GSCE Biology - Coordination
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
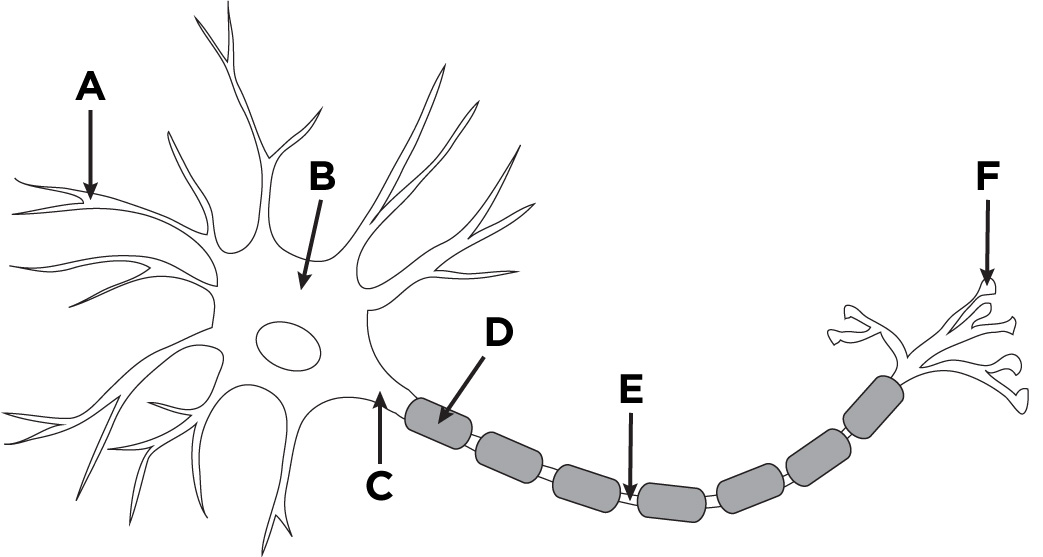
What is the name of A?
Dendronites
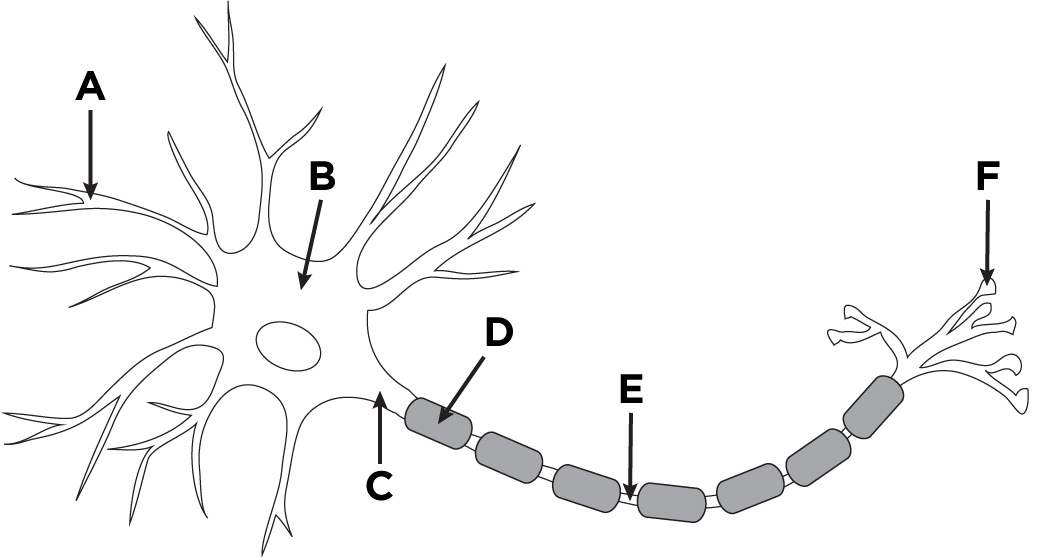
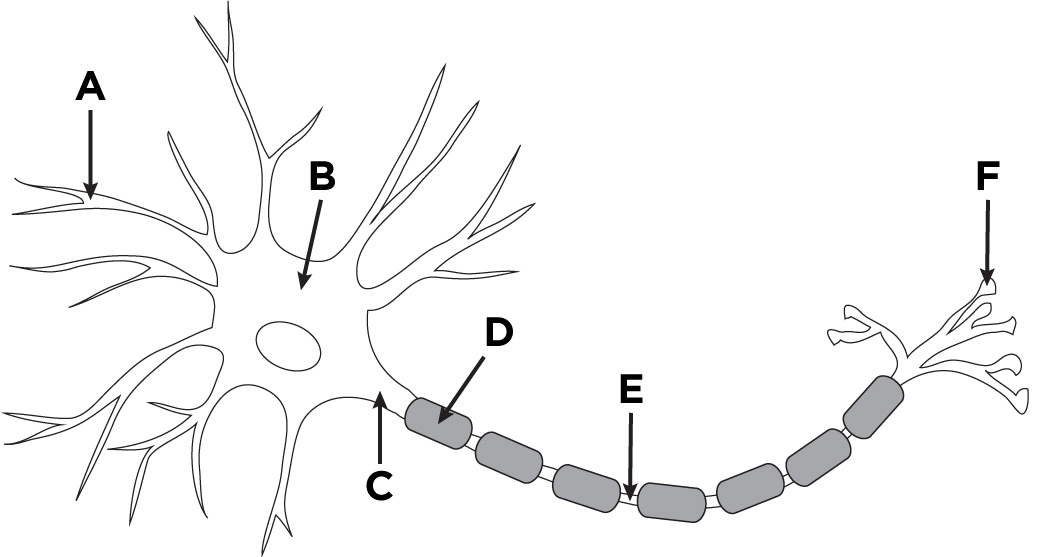
What is the name of B?
