Genetic diversity and adaption
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
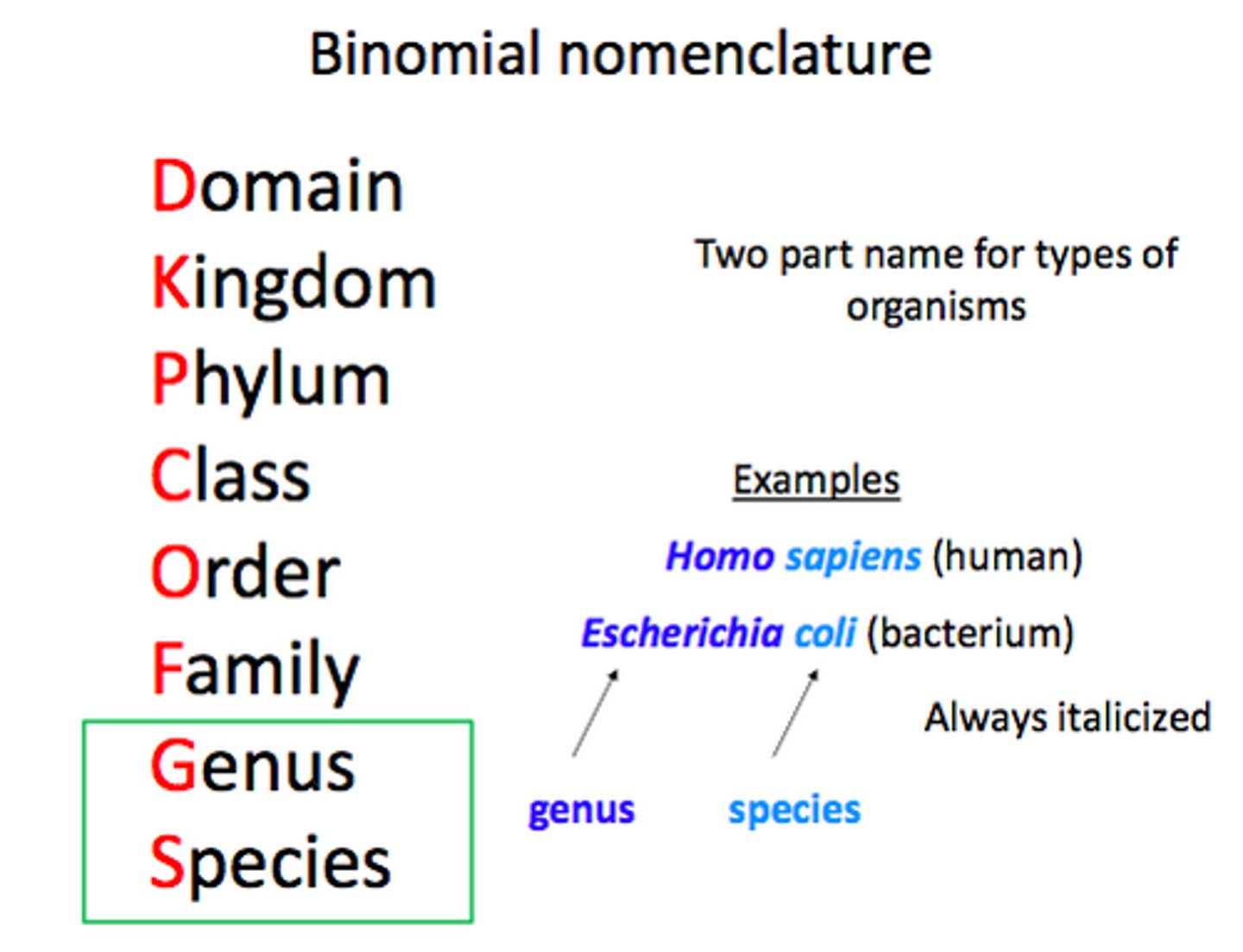
Linnean Classification System
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
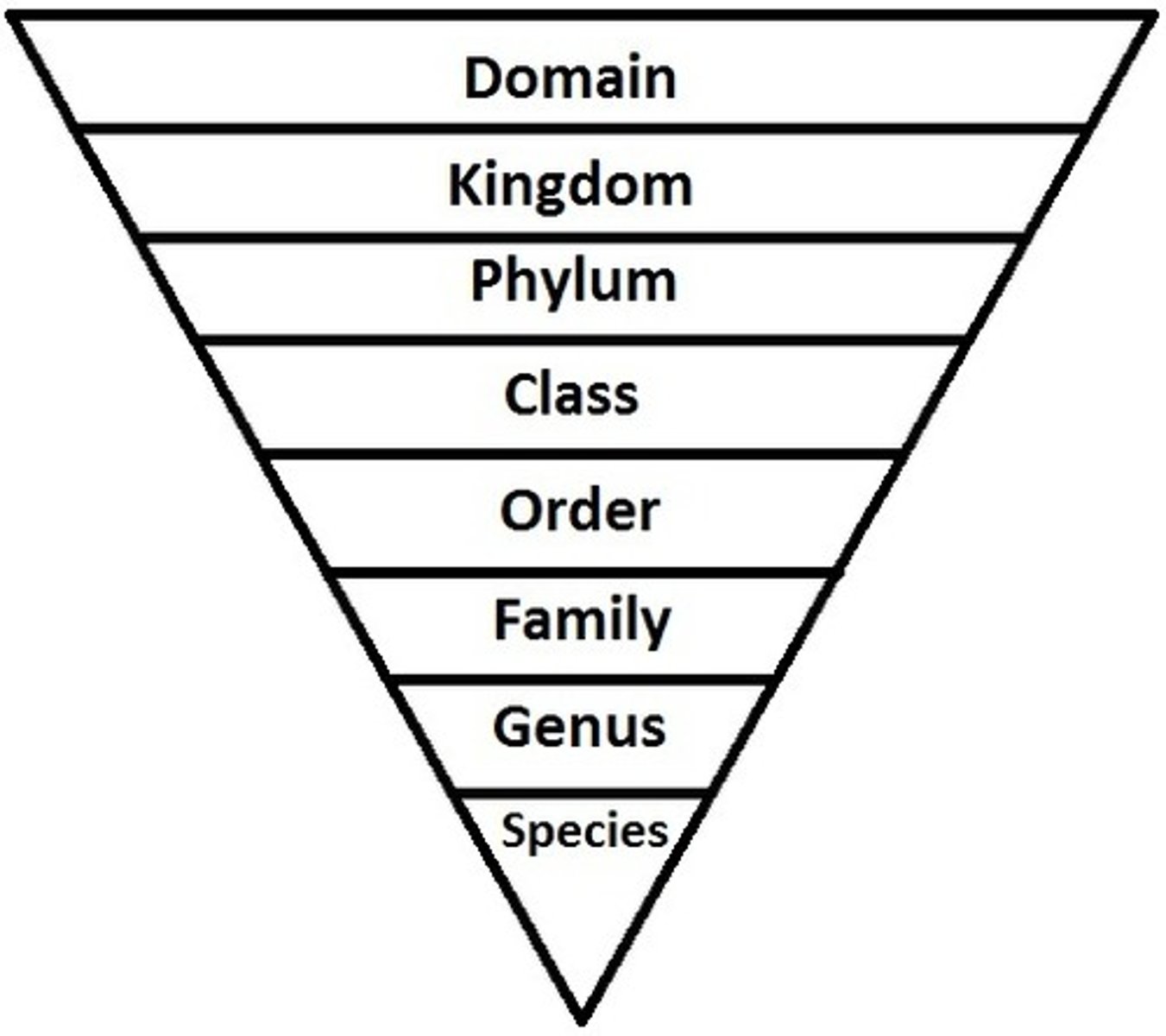
What is a taxonomic group?
the hierarchical groups of classification
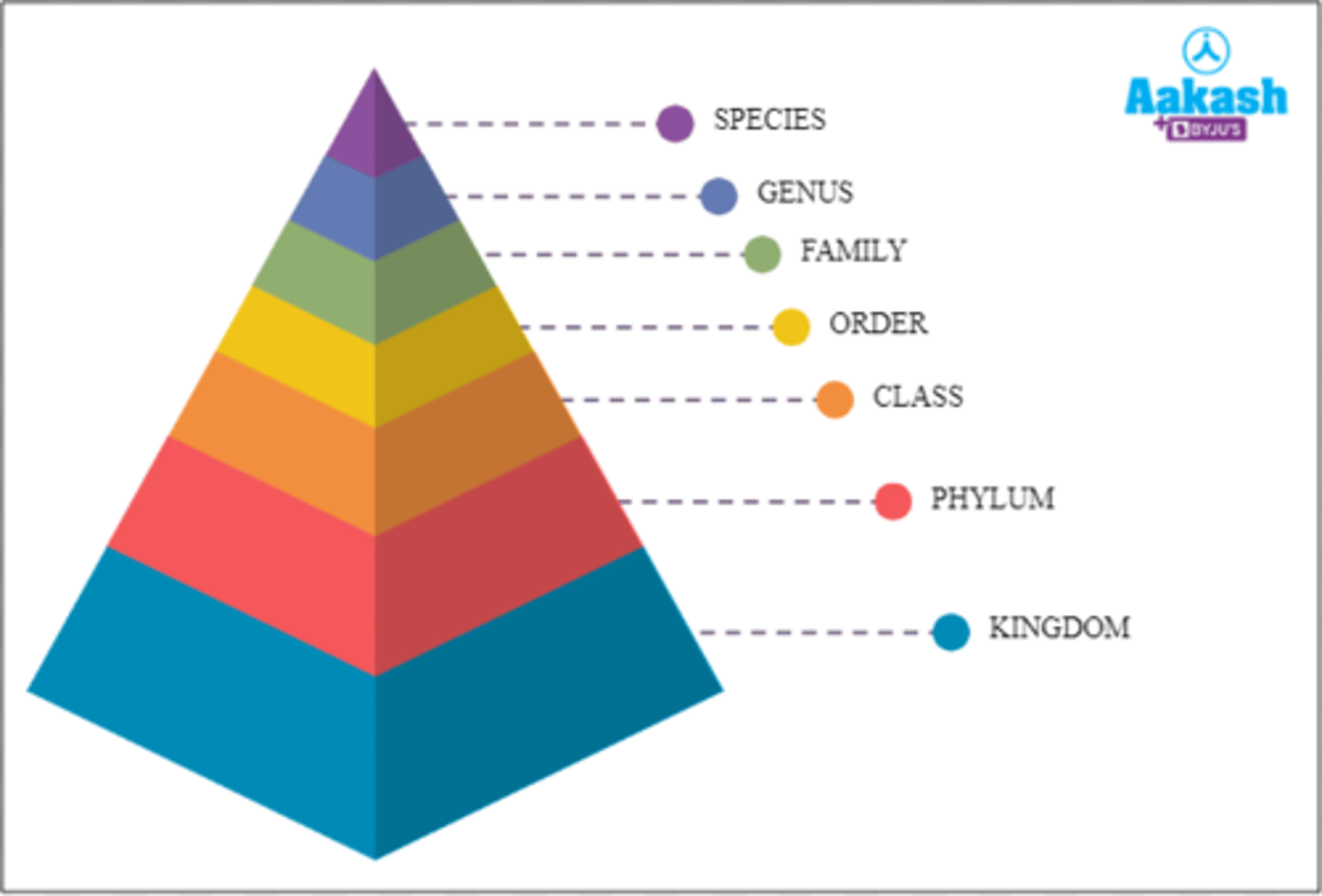
What is each individual group called in a taxonomic group?
a taxon
What does the binomial name consist of?
genus and species
What are the rules for binomial names?
