08 - Macular OCT
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
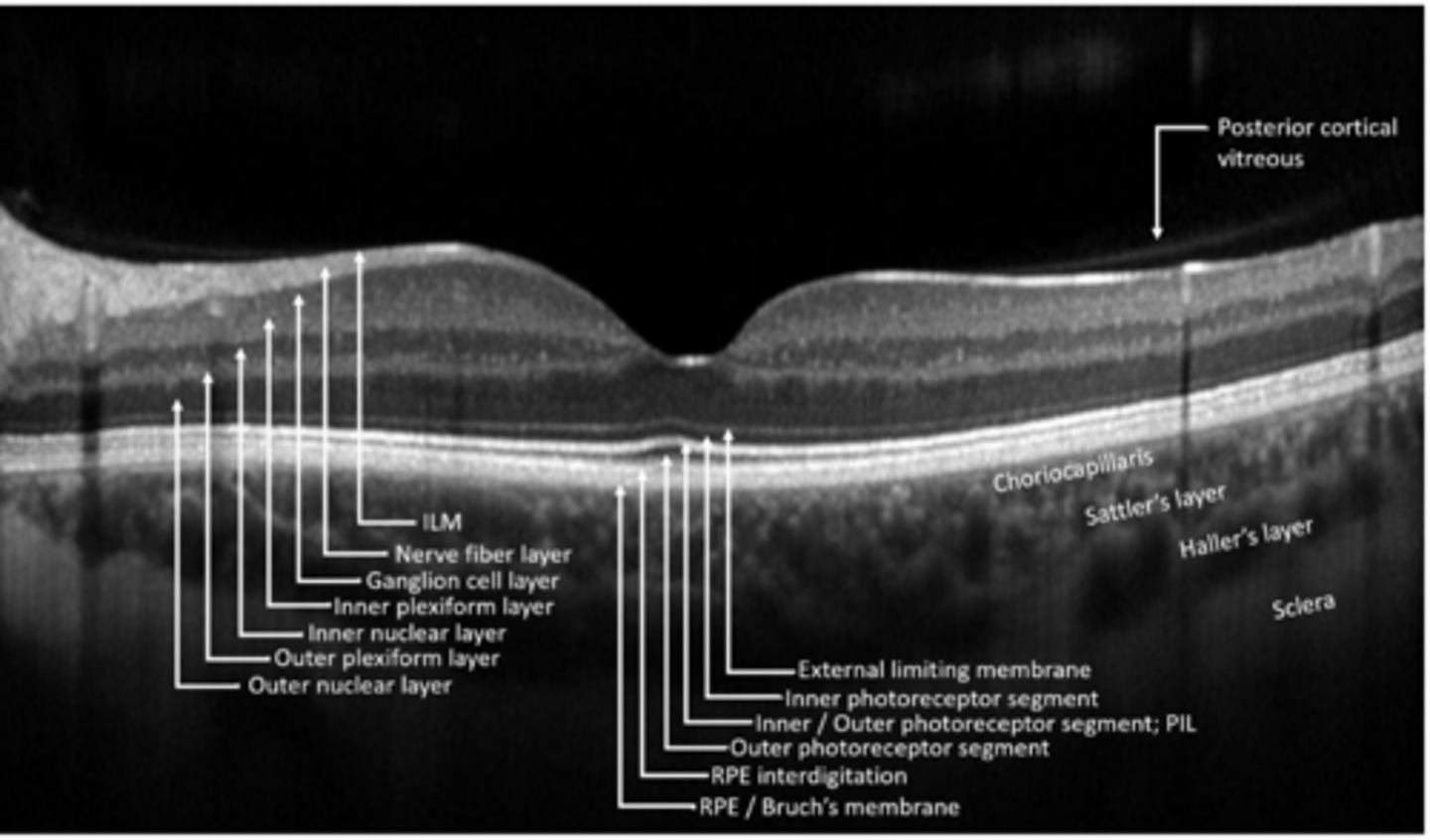
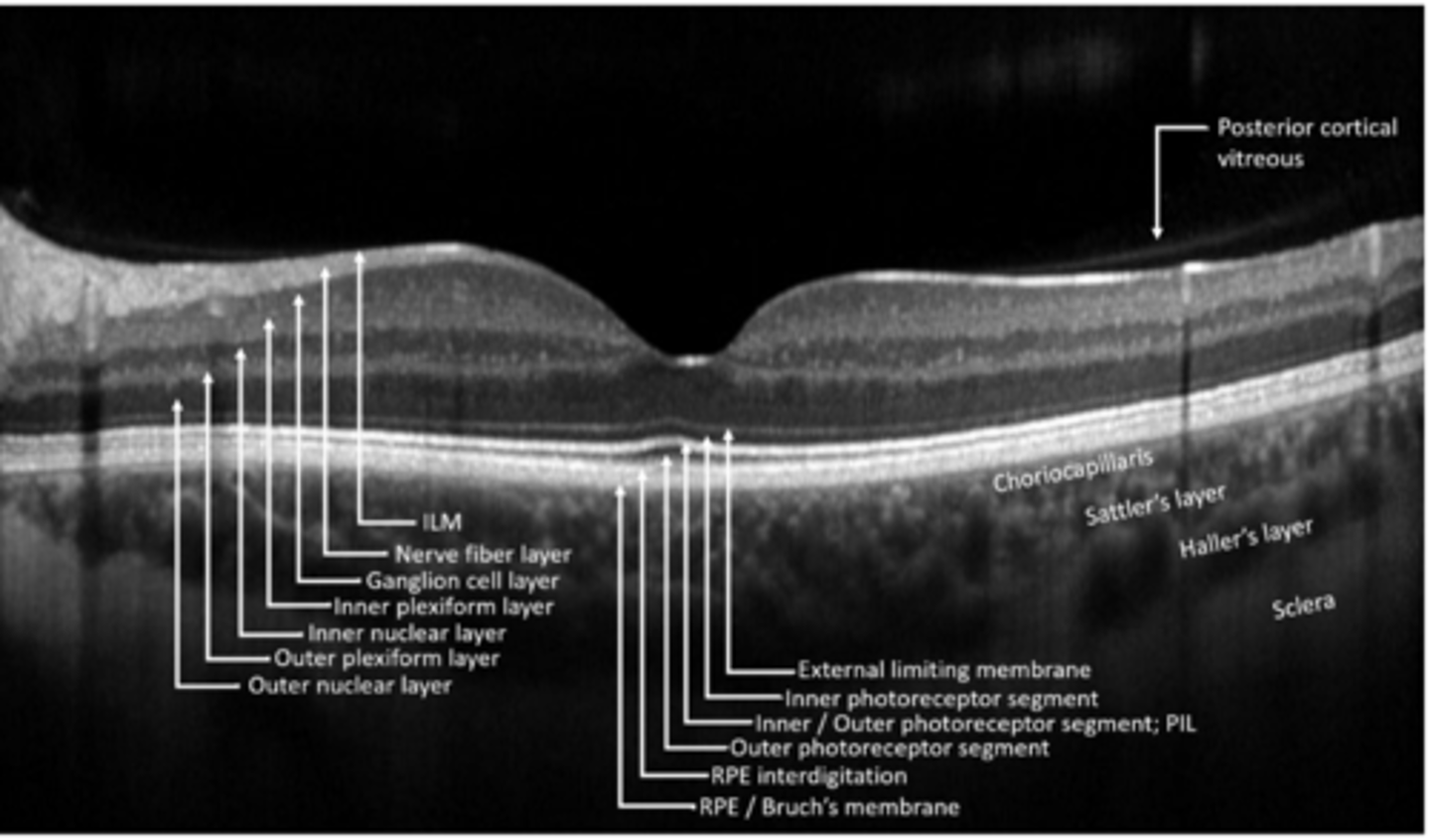
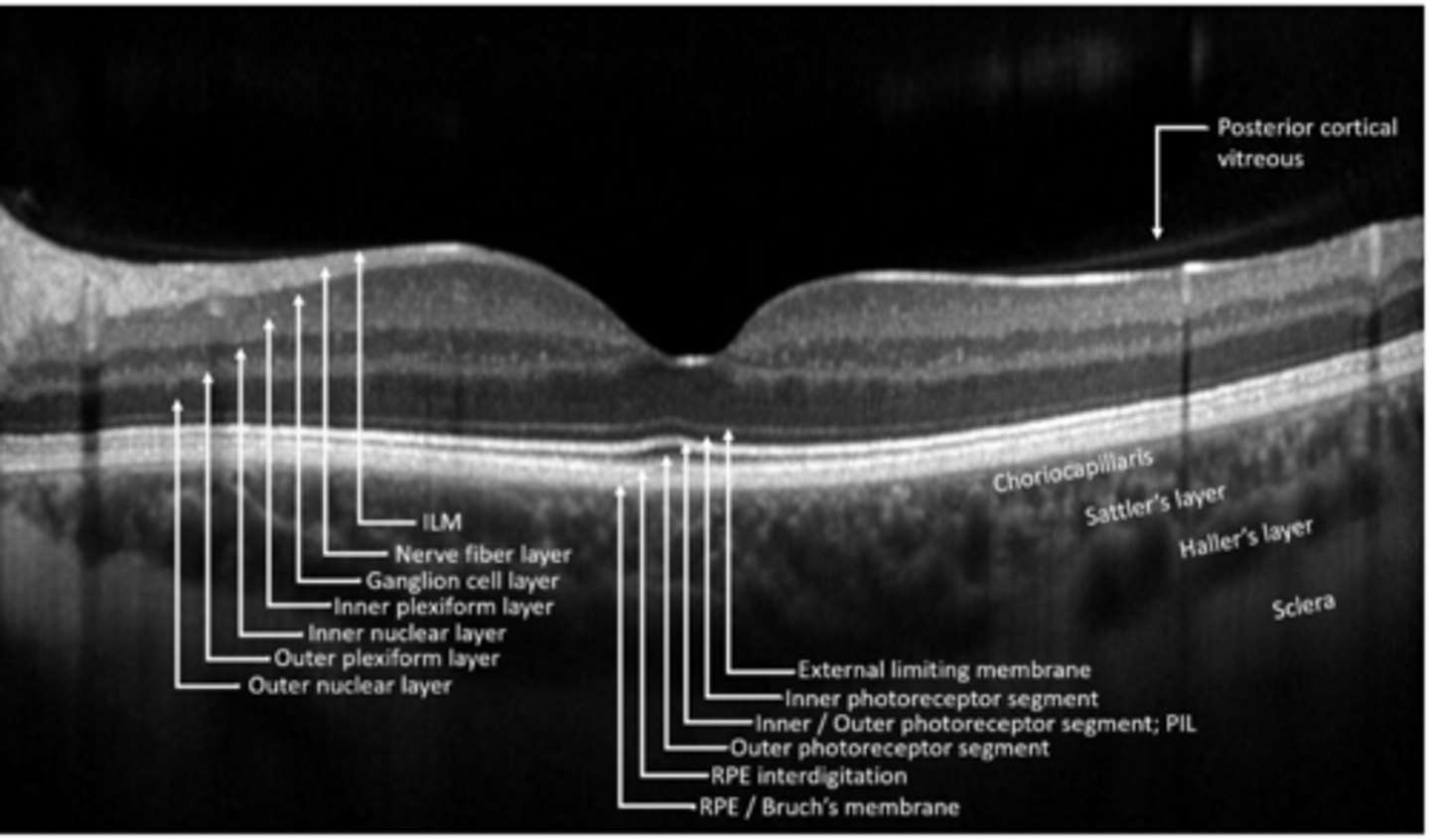
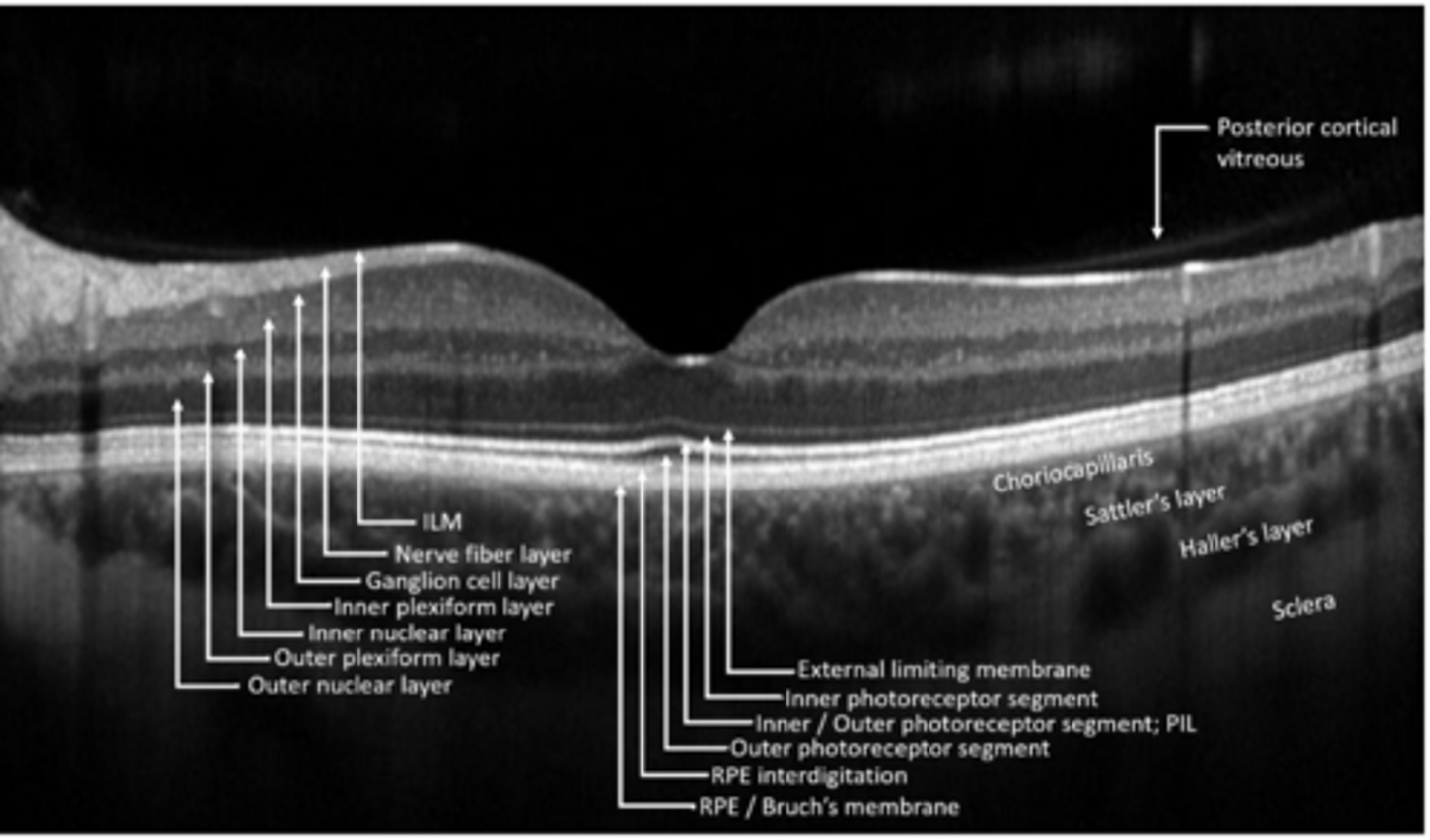
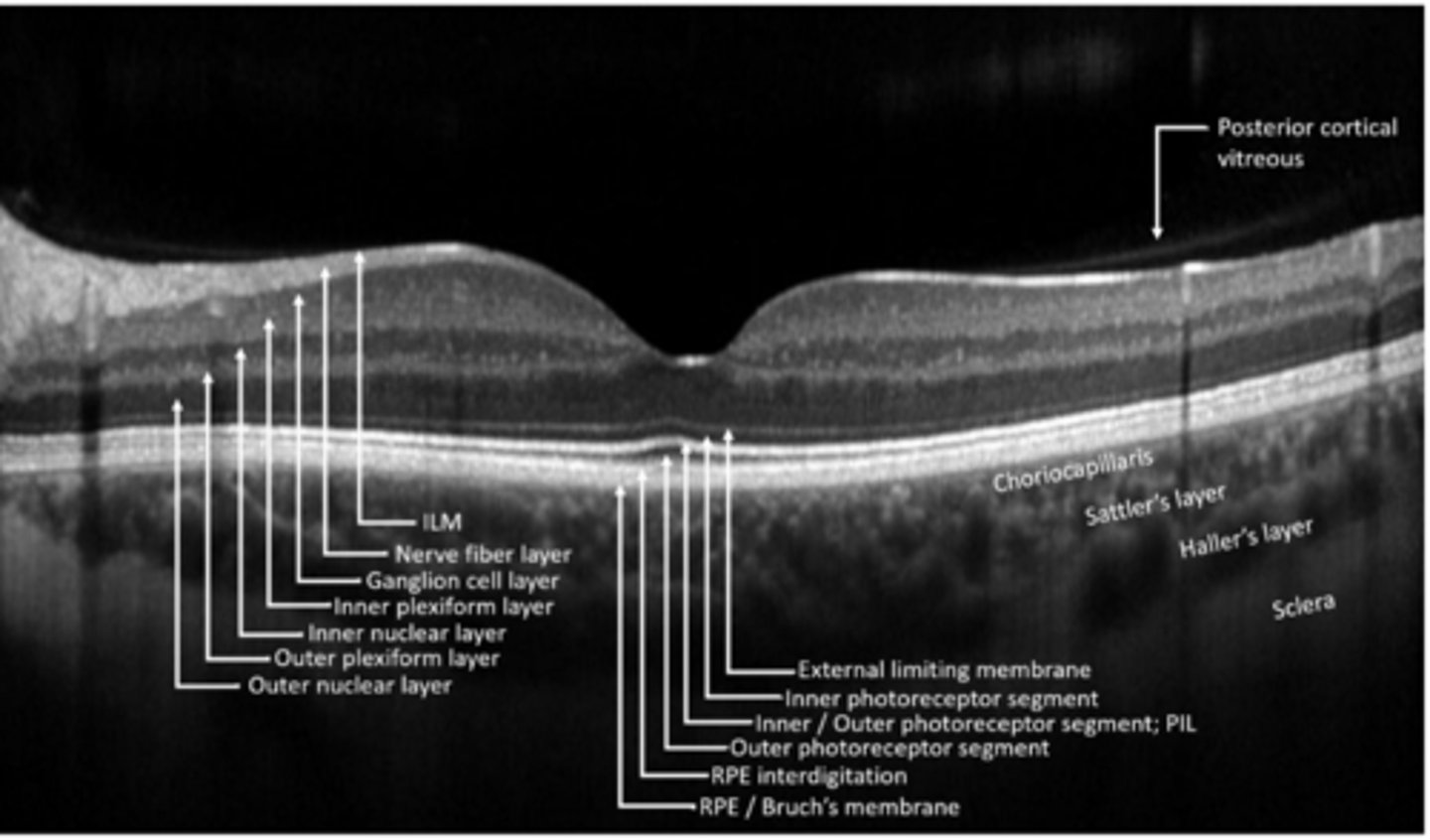
ILM
NFL
GCL
IPL
INL
OPL
ONL
ELM
PR
RPE
What are the 10 main retinal layers, from inner to outer?