The cell body.
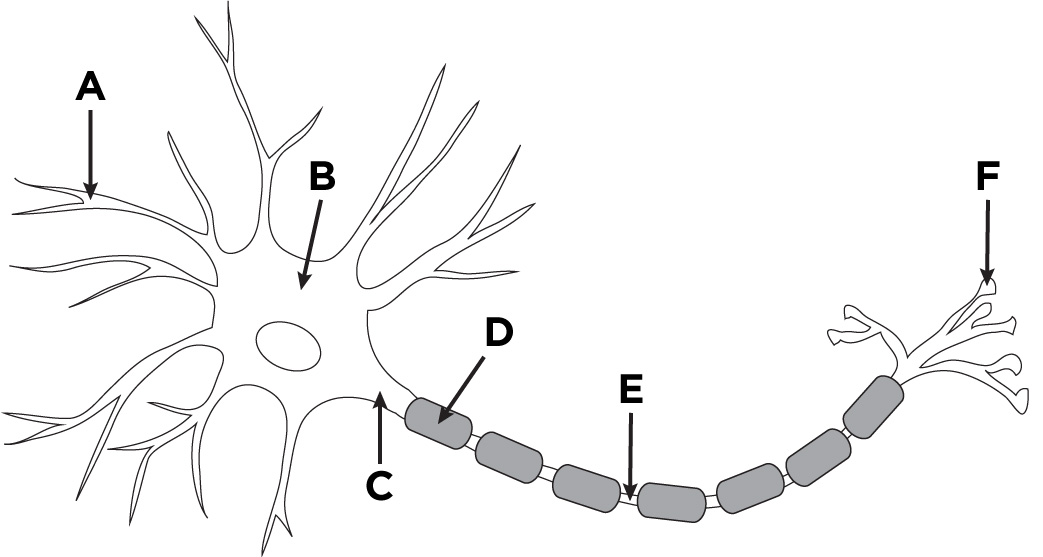
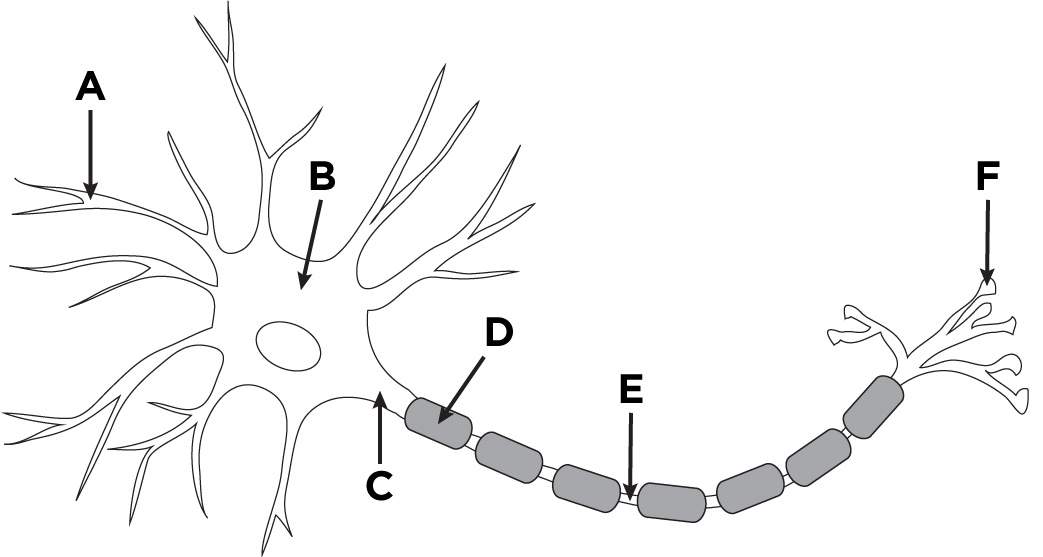
What is the name of D?
