Basic Ultrasound Imaging (copy)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Coronal Plane Scan
Top is lateral, bottom is medial. Left is superior and right is inferior
Transverse Plane Scan
Top is anterior, bottom is posterior. Left is right and right is left. Move transducer up or down.
Longitudinal Plane Scan
Top is anterior, bottom is posterior. Left is superior and right is inferior. Move transducer left or right.
Screen Orientation
Top of screen always refers to what transducer is touching. Left side of screen always refers to where the notch is pointing.
Echogenic
Having echoes.
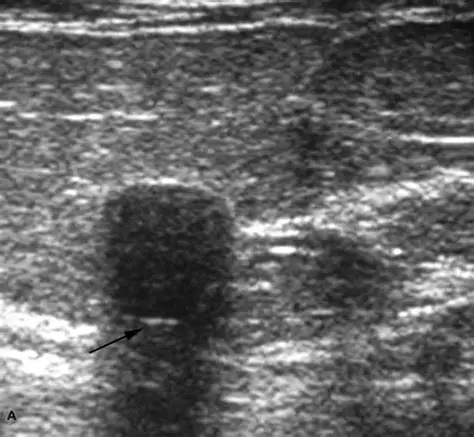
Posterior Shadowing
Sound is more attenuated, and area appears darker.
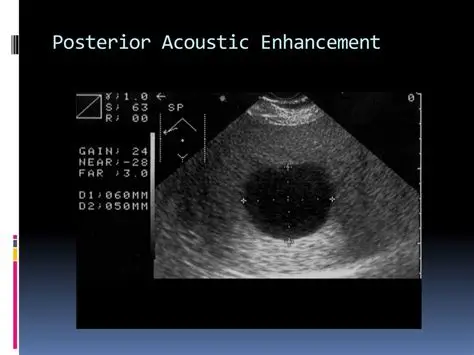
Posterior Enhancement AKA enhancement through transmission
Posterior to anechoic fluid-filled structures. Sound is less attenuated.
Homogeneous
Uniform in texture or echogenicity. Typically refers to sonographic appearance of a single structure.
Fluid-Fluid level
Interface between two fluids with different acoustic features. Will move when pt moves.
Heterogeneous AKA inhomogeneous
Not uniform in textured or echogenicity.
Border Descriptors and purpose
Irregular, ill-defined, round/oval or well-defined. Can help identify malignancy.
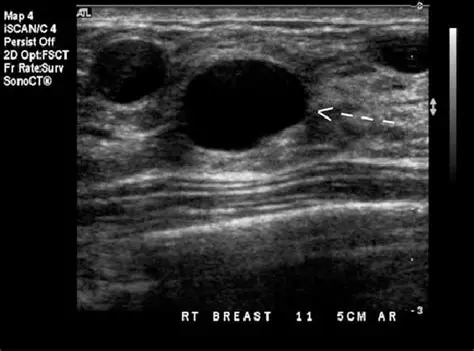
Simple Composition
Anechoic fluid filled structure. (predominantly cystic structure)
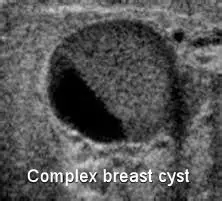
Complex Composition
Combination of simple and solid.
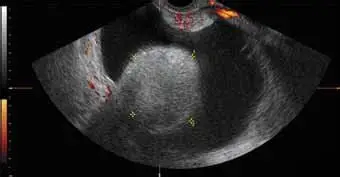
Solid Composition
Made up of tissue. (predominantly cystic structure)
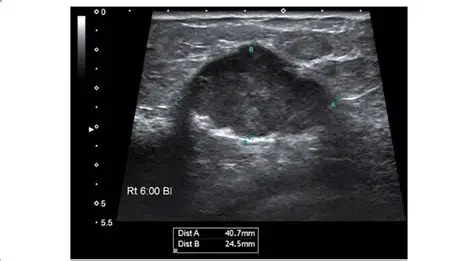
Lobulated border
Appears like a cloud, can be micro or macro.