BM of RPE
inner collagen layer
middle elastic layer
outer collagen layer
BM of choriocapillaris
What 5 sublayers make up Bruch's membrane?
outer segments (dark)
PIL aka cilium of OS-IS junction (light)
inner segments (dark)
What is present in the photoreceptor layer?
zonula adherens between PR's and Muller cells
What makes up the external limiting membrane?
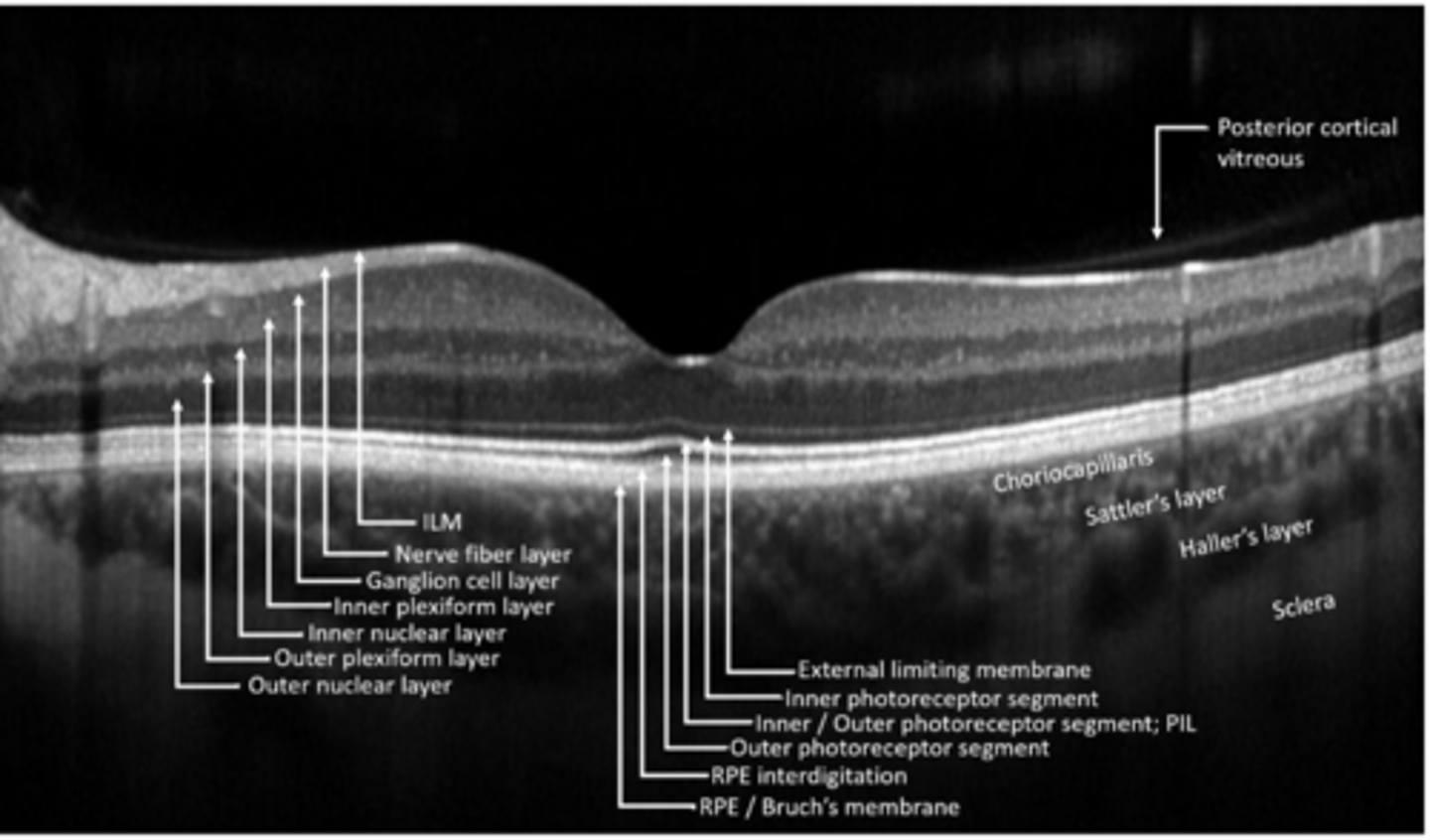
nuclear = hypo
plexiform = hyper
A good rule of thumb is that nuclear layers are __________ while plexiform layers ______________.
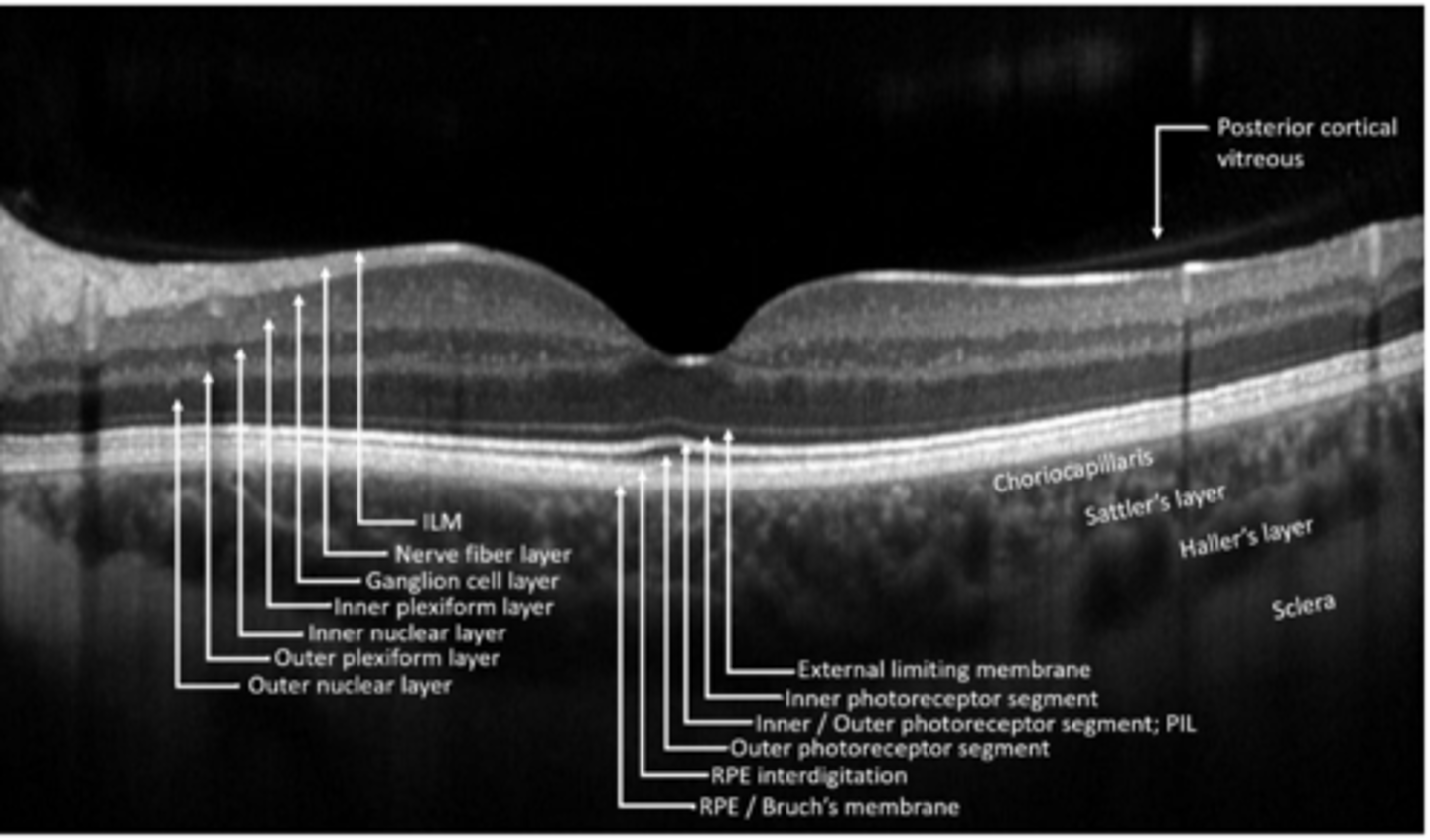
PR cell bodies
What makes up the outer nuclear layer?
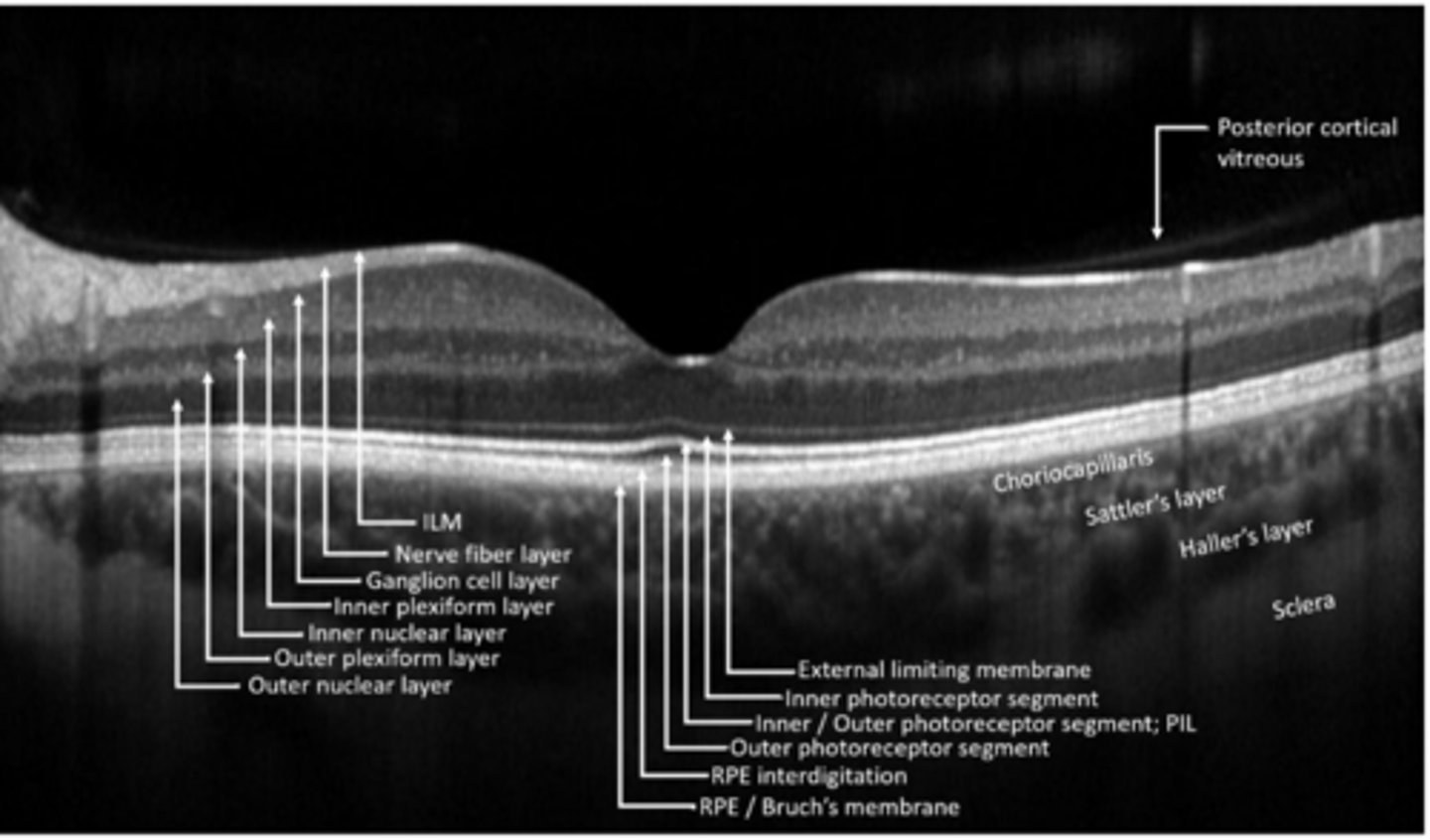
PR synapses with bipolar and horizontal cells
What makes up the outer plexiform layer?
bipolar, horizontal, amacrine cell bodies
What makes up the inner nuclear layer?
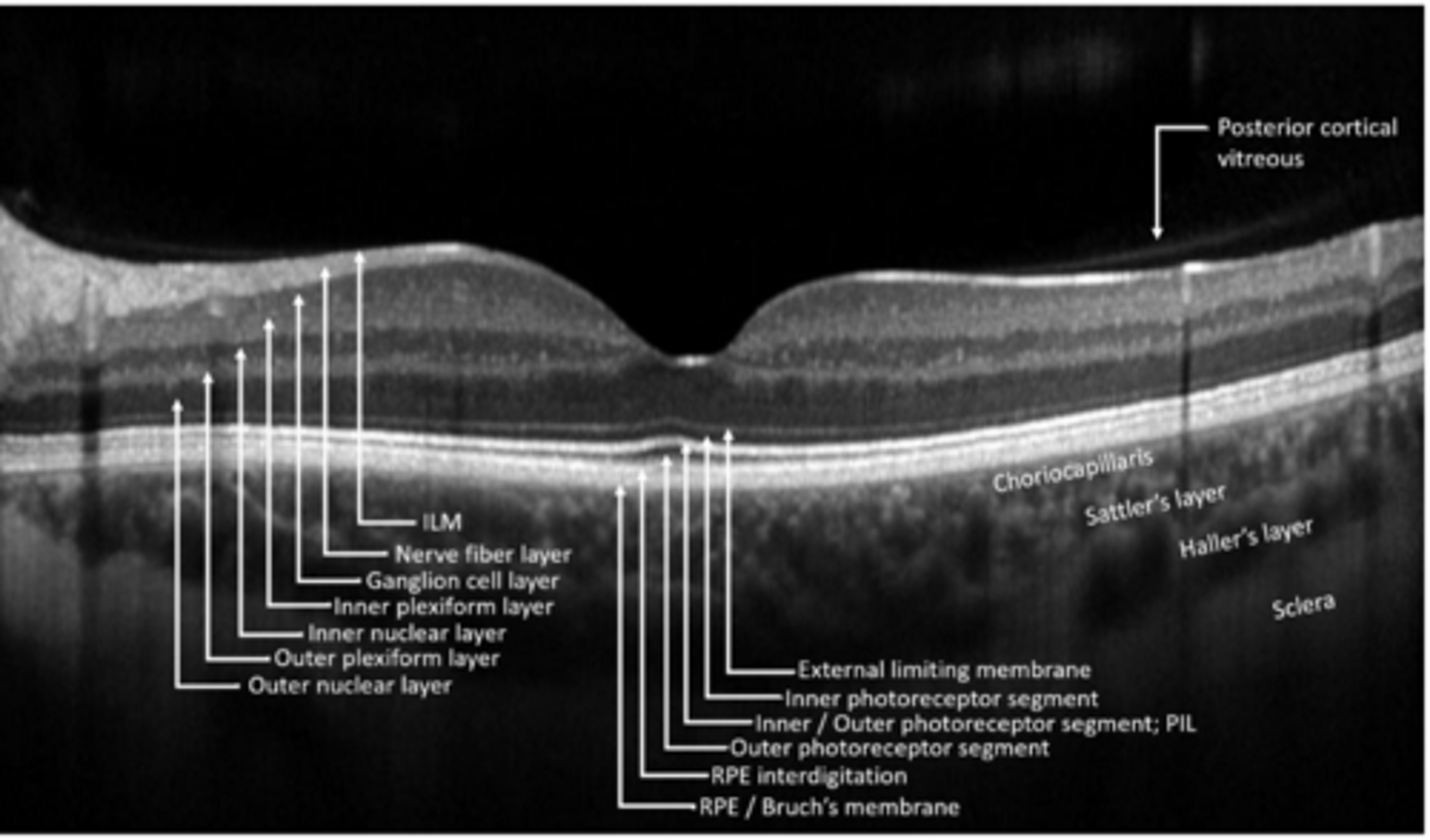
bipolar, horizontal, amacrine cells synapse with ganglion cells
What makes up the inner plexiform layer?