Myelin sheath
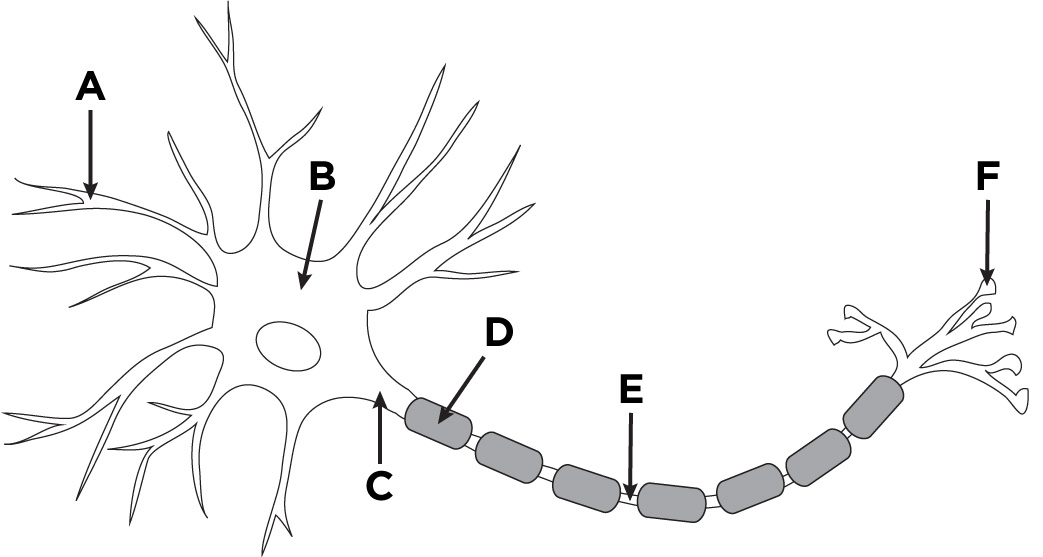
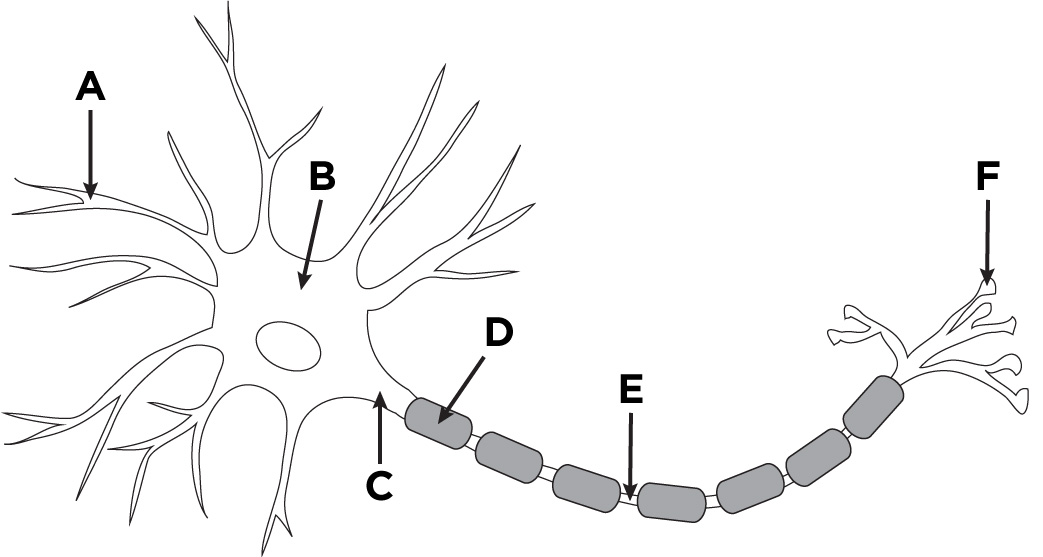
What is the name of E?
