FOPC EXAM ONE
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
1
New cards
What are the three types of ultrasound probes and what are they used for?
1. Phased Array
1. Lowest frequency probe
2. high resolution but poor penetration
2. Linear Array
3. Curvilinear Array
1. Curvilinear transducers are used for evaluating deeper structures such as hip, piriformis muscle, and sciatic nerve.
2. Best probe as it has a pretty even resolution to penetration ratio
2
New cards
What is ultrasound? How does it work?
Ultrasound, also known as ultrasonography, is a medical imaging technique that **uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside of the body**. It's commonly used for visualizing internal structures, monitoring pregnancies, and diagnosing various medical conditions. Here's how ultrasound works:
1. **Generating Sound Waves:** An ultrasound machine consists of a transducer, which is a handheld device that emits and receives sound waves. **The transducer contains piezoelectric crystals that can generate and detect sound waves.** When an electrical current is applied to these crystals, they vibrate at a high frequency, creating sound waves in the ultrasound range (typically 2 to 18 megahertz).
2. **Sending Sound Waves:** The transducer is placed on the skin over the area of interest. **It emits a focused beam of sound waves into the body.** These sound waves are at a frequency that's too high for humans to hear, hence the name "ultrasound."
3. **Sound Wave Interaction:** The emitted sound waves travel through the body and encounter different tissues and structures. **When the sound waves encounter a boundary between two different types of tissues (e.g., between fluid and soft tissue, or between soft tissue and bone), some of the waves are reflected back to the transducer while others continue deeper into the body.**
4. **Echo Reception:** The transducer acts as both a sender and a receiver. **When the reflected sound waves return to the transducer, the piezoelectric crystals in the transducer convert these echoes into electrical signals.**
5. **Signal Processing:** The electrical signals containing information about the intensity and timing of the echoes are sent to a computer. The computer processes these signals and constructs a visual representation of the internal structures.
6. **Image Formation:** **The computer uses the time it takes for the sound waves to travel to and from different structures to determine their distances and positions.** It then generates a grayscale image that represents the density and composition of the tissues. **Brighter areas in the image typically represent dense or reflective tissues, while darker areas represent less dense or absorptive tissues.**
7. **Real-Time Imaging:** Modern ultrasound machines can generate real-time images by continuously emitting sound waves and updating the images as the transducer moves across the body. This is particularly useful for visualizing moving structures, such as a beating heart or a developing fetus during pregnancy.
8. **Doppler Ultrasound:** In addition to basic imaging, ultrasound can also be used to assess blood flow by utilizing the Doppler effect. This involves measuring the frequency shift of the sound waves reflected off moving blood cells. Doppler ultrasound is commonly used to evaluate blood flow in vessels and the heart.
Ultrasound is considered safe, non-invasive, and does not involve ionizing radiation like X-rays or CT scans. However, its effectiveness can be limited in certain cases, such as when imaging structures behind bone or air-filled organs.
1. **Generating Sound Waves:** An ultrasound machine consists of a transducer, which is a handheld device that emits and receives sound waves. **The transducer contains piezoelectric crystals that can generate and detect sound waves.** When an electrical current is applied to these crystals, they vibrate at a high frequency, creating sound waves in the ultrasound range (typically 2 to 18 megahertz).
2. **Sending Sound Waves:** The transducer is placed on the skin over the area of interest. **It emits a focused beam of sound waves into the body.** These sound waves are at a frequency that's too high for humans to hear, hence the name "ultrasound."
3. **Sound Wave Interaction:** The emitted sound waves travel through the body and encounter different tissues and structures. **When the sound waves encounter a boundary between two different types of tissues (e.g., between fluid and soft tissue, or between soft tissue and bone), some of the waves are reflected back to the transducer while others continue deeper into the body.**
4. **Echo Reception:** The transducer acts as both a sender and a receiver. **When the reflected sound waves return to the transducer, the piezoelectric crystals in the transducer convert these echoes into electrical signals.**
5. **Signal Processing:** The electrical signals containing information about the intensity and timing of the echoes are sent to a computer. The computer processes these signals and constructs a visual representation of the internal structures.
6. **Image Formation:** **The computer uses the time it takes for the sound waves to travel to and from different structures to determine their distances and positions.** It then generates a grayscale image that represents the density and composition of the tissues. **Brighter areas in the image typically represent dense or reflective tissues, while darker areas represent less dense or absorptive tissues.**
7. **Real-Time Imaging:** Modern ultrasound machines can generate real-time images by continuously emitting sound waves and updating the images as the transducer moves across the body. This is particularly useful for visualizing moving structures, such as a beating heart or a developing fetus during pregnancy.
8. **Doppler Ultrasound:** In addition to basic imaging, ultrasound can also be used to assess blood flow by utilizing the Doppler effect. This involves measuring the frequency shift of the sound waves reflected off moving blood cells. Doppler ultrasound is commonly used to evaluate blood flow in vessels and the heart.
Ultrasound is considered safe, non-invasive, and does not involve ionizing radiation like X-rays or CT scans. However, its effectiveness can be limited in certain cases, such as when imaging structures behind bone or air-filled organs.
3
New cards
Compare and contrast high and low frequency with ultrasound.
Ultrasound waves have frequencies above the range of human hearing, typically in the range of 2 to 18 megahertz (MHz). Higher-frequency waves provide better resolution but have reduced penetration capabilities. Lower-frequency waves penetrate deeper but may sacrifice resolution.
4
New cards
Depth & Gain in ultrasound
Depth in ultrasound refers to the distance from the transducer (the device that emits and receives ultrasound waves) to the point within the body where the ultrasound waves are being directed.
\
Gain in ultrasound refers to the amplification of the received echoes from tissues. It affects the brightness or intensity of the displayed echoes on the ultrasound image.
\
Gain in ultrasound refers to the amplification of the received echoes from tissues. It affects the brightness or intensity of the displayed echoes on the ultrasound image.
5
New cards
Anechoic
* Definition: Anechoic refers to an area or structure within the body that appears completely black or echo-free on an ultrasound image. Anechoic structures do not reflect any of the ultrasound waves and appear as voids.
* Example: Fluid-filled structures, such as cysts or blood vessels filled with non-clotted blood, often appear anechoic on ultrasound images.
* Example: Fluid-filled structures, such as cysts or blood vessels filled with non-clotted blood, often appear anechoic on ultrasound images.
6
New cards
Hypoechoic
* Definition: Hypoechoic describes a tissue or structure that reflects fewer ultrasound waves than the surrounding tissues. Hypoechoic areas appear darker than the surrounding tissues but are not completely echo-free.
* Example: Tumors or organs with a decreased density of cells, like a thyroid nodule with less dense tissue compared to normal thyroid tissue, may appear hypoechoic.
* Example: Tumors or organs with a decreased density of cells, like a thyroid nodule with less dense tissue compared to normal thyroid tissue, may appear hypoechoic.
7
New cards
Hyperechoic
* Definition: Hyperechoic refers to a tissue or structure that reflects more ultrasound waves than the surrounding tissues. Hyperechoic areas appear brighter than the surrounding tissues.
* Example: Bone, calcifications, and other dense structures typically appear hyperechoic on ultrasound images due to their high ability to reflect ultrasound waves.
* Example: Bone, calcifications, and other dense structures typically appear hyperechoic on ultrasound images due to their high ability to reflect ultrasound waves.
8
New cards
Isoechoic
* Definition: Isoechoic indicates that a tissue or structure has similar echogenicity to the surrounding tissues. In other words, it has the same level of reflectivity as the neighboring structures.
* Example: A tumor or lesion that has a similar appearance in terms of echogenicity to the surrounding normal tissue may be described as isoechoic.
* Example: A tumor or lesion that has a similar appearance in terms of echogenicity to the surrounding normal tissue may be described as isoechoic.
9
New cards
Acoustic Shadow
* Definition: An acoustic shadow is an area on an ultrasound image that appears dark or black due to a reduction in the intensity of ultrasound waves reaching that particular region. This reduction in intensity occurs when the ultrasound waves encounter a highly reflective or attenuating structure that absorbs or scatters a significant portion of the waves.
* Cause: Acoustic shadows commonly occur when ultrasound waves encounter structures that strongly reflect or absorb the waves, preventing them from passing through to deeper tissues. These structures block the transmission of ultrasound waves, leading to a shadow that appears behind them on the image.
* Example: An example of an acoustic shadow is the shadow cast by a gallstone or kidney stone. These calcified structures strongly reflect ultrasound waves, causing a shadow behind them where the waves are unable to penetrate.
* Cause: Acoustic shadows commonly occur when ultrasound waves encounter structures that strongly reflect or absorb the waves, preventing them from passing through to deeper tissues. These structures block the transmission of ultrasound waves, leading to a shadow that appears behind them on the image.
* Example: An example of an acoustic shadow is the shadow cast by a gallstone or kidney stone. These calcified structures strongly reflect ultrasound waves, causing a shadow behind them where the waves are unable to penetrate.
10
New cards
Acoustic enhancement
* Definition: Acoustic enhancement is an increased brightness or intensity of echoes seen on an ultrasound image that lies beneath or beyond a low-attenuating structure. In other words, the area beyond a less attenuating structure appears brighter than expected due to increased transmission of ultrasound waves.
* Cause: Acoustic enhancement occurs when an area of the body is filled with a substance that allows more ultrasound waves to pass through than the surrounding tissues. This can happen with fluids, such as cysts, which transmit ultrasound waves more effectively than soft tissues. As a result, the echoes from structures beyond the fluid-filled area appear brighter.
* Example: When imaging a cyst, the structures behind the cyst may appear brighter than expected due to the enhanced transmission of ultrasound waves through the fluid-filled cyst.
* Cause: Acoustic enhancement occurs when an area of the body is filled with a substance that allows more ultrasound waves to pass through than the surrounding tissues. This can happen with fluids, such as cysts, which transmit ultrasound waves more effectively than soft tissues. As a result, the echoes from structures beyond the fluid-filled area appear brighter.
* Example: When imaging a cyst, the structures behind the cyst may appear brighter than expected due to the enhanced transmission of ultrasound waves through the fluid-filled cyst.
11
New cards
Reverberation
Reverberation is an ultrasound artifact that occurs when sound waves are reflected back and forth between two strong reflectors in the ultrasound beam's path. This results in the creation of multiple false echoes on the ultrasound image. Reverberation artifacts are characterized by closely spaced, parallel lines that appear at regular intervals, often resembling a ladder-like pattern.
12
New cards
Ring Down Artifact
The primary cause of a ring-down artifact is the presence of gas bubbles or air trapped within tissues or body cavities.
