Fundamental Cell and Molecular Bio Lab Practicum 1
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Total Magnification
Objective Lens + ocular lens= total magnification
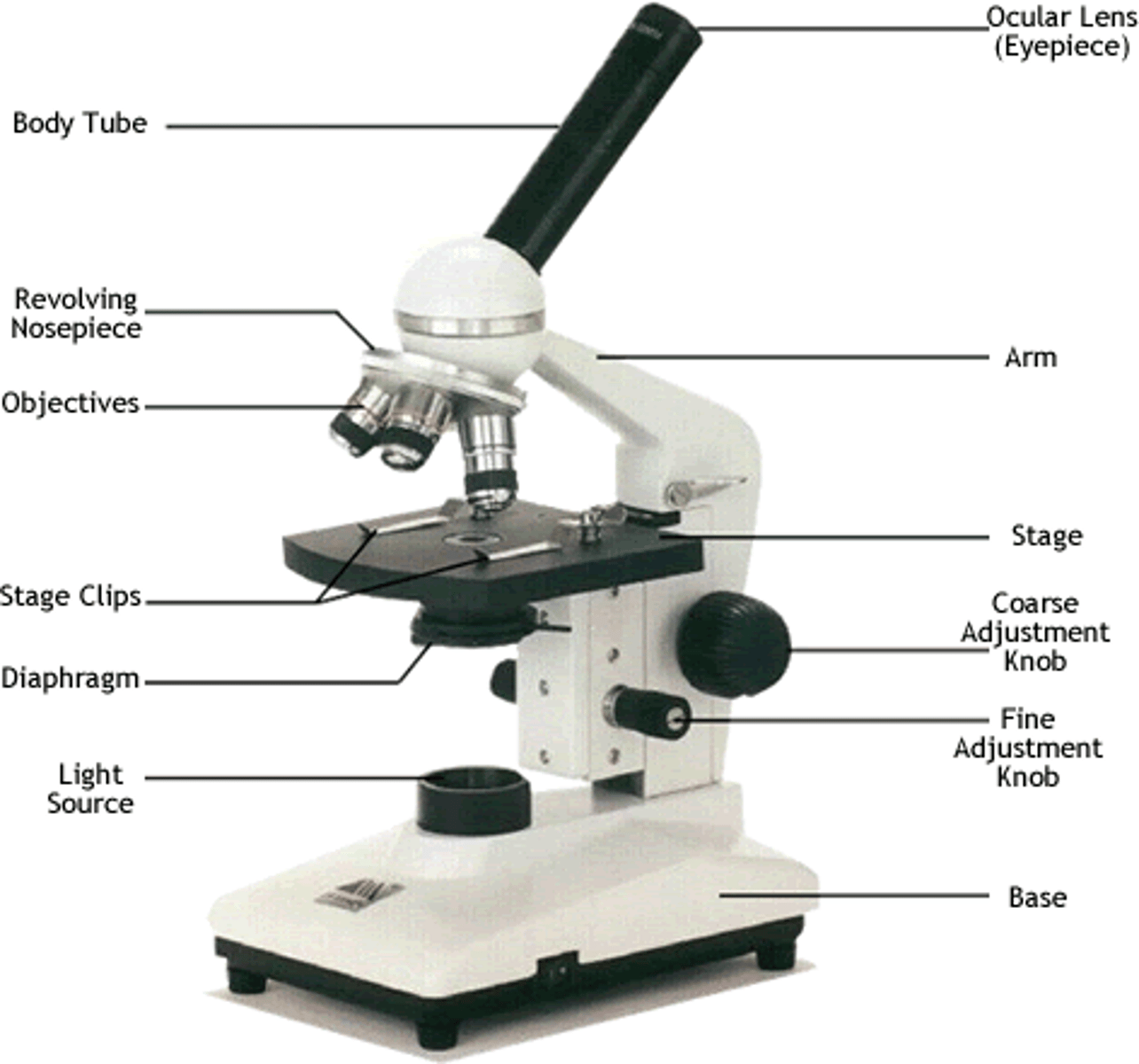
What does a Kim wipe clean?
ocular and objective lens
How to carry a microscope
One hand on base, other on arm (two hands at all times)
What lenses to use?