Genus is capitalised and name is italicised
Define species
group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring
What is intraspecific variation?
variation within a species
What are the causes of variation?
genetic and environmental
What is genetic variation caused by?
The genetic material an organism inherits
What is a mutation?
change in DNA sequence
What are the three types of mutation?
substitution, insertion, deletion
What is a substitution mutation?
Replacement of a single nucleotide by another nucleotide
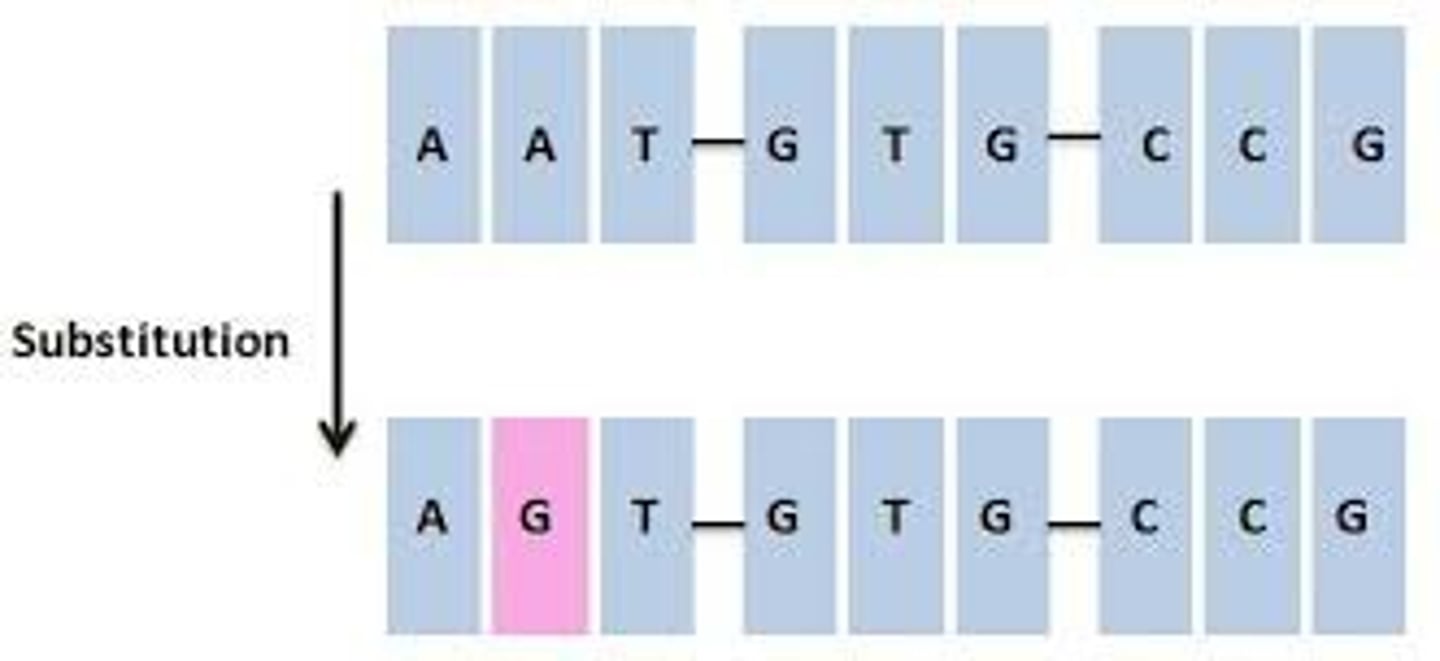
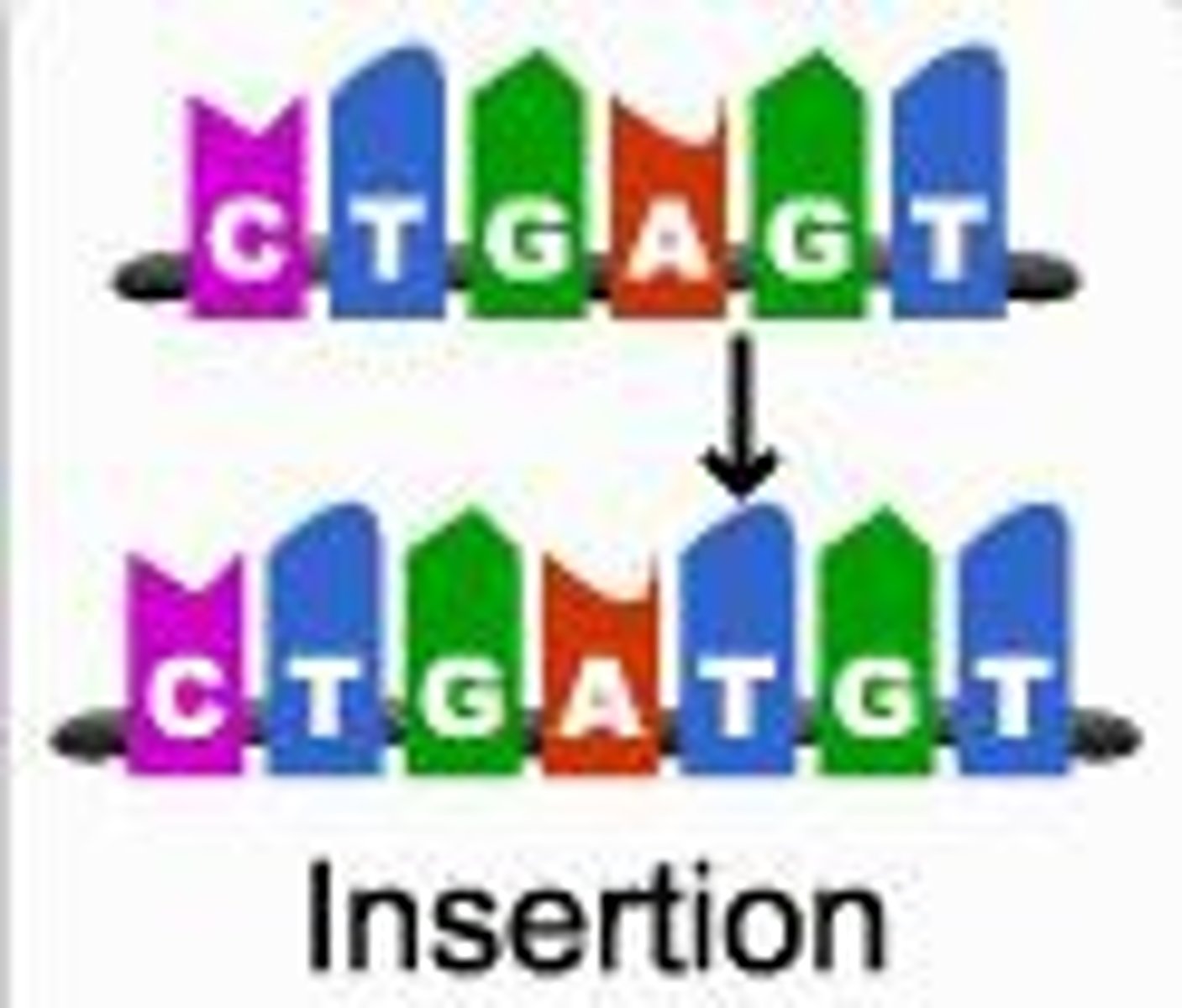
What is an insertion mutation?
addition of one or more bases
What is a deletion mutation?
one nucleotide is taken away from a gene or DNA sequence

Why do mutations not always affect amino acid sequence?
degenerate code
Why are frameshift mutations (insertion and deletion) more detrimental than substitution mutations?
