2-4. The inflammatory response: neutrophils and macrophages
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What are the most common pathways of infection?
inhalation, ingestion, open wounds
__________ cells can recognize invaders and generate signals to attract/ activate defensive cells to site of invasion
sentinel
what are the 3 main types of defensive cells?
dendritic cells, mast cells, macrophages
T/F: an inflammatory/ immune response can be due to cellular damage, a pathogen, or both
t
DAMPs
Damage-associated molecular patterns signaling tissue damage which is recognized as foreign
PAMPs
pathogen associated molecular patterns
uniques components of microorganisms ESSENTIAL FOR SURVIVAL
T/F: PAMPS are found on normal host tissue
FALSE
What transmembrane proteins mediate PAMP recognition? where are they found
toll like receptors
dendritic cells, macrophages, mast cells, + eosinophil and mucosal epithelial cells
What is the major regulator of inflammatory gene transcription that regulates expression of chemokines, cytokines, etc?
nuclear factor kappa B
What is the hallmark of acute inflammation?
VASODILATION
What is the primary effector cells when TLRs release cytokines to attract phagoytic cells?
neutrophil
Explain what causes the production of cytokines?
sentinel cells recognize pathogen via PAMP/ TLR -> activate NFkB -> proinflammatory genes -> produce cytokines
What cell is a source of all cytokines?
macrophages
which cytokines active endothelial cells?
TNFa and IL-1
Which cytokine stimulates liver to produce acute phase proteins? what does this cause?
IL-6- however both TNFa and IL-1 also
sickness behavior
What is the main intended action of cytokines?
attract leukocytes to site of infection to suppress the inflammatory response
what are the effects of cytokines on the hypothalamus?
loss of appetite
why is it important that one of the effects of cytokines on the liver is iron sequestration?
bacteria needs iron to grow, so depriving it of iron will kill it
The liver produces many acute phase proteins in response to proinflammatory cytokines.
Explain the role of: Seroid Amyloid A
leukocyte chemotaxis, induction of enzymes that degrade cellular matrix
The liver produces many acute phase proteins in response to proinflammatory cytokines.
Explain the role of: fibrinogen
hemostasis
The liver produces many acute phase proteins in response to proinflammatory cytokines.
Explain the role of: C reactive protein
assist in complement binding to antigenic or damaged cells
The liver produces many acute phase proteins in response to proinflammatory cytokines.
Explain the role of: Ceruloplasmin
oxidize iron, facilitate ferritin, inhibit microbe iron uptake
The liver produces many acute phase proteins in response to proinflammatory cytokines.
Explain the role of: AGP
role unclear
Acute phase proteins have different protein fractions in serum electrophoresis. Which fractions are features of inflammation? which is where antibodies are found?
alpha 1 and 2, beta
gamma
what are the 5 cardinal signs of inflammation
redness, heat, swelling, pain, loss of function
Inflammation centers on the vascular response of small blood vessels in the area of infection. what are the three main changes that occur?
arterioles dilate
capillaries become more permeable = transudate
leukocytes migrate through venule walls = exudate
T/F: transient vasoconstriction occurs before vasodilation
T, it has no role in inflammatory response but does activate platelets which is important in hemorrhage
What mediates the leukocyte adhesion cascade? what is the importance of this?
cytokines
ensure the appropriate WBC enter the correct vessel
Explain the process of the leukocyte adhesion cascade
1. cytokines are released from sentinel cell and act on vascular endothelium and leukocyte
2. Margination: which moves leukocyte toward endothelium
3. Rolling: in which glycoproteins bind to selectin ligands
3. Integrin activation by chemokines - transfers integrin to high affinity state
4. stable adhesion
5. migration through endothelium
what is the major blood leukocyte that kills most invading organisms?
neutrophil
what cells cleans up the mess left behind by neutrophils?
macrophages
T/F: neutrophils have surface receptors that must correctly be triggered to perform an action
true
what is the purpose of a neutrophil net?
directs neutrophil granules and contents toward inflammatory stimulus
what must rupture in order for the neutrophil net to be released?
