Biopsychology Uark
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Josiah
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Words to describe planes of the brain
Sagittal, Coronal, Axial
Words to describe position in anatomy
Inferior, Superior (ventral, dorsal), medial, lateral, posterior, anterior
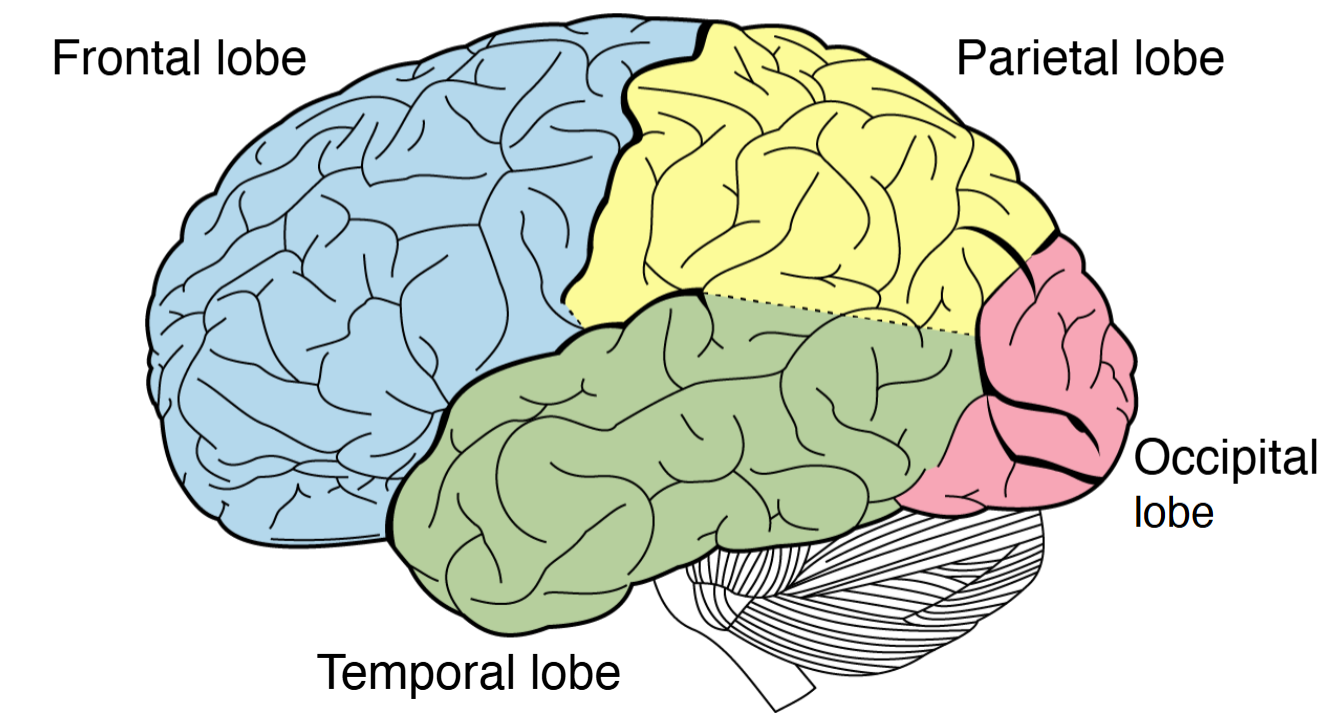
Lobes of the brain
Frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital
Gyrus (gyri for plural)
folds of the brain
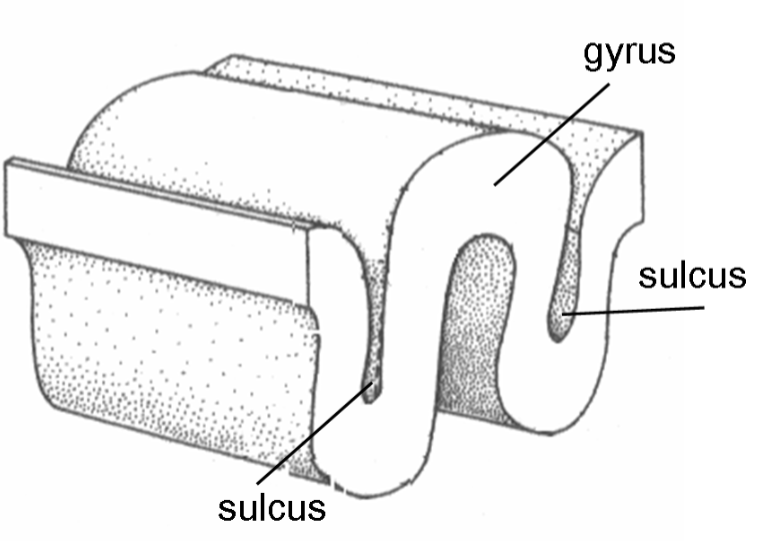
Sulcus (sulci for plural):
gaps between the folds
Gray matter:
outer layer of neurons ("cortex" = Latin for "bark")
White matter:
myelinated axons and support cells ("glia" = Latin for "glue")
Meninges:
layers of tissue wrapped around gray matter. Pia mater, Arachnoid, Dura Mater
CerebroSpinal Fluid (CSF)
• Clear liquid between the arachnoid layer and pia mater
• Created by the choroid plexus in the ventricles
• Provides nutrients, removes waste, cushions brain
