3.2 physical chemistry
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Why can a reaction be exothermic?
If more energy is released when forming bonds, than energy used to break bonds
Why can a reaction be endothermic?
If more energy is used to break bonds, than energy being released when forming bonds
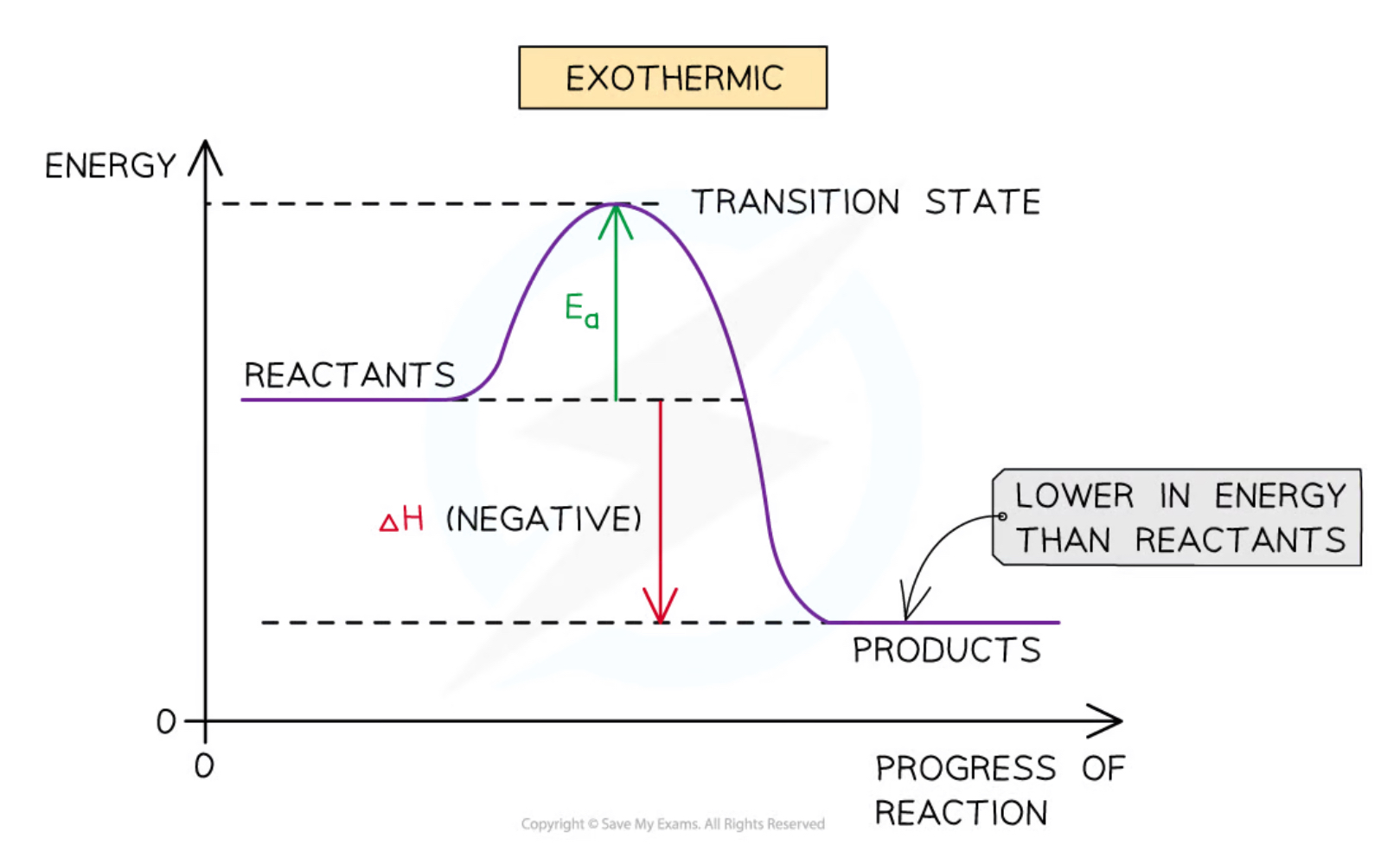
Exothermic energy profile diagram
Goes ‘down’
Delta H arrow is down
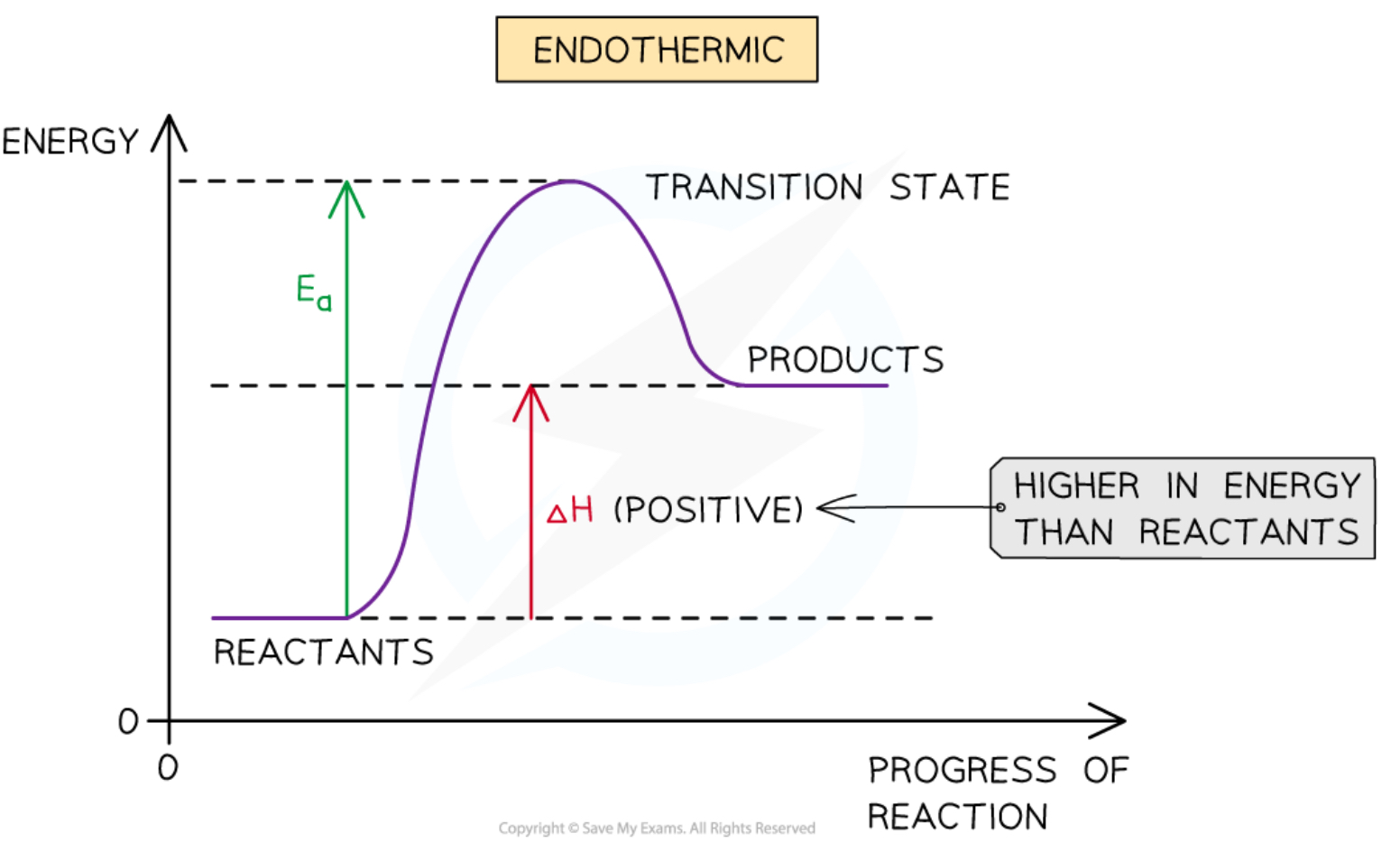
Endothermic energy profile diagram
Goes ‘up’
Delta H arrow is up
What are standard conditions?
