Unit 2 Chemistry Honors
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
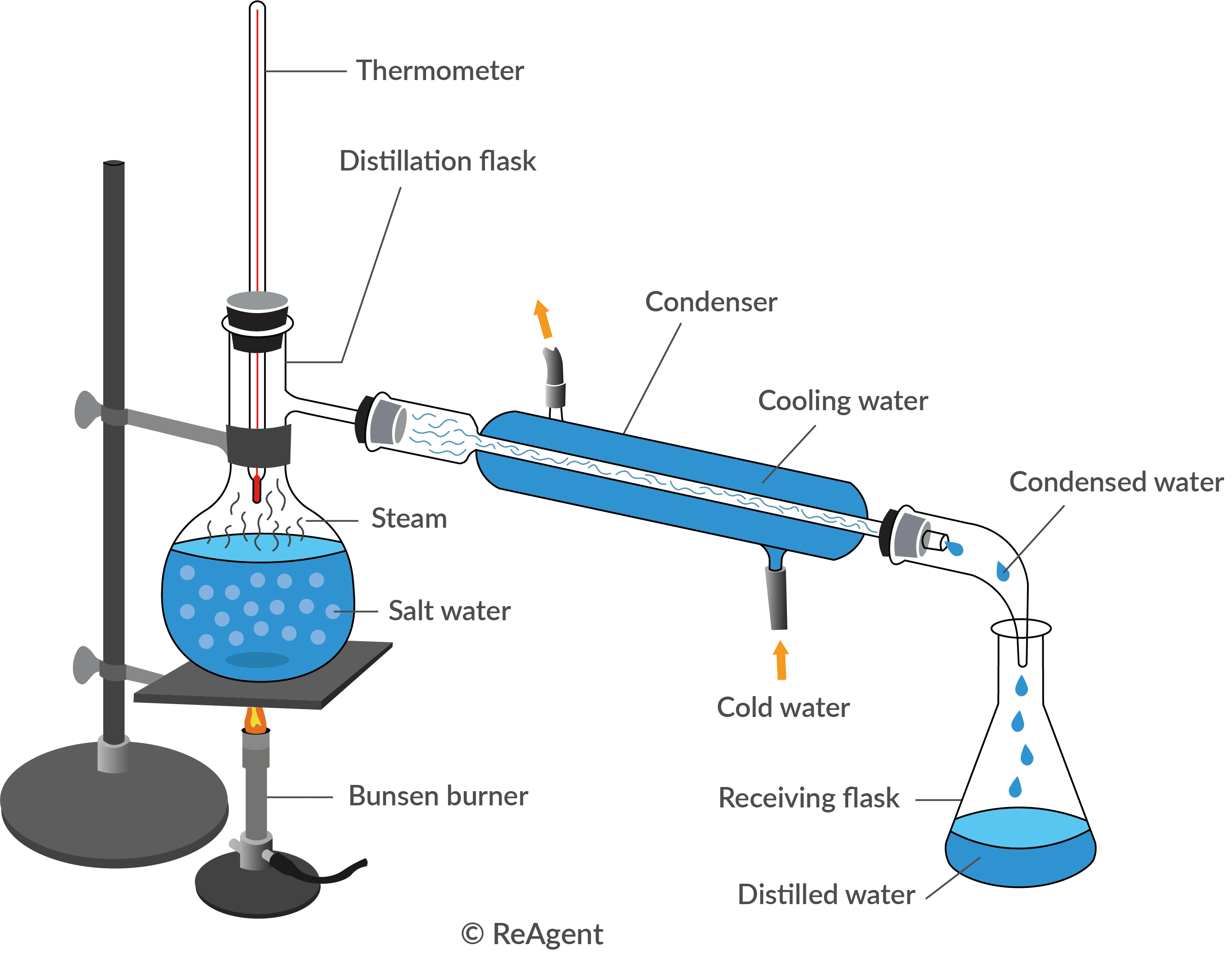
distillation
A separation technique that uses heat to boil a liquid, causing it to vaporize, and then cools the vapor to return it to a liquid state, effectively separating components based on differing boiling points.
