MEDICAL IMAGING TEST 2
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GOOOOOOOOOD IDK WHAT IM GONNA DOOOOOOO
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
3 Major Domains of Learning
Cognitive, Psychomotor, Affective
Cognitive Learning
includes behaviors requiring various levels of thought : knowledge, understanding, reason, judgement
Psychomotor Learning
includes behaviors involving physical interactions, neuromuscular manipulations, and coordination
Affective Learning
includes behaviors required guided by feelings and emotions that are influenced by an individuals interests, attitudes, values, beliefs
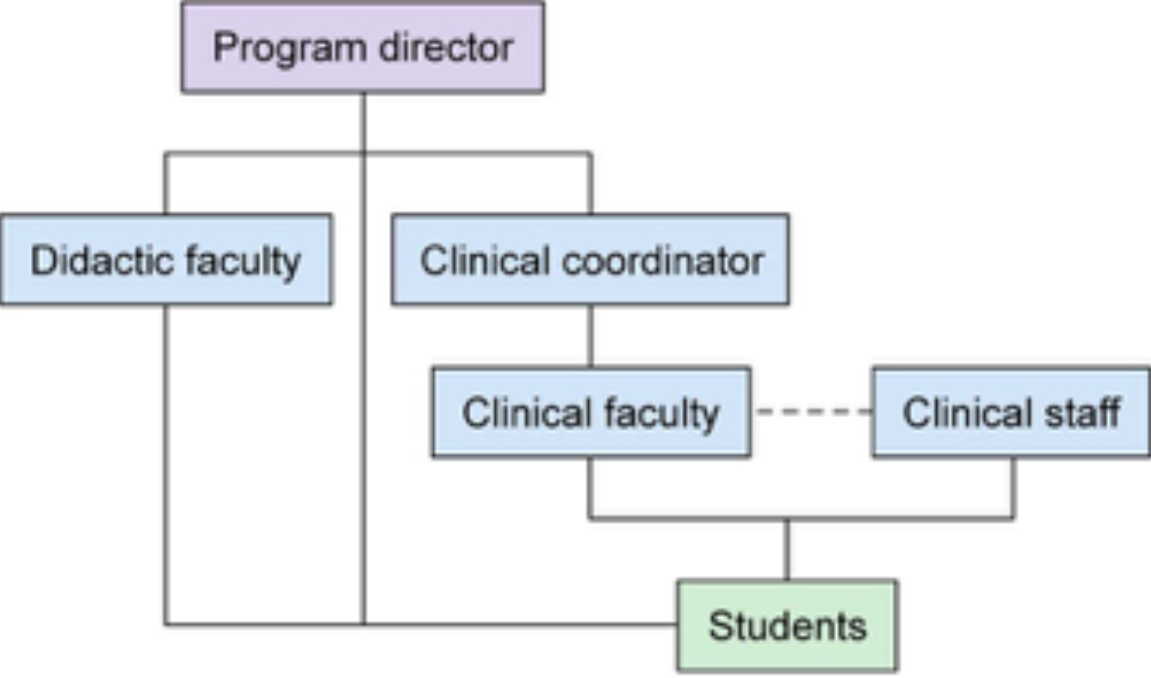
Program Officials
Program Director, Clinical Coordinator, Clinical Instructor
Program Director
works in organizing, administering, and assessing the radiography program
Clinical Coordinator
works closely with the program director in ensuring program effectiveness
Clinical Instructor
works directly with the student in clinical setting
Phases of Clinical Learning
Phase 1- Extensive Observation
Phase 2- Assistance
Phase 3- Performance
Extensive Observation
gain confidence, integrate cognitive, psychomotor, and affective behaviors
Assistance
students aid and support, hands on experience, take an increasingly more active part in the procedure
Performance
when a student is confident, they will perform the entire procedure independently with supervision. Demonstrate necessary tasks at the required skill level
Direct Supervision
Qualified Radiographers are required to
Review the request for examination in relation to the students achievement
Evaluate the condition of the patient in relation to the students knowledge
Be physically present during the conduct of the procedure
Review and approve the procedure and image
Indirect Supervision
Qualified Radiographers are required to
Reviews, evaluates, and approves the procedure, and is immediately available to assist students regardless of the level of student knowledge
Mission Statement
the defining and guiding force that outlines the reason for existence
Organizational Chart
how managers and employees carry out their functions within the institution in an organized and logical manner
Board of Directors/ Governing Board
authorized by law to operate a hospital
Chief Executive (CEO)
the president, defines how hospital is maintained or conducted
Medical Staff
formal organized structure of physicians within hospitals with authorized privileges, by laws, elected officers, committees.
Administrative Director of Radiology
Typically reports directly to upper hospital administration
Requires strong business management skills, not necessarily a radiologic technician
Works closely with medical director of radiology
Medical Director
Typically a physician
Responsible for overseeing the quality of patient care
Approves clinical protocols, reviewing policies and procedures, recommends improvements to quality and safety of care, equipment purchases, and technology acquisitions
Works closely with administrative director
May also serve as department chair
Radiation Safety Officer (RSO)
responsible for the safe operation and use of radiation and radioactive materials, as well as implementing the radiation protection program. Usually a physicist or a radiologist.
Radiology Administration
Varies depending on size and scope
Often consists of sub departments
Requires support services
Led by administrative director
Primary Functions :
planning, organizing, facilitating, staffing, directing, controlling, and coordinating
External Agencies
The Joint Commission (TJC), Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), HIPAA
Internal Agencies
Safety Committee, Infection Control Officer, Radiation Safety Committee (RSC), Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee, Risk Management and Corporate Compliance, Picture Archive and Communications Systems (PACS)
The Joint Commission (TJC)
Regulates the quality and safety of care provided to patients and the way health care organization is supervised and operated
Nuclear Regulatory Commission
For control of equipment and technologists. NRC conducts inspections and levy fines for noncompliance with regulations that vary from state to state.
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
Federal agency that establishes standards for safety in the workplace
Health insurance portability and accountability act of 1996 (HIPAA)
Health care information cannot be obtained or shared without the permission of the individual
Establishes a set of nationalists standards for the protection of certain personal health information
Developed to increase public trust, holds providers and payers accountable
Increase data integrity
Safety Committee
required by TJC to establish a safety committee that directs education of employees on safety policies and procedures, and safe operation of the facility for the patients and employees
Infection Control Officer
regulates infection control policies and procedures
Radiation Safety Committee (RSC)
required by NRC and TJC. RSC regulates hospital activities for radiation safety and nuclear medicine activities. They also define safe handling of radioactive materials and policies for patient or staff exposed to radiation
Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee
required committee of the hospital responsible for reviewing drugs and their use in the hospital
Risk Management and Corporate Compliance
Manage and Control the amount of legal and financial risk and ensure that the hospital continues to remain in good staning with its reputation
Picture Archive and Communications Systems (PACS)
digital alternative to film-screen imaging devices in the late 1990’s
Image Production
Basic mechanism of x-ray production. A beam of x-rays traverses a patient, and is partially absorbed in the process, the remaining x-rays are absorbed by the IR (Image Receptor)
Image Receptor (IR)
devices that capture and convert radiation or light into a visible image
intercepts the x-ray photons that are able to exit the patient
Types of image receptors
Different RI systems, Film-screen systems, Computed Radiography (CR)- cassette based system, Digital Radiography (DR)- cassette-less system, Fluoroscopic imaging systems
Digital Radiography (DR)
No cassette
No film
No imaging plate
No reader
Nothing to carry
Can be used again
Image displays instantly on a monitor
Digital Capture (DR)
Devices that convert incident x-ray energy directly into an electrical signal, which then sends the electrical signal to the computer for processing and viewing
Indirect Capture DR
devices that absorb x-rays and then convert them into light; the light is then detected by a TFT: which is then converted into an electrical signal to the computer for processing and viewing