Lesson 4.4. Anti-Seizures
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Epilepsy
a disorder where there are recurrent seizures unprovoked by identifiable causes
Seizure
symptom for disturbed electrical activity in the brain
Absence (petit mal)
3 Generalized seizures:
brief loss of awareness (blank stare)
postseizure amnesia but with no loss of motor activity
Myoclonic seizures
3 Generalized seizures:
no loss of consciousness and involves short seizure duration
Tonic-Clonic (grand mal)
3 Generalized seizures:
bilateral muscular jerking
loss of consciousness
tonic-clonic spasms
Simple
Partial seizures:
affects an entire hemisphere or a lobe within a hemisphere of the brain.
Complex
Partial seizures:
temporal/psychomotor seizures
mistaken for psychotic behavior
ion channel or receptor function
Mechanism of Action:
Anti-seizure drugs alter __________________________ to promote synaptic inhibition or modulate synaptic excitation.
Ureides
OLD AGENTS:
class of drugs and their derivatives with a similar pharmacophore
hydantoins, barbiturates, oxazolidinediones, succinimides
Ureides includes:
Ureide Pharmacophore
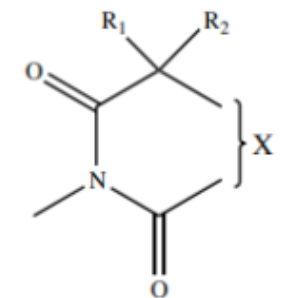
Barbiturate
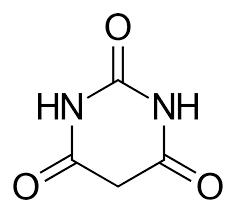
Hydantoin
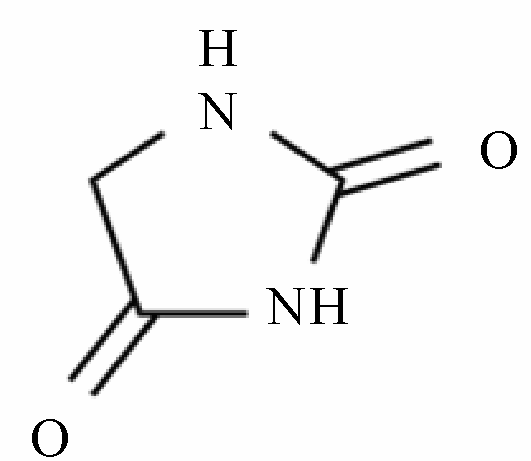
oxazolidinedione
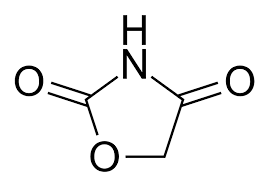
Succinimide
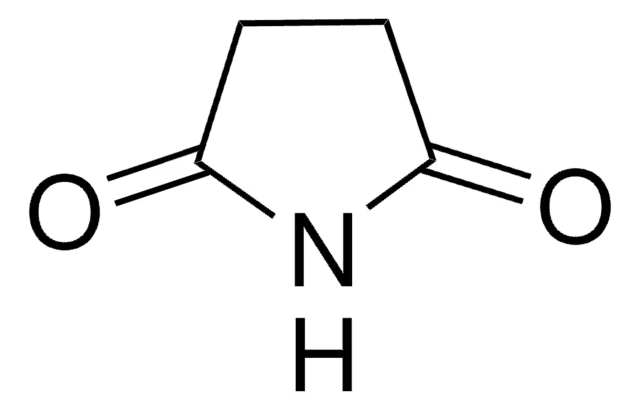
Phenytoin and Fosphenytoin
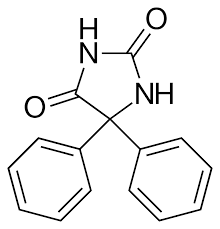
Drugs under Hydantoins
bulky C5
Structure Activity Relationship of Hydantoins:
________________ is optimal for activity (at least 1)
Phenytoin has a ________________ giving it maximal activity.
1 = ?
5,5-diphenyl
Structure Activity Relationship of Hydantoins:
________________ is optimal for activity (at least 1)
Phenytoin has a ________________ giving it maximal activity.
2 = ?
disodium phosphate
Structure Activity Relationship of Hydantoins:
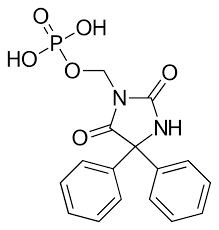
Fosphenytoin is a ____________________ ester of phenytoin
____________ soluble
better stability for _______________
1 = ?
water
Structure Activity Relationship of Hydantoins:
Fosphenytoin is a ____________________ ester of phenytoin
____________ soluble
better stability for _______________
2 = ?
parenteral administration
Structure Activity Relationship of Hydantoins:
Fosphenytoin is a ____________________ ester of phenytoin
____________ soluble
better stability for _______________
3 = ?
generalized seizures, partial seizures, status epilepticus
use of Hydantoins
CYP 2C9
Metabolism of Hydantoins:
____________________ catalyzed aromatic hydroxylation
____________________
______________
1 = ?
glucuronidation
Metabolism of Hydantoins:
____________________ catalyzed aromatic hydroxylation
____________________
______________
2 = ?
sulfation
Metabolism of Hydantoins:
____________________ catalyzed aromatic hydroxylation
____________________
______________
3 = ?