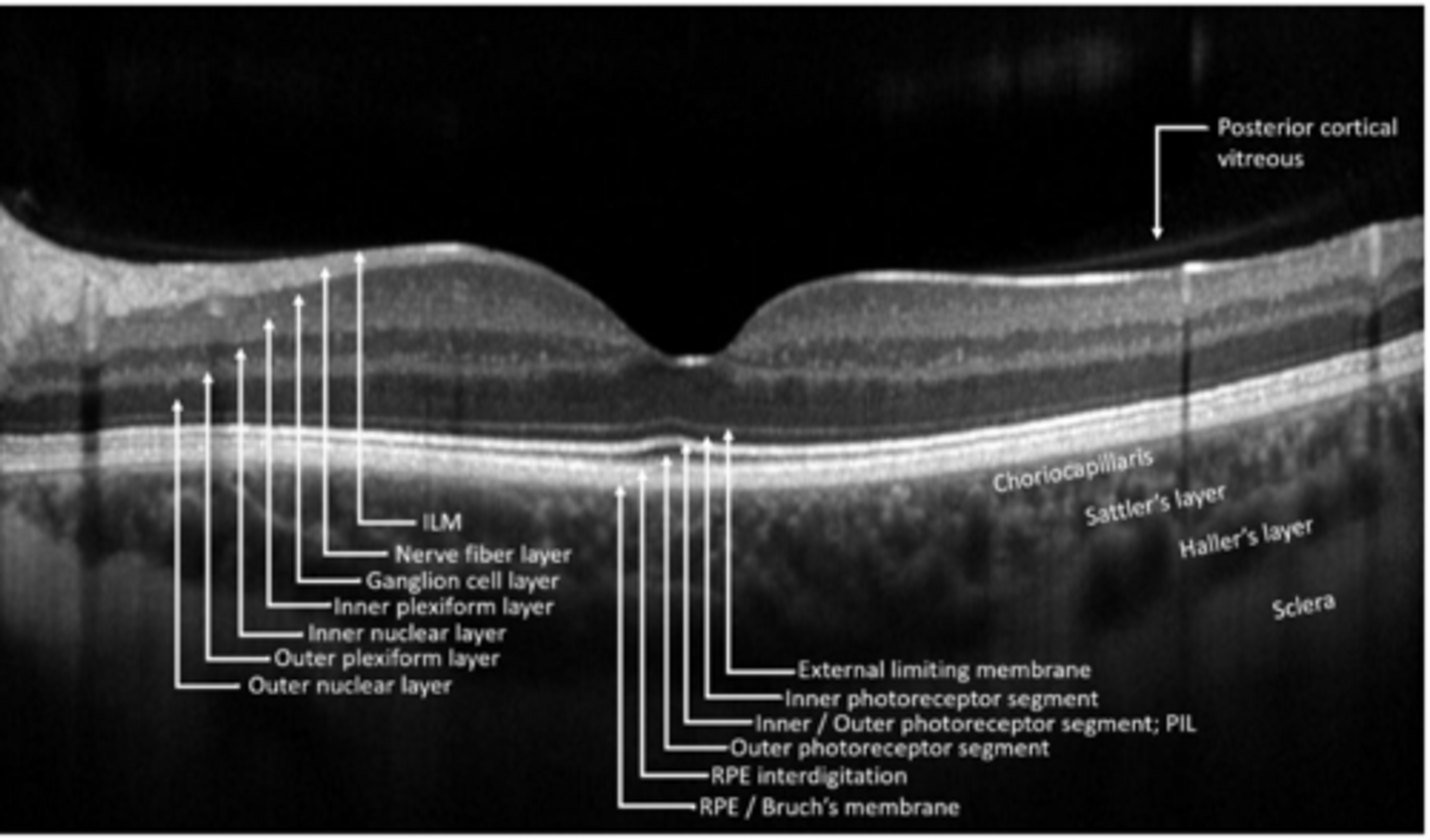
ganglion cell bodies
What makes up the ganglion cell layer?
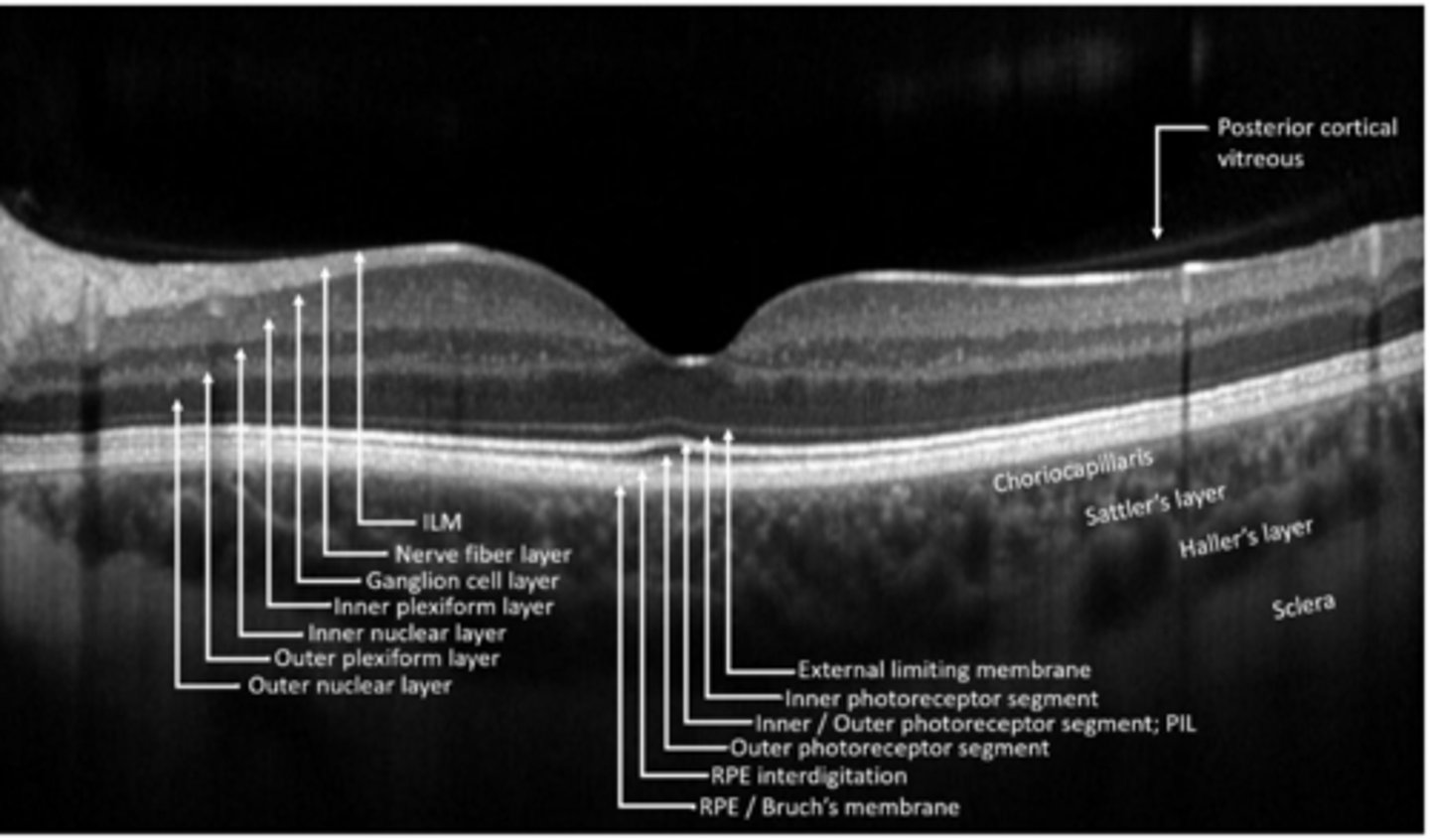
ganglion cell axons
What makes up the nerve fiber layer?
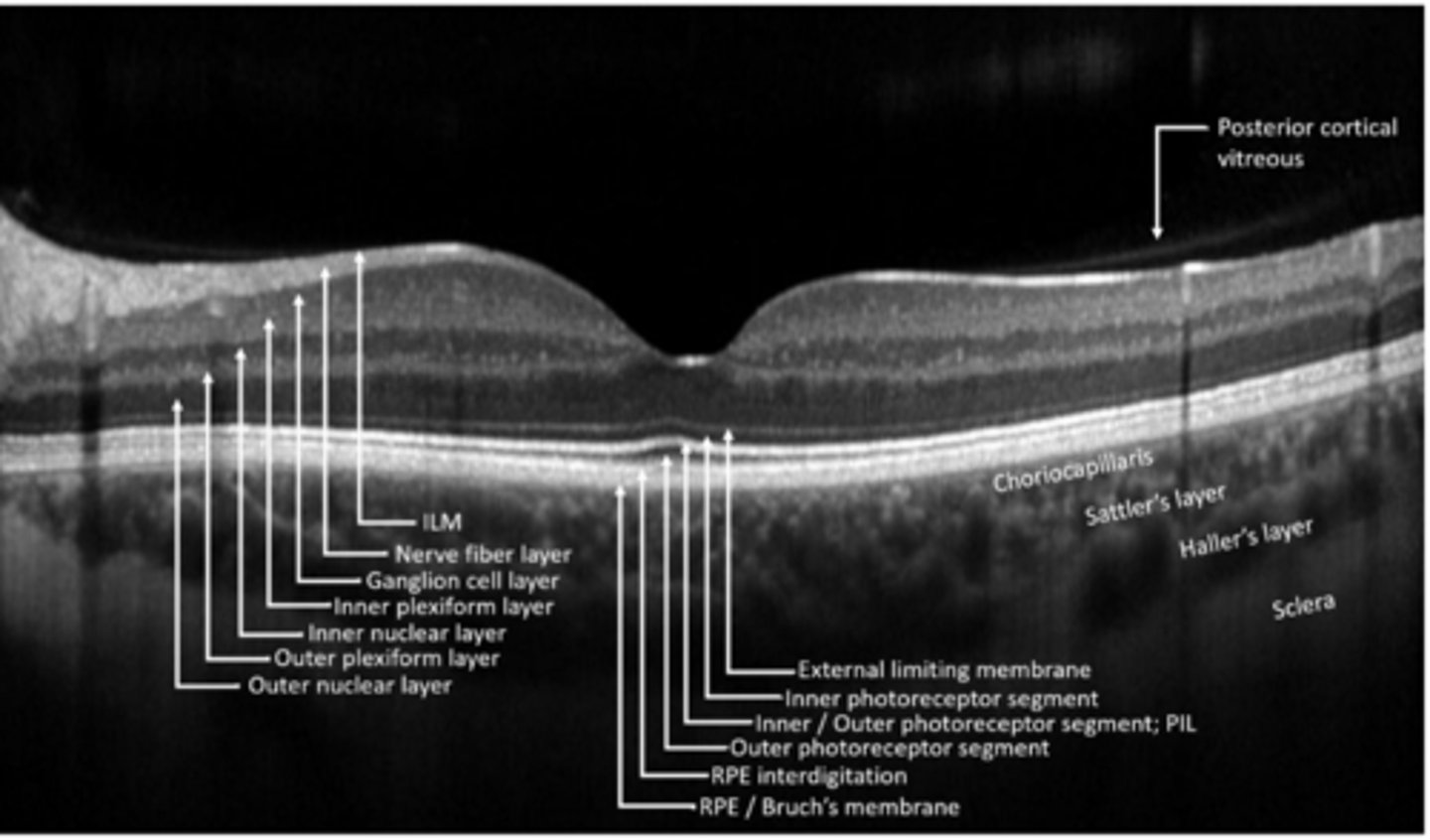
Muller cell footplates
What makes up the internal limiting membrane?
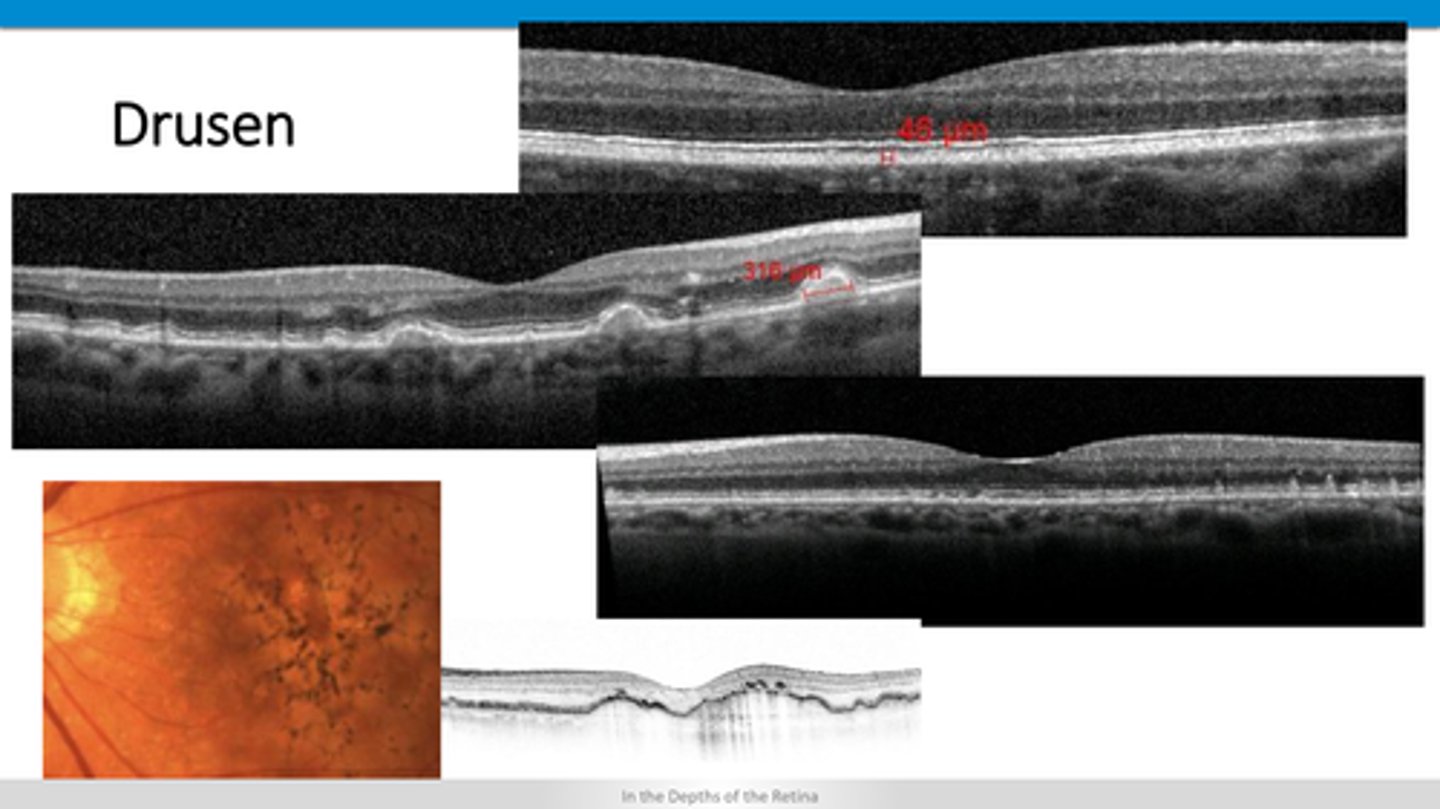
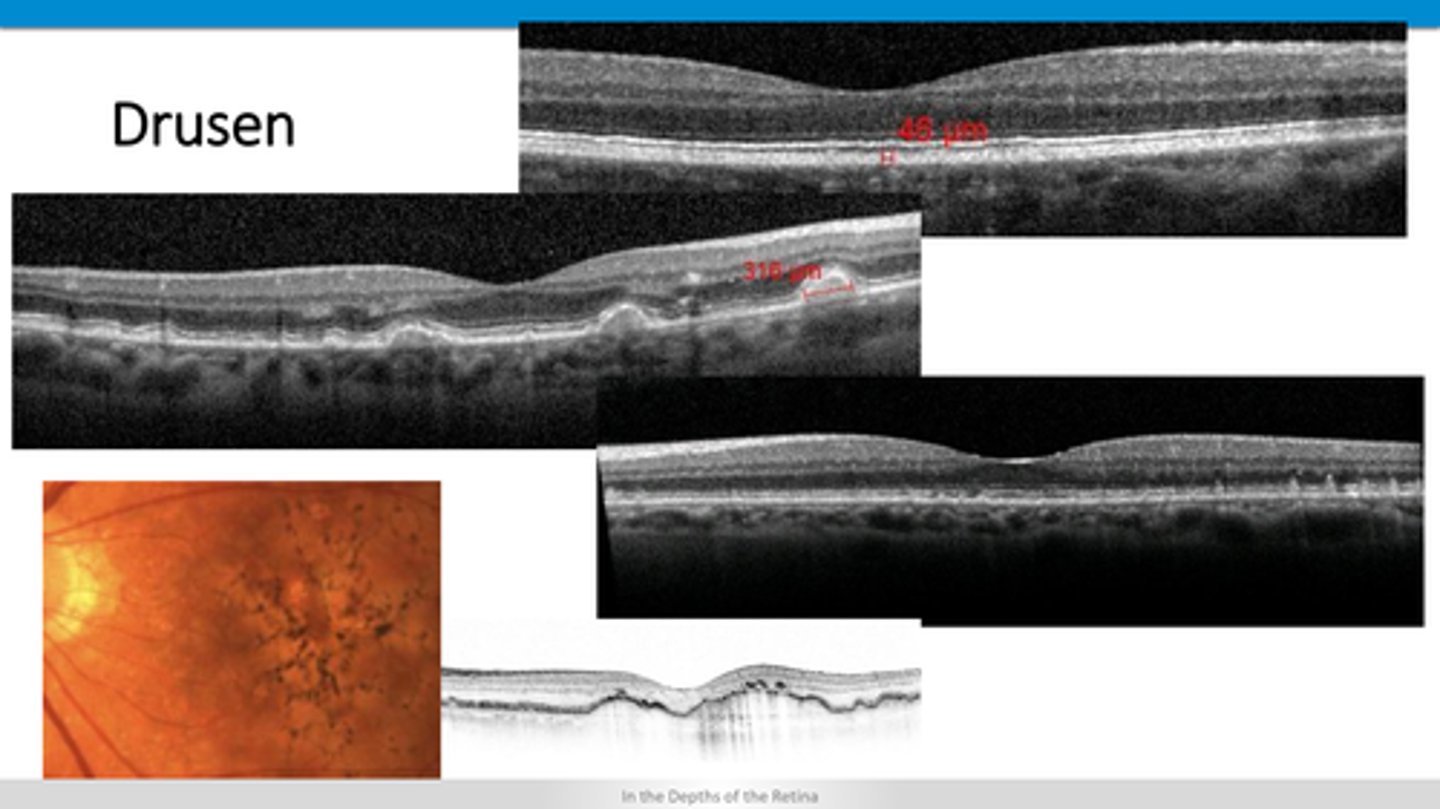
pigment migration and drusen underneath RPE (PED)
What is ARMD?
