Week 8/9: Regulated Health Professions; Legislative Framework
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
At what legislative level is nursing regulated?
provincial/territorial level — NOT federal
Self regulation
privilege granted to a profession by P/T government to be regulated by people in the profession instead of the govt
Self-regulation of nursing in ON + priority
by CNO (regulatory body)
PRIORITY = protection of public interest/safety
Self regulation allows a profession to (5)
Govern members
Set standards for entry (entry-to-practice competencies)
Establish educational requirements
Deal with complaints
Discipline members
2 legislations that regulate nursing profession in ON
Regulated Health Professions Act (RHPA) + Nursing Act
Regulated Health Professionals Act (1991) — OUTLINES (2)
Umbrella law that governs all health professions in ON
scope of practice
controlled acts authorized to regulated professions (pose risk to public if not performed by qualified practitioner)
grants self-regulating authority to all regulated health professions in ON as long as they follow the rules embedded w/in HPP
Health Professions Procedure Code (RHPA) — HPPC
legislation in RHPA
outlines rules/responsibilities of each professional college of self-regulating professions in ON under profession-specific Acts = NURSING ACT
HPPC (RHPA): Responsibilities of Professional Colleges in ON (8)
_ members
handling _
conducting _
_ + _ hearings
_ + _ programs
mandatory _
funding for _
_ processes re: registration & complaint decisions
registering members
handling complaints
conducting investigations
disciplinary + fitness to practice hearings
quality assurance + patient relations programs
mandatory reporting
funding for victims of sexual abuse by members
appeal processes re: registration & complaint decisions
**How are College responsibilities outlined by RHPA?
HPPC contains practical rules CNO must follow to be allowed to govern the practice of nurses (self-regulation)
linked to Nursing Act → sets guidelines for CNO (regulatory body)
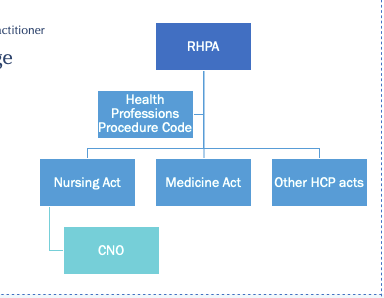
Nursing Act (1991)
informed by RHPA — details how nursing will self-regulate by
…establishing mandate for CNO
…defining scope of practice
i.e., how RHPA/HCCP rules are operationalized w/in the nursing profession in ON
…Eg: RHPA = all profesional colleges must have QA program → Nursing Act determines what the QA program regulated by CNO will look like
Nursing Act: Regulations (7) — 2 KEY
scope of practice
controlled acts
registration
entry to practice
title protection
quality assurance
professional
are nursing regulatory college + professional association combined in ON
NO!
separate regulatory college (CNO) + separate professional association (RNAO)
CNO vs. RNAO (4v3)
CNO: regulatory college — protect public’s interests
…entry to practice requirements
…practice standards
…QA program
…enforce practice + conduct standards
RNAO: professional association — protect/support nurses in providing best QoC
…avocacy (professional + political)
…malpractice insurance
…lobby govts in nurses’ professional interests
Scope of Practice Statement (Nursing Act 1991) + who it applies to
Practice of nursing is the promotion of health + assessment/provision of care/ treatment of health conditions by supportive, palliative, preventative, therapeutic, rehabilitative means in order to attain/maintain optimal function
Applies to ALL categories of nurses – RNs, RPNs, NPs
CNO Nursing Registration — 3 Categories
Practical Nurses (RPN): less complex pt, predictable trajectory (↓risk neg outcomes)
Registered Nurses: ↑ acuity/more complex pts in more unpredictable situations (↑ risk neg outcomes)
Advanced Practice Nurses (NPs): larger scope of practice + more controlled acts
Each CNO nurse category has (3) + RN General Class example
specific education requirements + ETPCs + practice standards
RN General Class Entry to Practice in ON
…education requirement = BScN
…evidence of nursing practice = clinical placements
…complete NCLEX + jurisprudence exam
…English / French language proficiency
…proof of citizenship/ PR/ authorization work under under IRPA
…complete Declaration of Registration Requirements
Registration vs. Licensing
REGISTRATION (≠ license):
… application + acceptance as a member of the college
… publicly recognized as member of the profession
LICENSING
… license to practice = authority to perform controlled acts authorized to nurses
… 5 classes: General (RN/RPN), Temporary, Extended (NP), Special, Emergency
How can a nurse taking a break from the profession retain the ability to practice nursing again in the future?
register in non-practicing license class
= still registered w/ CNO → allows for reinstatement of license if want to nurse again later on
What happens if a non-practicing nurse gives up registration and later decides to nurse again?
must restart whole ETP process again (NCLEX, jurisprudence exam)
Temporary license
applicants who have met all requirements to register in the General Class, except for the education + registration exam requirement
Emergency license
provincial government or CNO council determines that it is in the public interest to issue Emergency certificates of registration to qualified nurses
Controlled Acts
act that could cause harm if performed by someone who does not have the knowledge, skill, judgement to do it
i.e., competence to perform it safely
How many controlled acts exist under RHPA? How many of these can nurses do?