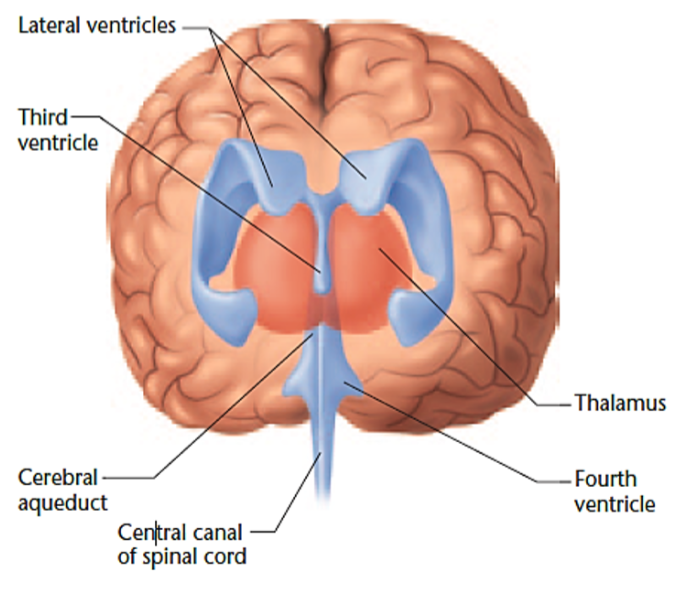
Ventricular system
CSF flows between the 4 ventricles in the brain and down the
spinal cord
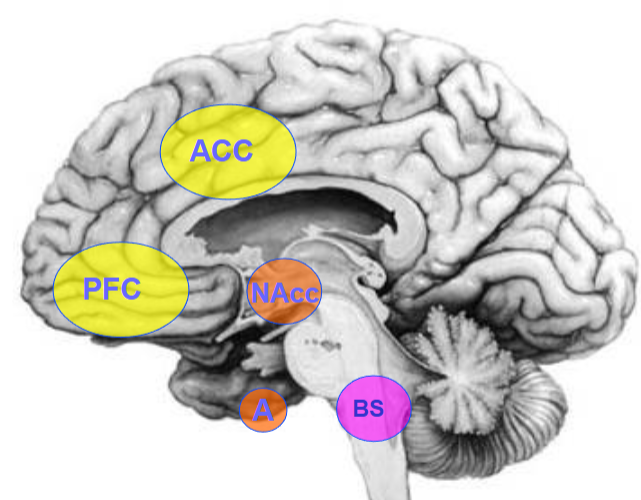
Neuroanatomy (mid-sagittal view)
• Amygdala (A; Amy; Amyg)
• Anterior Cingulate Cortex (ACC)
• Brainstem (BS)
• Nucleus Accumbens (NAcc)
• PreFrontal Cortex (PFC)
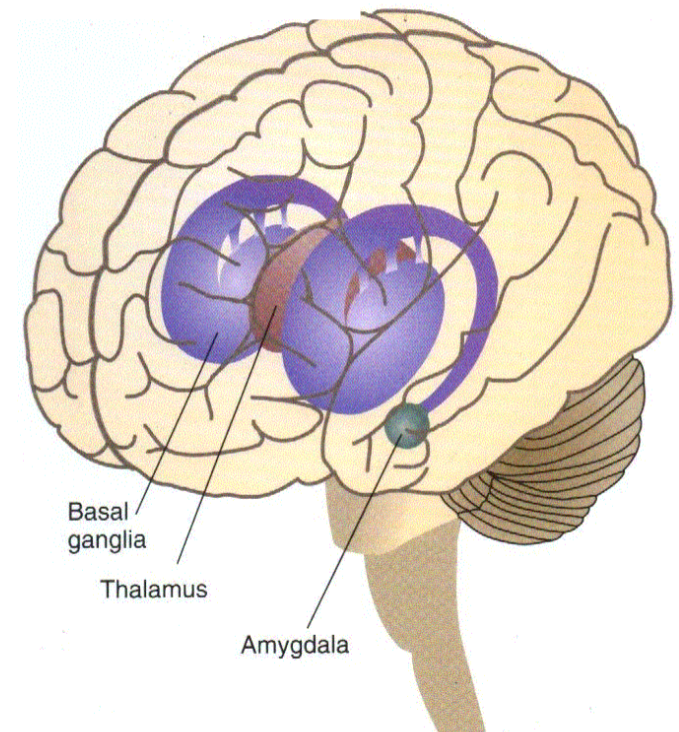
Neuroanatomy (sub-cortical circuits)
• Basal ganglia (motor control and more)
• Thalamus "relay station"
-routes signals from sense organs to cortex, and more
Hippocampus (Greek for seahorse):
marks engrams for memory storage and retrieval
Amygdala (Latin for almond):
- not the "fear center"
- detects salient (a.k.a. important) things
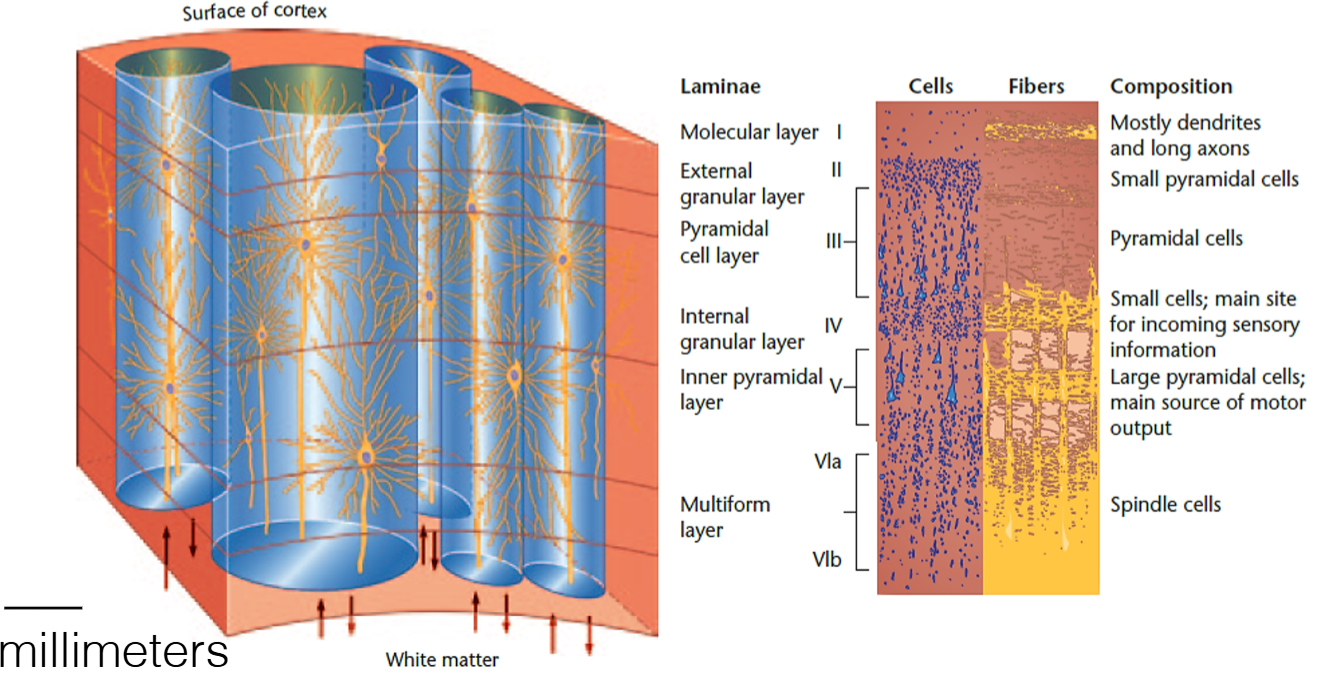
How are neurons organized in gray matter
Neurons are organized in columns and layers ("laminae")
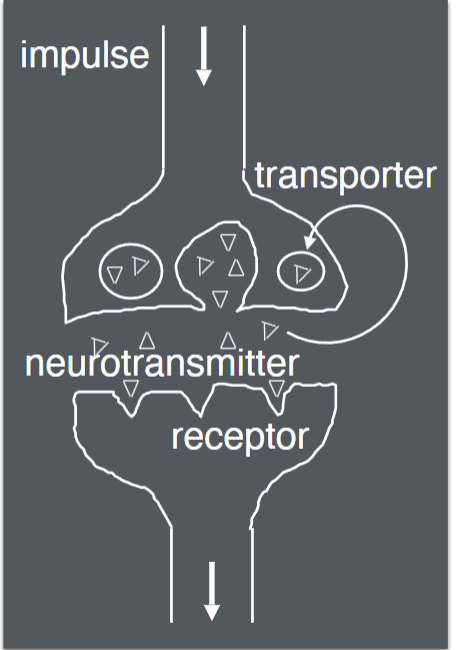
Neurotransmission:
• Action potential causes presynaptic neurotransmitter release
• Neurotransmitters fit receptors
• Generates postsynaptic impulse
• Transporters re-uptake presynaptic neurotransmitters
Neuromodulators (special neurotransmitters):
• Dopamine, norepinephrine / adrenaline, serotonin, acetylcholine, etc
Mesolimbic dopamine system
The ventral tegmental area (VTA) produces the neuromodulator dopamine, and releases it to the Nucleus Accumbens (NAcc) and Medial PreFrontal Cortex (MPFC)
Somatic nervous system
• body movement
-voluntary part of the peripheral nervous system, controlling conscious movements of skeletal muscles and processing sensory information from skin, muscles, and joints, including touch, sound, taste, and smell
Autonomic nervous system
• things we can't control
-a component of the peripheral nervous system that regulates involuntary physiologic processes including heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, digestion, and sexual arousal.