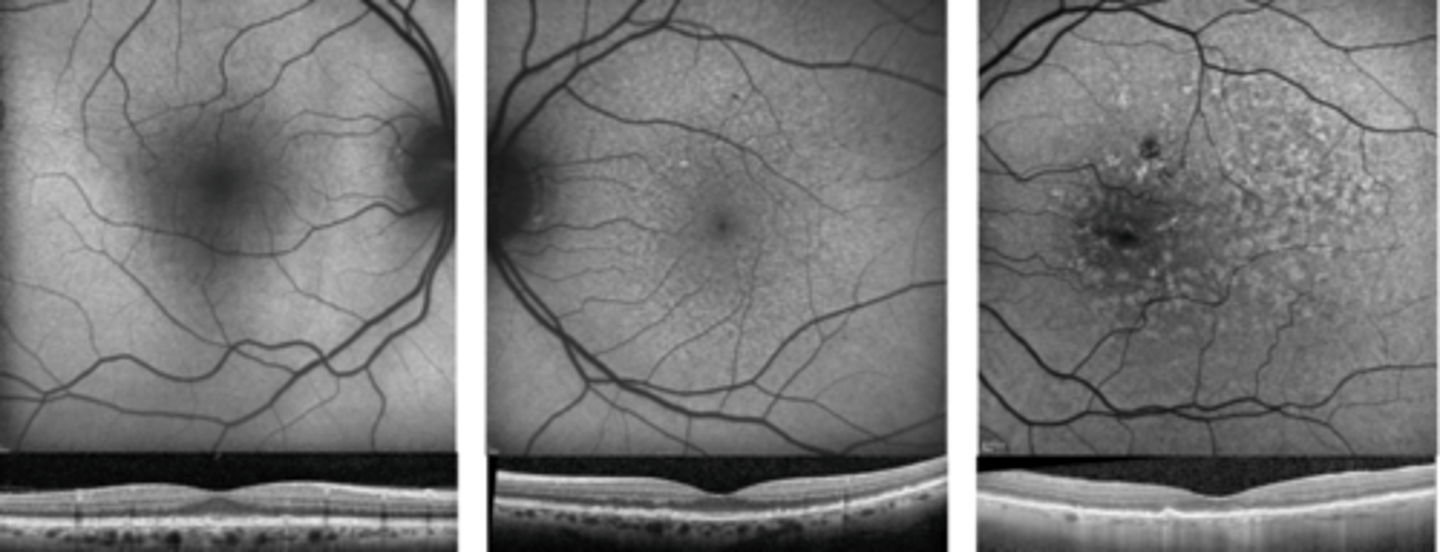
lipofuscin will hyperAF
How does ARMD appear on FAF?
PEDs beneath the RPE
How does ARMD appear on OCT?
loss of RPE = hypoAF
How does ARMD geographic atrophy appear on FAF?
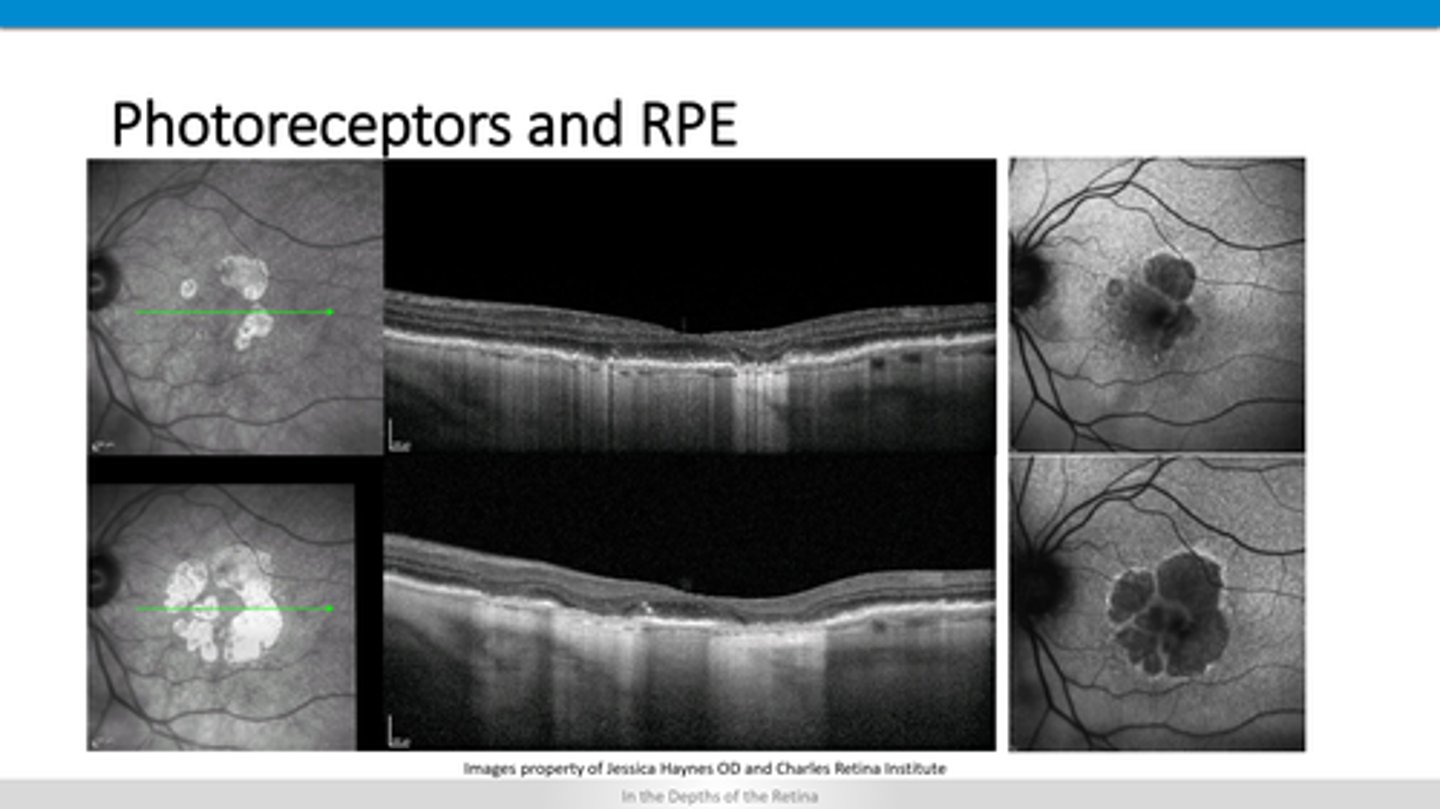
loss of RPE = hyperfluorescence undeneath in the choroid
How does ARMD geographic atrophy appear on OCT?
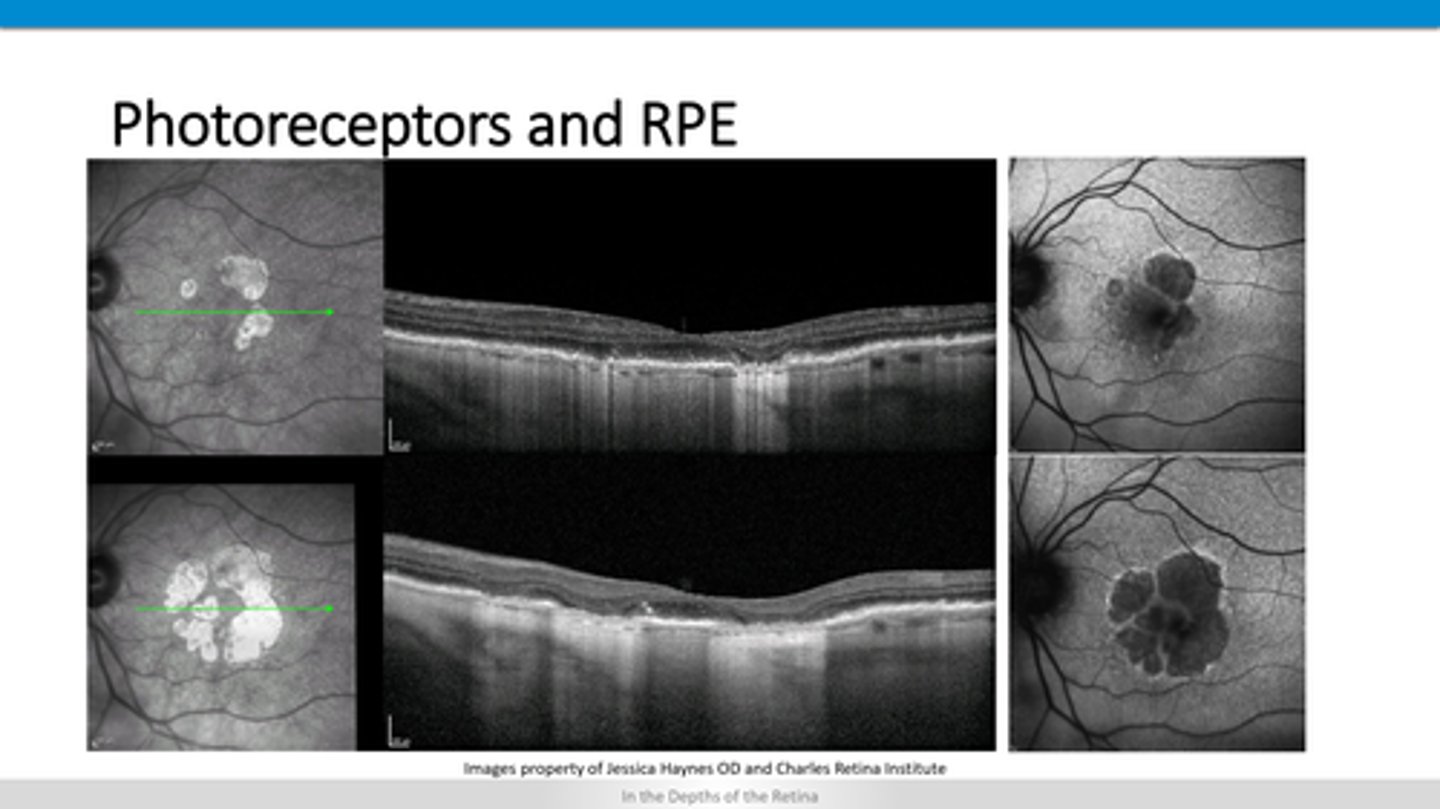
underneath RPE = elevation of RPE and retina
diffuse IVFA leakage in late phase
How does ARMD type 1 CNV appear on OCT and FAF?
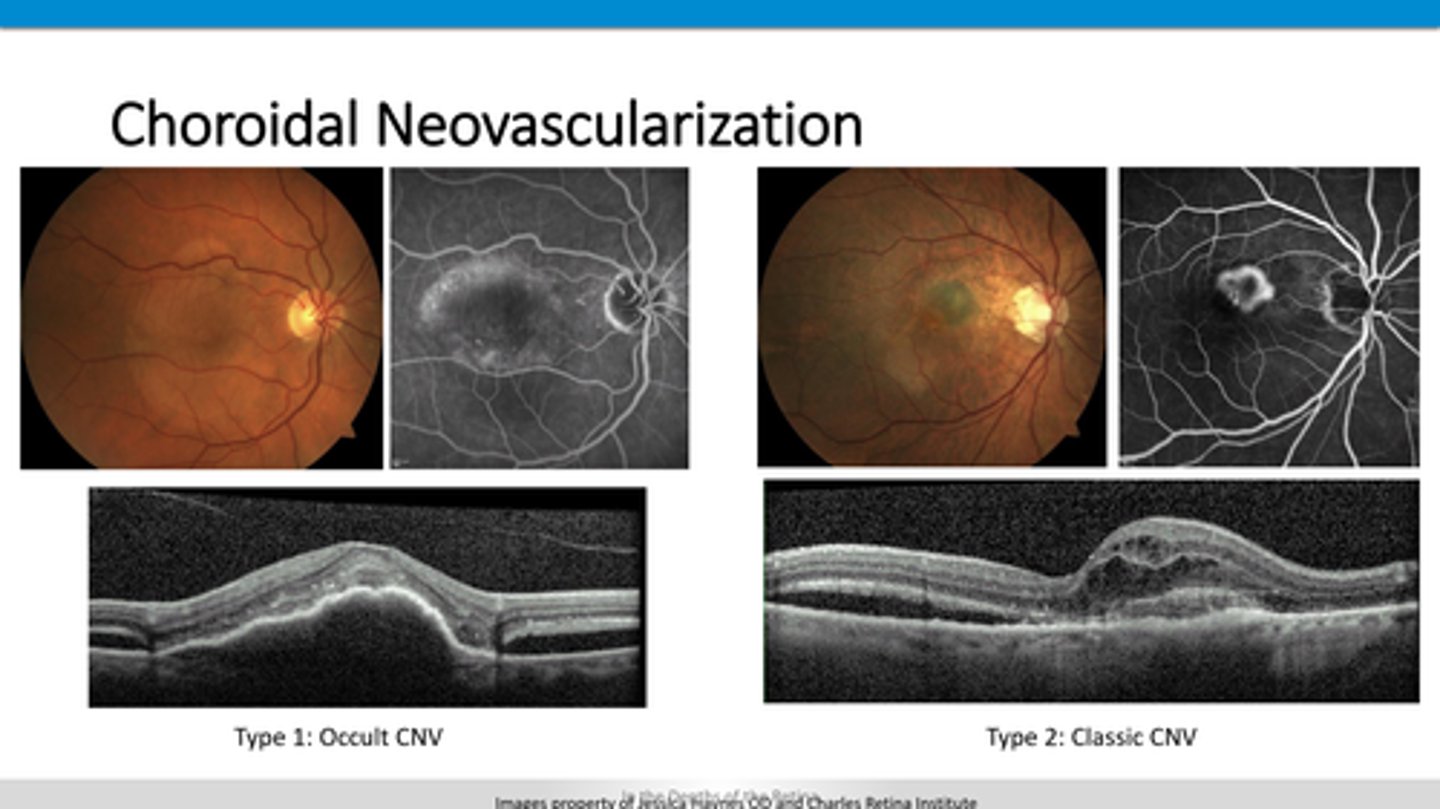
on top of RPE = elevation of retina
early, defined IVFA hyperF
How does ARMD type 2 CNV appear on OCT and FAF?
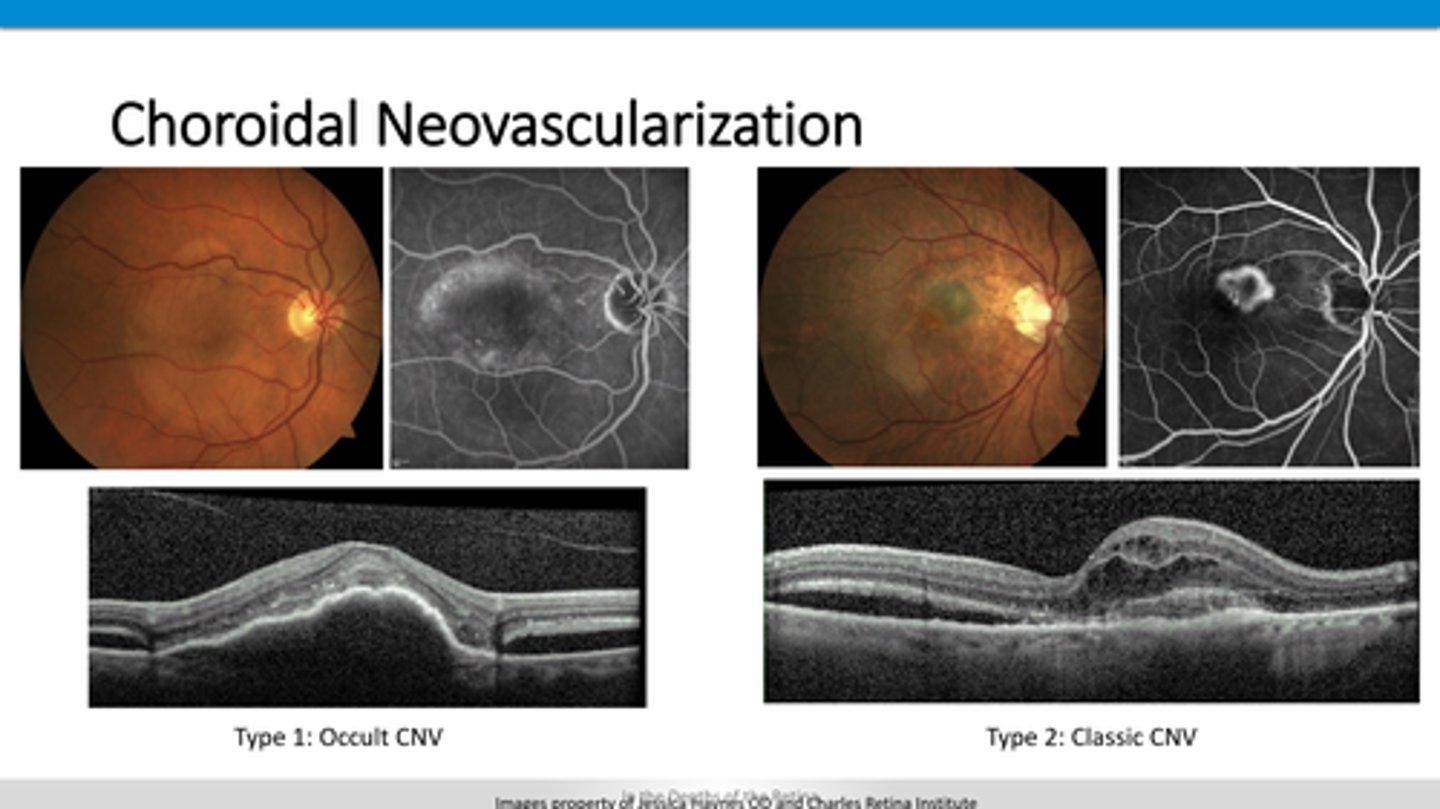
loss of retina and RPE = hyperfluorescence undeneath in the choroid
How might myopic degeneration lacquer cracks appear on OCT?
