Biochemistry Class 2.3 - Electron Transport Chain
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Where does electron transport occur?
Across the inner mitochondrial membrane
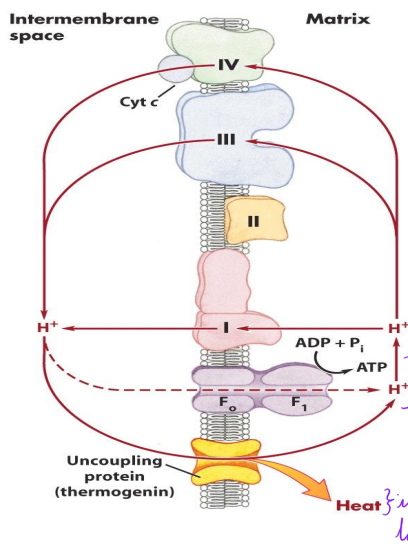
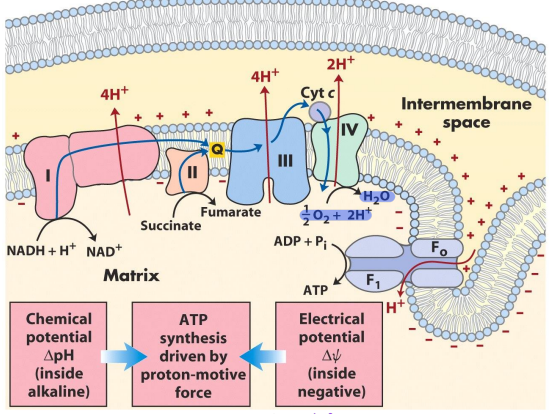
What is the chemiosmotic model?
Electrons in the matrix → pass through complex I (NAD+ created) → electrons to Q (4H+ pumped to the intermembrane space) → electrons passed to complex III (4 H+ pumped to the intermembrane space) → electrons to cytochrome C and complex IV (2 H+ pumped to intermembrane space) → electrons accepted by oxygen → proton gradient used to fuel ATP synthase
Why are metals important to the ETC?
They have two oxidation states, and can transition between them
How is Fe3+ used in complex I?
Fe3+ in complex I accepts electron → reduces into Fe2+ → passes to Q → Q is reduces, and Fe2+ is oxidized back into Fe3+
Reduction of iron coupled to oxidation of NADH (NADH → NAD+)
How do electrons flow through the ETC when they come from NADH or FADH2?
NADH → complex I → Q → complex III → complex IV
FADH2 → complex 2 → Q → complex III → complex IV
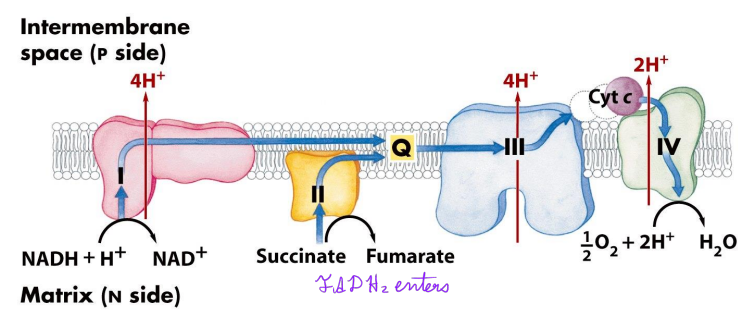
How many protons are pumped through the ETC using NADH?
10 per NADH
(3 NADH per CAC, 2 CAC per glycolysis)
How many protons are pumped through the ETC using FADH2?
6 per FADH2
1 FADH2 per CAC, 2 CAC per glycolysis
Why do the electrons flow?
Reduction potentials
What is the equation for reduction potentials and delta G^’0?
Delta G^’0 = -nF deltaE
n = number of electrons
F = 96.5 kJ/mol
Delta E = change in potential
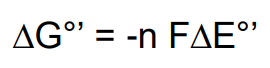
What does a positive reduction potential mean?
The more positive the reduction potential, the more it wants to be reduced
How much energy is in the proton gradient?
200 kJ/mol from NADH, 120 kJ/mol from FADH2
10 kJ/mol per H+
How is cytosolic NADH processed in the liver?