13
New cards
Edge Shadow Artifact
The "edge shadow artifact" is a type of ultrasound artifact that occurs when the ultrasound beam encounters a strong interface between two tissues with different acoustic properties. This artifact creates a shadow that appears as a dark area extending behind the interface on the ultrasound image. The edge shadow artifact can obscure structures located beyond the interface and may affect the interpretation of the image.
\
The artifact occurs when the ultrasound beam encounters a sharp boundary between two tissues with significantly different acoustic impedances. One side of the boundary reflects most of the ultrasound waves, while the other side allows the waves to pass through.
\
The artifact occurs when the ultrasound beam encounters a sharp boundary between two tissues with significantly different acoustic impedances. One side of the boundary reflects most of the ultrasound waves, while the other side allows the waves to pass through.
14
New cards
Mirror Artifact
\n The "mirror artifact" is a type of ultrasound artifact that occurs when an ultrasound beam encounters a strong reflector at a perpendicular angle. This artifact creates a mirrored or duplicated image on the ultrasound display, appearing as if the same structure is repeated on the opposite side of the actual structure. The mirror artifact can lead to confusion and misinterpretation of the image.
Here's how the mirror artifact occurs:
1. Strong Reflector: The mirror artifact occurs when the ultrasound beam encounters a strong reflector, often a smooth, flat surface or a large acoustic impedance mismatch.
Here's how the mirror artifact occurs:
1. Strong Reflector: The mirror artifact occurs when the ultrasound beam encounters a strong reflector, often a smooth, flat surface or a large acoustic impedance mismatch.
15
New cards
What are some contraindications for MRI and CT?
MRI: Pacemakers, heavy metal
\
CT: Heavy metal, allergic to contrast
\
*Pregnant woman and children are always sus.*
\
CT: Heavy metal, allergic to contrast
\
*Pregnant woman and children are always sus.*
16
New cards
What are the five main imaging modalities and what are they primary used to image?
1. XR/CT: Bone
2. MRI: Bone and soft tissue
3. NM: Bone
4. US: Soft tissue
17
New cards
What are some key points when describing fractures?
1. Location
1. Specific location on bone
2. Displaced or nondisplaced
1. *In a alignment?*
3. Extent—Complete or incomplete
4. Simple or comminuted
5. Intra-articular or extra-articular
6. Open or closed
7. Displacement
8. Impaction or Distraction
9. Avulsion
\
18
New cards
What are the eight types of fractures? Describe them.
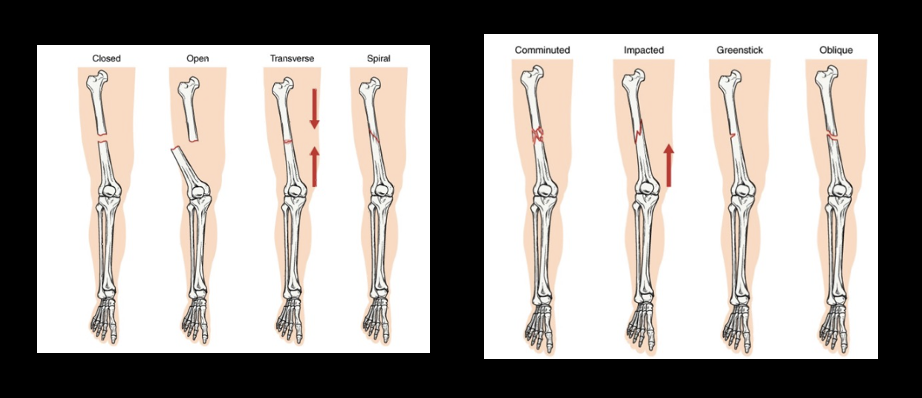
19
New cards
Open Fracture Classification (Gustilo and Anderson)
* Grade 1: clean wound < 1 cm in length, simple fracture
* Grade 2: open wound 1–10 cm, no flaps or extensive tissue damage
* Grade 3: open segmental fracture with extensive soft tissue injuries, also includes wounds more > 8 hours old
* Grade 3a: adequate soft tissue covering of the fracture despite extensive soft tissue damage
* Grade 3b: inadequate soft tissue covering; periosteal stripping
* Grade 3c: open fracture with a vascular injury that requires surgery for viability of the limb
* Grade 2: open wound 1–10 cm, no flaps or extensive tissue damage
* Grade 3: open segmental fracture with extensive soft tissue injuries, also includes wounds more > 8 hours old
* Grade 3a: adequate soft tissue covering of the fracture despite extensive soft tissue damage
* Grade 3b: inadequate soft tissue covering; periosteal stripping
* Grade 3c: open fracture with a vascular injury that requires surgery for viability of the limb
20
New cards
What are two secondary signs of fracture?
Joint effusion and Periosteal reaction of callus formation
21
New cards

\
Colles Fracture. Fracture of both the distal radius and ulna. This has an ulnar styloid avulsion fracture for the ulnar fracture on these images. FOOSH with extended hand.

22
New cards
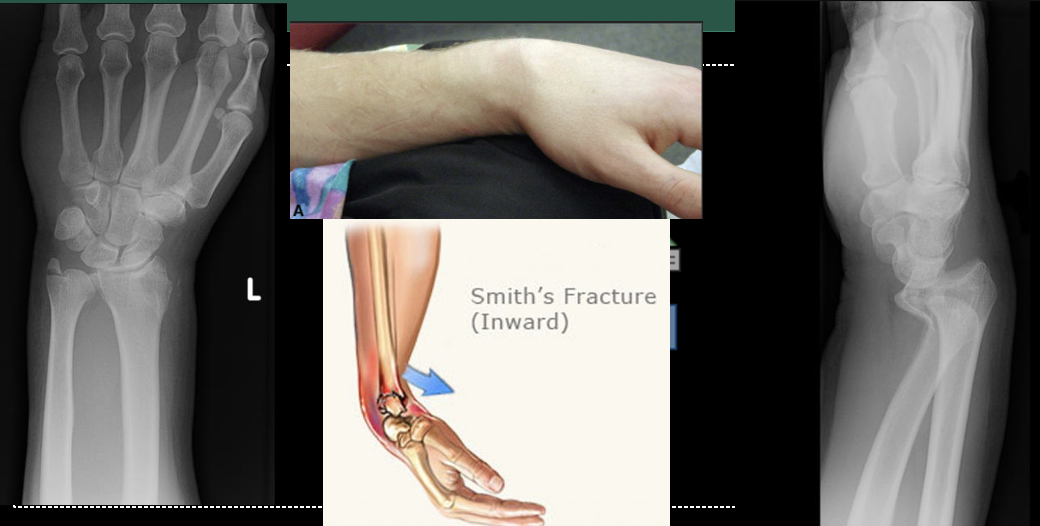
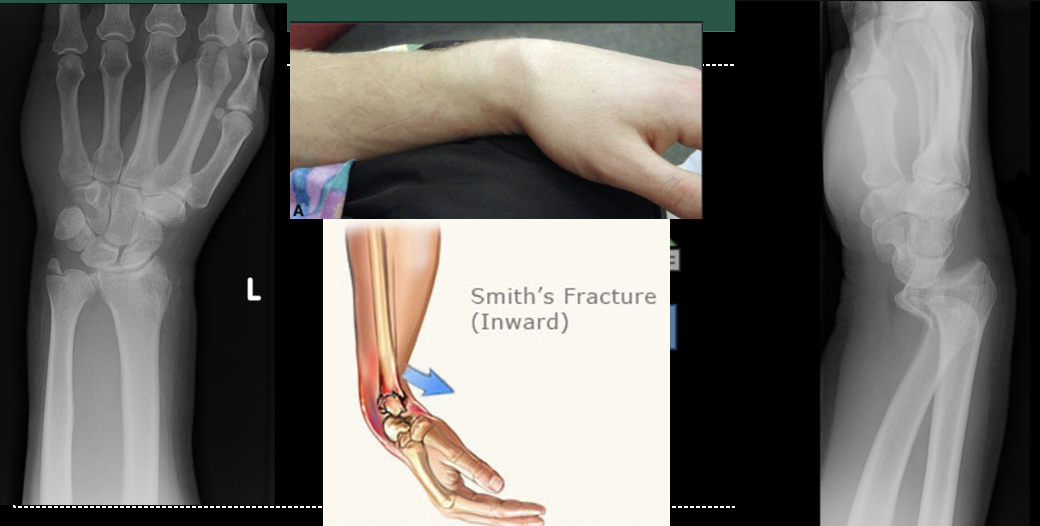
\
Smith’s Fracture. FOOSH with flexed hand. In contrast to a Colles' fracture, a Smith's fracture involves the distal radius bone breaking and the fractured fragment being displaced volarly (toward the palm of the hand). This leads to a deformity where the wrist and hand appear angulated and bent toward the palm side.
23
New cards
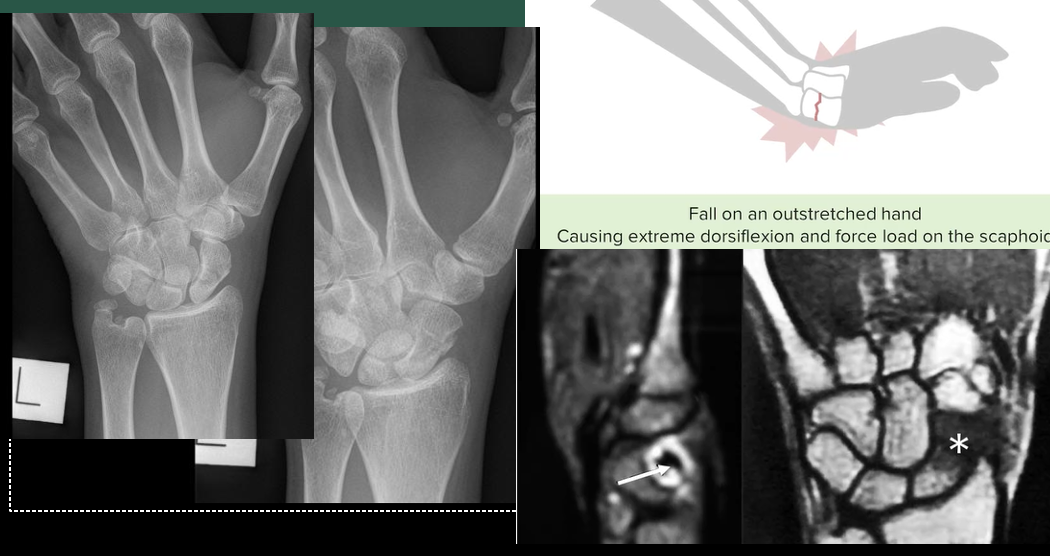
\
Anatomical Snuff Box Fracture. A "snuff box fracture" refers to a specific type of wrist fracture that involves the scaphoid bone and often occurs as a result of a fall on an outstretched hand.