Autonomic nervous system is broken up in what three ways:
• Sympathetic nervous system (“fight-or-flight”)
• Parasympathetic nervous system (“rest-and-digest”)
• Enteric nervous system (gut talking to brain)
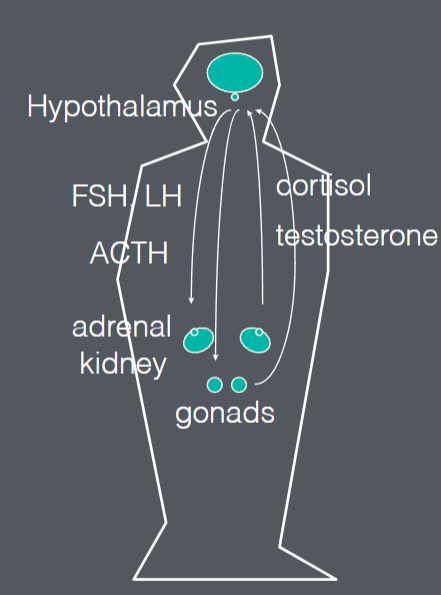
Hormones
Hypothalamus talks to pituitary gland
• Pituitary gland releases trophic factors in blood
• Trophic factors reach peripheral glands
• Peripheral glands release hormones
• Feedback to brain
Concentration gradient:
difference in amount of ions
Electrical gradient:
difference in charge
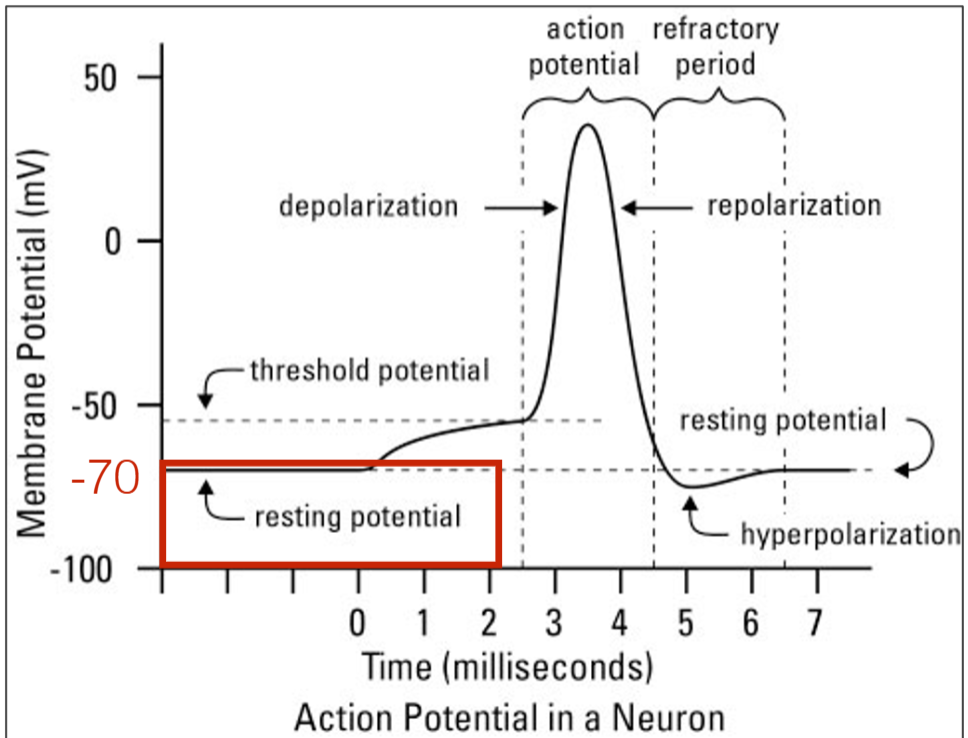
Resting potential
At rest, membrane potential is around -70 milliVolts (mV)
because more sodium (Na+) ion outside than inside
2 types of ion channels:
1) voltage-gated ion channels
2) ligand-gated ion channels
Voltage-gated ion channels open:
if the membrane potential reaches a certain threshold
Ligand-gated ion channels open:
if a neurotransmitter binds to the receptor on the channel (like lock and key)
Changing the membrane potential uses:
Excitatory PostSynaptic Potential (EPSP):de-polarize membrane potential (make less negative)
Inhibitory PostSynaptic Potential (IPSP): hyper-polarize membrane potential (more negative)
Neurotransmitters attach to:
• Glutamate attaches to:
• GABA attaches to
receptors on ligand-gated ion channels
receptors on ligand-gated Na+ channels -> EPSP
receptors on ligand-gated Cl- channels -> IPSP
Action potential
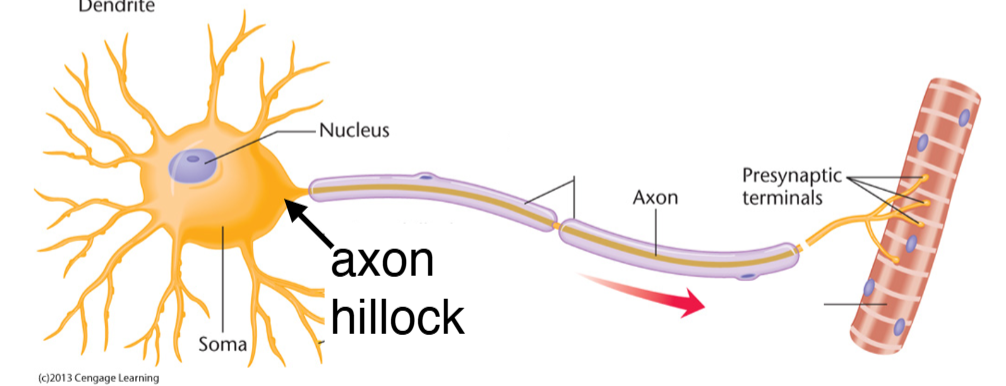