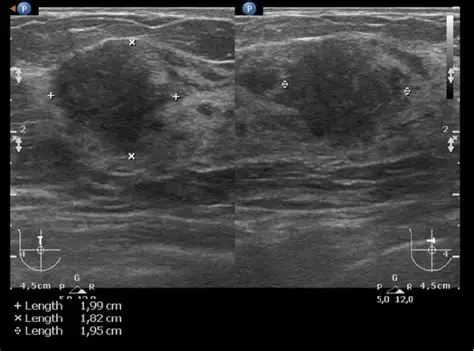
Indistinct border
Hard to determine borders
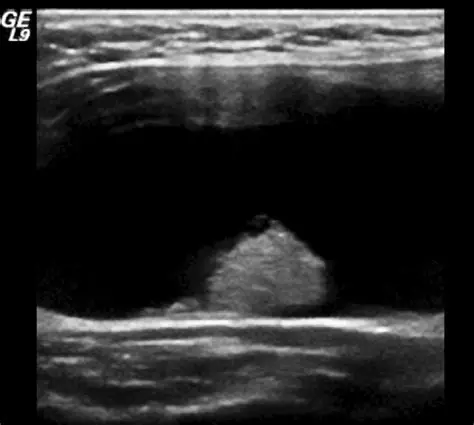
Mural Nodule
solid growth attached to the wall (can be used to describe a complex structure)
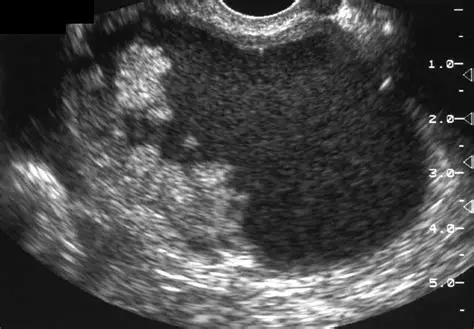
Papillary Projection
projecting into the center of lesion, growing off the wall (can be used to describe a complex structure)
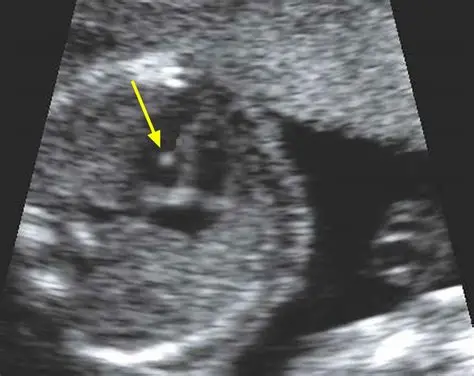
Echogenic Foci (focus)
hyperechoic little white spots
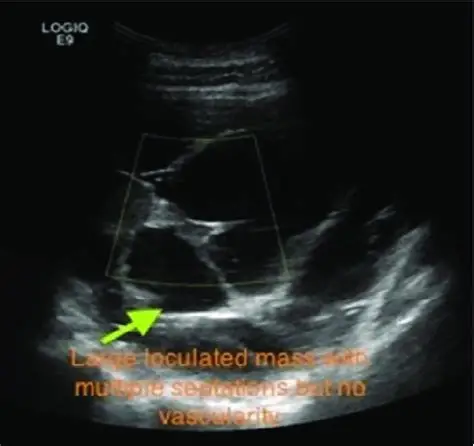
Loculated Composition
Multiple fluid compartments, free fluid
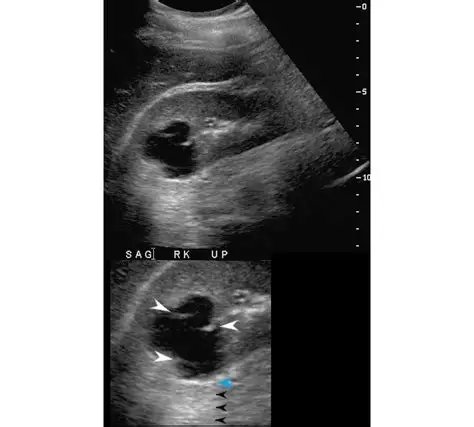
Septated Composition
within a well-define cystic structure
Sonographic Artifacts
Occur as structures that are: not real, missing, misplaced, or improper brightness/shape/size. In some cases, can be help diagnostically such as posterior shadowing/enhancement.