Axon
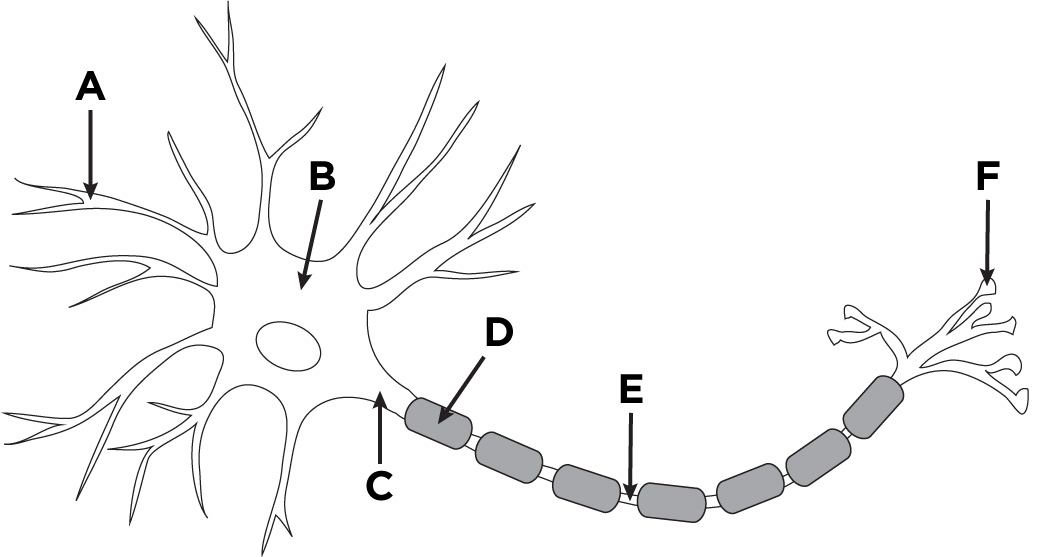
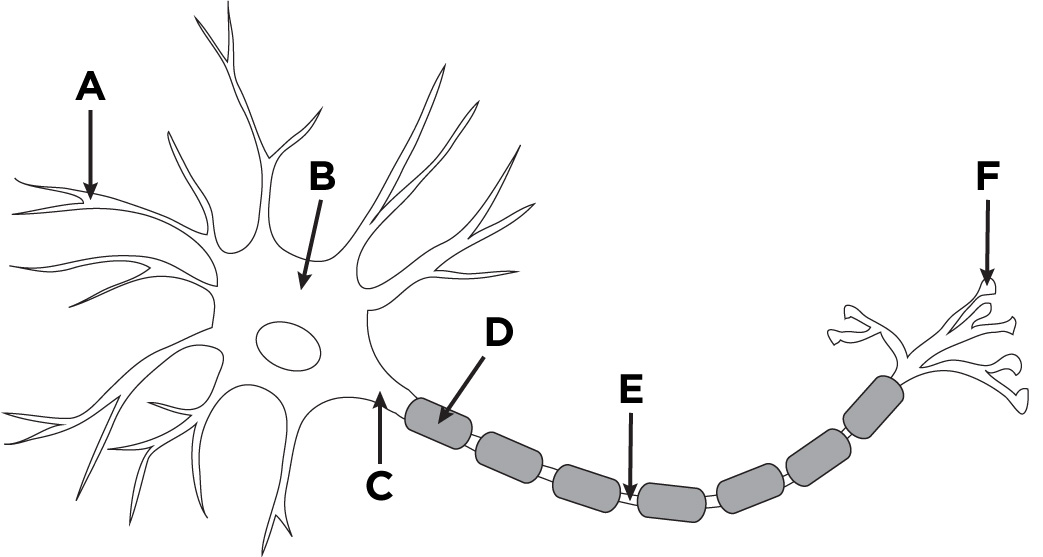
What is the name of F?
Axon terminals.
Myelin sheath
An insulating layer, or sheath, that forms around nerves, including those in the brain and spinal cord.
Cell body
The spherical part of the neurone that contains the nucleus
Axon
Where electrical impulses from the neurone travel to be received by other neurone.
Dendrite
The receiving or input portions of a neuron
Motor neurone
Cells in the brain and spinal cord that allow us to move, speak, swallow and breath by sending commands from the brain to the effectors (muscles) that carry out these functions.