They can misalign all other codons within that sequence
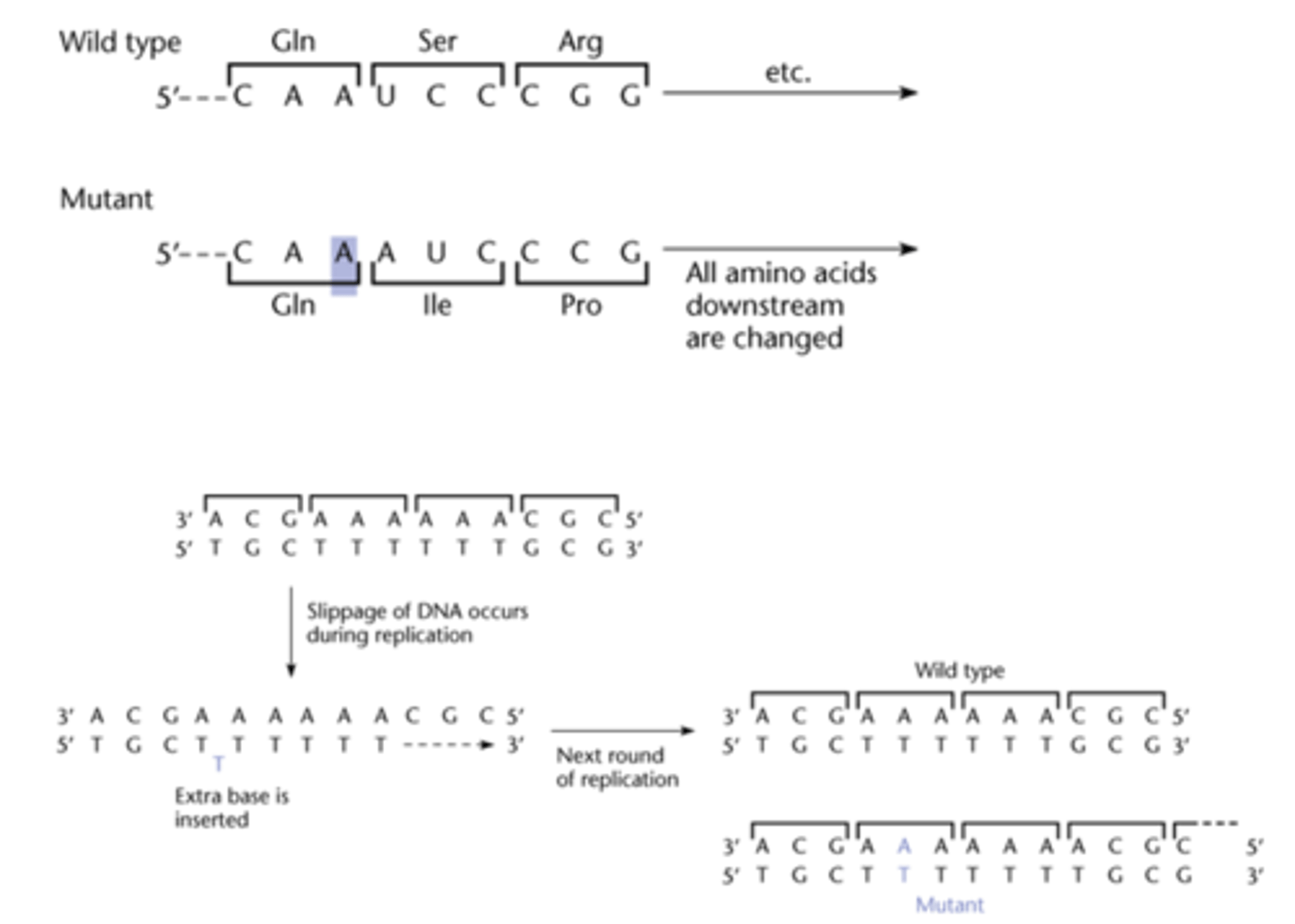
How are mutations passed on to offspring?
occurs in gametes
What are polyploidy chromosome mutations?
When an individual has three or more sets of chromosomes instead of two
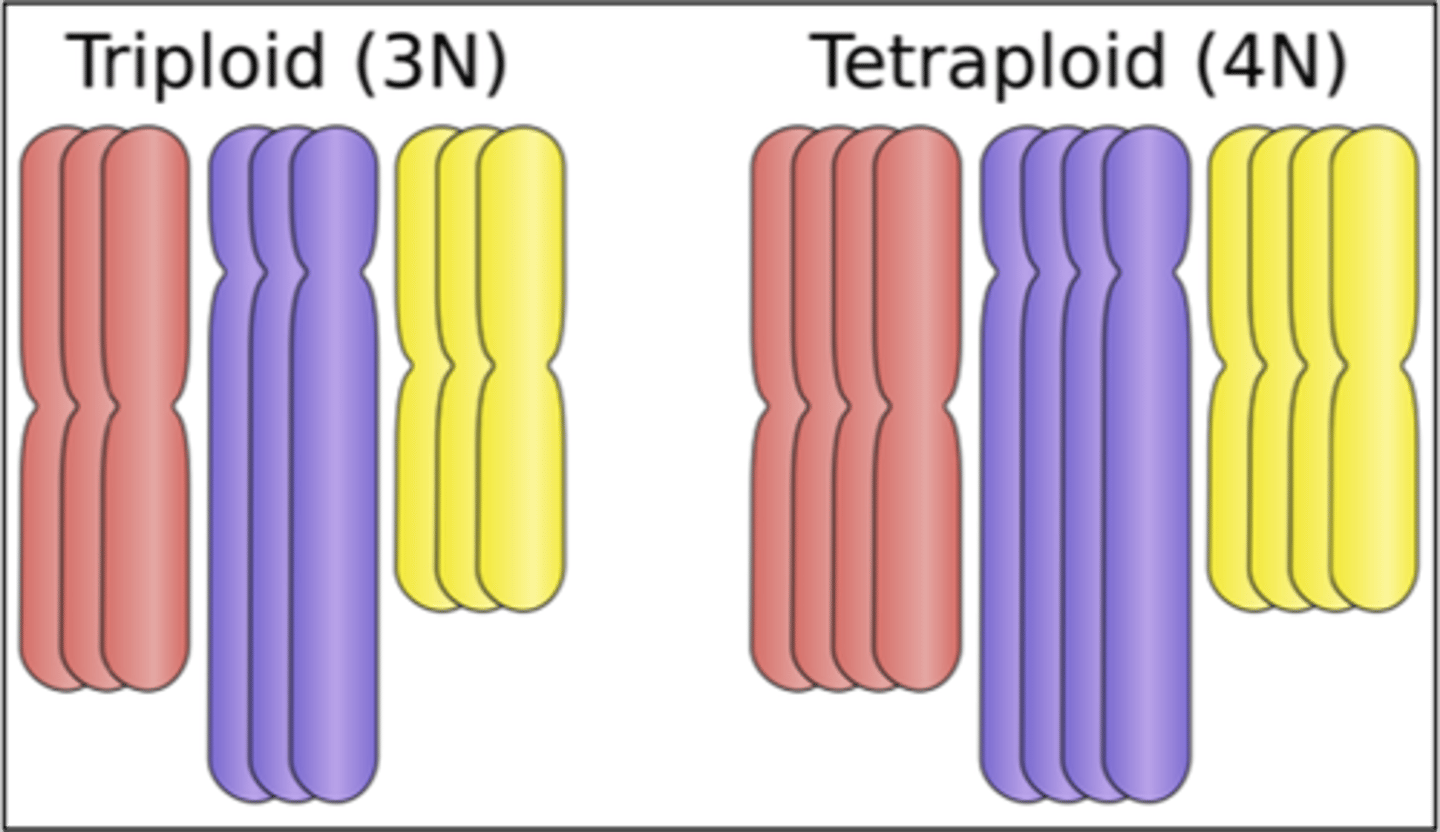
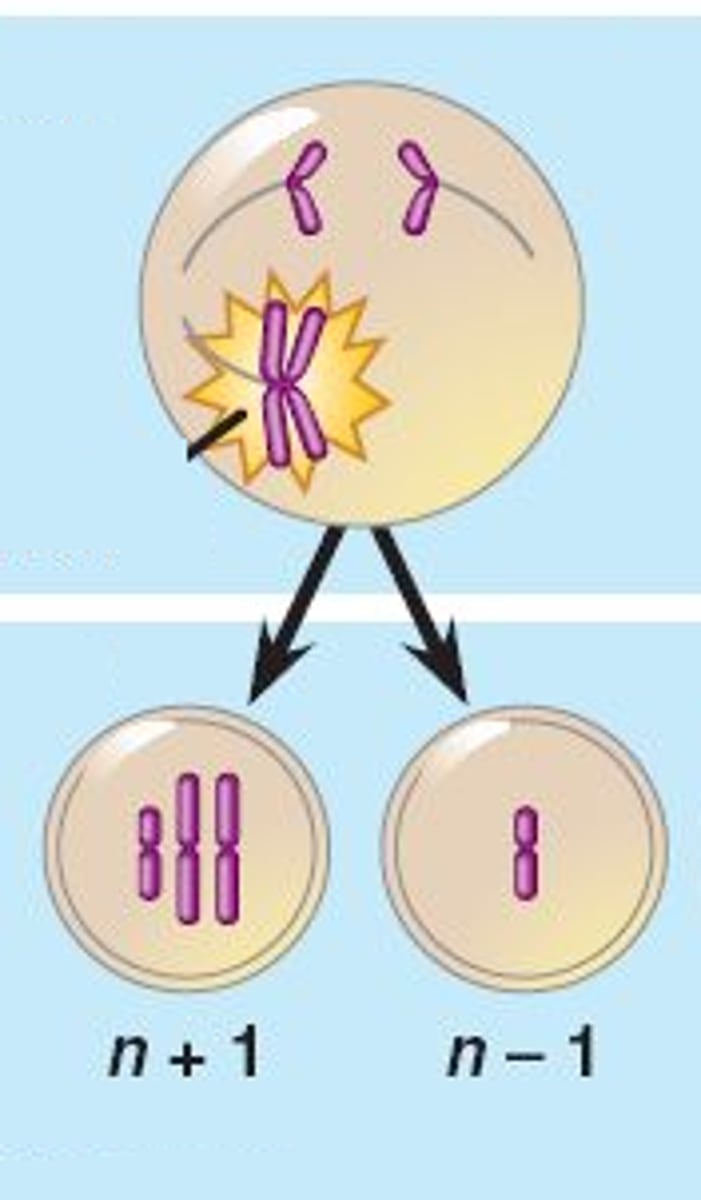
What is chromosome non disjunction?
When chromosomes fail to separate correctly in meiosis, resulting in gametes with one more or less chromosome than normal.
