Lecture 1 Bacteriology Classification and Bacteria Structure
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Cocci, bacilli/rods, spirochetes
3 shapes used to classify bacteria
Mycoplasm
What specific type of bacteria doesn’t have a cell wall?
Gram Stain
What type of staining uses crystal violet and red dye safranin?
Gram Positive and Gram Negative
Gram staining separates bacteria into these two groups based on the composition of the cell wall
Blue/purple, iodine, organic solvent, red dye
Gram stain procedure
Crystal violet stains all cells ____/______
______ solution added (all cells remain blue)
_______ _______ extracts blue dye from lipid-rich, thin-walled gram (-) bacteria > lipid poor, thick-walled gram (+)
____ ____ stains gram (-) cells red/pink and gram (+) remains blue
Acid-Fast stain
Which type of staining is specific for mycobacteria (Ex: M. tuberculosis) and results from high lipid content of the cell wall
Gram (+)
Bacteria with thicker peptidoglycan layer, + / - teichoic acid
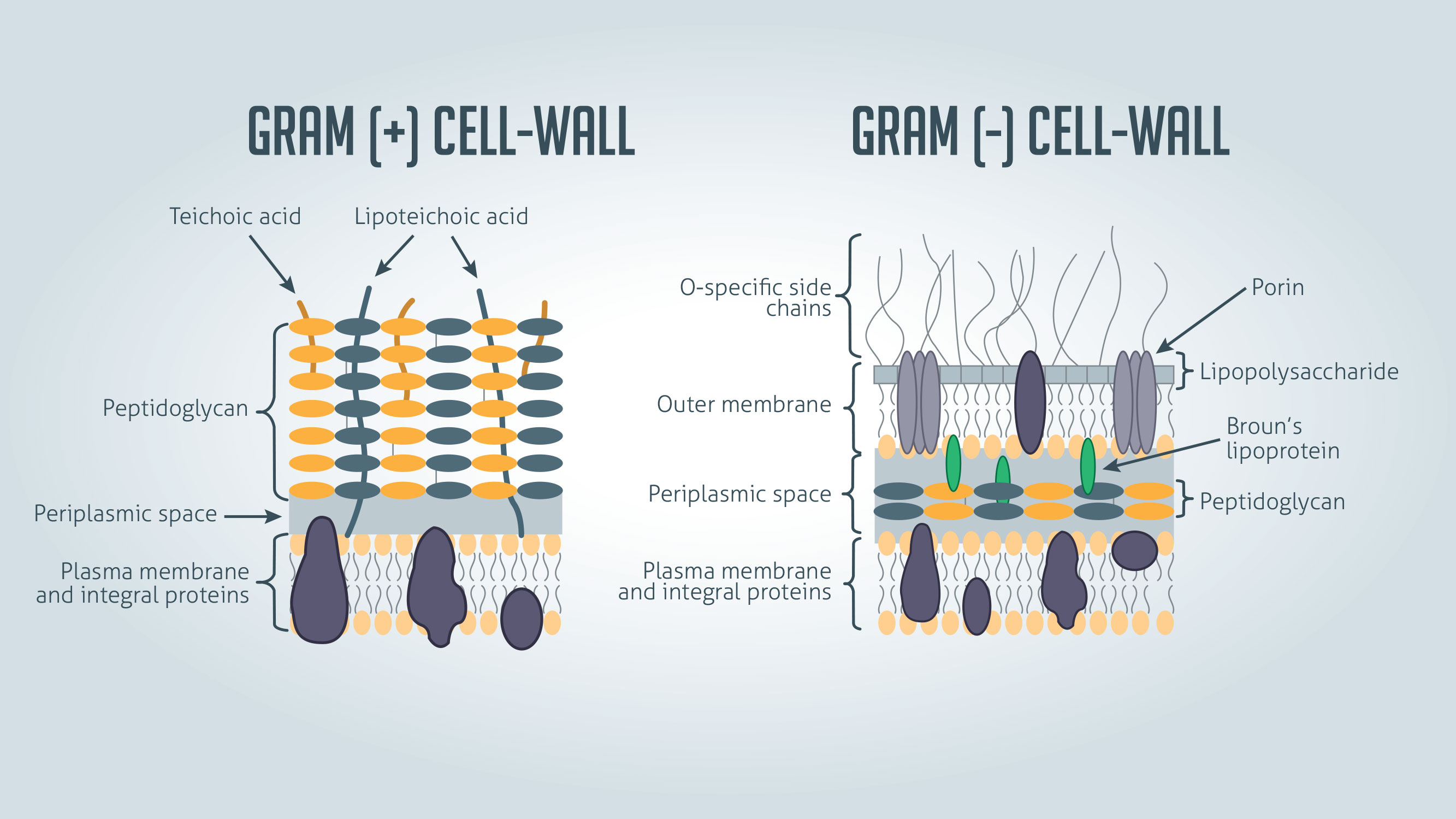
Teichoic
________ acid is unique to gram (+) bacteria.
Gram (-)
bacteria with a complex outer layer
lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin), lipoprotein, and phospholipid
Periplasmic Space
location of beta-lactamases
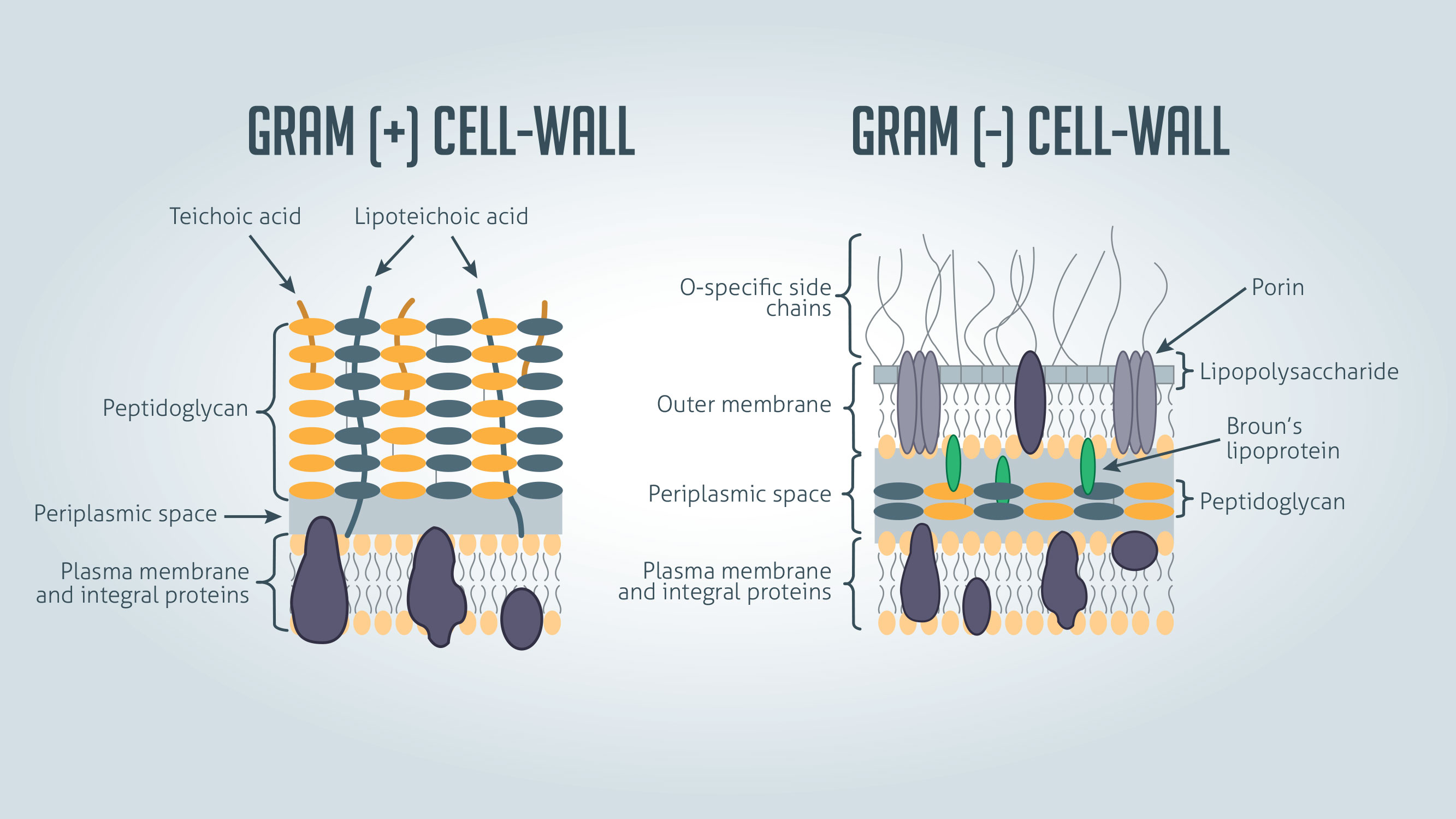
beta-lactamases
What is sometimes located in the periplasmic space of gram (-) cells and degrades penicillin in some species?
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
only on Gram-negative bacteria
forms outer membrane
Acts as endotoxin
responsible for fever and shock
Teichoic Acid
only in cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria
induces septic shock with infection of certain bacteria
Mediates attachment of staphylococci to mucosal cells
Periplasmic Space
Gram negative bacteria ONLY
space between peptidoglycan layer and outer LPS membrane containing
components of transport systems for iron, proteins, sugars
enzymes involved in breakdown of macromolecules
lytic virulence factors including beta-lactamase
Peptidoglycan
Present only in bacterial cell walls
Provides rigid support and maintains shape of cell
Thicker in Gram positive cells
target of antimicrobials
because human cells don’t have this
Active, oxidative phosphorylation, cell wall, toxins
Importance of cytoplasmic membrane
______ transport of molecules into the cell
Site of energy generation
_________ _______________
Synthesis of ____ ____ precursors
Secretion of enzymes and ______
Nucleoid
The region within a bacterial cell where the genetic material (DNA) is located
Introns
Bacterial DNA contains no _______
Haploid
Bacteria contain single circular DNA molecule per cell, making it _______.
