Study Guide 19: Integrated osmolarity and BP
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
The water volume in various compartments of the body is relatively ____.
constant
In what ways can water and solutes move
from one compartment to another?
Osmosis
Capillary filtration
Membrane transport
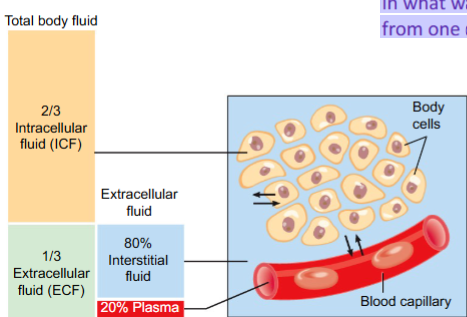
What are the divisions of fluid in the body?
A person eats a tasty meal that is high in sodium (table salt = NaCl),
which is absorbed in the GI tract and then into the blood. The ingested
salt increases the osmolarity of the blood. What immediate effect
would this have on the other fluid compartments of the body?
A) the ECF would become hypertonic to the body cells
B) the ECF would become hypotonic to the body cells
C) The ECF would remain isotonic to the body cells
A) the ECF would become hypertonic to the body cells
Capillary walls vs cell membranes: different permeability to ___ and ___
water and sodium
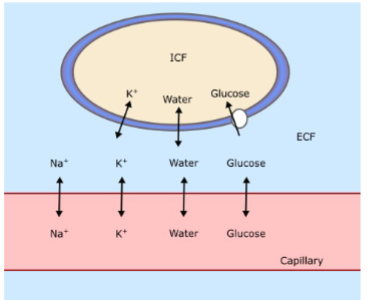
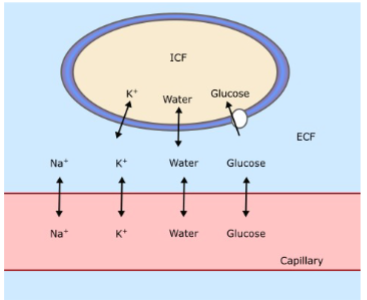
The cell shown here is a typical cell.
Why did the artist draw K+ being able to cross the membrane, but not sodium?
Typical cells have higher K+ permeability than Na+
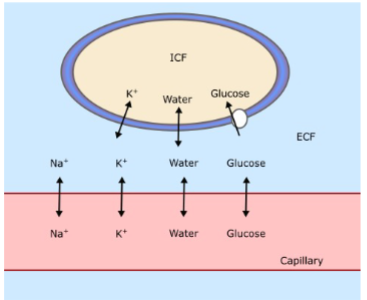
The ____ of the blood must be regulated to ensure fluid balance between ECF and ICF
If the ECF/blood has a high osmolarity, it is likely to be _______tonic to
the body cells and cause them to _________.
OSMOLARITY
hyper
shrink
_____ neurons in the _____ sense osmolarity based on the effect that shrinking/swelling has on _____.
osmosensitive
hypothalamus
membrane potential
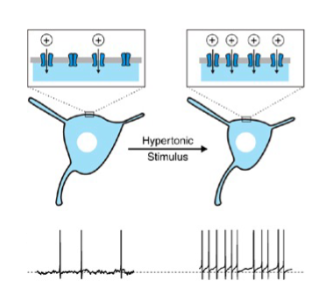
In the presence of a hypertonic stimulus. _____ neurons in the hypothalamus trigger other _______ neurons to stimulate _____.
Osmosensitve
hypothalamic
thirst and release more ADH from post. pituitary
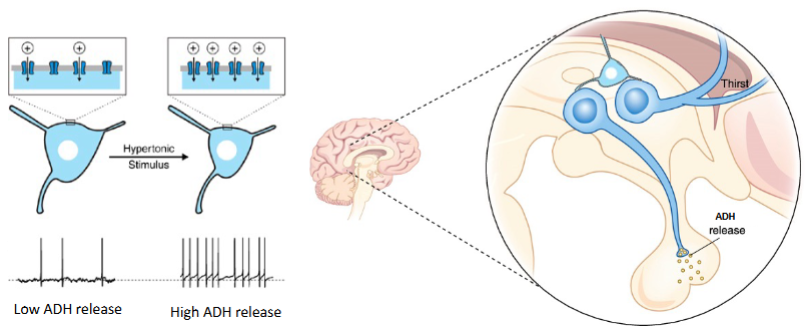
Cells in the collecting duct respond to ADH by increasing _____ expression.
