AP Bio Chapter 3 Unit 1: Chemistry of Life
1/39
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Carbon
A chemical element that naturally occurs in all organic compounds and is found in all forms of life
It can form large, complex, varied molecules
Hydrocarbon
Organic molecules consisting only of carbon and hydrogen
Vitalism
Mechanism
Organic molecules
Macromolecules made up of carbon and hydrogen but can include other elements
Examples: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
Valence
Unpaired electrons on the outer shell
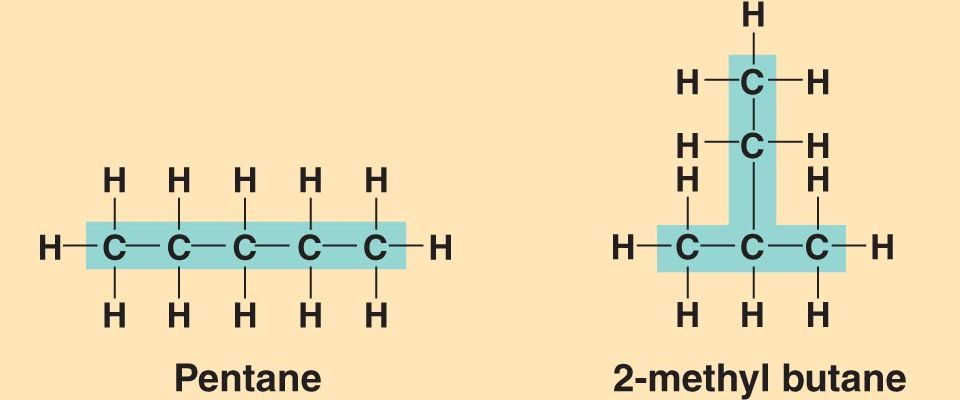
(Structural) Isomer
One of two or more compounds that have the same number and kinds of atoms but with different geometric arrangements
Example: Pentane and 2-Methylbutane
Cis-trans isomer
The carbons have covalent bonds to the same atom, but the atoms differ in spatial arrangement due to inflexible double bonds
Example: cis— But-2-ene & trans— But-2-ene
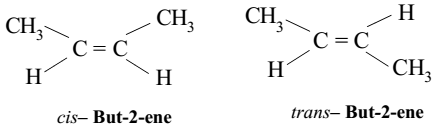
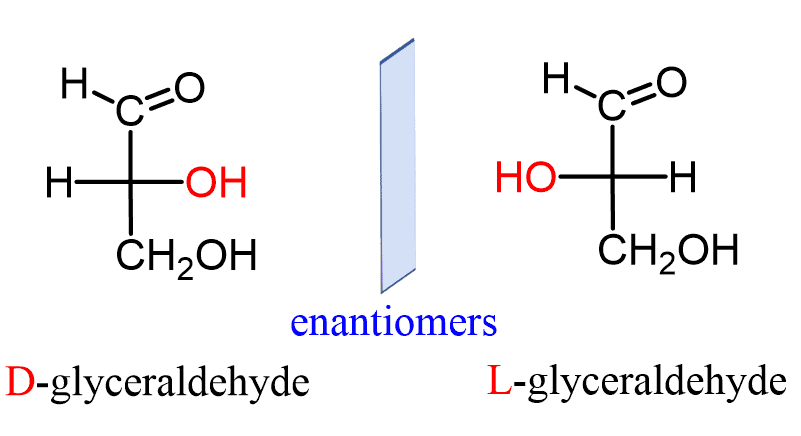
Enantiomers
Isomers that are mirror images of each other (cannot be superimposed on top of each other); usually only one is biologically active
Example: L-glucose and D-glucose
Macromolecules
A molecule containing a very large number of atoms
Examples: Any organic molecules, synthetic polymers such as polyester or nylon
Polymer
Long molecule consisting of monomers
Example: Any organic molecules, cellulose, etc.