If enough depolarization of membrane potential, then voltage-gated sodium (Na+) channels open at the axon hillock and sends electrical charge down the axon.
"All-or-none" law: action potentials cannot stop midway,
and are equal in intensity and speed within a given neuron
After the action potential:
Reset the membrane potential to -70 mV
• close Na+ channels
• open K+ channels (concentration gradient so K+ leaves)
• Sodium-Potassium Pump: out 3 Na+, in 2 K+
• keep in chloride (Cl-) and negatively-charged proteins
Refractory period
• Neuron cannot immediately fire another action potential
• Absolute refractory period (during re-polarization)
• Relative refractory period (during hyper-polarization)
Myelination:
Axons are wrapped in fat called myelin.
Myelin prevents positive ions from leaking out of axon
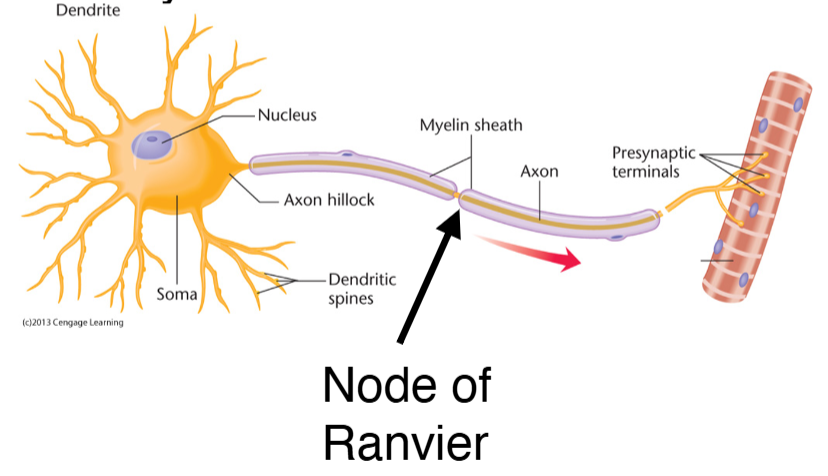
Nodes of Ranvier:
Speeds the electrical charge going down the axon via saltatory conduction
voltage-gated sodium (Na+) channels replenish the electrical charge
Glia cells:
cells that support neurons- supply nutrients, remove waste, create myelin
Oligodendrocytes create myelin in central nervous system
Schwann cells create myelin in peripheral nervous system
Neural codes, Rate coding:
Number of action potentials (a.k.a. neurons "firing" or "spiking") in a period of time
Examples:
• reward (brainstem dopamine; VTA-DA) Neurons fire more times when you get reward or punishment that you did not expect.