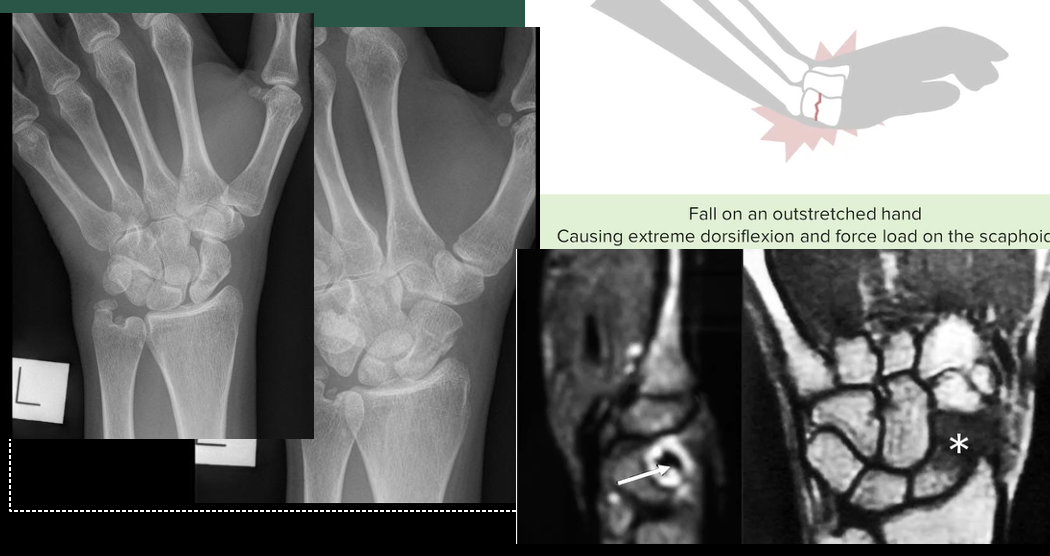
24
New cards
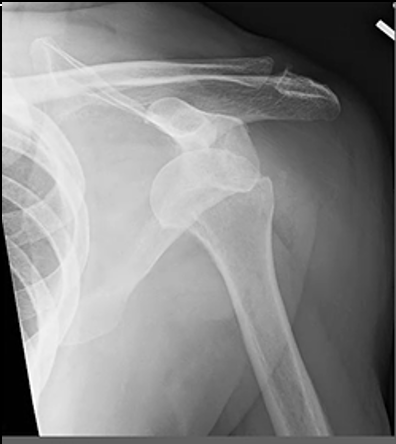
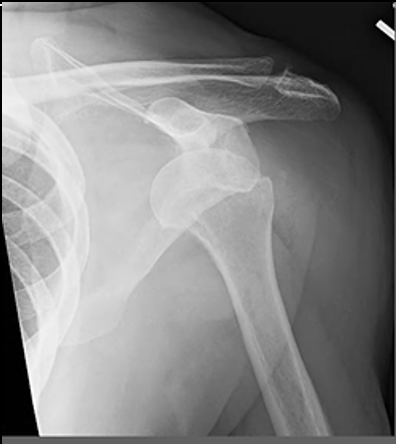
\
A Hill-Sachs lesion, also known as a Hill-Sachs deformity, is a specific type of injury to the humerus bone (upper arm bone) that occurs in conjunction with certain shoulder dislocations. This injury is commonly associated with anterior shoulder dislocations, where the humeral head dislocates from the glenoid cavity of the scapula (shoulder blade). The Hill-Sachs lesion results from the impaction of the humeral head against the glenoid rim during the dislocation event.
25
New cards
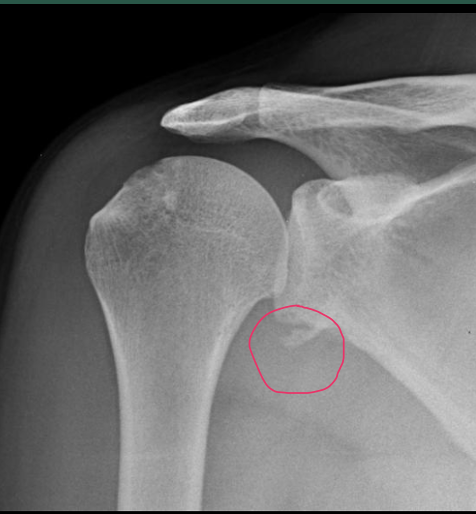
\
A Bankart lesion is a specific type of shoulder injury that involves damage to the labrum of the glenoid cavity (the socket of the shoulder joint). This injury often occurs in conjunction with anterior shoulder dislocations or subluxations, where the humeral head (upper arm bone) partially or completely moves out of the glenoid cavity. The Bankart lesion is an important consideration in cases of recurrent shoulder instability.
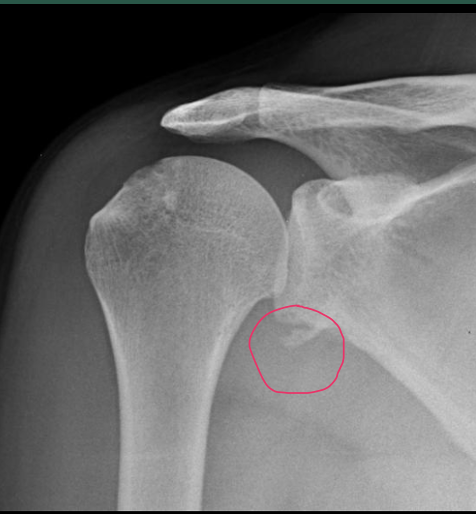
26
New cards
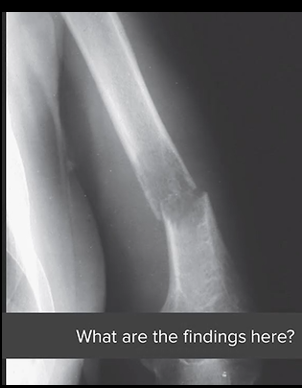
Left humerus, distal, simple, displaced, darker area (lytic lesion)
27
New cards
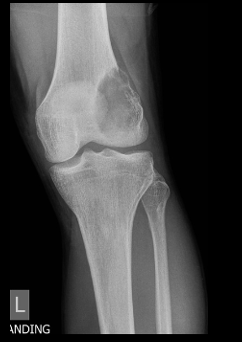
Distal, left femur, osteoblastic lesion
28
New cards
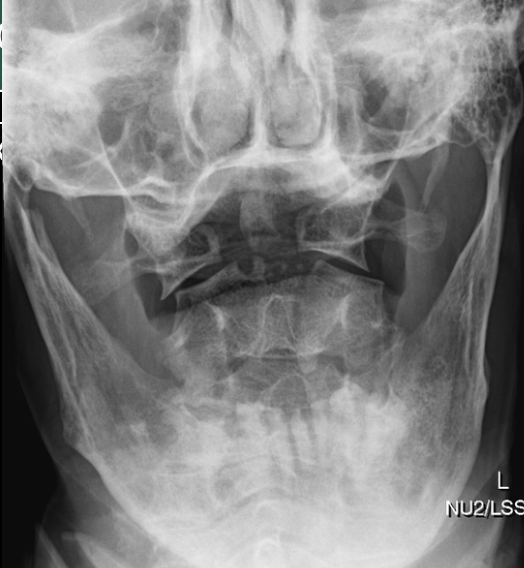
\
Odontoid Fracture
29
New cards
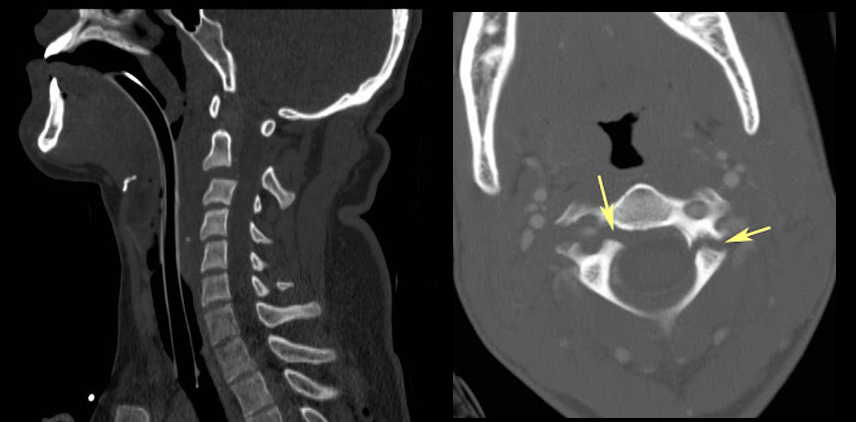
Hangman’s fracture
\
A "hangman's fracture" is a specific type of cervical spine fracture that involves the second cervical vertebra, known as the axis (C2). This fracture is typically associated with traumatic injuries, such as high-impact accidents or falls, and is characterized by a break in a specific part of the C2 vertebra called the "pars interarticularis." Hangman's fractures can lead to instability of the cervical spine and potentially severe neurological complications.
\
A "hangman's fracture" is a specific type of cervical spine fracture that involves the second cervical vertebra, known as the axis (C2). This fracture is typically associated with traumatic injuries, such as high-impact accidents or falls, and is characterized by a break in a specific part of the C2 vertebra called the "pars interarticularis." Hangman's fractures can lead to instability of the cervical spine and potentially severe neurological complications.
30
New cards
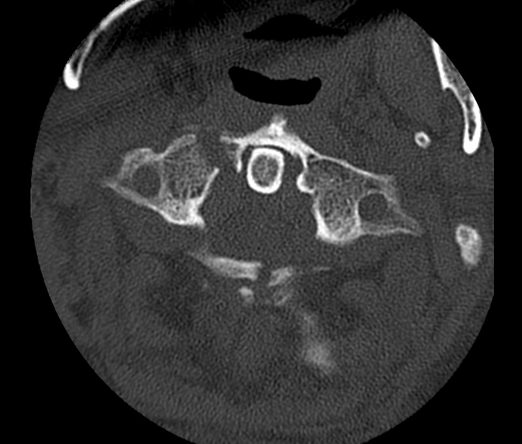
Jefferson’s fx
Burst fracture of the atlas. Originally described as a four part fracture, but may only be a two or three part fracture.