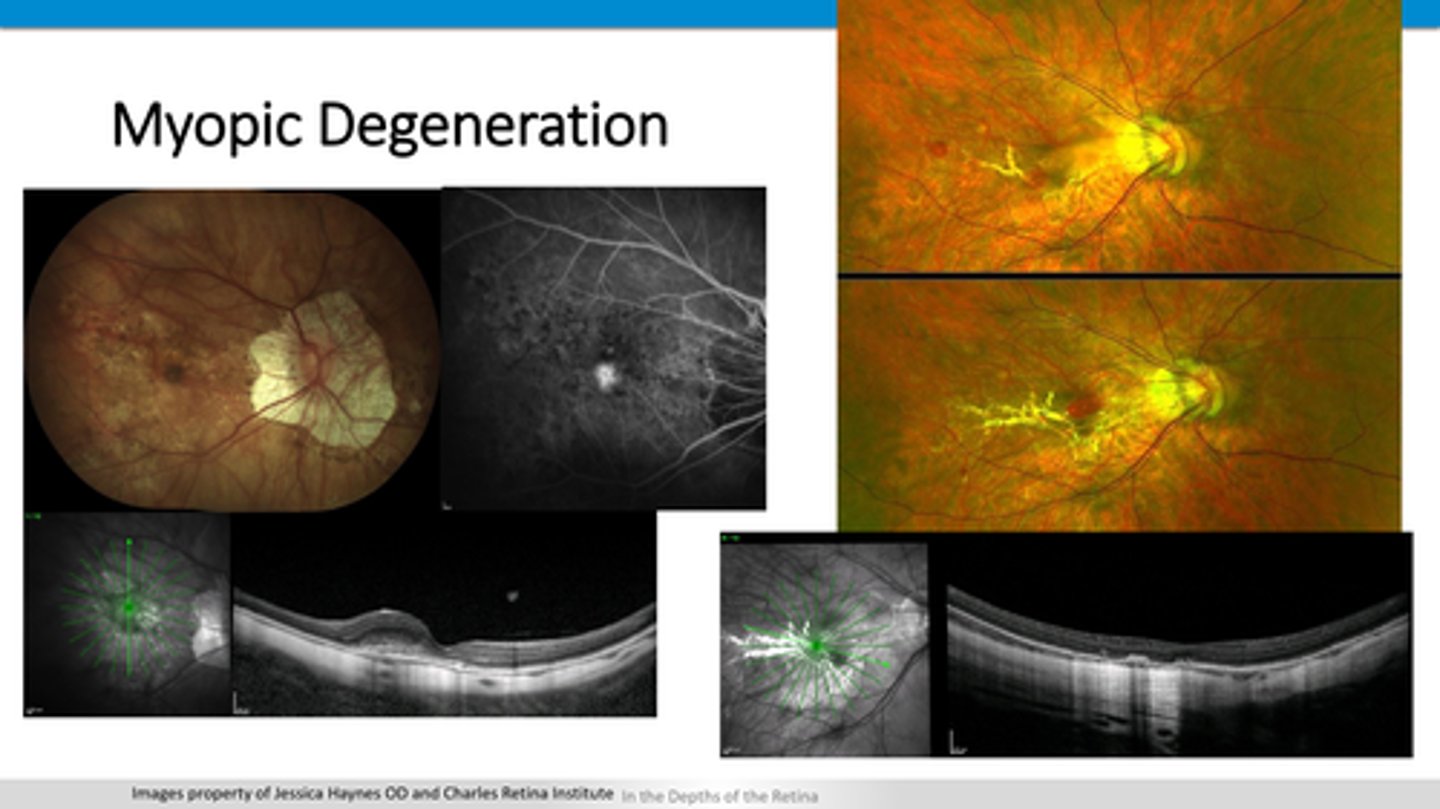
serous (dark) RD between PR's and RPE
+/- serous PED
+/- thicker choroid
How does acute CSR appear on OCT?
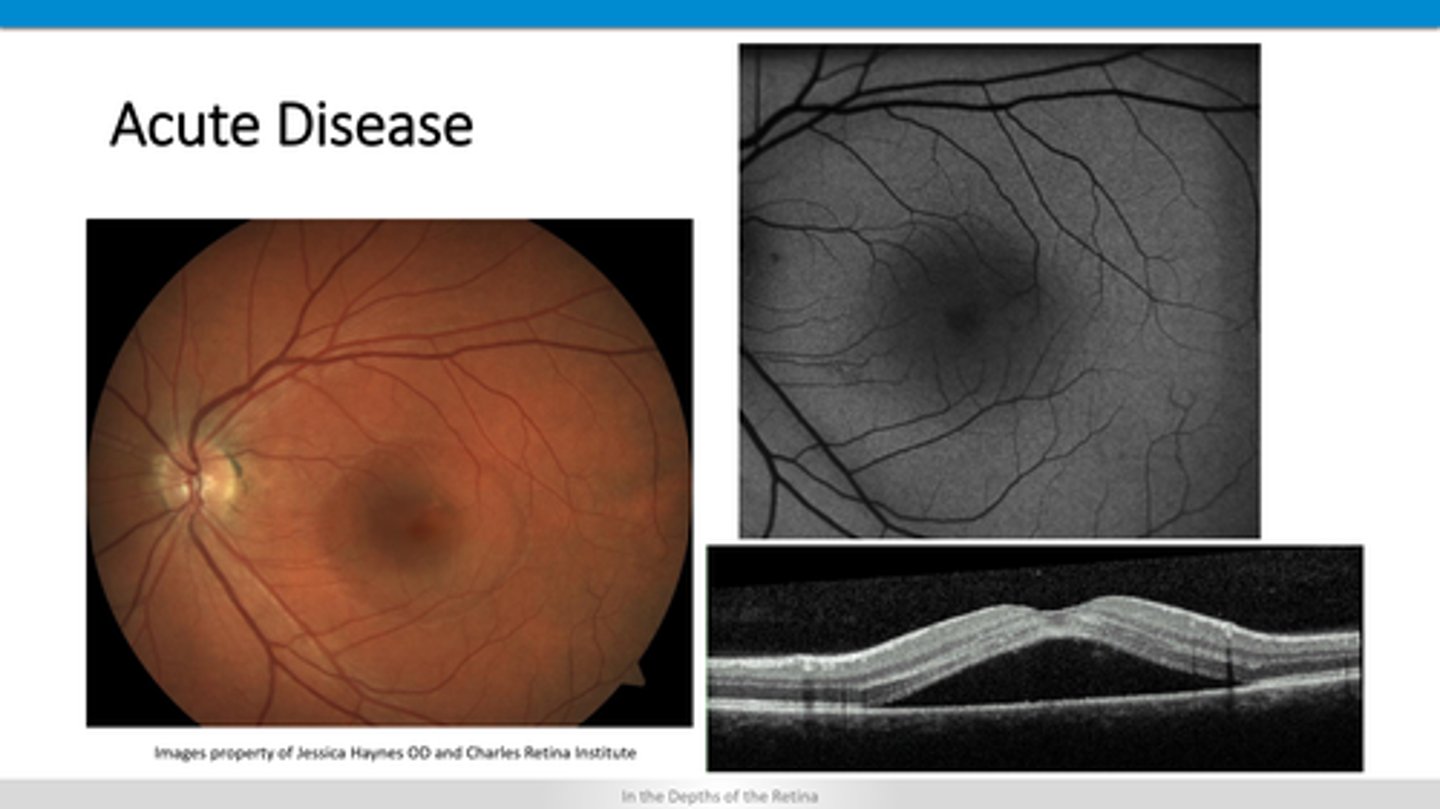
shaggy PR's, disrupted RPE
How does chronic CSR appear on OCT?
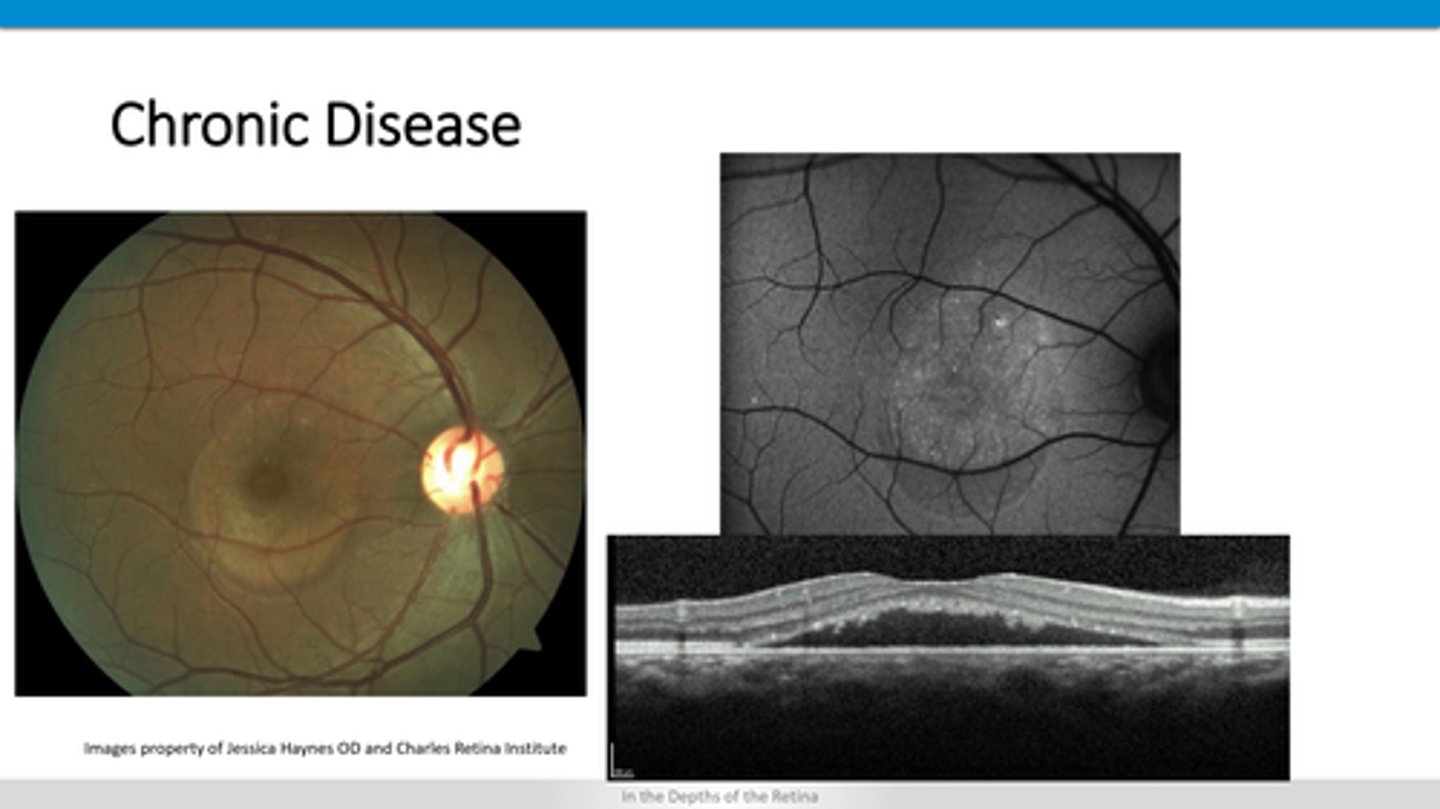
outer retinal atrophy temporal to fovea
crystalline deposits
atrophic hole with ILM drape
+/- CNVM
How does type 2 macular telangiectasia appear on OCT?
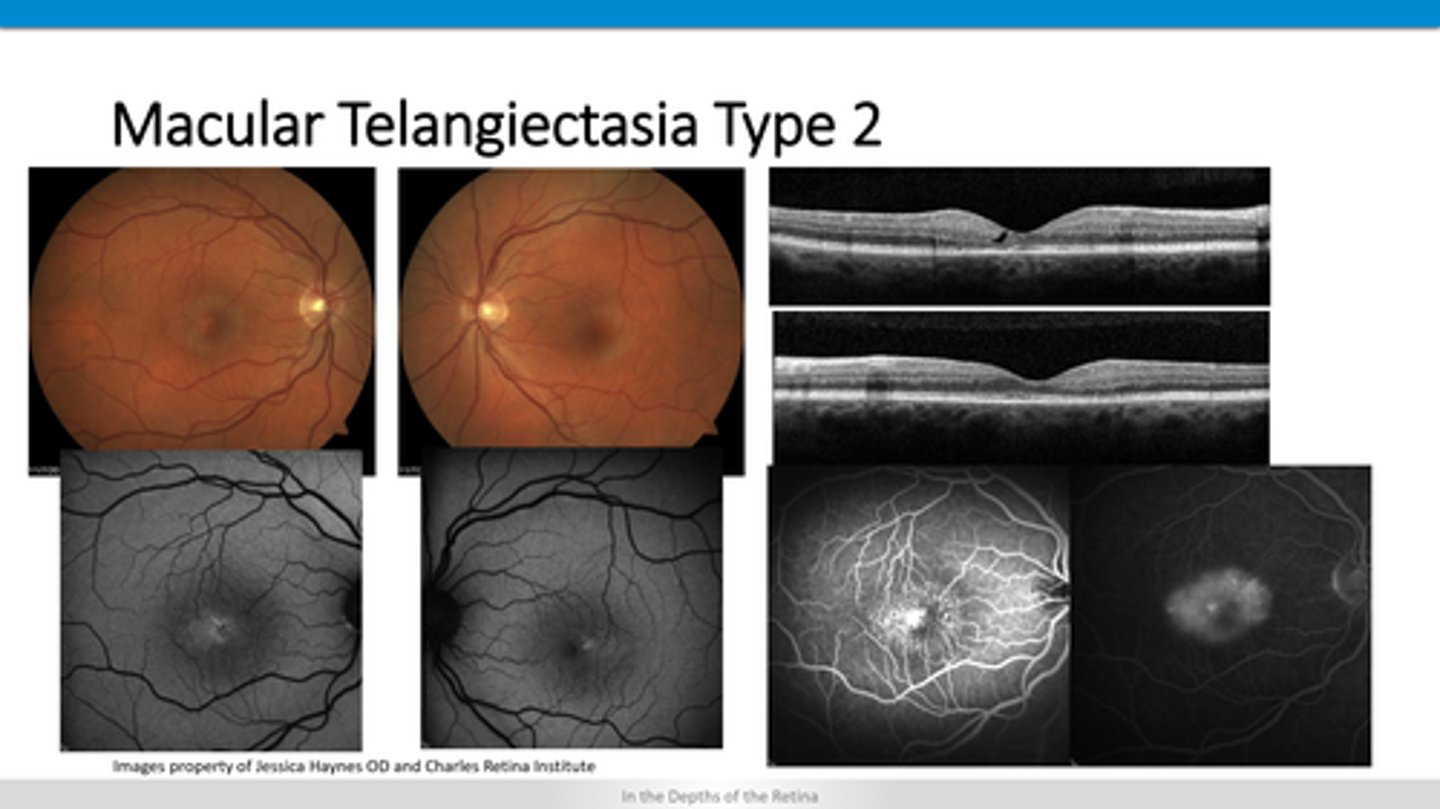
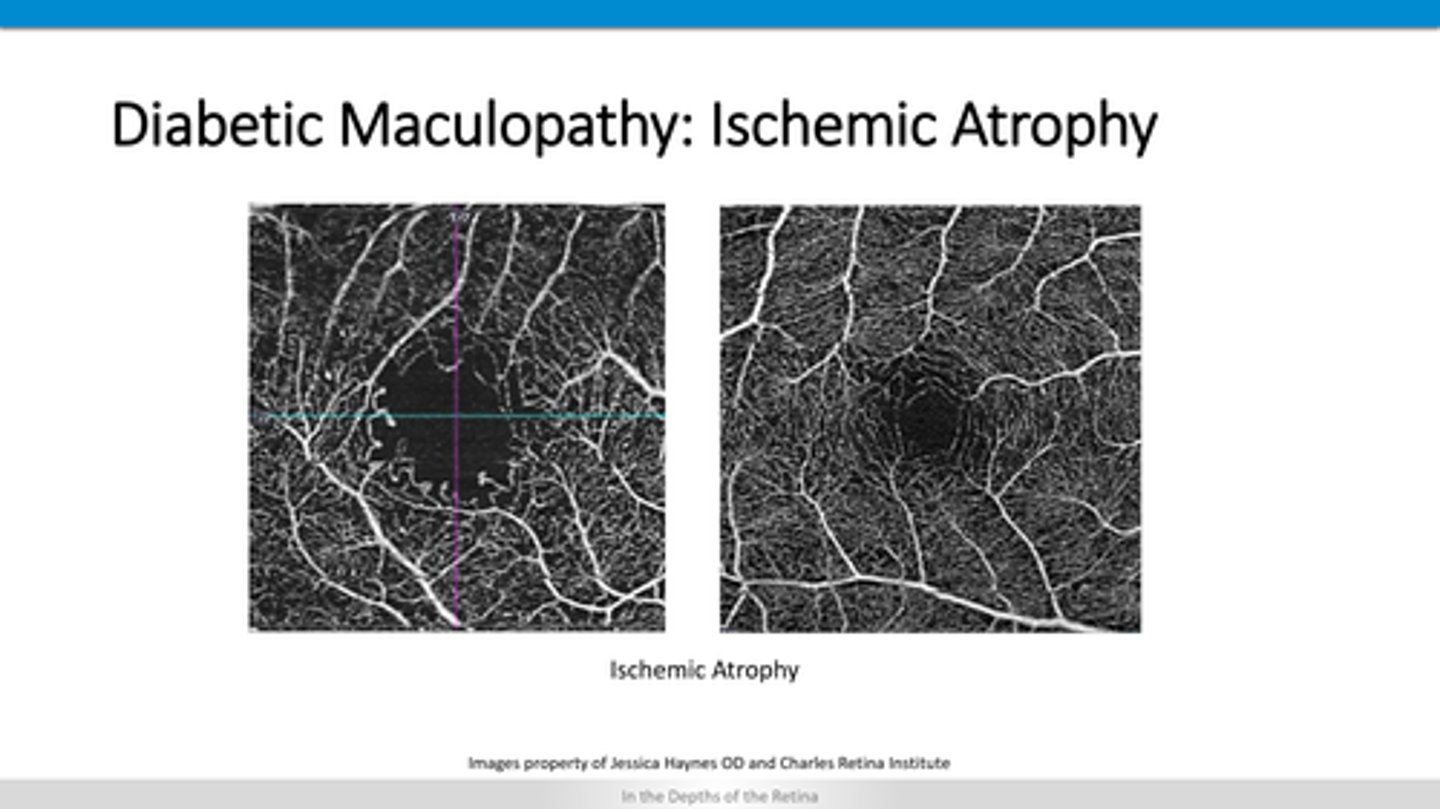
atrophy of capillary beds (OCTA)
atrophy of retinal layers
How does diabetic retinopathy appear on OCT?