• vision (primary visual cortex; V1)Neurons fire more times to edges oriented at X angle
Neural codes, Temporal coding:
• Precise timing of a neuron's action potentials ("spikes")
• time lag to first spike after event
• spike randomness (probability distributions)
Example:
Gustation/olfaction — lots of tastants/odors, cannot use only number of spikes for each one
Neural codes, Population coding:
Summing action potentials across many neurons
Example: Visual motion neurons (area MT)
• each neuron has preference for a certain direction (vector) of motion
• population vector is sum of individual vectors
Neural codes, Sparse coding:
• Networks of neurons across brain firing together in specific pattern to code an event
• Analogy with language
• small set of symbols (26 in English alphabet), but different combos (order of letters and words) creates full linguistic array
Example:
Elaboration of long-term memories — new experiences add small tweaks to the "engram" for your memories
Neural codes summary:
• Rate coding - how many times 1 neuron fires action potentials
• Temporal coding - when the neuron fires
• Population coding - summing across many neurons' action potentials in 1 brain area
• Sparse coding - pattern of neurons firing across the brain
neuroscience methods do not cleanly fit what model:
normal models of manipulating independent variable and measuring dependent variable.
Organizing methods of studying the brain along 3 axes:
• Brain structure versus brain function
• Measurement versus manipulation
• Resolutions
-spatial (size)
-temporal (speed)
-chemical (specificity)
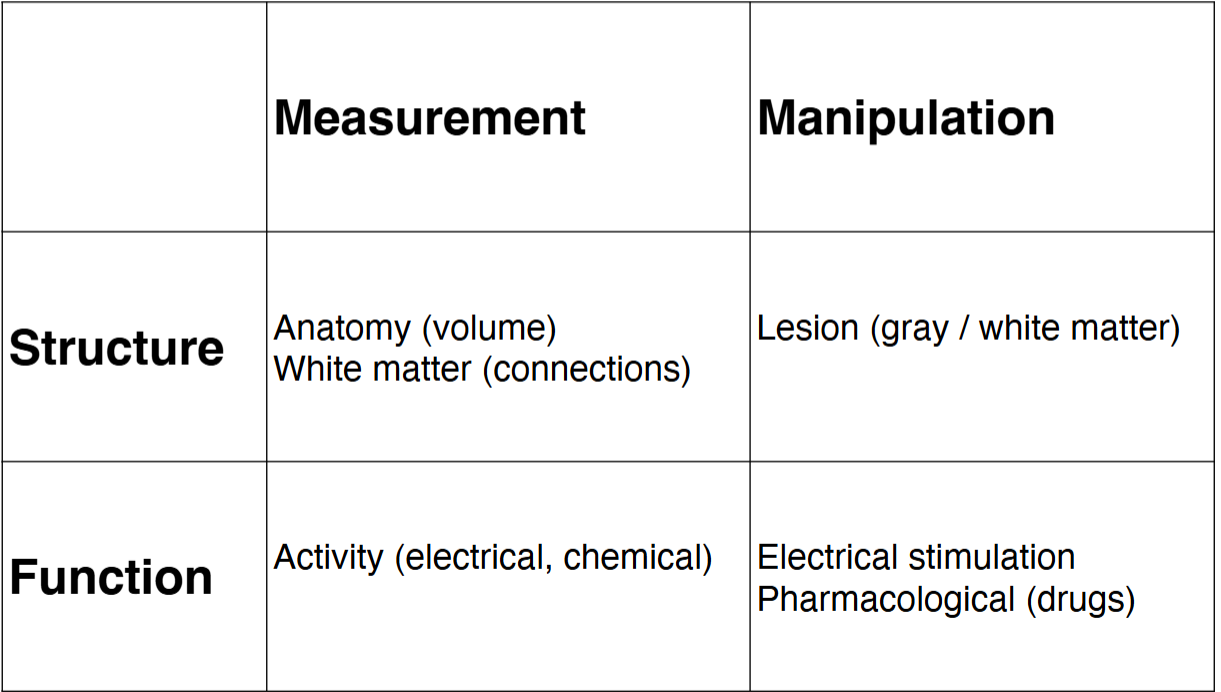
Measurement versus manipulation
measurement studies things already there.
