Pharmacology of Anti platelets and anti coagulants
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
what does prostacyclin do?
STOPS platelet aggregation.
released from endothelial cells
what does thromboxane do?
stimulates platelet aggregation and vasoconstriction.
released from platelets.
diagram of how PGs and thromboxane are produced
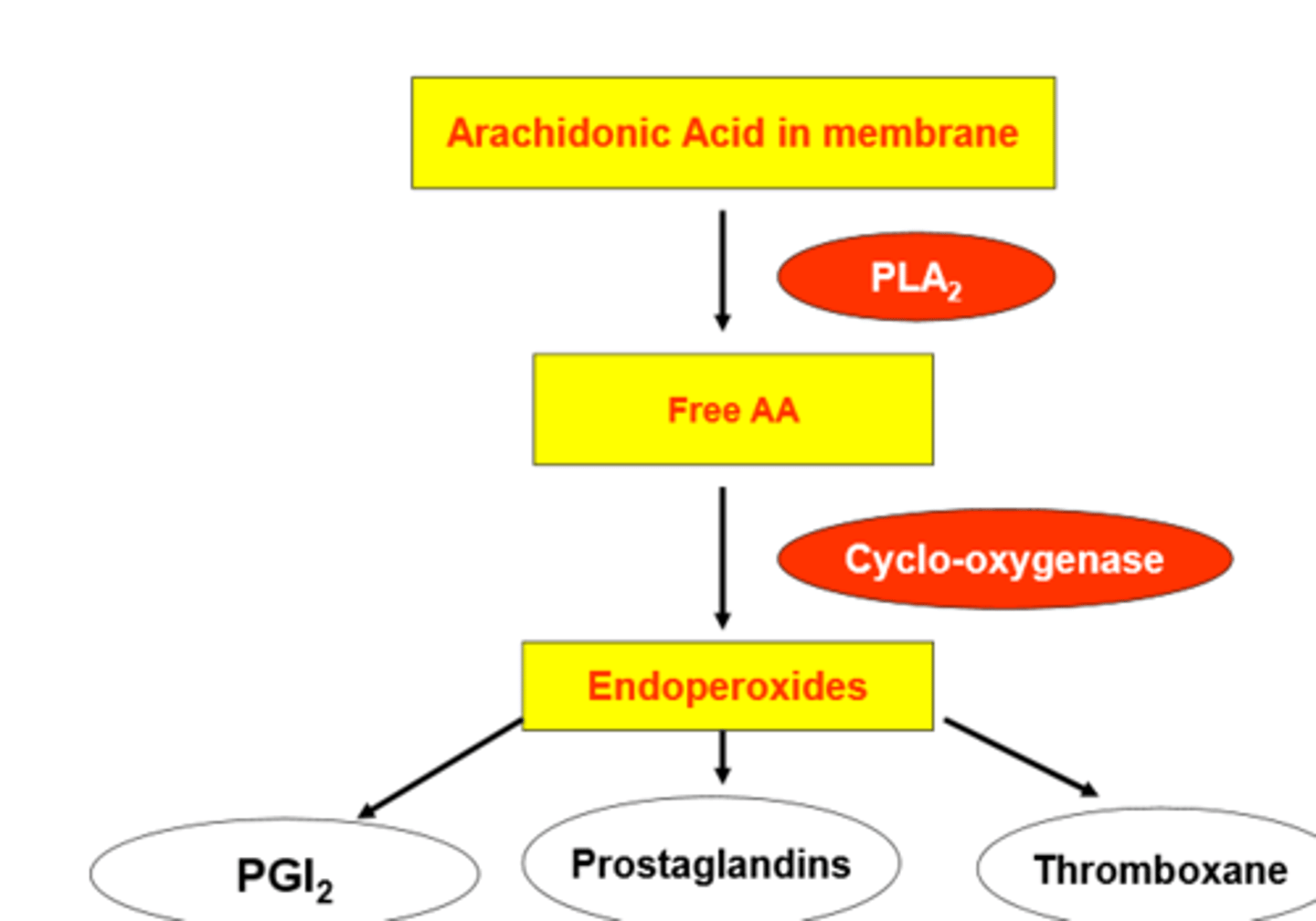
when are antiplatelet drugs used?
used to prevent MI in patients who have previously had an MI.
reduces stroke incidence.
what do antiplatelet drugs do?
inhibits cyclo-oxygenase (irreversible)
Prevent arichidonic acid → protaglandins → thrmboxane (platlet aggregation)
example of antiplatelet drugs?
