BIOL TISSUES
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
bone tissue
“osseous”; contains very little ground substance, contains a dense mineralized (calcified) matrix called hydroxyapatite, surrounded by a periosteum, osteocytes, osteocytes live in chambers called lacunae, osteocytes depend on diffusion of nutrients through channels called canaliculi, two form of bone: compact and spongy
hydroxyapatite
calcified matrix in bone tissue
osteocytes
bone cells; function of build and maintain
canaliculi
channels through which osteocytes depend on diffusion of nutrients
compact and spongy
two forms of bone
spongy
acts as scaffolding to provide strength and support without the greater weight of compact bone; in the interior of the bones of the skull, vertebrae, sternum, and pelvis, in the ends of the long bones
compact
provides great strength and support, forms a solid outer shell on bones that keeps them from being easily broken or punctured; in the outer portions of all bones, the shafts of long bones
blood and lymph
two types of fluid connective tissues
fluid matrix
each fluid connective tissue contains a distinctive collection of cells called
formed elements and plasma
blood consists of what and what?
red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
what elements are in the formed elements in fluid connective tissue?
blood vessels
conduct blood throughout the body (pumped by the heart)
interstitial fluid
lymph is composed of WHAT? entering lymphatic vessels
lymphocytes
immune cells; 99% of cells in lymph are this
pump
blood has NO what??
connective tissue proper
syrupy ground substance, various fiber types, and wide variety of cells which are not permanent residents of the tissue; they migrate through connective tissues and aggregate at sits of injury
collagen, reticular and elastic
three types of protein fibers in CT proper?
collagen fibers
long, straight (unbranched) collagen protein; function as ropes and/or cables; aligned in parallel in tendons; haphazard in skin
reticular fibers
branching, interwoven network of protein fibers; tough yet flexible; resists forces applied from any direction
elastic fibers
branched and wavy elastin protein fibers; can stretch and recoil to original length
tendon
attach muscle to bone
ligaments
attach bone to bone
CT proper: loose
packing material of the body; fills in empty spaces; cushions and stabilized organs; supports epithelia, blood vessels and nerves
areolar CT proper loose
a packing material that cushions and protects soft organs
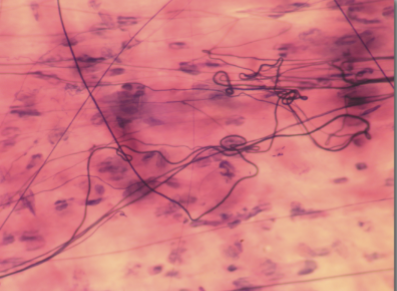
areolar CT proper loose
surrounds most organs, forms lamina propia of mucous membranes
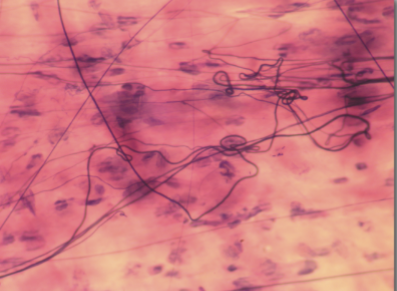
reticular CT loose
reticular fibers create a SKELETON-LIKE FRAMEWORK that supports other cell types, including those that support blood cell development
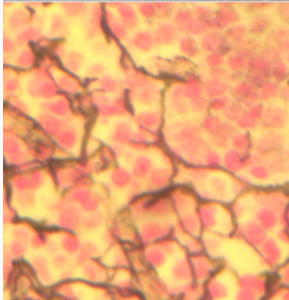
reticular CT loose
in the spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow, liver
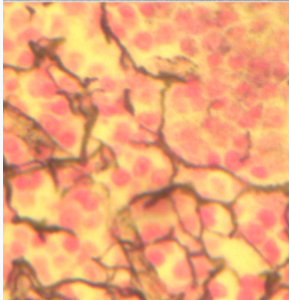
adipose CT proper loose
store energy in the form of triglycerides; soft padding between moving organs and joints; heat conservation
adipose CT proper loose
surrounds most organs and joints; significant amounts beneath the dermis of the skin; major portion of female breasts
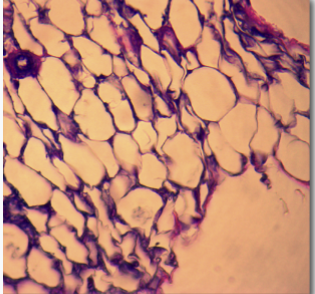
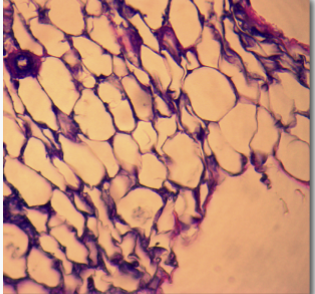
dense CT proper
consists mainly of densely packed collagen fibers
regular and irregular
two types of dense CT tissue?
dense regular CT proper
the collagen fibers are arranged in PARALLEL; includes tendons, ligaments, aponeuroses
dense irregular CT proper
the collagen fibers are arranged RANDOMLY and haphazardly; includes blood vessels and dermis of the skin
dense regular CT proper
incredibly strong when pulled in one direction
dense irregular CT proper
strong pulled in any direction
dense regular CT proper
forms tendons and ligaments; withstands great tensile strength from one direction

dense regular CT proper
tendons, ligaments, aponeuroses

dense irregular CT proper
allows organs (such as the skin) to be pulled in any direction; withstands considerable tensile strength from many directions
dense irregular CT proper
dermis of the skin, fibrous joint capsules, vessels
mucous, serous, synovial, and cutaneous
four types of body membranes?
epithelial and connective tissues
body membranes are simple organs composed of what tissue (s)??
body membranes
line and cover body surfaces and form barriers
mucous membranes
line cavities that communicate the body exterior or outside environment; composed of simple epithelium on areolar CT; epithelial surface is kept moist by the secretion of mucus onto apical surface

