chem chapter 14 problems
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
change in concentration/time
Rate of reaction
K, a proportionality constant in the rate law that quantifies the rate of a chemical reaction by relating it to the concentrations of reactants
The rate constant, ____, is
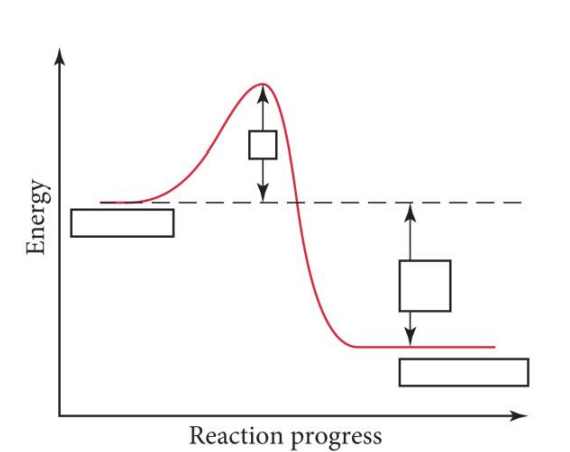
Ea, the minimum amount of energy required to initiate a chemical reaction by allowing reactant molecules to overcome an energy barrier to form products
The activation energy, ____, is
activity, selectivity, stability
List 3 properties of a catalyst
t1/2, the length of time it takes for the concentration of the reactant to fall to ½ its initial value
The half-life, ___, is
the individual, fundamental stages that a chemical reaction progresses through, describing the sequence of molecular events, such as bond breaking and forming, that ultimately transform reactants into products
Elementary steps
the slowest step that controls the overall rate of the reaction
The rate determining step in a reaction mechanism is
9 times
The reaction A + 2B → products has been found to have the rate law, rate = k[A] [B]2 . While holding the concentration of A constant, the concentration of B is increased from x to 3x. Predict by what factor the rate of reaction increases.
2 times
The reaction A + B → products has the rate law, rate = k[A]2 [B]. If the concentration of B is doubled while that of A is unchanged, by what factor will the rate of reaction increase?
min⁻¹