Sensory neurone
A nerve cell that detects and transmits sensory information from the environment to the brain
Relay neurone
A cell in the CNS that acts as a messenger between sensory and motor neurones
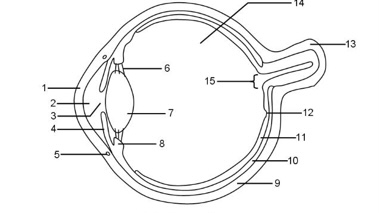
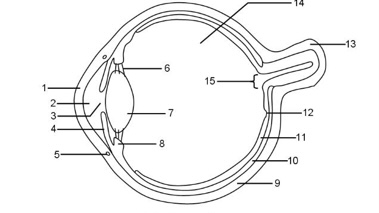
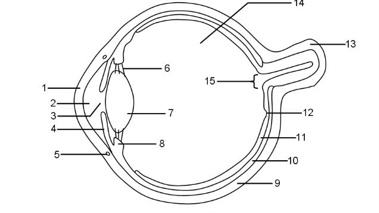
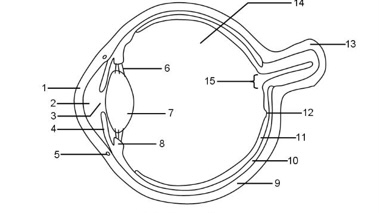
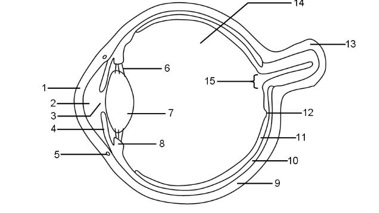
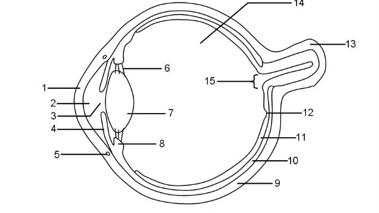
1
Cornea
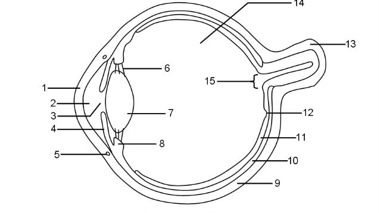
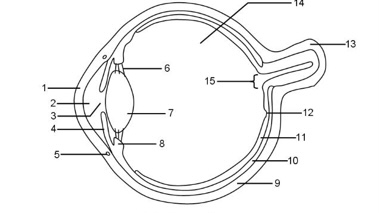
2
Aqueous humour
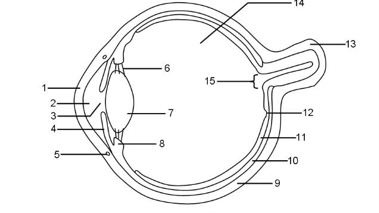
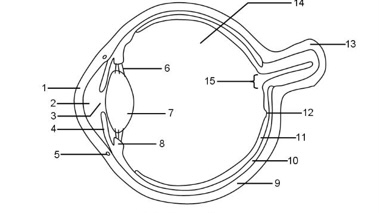
3
Pupil
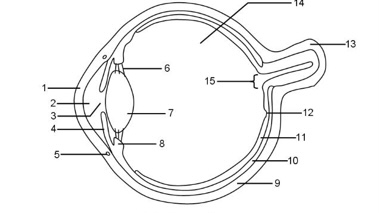
4
Iris
5
Tear duct
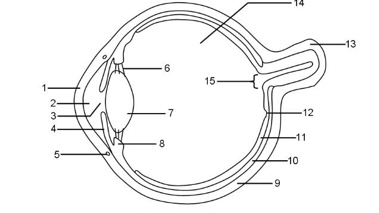
6
Suspensory ligaments
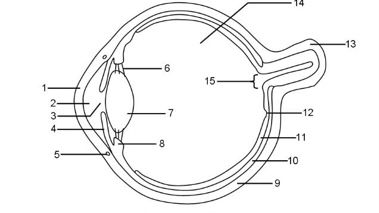
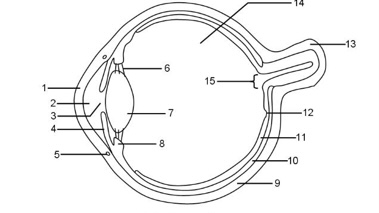
7
Lens
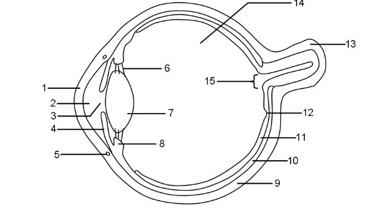
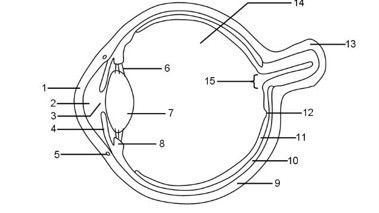
8
Ciliary muscle
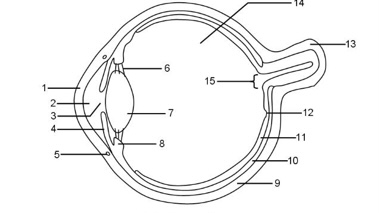
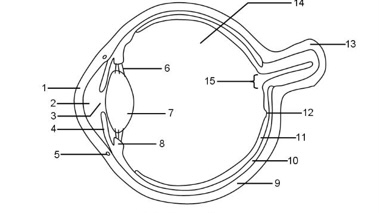
9
Sclera
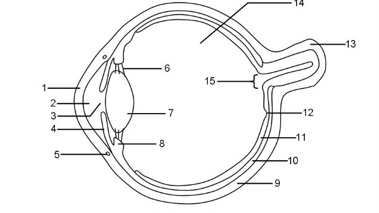
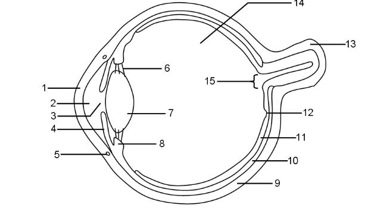
10
Choroid
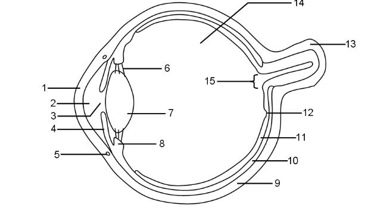
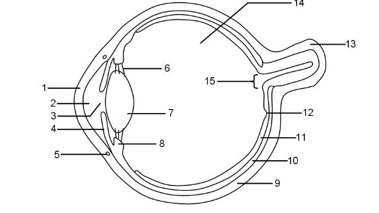
11
Retina
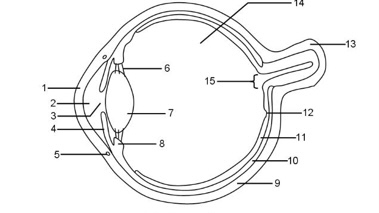
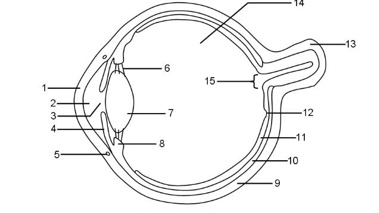
12
Fovea
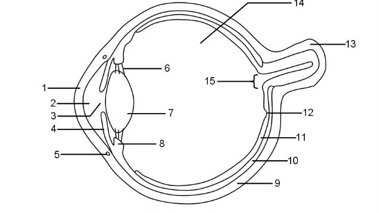
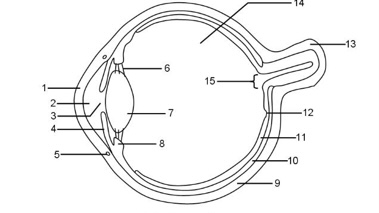
13
Optic nerve
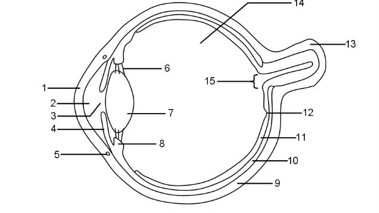
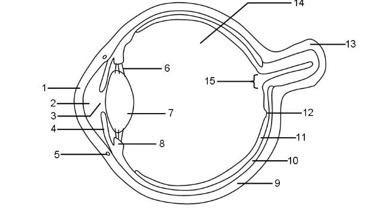
14
Vitreous humour