serous membranes
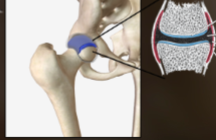
synovial membrane
protects and lubricates bones in joint
cutaneous membrane
covers the entire body surface; is comparatively thick and dry; consists of stratified squamous epithelia on a layer of areolar and adipose connective tissues
synovial membrane
line synovial joints; produce a transudate called synovial fluid
fascia
connective tissue framework of the body
fascia walls
separate the body trunk into several layers; each layer composed of muscle and/or bone; provide strength and durability, separate and maintain positions of internal organs, provide routes for vessels and nerves
superficial, deep and subserous fascia
3 types of fascial walls?
superficial fascia

deep fascia

subserous fascia

superficial fascia
most superficial layer of fascia
deep fascia
separate muscle groups and bone in the body wall
subserous fascia
deepest layer of fascia that lines the ventral body cavity
deep fascia
what kind of fascia separates the solid limbs into compartments?
true
T/F? compartments separate muscle groups by action
true
T/F? limb compartments assist the heart in moving blood through veins
laminin
major protein of the basal lamina
basal lamina
what is the glue that holds epithelial tissue to connective tissue in body membranes
laminin
protein made of three polypetides intertwined in the shape of a cross
true
T/F? crosses connect together to form a meshwork
muscle tissue
specialized for contraction
myocytes
muscle cells
pull, never push
all myocytes only WHAT? they NEVER WHAT??
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
3 types of muscle tissue?
skeletal muscle
voluntary movement of the skeleton
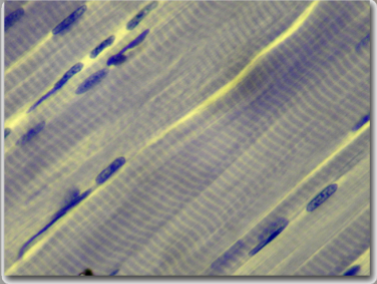
skeletal muscle
attached to every bone of the skeletal system and to portions of the skin
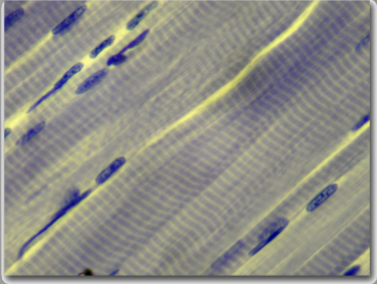
skeletal muscle
very long, unbranched, and multinucleate; striated; under voluntary control
cardiac muscle
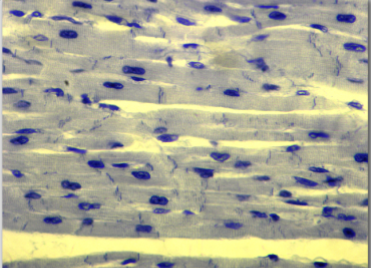
cardiac muscle
striated; involuntary; short and branched
cardiac muscle
propel blood throughout cardiovascular vessels
cardiac muscle
found exclusively in the heart
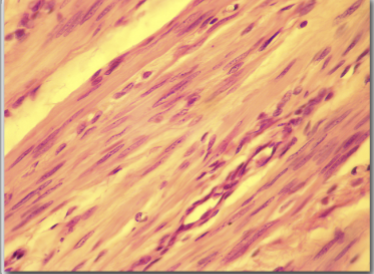
smooth muscle
around tubes; not striated and not under voluntary control; easily regenerated if injured
smooth muscle
constriction of tubular structures such as blood vessels; movement of substances through TUBULAR STRUCTURES via peristalsis; not under voluntary control
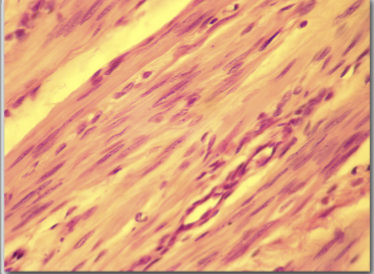
smooth muscle
around blood vessels the bronchioles; sphincter muscles; the pupil of the eye
nervous tissue
transmit and process information rapidly. transmission is achieved via electrical impulses called action potentials propogated through axons and dendrites. information processing is achieved via neural circuits composed of many neurons
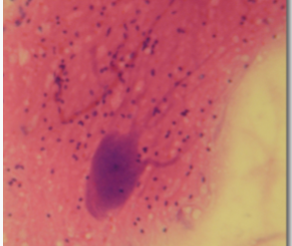
nervous tissue
brain, spinal cord, ganglia, peripheral nerves
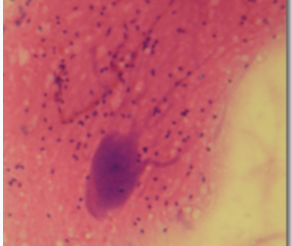
neurons and neuroglia
two main cell types in nervous tissue?
neurons
transmit and process information
neuroglia
physically and metabolically support neurons
inflammation and regeneration
the body’s response to injury or disease
homeostasis
goal to restore from tissue injury is??
true
T/F? inflammation and regeneration are tissue level responses
inflammatory response
a predictable suite of responses to injury
swelling, redness, warmth, and pain
mast cells
migrating CT cells
response of tissue injury triggered by what?
histamine, prostaglandins, and heparin
mast cells release WHAT 3 THINGS to initiate and maintain inflammation?
true
these chemicals local blood vessels to dilate and increase their permeability