The appropriate unit for a first order rate constant is
M⁻¹ s⁻¹
The appropriate unit for a second order rate constant is
2
What is the overall order of the following reaction, given the rate law? NO(g) + O3(g) → NO2(g) + O2(g) rate =k[NO][O3]
M-1 s-1
What are the units of k in the following rate law? Rate = k[X][Y]
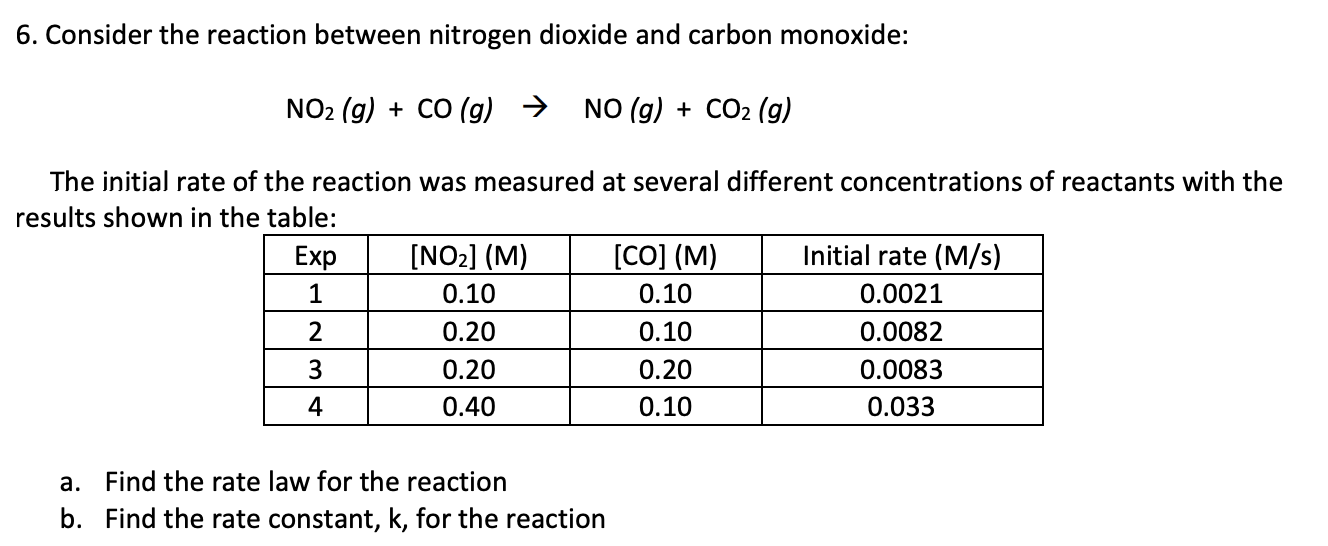
rate = k [NO2]2 ; k = 0.21 M-1 s -1
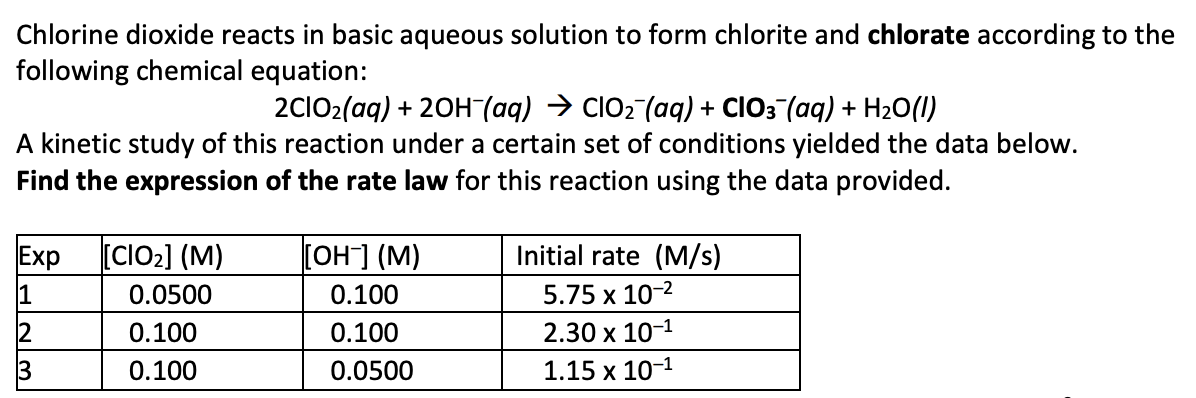
rate = k[ClO2]2 [OH-]
k[NO]2

rate = k[S2O8 2– ][I – ]
𝑘=6.1×10−3 M−1s−1

2300 min
The first-order reaction SO2Cl2 → SO2 + Cl2 is 10% complete in 80 min. How long would it take for the reaction to be 95% complete?
284 min
It takes 42.0 min for the concentration of a reactant in a first-order reaction to drop from 0.45 M to 0.32 M at 25°C. How long will it take for the reaction to be 90% complete?
11430 years
The radioactive decomposition of Carbon-14, 14C, has a half-life of 5715 years and follows a first order reaction. If a piece of wood has converted 75% of the carbon-14, then how old is it?
-Ea/R
The Arrhenius equation is k = A e –Ea/RT
The slope of a plot of ln k vs. 1/T is equal to
1.2 times
If Ea for a certain biological reaction is 50.0 kJ/mol, how many times will the rate of this reaction increase when the body temperature increases from 37°C (normal) to 40°C (fever)?
+90kJ/mol
The reaction C4H10 → C2H6 + C2H4 has an activation energy Ea = 350 kJ/mol for the forward reaction, and an Ea of the reverse reaction of 260 kJ/mol. Calculate ΔHrxn, in kJ/mol, for the reaction as written above.