aquaporin
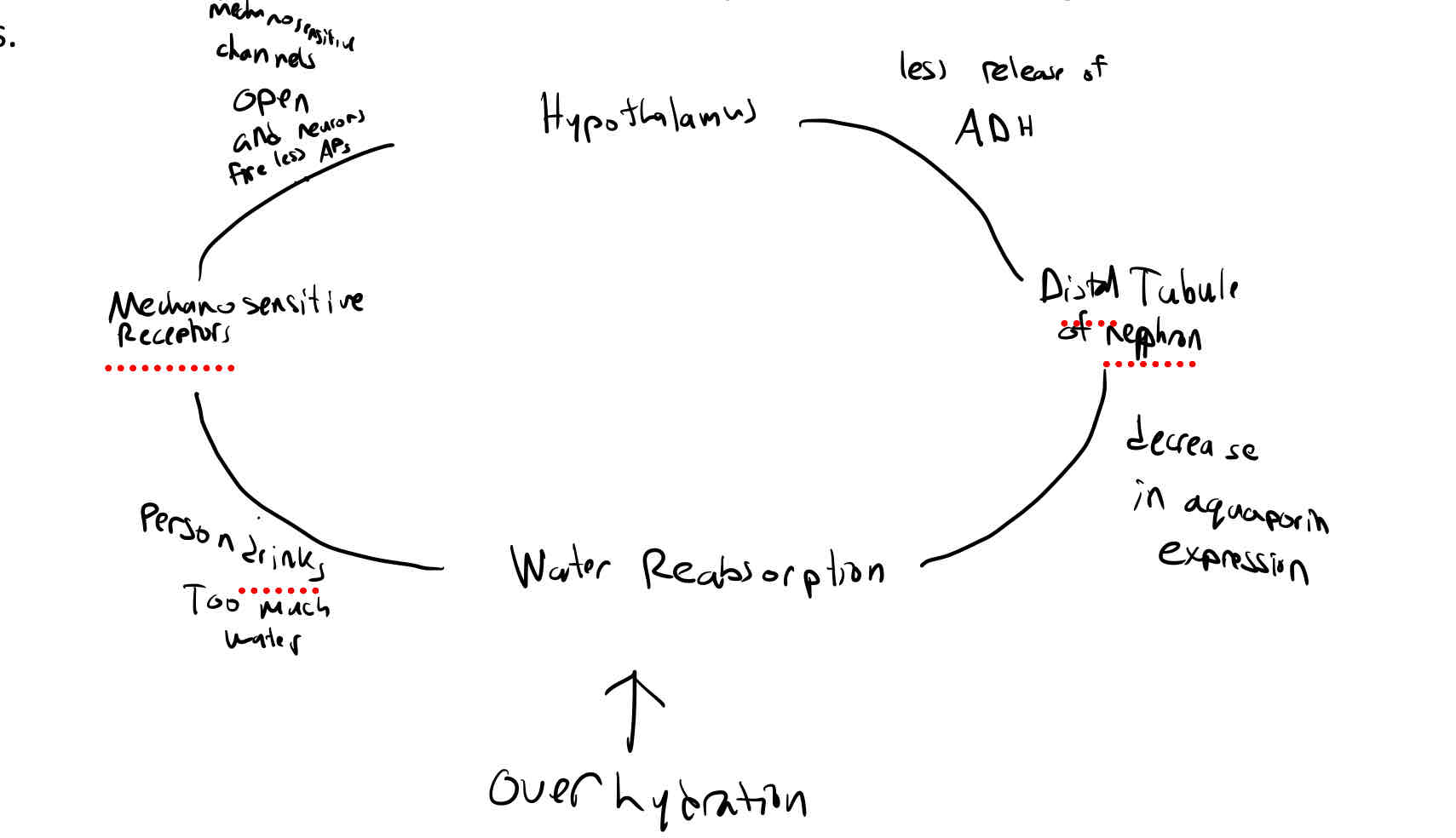
Diagram the homeostatic response that would occur if a person, initially within the osmotic set point range, drinks a large bottle of water and overhydrates.
see pic
What does “physiology is integrative mean”
Certain organ systems are specialized to do certain tasks......but most physiological processes involve multiple organ systems working together.
The ______ of blood in circulation can affect mean arterial pressure. Explain through which organ systems.
volume
We have already discussed how MAP can be regulated by the cardiovascular system...with the assumption that blood volume is constant.
However, the kidneys can also regulate blood pressure!

What art of this equation can be modulated by kidneys?
Kidneys can promote water LOSS or CONSERVATION through the urine, but they cannot increase the volume of the blood.

What is RAS stand for?
The Renin-Angiotensin System
Also called RAAS, for Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System
Important for increasing blood pressure when low
What is the pathway of RAS and how are they made?
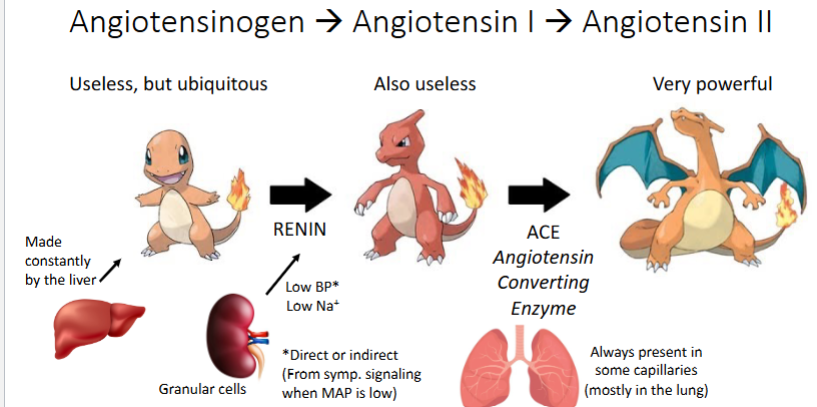
True or False? Renin is a hormone made by the kidneys.