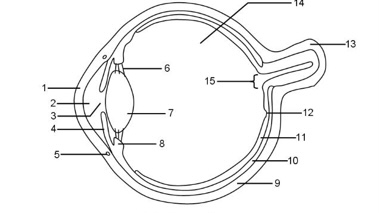
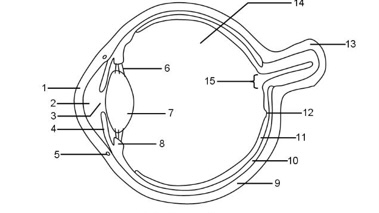
15
Blind spot
Cornea
It refracts light and protects the eye
Iris
Controls how much light enters the pupil
Lens
Focuses light onto the retina
Optic nerve
Bundle of sensory neurones that carry impulse to the brain
Retina
Layer of tissue at the back of the eye that contains light receptor cells (rods + cones)
Fovea
Area of the retina with the highest concentration of cone cells that provide sharp vision
Aqueous humour
Maintains pressure in the eye and nourishes the cornea
Vitreous humour
Maintains the shape of the lens in accommodation
Sclera
Tough outer layer that the muscle that moves the eyeballs attach to
Pupil
Hole in the center of the eye that lets light in
What happens to the eye in bright light?
circular muscle contracts
Radial muscles relax
Pupils constrict
What happens to the eye in dim light?
circular muscles relax
Radial muscles contract
Pupil dilate
What happens to the eye when it’s focusing on a distant object?
ciliary muscles relax
Suspensory ligaments pulled tight (stretched)
Lens flatten
What happens to the eye when its focusing on a nearby object?
ciliary muscles contract
Suspensory ligaments slacken
Lens more rounded (convex)
Homeostasis
The maintenance of a constant internal environment e.g. temperature
Nervous control system
nerve impulses
Travel fast
Short-lived effect
Localised effect
Hormonal control systems
hormone in blood
Travel more slowly
Long-lived effect
Widespread effect
What happens to the body when we are too hot?