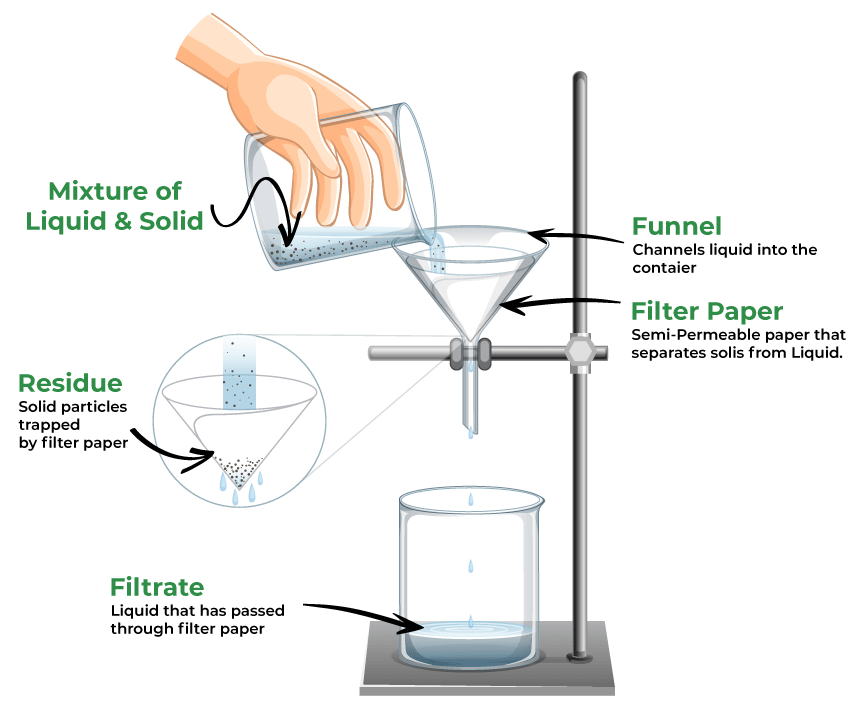
filtration
A separation process that uses a porous material to separate solids from liquids or gases based on particle size.
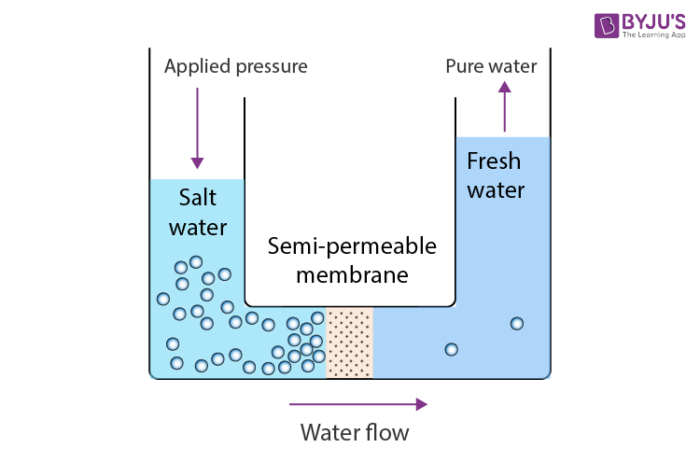
reverse osomosis
A water purification technique that removes contaminants by forcing water through a semipermeable membrane, allowing only water molecules to pass while blocking larger molecules and impurities.