+120kJ/mol
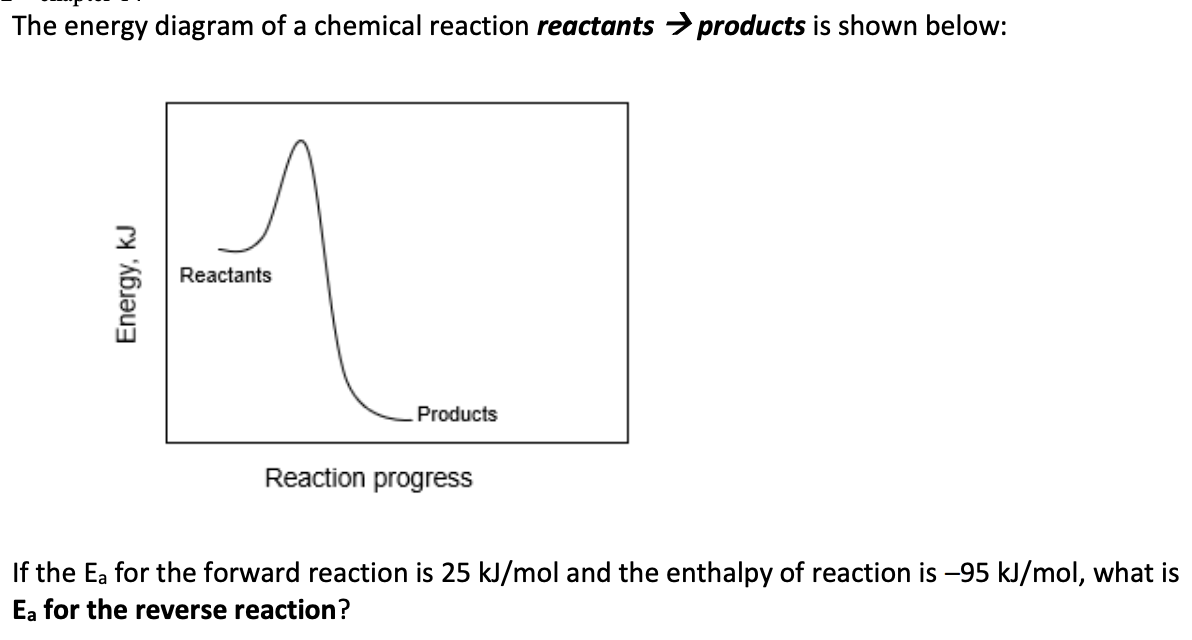
1.34 atm
At a particular temperature the gas-phase reaction 2N2O5 → 2N2O4 + O2 is first-order and has a half-life for the disappearance of dinitrogen pentoxide of 3240 s. If 1.00 atm of N2O5 is introduced into an evacuated 5.00 L flask, what will be the total pressure of the gases in the flask after 1.50 hours?
-36kJ/mol
Nitric acid is formed by the gas-phase hydrolysis of N2O5. For the reaction N2O5 + H2O → 2HNO3, Ea(forward) = 15 kJ/mol and Ea(reverse) = 51 kJ/mol. Calculate ΔHrxn
1.7 × 103 s
The rate constant, k, for a first-order reaction is equal to 4.2 × 10-4 s-1. What is the half-life for the reaction?
1.92 × 104 s-1
A particular first-order reaction has a rate constant of 1.35 × 102 s-1 at 25.0°C. What is the value of k at 75.0°C if Ea = 85.6 kJ/mol
HOI and OH-
The rate law for the reaction H2O2 + 2H+ + 2I – → I2 + 2H2O is rate = k[H2O2][I – ]. The following mechanism has been suggested. H2O2 + I – → HOI + OH– slow OH– + H+ → H2O fast HOI + H+ + I – → I2 + H2O fast Identify all intermediates included in this mechanism, and list them:
2.77kJ/mol
At 30°C, by how much is a reaction's activation energy decreased by the addition of a catalyst if the catalyst triples the reaction rate?
frequency of molecular collisions
When the concentration of reactant molecules increases, the rate of reaction increases. The best explanation for this phenomenon is that as the reactant concentration increases, the ____ increases as well.