nuclear envelope then plasma membrane
- need to be able to break down CT
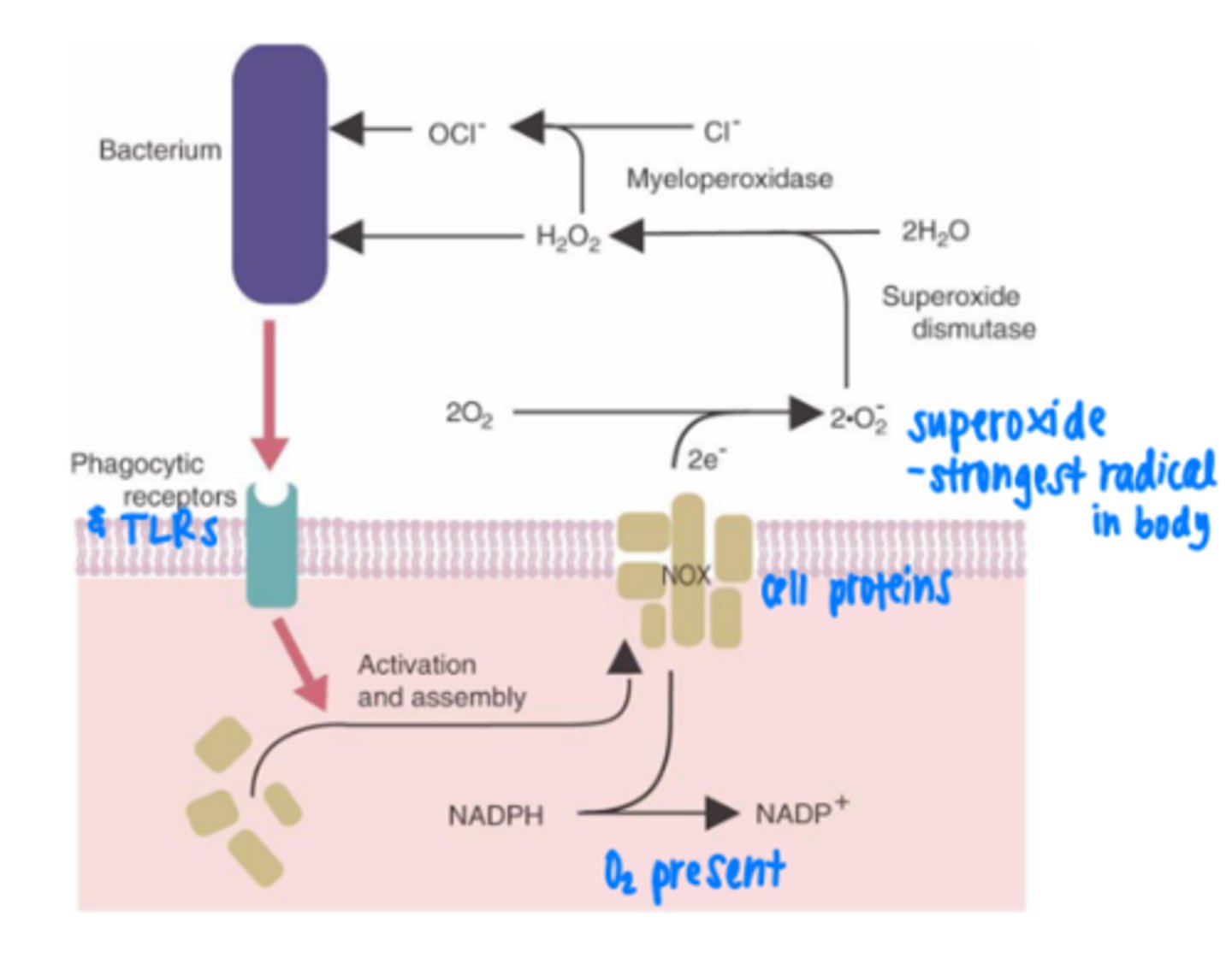
respiratory burst
process in which antimicrobial compounds/ radicals are produced that can neutralize or eliminate pathogens
What must be present for respiratory burst to occur in neutrophils?
oxygen
what are the key steps of respiratory burst?