Oxaloacetate converted to malate by malate dehydrogenase in the intermembrane space (NADH → NAD+) → malate transported into the matrix → malate to oxaloacetate by malate dehydrogenase (NAD+ → NADH) → oxaloacetate to aspartate (concurrently glutamate → alpha KG) both by aspartate aminotransferase → aspartate transported into the intermembrane space → converted to oxaloacetate by aspartate aminotransferase (coupled to conversion of alpha KG to glutamate)
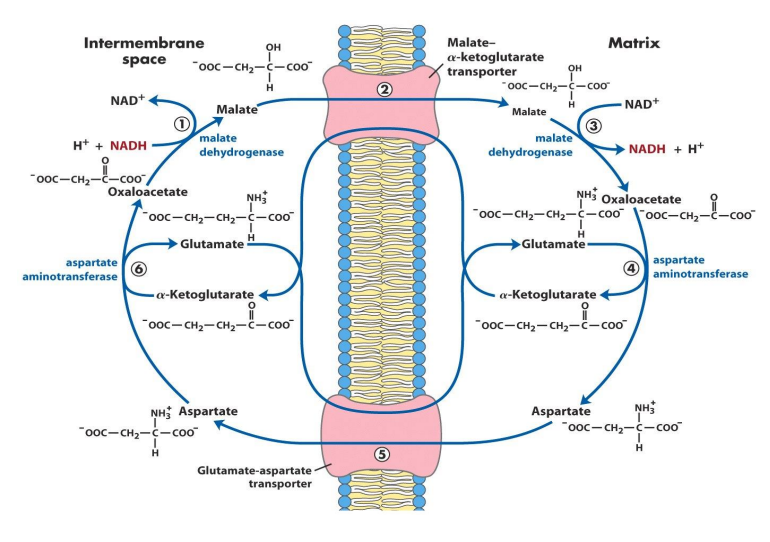
How is malate transported into the matrix?
Coupled to the transport of alpha KG into the intermembrane space
How is aspartate transported into the intermembrane space?
Coupled to the transport of glutamate into the matrix
How are carriers recycled in anaerobic conditions?
Pyruvate → lactate (NADH → NAD+) → NAD+ used for 1,3-BPG → 3-PG (makes NADH
Pyruvate → lactate is reversible
How is cytosolic NADH processed in muscles and brain?
DHAP → G-3-P (coupled to NADH → NAD+) by G-3-P dehydrogenase → G-3-P to DHAP (coupled to FAD → FADH2) → FADH2 → Q → complex III → 6 H+ pumped
What is the ATP yield of glycolysis? Where does it come from?
3 ATP from 2 cytosolic NADH in the muscle
5 ATP from 2 cytosolic NADH in the liver
2 ATP from glycolysis running
How many ATP from the oxidation of pyruvate? Where do they come from?
5 from 2 NADH in the mitochondrial matrix
How much ATP per CAC? Where do they come from?
15 ATP from 6 NADH in the mitochondrial matrix
3 ATP from 2 FADH2 in the matrix
2 ATP from CAC
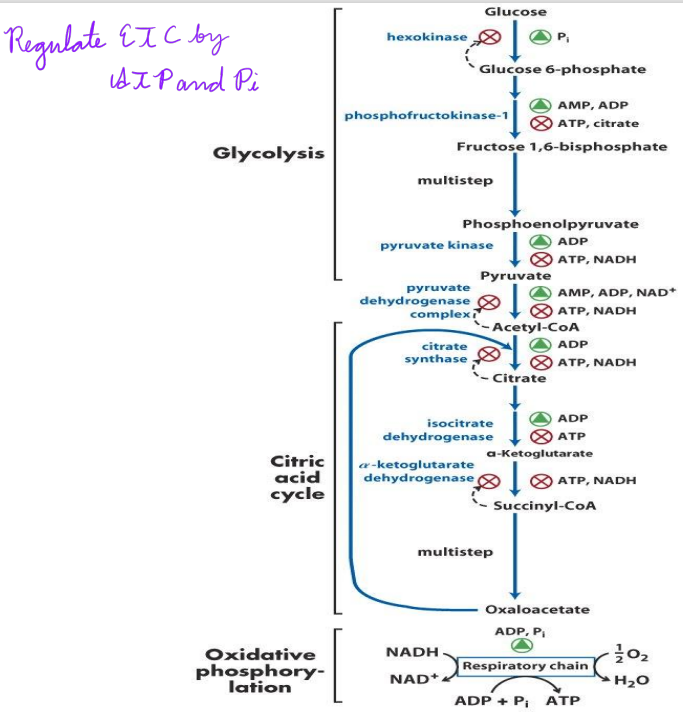
What regulates the ETC?
ATP stops it
Pi and ADP make it go
If there is no O2, you cannot do it
How does carbon monoxide affect the ETC?
Binds to iron in complex I → cannot pass electrons → no ETC
What is thermogenin? What does it do?
Forms a pore in the inner mitochondrial membrane in babies
Newborns lose lots of heat because of surface area to volume ratio → transporting H+ through thermoglobin channel without making ATP makes hear → babies don’t die