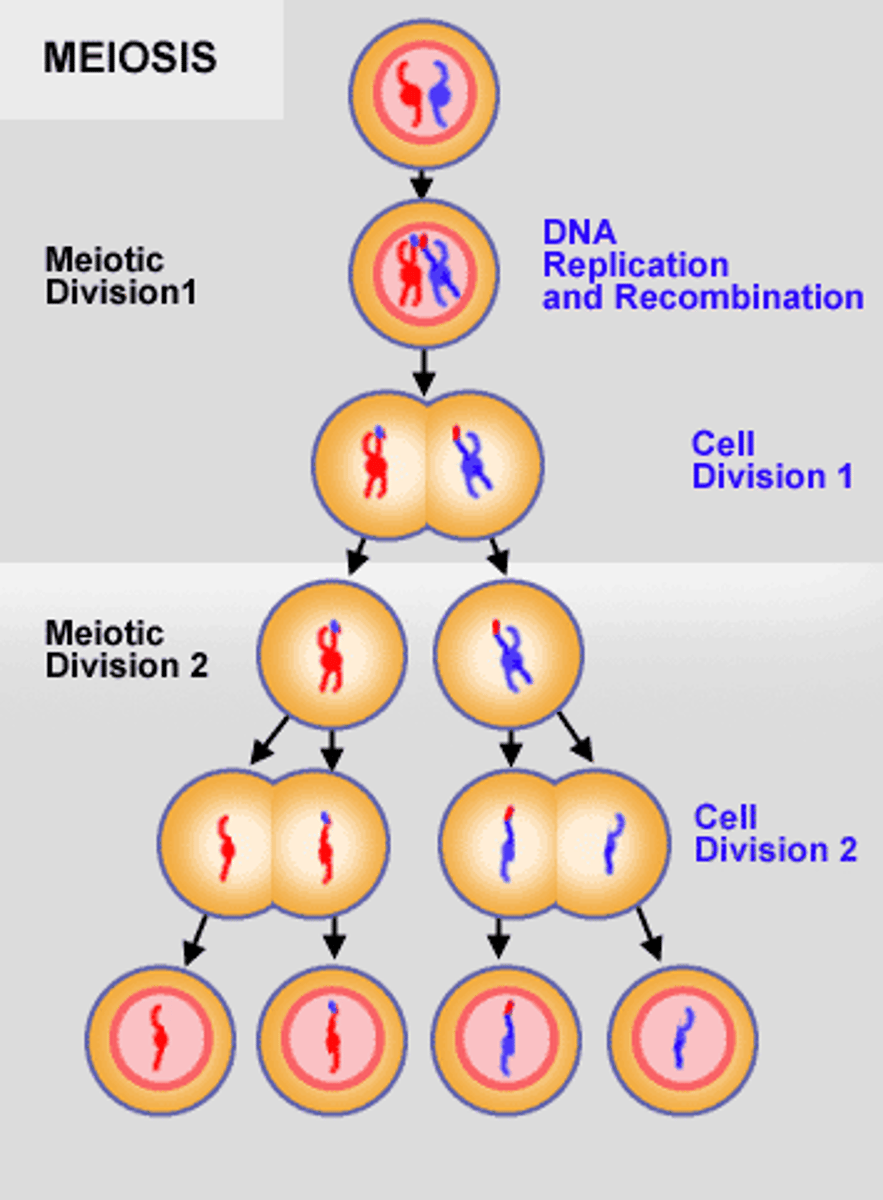
What is meiosis?
a type of cell division that results in four genetically different haploid cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell
What happens in meiosis 1?
Homologous chromosomes separate
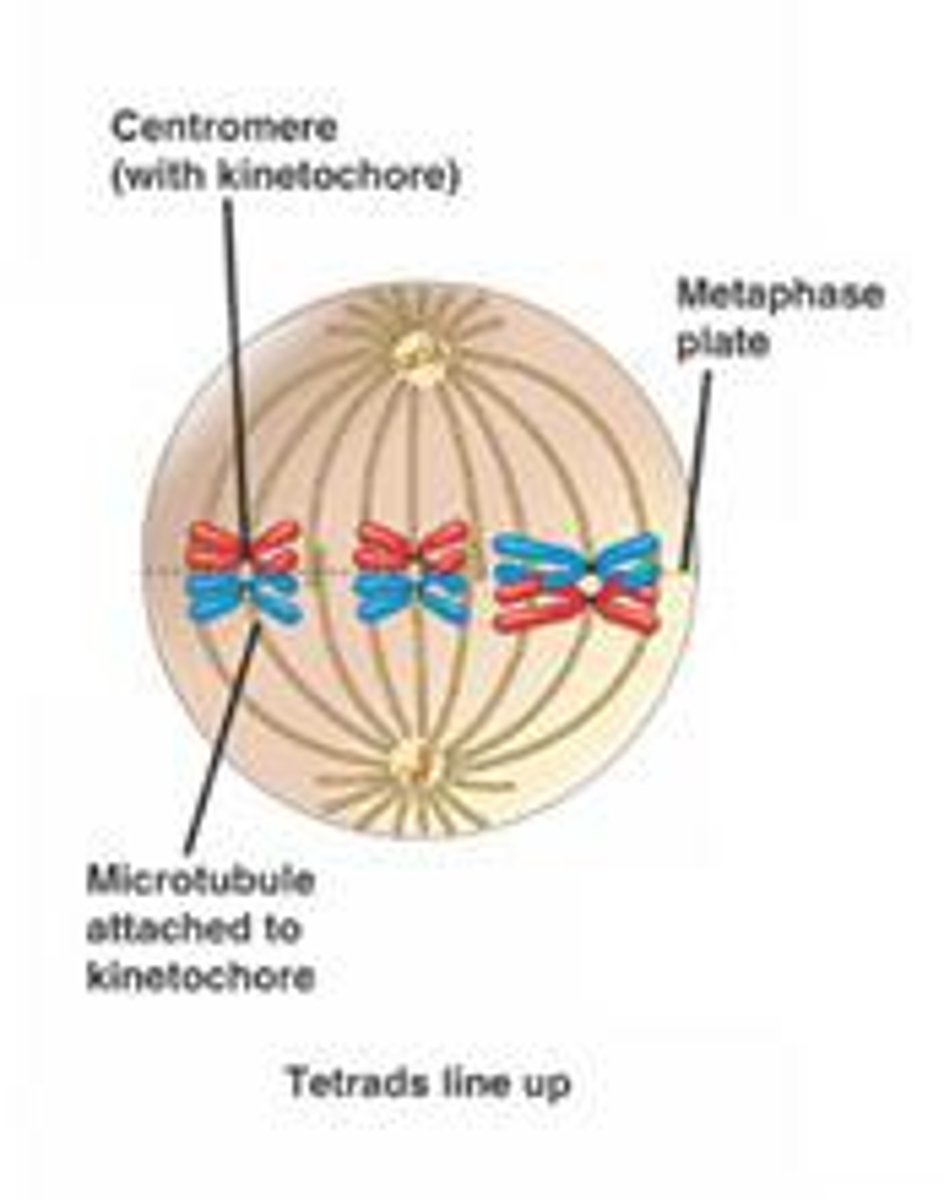
Describe the process of Meiosis 1
-Homologous chromosomes pair up and their chromatids wrap around each other
-Crossing over occurs at chiasmata
-By the end homologous pairs separate, with one chromosome from each pair going into one of the two daughter cells
What happens in Meiosis II?
- Sister chromatids separate
- 4 haploid daughter cells are formed
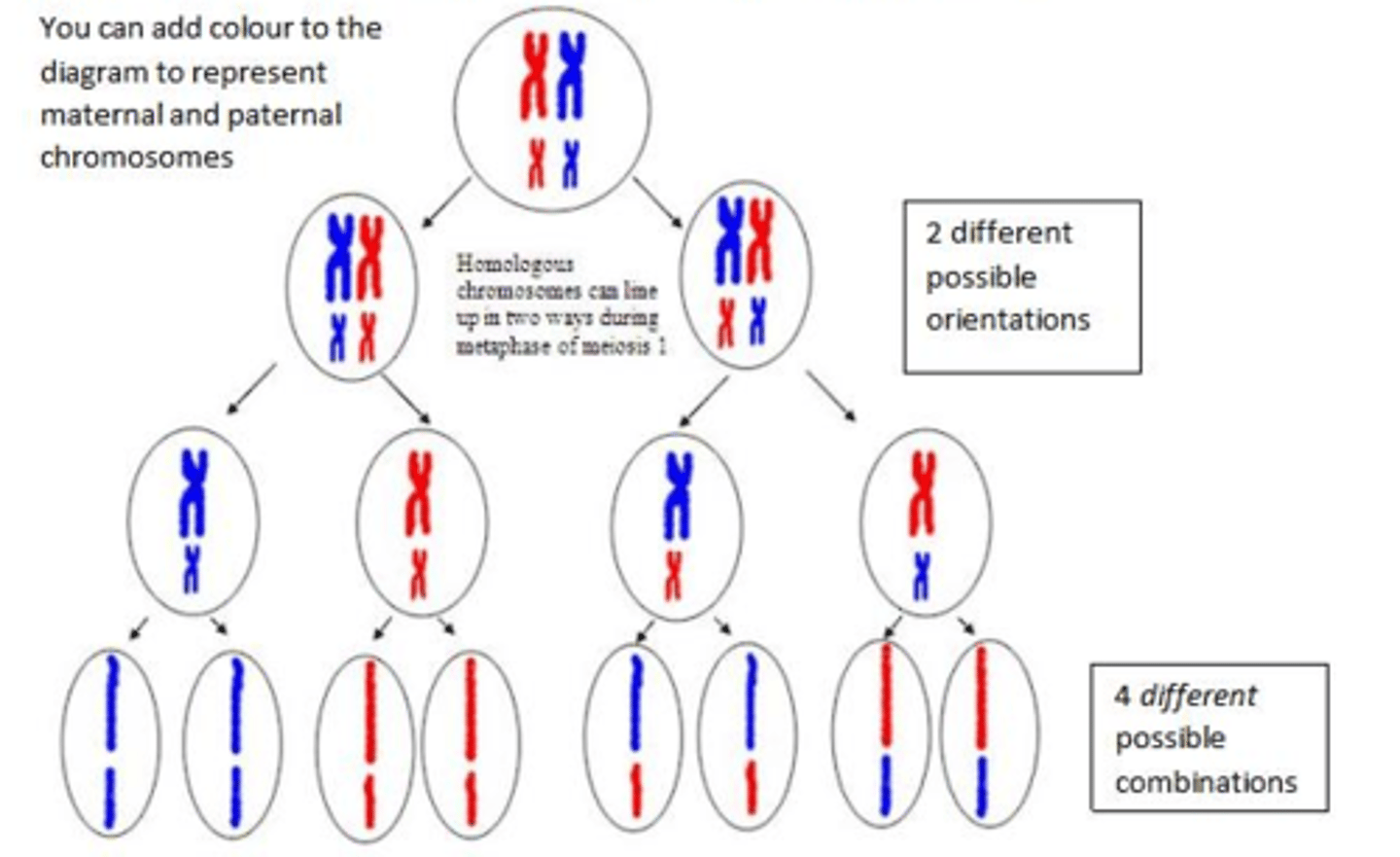
What happens in independent segregation/random assortment of chromosomes?
During meiosis 1 homologous chromosomes line up in pairs, the arrangement of these pairs is random, meaning that the division into the daughter cells is also random.