Coarse focus only at 40x, and fine focus knob on all of them
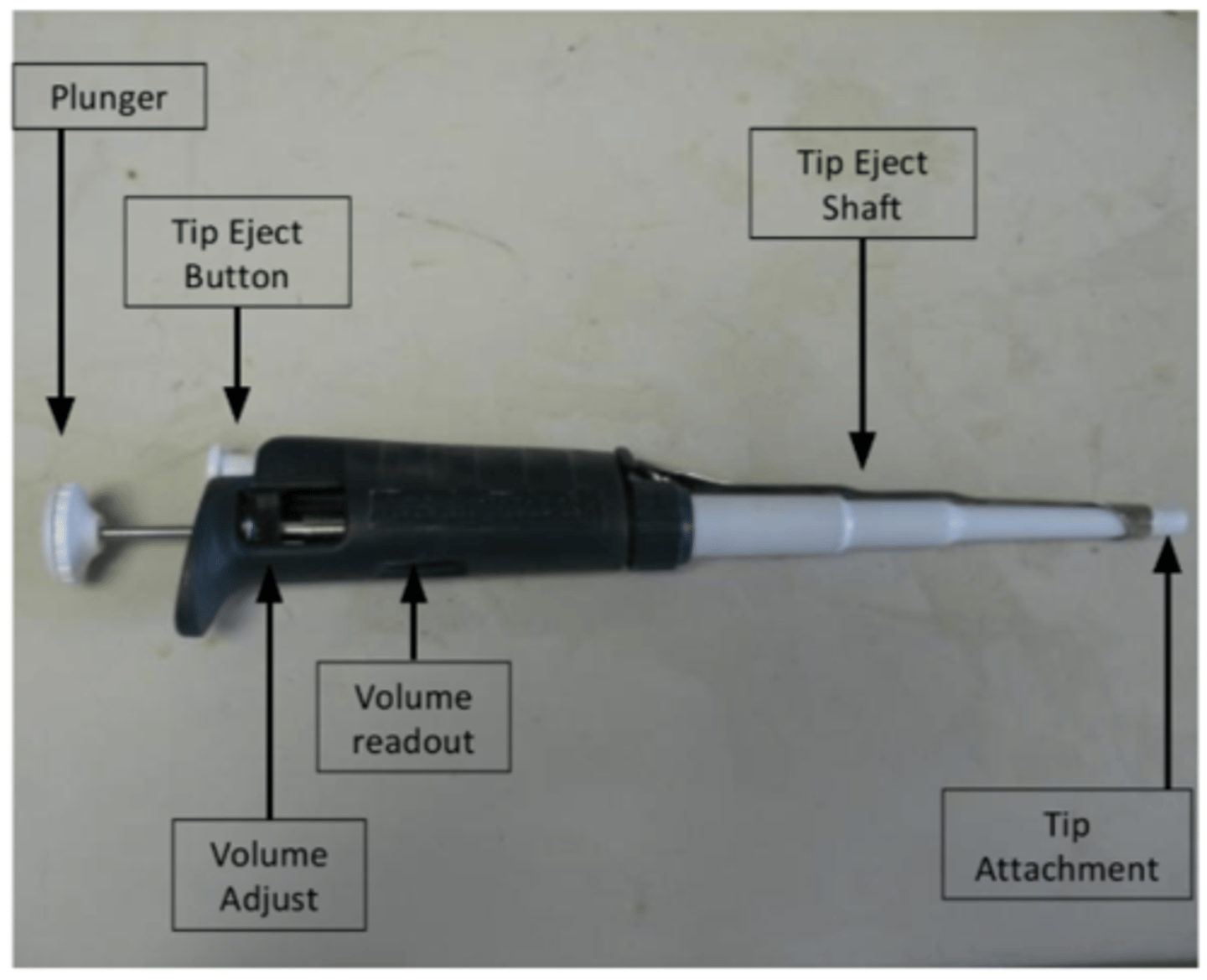
Micropipettes vs. Serological Pipettes
Micropipettes measure 1-1,000uL (Gilson and Fisherbrand pipetteman)
Serological Pipettes 1,-50mL
Size range of a microscope at scanning objective
At 40x, about 5mm
Average size of a yeast cell
3-5 micrometers
Highest power objective?
The oil immersion is the highest power objective (1000x) and oil is needed to help zoom in because it is so close
Successful serial dilutions
Each successive dilution is 1/2 the value of the previous well
What role does Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) play in DNA isolation?
SDS disrupts the lipid membrane and denature the proteins because of its polar and nonpolar ends, it lyses the cell
Role of phenol and chloroform in DNA isolation
they are protein solvents and will denature the proteins, phenol is only partially soluble so it forms a layer on the bottom with the proteins, lipids, cell lysate (While nucleic acids will be on the top layer in the aq phase)
Role of ethanol/salt in DNA isolation
Ethanol will concentrate the nucleic acid, and precipitate it turning it into a solid again
How is the RNA separated from the DNA?
The RNAse digests the RNA concentrating the DNA
How UV absorbance at 260nm and 280nm is used to determine DNA purity and the significance of the 260/280 ratio.
absorbance of DNA is at 260nm, and OD260/OD280 should equal 1.8, 260 is the peak
Purpose and role of Centrifuge
Centrifuge uses density and gravity to separate cellular components, it spins super fast causing the heavier and more dense materials to go to the bottom and creates layers
Purpose of a fume hood
Fume hoods prevent hazardous chemicals from mixing with the general room air.
Understanding how colchicine disrupts cell division
Colchicine inhibits the polymerization of microtubules which stops the spindle formation which draws the chromosomes in cell division
The effects of trypsin on breaking down cell structures in chromosome analysis.
Trypsin digests the proteins and they are washed away by the chilled PBS
The importance of using testicular tissue in karyotyping
Due to it's high rate of cellular division, when cells are dividing the chromosomes are most visible, additionally meiosis is happening at a high rate in the formation of gametes which are necessary for zygote formation
Techniques for preparing chromosome spreads
Thermal lysing: warming the slides, and mechanical lysing is dropping the solution from high above to break open the cellular components
How are chromosomes identified
length and banding patterns
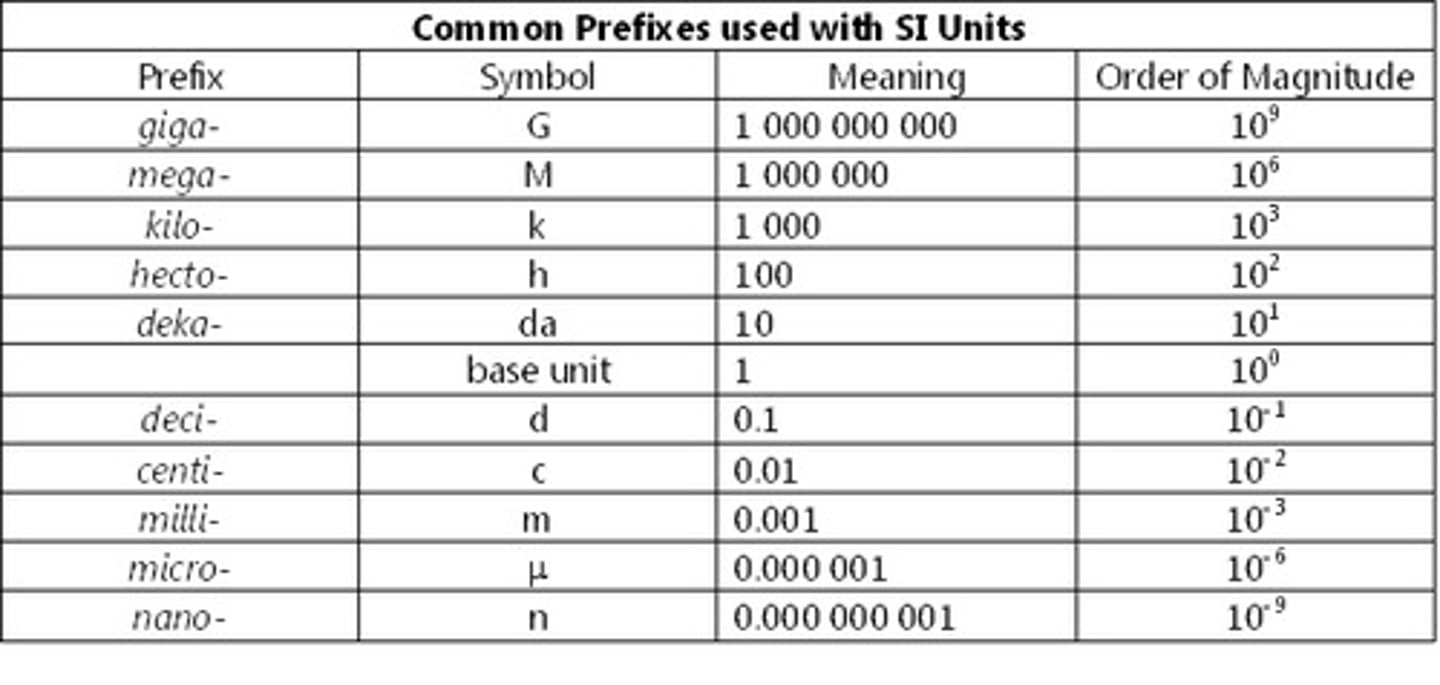
Conversion between units
micro (10^-6) in comparison to L, milliliters (10^-3) in comparison to L
Volume of a cylinder
V=πr²h
Properties of phospholipid bilayer and what can pass through it
polar heads (like water, usually charged), nonpolar tails, double membrane, only small nonpolar molecules can pass through easily (and through simple diffusion) (C, O), H2O through concentration gradient, through facilitated diffusion larger molecules like glucose, charged ions, and large polar molecules can pass through
Osmotic stages
Isotonic (equal levels of solute and water on each side), Hypotonic (low amounts of solute outside membrane so water comes into the cell making it burst), hypertonic (higher solute outside, water leaves making it shrivel )
Independent vs Dependent Variable
An independent variable is the variable that is changed or controlled in a scientific experiment, the dependent variable is the one effected and observed (dependent on x, independent on y), x is usually time
Diameter of scanning objective
40x has about a 5mm field of view
Average size of a yeast cell
3-5micrometers
Use of oil immersion objective
Oil immersion is the highest power objective at 1000x, oil helps to view things clearly and zoom in
How are we able to predict the absorbance values based in dilution factors?
The more dye, the higher the absorbance value, the graph should be a straight line because the serial dilutions should be very exact
How to make sense of the DNA 260/280 ratio
DNA's absorbance is 260nm while proteins is at 280, basically DNA is measured at 260 so a high amount should be at the 260 value, and we don't want a high amount at 280 because then that would indicate that there is a significant amount of proteins being measured (there still will be some because they can't fully be separated, but we test the DNA purity by dividing OD260/OD280 to get 1.8)
What molecule is amphipathic when extracting the DNA and what is its purpose?
The SDS is amphipathic so it has both a polar and non polar side basically taking apart the phospholipid bilayer of the cell (like dissolves like)
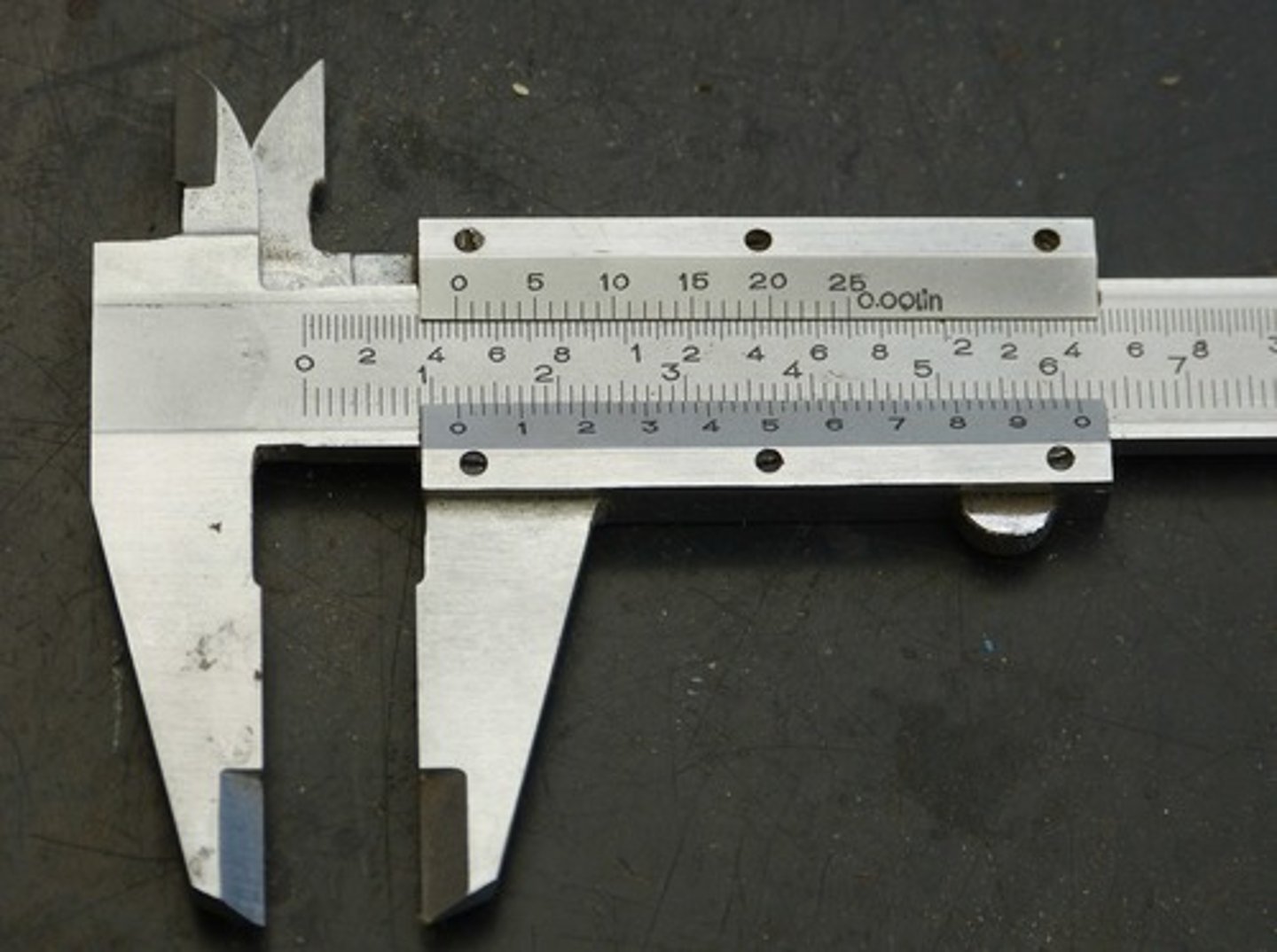
Read this caliper measurement
1.21

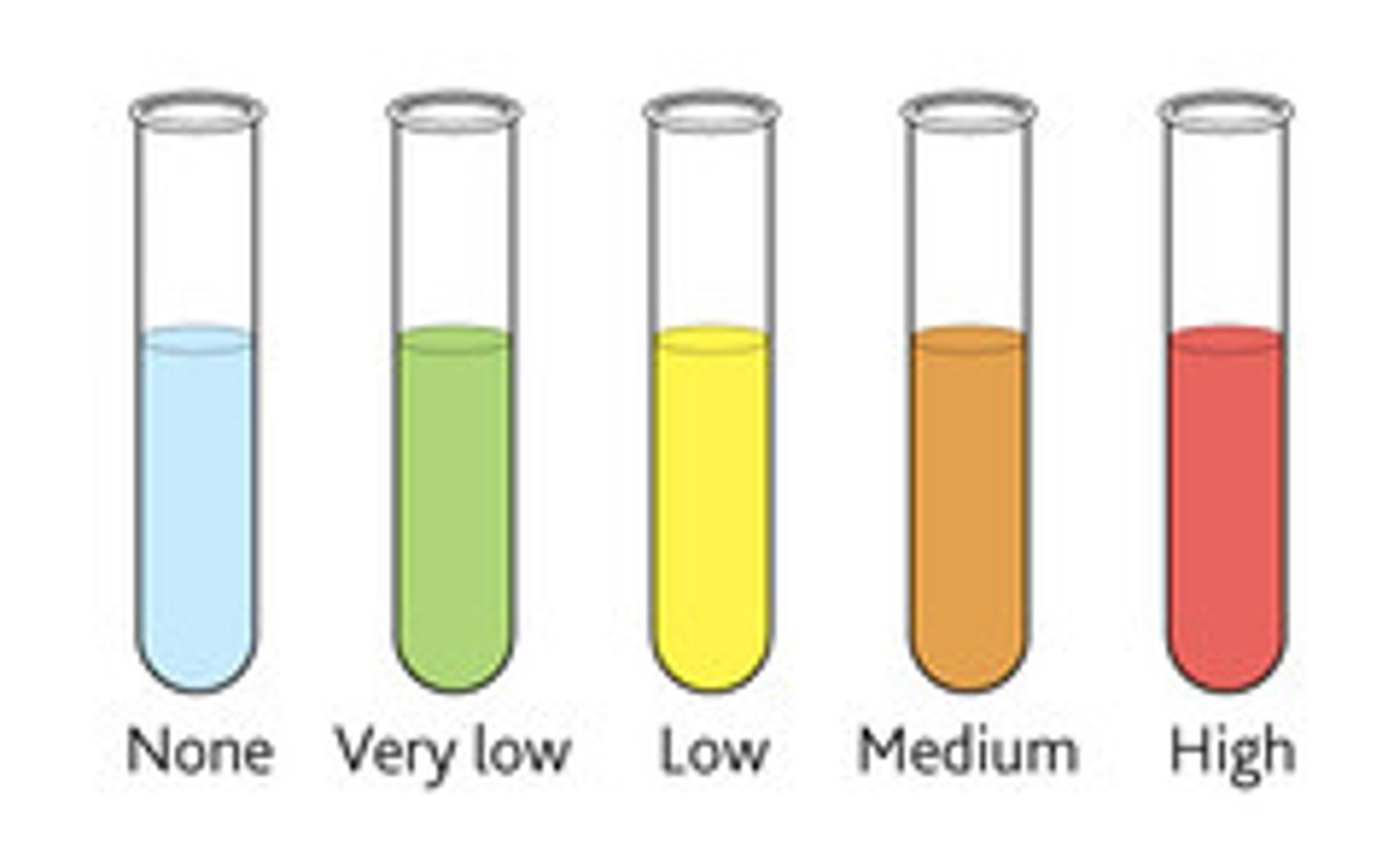
The principles of Benedict's test for detecting glucose and interpreting results
Blue (no glucose) red (high glucose)

The use of iodine for detecting starch and how to enhance faint results
Dark blue is positive for starch and yellow is negative