Tiny blood vessels called capillary loops - blood flow through these loops, radiating heat to the outside, cooling the body
Reduce muscle activity
Vasodilation - arterioles dilate increasing blood flow to skins surface
Sweat glands - produce greater amounts of sweat - the energy supplied to evaporate sweat is from body heat
Hairs - relax flat on skins surface
What happens when we are too cold?
hair - stands up trapping a layer of air for insolation
Vasoconstrictions - arterioles contract = less blood flow - less heat lost
Shiver - muscle contract respirations generating heat
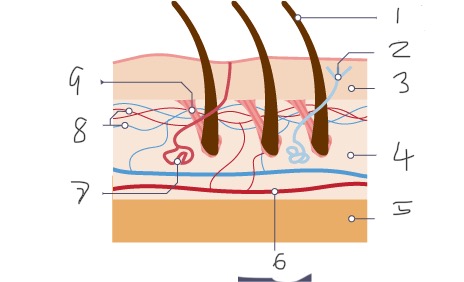
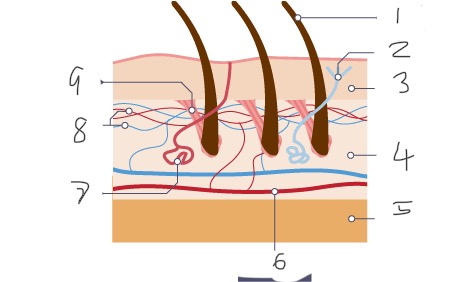
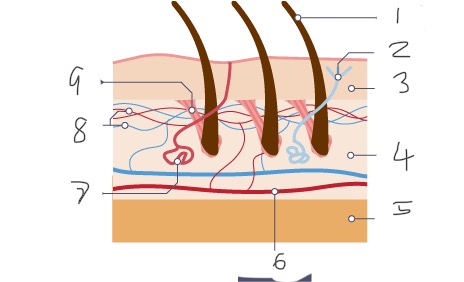
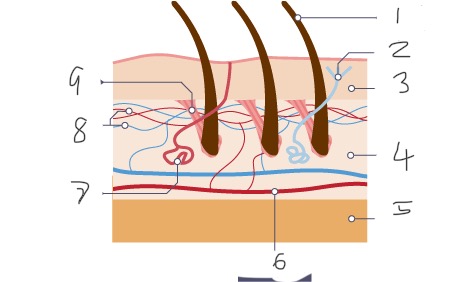
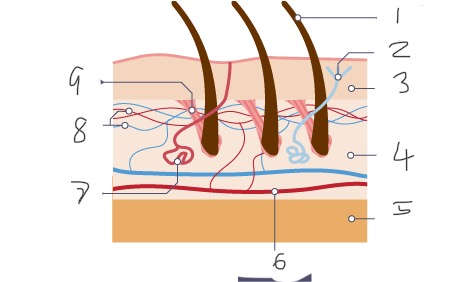
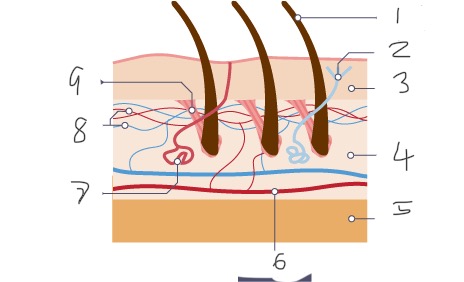
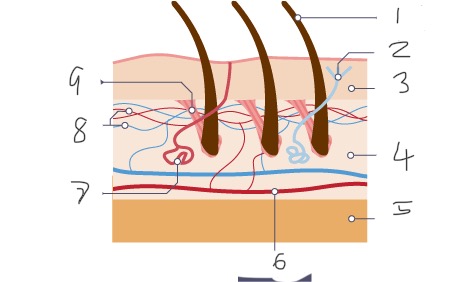
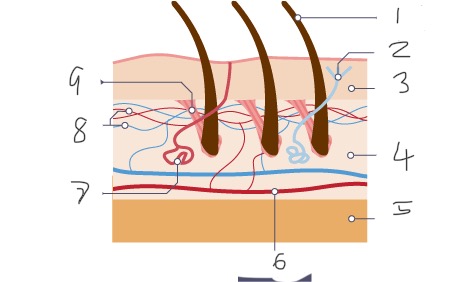
