Gravitational Field Equations
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Kepler’s 3rd Law
\frac{GMm}{r^2}=\frac{mv^2}{r}
What is the symbol for the universal gravitational constant, and what is its value and SI unit?
G, 6.67 × 1011 NM2/kg2
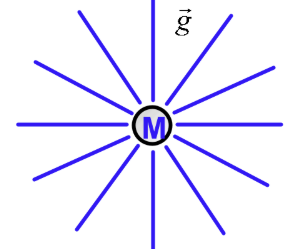
g is now being redefined from gravitational acceleration to the gravitational field - it is a vector field, as shown by the image.
Thus, gr = ___ = ___
Fg, GM / r2
W (weight) = ___ = ___
Fg or mg, GMm / r2

If you want to find the gravitational field (gr) of a uniform thin spherical shell, you use the equation:
gr = ____ for r\ge R
gr = ____ for r<R
-GM / r2, 0
Gauss’ Law for Gravity states that…
gr = ____ for r\ge R
gr = ____ for r<R
-GM / r2, 0
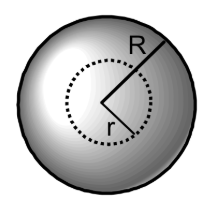
A solid sphere of radius R would have an infinite number of uniform thin spherical shells inscribed inside. Each shell has a gravitational field outside of it that depends only on its mass.
Thus, let’s say the mass within the sphere of radius r is defined as m.
The mass of the sphere of radius R is defined as M. The gravitational field at r is due solely to the mass within the smaller field.
What’s the equation for m?
m=\frac{Mr^3}{R^3}
The gravitational force (g) of a solid sphere:
gr = ____ for r\le R
gr = ____ for r\ge R
And then what happens when r = R?
-GMr / R3, -GM / r2
The two values for gr are equal for r = R.