Some Sonographic Artifacts
Shadowing, Enhancement, Reverberation, Comet tail/ring down, Mirror image or Dirty Shadow
Criteria for Identifying Abnormalities: Border
smooth and well-defined or irregular
Criteria for Identifying Abnormalities: Texture
homogeneous or heterogeneous
Criteria for Identifying Abnormalities: Characteristic
anechoic, hyperechoic, echogenic, isoechoic, or hypoechoic
Criteria for Identifying Abnormalities: Transmission of sound
Increased (enhanced) decreased (shadow) or unchanged.
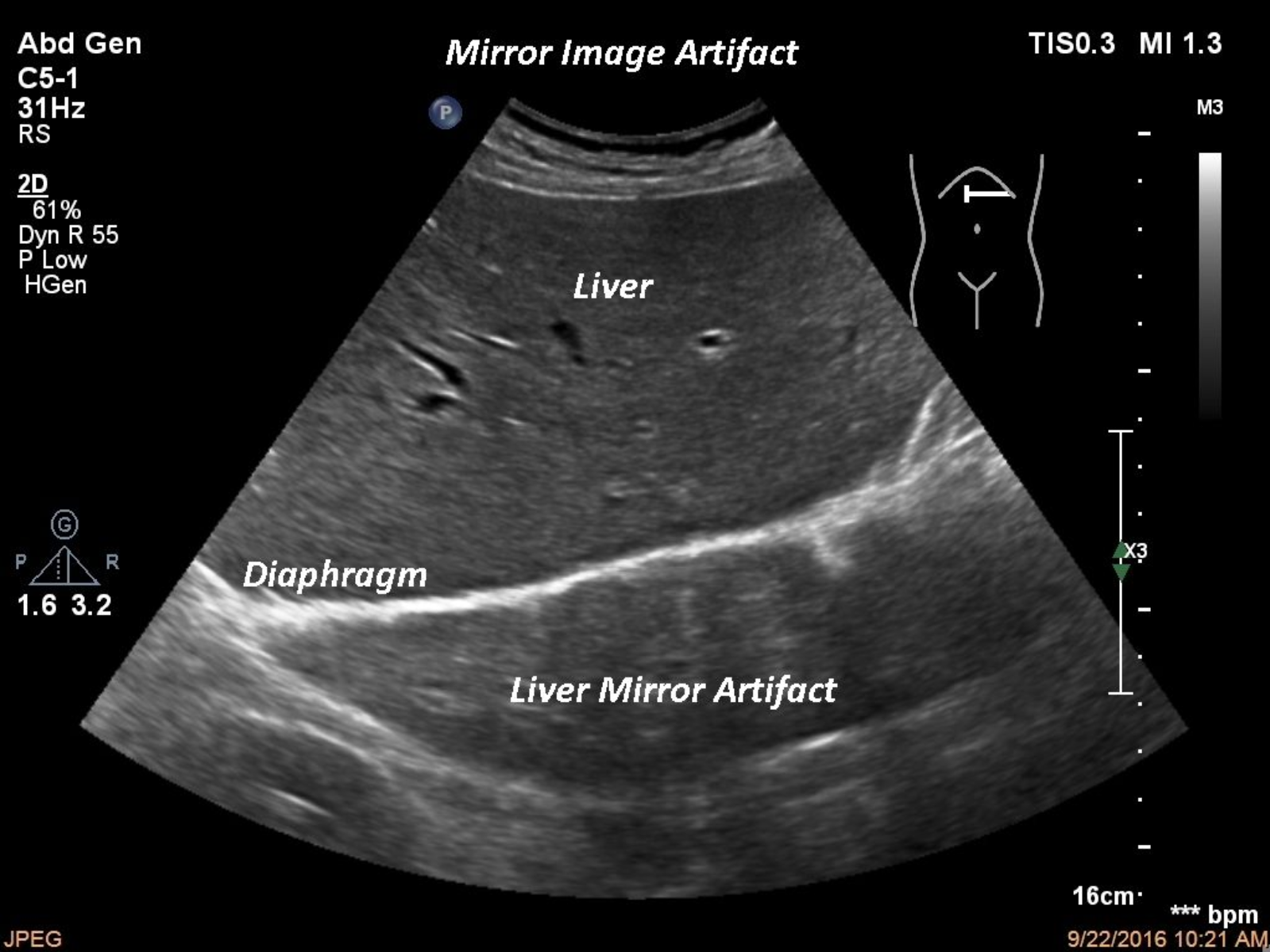
Mirror Image
Shows an extra copy of a reflector deep to the actual structure. Caused by a strong reflector.
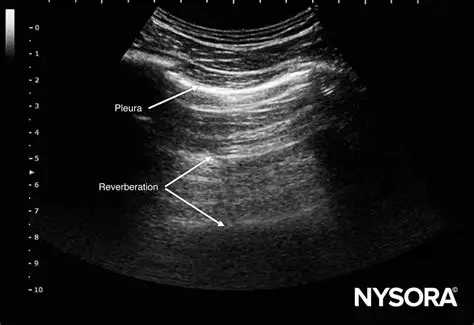