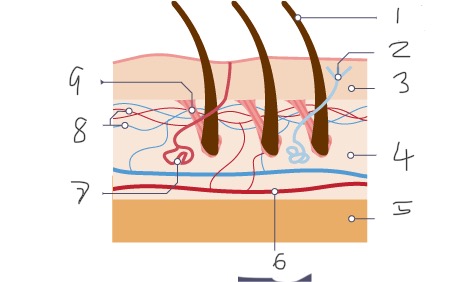
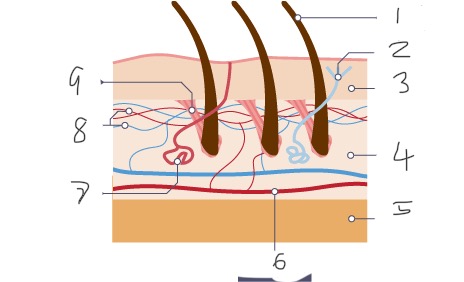
1
Hair
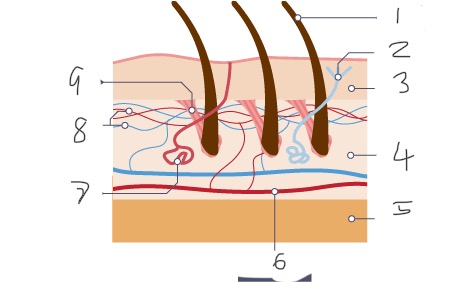
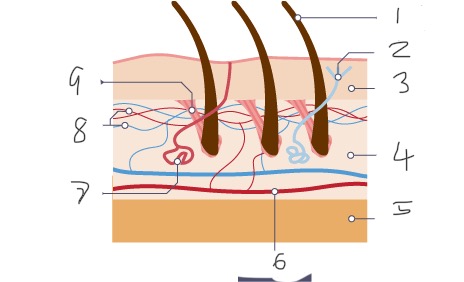
2
Nerve
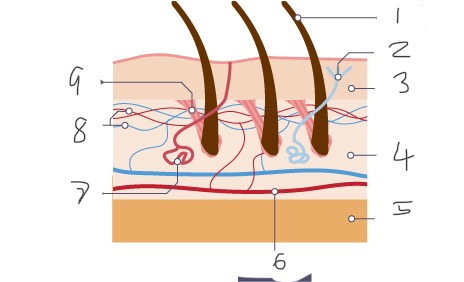
3
Epidermis
4
Dermis
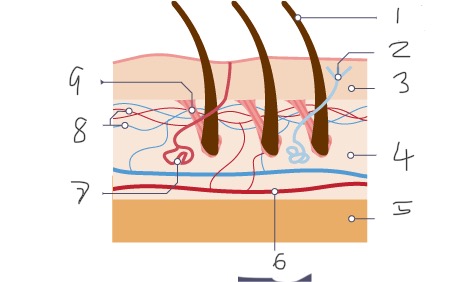
5
Fatty tissue
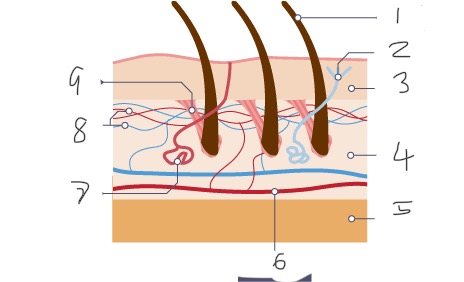
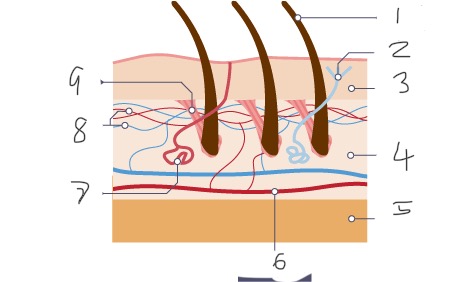
6
Arteriole
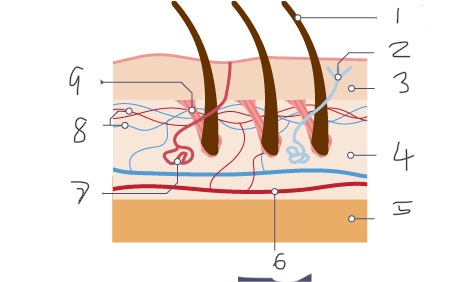
7
Sweat gland
8
Capillaries
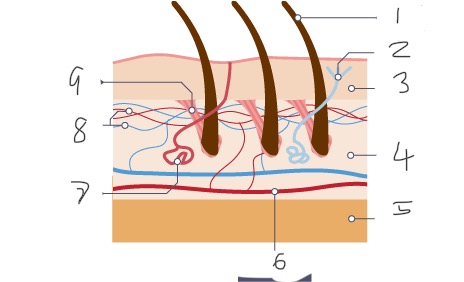
9
Muscle
Geotropism
the growth of an organism according to gravity
shoots will always grow upwards (negatively geotropic)
Roots will always grow downwards (positively geotropic)
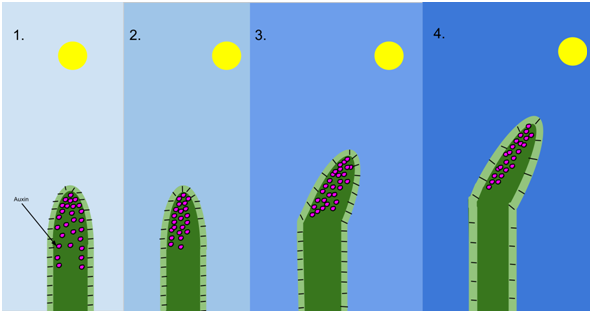
Phototropism
The growth of an organism according to light
shoots always grow towards light
They are positively phototropic
Roots are not sensitive to light