False, Renin is an ENZYME not a HORMONE
What are the effects of Angiotensin II?
Angiotensin II has many effects
Tropic hormone → stimulates aldosterone release from adrenal cortex
Direct effects:
• Vasoconstriction (most vessels)
• Signals to hypothalamus to promote ADH secretion and thirst

Explain the integrated homeostatic feedback loop of Low Blood Pressure.
see pic
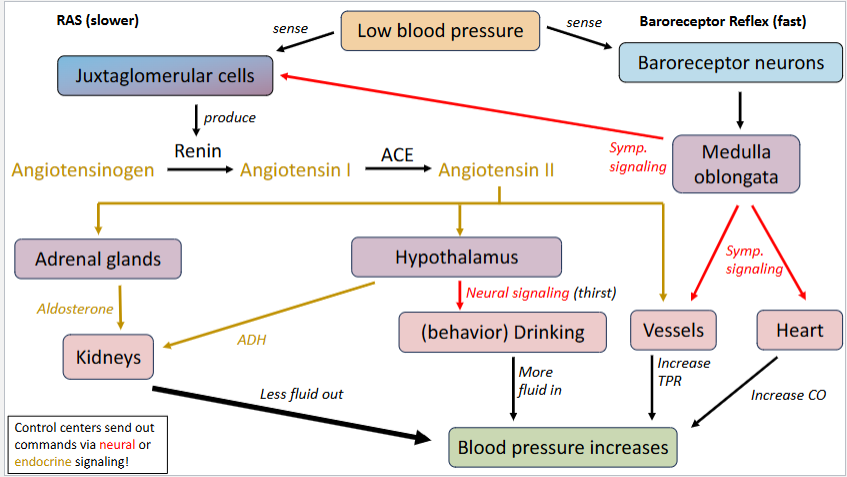
Which of the following would NOT be an effective drug used to treat high blood pressure?
A. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor
B. Renin antagonist
C. Renin receptor agonist
D. A diuretic
E. Angiotensin receptor blockers
C. Renin receptor agonist
Renin is an ENZYME! It doesn’t have a receptor!!!
What are two ways the baroreceptor reflex increases blood pressure?
Signaling to the medulla oblongata
sympathetic signaling to
heart: increased CO
vessels: increased TPR
Stimulates juxtaglomerular cells
stimulates RAS pathway response
What are three ways that RAS activation increases blood pressure?
Makes Angiotensin II which:
Increases Aldosterone production in adrenal glands
less fluid excreted
Increases ADH production from hypothalamus signaling (to kidneys)
less fluid out
increases thirst response through hypothalamus signaling
increased fluid intake
The fluid inside a cell is considered ____ (aka the cytosol). The fluid outside
of cells is considered _____. This fluid can be found in the spaces between
cells or in the in specialized body fluids like the plasma
intracellular fluid
extracellular fluid
Although the different fluid compartments of the body are generally stable in volume, water and solutes can be exchanged between the compartments by:
filtration, reabsorption, diffusion, and osmosis
Another name for dissolve inorganic ions dissolved is:
electrolytes
The main way our bodies gain water is through _____, whereas the main way we lose water is through _____
ingestion
excretion (kidneys)
Why is salt excretion so closely tied to water balance?
”water follows salt” so salt retention or secretion can cause more or less water to be secreted too
Draw where aquaporins are found before and after ADH. What does ADH do to change their location?
Before → in the membranes of vesicles. ADH causes those vesicles to fuse to the plasma membrane, such that the aquaporins are now embedded in the cell membrane.
What effect does ADH alone have on the volume and concentration of blood and of urine?
Blood → greater volume of more dilute blood. (blood volume maintained)
Urine → smaller volume of more concentrated urine
Why can drinking alcoholic beverages cause dehydration, even though the act of drinking a beverage increases the volume of fluid in the body?
Mass balance. More fluids in, but...dehydration can still occur if the amount of fluid lost exceeds the amount of fluid gained.
Alcohol can promote fluid loss by inhibiting ADH release
When blood volume is low, sodium is retained thanks to the effects of ____ which in turn promotes obligatory water reabsorption to avoid additional loss of blood volume
aldosterone
When blood volume is high, sodium is excreted at higher levels thanks to the effects of _____ which has the opposite effect (more sodium and water excretion).
atrial natriuric peptide
How can a change in solute concentrations lead to a shift in the relative fluid volume in different body compartments?
If solute concentrations change intra/extracellular fluid may no longer be isotonic, causing osmosis of water from one compartment to another
How can drinking a LOT of water in a short period of time lead to coma or even death?
Water intoxication: Osmosis of water from the hypotonic interstitial fluid into the neurons can cause them to swell considerably