manipulation stimulates area in some way
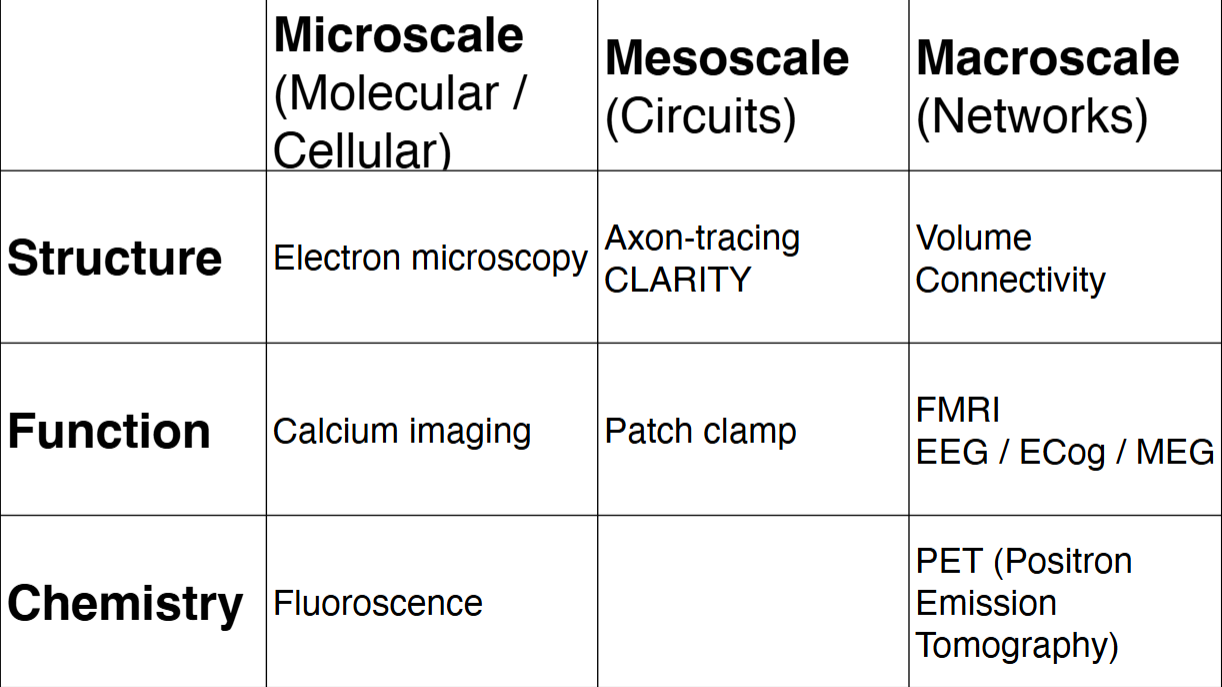
Measuring the brain, three scales at which is possible:
Microscale (Molecular / Cellular)
Mesoscale (Circuits)
Macroscale (Networks)
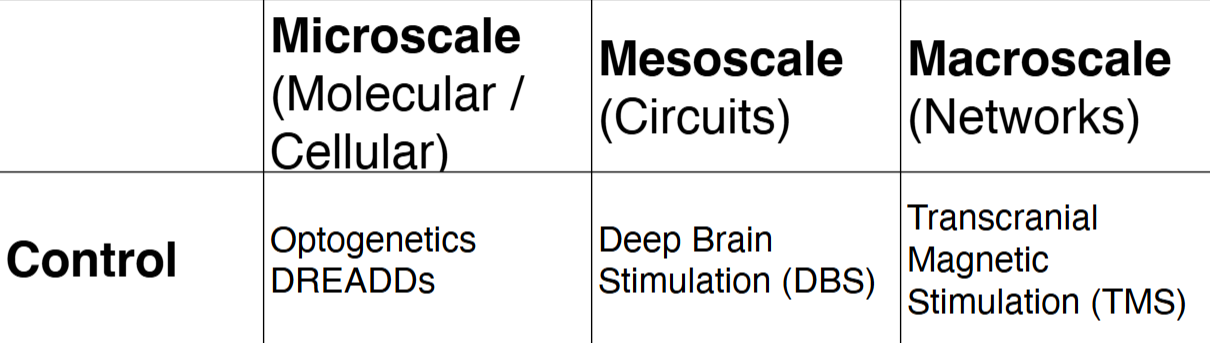
Methods for manipulating the brain:
Optogenics, DREADDs; Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS); Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) uses:
• Magnetic field
• Radio frequency
• Precession
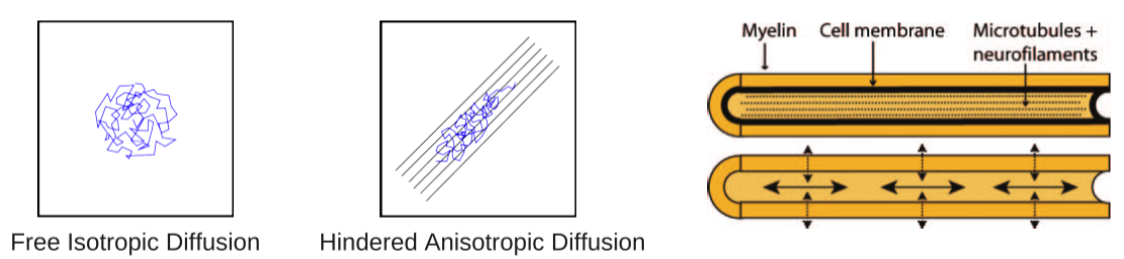
Diffusion MRI used to:
measure structural white-matter connections
Axon Tracing in animals
(monkeys and rodents)
• Inject tracer in neuron's soma, it flows down axon, hops across synapse, and stains next neuron's soma
• Anterograde tracer: inject tracer in brain area A, see if it stains B
• Retrograde tracer: inject tracer in brain area B, see if it stains A
• So we can infer directionality: e.g., A talks to B, but B can't talk to A
Deconstructing human choice
• Reward magnitude & valence (amount of gain or loss)
• Probability of getting it
• Time (now or later)
• Risk (potential gain and potential loss)
Paul MacLean’s “Triune” Brain
• Neomammalian: human: cortex; function: symbolic processing
• Paleomammalian: human: "limbic system"; function: emotions (social)
• Reptilian: human: brainstem; function: 4 F's
Nucleus Accumbens (NAcc) correlates with:
activity during gain anticipation; correlates with more self-report happiness (a.k.a. excitement)
Anterior Insula (AIns) activity correlates with:
larger "endowment effect"; loss anticipation,
Reward magnitude
• gain coded in Nucleus Accumbens (NAcc)
• loss coded in Anterior Insula (AIns)
Probability of getting reward coded in:
Medial PreFrontal Cortex (MPFC)
Time (now or later) refers to
delayed reward coded in Lateral PreFrontal Cortex (LPFC), valuing future reward
Risk:
Balancing potential gain and potential loss, Humans like positively-skewed risks (NAcc), Stronger AIns to NAcc structural connection correlates with not gambling
Plasticity:
The brain changes due to experiences with the environment on many spatial and temporal scales.
Types of plasticity:
Grey matter
-Grow and organize neurons in cortexWhite matter
-Improve wiring to synchronize activity between neurons ("cells that fire together wire together")Synaptic
-Strengthen and/or make more synapses between neurons (neurons more likely to fire together in future)
Grey-matter plasticity
Growing and organizing neurons in columns and layers
Taxi drivers have great spatial memory
effects of monocular deprivation on primary visual cortex
White-matter plasticity
Speed signal and synchronize activity between brain areas
• Increase myelination of axon
• Increase axon diameter