low dose aspirin
aspirins effects diagram
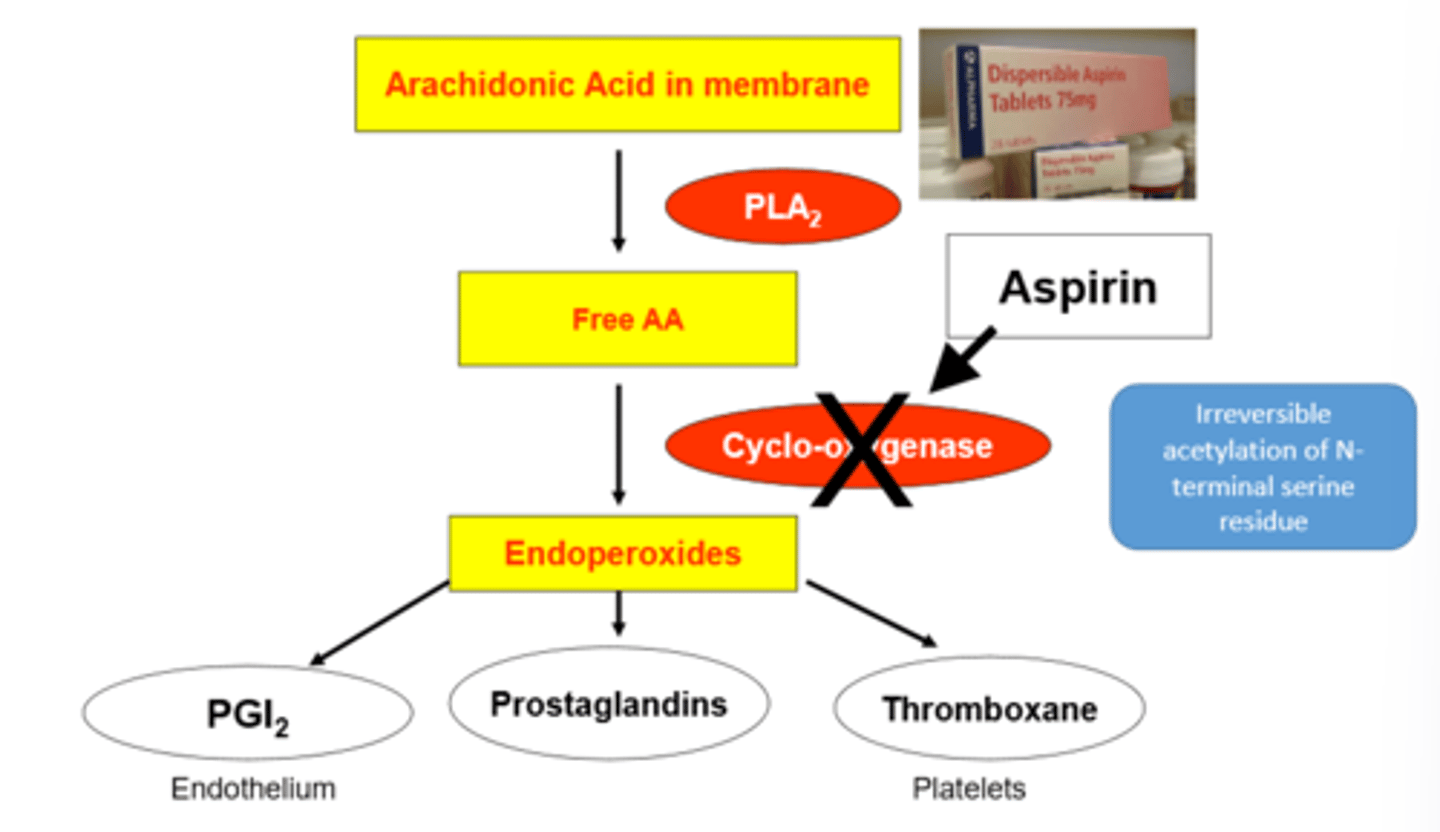
how is aspirin selective?
it only effects the platelets due to them not having a nucleus and therefore not being able to produce new COX.
why is aspirin only a small dose?
if it was a larger dose then aspirin inhibits COX-2 in endothelial cells, reducing prostacyclin (PGI2) production.
Increases chance of clotting → heart attack
what is clopidogrel?
ANTI PLATLET DRUG
P2Y12 receptor antagonist . → prevents activation of ADP athway → inhibits aggregation
what does plasmin do?
digests the fibrin of the clot (and some of the clotting factors)
what is activated to make plasmin?
→ plasminogen.
via streptokinase.
what is the issue with streptokinase?
it is a protein so the body can create antibodies against it.
means cant really be used more than once.
what is alteplase?
Thrombolytic drug
human made plasminogen activator - > makes plasmin - > break fibrin → break clot
when is alteplase given?
immediate after myocardial infarction (MI)
what drugs are used to prevent coagulation?
heparins
oral anti-coags = warfarin
direct oral anti-coags (DOACs) = rivaroxaban.
heparin
Heparin is an anticoagulant (blood thinner) used to prevent and treat blood clots.
It works by inhibiting thrombin and factor Xa,
prevent DVT + acute myocardial infarction.
what do heparins activate?
anti thrombin III
how is heparin administered?
injected.
What does warfarin do?
blocks unwanted coagulation.
vitamin K reductase inhibitor.
does warfarin interact with other drugs?
yes, with most others.
what is reducing vitamin K essential for?
production of prothrombin and factors VII, IX and X - importent for preventing too much clotting
what is warfarin's TW?
narrow - risk of bleeding.