1.1 Chemical Elements and Biological Compounds.
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Name 4 inorganic ions important for life.
Magnesium, iron, calcium and phosphate.
What is a magnesium ion used for?
A constituent of chlorophyll, so needed for photosynthesis. Also strengthens bone.
What happens if a plant does not have magnesium in its soil?
Cannot make chlorophyll and so the leaves are yellow, a condition known as chlorosis.
What is an iron ion used for?
A constituent of haemoglobin, which transports oxygen in red blood cells.
What is a phosphate ion used for?
For making nucleotides (DNA, RNA and ATP) and also a constituent of phospholipids, found in biological membranes.
What is a calcium ion used for?
Important structural component of bones and teeth. Also in plant cell walls, providing strength.
Water is a dipole molecule. What does this mean?
It has a delta positive hydrogen end and a delta negative oxygen end.
What forms between adjacent water molecules?
Hydrogen bonds form between the H and the O of different water molecules.
7 properties of water
Metabolite
High specific heat capacity
High latent heat of vaporisation
Cohesion
High surface tension
Solid lower density than liquid
Water is transparent
What can dissolve in water?
ions and polar organic molecules.
What cannot dissolve in water?
Non-polar substances.
Why is water as a solvent important?
Allows dissolved substances to be transported in the body e.g. in the blood.
Give to ways water can be used as a metabolite?
Hydrolysis
Condensation
Water has a high specific heat capacity. What does this mean?
It takes a lot of heat energy to raise waters temperature due to the number of hydrogen bonds.
Why is a high specific heat capacity of water important for life on earth?
Promotes the thermal stability of oceans, limiting the temperature change This is important for organisms to be able to adapt and for life to evolve.
Why are water molecules cohesive?
Hydrogen bonds individually are weak, but there are many. So, the molecules stick together in a lattice.
Why is cohesion of water molecules important for life?
Allows columns of water to be drawn up the xylem vessels in plants.
What can be said about the density of solid water (ice)?
Has a lower density than the liquid form. This is because ice has an open, fixed lattice structure formed by the stabilisation of hydrogen bonds.
Why is the density of water important for life on earth?
It forms a habitat for polar animals in Arctic regions.
Water is transparent. Why is this important for life?
Lets aquatic plants to photosynthesise effectively as light is able to pass through water.
Water has a high latent heat of vaporisation. What does this mean?
A lot of heat energy needs to be absorbed to evaporate water.
Why is the high latent heat of vaporisation important?
Has a cooling effect on bodies due to sweating.
What is the general formula for a monosaccharide?
(CH2O)n
What are the two isomers of the hexose sugar glucose?
Alpha glucose and beta glucose.
What does a molecule of an alpha glucose?
The OH group on the carbon-1 atom is on the bottom.
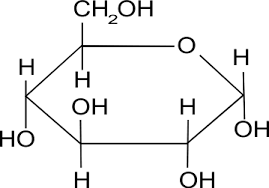
How is beta glucose different to alpha glucose?
The OH group on the carbon-1 atom is on the top, not on the bottom.
What type of reaction joins two monomers of glucose together? What is made? Name the bond formed?
Condensation. Maltose. Glycosidic.
Give 4 functions of monosaccharides?
Energy source for respiration - C-C and C-H bonds can be broken to release energy.
Building blocks for larger molecules e.g. glucose forms polysaccharides starch, glycogen, cellulose and chitin.
Intermediates in reactions, e.g. trios in respiration and photosynthesis.
Constituents of nucleotides e.g. ribose in RNA.
Name the component monosaccharides for the disaccharide maltose and state where it is found.
Glucose + glucose.
Found in germinating seeds.
Name the component monosaccharides for the disaccharide sucrose and state where it is found.
Glucose + fructose
Transport in phlegm of flowering plants.
Name the component monosaccharides for the disaccharide lactose and state where it is found.
Glucose + galactose
Found in mammilian milk.
What is the biochemical test for a non-reducing sugar like sucrose?
Add equal volumes of Benedict’s reagent and the solution being tested are heated for 5 mins between 70 and 90C.
What is the biochemical test for a non-reducing sugar like sucrose?
When the Benedict’s test fails. Add hydrochloric acid and an alkali to the sample and then do the test as normal.
Where is starch found?
Starch is food