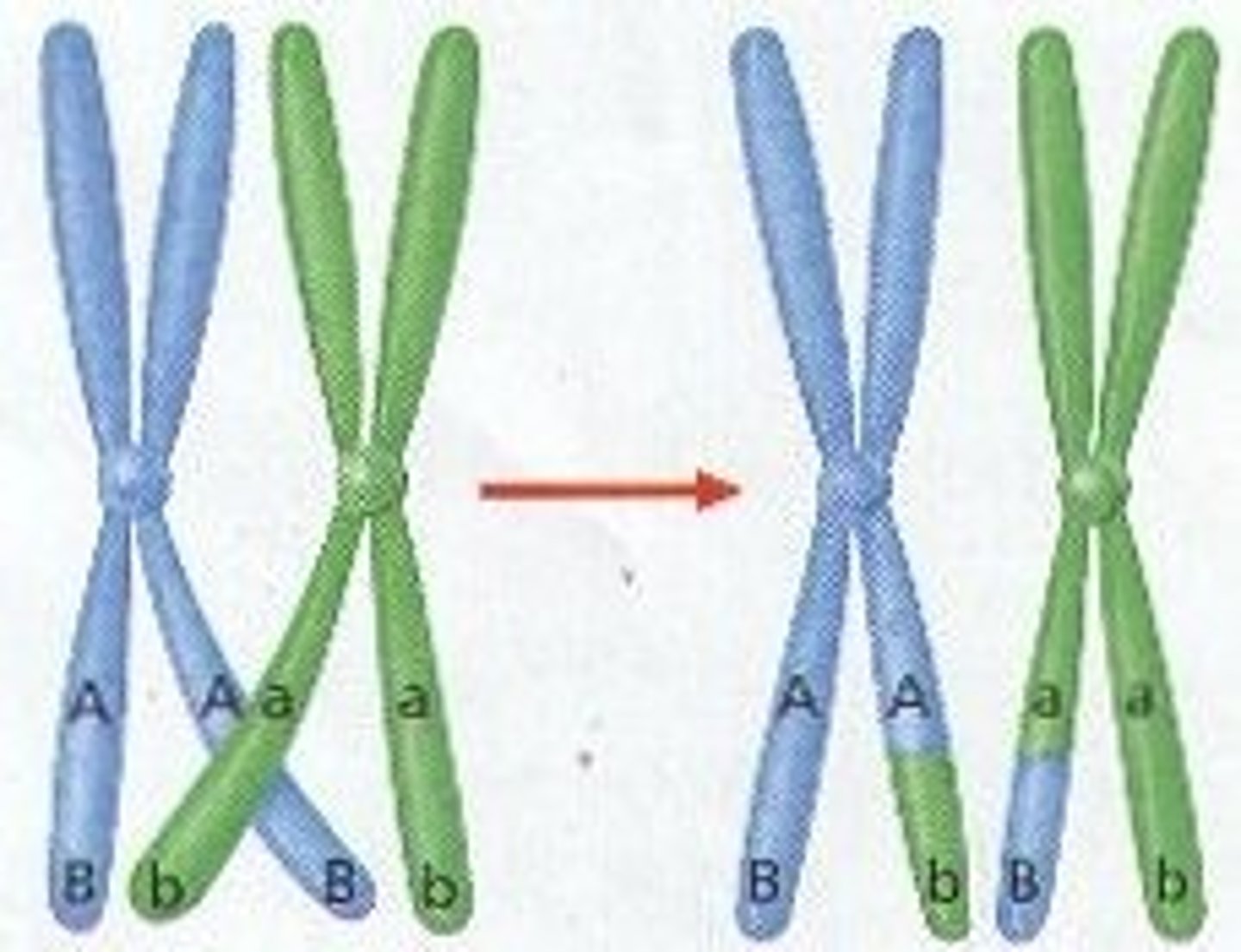
Describe the process of crossing over of chromosomes
- Homologous pairs of chromosomes associate
- Chiasmata form
- Equal lengths of alleles are exchanged
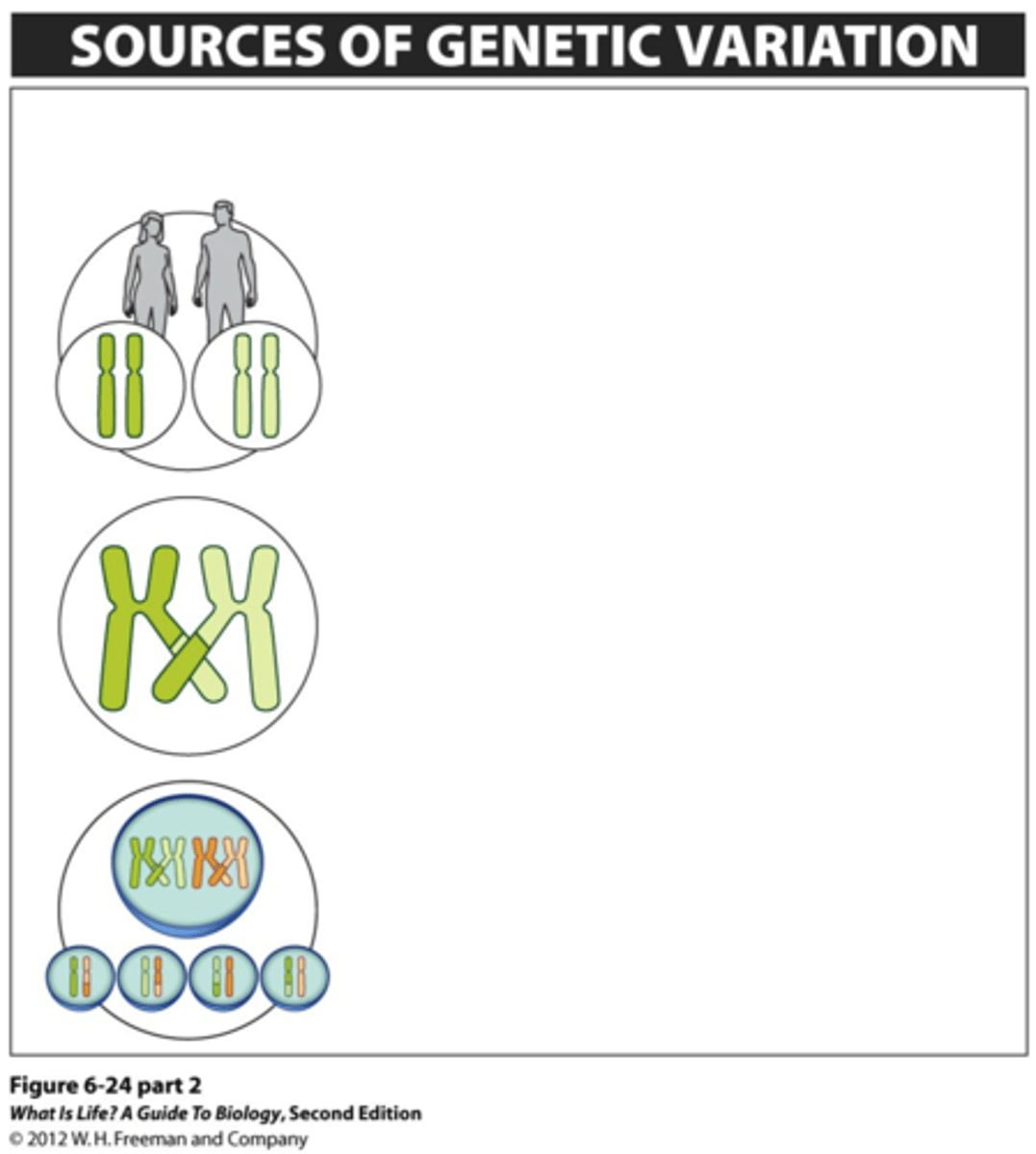
How does meiosis bring about genetic variation?
1) Independent segregation of homologous chromosomes
2) Crossing over between homologous chromosomes
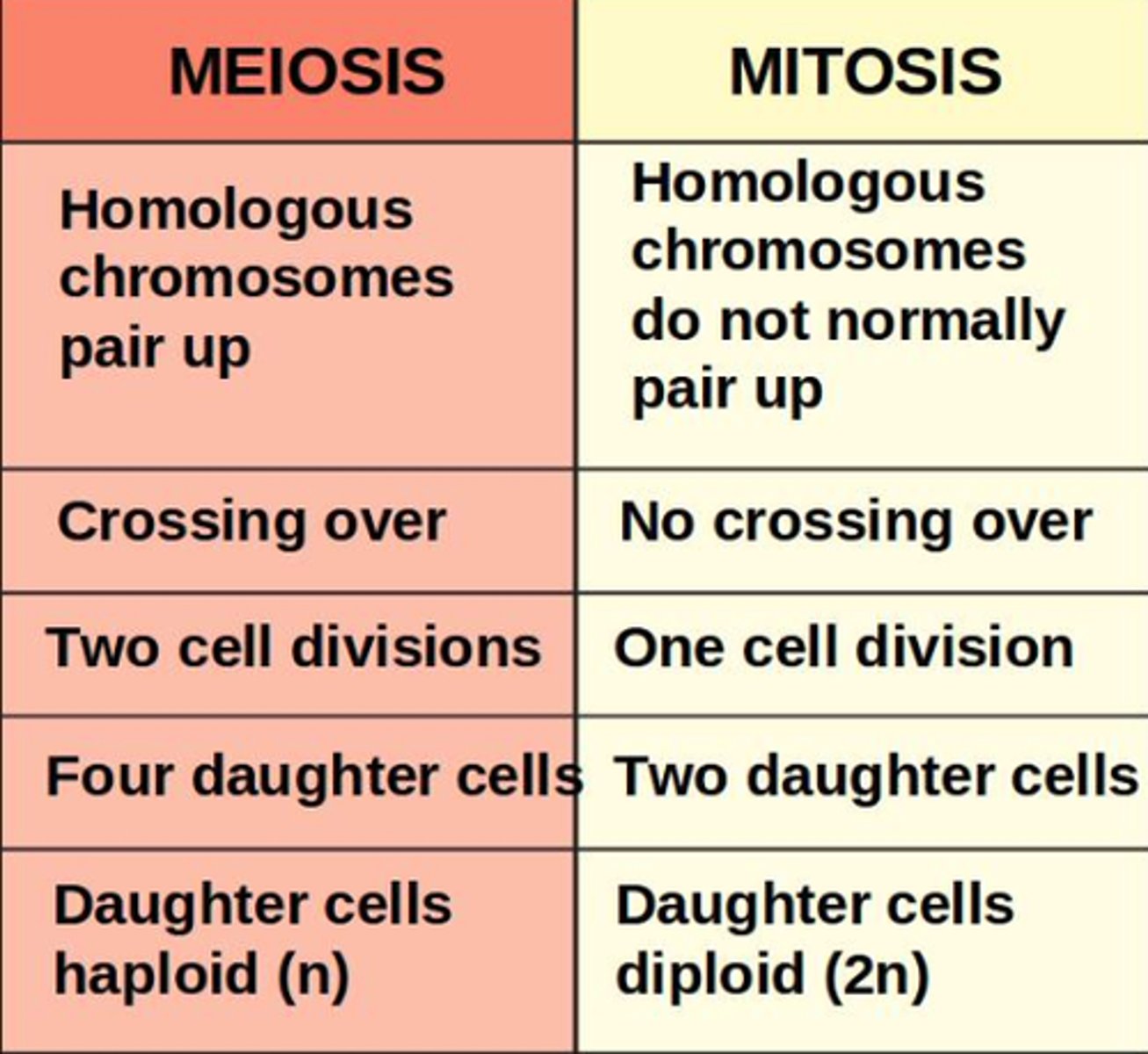
What are the differences between mitosis and meiosis?