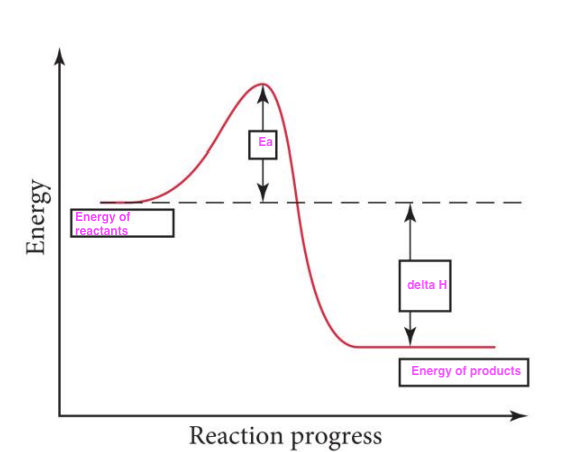
Label
Fe3+

6.25%
Knowing that the half-life of radioactive iodine-131 is 8 days draw a graph to calculate the amount of iodine-131 still present (in %) after 32 days
After 8 h: 50%
After 16 h: 25%
After 24 h: 12.5%
After 48 h: 1.5625%
Knowing that the half-life of cetirizine (an antihistamine drug) is 8 hours in the human body, calculate the amount of cetirizine that is left in the body after 8 h, 16 h, 24 h, and 48 h. Start at 100% at time zero.
a. 85.6 min
b. 129.6 min
c. 0.122 M
The decomposition of SO2Cl2 is first order in SO2Cl2 and has a rate constant of 1.35 x 10-4 s -1 at a certain temperature.
a. Calculate the half-life of the reaction
b. How long will it take for the concentration of SO2Cl2 to decrease to 35% of its initial concentration?
c. If the initial concentration of SO2Cl2 is 0.125 M, what is the concentration of SO2Cl2 after 150 s?
+153.8kJ
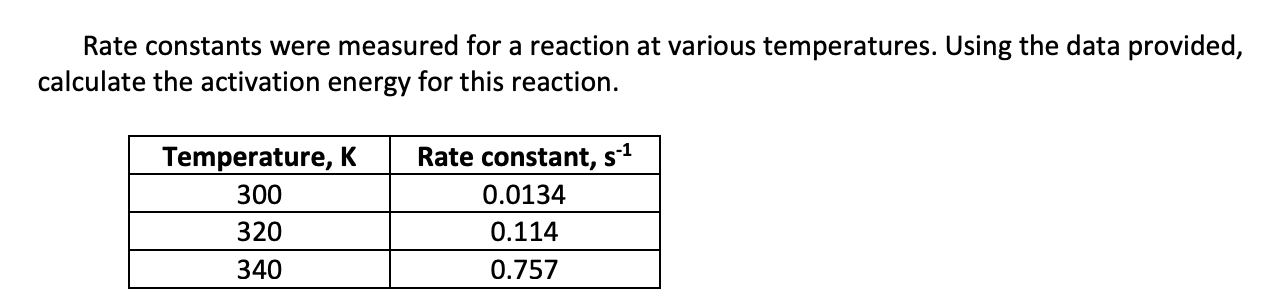
The rate constant, k, for a reaction was measured as a function of temperature. A plot of lnk versus 1/T (in K) is linear and has a slope of −1.85×104 K. Calculate the activation energy for the reaction.
+85.5kJ/mol
k [A]^m [B]^n
Rate law equation
ln[A]t/[A]0= -kt
First order reaction rate law equation
0.693/k
Half life for first order reaction
1/[A] = kt + 1/[A]initial
Second order reaction rate law equation
1/k[A]0
Half life for second order reaction
[A]= -kt + [A]initial
Zero order reaction rate law equation
[A]0/2k
Half life for zero order reaction
M s-1
Unit of rate constant for zero order reaction