Basic financial and economic concepts
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
business cycle
The natural rise and fall of economic activity over time, consisting of periods of expansion, peak, contraction, trough, and recovery.
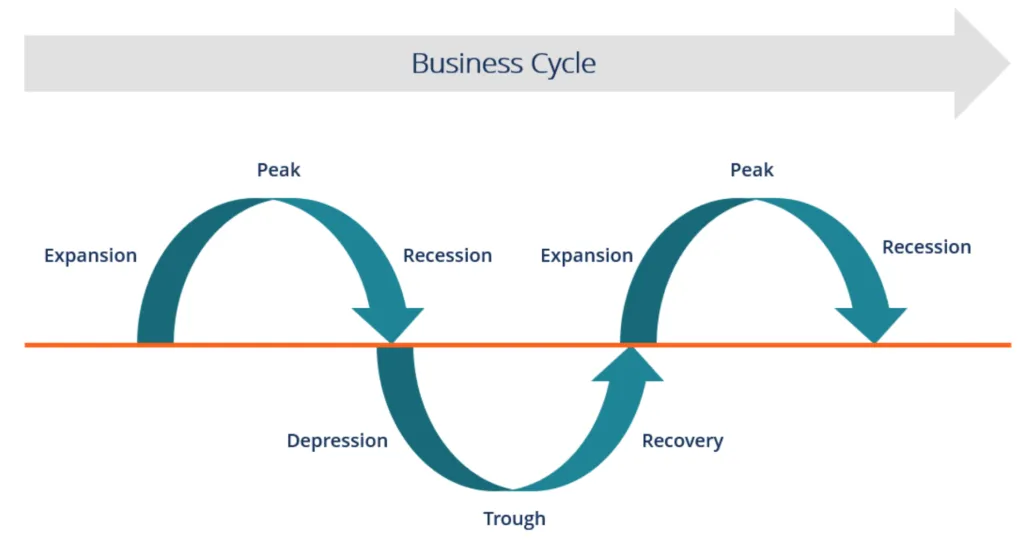
expansion
A phase in the business cycle when the economy grows, output increases, unemployment falls, and consumer spending rises.
recovery
A return to a better or normal state after a decline; in economics, the phase in the business cycle when an economy begins to grow again
peak
The highest point of economic activity in the business cycle, just before growth slows down.
contraction
A phase in the business cycle when economic activity slows, GDP falls, and unemployment rises.
trough
The lowest point of economic activity in the business cycle, marking the end of a contraction and the start of recovery.
housing bubble
A situation where house prices rise rapidly to unsustainable levels, often followed by a sharp fall.
mortgage
A loan taken from a bank or lender to buy property, usually repaid with interest over many years
(take out …, … loan, pay off ….)
tax cut
A reduction in the amount of tax that individuals or businesses must pay.
frictional unemployment
Temporary unemployment that occurs when people are between jobs or entering the workforce for the first time.
cyclical unemployment
Unemployment that rises during economic downturns or recessions and falls when the economy recovers.
structural unemployment
Long-term unemployment caused by fundamental changes in the economy, such as industries declining or new technologies replacing workers, requiring workforce different from the previous one.
seasonal unemployment
Unemployment that happens because certain jobs are only available during specific times of the year, e.g. certain agricultural jobs.