RHPA = 14 → Nurses = 5
Controlled Acts authorized to nurses (5)
Performing a procedure on tissue below dermis (mucus membrane surface)
…drawing blood, packing woundAdministering substance by injection or inhalation
…high humidity oxygen (O2 therapy)Putting instrument/hand/finger beyond body opening (ENT, pp, anus, etc.)
Dispensing drug (drug given to pt to take at a later date (≠ in hospital)
Psychotherapy (specialized nurses tx mood/thought/emotion/cognition d/o)
Expanded Nursing Services for Patients Act (1997)
amended RHPA + Nursing Act to give NPs extended scope of practice in ON
i.e., expanded scope of practice for RNs w/ extended certificate of registration = NPs
Additional Controlled Acts for NPs beyond RN scope (4)
Communicate Dx + order Dx tests (XR)
Apply/order energy (defibrillation)
Set/cast bone fracture
Prescribe + dispense + sell + compound meds (incl controlled subtances)
(…RNs can only dispense)
Exceptions re: Controlled Act Authorization (9)
situations where authorization is not required for controlled acts if a person is trained + competent (lay person)
Daily activities (BG testing)
First aid/emergency
Nursing students (under preceptor supervision)
Treating person by spiritual means
Body piercing
Tattooing
Electrolysis
Male circumcision as part of a religious ceremony
Lab personnel taking blood in a licensed lab
PRACTICE Q — pt you are triaging in ED goes into cardiac arrest. What can you do within your RN scope of practice?
A: get crash cart immediately + apply energy (defibrillate the pt asap)
B: begin compressions + call a code
C: intubate the patient if they're not breathing
D: administer EPI before the code team arrives
A: get crash cart immediately + apply energy (defibrillate) → no, outside scope
B: begin compressions + call a code → yes, w/in scope
C: intubate the patient if they're not breathing → no, RT job
D: administer EPI before the code team arrives → no, no order
Initiating a Controlled Act + 5 criteria
Competence:
Client factors:
Environmental supports:
Documentation:
Nurse Accountability:
Mechanisms by which a nurse is granted authority to perform a CA
Competence: knowledge, skill, judgement to do it safely + effectively
Client factors: must have nurse-pt relationship + does condition warrant procedure?
Environmental supports: resources available to do it safely + if it goes wrong
Documentation: must record on pt chart that they’ve initiated a controlled act
Nurse Accountability: take responsibility for initiating + give rationale for why
Limitations to RN initiation of CAs independently re: Public Hospitals Act (ON)
RNs have authority under regulations to initiate but other legislation/practice setting policy limit WHERE we can do it
under PHA — RNs NOT allowed to initiate CAs u hospital w/o order from MD/NP
Discipline
Internal matter governed by nursing regulatory body (CNO)
≠ criminal charges UNLESS criminal negligence
…per HPPC (RHPA): each college must deal w/ discipline matters w/in their college
Discipline may involve violation of (2)
Code of Ethics
Professional misconduct
Discipline Proceedings — role (2) + process (1)
protect public from unsafe nursing services + preserve public confidence in the nursing profession
address serious cases of misconduct and incompetence
…nurses sit in front of panel → hear evidence to determine presence ± extent of professional misconduct → decide how to proceed/disciplinary action
Alternative dispute resolution process
Less serious cases
How are complaints handled & recorded by CNO?
ALL complaints brought to CNO are investigated to determine the best course of action to resolve the issue
ALL discipline hearings are publicly available in “The Standard” on CNO wesbite
Reporting a Colleague re: improper professional conduct/failure to meet practice standards — responsibilities (2), process (1), exception (1)
LEGAL obligation! Failure to report = professional misconduct!!