Reverberation
Multiple equidistant reflections that occur between the transducer and a strong reflector. Has a stepladder appearance, only the first one is real and will be the brightest.
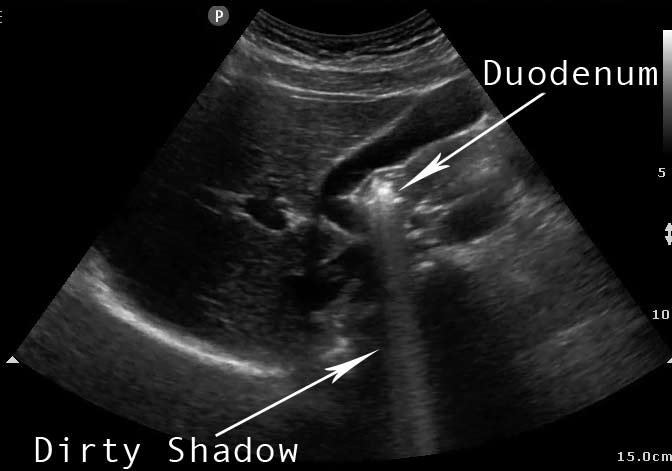
Dirty Shadow
Shadow AND reverberation together. Due to bowels, silicone breast implants, etc.
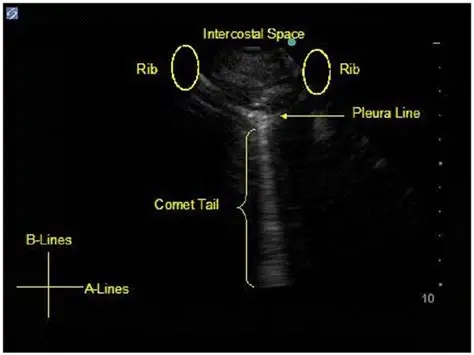
Comet tail/ring down
Reverberation without spaces. Seen posterior to air bubbles. Has a flashlight appearance, similar to a lighter shadow.
Prone
Supine
Right Lateral Decubitus
knees bent, typically arms over head
Left lateral decubitus
knees bent, typically arms over head
Right posterior oblique
Left posterior oblique