Burst fracture of the atlas. Originally described as a four part fracture, but may only be a two or three part fracture.
31
New cards
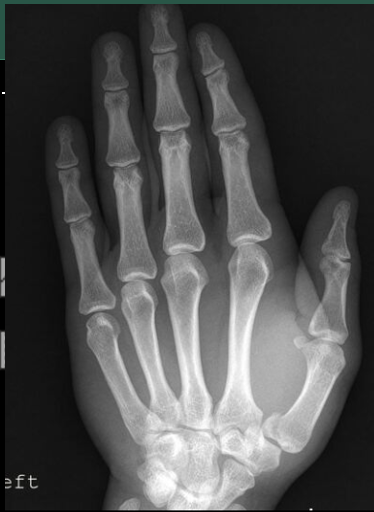
Bennett Fracture
\
A Bennett fracture is a specific type of fracture that involves the base of the first metacarpal bone, which is the bone that connects the thumb to the wrist. This type of fracture often occurs as a result of a forceful impact to the thumb, such as during a fall or other traumatic event. Bennett fractures can result in pain, swelling, and instability of the thumb joint.
\
A Bennett fracture is a specific type of fracture that involves the base of the first metacarpal bone, which is the bone that connects the thumb to the wrist. This type of fracture often occurs as a result of a forceful impact to the thumb, such as during a fall or other traumatic event. Bennett fractures can result in pain, swelling, and instability of the thumb joint.
32
New cards
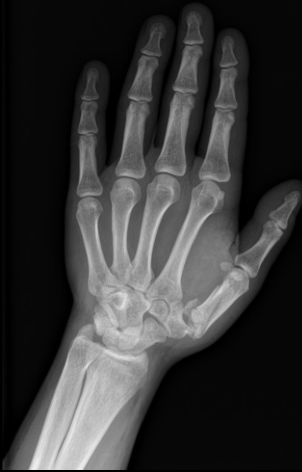
Rolando Fx
\
A Rolando fracture is a specific type of comminuted intra-articular fracture that involves the base of the first metacarpal bone, which connects the thumb to the wrist. Similar to a Bennett fracture, a Rolando fracture typically occurs as a result of a forceful impact to the thumb and is often seen in scenarios such as falls or direct trauma. However, a Rolando fracture is characterized by a more complex and three-part fracture pattern.
\
A Rolando fracture is a specific type of comminuted intra-articular fracture that involves the base of the first metacarpal bone, which connects the thumb to the wrist. Similar to a Bennett fracture, a Rolando fracture typically occurs as a result of a forceful impact to the thumb and is often seen in scenarios such as falls or direct trauma. However, a Rolando fracture is characterized by a more complex and three-part fracture pattern.
33
New cards
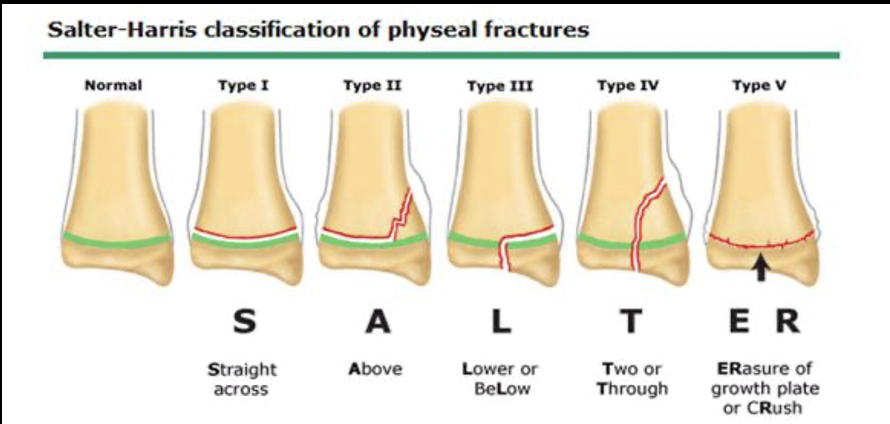
Salter-Harris Fracture Classification
Destroying the growth plate
\
S-slipped/separated
A-Away from joint
L-Lower (towards joint)
T-Through
R-Rammed
\
S-Slipped
M-Metaphysial
A-Articular
C-Complete
K-Krushed!
\
\
S-slipped/separated
A-Away from joint
L-Lower (towards joint)
T-Through
R-Rammed
\
S-Slipped
M-Metaphysial
A-Articular
C-Complete
K-Krushed!
\
34
New cards
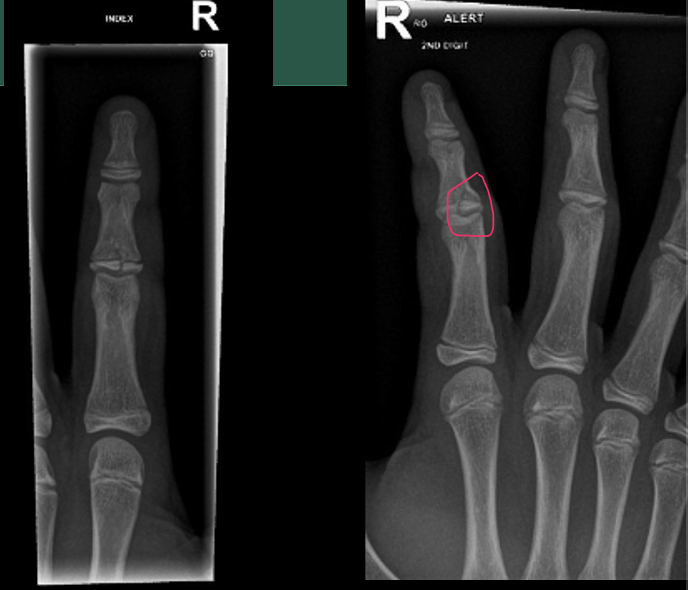
Type IV Salter-Harris fractice 2nd digit on the right hand, PIP
35
New cards
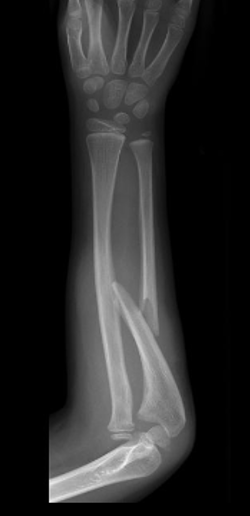
Monteggia: Ulnar fracture with proximal radial dislocation
36
New cards
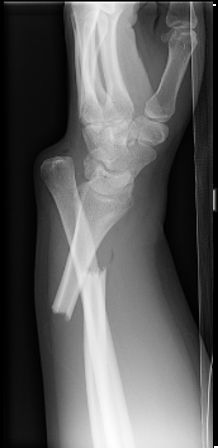
Galeazzi:
Fracture of the radius with distal ulnar dislocation
Fracture of the radius with distal ulnar dislocation
37
New cards
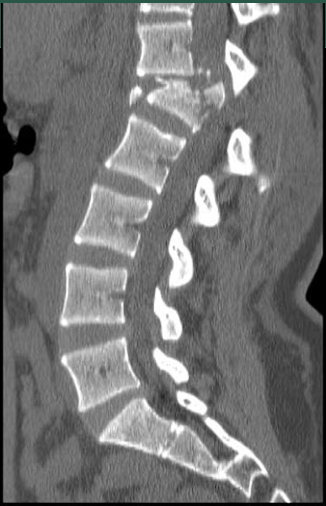
Chance Fracture: A Chance fracture, also known as a seatbelt fracture, is a specific type of vertebral fracture that typically occurs in the thoracolumbar spine (the transition area between the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spine). This type of fracture is often associated with high-impact accidents, such as car accidents, and is characterized by a horizontal break extending across the vertebral body. Chance fractures are often caused by a combination of flexion and compression forces applied to the spine.