1st approach the person → then employer if needed (try resolve w/o going to CNO)
per HPPC — must report SUSPECTED SEXUAL ABUSE of pt IMMEDIATELY to CNO FIRST (not employer first)
Failure to report suspected sexual abuse of a client to CNO
$25,000 fine + liable for professional misconduct
Fitness to practice (not always professional misconduct) + process (3)
mostly re: incapacity — physical/mental ability to practice safely
Physical + psychological exams
Hearing to decide if a nurse is fit to practice
Nurses entitled to a lawyer (license may be suspended during process)
Collaborative practice in HC — WHO definition
multiple health workers from different professional backgrounds provide comprehensive services by working with patients, families, caregivers, communities to deliver the highest quality of care across settings
Nursing Act 1991 scope of practice
promotion of health
assessment + provision of care for + tx of health conditions
supportive, therapeutic, palliative, rehabilitative means
attain/maintain optimal function
simple definition of scope of practice
range of activities that nurses have legislative authority to perform → under Nursing Act (1991) + RHPA (1991)
3 things that can impact scope of practice
Employer policies
Practice setting requirements
Individual nurse competence
CNO Scope of Practice Standard (2025): Nursing Accountabilities (3)
Authority — know their legislative scope of practice (incl. controlled acts & authorizing mechanisms)
Context — determine if their practice setting supports performing the activity + has available resources to support safe client care
Competence — ensure they have individual knowledge/skill/judgement to perform activity
How do you determine who is most appropriate care provider (RN vs. RPN) for a particular pt at a particular time in a particular situation?
Nurse registration class doesn’t determine who should provide care for specific Dx or S/S → 3 accountabilities from CNO Scope of Practice statement help determine
Authority → consider complexity & predictability of pt’s condition + needs r/t controlled acts & authorizing mechanisms
Context → consider stability/predictability of practice environment, availability of necessary resources/supports for safe patient care or backup in place
Competence → be aware of limits to individual competence, consult w other HCPs if needed + reflect on own knowledge/skill/judgment before proceeding
PRACTICE Q – Pt admitted w/ pre-eclampsia requires close monitoring (med emergency) → Who is the most appropriate care provider to assign to this pt?
A) Registered Practical Nurse
B) Personal Support Worker
C) Registered Nurse
D) Licensed Practical Nurse
A) Registered Practical Nurse
B) Personal Support Worker
C) Registered Nurse
D) Licensed Practical Nurse
PRACTICE Q – Nurse working on an acute medicine unit of large teaching hospital has been assigned a pt w/ CHF who requires I&Os to be monitored q1h. The patient also has elevated BP → This nurse is most likely a
A) RN, as the situation presents high risk for negative outcomes and an RPN couldn't manage the acuity
B) NP, as CHF patients always require NP support
C) An experienced RPN, as they would have access to many consultation resources w/in the teaching hospital
D) PSW, as they can collect vital signs
A) RN, as the situation presents high risk for negative outcomes and an RPN couldn't manage the acuity → “RPN couldn't manage the acuity” = FALSE
B) NP, as CHF patients always require NP support → NP usually doesn’t have pt assigned = provider (oversee orders, scripts)
C) An experienced RPN, as they would have access to many consultation resources w/in the teaching hospital
Context → teaching hospital = many consultation resources + collab available
Authority → CHF suggests HTN isn’t new concern = RPN is regulated to perform all those tasks + assuming we have order
D) PSW, as they can collect VS → consider Competence (unregulated care provider won’t have apt knowledge/skill/judgement)
Authorizing mechanisms
Mechanisms by which nurses receive authority to perform procedures
3 authorizing mechanisms re: nurse performing controlled acts
Orders
Delegation
Initiation
Initiation — authorizing mechanism (1) + limitation (1)
independent decision-making by a nurse that a CA is necessary + then performing that CA in the absence of an order
NOT ALLOWED IN HOSPITALS in ONTARIO dt Public Hospitals Act legislation
…nurses NEED MD/NP ORDER to be able to perform a controlled act in hospital
Order — authorizing mechanism (1) + who (4) + types (2)
prescription/direction from RHP w/ legislative ordering authority for a procedure, Tx, drug, intervention that permits performance of procedure by another person
= decision to perform the procedure for a particular pt or group of pts
WHO? → MD, NP, midwives, dentists
HOW? → direct orders and directives.
Orders are required when the procedure is… (3)
a controlled act authorized to nursing but nurse has no authority to initiate
required under Public Hospitals Act or other legislation governing pt services
required by practice setting policy or per MD’s plan of care
Direct Orders — for who + how
pt-specific direction/instruction re: an activity
written or verbal (verbal ONLY if emergency & prescriber unable to document order)
Directives — for who + how + from who
pre-WRITTEN order for an activity or series of activities
…can be implemented for a number of pts who meet specific conditions w/in specific circumstances
…RHP w/ legislative authority to order the activity has the ultimate responsibility
Eg: MDs write directives for ED nurses if someone presents w/ CP, SOB → b/o on that directive, nurses can immediately proceed w/ care like ordering ECG, supp O2, draw blood, give specific meds w/o pt being screened/assessed by MD
PRACTICE Q – When assessing a pt in hospital, the nurse determines that their wound is not healing well & they would benefit from a vac dressing. Can the nurse initiate the controlled act of performing a procedure below the dermis to ensure the pt’s wound healing improves? → Y/N?