Phenytoin
can induce CYP 3A4 levels increasing the risk of drug-drug interaction
Phenytoin Structure
Fosphenytoin Structure
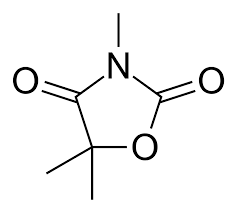
Trimethadione
drugs under oxazolidinedione
Oxazolidinedione
Oxygen replaces the first nitrogen in Hydantoins
no bulky C5
Structure Activity Relationship of Oxazolidinedione:
has ____________ groups
eliminates activity for grand mal, but increases activity for _____________________
_______________________ limits therapeutic applications
1 = ?
petit mal (absence seizure)
Structure Activity Relationship of Oxazolidinedione:
has ____________ groups
eliminates activity for grand mal, but increases activity for _____________________
_______________________ limits therapeutic applications
2 = ?
high toxicity
Structure Activity Relationship of Oxazolidinedione:
has ____________ groups
eliminates activity for grand mal, but increases activity for _____________________
_______________________ limits therapeutic applications
3 = ?
Trimethadione Structure
Ethosuximide
Succinimide Drugs
absence seizure (petit mal)
Succinimide is a drug of choice for _______________________
no C3 bulky
Structure Activity Relationship for Succinimide:
has ________________ group
replaced the -O- (in oxazolidinedione) with ________
______ with retained activity
1 = ?
-CH2
Structure Activity Relationship for Succinimide:
has ________________ group
replaced the -O- (in oxazolidinedione) with ________
______ with retained activity
2 = ?
safer
Structure Activity Relationship for Succinimide:
has ________________ group
replaced the -O- (in oxazolidinedione) with ________
______ with retained activity
3 = ?
~20%
Metabolism of Succinimide:
__________ excreted unchanged
CYP ____________
1 = ?
3A4 and 2E1
Metabolism of Succinimide:
__________ excreted unchanged
CYP ____________
2 = ?
Structure of Succinimide
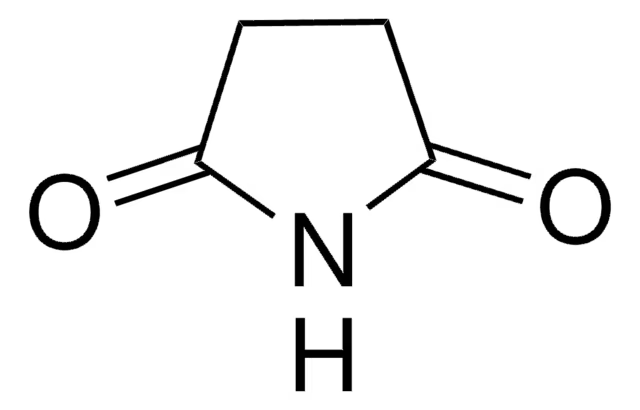
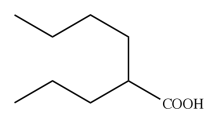
Valproic acid
2-propylpentanoic acid and is used for both grand and petit mal
hepatotoxicity and teratogenicity
2 rare side effects that limits the use of Valproic acid
promotes GABA transmission
Mechanism of Action of Valproic Acid:
________________________ by inhibiting GABA metabolism
________________________________, decreasing excessive neuronal firing
1 = ?
blocks Voltage Gated Sodium Channel
Mechanism of Action of Valproic Acid:
________________________ by inhibiting GABA metabolism
________________________________, decreasing excessive neuronal firing
2 = ?
Valproic Acid Structure
Carbamazepine
drugs under Iminostilbene
tricyclic antidep (TCAs)
Carbamazepine are derivatives of:
Carbamazepine Structure
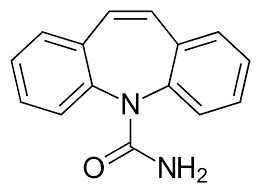
Carbamazepine
prototype iminostilbene used for grand mal and partial seizures
2 phenyl groups
Structure Activity Relationship of Carbamazepine:
________________ are essential for activity
______________________ can be substituted at C10 = less potent but active
1 = ?
keto, hydroxy, or acetate ester
Structure Activity Relationship of Carbamazepine:
________________ are essential for activity
______________________ can be substituted at C10 = less potent but active
2 = ?
blocks Voltage Gated Sodium Channels
Mechanism of Action of Carbamazepine:
_____________________ resulting to inactivation of excessive neuronal firing
Gabapentin and Pregablin
Drugs under GABA Analogs
Structure of Gabapentin
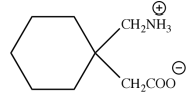
Structure of Pregablin
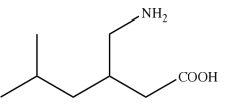
modulates Ca+2 influx by regulating VGCC
Mechanism of Action of GABA Analogs:
________________________________ resulting activation of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) resulting to glutaminergic neurotransmission inhibition.
minimal
Metabolism of GABA Analogs:
Structure of Phenyltriazine
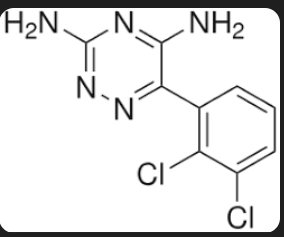
Lamotrigine
drugs under Phenyltriazine
Phenyltriazine
useful for both grand mal, petit mal, and partial seizures for adults
blocks both VGSC and VGCC
Mechanism of Action of Phenyltriazine:
___________________________, stabilizing presynaptic neuronal membranes, inhibiting glutamate release producing no excitatory response.
Glucuronidation
Metabolism of Phenyltriazine
Felbamate
drugs under Dicarbamate
Dicarbamate Structure
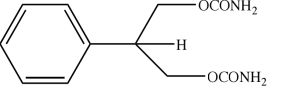
Dicarbamate
very potent and widely used agent but has very toxic severe side effects: aplastic anemia and hepatic failures
interacts with NMDA
Mechanism of Action of Dicarbamate:
________________________ decreasing glutamate transmission resulting to decreased neuronal excitation
ester hydrolysis and oxidation
Metabolism of Dicarbamate