Monomer
Atoms or small molecules that bond together to form polymers
Dehydration
Two monomers bond together through the loss of a water molecule (synthesizing)
Hydrolysis
The bond between two monomers break when a water molecule is added (breaking down)
Carbohydrates
An organic compound made of sugars used as fuel or building materials
Monosaccharides
Simplest forms of sugar; most basic units which make up disaccharides and polysaccharides
Example: glucose, fructose, galactose
Disaccharides
Sugars made up of two monosaccharides
Example: sucrose, lactose, maltose
Polysaccharides
Sugars made up of more than two monosaccharides
Examples: starch, glycogen, cellulose
Lipids
Organic compounds that are hydrophobic and made of mostly hydrocarbons in covalent bonds; used in energy storage, cell membrane structural components, insulation
Hydrophobic
Little to no affinity for water
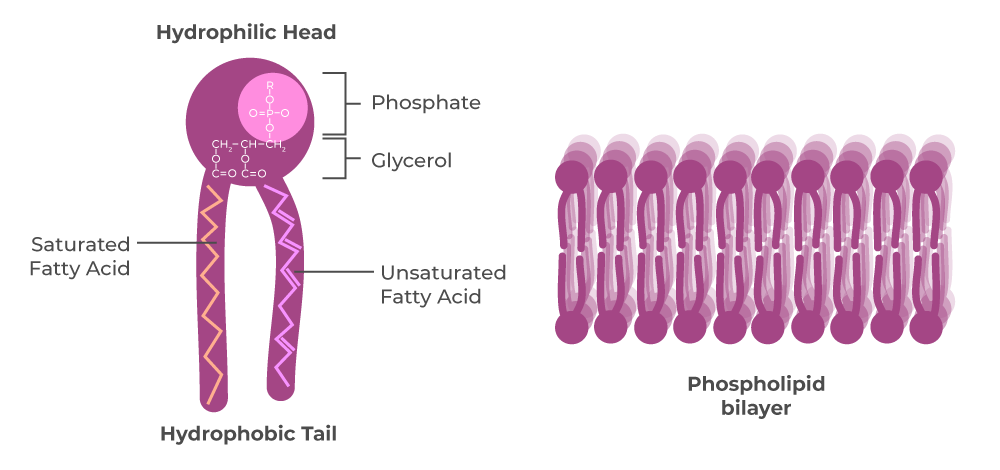
Phospholipids
Major component of the cell membrane (phospholipid bilayer); made up of 2 fatty acids and a phosphate group; kink due to double bonds
Steroids
Lipids made up of four fused rings
Examples: sex hormones (testosterone and estrogen), cholesterol, bile acids
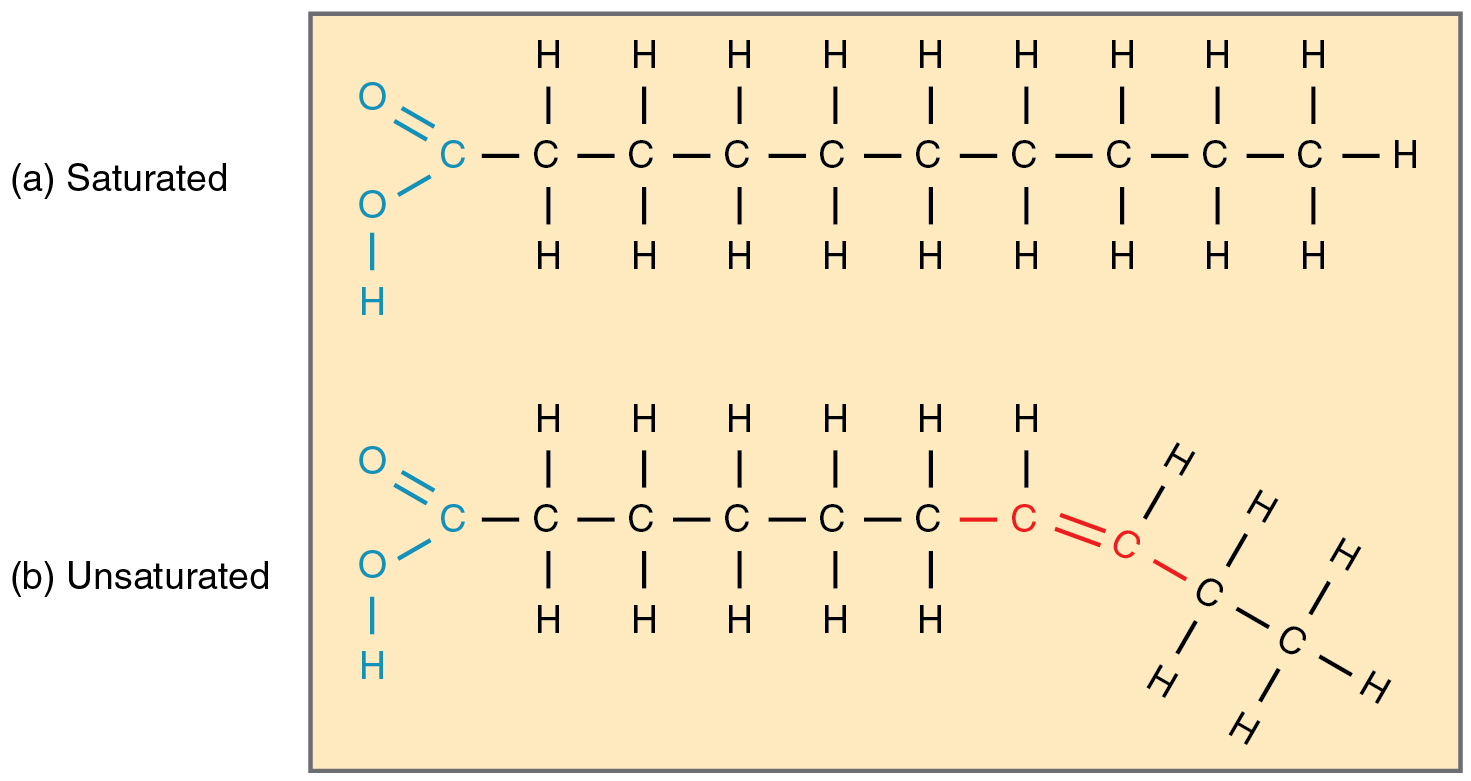
Saturated fat
Fatty acid molecule WITHOUT double bonds
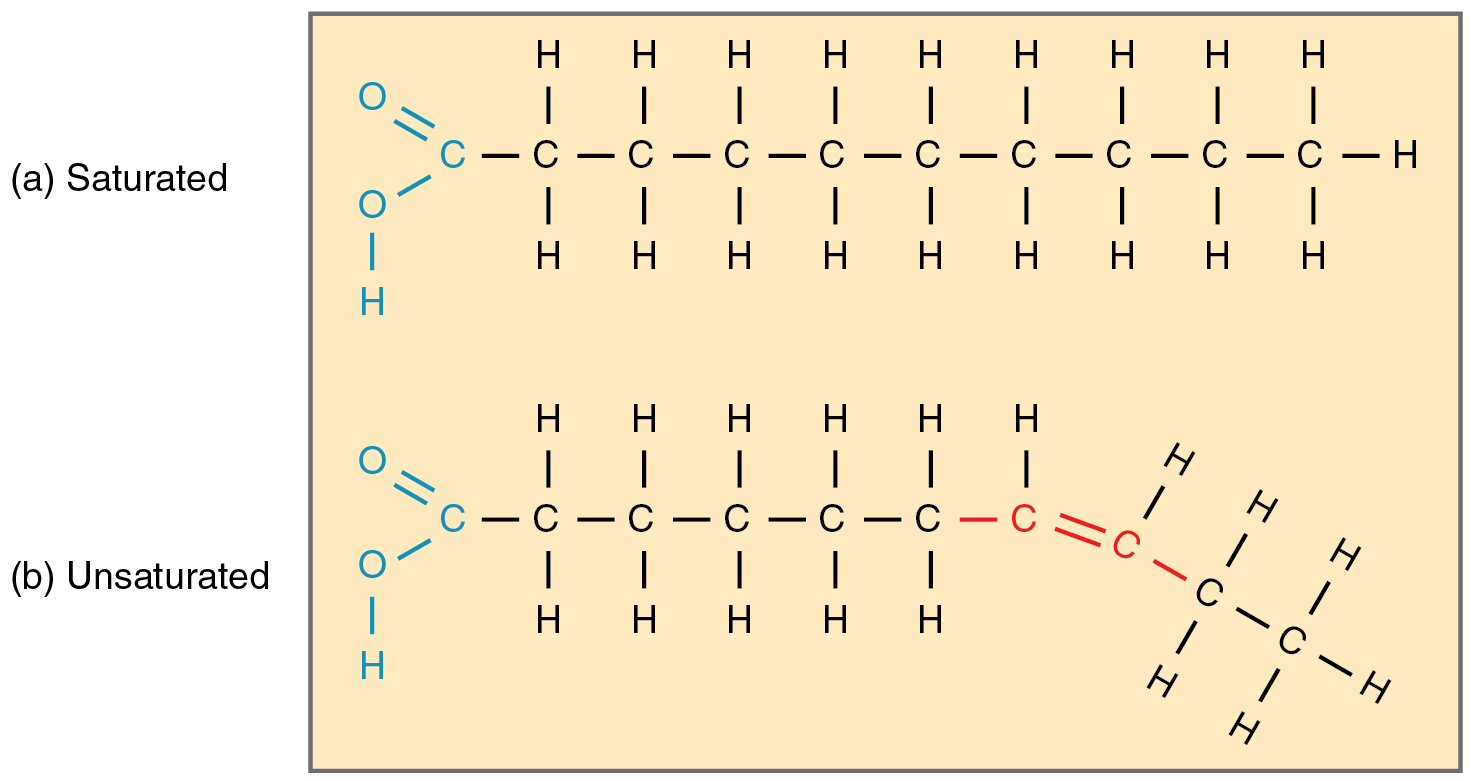
Unsaturated fat
a fat or fatty acid in which there is at least one double bond within the fatty acid chain
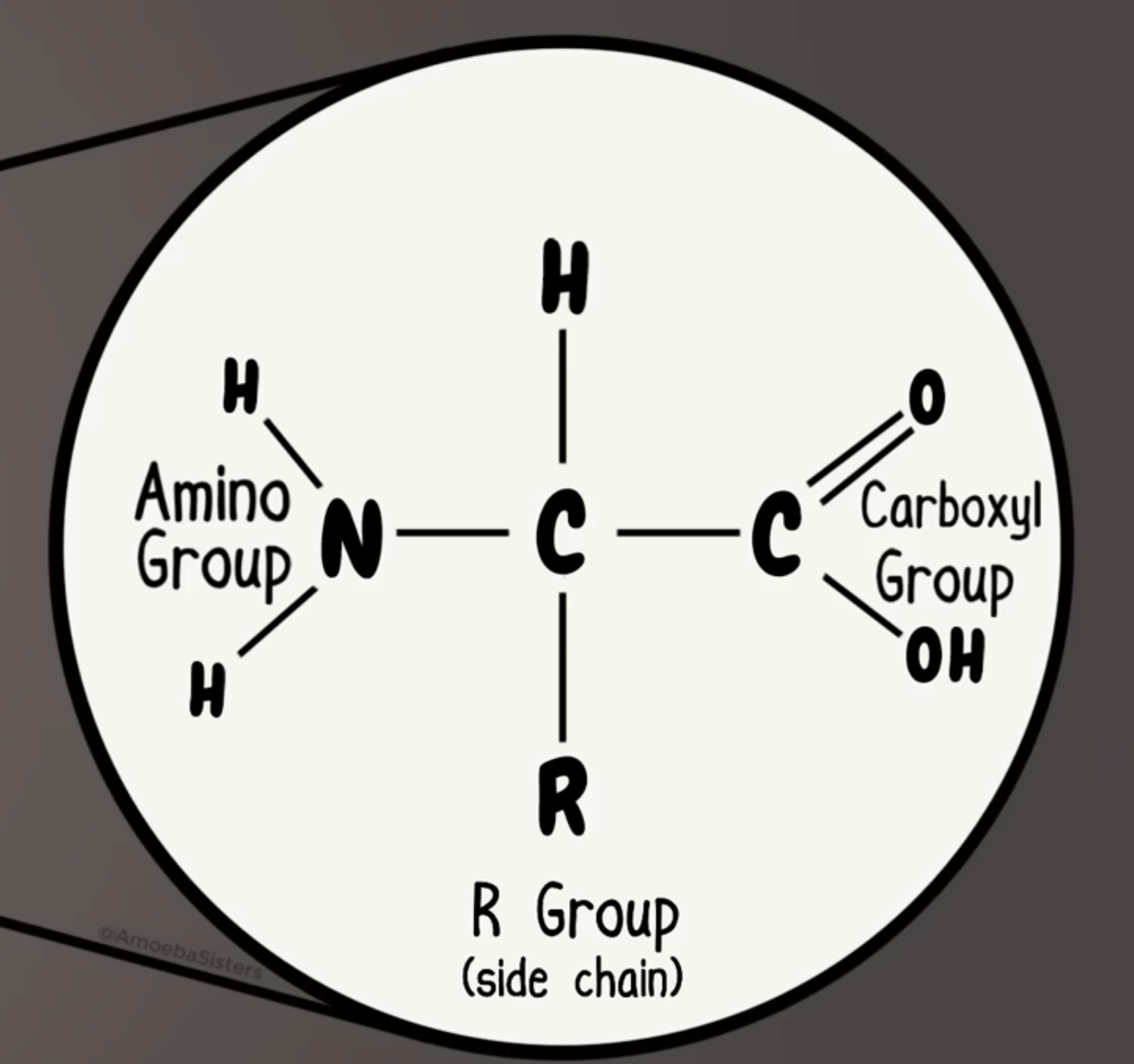
Proteins
Organic macromolecule made up of polypeptide chains that are joined by peptide bonds; contain a carboxyl group, amino group, and r group
Types of proteins
antibodies, contractile proteins, enzymes, hormonal proteins, structural proteins, storage proteins, and transport proteins
Denaturation
The loss of a protein’s native structure due to amino acid sequence alterations or a change in pH, salt concentration, or temperature
Nucleic acids
Also called polynucleotides; made up of nucleotides; store and express genomic information
Examples: DNA and RNA
Nucleotides
Monomers of nucleic acids; consist of a nitrogenous base, a pentane sugar, and one or more phosphate groups (only has one in DNA)
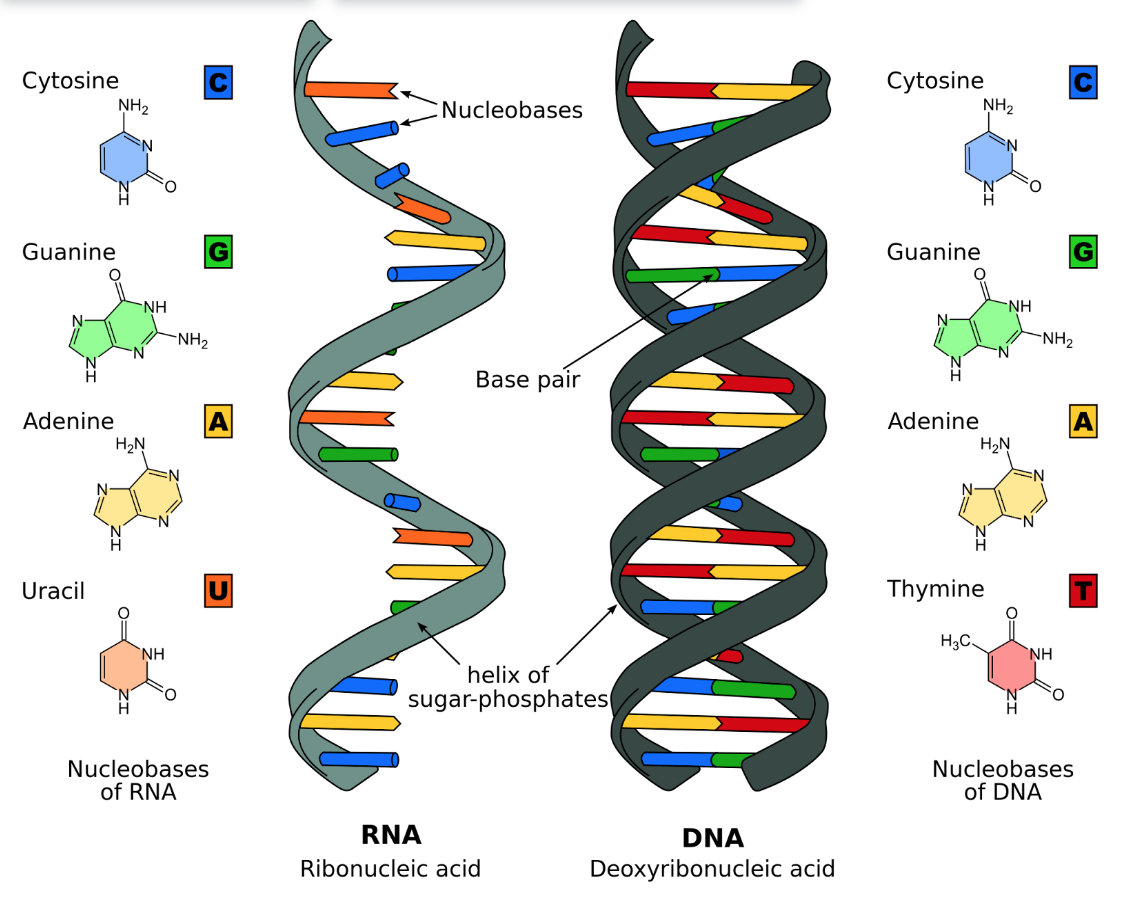
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid; a type of nucleic acid which carries genetic information; made up of a double-stranded helix that consist of nucleotides with one phosphate group and a deoxyribose sugar; has directionality with 5’ and 3’ ends
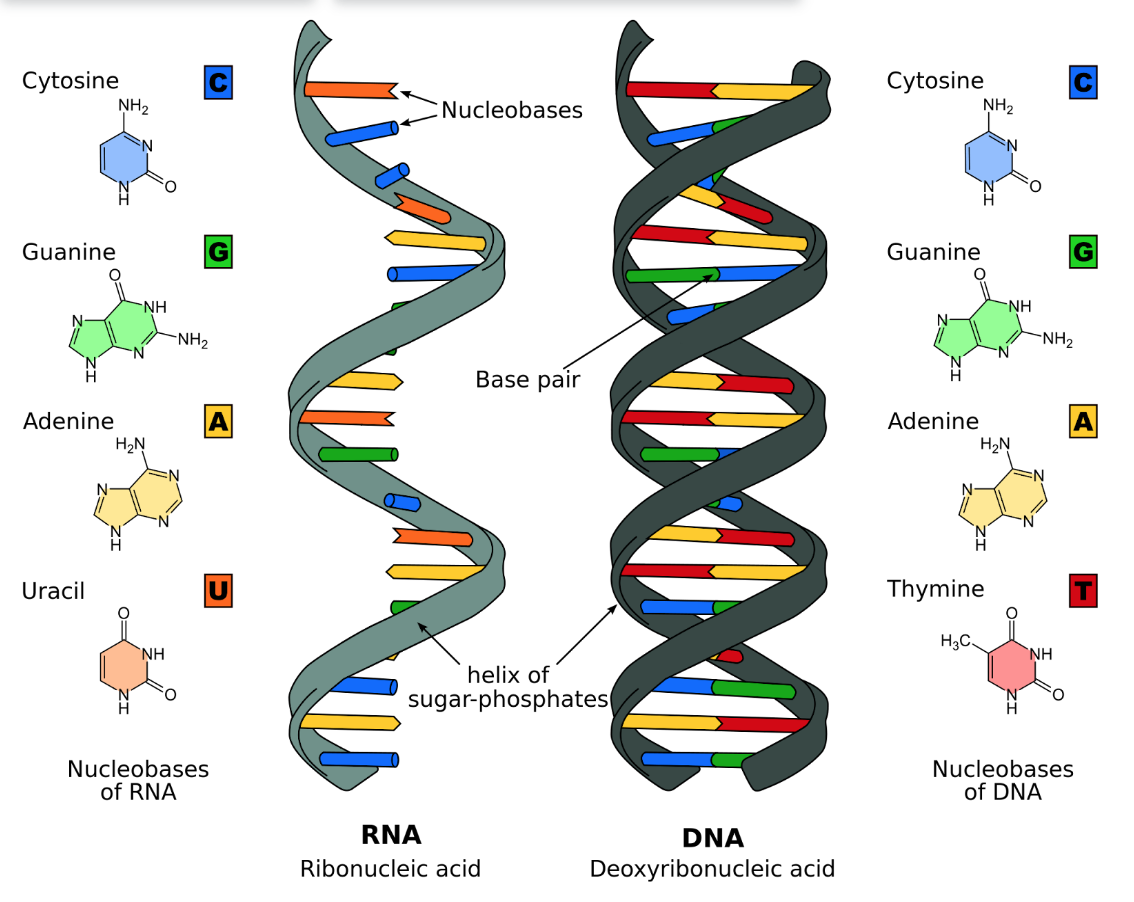
RNA
Ribonucleic acid; a type of nucleic acid which contain instructions for protein synthesis; made up of a single-stranded helix that consist of nucleotides with one phosphate group and a ribose sugar
Primary level
The sequence of amino acids that make up the protein (determined by genes + linked by peptide bonds)
Secondary level
The folding of the amino acid chain; depends on the amino acid arrangement and hydrogen bonds
Tertiary level
Folding into 3D shape of the protein caused by the interactions of different R-groups in each amino acid
Examples: hydrophilic interactions, hydrophobic interactions, ionic bonds, Van Der Waals interactions. hydrogen bonds, disulfide bonds
Quaternary level
Protein consisting of more than one polypeptide chain
Polypeptide
unbranched polymers built from the same set of 20 amino acids
Amino acid
Molecules that make up proteins and polypeptide chains
Glycerol
3-carbon chain that forms triglycerides with fatty acids
Fatty acids
Serve as a source of energy and are an important component of triglycerides
Triglycerides
Type of lipid formed by glycerol and fatty acids; used for energy storage