- One division in mitosis, two divisions in meiosis
- Daughter cells genetically identical in mitosis, daughter cells genetically different in meiosis
- Two cells produced in mitosis, four cells produced in meiosis - Diploid to diploid in mitosis, diploid to haploid in meiosis
- Separation of homologous chromosomes only in meiosis
- Crossing over only in meiosis
- Independent segregation only in meiosis
What is a mutagenic agent?
A factor that increases rate of gene mutation, e.g. ultraviolet (UV) light or alpha particles.
In organisms that carry out asexual reproduction, what is the only way for genetic variation to increase?
mutations
In organisms that carry out sexual reproduction, what are the 3 ways genetic variation increases?
- receiving alleles from 2 different parents
- genetically different gametes
- random fertilisation of gametes
What are environmental causes of variation?
climate, diet, accidents, culture and lifestyle
What is discontinuous variation?
A characteristic that can only result in certain values
What is discontinuous variation also known as?
discrete variation
What are discontinuous features often controlled by?
a single gene
What is continuous variation?
A characteristic that can take any value within a range
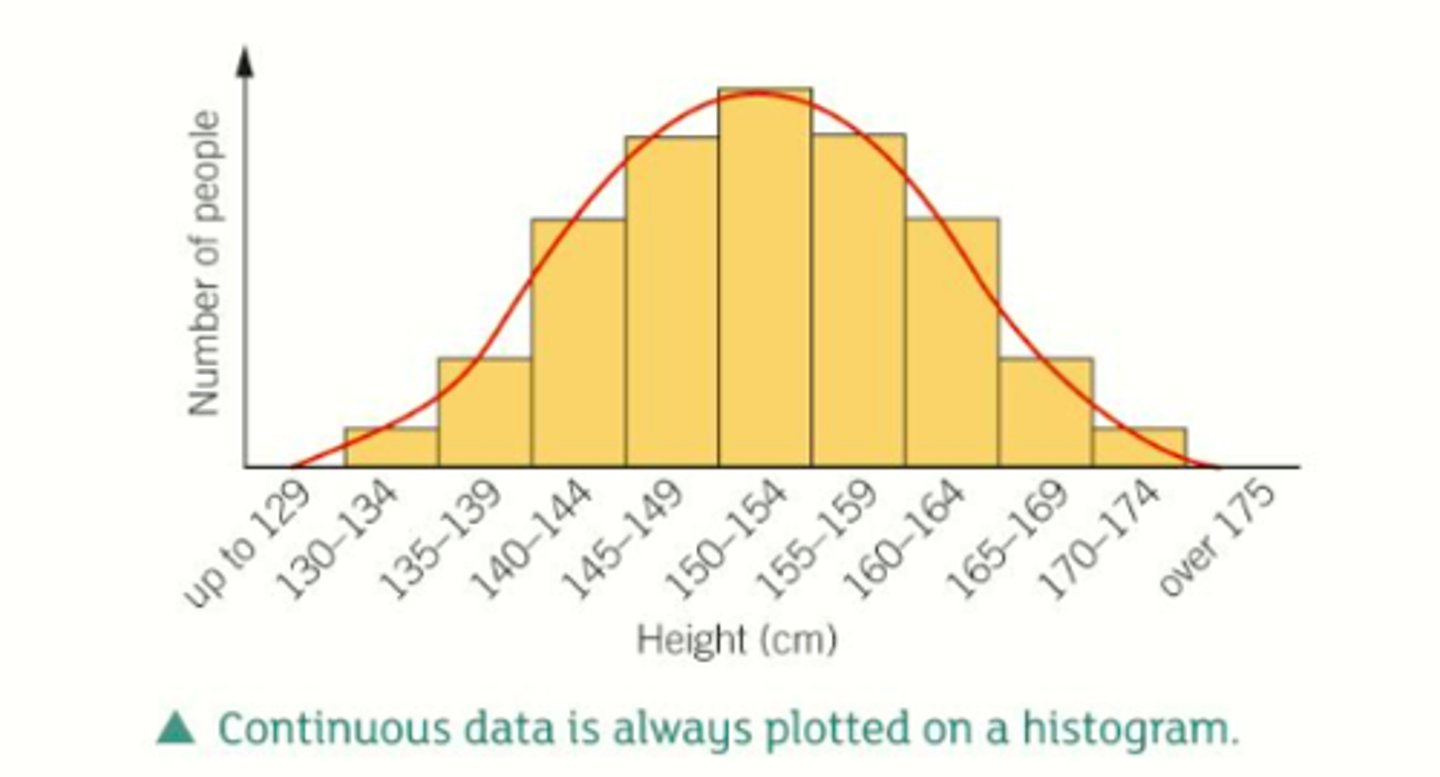
How is continuous variation represented?
histogram
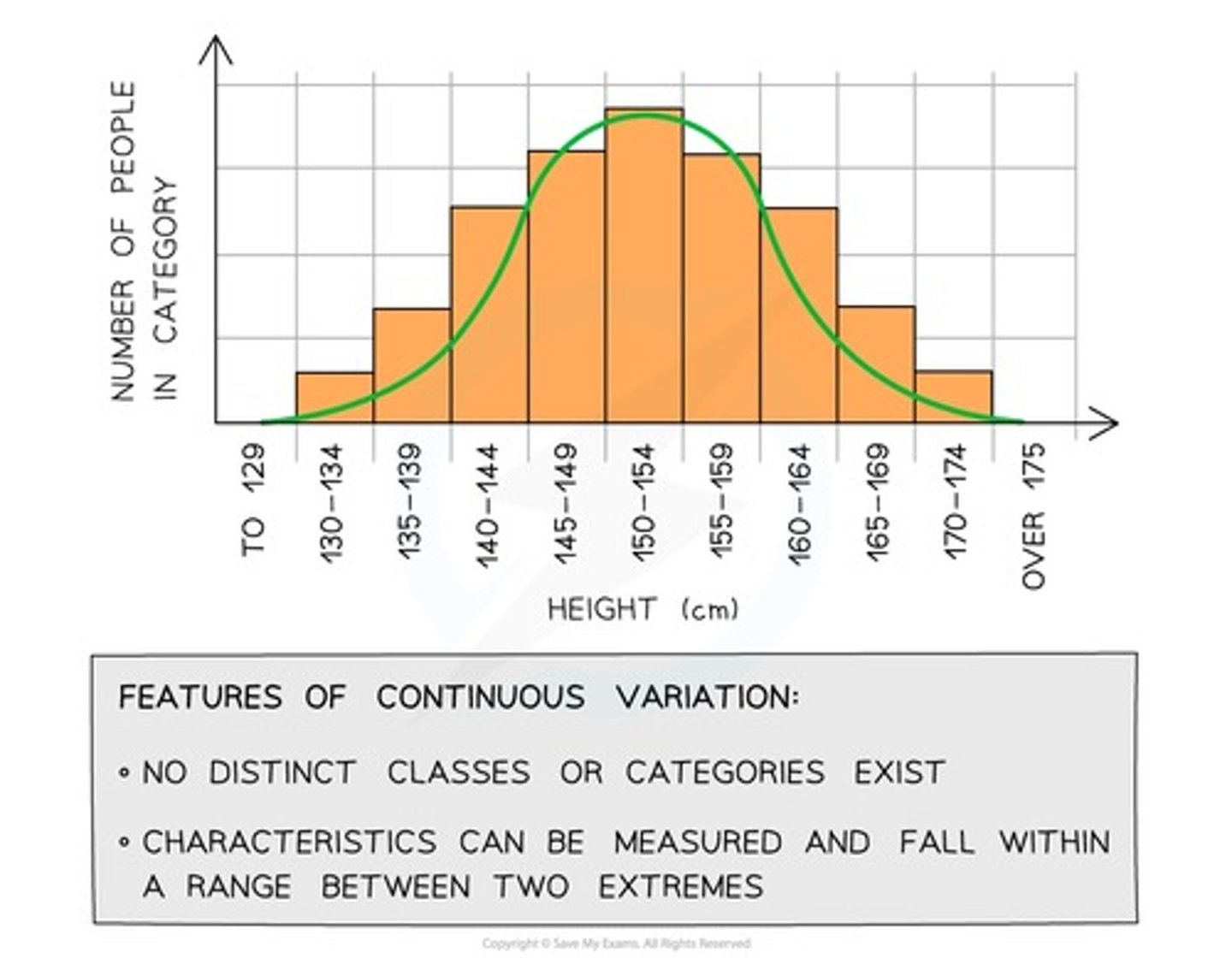
What are continuous features often controlled by?