• Increase number of axons within "fascicle"
Synaptic plasticity, NMDA receptor?
• If Glutamate and Calcium are both released in synapse at same time it activates NMDA receptors, "coincidence detector" After NMDA receptor is activated, then the post-synaptic neuron should make it easier for the pre-synaptic neuron to talk to it again
Synaptic plasticity, how does firing together lead to more firing together?
Long term potentiation (LTP):
• Grow more dendrites (thus more synapses)
• Grow more receptors (thus receive more neurotransmitters)
Types of learning
• Classical conditioning: (Pavlov and Watson)
• Operant / instrumental conditioning: (Thorndike and Skinner)
Learning about rewards (how the brain does it):
• Ventral Tegmental Area = VTA (also called dopaminergic midbrain)
• Reward prediction error = neurons fire more times when an outcome does not match the prediction
Shaping is:
a technique for gradually behavior toward some desired target.
Differential reinforcement of successive approximations of the desired behavior.
Goal of reinforcement:
is to increase a behavior.
The goal of punishment is:
to reduce a behavior.
Behaviorism:
Psychology can only be a science if it focuses on what is observable and objective
2 main reasons we cannot infer that a person is feeling/thinking a specific thing even when we measure activity in a specific brain area
Brain Areas Are Not Functionally Exclusive: Most brain regions are involved in multiple cognitive and emotional processes
Correlation ≠ Specific Mental State: Measuring brain activity shows a correlation between a task or stimulus and neural firing, but it does not tell us exactly what mental content is present.
what technologies and industries in the past inspired metaphors for understanding the human brain
Hydraulic Systems, Mechanical Clocks, Telegraph Systems, Computers
what are the practical benefits of the action potential or "spike?"
Long-Distance, Reliable Communication: action potentials are all-or-none signals that do not degrade with distance
Precise Timing and Encoding: Spikes can carry information not just by their frequency (rate coding) but also by their timing (temporal coding), etc.
Energy Efficiency: Spikes only occur when the membrane potential reaches a threshold
Technological Innovations in Neuroscience (1964–2014):
Patch-clamp electrophysiology, CT and MRI scanning, fMRI and PET imaging, Transgenic animals, Optogenetics
Technological advancements to get to where want to go by 2064:
Better Large-Scale Recording; Whole-Brain, Cell-Type-Specific Manipulation; Integration Across Scales; Computational Infrastructure, nanobots
The structural white-matter connection between the left and right hemisphere is called the
corpus callosum