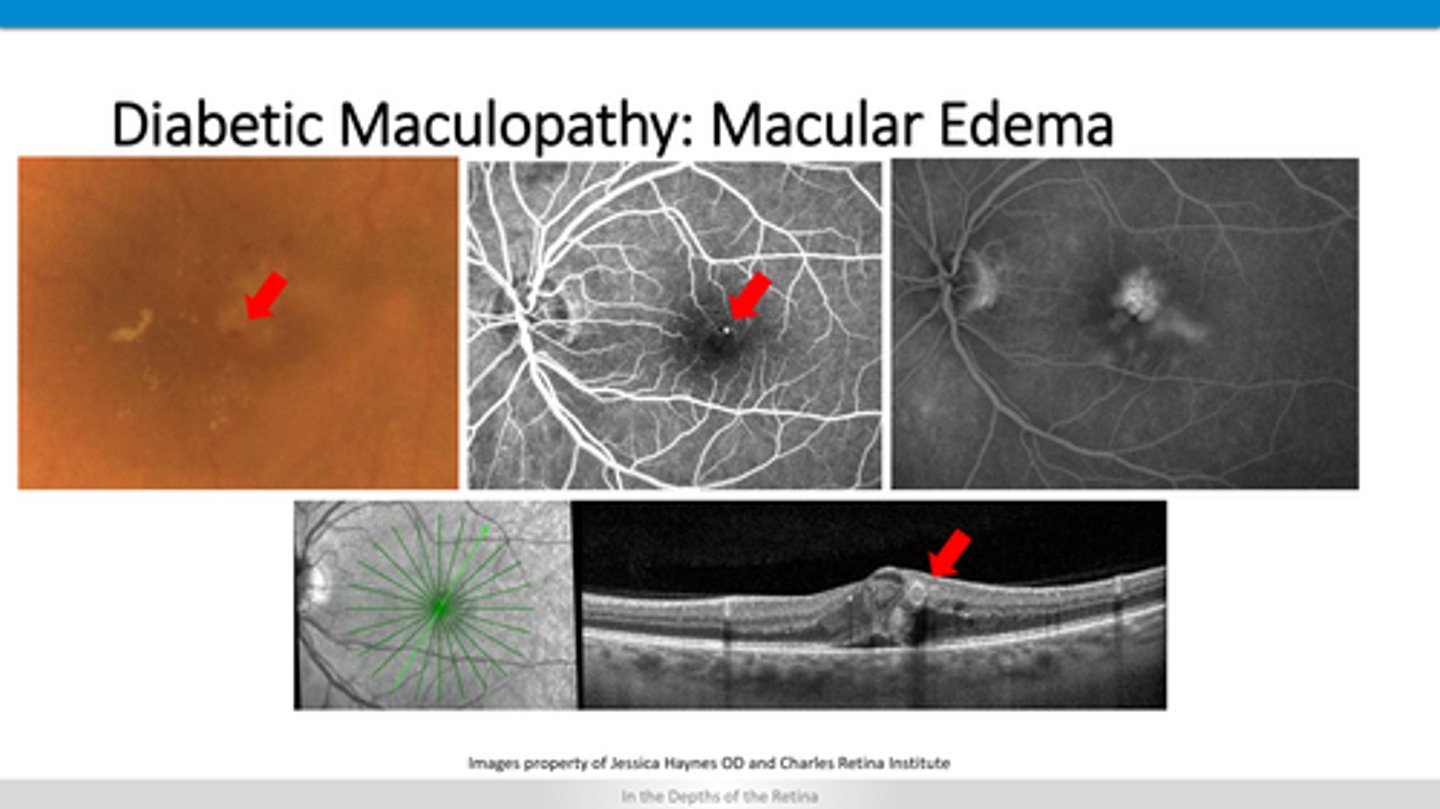
cystic spaces
exudates after fluid resolves
How does diabetic macular edema appear on OCT?
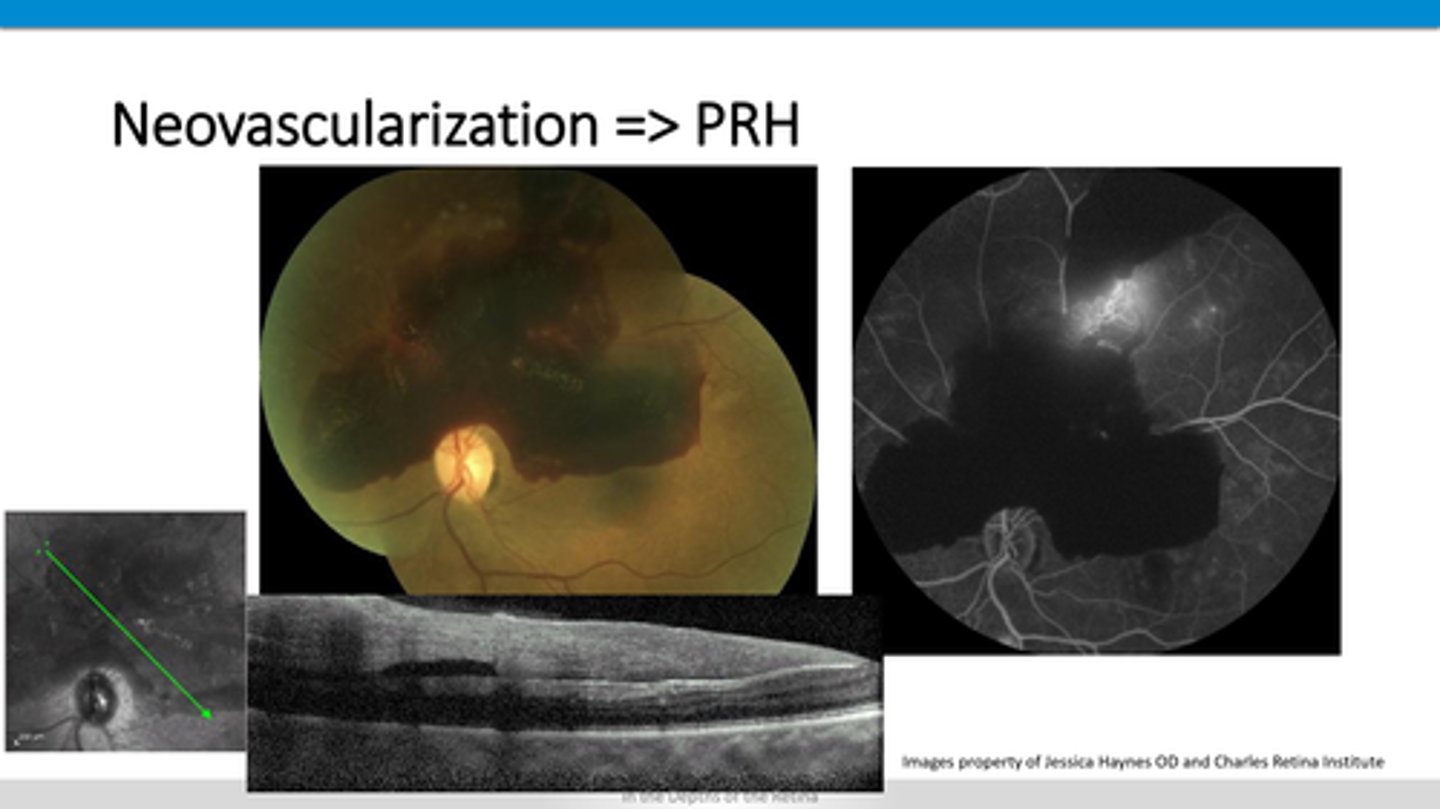
additional hyperF material on top of retinal layers
How does neovascularization and preretinal hemes appear on OCT?
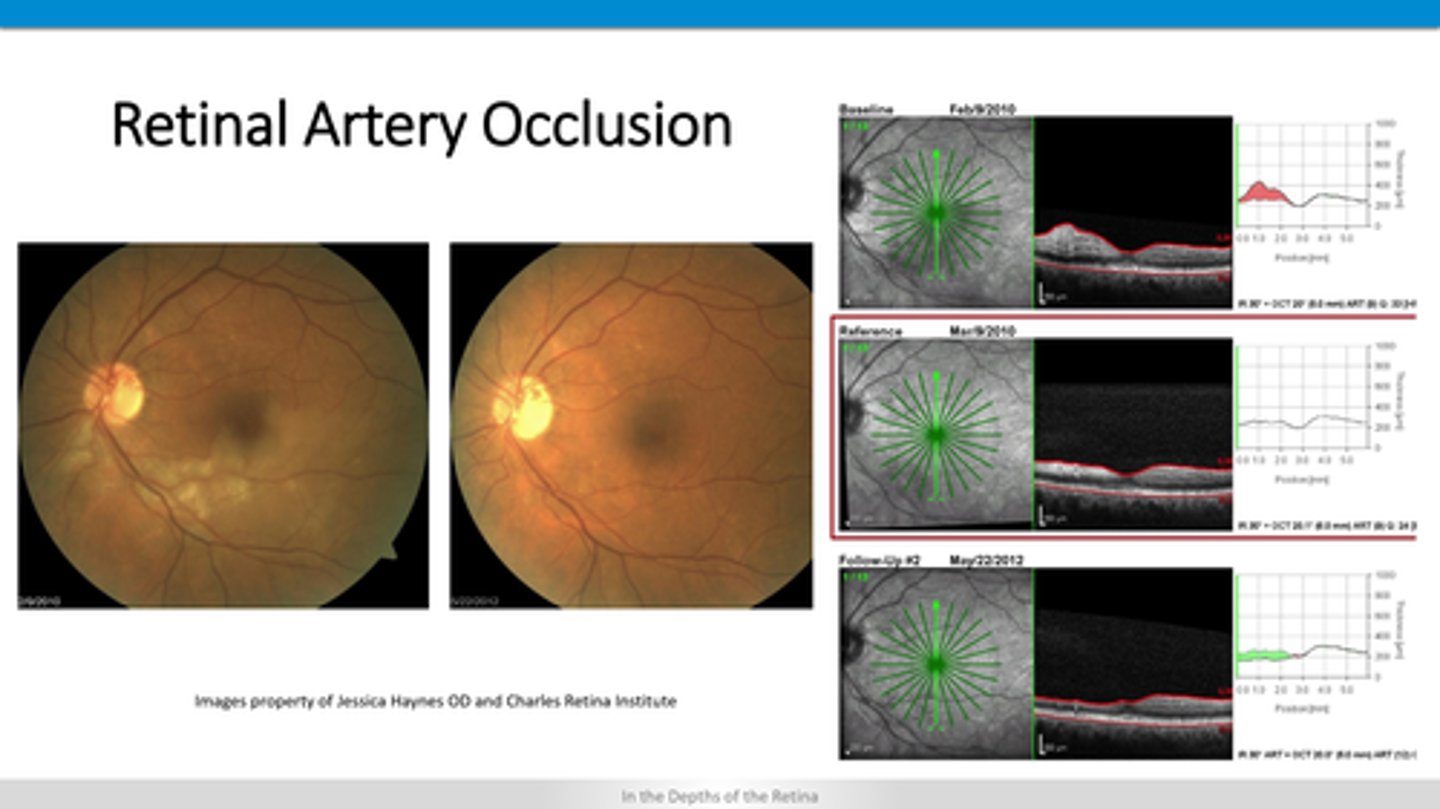
acute = thick, ischemic, inflamed retina layers
chronic = thinned retina due to atrophy
How does BRAO and CRAO appear on OCT?
macular edema
neo
ischemic atrophy
How does BRVO and CRVO appear on OCT?
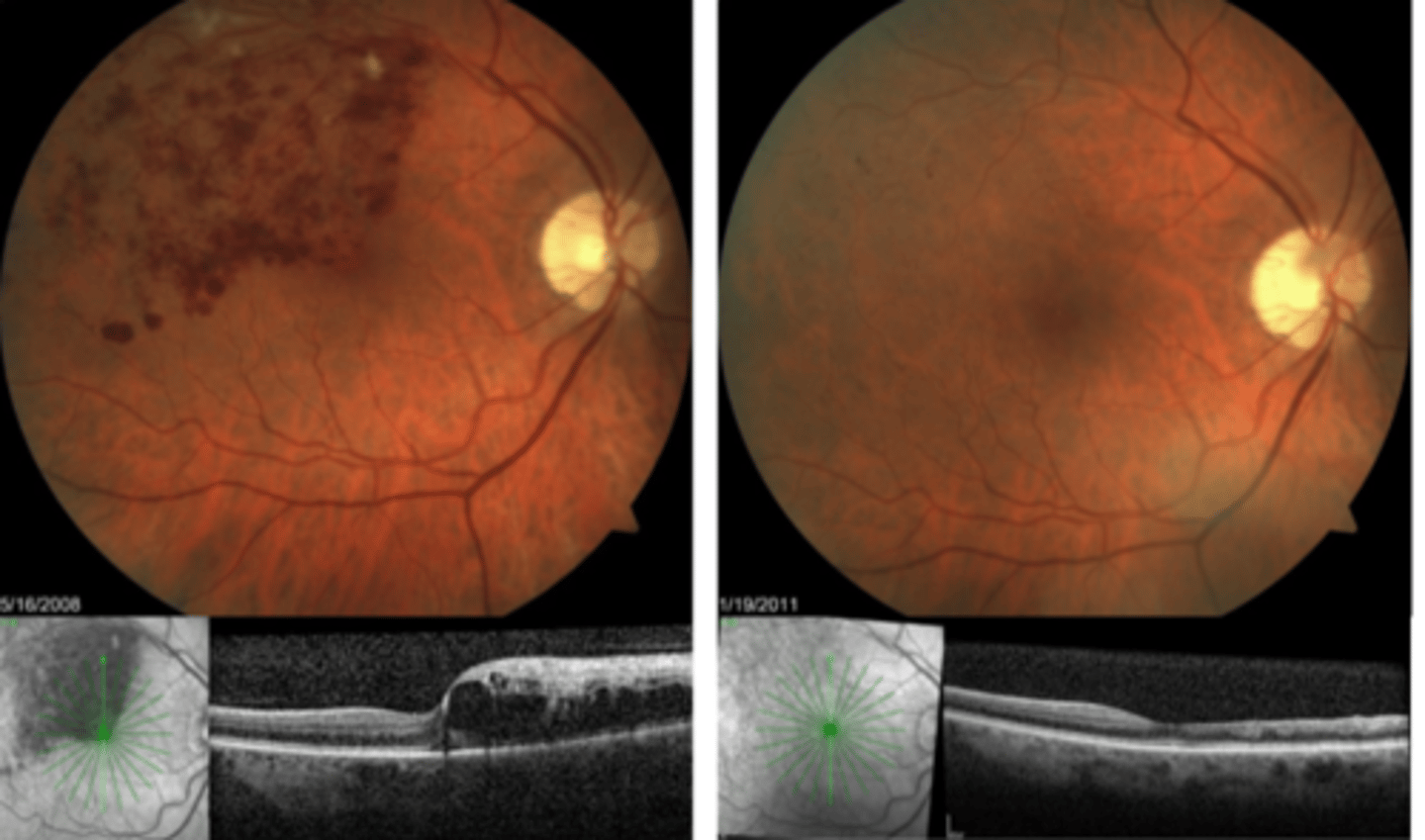
acute = superficial lesions in retina, vitreal haze
chronic = old scars in entire retinal thickness
How does toxoplasmosis retinitis appear on OCT?
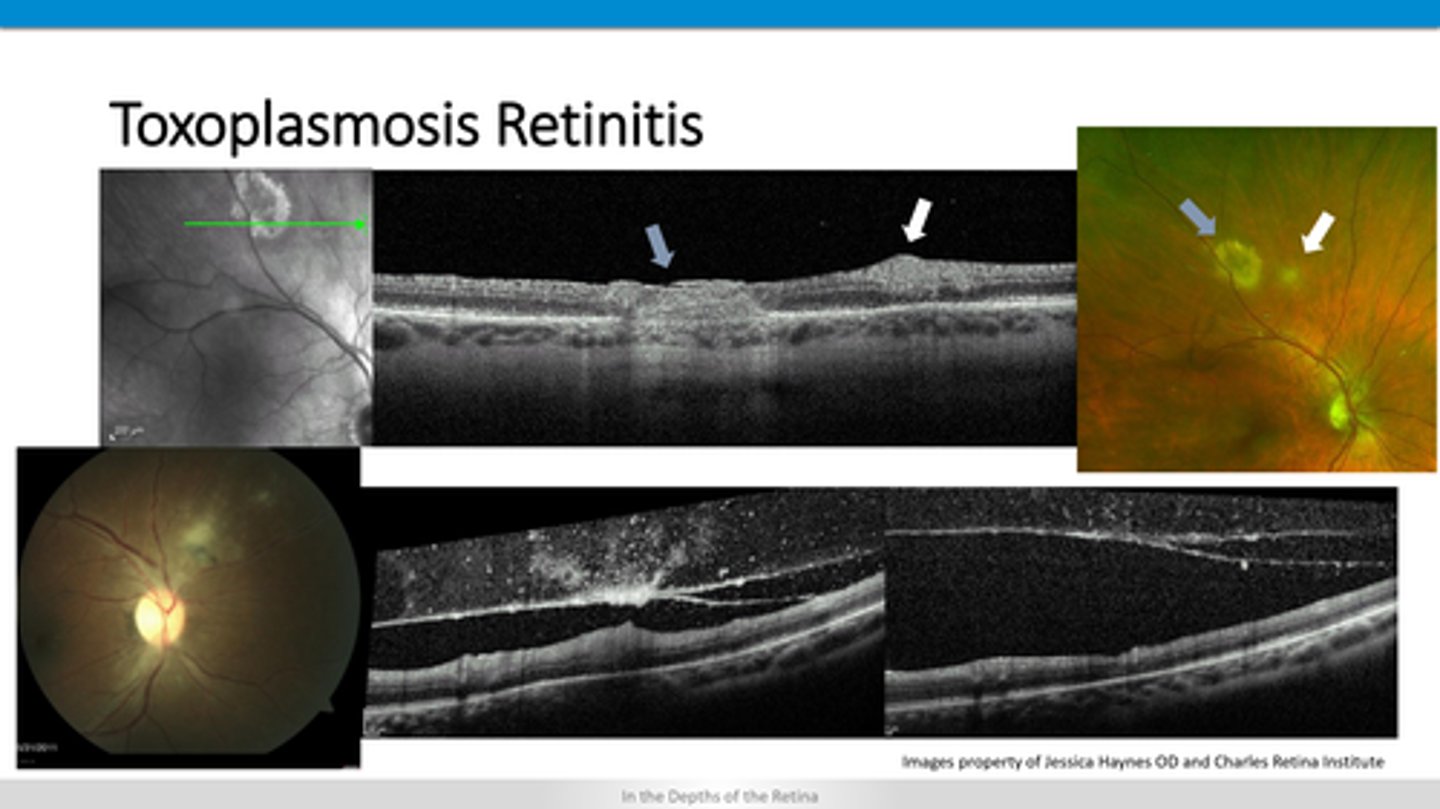
darkened area in choroid
+/- hyperF right below RPE
How does a choroidal nevus appear on OCT?