298K and 100kPa
What is the enthalpy change of reaction?
The enthalpy change associated with a given reaction
What is the enthalpy change of formation?
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements in their standard state
What is the enthalpy change of combustion?
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance is completely combusted
What is the enthalpy change of neutralisation?
The enthalpy change when an acid and an alkali react together to form 1 mole of water
If a question asks for the standard enthalpy change of ‘x’, what should you add to its original definition?
Under standard conditions
And state them - 298K and 100kPa
How do you calculate a q=mcdeltaT question?
Find delta T with the initial and final temps given - if temp has increased the final answer will be -ve as it is an exothermic reaction, vice versa
Find q using mass of water given - could be in grams or cm3, 4.18 and the delta T already worked out above
When you get the first value of q, it will be in joules so we divide by 1000 to get it into kJ
Use equation delta H (enthalpy change) = q/moles
Work out moles of substance using the given mass and then sub into the equation
Write final answer in kJ mol-1 and check the sign again
Hess cycle - enthalpy change of reaction
Arrows go down then up
Reactants + Products
Hess cycle - enthalpy change of formation
Arrows go up
Products - Reactants
Hess cycle - enthalpy change of combustion
Arrows go down
Reactants - Products
What is the enthalpy of formation for any element?
Zero
Common exam question: explain using Boltzmann distribution why increasing the temperature and adding a catalyst both increase reaction rate
Draw the Boltzmann distribution with x-axis as energy and y-axis as number of molecules
Draw T2 curve at higher temp - shifted to the right
Label Ea and then Ec more to the left or at lower energy on the x-axis
Increasing temperature, increases the frequency of successful collisions and there is the same area under the curve but more molecules have energy above Ea
Using a catalyst lowers Ea, so a higher proportion of molecules can exceed the Ea limit
What other factors increase reaction rate?
Increasing the concentration
Increasing pressure
Adding catalysts
What is a catalyst?
A substance which increases the rate of reaction by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower Ea and it is chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction
What is a heterogeneous catalyst?
A catalyst that is in a different phase/physical state to the reactants e.g. solid iron catalyst in Haber process with gases
What is a homogeneous catalyst?
A catalyst that is in the same phase/physical state as the reactants
Economic advantages of using catalysts for industrial processes
Lower production costs
Gives higher yield in shorter time
Environmental advantages of using catalysts in industrial processes
Less carbon dioxide released
Reduces waste
Better atom economy
How can we investigate reaction rates?
Change in mass
Volume of gas given off
How do you calculate reaction rate?
Draw a tangent at the time given and use Gradient = change in y / change in x (g/min-1)
What’s dynamic equilibrium?
When the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the backward reaction
What are the conditions of a system in dynamic equilibrium?
Closed system
Concentration of reactants and products remain the same
What is Le Chatelier’s Principle?
It says that if a change is made to system in dynamic equilibrium the position of equilibrium moves to counteract thus change
How to answer a question that asks to Explain how le Chatelier’s principle can be used to predict the conditions of temperature and pressure for a maximum equilibrium yield of ammonia in the Haber process.
Identify whether the reaction is endothermic, delta H is positive or exothermic, delta H is negative - the Haber process is exothermic
Think of temperature:
If the reaction is endothermic, using high temperature will favour the forward reaction which is endothermic and shift equilibrium to the right
If the reaction is exothermic, using low temperature will favour the forward reaction which is exothermic and shift equilibrium to the right (what we would use in the Haber process question)
Think of pressure:
If the reaction has more gas molecules on the right side (where the products are) then we use low pressure
If the reaction has less gas molecules on the right side (where the products are) then we use high pressure (what we would use in the Haber process)
If a question asks to state how the equilibrium conditions could be changed to achieve a compromise between equilibrium yield, rate and other operational factors you would do the following: