Wk 10 - Respiratory pt1 + 2 (Exam and Coughing)
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
History questions
SHEDC
S - _______________
H- _______________
E - _______________
D - _______________
C - _______________
signalment; health; environment; diet; complaint
Hands-on exam
airway _______________
sinus/thoracic _______________
_______________ palpation
auscultation
bronchovesicular vs adventitial sounds
don’t forget to _______________ the animal
patency; percussion; laryngeal/tracheal; rest
Abnormal resp sounds
abnormal UPPER airway sounds
_______________
_______________
_______________
stertor; stridor; tracheal rattle
Abnormal resp sounds
abnormal LOWER airway sounds
_______________
_______________
_______________
absent lung sounds
crackles; wheezes; pleural friction rubs
Abnormal LOWER airway sounds
absent lung sounds
dorsally = possible _______________
ventrally = possible _______________
pneumothorax; pleural effusion
Rebreathing exam
encourages _______________ through rebreathing of expired CO2
enhances detection of abnormal lung sounds
Goal = _______________
deep breaths; localize resp disease
Rebreathing exams
Focus on:
how well patient tolerated exam
normal = deeper breaths but NO _______________ and NO _______________
quality of lung sounds
normal = _______________
how well/quickly patient recovered
normal = _______________ deep breaths after removal of bag with NO _______________
distress; cough; clear (bronchovescicular); 3-5
Rebreathing exam - tips
don’t _______________
let horse get used to bag
keep bag AWAY from _______________
continue auscultating _______________
rush in; nostrils; after bag is removed (will take deeper breaths)
Resp diagnostics
bloodwork (CBC, Chem)
upper airway sampling
_______________ swab
_______________ wash or swab (NPW/NPS)
_______________ lavage
imaging
rads, US, endoscopy
lower airway sampling
_______________ lavage
_______________ wash
fluid/tissue sampling
thoracocentesis
lung Bx, FNA, biopsy mass, etc
nasal; nasopharyngeal; guttoral pouch; bronchoalveolar; trans tracheal
Bloodwork
CBC
may be non-specific
Chem
_______________
blood gas
venous
_______________ assessment of pulmonary function
PvO2, PvCO2, SvO2, pH, HCO3-, lactate
arterial
_______________ assessment of pulmonary function
PaO2, PaCO2, SvO2, FIO2, A-a gradient, pH, HCO3-, lactate
pathogen-specific testing
serum amyloid A (SAA); indirect; direct
What upper airway sampling method is the most sensitive?
nasopharyngeal wash (covers more surface area)
Upper airway sampling
_______________ = enemy of _______________ and _______________
debris; PCR; culture
Upper airway sampling
tips
_______________ swabs preferred over _______________
wipe outer nares of any _______________ before sampling
aim “_______________” in nostril
if grossly dirty (brown), get a new sample
synthetic; cotton; debris; central and ventral
Thoracic US
most field vets wont be able to take rads
normal lung
filled with air → _______________
can only see as far as the _______________ when scanning healthy lungs
can “see” into _______________ tissue (i.e. _______________ lung)
dirty shadow; pleural surface; non-aerated; consolidated
Thoracic US
helpful for _______________ lung disease
_______________ lung disease
_______________ disease
diffuse; peripheral; pleural
Thoracic US Exam
typically work caudal to cranial and scan dorsal to ventral in each rib space
_______________ artifacts = _______________
sheets or coalescing = suggestive of _______________
comet tail; pleural irregularities; pulmonary edema
Thoracic rads
portable/field machine for ______________ ONLY
in-house generator needed for ______________
foals/minis; adults
What lung is usually affected by resp infection?
right ventral lung
Endoscopy
______________ scope used for UPPER airway
______________ scope used to see past ______________
1m; 1.5m; tracheal bifurcation
Lower airway sampling
Bronchoalveolar lavage
procedure: ______________ passed up nostrils to trachea
trans tracheal wash
procedure: incision made over ______________ trachea, ______________ inserted, catheter passed to ______________
tube; mid ventral; trocar; thoracic inlet
Lower airway sampling
BAL
wedges in bronchus
______________ml saline injected and aspirated
______________ procedure
TTW
______________ml of saline injected and aspirated
______________ procedure
250-300; non-sterile; 15-30; sterile
Lower airway sampling
BAL
lab submissions
______________
______________
TTW
lab submissions
______________
______________ (exception = ______________)
cytology; EHV-5 PCR;
cytology AND culture; organism-specific PCR; EHV-5
Lower airway sampling
BAL
primary disease rule out:
______________
TTW
primary disease rule out:
______________
equine asthma; bacT pneumonia
T/F: You can do a trans tracheal wash through an endoscope
True
What is a normal neutrophil count for trans tracheal wash?
<5%
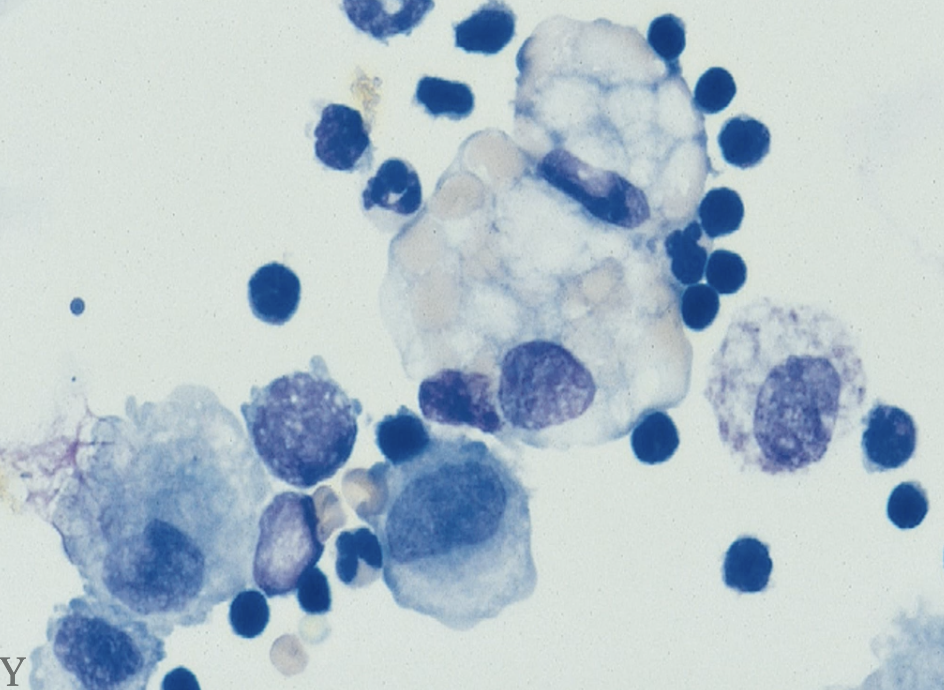
What do you think this horse has?
exercise induced pulmonary hemorrhage (EPH - macrophages + RBC)
What do you think this horse has?
pleuropneumonia (fibrin present; ALWAYS do TTW)
Tissue sampling
______________ = more commonly done
Indicated for:
______________
______________
lung biopsy; atypical interstitial pneumonia; superficial pulmonary masses
Tissue sampling
Indicated for:
atypical interstitial pneumonias
______________, ______________, ______________
superficial pulmonary masses
EMPF (equine multinodular pulmonary fibrosis); silicosis; toxins
Tissue sampling
primary risks
______________
______________
______________
hemorrhage; pneumothorax; sudden death
What triggers a cough:
mechanical
tracheal ______________
______________
______________ accumulation
inhaled particles
______________ airway compression
compression; bronchoconstriction; mucous; intra or extramural
What triggers a cough:
mechanical
intra or extramural airway compression
______________
decreased pulmonary ______________ (______________ or ______________)
mass; compliance; fibrosis; pleural effusion
What triggers a cough:
chemical
inert dust:
irritant ______________
______________
biological mediators
______________
______________
gases; carbon; histamine; prostaglandin
What triggers a cough:
others
exposure to ______________ or ______________
infectious diseases
______________
cold; hot air; epithelial sloughing
Where can a cough be localized to:
nasal passages
______________
______________
pharynx
trachea
______________
______________
sinus; guttoral pouch; bronchioles; alveoli
Coughing - Diagnostics
Bloodwork
CBC
blood gas
serology
______________
______________
______________
PCR
blood cultures
Strep equi equi; Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis; C. immitis (Coccidioidomycosis)
Coughing - diagnostics
imaging
US
______________
______________
______________
rads
______________
______________
______________
endoscopy
guttoral pouch
upper and lower airway
cardiac; thoracic; throatlatch/SMLN; skull; neck; thorax
Coughing - diagnostics
airway sampling
nasal swab
______________
______________
nasopharyngeal wash/swab
______________
______________
BAL
______________
TTW
______________
______________
culture; PCR;
culture; PCR;
cytology;
cytology; culture
Coughing - diagnostics
thoracocentesis
______________
______________
lung biopsy
histopath
______________
______________
cytology; culture; PCR; culture
Upper vs lower airway coughing
Upper - CS
______________
______________
airflow from ______________
unilateral nasal discharge; stridor; only 1 nostril
Upper vs lower airway coughing
lower - CS
______________
______________
______________
______________
pleurodynia; crackles; wheezes; pleural friction rub
Baseline auscultation is often ______________ for detecting lung pathology
how can we improve this?
______________
consider signalment, timing/quality, PE to help localize
insensitive; rebreathing exam
Infectious cough
PE
______________
______________ nasal discharge
______________
run a ______________
FEVER; purulent; enlarged SMLN (submandibular LN); CBC
What is the first thing you should do if you suspect a horse has an infectious cough?
ISOLATE (don’t wait)
Cough - Workup
age matters - Ex: coughing TB gelding
3m
______________
3yr
if healthy: ______________
if sick: ______________
15yr
______________
rhodococus equi pneumonia;
lymphoid pharyngitis; shipping fever;
equine asthma
Lymphoid pharyngitis
common cause of cough in ______________ horses
pathophysio
______________ secondary to
______________ resp diseases
______________
1-3yr (young); lymphoid hyperplasia; infectious (often viral); local irritant
Lymphoid pharyngitis
2 forms
______________
will also have ______________
______________
acute; nasal discharge; chronic
Lymphoid pharyngitis
PE
usually look ______________
Diagnostics
______________
______________
healthy; upper resp endoscopy; nasopharyngeal swab/wash
Lymphoid pharyngitis - Tx
mostly ______________
± ______________
± ______________
± ______________
symptomatic; systemic anti-inflam; topical anti-inflam; topical Abx
Equine (pleuro) pneumonia
aka “______________”
rare, spontaneous disease
occurs in ______________ horses
usually requires 1 or more ______________ and/or breakdown in ______________ mechanisms
shipping fever; adult; risk factors; protective
Equine (pleuro) pneumonia
risk factors
______________
______________
______________
poor ______________
______________
______________
recent/current ______________ infection
travel; exercise (strenuous); stress; ventilation; GA; choke; viral URT
Equine (pleuro) pneumonia
risk factors
travel
______________
______________
strenuous exercise
esp in ______________
long distances; head elevated; young TB racehorses
Equine (pleuro) pneumonia
protective mechanisms
______________
______________
______________
______________
COUGH; mucociliary escalator; gravity; local immune cells
Equine (pleuro) pneumonia
pathogens involved
______________ / ______________ / ______________ bacT
often ______________
commensal; opportunistic; environmental; polymicrobial
Equine (pleuro) pneumonia
most common pathogen = ______________
others:
______________ (Actinobacillus, Pasteurella, E. coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, etc)
______________ (Bacteroides fragilis, Fusobacterium, Peptostreptococcus, Clostridium)
Strep equi zooepidemicus (G+); G- aerobes; anaerobes
Equine (pleuro) pneumonia
CS
fever, lethargy, cough
______________
______________
______________
tachypnea; nasal discharge; crackles or wheezes
Equine (pleuro) pneumonia
signs suggestive of this
______________
______________
______________ on the thorax above which lung sounds can be heard
pleurodynia; pleural friction rub; horizontal line
Equine (pleuro) pneumonia - Dx
if overtly abnormal lung sounds, DO NOT do a ______________
CBC
mild to severe ______________
increased ______________
rads or US first?: ______________
BAL or TTW?: ______________
rebreathing exam; inc WBC; SAA; US; TTW
Why do you want to do a TTW instead of a BAL for a patient with (pleuro) pneumonia?
less fluid given and can send for culture
When would you want to do a thoracocentesis in a patient with (pleuro) pneumonia?
evidence of pleural fluid on US
Pleuropneumonia - Progression
starts as ______________
left untreated (or treated inappropriately) → pleura becomes ______________ → ______________
bronchopneumonia; inflamed; pleuropneumonia
Pleuropneumonia - Progression
______________ stage
______________ stage
______________ stage
exudative; fibrinopurulent; organization
Pleuropneumonia - Progression
exudative stage
pleural fluid is initially ______________
fibrinopurulent stage
neut/bacT → ______________
organization stage
______________ migrate and produce the ______________ that encases the lung
sterile; fibrin deposit; fibroblasts; pleural peel
(Pleuro) pneumonia - Tx
______________
______________
if significant pleural fluid present → ______________
supportive care
ABx; anti-inflammatories; DRAIN IT
(pleuro) pneunmonia - Tx
ABx
NEVER give ______________
if sedated with ______________, DO NOT give ______________
IV doxycycline; a2 agonist; IV TMS
Foal cough - DDx
<30d old
______________
______________
1-6 months
______________
dysphagia; pneumonia; Rhodococcus equi pneumonia
Foal cough - DDx
<30d old
dysphagia
congenital upper airway defect
______________
______________
pneumonia
in utero infection (______________ or ______________)
secondary to ______________
______________ spread
pharyngeal paresis; HIE/NMS; EHV-1; EAV; aspiration; hematogenous
Rhodococcus equi
severe problem in breeding farms
bacT classification
Gram ______________
______________ bacT
grows in ______________
virulence - associated ______________
positive cocci; intracellular; macrophages; protein A (VapA)
Rhodococcus equi
route of infection: ______________
shed in ______________ of adults and foals
mostly affects foals
______________ and ______________ diseases
inhaled; feces; pulmonary; extra-pulmonary
Rhodococcus equi - Manifestations
______________ = most common form
causes ______________ disease
will see ______________ with ______________
pulmonary; subclinical; suppurative bronchopneumonia; absessation
Rhodococcus equi - manifestations
extrapulmonary
______________
ulcerative ______________
______________
______________
______________
abdominal abscess; enterocolitis/thyphlitis; osteomyelitis; polysynovitis; uveitis
When to suspect R. equi pneumonia
patient is a ______________
CS of ______________ disease
cytologic evidence of ______________
evidence of ______________ on imaging (rads or US)
foal; lower resp; airway inflammation; bronchopneumonia
How to test for R. equi:
______________
± vapA PCR
______________
± vapA PCR
______________
± vapA PCR
______________
nasal swab culture; TTW culture; fecal culture; vapA PCR
R. equi - when to treat
clinical cases with appropriate diagnostics performed
Treating subclinical foals based on:
evidence of inflammation on ______________
NOT very sensitive
increased ______________ or ______________
NOT sensitive or specific
______________ of lung on US
based on amount
CBC; fibrinogen; SAA; consolidation
What cumulative amount of consolidation do you need to see on US to treat subclinical R. equi?
>8-10cm
R. equi - Tx
classic Tx
______________ (______________, ______________ or ______________) + ______________
macrolide; azithromycin; clarithromycin; erythromycin; rifampin
R. equi - Tx
side effects
macrolide - ______________ (esp for mare), ______________
rifampin - ______________
colitis; hyperthermia; urine discoloration
R. equi - prevention
NO ______________
regular screening of foals on ______________ farms
decrease mare/foal stocking density??
admin ______________ on ______________ farms**
Vx; endemic; R. equi plasma; endemic