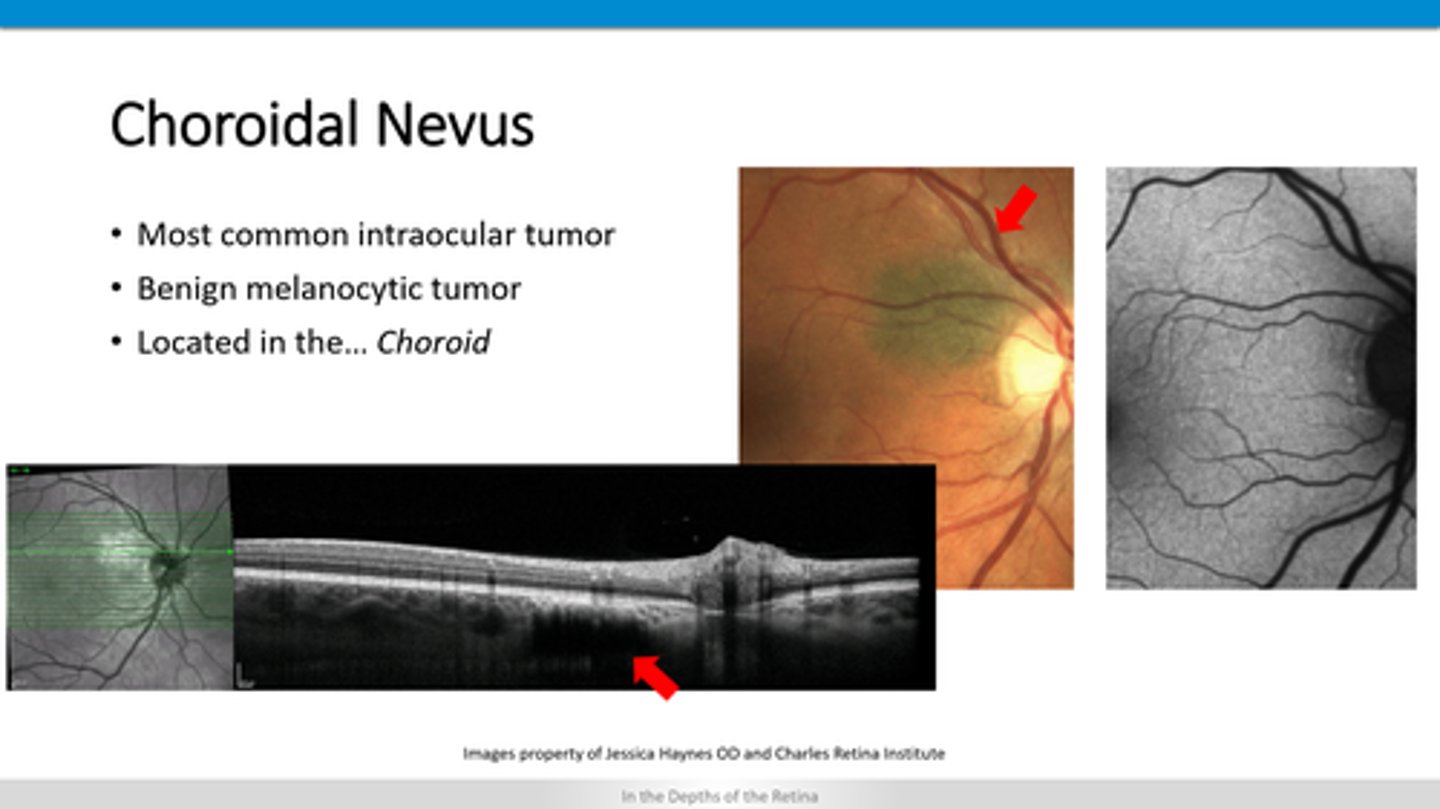
outer retinal atrophy
RPE thicker
+/- lacunae with window defect (no RPE)
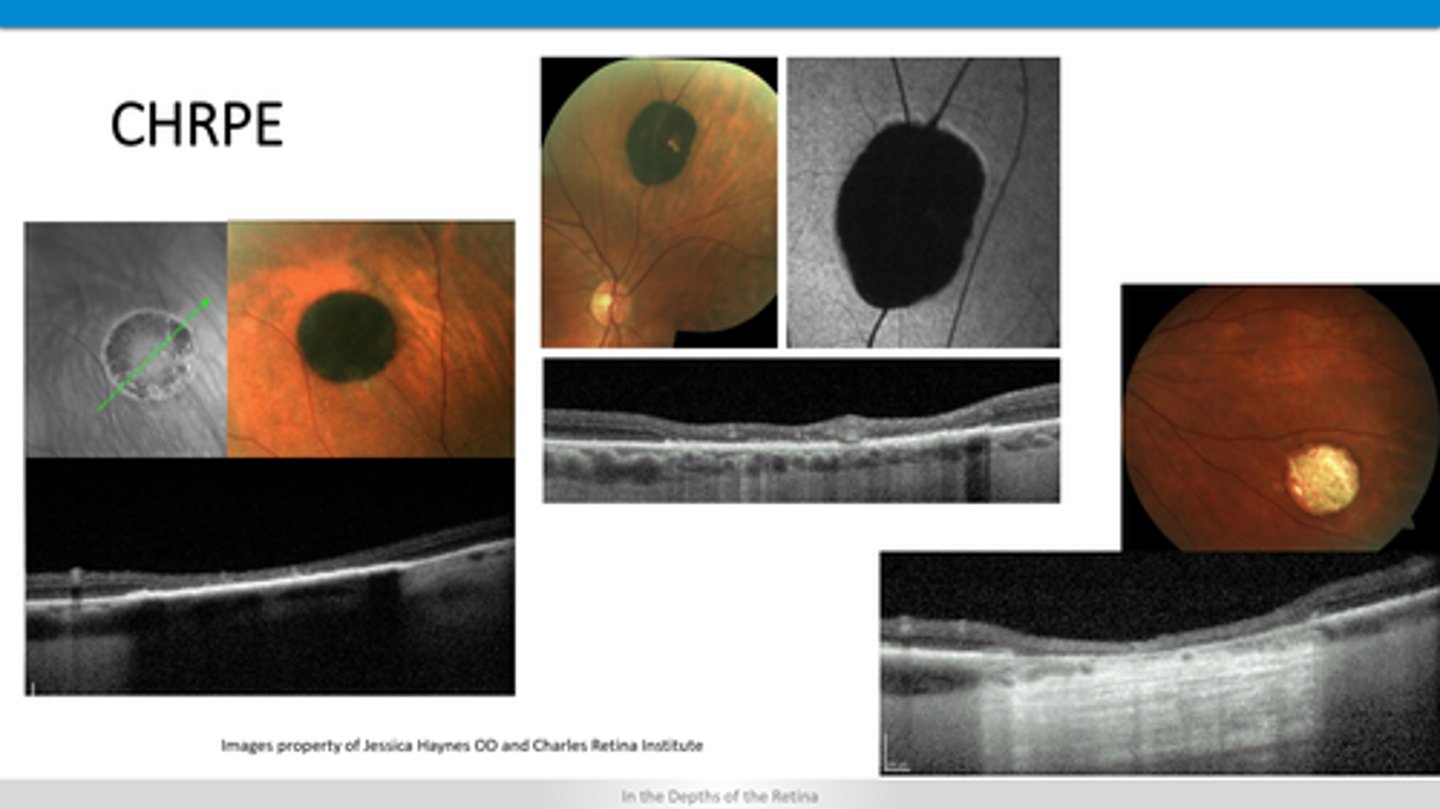
How does a CHRPE appear on OCT?
loss of RNFL and GCC (thinning)
How does NAAION appear on OCT?
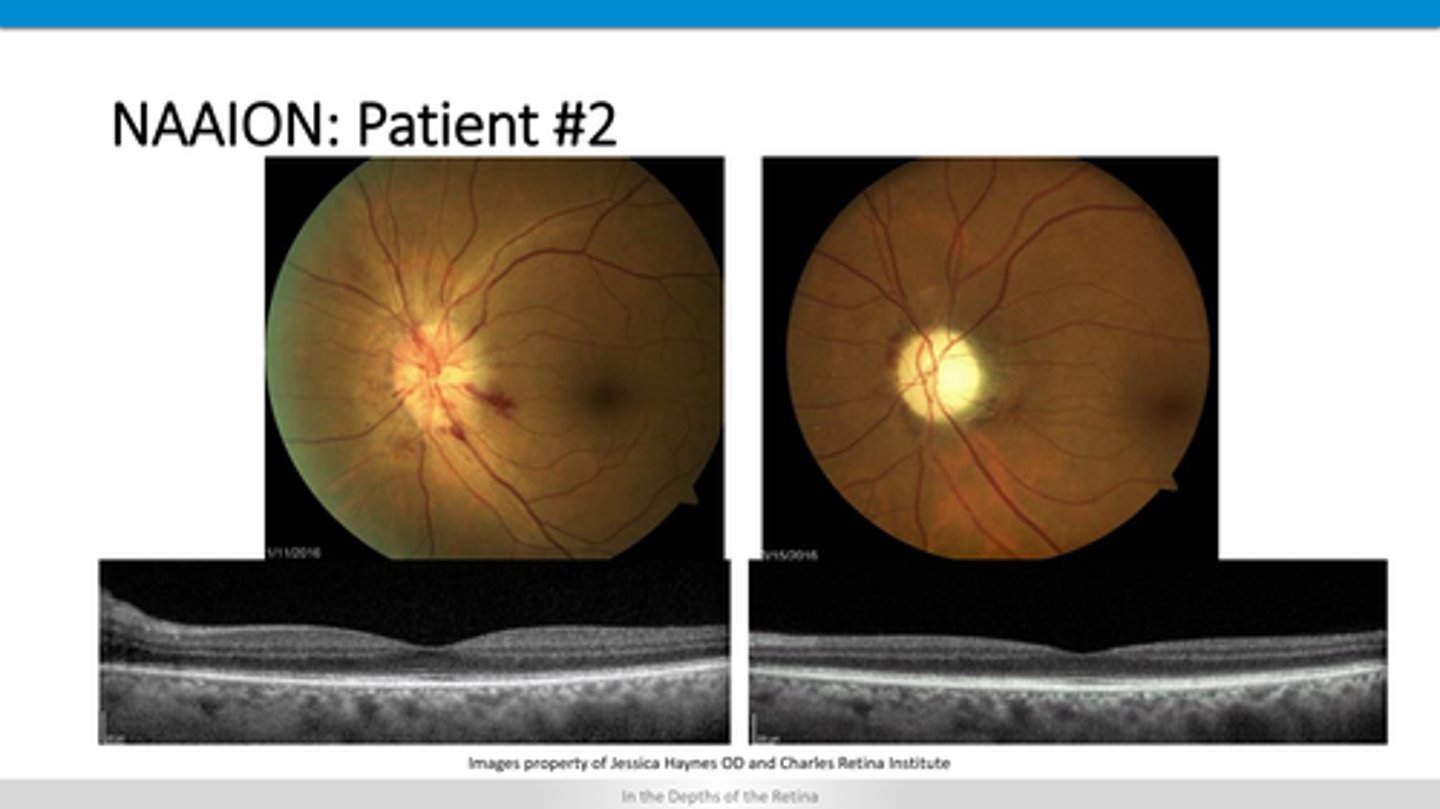
missing area of retina above RPE
How does a retinal hole appear on OCT?
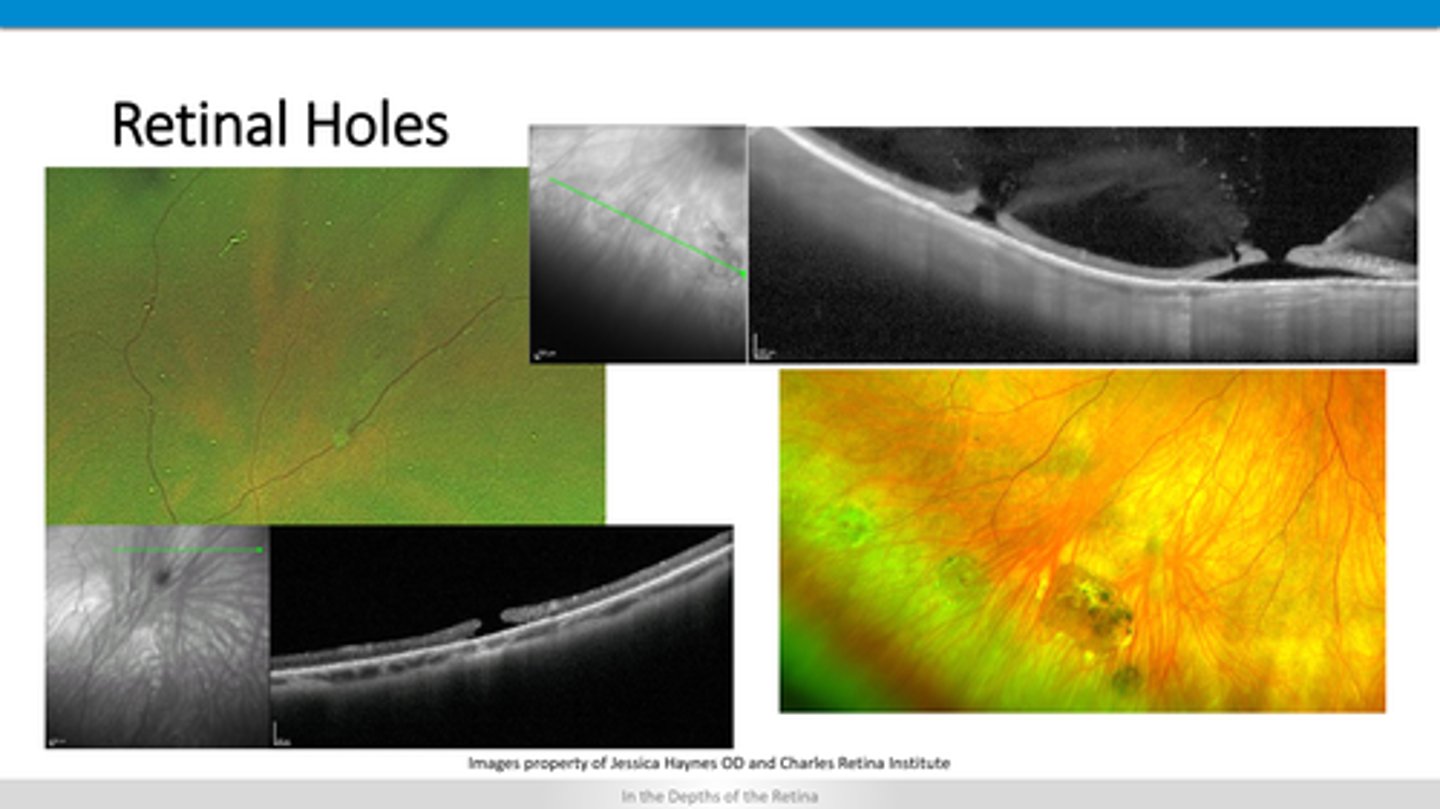
lifting of retinal layers off of RPE
How does a retinal detachment appear on OCT?
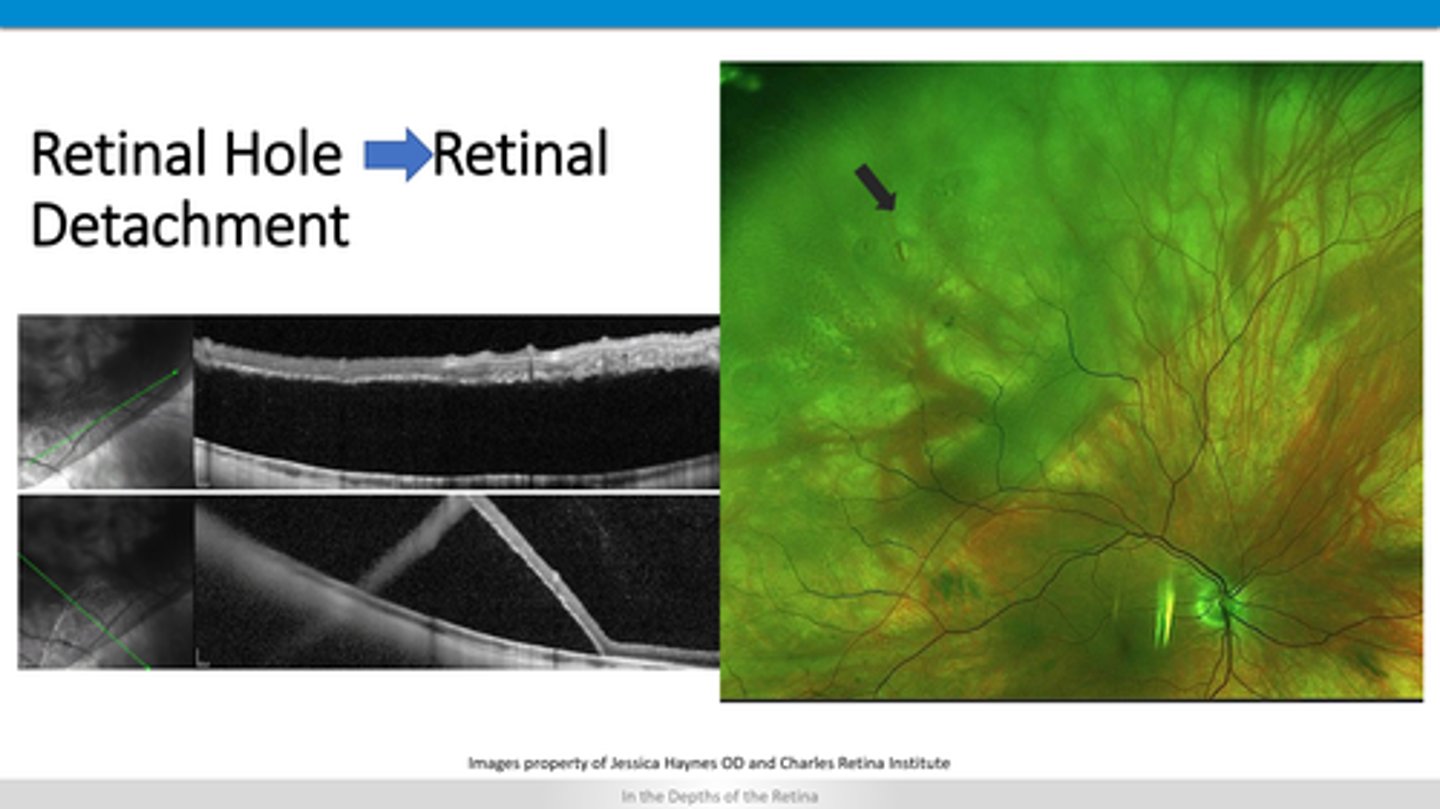
retinal tissue above retinal layers
How does a retinal tuft appear on OCT?