38
New cards
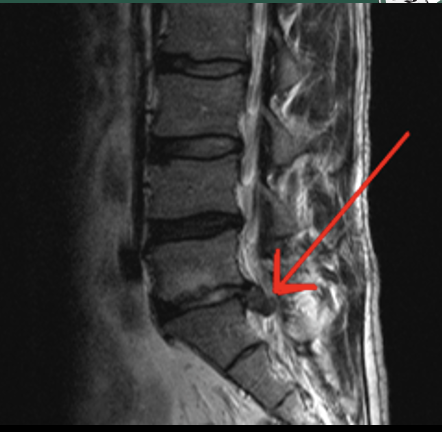
Disc Herniation
39
New cards
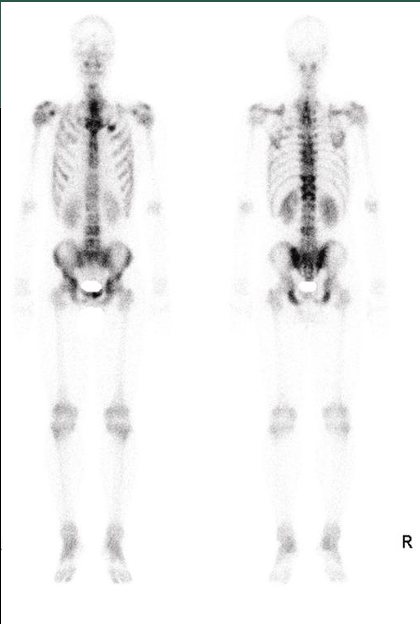
METS
40
New cards
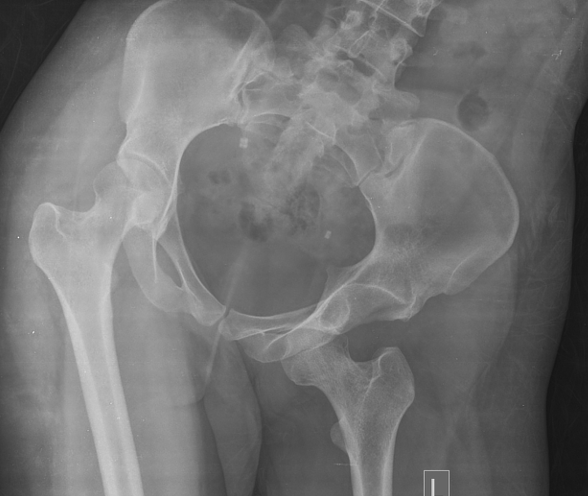
Hip dislocation, most common is posterior
41
New cards
Types of hip fractures
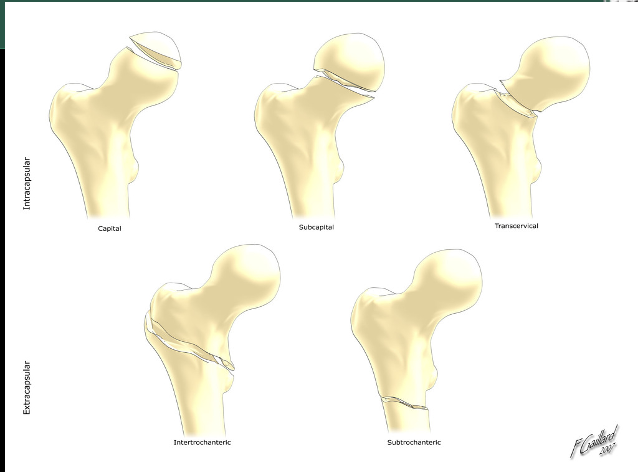
42
New cards
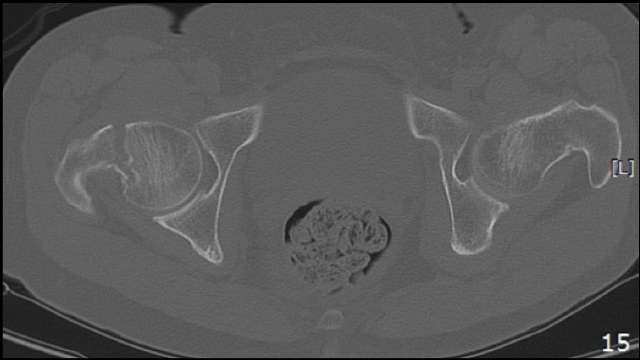
Right subcapital Hip fx
43
New cards
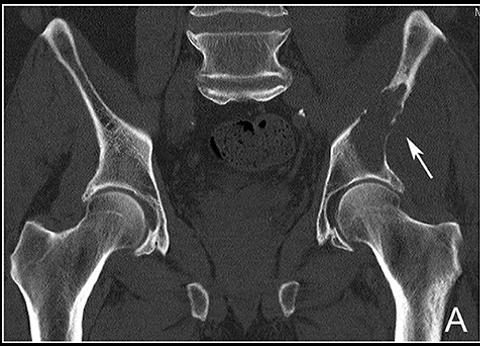
METs, decreased lucency in left iliac crest
44
New cards
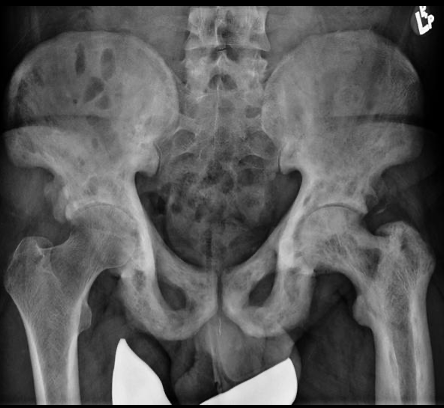
Paget’s Disease
45
New cards
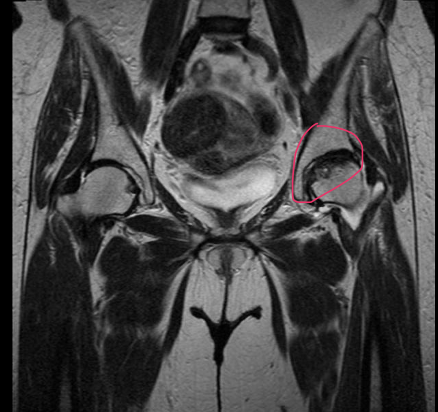
AVN of left femur
46
New cards
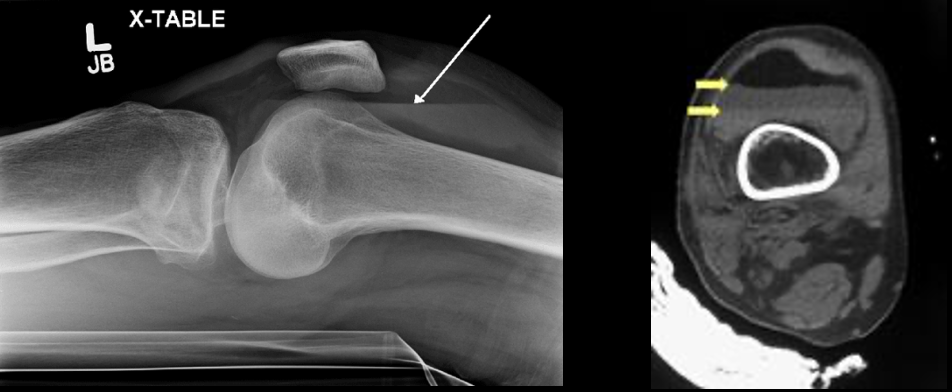
**Lipohemarthrosis** is a medical term used to describe a specific type of joint effusion (accumulation of fluid) that contains a combination of blood and fat within a joint space. It often occurs as a result of significant trauma or injury, such as fractures or dislocations involving bones near the joint. Lipohemarthrosis is commonly seen in the knee joint and can provide valuable diagnostic information to healthcare professionals.
47
New cards
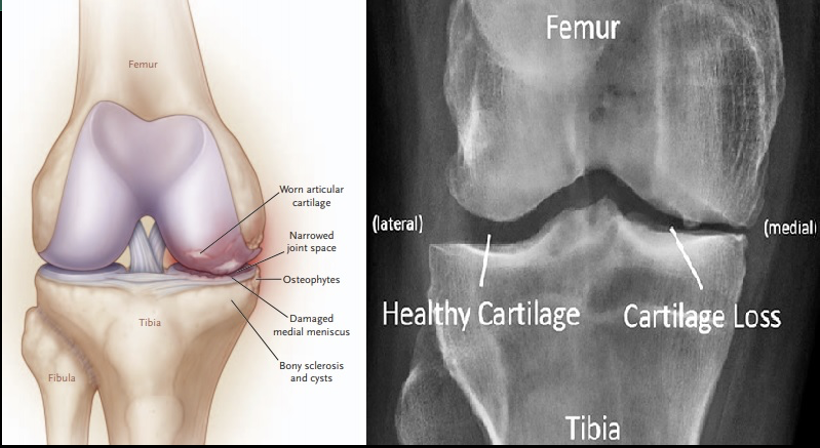
Arthritis
48
New cards
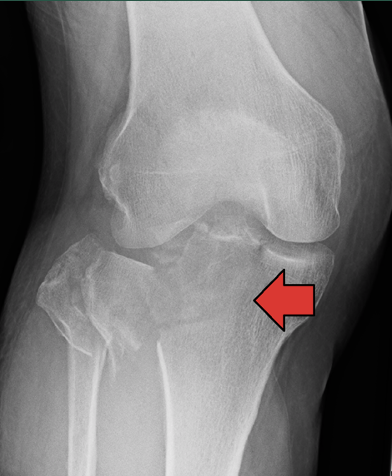
Tibia Plateau Fracture
49
New cards
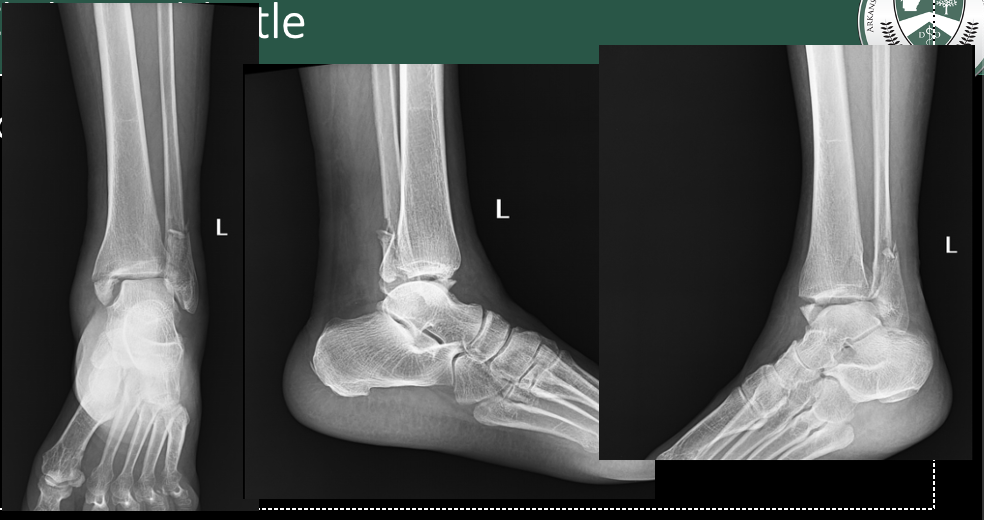
Medial and lateral malleolus and intra-articular fracture of the tibial plafond
Tri-malleolar fracture
50
New cards
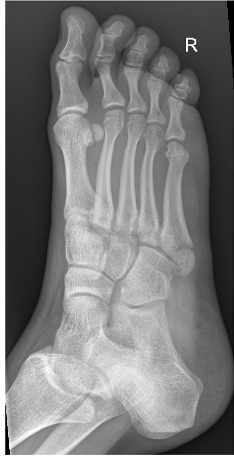
Jone’s Fracture
\
A Jones fracture is a specific type of fracture that occurs in the fifth metatarsal bone of the foot, which is the bone that connects to the pinky toe. This fracture is located at the base of the fifth metatarsal, and it is characterized by its unique location and potential for healing challenges. Jones fractures are commonly seen in athletes and individuals who engage in activities involving repetitive stress or twisting motions of the foot.
\
A Jones fracture is a specific type of fracture that occurs in the fifth metatarsal bone of the foot, which is the bone that connects to the pinky toe. This fracture is located at the base of the fifth metatarsal, and it is characterized by its unique location and potential for healing challenges. Jones fractures are commonly seen in athletes and individuals who engage in activities involving repetitive stress or twisting motions of the foot.
51
New cards
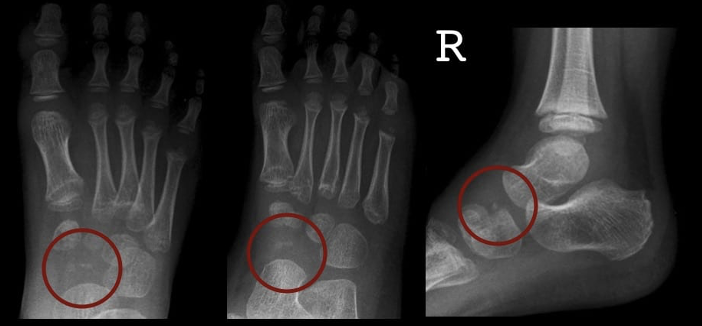
Navicular AVN, *Köhler Disease*
52
New cards
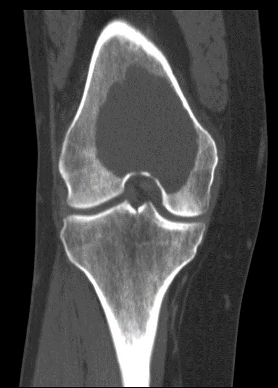
Bone Tumor
53
New cards
What are the four key features of a MSK complaint?
