Unit D2: The Circulatory System T1-2
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Circulatory System
the organs and tissues involved in circulating blood and lymph through the body
Functions of the circulatory system
Oxygen/Nutrients transport, pH/Temperature regulation, Defensive Mechanisms, Clotting and Healing
regulation of circulatory system
fluid balance, stabilizes pH, and temperature control
immune system
a complex response system that protects the body from bacteria, viruses, and other foreign substances
blood clotting
the process by which blood becomes thick and stops flowing, forming a solid cover over any place where your skin has been cut or broken.
platelets
thrombocytes, small blood fragment that collects at sites of injury to begin the clotting process
Heart
A hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
Cardiovascular system
The heart and blood vessels, responsible for carrying oxygen and nutrients to the body through blood
blood
Connective tissue made of plasma, erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets.
white blood cells
leukocytes, function in the immune system; fights disease
red blood cells
erythrocytes, blood cells that carry oxygen from the lungs to the body cells.
closed circulatory system
A circulatory system in which the oxygen-carrying blood cells never leave the blood vessels. Mostly vertebrates, some invertebrates
open circulatory system
A circulatory system that allows the blood to flow out of the blood vessels and into various body cavities
artery
A blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart
vein
A blood vessel that carries blood back to the heart.
Capillaries
fine branching blood vessels that form a network between the arterioles and venules.
Arterioles
small vessels that receive blood from the arteries
Venules
small vessels that gather blood from the capillaries into the veins
Blood vessels
tubelike structures that carry blood throughout the body
vena cava
a large vein carrying deoxygenated blood into the heart
superior vena cava
receives blood from the head and arms and chest and empties into the right atrium of the heart
inferior vena cava
carries blood from lower regions of the body to right atrium of the heart
pulmonary vein
Deliver oxygen rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium
pulmonary artery
Carries deoxygentated blood from the heart to the lungs
descending aorta
carries blood away from the heart down the midline of the body
Aorta
The large arterial trunk that carries blood from the heart to be distributed by branch arteries through the body.
Common carotid artery
Supplies blood to the head and neck.
Pericardium
Fluid-filled double-layered membrane surrounding the heart, preventing friction
cardiomyocytes
Specialized contractile heart muscle cells
the heart wall
3 layers: epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
chambers of the heart
right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle
myocardium
muscular, middle layer of the heart
right atrium
Receives deoxygenated blood from the body
right ventricle
pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs
left atrium
receives oxygenated blood from the lungs
left ventricle
pumps oxygenated blood to the body
striated
marked with thin, narrow grooves or channels
Ventricular septum
Divides the right and left chambers of the heart
pulmonary circulation
The path of blood from the right atrium through the right ventricle to the lungs and return to the left atrium
systemic circulation
circulation that supplies blood to all the body except to the lungs
Tricuspid valves
The atrioventricular valves between the right atrium and right ventricle.
right semilunar valve
Pulmonary valve, between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk
bicuspid/mitral valve
valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle
aortic arch
a curved blood vessel from which arteries branch to the head and neck.
left semilunar valve
between left ventricle and aorta, aortic valve
Valves
permit the flow of blood in one direction only
Atrioventricular valves
Valves between atria and ventricles, prevent backflow.
Semilunar valves
-Pulmonary and aortic valves
-Prevent backflow of blood into ventricles
thrombocytes
another name for platelets
Leukocytes
another name for white blood cells
Erythrocytes
another name for red blood cells
mitral valve
valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle; bicuspid valve
chordae tendineae
thin bands of fibrous tissue that attach to the valves in the heart and prevent them from inverting
systole
contraction phase of the heartbeat
Diastole
relaxation phase of the heartbeat, fills with blood
lub
closing of AV valves; at the beginning of ventricular systole
dub
caused by the closure of aortic and pulmonic valves, at the end of ventricular systole
ascending aorta
Branches off the left ventricle; carries oxygen rich blood to parts of the body above the heart
coronary arteries
blood vessels that branch from the aorta and carry oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle
Venous return
blood returned to the heart by the veins
Myogenic
Describes muscle tissue that generates its own contractions.
sinoatrial node
"Pacemaker" in the right atrium, and that originates the electrical impulses through the atria, making them contract
atrioventricular node
Receives impulses from SA node, relays to purkinge fibres, located around right atrioventricular region
Purkinje fibers
fibers in the ventricles that transmit impulses to the right and left ventricles, causing them to contract from the bottom up
The cardiac cycle
A complete heartbeat consisting of contraction and relaxation of both atria and both ventricles
Stages of a cardiac cycle
atrial and ventricle diastole, atrial systole, ventricular systole
Atrial and Ventricular diastole
All chambers in diastole, decreased pressure allows blood to easily return from body and fill atria
Atrial systole
atrial contraction forces remaining additional blood into ventricles
ventricular systole
contraction of ventricles pushing blood into pulmonary arteries and aorta
medulla oblongata
Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, blood pressure, and digestion.
