Equilibrium constants
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
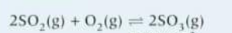
Construct and equation for Kc and work out the units
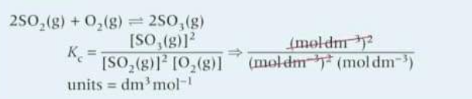
What is homogenous equilibria?
Species that all have the same state or phase

What are hetrogenous equilibria?
species that have different state or phases
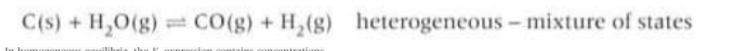
True or false in homogenous equilibria the Kc expression contains concentrations of all species
true
Why are any species that are solids or liquids omitted from the Kc expression in a heterogeneous equilibria?
Because their concentrations are essentially constant so they are automatically incorporated within the overall equilibrium constant

What are the only states that Kc includes?
(g) and (aq)
What is the mole fraction of a gas?
The same as its proportion by volume to the total volume of gases in a gas mixture
What is the formula for a mole fraction?

What does the sum of the mole fractions equal?
1
What is the partial pressure of a gas?
the contribution that the gas makes towards the total pressure
What does the sum of the partial pressures of each gas equal?
the total pressure
What is the formula for partial pressure?

What is Kp - how is it similar to Kc
similar to Kc but with partial pressures replacing concentration terms
What are suitable units for partial pressures?
kPa, Pa, atm
True or false when calculating partial pressure the same unit must be used for all gases
true
Why does Kp only inlcude gases what does this mean for other species in the equation?
Because only gases have partial pressure. Any other species must be ignored
If the forward reaction is exothermic, what happens to the equilibrium constant and yield when the temperature increases?
The equilibrium constant and the yield decrease
(because the equilibrium shifts to the left so the concentration/pressure of the reactants increase and the concentration/pressure of the products decrease so Kc/p decreases
If the forward reaction is endothermic, what happens to the equilibrium constant and yield when the temperature increases?
The equilibrium constant increases and the equilibrium yield of products increases
True or false the value of the equilibrium constant changes with temperature
true
Why does the value of the equilibrium constant change with temperature? (use temp increasing as example) use Kp
If temp increases the system is no longer in equilibrium as the new equation for Kp is greater than the original Kp value. So the equilibrium partial pressures that gave the original Kp value must change to give a new value at a different temperature. The partial pressure of the reactants would increase and the partial pressure of the products would decrease so the position of equilibrium would shift to the left and a new equilibrium will be reached with a different Kp value
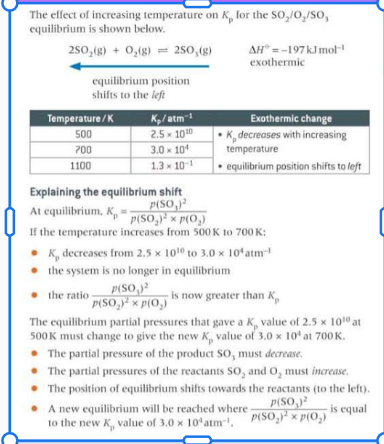
True or false the equilibrium constant is unaffected by changed in concentration or pressure
true
What does the equilibrium shift in le chatlier’s principle come from?
the fact that the equilibrium constant doesn’t shift

What happens to Kc when the concentration is increased - what happens when (picture) happens


What happens when this happens?
Using le chatlier’s principle, you predict a shift in the equilibrium position from right to left to the side with fewer gaseous moles. This shift has been directed by the value of Kp being restored.

If there are fewer moles of gaseous product and the ratio is smaller than the equilibrium constant what is the effect on the products and reactants and equilibrium?
products increase and reactants decrease
shift to the right
If there are more moles of gaseous products and the ratio is larger than the equilibrium constant what is the effect of increasing the pressure products, reactants and equilibrium?
products decrease and reactants increase
equilibrium shifts to the left
If there are the same number of moles of gaseous reactants and products and the ratio = K what is the effect of increasing the pressure on the products, reactants and equilibrium?
no change
no effect
How do catalysts affect the equilibrium constant?
Equilibrium constants are unaffected by catalysts
Why are equilibrium constants unaffected by catalysts?
Because they affect the rate of the chemical reaction but not the position of equilibrium.
What affects do catalysts have on the equilibrium (hint I am not asking about the position of equilibrium I am asking about equilibrium in general)
They speed up both the forward and reverse reactions in the equilibrium by the factor. The equilibrium is reached quicker but the equilibrium position is not changed.