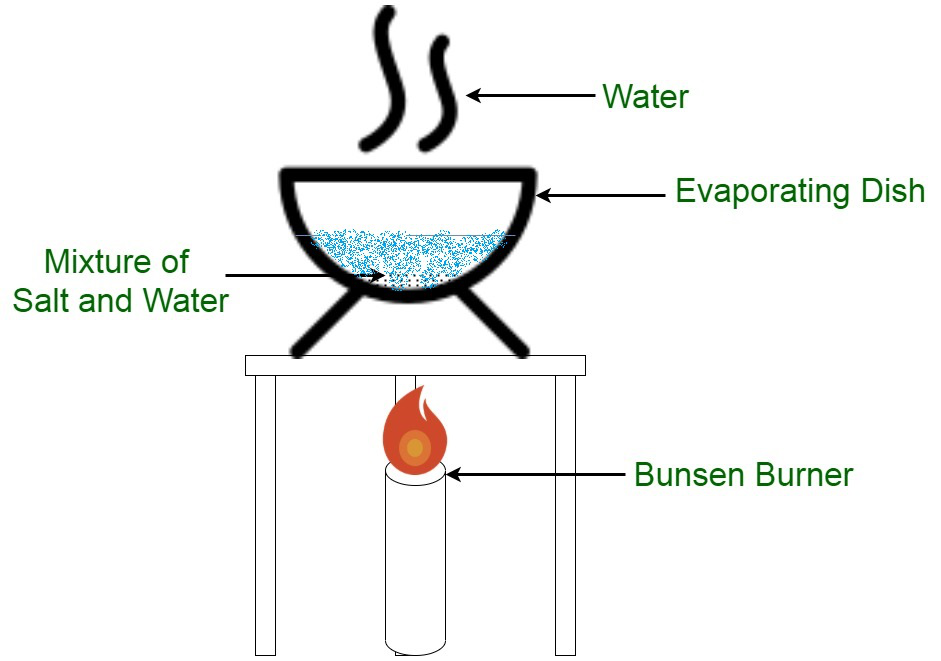
evaporation
The process of heating a liquid to create vapor, which can then be condensed back into a liquid, allowing for the separation of components based on volatility.
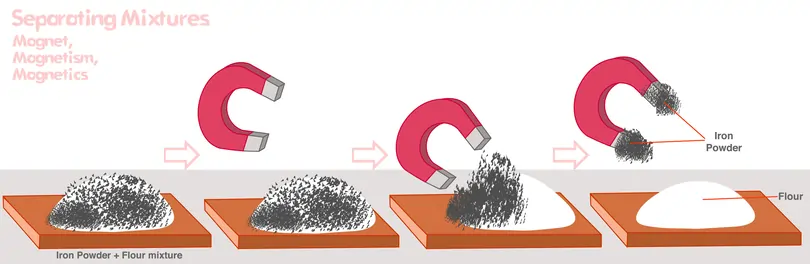
magnetization
A process that uses a magnetic field to separate magnetic materials from non-magnetic ones, often applied in recycling and purification.
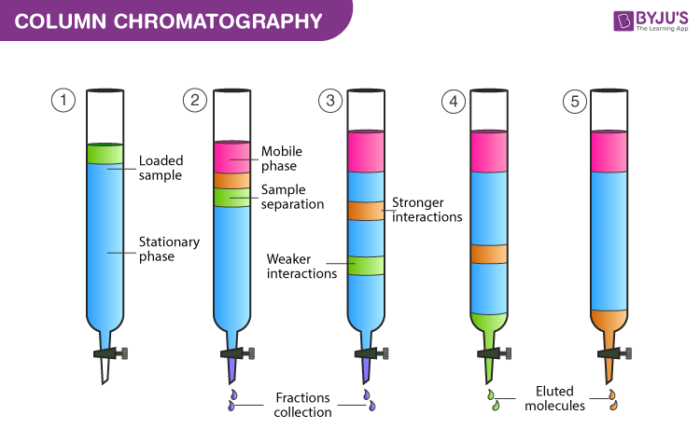
chormatography
A technique used to separate components in a mixture based on their different affinities for a stationary phase and a mobile phase, commonly used in chemical analysis.
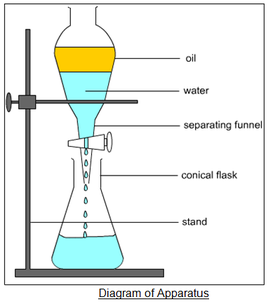
separatory funnel
A piece of laboratory equipment used to separate immiscible liquids based on density, allowing for the controlled removal of one liquid layer from another.
