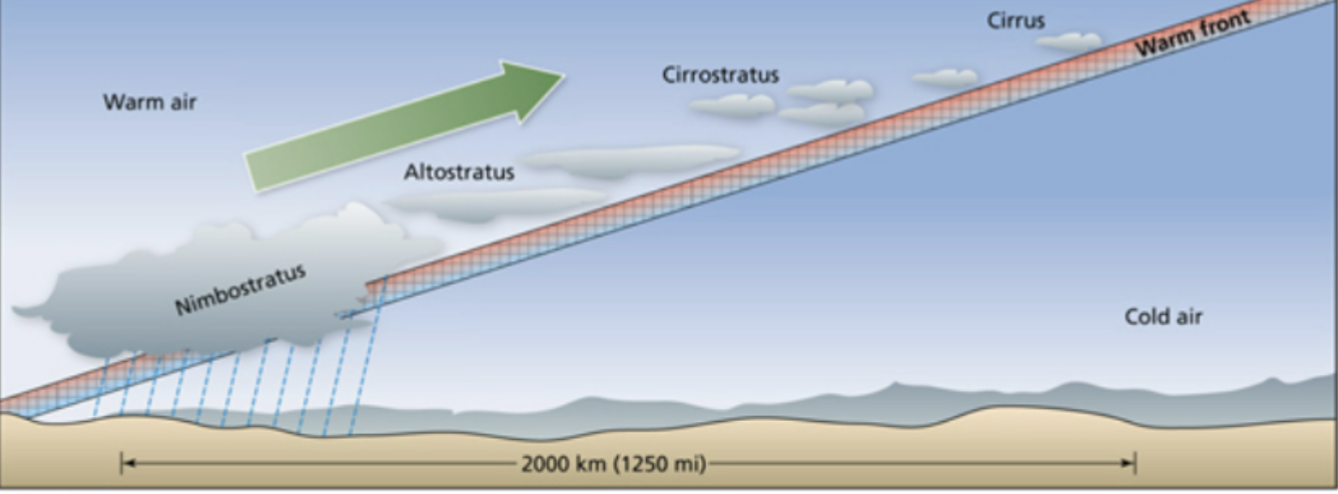
warm front
slow, gradual, light precipitation, fog.
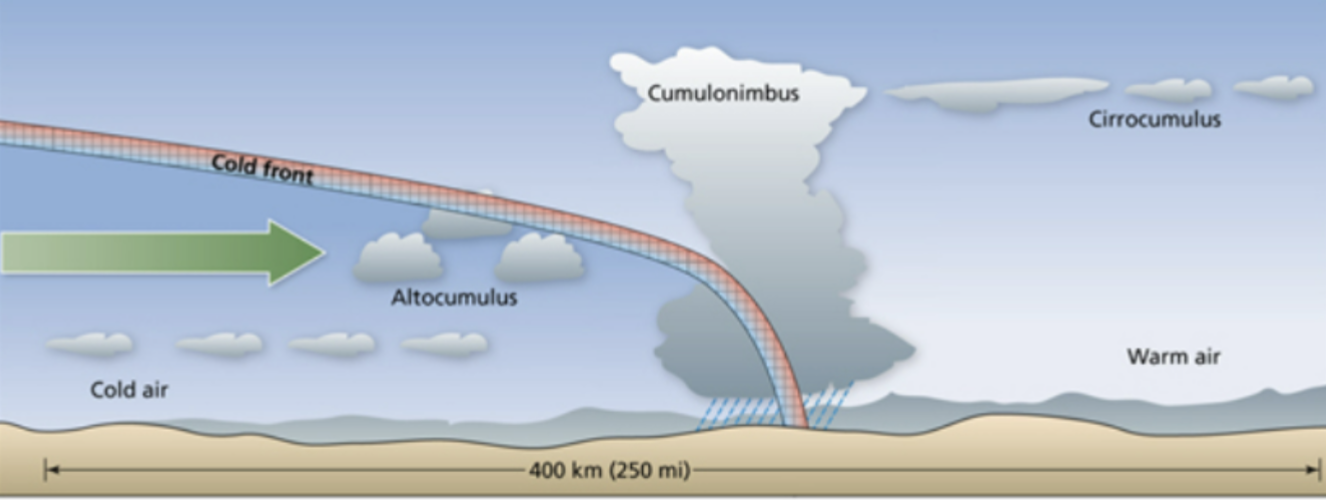
cold front
fast, intense storms, thunderstorms, possible severe weather.
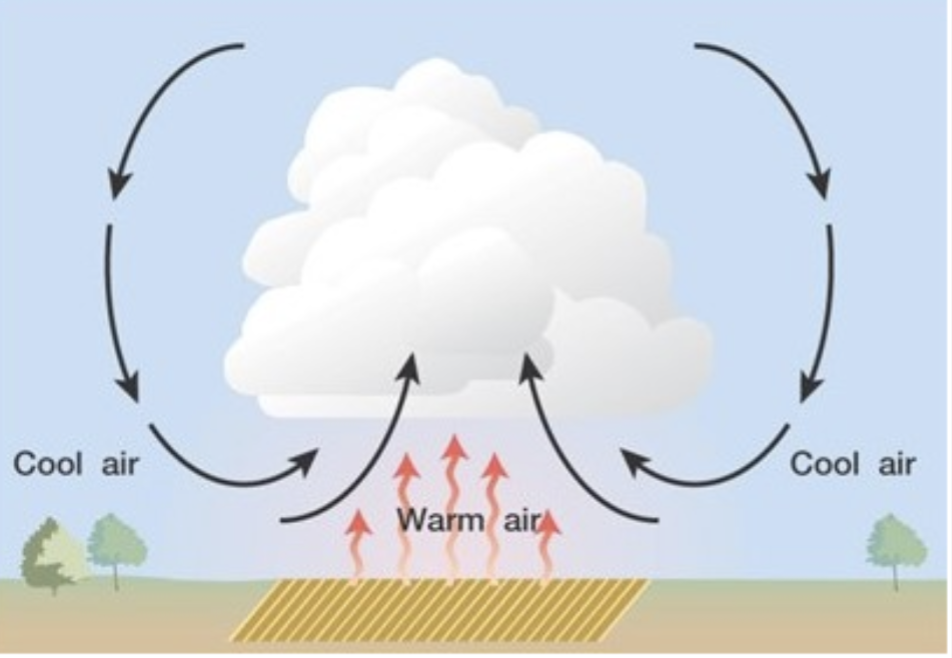
convectional lifting
spontaneous vertical movement due to buoyancy differences. ex: thunderstorms, tornadoes
orographic lifting
air masses forced upwards by an obstacle.
ex.mountains, rain shadow effect
Tropical Depressions
organized low wind speed (40 mph)
Requirements for evaporation
heat energy and unsaturated air
Tropical Cyclone (Hurricanes)
Highest wind speed, low pressure storm surge at sea