Bundle of his
neurological fibers extending from the AV node that fire the impulse from the AV node to the Purkinje fibers
sympathetic nervous system
a set of nerves that prepares the body for action in challenging or threatening situations, increases heart rate
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy, slows heart rate
beats per minute
What heart rate is measured in
Apex
lower tip of the heart
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
recording of the electrical changes that occur in the myocardium during a cardiac cycle
arrhythmia
irregular heart rhythm
Myocardial infarction
a condition in which blood flow to part of the heart muscle is blocked, causing heart cells to die
bradycardia
abnormally slow heartbeat
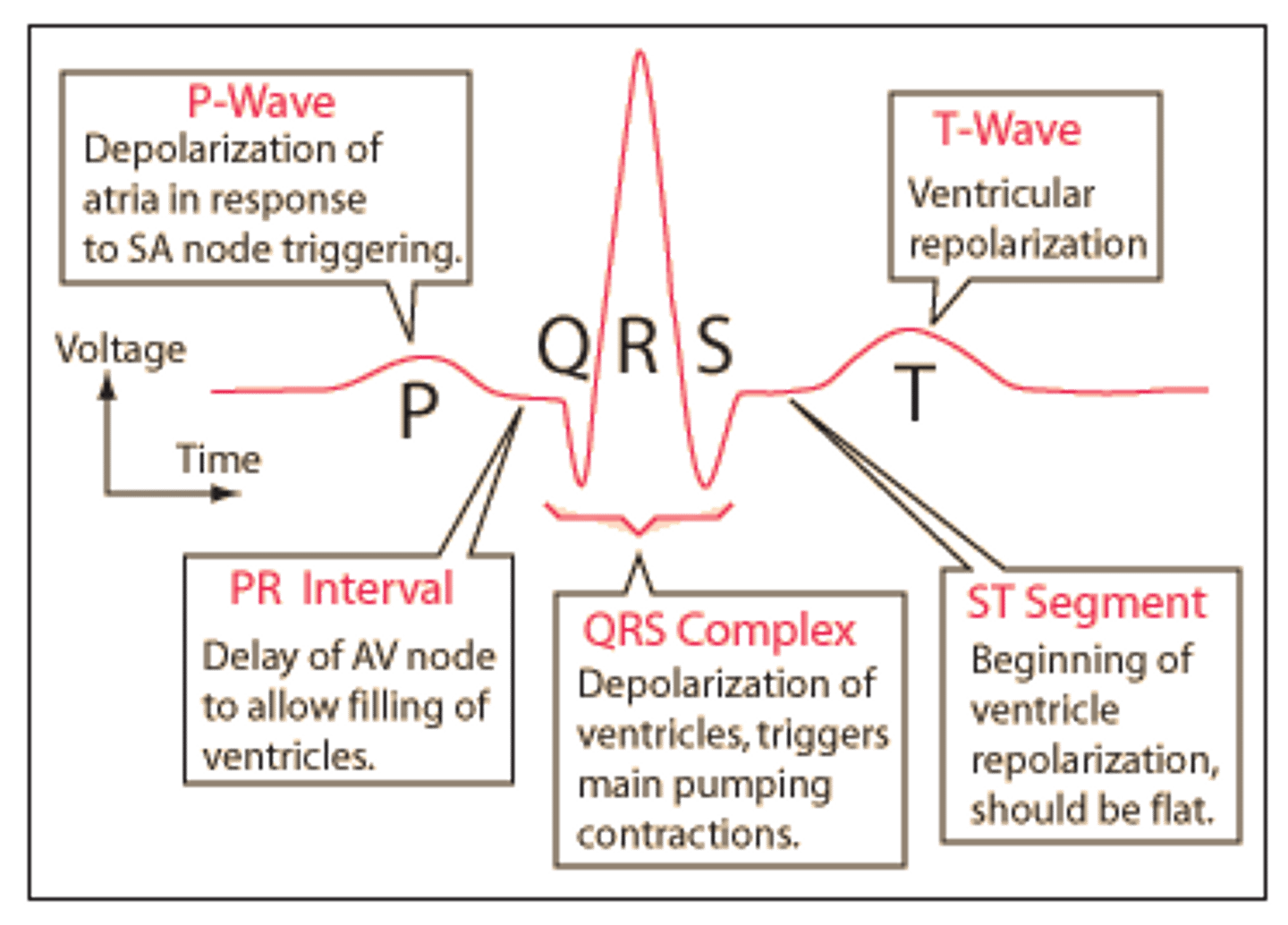
P wave
depolarization of the atria
depolarization
Contraction of the heart
repolarization
Relaxation of the heart
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization
T wave
repolarization of ventricles
PR Interval
Time for impulse to travel from SA node to the ventricles
ST segment
time between ventricular depolarization and repolarization
heart murmur
an abnormal sound from the heart produced by defects in the chambers or valves
heart block
interference with normal conduction of electrical impulses that control activity of the heart muscle
pacemaker
A device that delivers electrical impulses to the heart to regulate the heartbeat
Tachycardia
Abnormally rapid heartbeat