Several genes working together - polygenes
What is a normal distribution curve?
bell curve
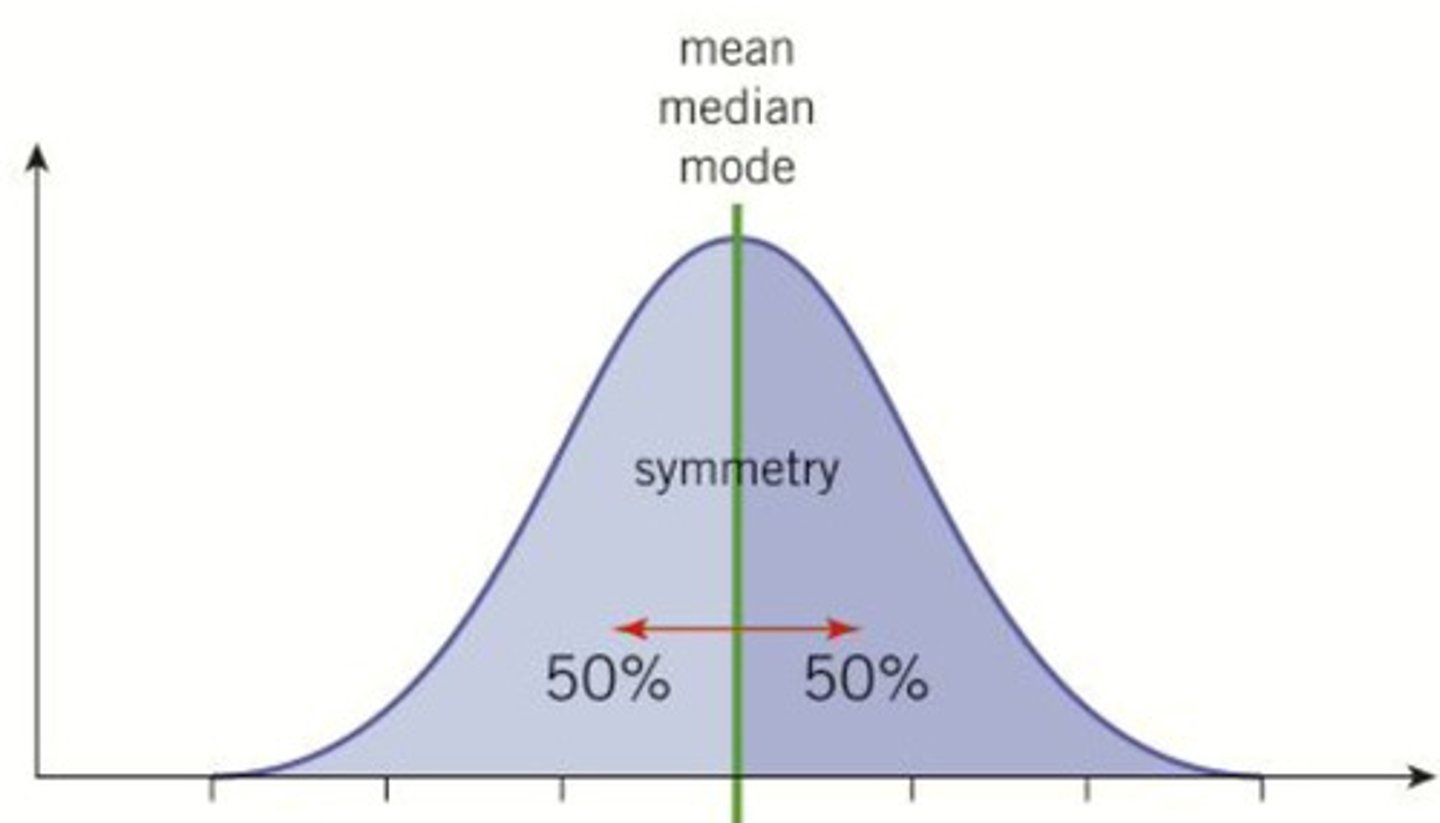
How can we quantify the spread of data around the mean?
using standard deviation
What does a small standard deviation mean?
data is clustered around the mean
What does a large standard deviation mean?
that values are more spread out.
What are anatomical adaptations?
physical features

What are behavioural adaptations?
Ways an organism acts that increase its chance of survival

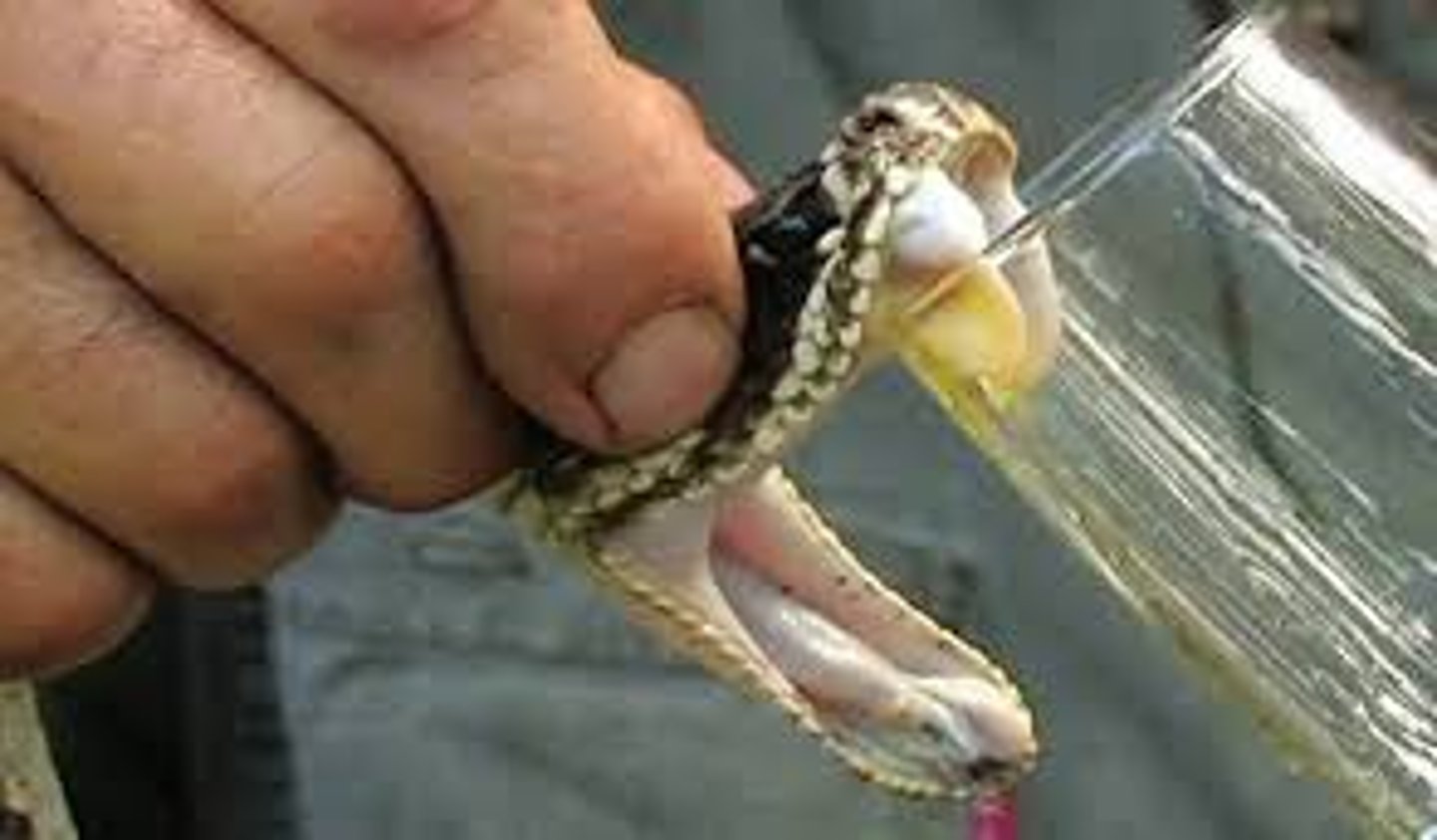
What are physiological adaptations?
Processes that take place inside an organism

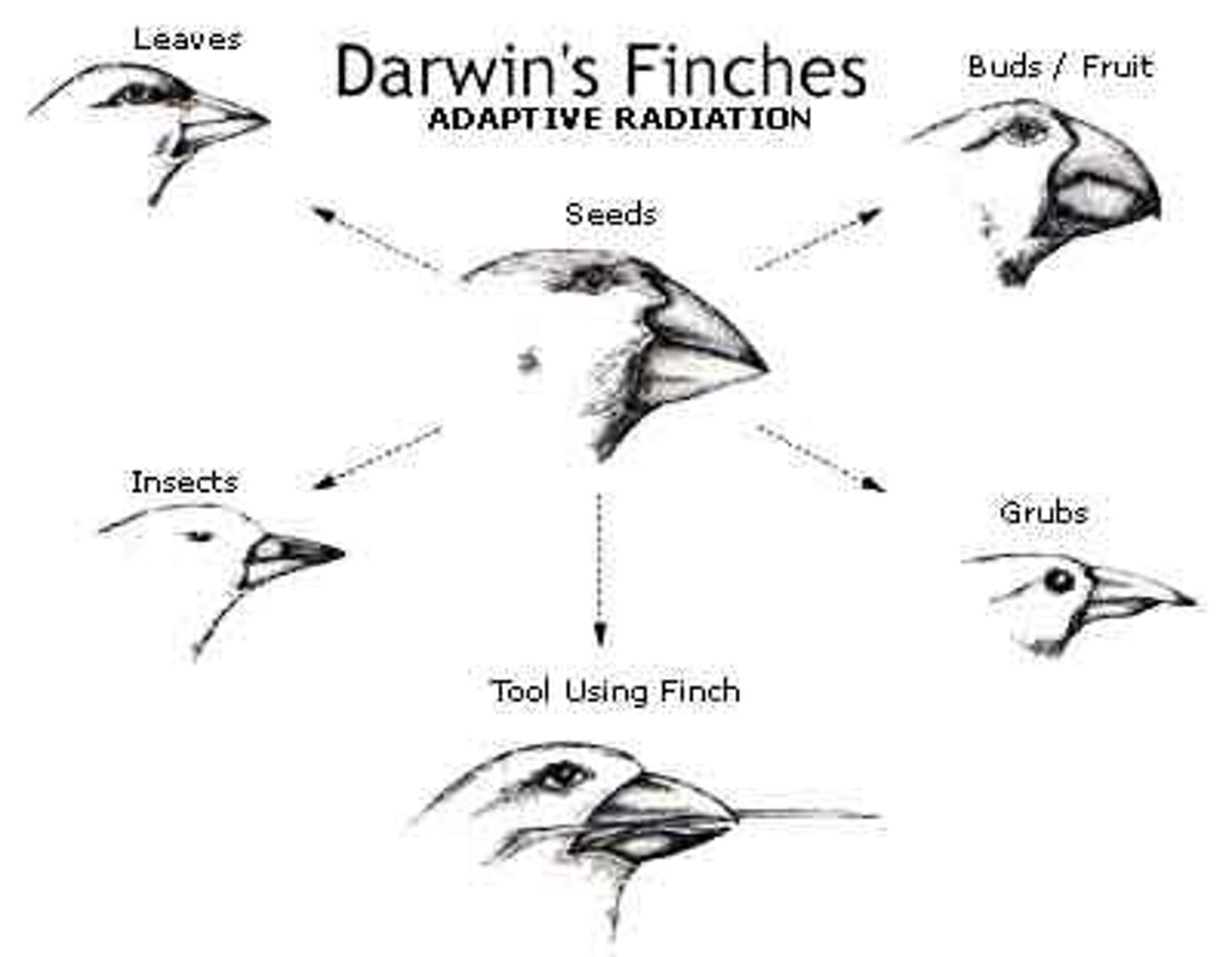
What is natural selection?
survival of the fittest
Describe the process of natural selection
- Populations are naturally varied due to random genetic mutations
- Some of these mutations provide a selective advantage
- These organisms survive and reproduce, passing on the successful genes
What does natural selection rely on?