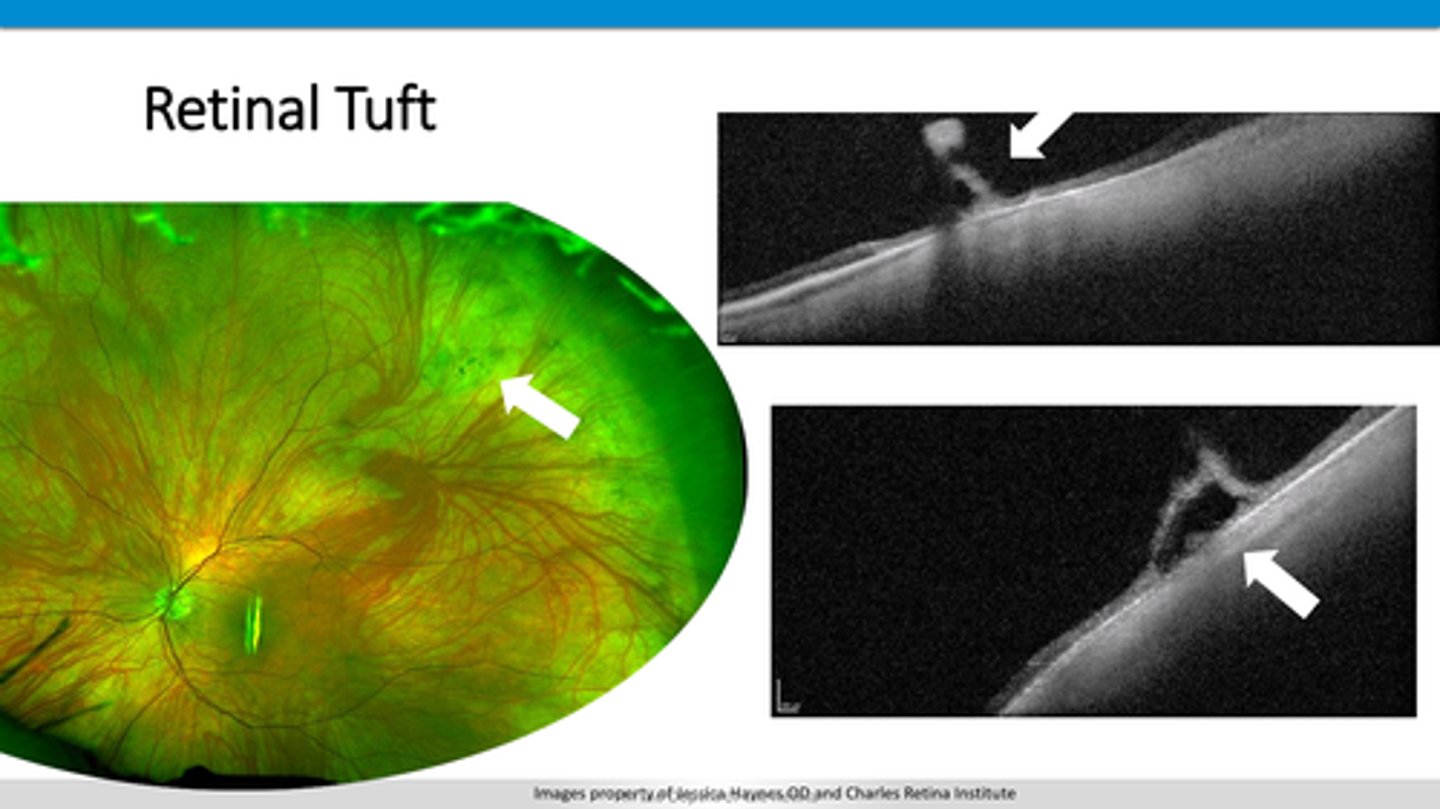
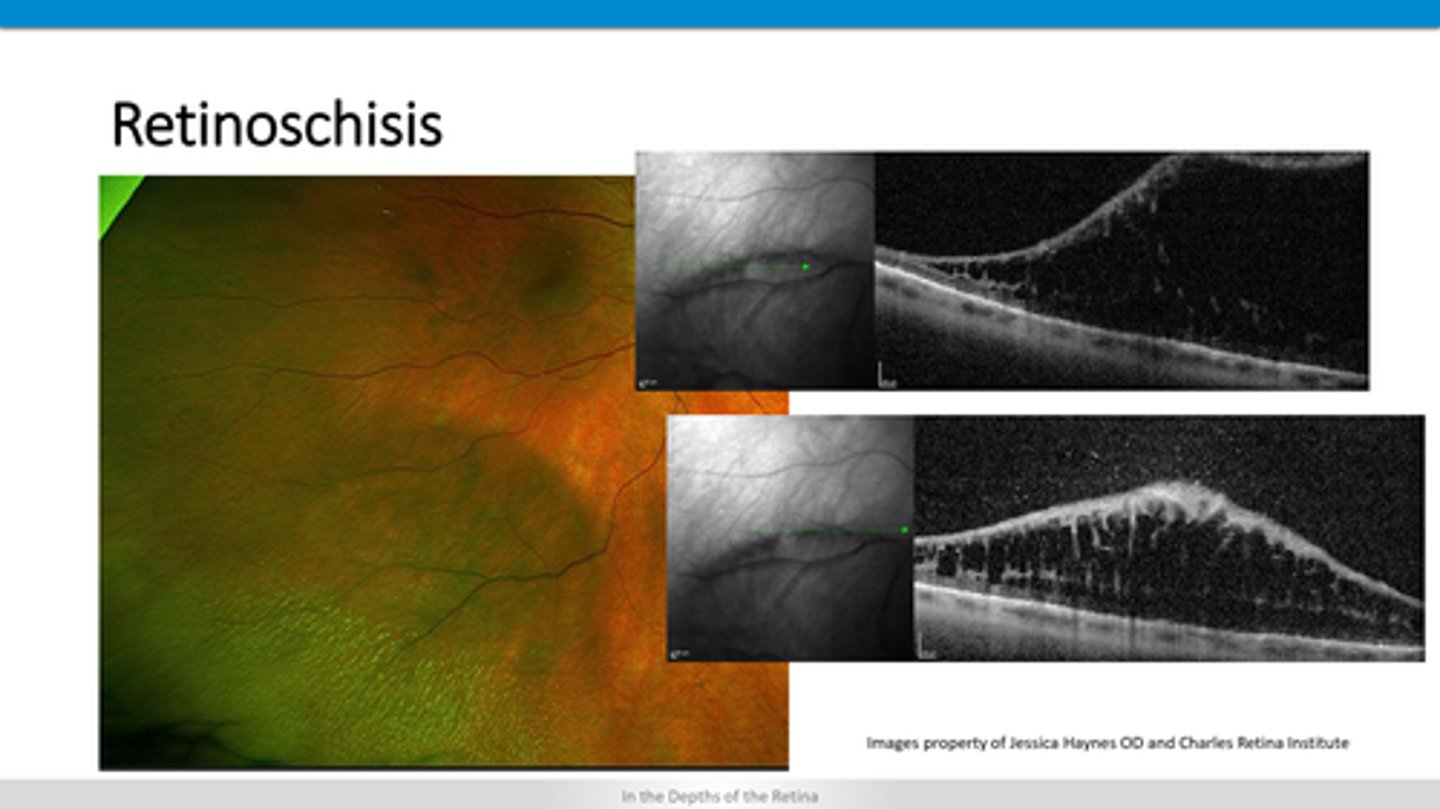
separation within retinal layers
How does a retinoschisis appear on OCT?
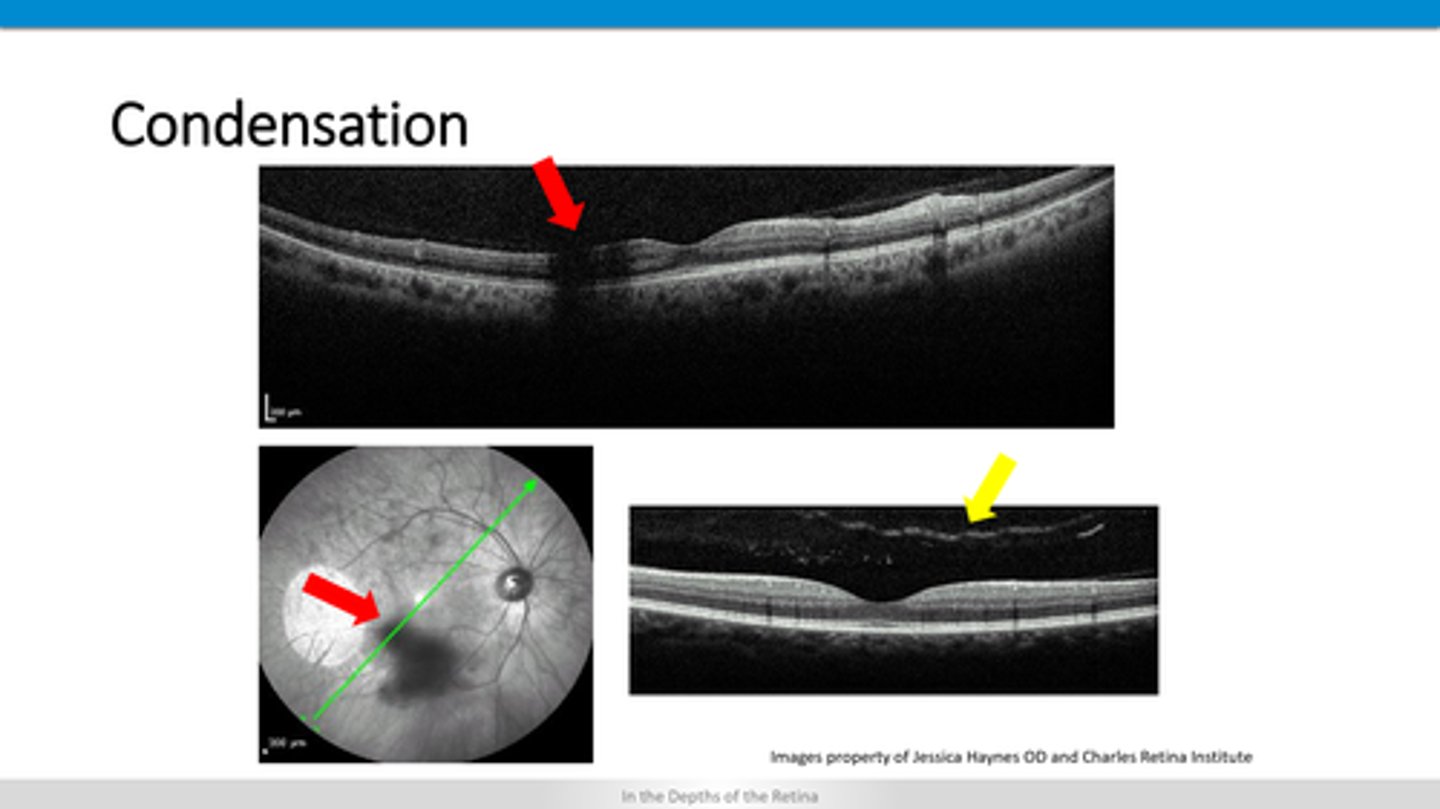
blocking defect = retinal layers behind the condensation are darker
How does vitreal condensation appear on OCT?
vitreal interface lifts of retina
+/- ERM
+/- retinal hole
+/- schisis
How does VMT appear on OCT?
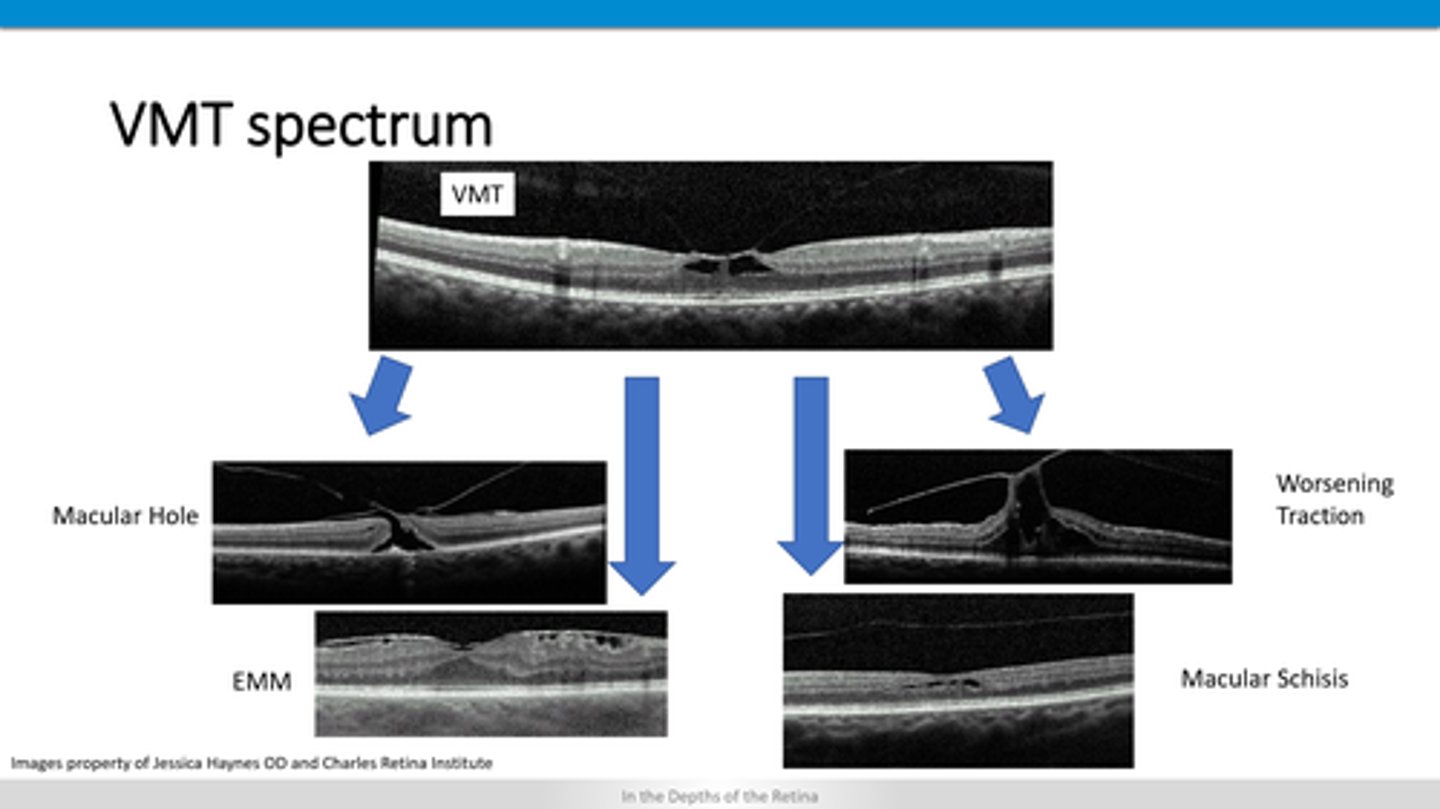
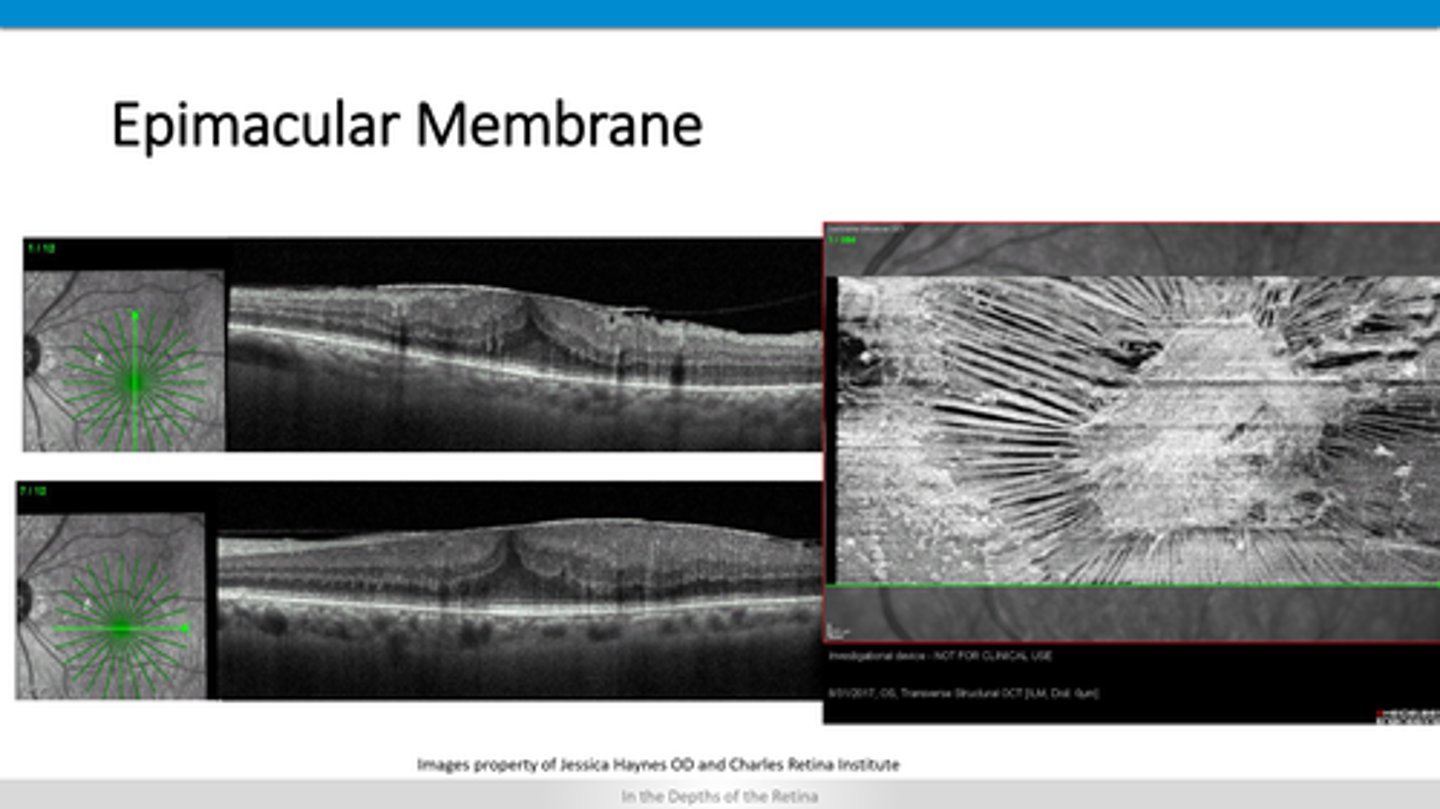
thickened ILM and pulling up on retinal layers
How does ERM appear on OCT?