1. Articular or Extra-articular
2. Acute or chronic
3. Inflammatory or Non-inflammatory
4. Localized or Diffuse
54
New cards
Articular Structures vs Extra Articular structures
In summary, articular structures are the components within the joint itself, including the bone surfaces and articular cartilage, while extra-articular structures are the supporting elements located outside the joint capsule, such as ligaments, tendons, muscles, and bursae. Both types of structures are crucial for joint stability, movement, and overall function.
55
New cards
Intra-articular vs extra-articular
1. ***INTRA-ARTICULAR***
1. **Definition:** Intra-articular refers to structures or conditions that are located within the joint space itself.
2. **Components:** Intra-articular structures include the articular cartilage, synovial membrane, synovial fluid, and any structures that are housed within the joint capsule, such as ligaments or menisci.
3. **Function:** Intra-articular structures are directly involved in joint movement, lubrication, and protection. Articular cartilage provides a smooth surface for bone articulation, while the synovial membrane produces synovial fluid that nourishes and lubricates the joint.
4. **Location:** Intra-articular structures are found within the joint cavity, which is the space enclosed by the joint capsule and containing the synovial fluid.
5. **Examples:** Ligaments inside the joint capsule (intracapsular ligaments), joint surfaces, and any structures that move within the joint (e.g., menisci in the knee) are considered intra-articular.
6. **Significance:** Injuries or conditions affecting intra-articular structures can directly impact joint function, leading to pain, instability, or limited range of motion.
2. ***EXTRA-ARTICULAR***
1. **Definition**: Extra-articular refers to structures or conditions that are located outside the joint space.
2. **Components**: Extra-articular structures include ligaments, tendons, muscles, bursae, fascia, nerves, and blood vessels that are situated around the joint but do not directly reside within the joint capsule.
3. **Function**: Extra-articular structures provide stability, support, and movement control to the joint. They help transmit forces generated by muscles and protect the joint from excessive stress or friction.
4. **Location**: Extra-articular structures are found surrounding the joint but not within the joint cavity itself.
5. **Examples**: Ligaments outside the joint capsule (extracapsular ligaments), tendons connecting muscles to bones near the joint, and bursae that reduce friction between structures are considered extra-articular.
6. **Significance**: Injuries or conditions affecting extra-articular structures can also impact joint function and movement. For example, a torn ligament or inflamed bursa can cause pain and affect joint stability.
56
New cards
MSK Diagnosis Flow Chart
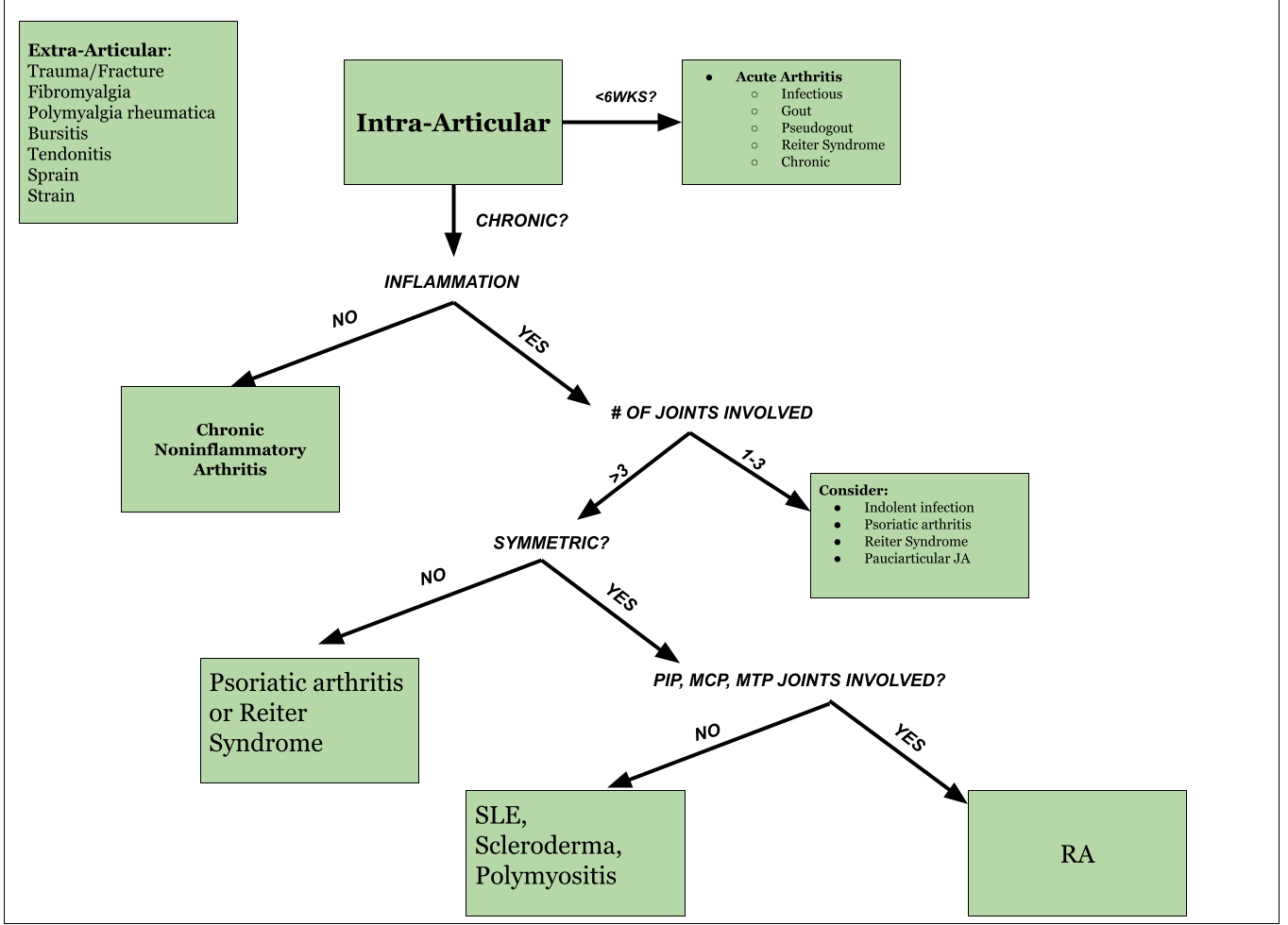
57
New cards
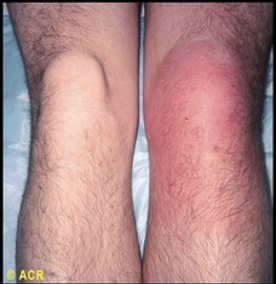
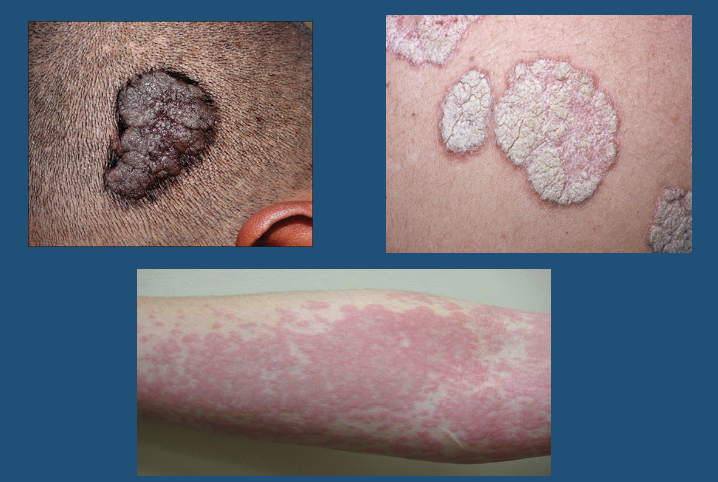
\
Septic Joint
58
New cards
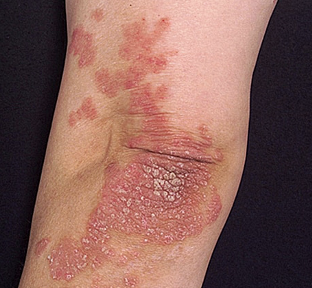
\
Psoriasis
59
New cards
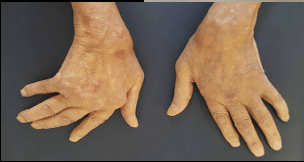
RA
60
New cards
What are the four signs of inflammation?
Pain, warmth, redness, swelling
61
New cards
What portion of the ROS is specific for MSK?
Joint pain, Joint swelling, Joint redness, Joint deformities, Neck pain, Back pain
\
\
62
New cards
What is the Nexus Criteria?
Normal alertness
No posterior midline cervical spine tenderness
No focal neurologic deficits
No evidence of intoxication
\
No posterior midline cervical spine tenderness
No focal neurologic deficits
No evidence of intoxication
\
63
New cards
What are four tips for a successful MSK examination?
Look for symmetry of involvement
Assess surrounding tissues
Test ROM
Test Muscle Strength
\
Assess surrounding tissues
Test ROM
Test Muscle Strength
\
64
New cards
When performing the examination, **ALWAYS** inspect ________________________, as well as the area itself
\
\
the joint above and below the area of complaint
65
New cards
Along with inspecting the joint what is also important to check with any MSK injury?
Distal pulses, capillary refill, ROM
66
New cards
What are important things to note about skin lesions?
* Color
* Size
* Shape and symmetry
* Border
* Texture/Consistency
* Configuration or arrangement
* Location/Distribution
* Symptoms: pruritus, pain, etc
* Size
* Shape and symmetry
* Border
* Texture/Consistency
* Configuration or arrangement
* Location/Distribution
* Symptoms: pruritus, pain, etc
67
New cards
Flexor Surfaces
These are areas of the body where the skin folds when a joint is bent. Examples include the inner elbows, inner wrists, and behind the knees.
68
New cards
Extensor Surfaces
These are areas of the body where the skin is stretched when a joint is extended. Examples include the outer elbows and the front of the knees.
69
New cards
Acral
This refers to the extremities of the body, including the hands, feet, fingers, and toes.