1. NADPH oxidation -> superoxide production
2. superoxide -> hydrogen peroxide
3. hydrogen peroxide -> ROS, ClO-
4. neutralization of ROS
List 4 primary neutrophil granules and their function
defensins- bactericidal
myeloperoxidase - respiratory burst
neutral and acid hydrolases - degrade bacteria
lysozyme - destroy bacterial cell walls
list 3 secondary neutrophil granules and their functions
lactoferrin - binds iron
collagenase - degrades CT
lysozyme - destroys bacterial cell walls
Why is it notable that elastase and cathepsin G (neutrophil granules) activate TNF alpha?
to stimulate macrophages
what do macrophages arise from?
myeloid stem cell -> monocyte in blood -> macrophage in circulation
T/F: same as neutrophils the correct receptor must be triggered for macrophages to perform a specific action
true
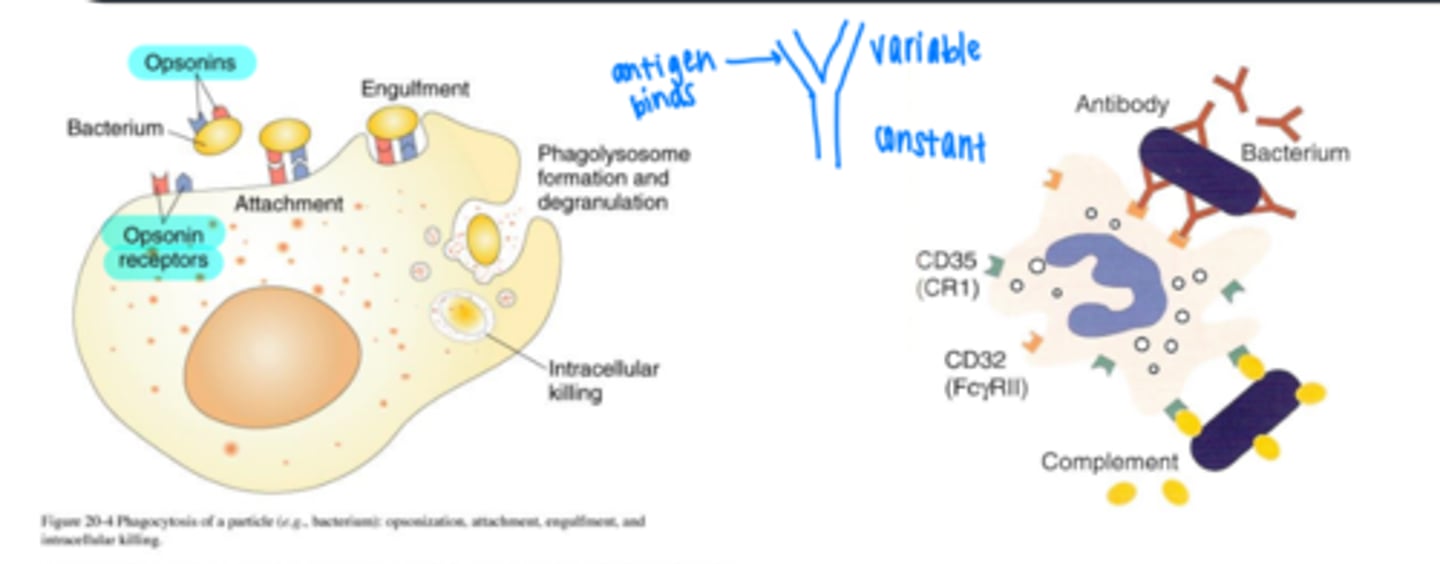
What are the 4 steps of phagocytosis?
chemotaxis
adherence
ingestion
digestion
what triggers phagocytosis?
binding of pathogen to receptors on surface on phagocyte
T/F: only one receptor is required to be triggered in order to both initiate and complete the phagocytic response
false
___________ is the main mechanism by which macrophages recognize pathogens
opsonization
explain opsonization
process by which molecules such as antibodies (called opsonins) bind to the surface of a pathogen and make it more susceptible to destruction
(PAMPs/DAMPs) cause a macrophage to release pro-inflammatory cytokines
PAMPs
DAMPs cause release of anti-inflammatory
How do macrophages and neutrophils crosstalk? why is this important?
cytokine networks
function for cellular activation and deactivation
in what species is the site of clearance of particles from the blood is the lung?
calf, sheep, cat
in what species is the site of clearance of particles from the blood is the liver/ spleen?
dog, rabbit, guinea pig, rat, mouse