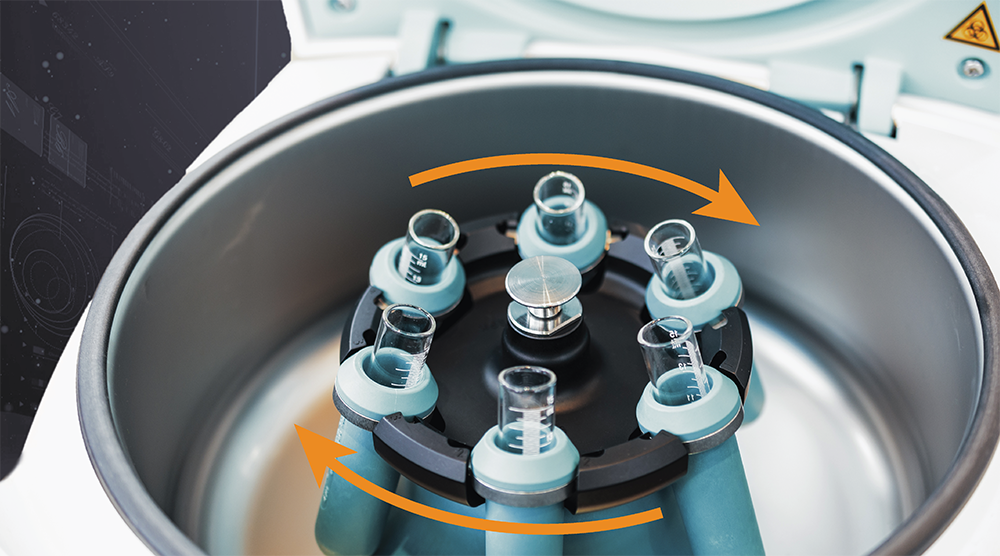
centrifugation
A method that uses rapid spinning to separate components of a mixture based on their density, commonly used in laboratories for separating liquids from solids or different liquid phases.

decanting
A separation technique used to remove a liquid from a solid sediment or from another liquid, typically by pouring the liquid off slowly without disturbing the sediment.

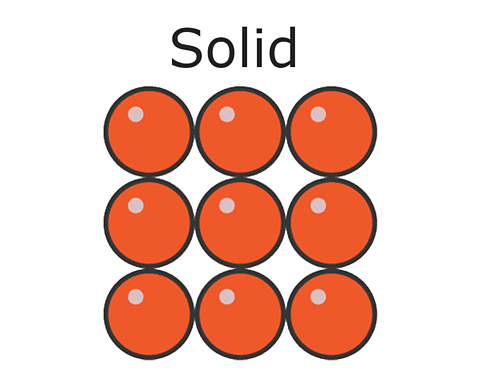
Particles of a Solid
Particles are packed tightly together in a fixed arrangement. Particles can vibrate but not move.
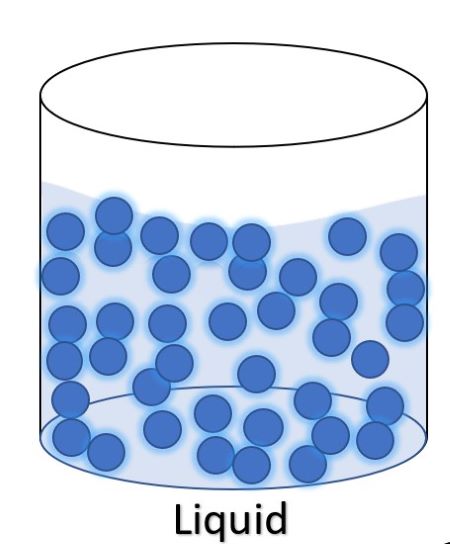
Particles of a Liquid
Particles are close together with no distinct arrangement. Particles can move and slide around each other.