70
New cards
Palmar/Plantar Surfaces
"Palmar" refers to the palm side of the hand, and "plantar" refers to the sole of the foot.
71
New cards
Sun exposed Areas
These are parts of the body that are regularly exposed to sunlight, such as the face, neck, arms, and legs.
72
New cards
Symmetry (*Skin Distribution)*
In dermatology, symmetry refers to the balanced and equal distribution of skin conditions on both sides of the body. Asymmetrical presentations may raise concerns about skin diseases.
73
New cards
Hearing Bearing Areas
These are regions of the body covered by hair, such as the scalp, beard area in men, and underarm regions.
74
New cards
Intertriginous
This refers to areas where two skin surfaces come into contact, such as skin folds. Intertriginous areas are prone to moisture and friction and can be more susceptible to certain skin conditions like fungal infections.
75
New cards
Dermatomal
This term relates to the distribution of nerves in the body. Dermatomal areas are regions of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve. It's relevant when assessing neurological conditions that follow specific nerve patterns.
76
New cards
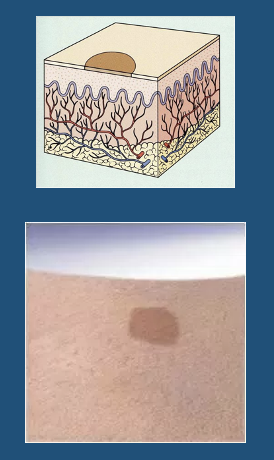
\
***Macule***
* L. macula, “spot”
* < 1 cm
* Completely flat
* Circumscribed alteration in skin color
* Macules may be of any color or shape
* Superficial
* *Macular* - having the form or structure of a macule
* L. macula, “spot”
* < 1 cm
* Completely flat
* Circumscribed alteration in skin color
* Macules may be of any color or shape
* Superficial
* *Macular* - having the form or structure of a macule
77
New cards
Macule
78
New cards
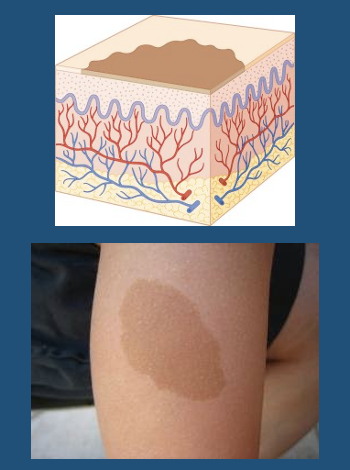
Patch
* Macule’s “big brother”
* Flat lesion
* Larger than 1 cm
* Superficial
* Any color
* Macule’s “big brother”
* Flat lesion
* Larger than 1 cm
* Superficial
* Any color
79
New cards
Patch
80
New cards
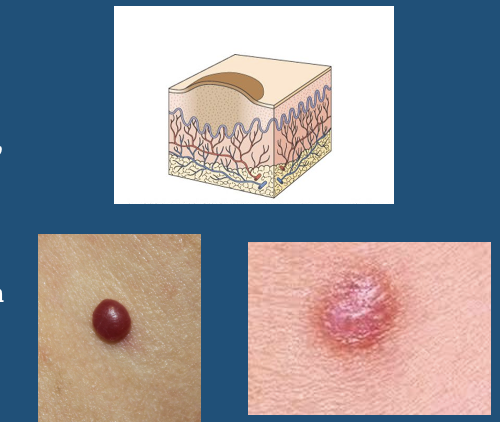
Papule
\
* Solid, well circumscribed, elevated lesion
* Less than 1 cm diameter
* Color may vary
* Superficial
* Papular - having the form or structure of a papule
\
* Solid, well circumscribed, elevated lesion
* Less than 1 cm diameter
* Color may vary
* Superficial
* Papular - having the form or structure of a papule
81
New cards
Papule
82
New cards
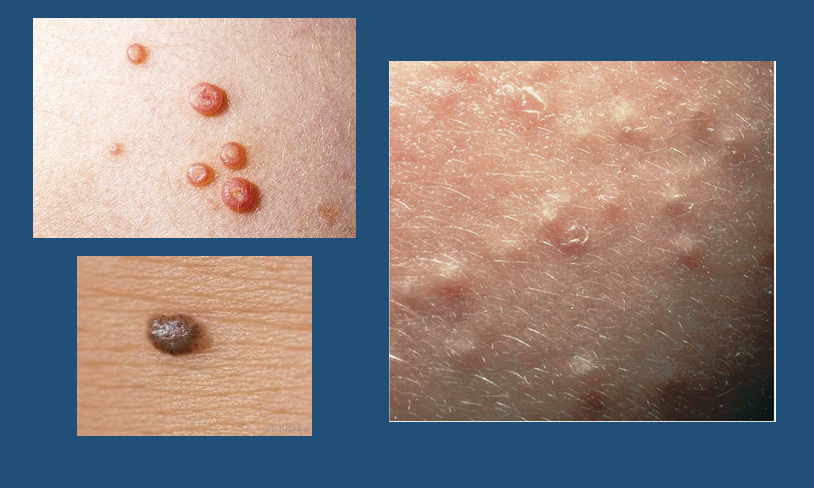
Plaque
●Papule’s “older brother”
●Solid, well circumscribed, elevated lesion
●Typically flat-topped
●> 1 cm diameter
●Like papules, plaques are superficial
●Papule’s “older brother”
●Solid, well circumscribed, elevated lesion
●Typically flat-topped
●> 1 cm diameter
●Like papules, plaques are superficial
83
New cards
Plaque
84
New cards
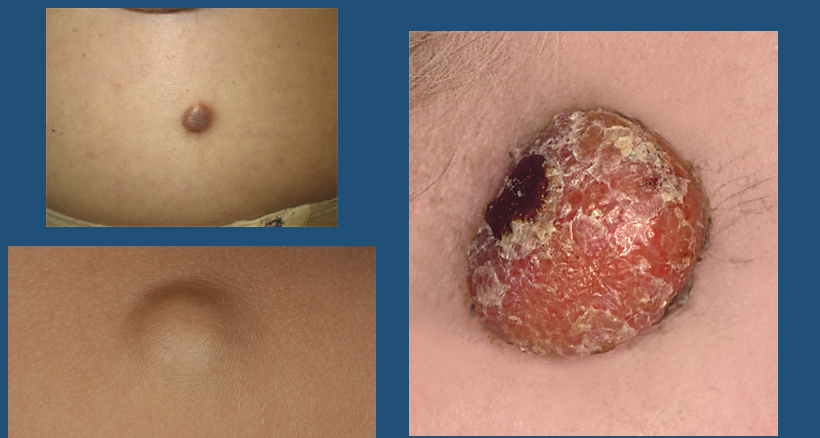
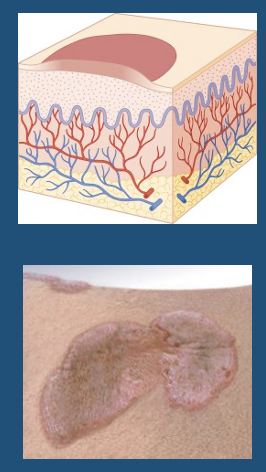
Nodule
\
●L. nodulus, “small knot”
●Raised solid mass
●< 2 cm
●May be in the epidermis, dermis, or subcutaneous tissue
●Its depth helps distinguish it from a papule
\
●L. nodulus, “small knot”
●Raised solid mass
●< 2 cm
●May be in the epidermis, dermis, or subcutaneous tissue
●Its depth helps distinguish it from a papule
85
New cards
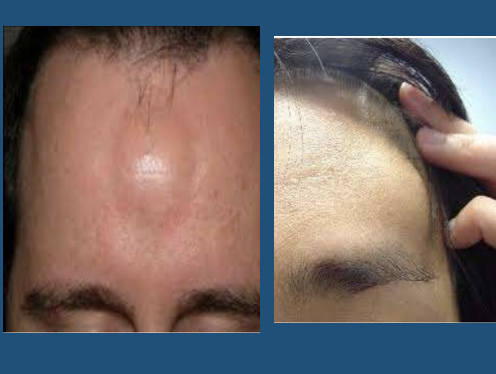
tumor
\
●Nodule’s “older brother”
●Solid, firm lesion
●> 2 cm
●Can also be called a “mass” – pro tip: when talking to a patient, “mass” is better than tumor