NO → nurse cannot independently initiate controlled acts in hospitals in ON dt PHA legislation → requires order
PRACTICE Q – are orders only required for controlled acts? → Y/N?
NO! can have orders for vital signs, certain diets, etc.
Delegation
formal process — RHP (who is authorized + competent to perform a CA procedure) delegates the performance of a controlled act to someone regulated OR unregulated (who is not authorized by legislation to perform it)
DELEGATION is ONLY rt CONTROLLED ACTS
Can nurses give or receive delegation? who decides?
BOTH → nurses can receive delegation (from MD/NP) + delegate to others (PSWs)
Based on organization policy
PRACTICE Q – which of the following are considered delegation?
A) Nurse asks PSW to weigh patient
B) RN asks RPN to insert catheter ordered by MD
C) Someone is asked to perform a controlled acts outside of legislation
A → NOT delegation
B → NOT delegation (both RN/RPN are authorized by legislation to perform that act)
C → DELEGATION! bc controlled act
PRACTICE Q – Which of the following statements is true?
A) Delegation requires an order
B) An order requires delegation
C) Delegation provides the legal authority to perform a controlled act
D) An order outlines how to perform a controlled act
E) Orders are only used for controlled acts
C → Delegation provides the legal authority to perform a controlled act
Nurse responsibility re: delegation (2)
responsible for decision to delegate or accept delegation
…ensure DELEGATED PERSON is competent to perform the CA + it is in the pts best interest
Nurse responsibility re: performing a CA that has been delegated to them (2)
responsible for the
…decision to carry out the CA
…performance of the CA
i.e., ensure YOU are competent to perform the CA before accepting a delegation
Delegation — how? what is required?
written or oral
…documentation is required for both
PRACTICE Q — Can nurses delegate a controlled act that has been delegated to them? → Y/N?
NO!
…nurse cannot further delegate a CA that they have been delegated to someone else → called sub-delegation
Subdelegation
Delegating a CA that has been delegated to you to someone else → NOT ALLOWED
Unregulated Care Providers (PSW) — who are they accountable to + regulated by?
accountable to their employers, not an external body (college)
NO regulatory mechanism to set standards/ monitor quality of service
Can nurses delegate controlled acts to UCP? when?
YES → delegation is appropriate if nurse ensures UCP is competent to perform it
…nurse is accountable for determining if it's apt to do so in that particular pt situation
What acts do UCP have the authority to perform?
non-controlled acts
controlled acts via exception or delegation
A nurse cannot assume that a UCP is _ so must ensure _
…competent to perform a procedure regardless of how straightforward it appears
…measures to promote continuing competence of UCP
Give an example of RN delegation to UCP
RN delegates a PSW working in the community to provide wound care/ heparin SC
The UCP must understand (3) before performing a delegated CA procedure
their responsibilities/competence
when + who to ask for help
process for reporting outcome of the procedure
6 requirements for nurse teaching UCPs re: delegation
The nurse…
has _, _, _ to _
has additional _, _, _ to _
accepts _
determined UCP has _ to _
may teach UCP a CA to _
evaluates _
The nurse…
has knowledge, skill, judgement to perform CA competently
has additional knowledge, skill, judgement to teach
accepts sole accountability for the decision to teach
determined UCP has acquired the knowledge/skill/judgement to perform the CA
may teach UCP a CA to perform it for more than one pt if appropriate
evaluates UCP’s continuing competence
Nurses are held accountable for
_ and _
teaching _
Knowing + understanding _
taking action to ensure _
Collaboration w/ _ to _
actions & decisions – accepting + giving delegations, teaching UCP
Knowing + understanding roles of other team members
Taking action to ensure pt safety
Collaboration w/ pts, other nurses, IPT _ benefit the pt
Is the nurse accountable for actions and decisions of other care providers when the nurse has no way of knowing those actions?
NO!
…Eg: student nurse performs procedure w/o preceptor knowing → preceptor would NOT be held responsible for the student's action
4 circumstances where a nurse can be found guilty of professional misconduct re: delegation
Violate/fail to meet practice standard
Direct someone to perform nursing tasks they are not competent to do (student, UCP)
Fail to inform employer of inability to accept responsibility rt areas where specific training required/not competent in
Violate Nursing Act / RHPA provision