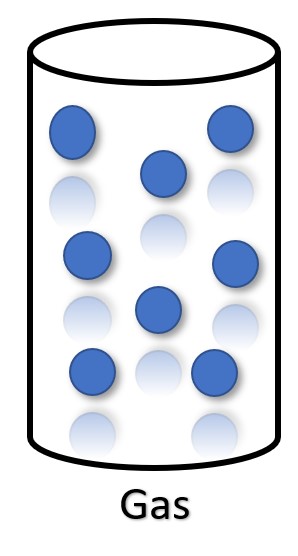
Particles of Gas
Particles are free-floating with no distinct arrangement. Particles move and collide with each other and/
Diatomic Element
consists of two atoms bonded together, either of the same or different elements. These elements exist in pairs in their stable molecular form.(Ex. F2) Elemental Compounds
Compounds
Substances formed when two or more elements are chemically bonded together. Unique properties and can be broken down into simpler substances through chemical reactions.(Ex.H2O and NaCl)
Elements
pure substances consisting of only one type of atom, which cannot be broken down into simpler substances. (Ex.O)
Pure Substance
A material that is composed of only one type of particle, either an element or a compound, and has consistent properties throughout. Examples include elements like gold and compounds like water.
Homogeneous
mixtures that have a uniform composition throughout, meaning the individual components are indistinguishable from one another. Examples include saltwater and steel. Solutions are considered this.
Heterogeneous
mixtures that do not have a uniform composition throughout, where the individual components can be easily identified. Examples include salad and dirt.
Solid to Liquid
Melting
Liquid to Solid
Freezing
Solid to Gas
Sublimation
Liquid to Gas
Vaporization
Gas to Liquid
Condensation
Gas to Solid
Deposition
Tera (T)
10^12.
Giga (G)
10^9
Mega (M)
10^6
kilo (k)
10^3.
deci (d)
10^-1
centi (c)
10^-2
milli (m)
10^-3
micro (μ)
10^-6
nano (n)
10^-9
pico (p)
10^-12
Order of Energies of the Different States of Matter
Gas>Liquid>Solids
length
meter (m)
mass
kilogram (kg)
temperature
Kelvin (K)
time
second (s)
amount of substance
mole (mol)
electric current
ampere (A)
luminous intensity
candela (cd)
Intensive property
A physical property that doesn’t depend on the amount of matter in a sample,remain the same when a sample is divided. Useful for identifying substances.
Density
Boiling/Melting Point
Color
Temperature
Conductivity (electrical, thermal)
Pressure
Extensive property
A physical property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample and changes when the sample is divided. Quantify the amount of substance.
Mass
Volume
Length
Energy
Weight
Momentum
The product of the mass and velocity of an object, indicating its motion and direction.
physical properties
observed without changing the identity and composition of substance. includes color, odor, density, melting point, boiling point, and hardness.
chemical properties
describes the way a substance may change, or react to form other substance during a chemical reaction, including flammability, acidity, and reactivity with other chemicals.
physical change
a substance change its physical appearance but not its composition, same substance before/after change such as changes in state, size, or shape.
Ex. water evaporates (LS) to (GS) but still composed of water molecules
chemical change
a substance is transformed into a chemically different substance
Ex. hydrogen burns in air, undergoes a chemical change + combines oxygen to form water. can be dramatic and often involves energy changes, such as heat or light.
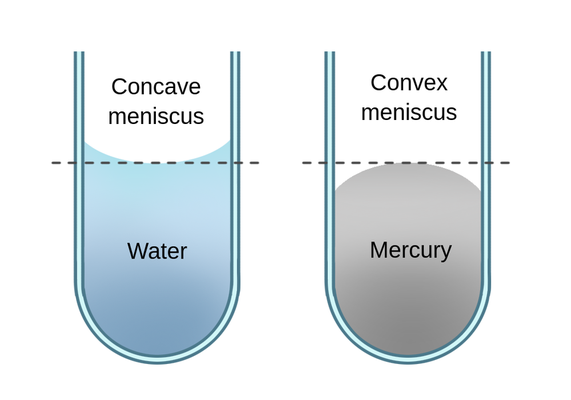
meniscus
the curved upper surface of a liquid in a tube or container, which is used to measure liquid volume accurately.
homogeneous mixture
a mixture that has a uniform composition throughout, often referred to as a solution.
heterogeneous
mixture that has a non-uniform composition, where the individual components can be distinguished.
compound
a substance formed when two or more elements chemically bond together, resulting in unique properties distinct from the individual elements.
solutions
a type of homogeneous mixture where one substance is dissolved in another, typically involving a solute and solvent.