Genetic diversity within a population
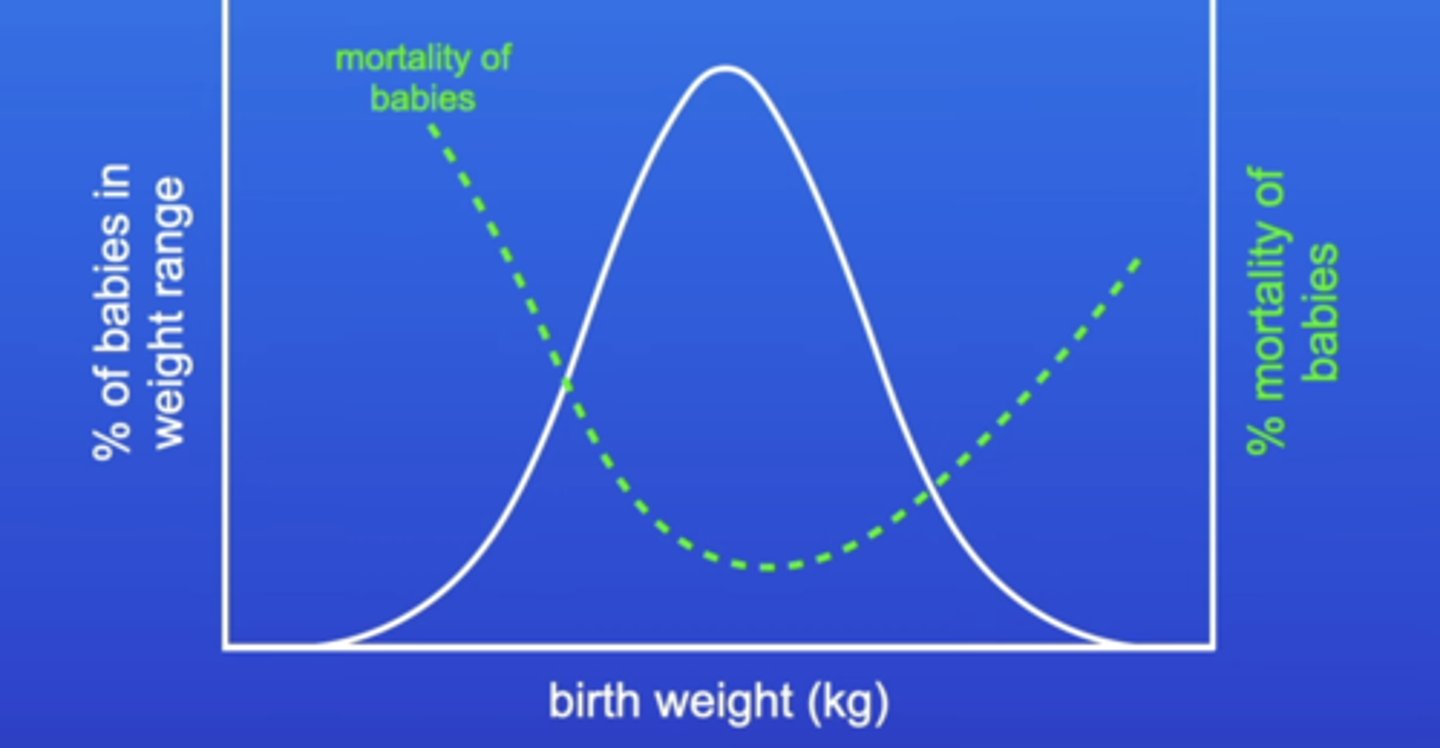
What is stabilising selection?
selection favouring average individuals
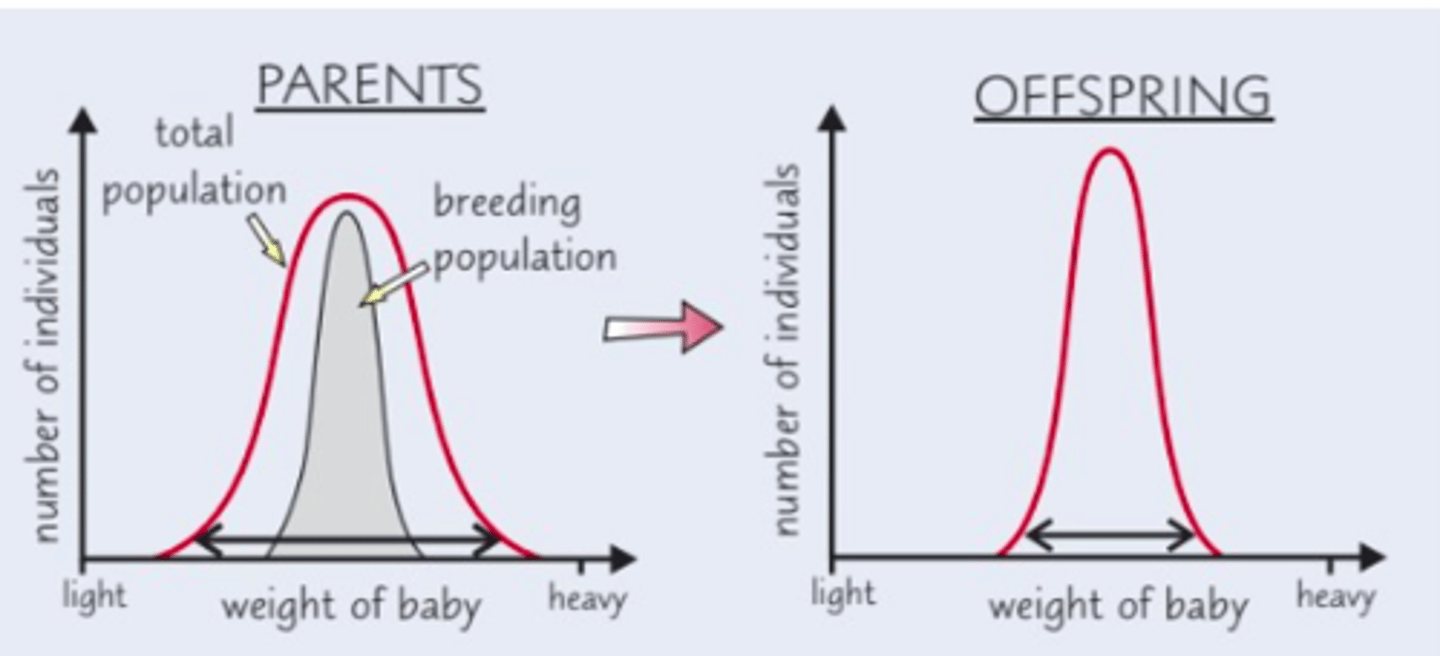
When does stabilising selection take place?
When environmental conditions aren't changing
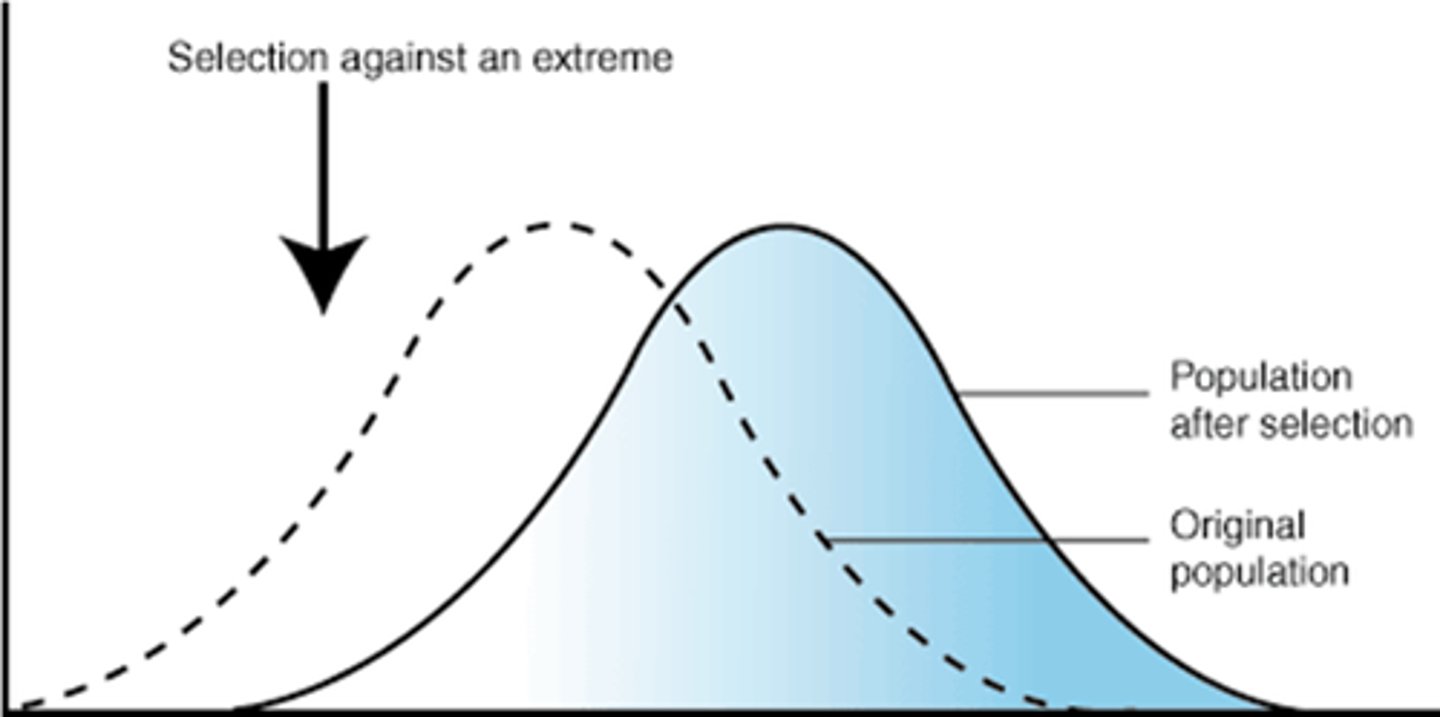
What is directional selection?
favors individuals at one end of the phenotypic range
What is an example of directional selection?
antibiotic resistance in bacteria