Amorphous Matrix
Ribosomes - 70s
Free in cytoplasm
Plasmids
Double-stranded circular DNA outside of nuceloid; transmissible or nontransmissible; carry genes for antibiotic resistance, resistance to heavy metals, UV light, Pili, and exotoxins
independently
Plasmids replicate ___________
Granules
Storage area for nutrients
Capsule
Gelatinous Layer composed of polysaccharide
Covers entire bacterium
virulence, serologic, vaccines, human
Importance of Capsule
Determinant of _________
Aids in identification of _________ type
Utilized as antigens in ________
Adherence to _____ tissue
Flagella
Whip-like appendages that aid in movement of certain bacteria towards nutrients/other attractants (Chemotaxis)
No
Are flagella present on all bacteria? (yes or no)
pathogenic, identification
Importance of flagella
May play a role in __________ nature of bacteria
Ex: E. Coli ability to propel from urethra to bladder
Flagella proteins used for bacteria _____________
Pili
Hairlike filaments found mainly on gram (-) bacteria
shorter and straighter than flagella
attachment, sex pilus
Importance of Pili
Mediate __________ of bacteria to receptors on human cell surface
____ _____ - forms attachment between cells during conjugation
Glycocalyx
Slime layer secreted by bacteria to allow adherence to many surfaces
skin
heart valves
prosthetic joints
catheters
teeth
Spore formation
occurs in response to adverse conditions
Bacillus and Clostridium
Which bacteria produce spores?
no, dormant, heat, chemicals, autoclaving
Spores have __ metabolic activity, remain _____ for years, resistant to ____ and _________, and require ___________ to sterilize against them.
binary fission
bacteria reproduce by ______ _______
replication, growth, segregation, splitting
Division by Binary Fission
__________ of DNA
______ of a cell
__________ of DNA
_________ of cells
Aerobic Bacteria (Aerobes)
Utilize oxygen in the final steps of energy production
superoxide dismutase
one of two enzymes required to clear toxic molecules in aerobes
reduces free radical superoxide (O2)
Catalase
one of two enzymes required to clear toxic molecules in aerobes
reduces hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
obligate aerobes
require oxygen to grow, no exceptions
Facultative Anaerobes
May grow with or without oxygen
respiration or fermentation
Most bacteria fall into this category
Grow faster in the presence of oxygen
obligate anaerobes
cannot grow in the presence of oxygen
lack catalase and / or superoxide dismutase
sugar, aerobic, oxygen, organic, identify/classify
Fermentation
Breakdown of _____ to produce energy
Less efficient than _______ metabolism
Utilized by facultative and obligate anaerobes in the absence of ______
Converts final pyruvate of glycolysis into other _______ molecules
Utilized as a means to ________/________ bacteria based upon fermentation end products
Haploid
Bacteria are _______, containing only a single copy of their genome
Bi-directionally
DNA replication in bacteria occurs _______________
Conjugation, transduction, transposition
Mechanisms of transferring DNA between cells
Transformation
Utilized in laboratories for the manipulation of DNA
Conjugation
Mating of two bacterial cells
Controlled by fertility (F) plasmid
encodes protein (pilin) that forms sex pilus
May contain genes for antibiotic resistance or virulence
F plasmid is transferred to donor cell and is now capable of instigating conjugation
high-frequency recombination
Hfr
F plasmid is integrated into bacterial DNA
Transduction
DNA transfer by a bacterial virus - bacteriophage
Piece of bacterial DNA incorporated in virion
Divided into two types
General
Specialized
General Transduction
random pieces (segments) of DNA
Specialized Transduction
DNA adjacent to integration site
Transformation
Transfer of DNA itself from one cell to another
Mechanisms
Uptake of free DNA fragments by a cell
unlikely to play a big role naturally in disease
Utilized for the manipulation of DNA in the laboratory
within, DNA, inverted repeats, drug resistance, disrupt/mutate
Transposons
Promotes transfer of DNA ______ bacterial cells
Small pieces of ____ that can move freely in chromosomal DNA, plasmids, and bacteriophages
Flanked by short sequence of ________ _______
May contain genes for ____ __________, toxins
may integrate and _______ / ______ genes
Recombination
Integration of DNA into host cell chromosome
Homologous recombination
exchange between similar sequences of DNA
Non-homologous recombination
exchange between unrelated sequences
produces insertions or deletions