\
●Nodule’s “older brother”
●Solid, firm lesion
●> 2 cm
●Can also be called a “mass” – pro tip: when talking to a patient, “mass” is better than tumor
86
New cards
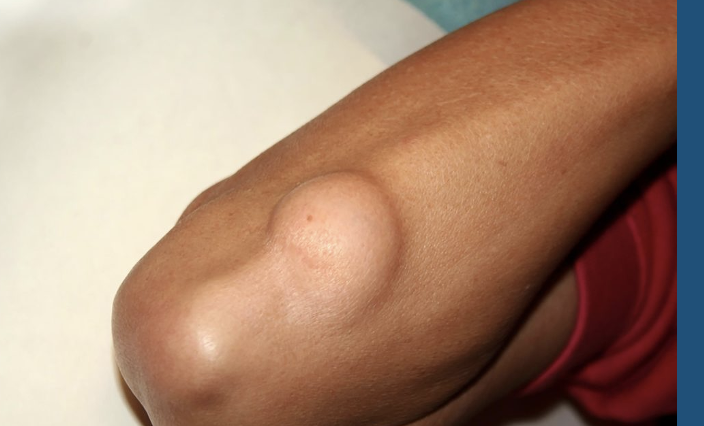
tumor
87
New cards
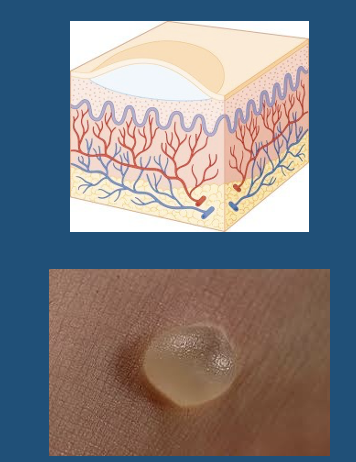
Vesicle
\
●L. *vesicula*, “little bladder”
●Circumscribed elevation containing clear fluid
●< 0.5 cm
●“Blister”
●Superficial
●*Vesicular* - having the form or structure of a vesicle
\
●L. *vesicula*, “little bladder”
●Circumscribed elevation containing clear fluid
●< 0.5 cm
●“Blister”
●Superficial
●*Vesicular* - having the form or structure of a vesicle
88
New cards
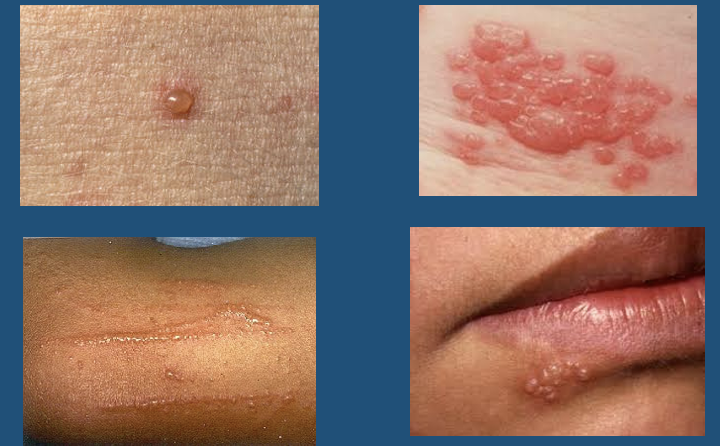
Vesicle
89
New cards
Bulla
\
●L. *bulla*, “bubble”
●Vesicle’s “older brother”
●> 0.5 cm diameter
●Superficial
●*Bullous* - having the form or structure of a bulla
\
●L. *bulla*, “bubble”
●Vesicle’s “older brother”
●> 0.5 cm diameter
●Superficial
●*Bullous* - having the form or structure of a bulla
90
New cards
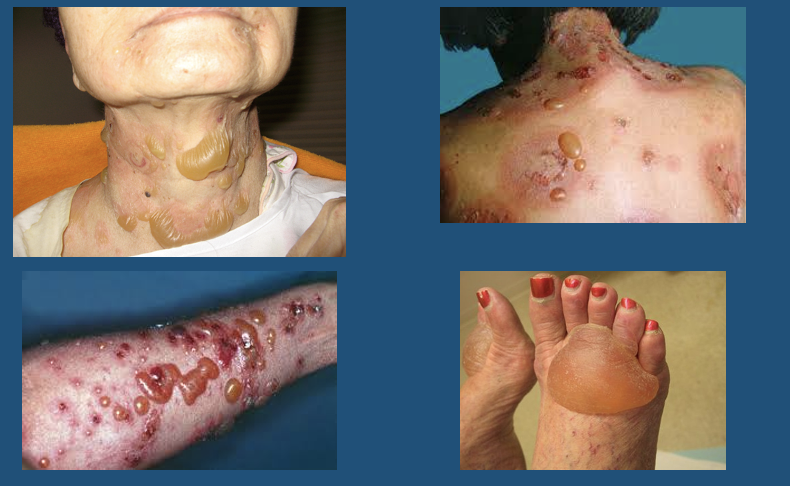
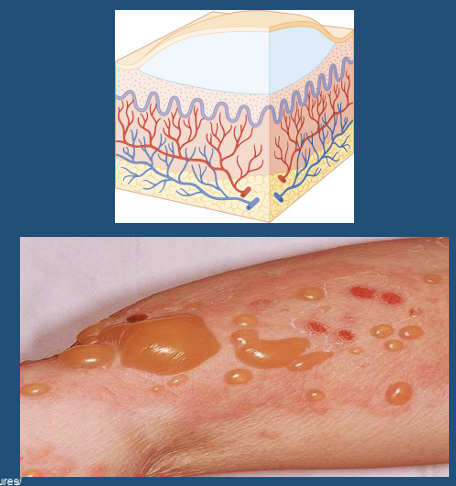
Bulla
91
New cards
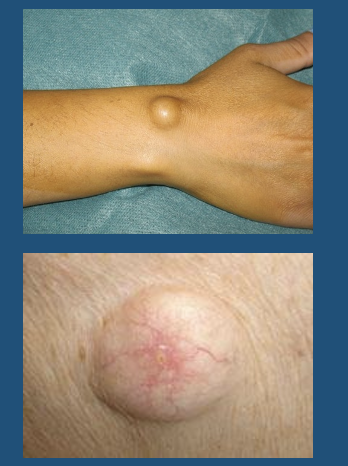
Cyst
\
●Closed sac that contains liquid or semi-solid material
●Contents are not purulent
●Feels “fluctuant”
\
●Closed sac that contains liquid or semi-solid material
●Contents are not purulent
●Feels “fluctuant”
92
New cards
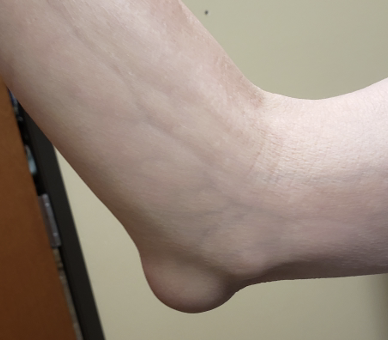
Olecranon Bursitis - used for cyst example
93
New cards
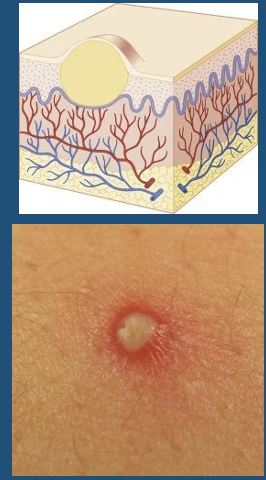
Pustule
\
●Circumscribed elevation of skin containing purulent material (i.e. fluid and leukocytes)
●< 1 cm
●Often surrounded by an erythematous base
\
●Circumscribed elevation of skin containing purulent material (i.e. fluid and leukocytes)
●< 1 cm
●Often surrounded by an erythematous base
94
New cards
Pustule
95
New cards
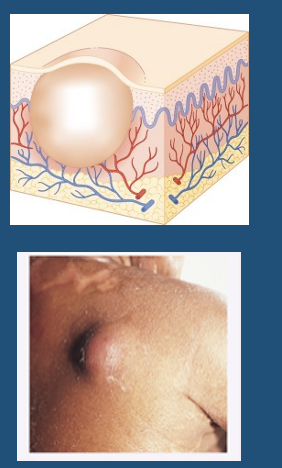
Abscess
●Localized collection of purulent material (“pus”)
●Vesicle’s big brother
●Located in the dermis or subcutaneous tissue
\
●Localized collection of purulent material (“pus”)
●Vesicle’s big brother
●Located in the dermis or subcutaneous tissue
\
96
New cards
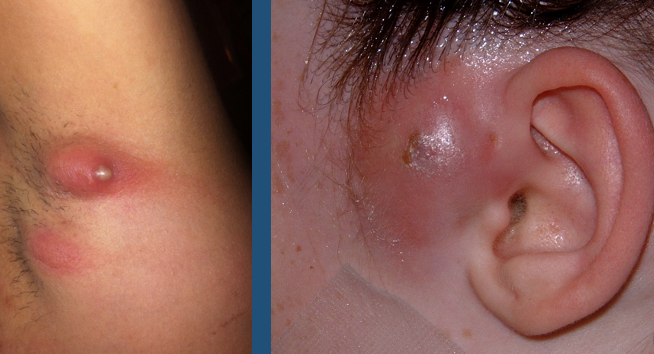
Abscess
97
New cards
More skin lesions
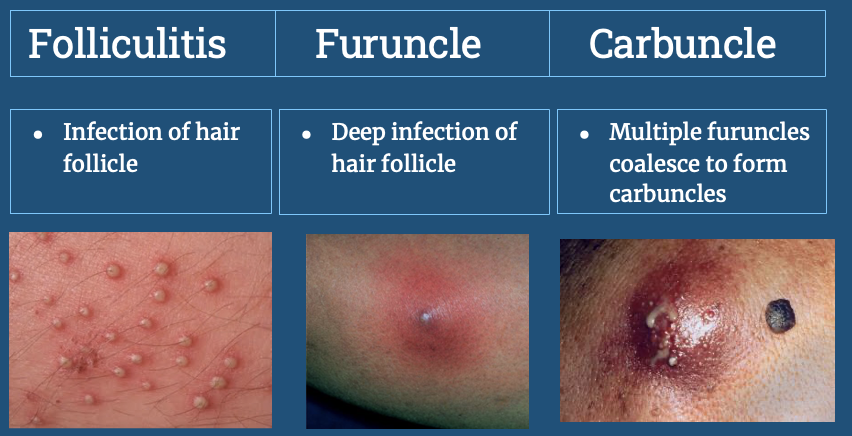
98
New cards
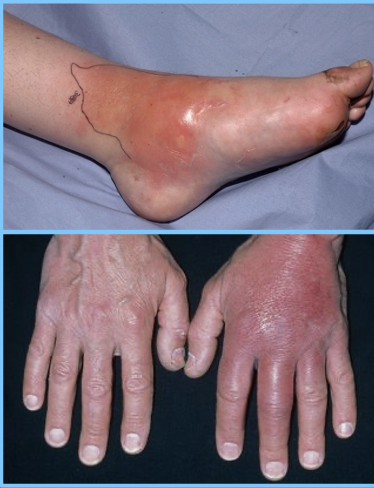
Cellulitis
●Bacterial skin infection of the dermal and subcutaneous tissue
●Presents with skin erythema, warmth, induration, and tenderness
●Group A strep or Staph aureus
●Bacterial skin infection of the dermal and subcutaneous tissue
●Presents with skin erythema, warmth, induration, and tenderness
●Group A strep or Staph aureus
99
New cards
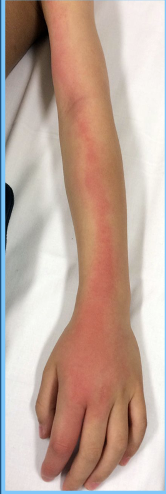
Lymphangitis
•Inflammation of the lymphatic channels that occur as a result of infection at a site distal to the channel
•Streptococcus
(β-hemolytic)
•Inflammation of the lymphatic channels that occur as a result of infection at a site distal to the channel
•Streptococcus
(β-hemolytic)
100
New cards
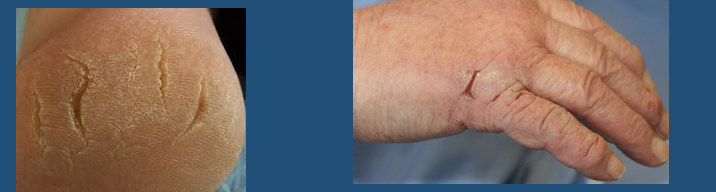
Fissure
●Sharply defined, linear or wedge-shaped tear in the epidermis
●Generally deeper than wide
●Sharply defined, linear or wedge-shaped tear in the epidermis
●Generally deeper than wide