Molecular Weight, Molarity, pH, and Amino Acid Chemistry
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
How is molecular weight (MW) determined?
By adding the atomic weights of all the atoms in the molecule.
What is the molecular weight (MW) of sodium chloride (NaCl)?
58.44 Da, calculated as 22.99 (Na) + 35.45 (Cl).
What is a mole in chemistry?
A mole is a unit that represents 6.02 x 10^23 molecules of a substance.
How many grams are in 1 mole of NaCl?
58.44 grams.
What is the molecular weight (MW) of sucrose (C12H22O11)?
342 Da, calculated as (12 x 12) + (22 x 1) + (11 x 16).
What is the molecular weight (MW) of sodium acetate (CH3COONa)?
82 Da, calculated as (2 x 12) + (3 x 1) + (2 x 16) + (1 x 23).
How much would 3 moles of mannitol (MW = 182 Da) weigh?
546 grams, calculated as 3 x 182 g.
What is molarity?
A measure of concentration defined as moles of solute per liter of solution.
What does [NaCl] = 0.1 M signify?
It means the concentration of NaCl is 0.1 moles per liter.
How much substance X is needed to make a 1 M solution in 1 L of water if MW = 100 Da?
100 grams.
How much substance X is needed for a 0.5 M solution in 1 L of water if MW = 100 Da?
50 grams.
What is the molecular weight of glucose (C6H12O6)?
180 Da, calculated as (6 x 12) + (12 x 1) + (6 x 16).
How much glucose is needed for a 0.5 M solution in 50 ml of water?
4.5 grams.
What is the pH of pure water?
7, indicating neutrality with equal concentrations of H+ and OH-.
What does a pH less than 7 indicate?
An acidic solution with more H+ ions than OH- ions.
What does a pH greater than 7 indicate?
A basic (alkaline) solution with more OH- ions than H+ ions.
What ion does H+ combine with in water?
It combines with another water molecule to form a hydronium ion (H3O+).
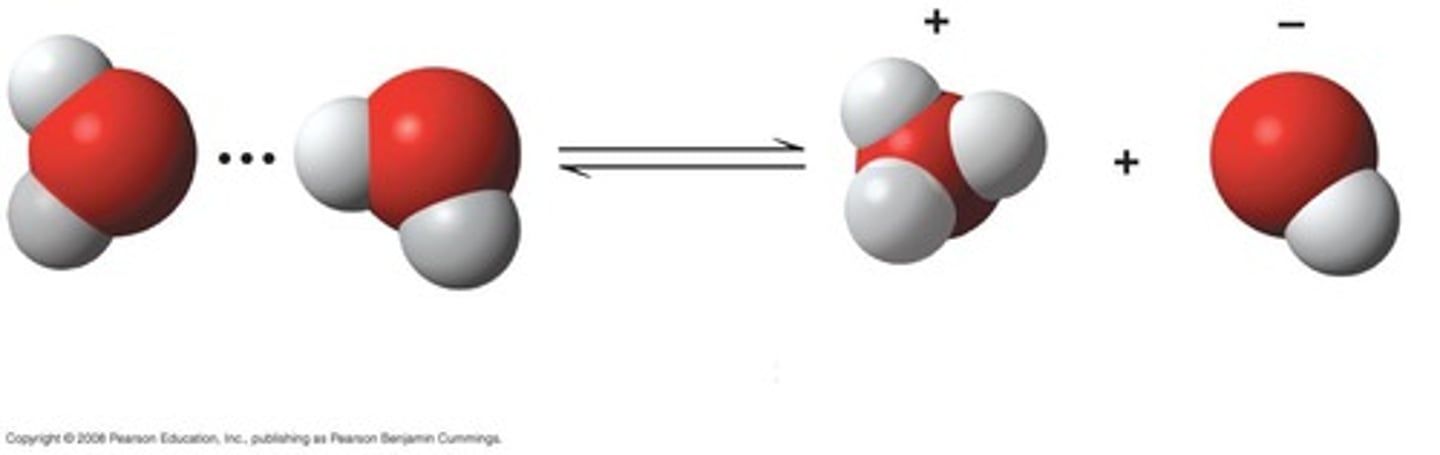
What is the significance of the balance between H+ and OH- ions in water?
It is critical to life's reactions, and small variations can have drastic consequences.
What is the conversion factor between grams and Daltons?
1 g = 6.02 x 10^23 Da.
What is the formula for calculating the weight of a substance needed for a specific molarity?
Weight (g) = Molarity (M) x Volume (L) x Molecular Weight (g/mol).
What does pH measure?
pH is a user-friendly way of stating the H+ ion concentration.
How is pH calculated?
pH = -log10 [H+]
What does a change of 1 unit in pH represent?
A change of 1 unit in pH represents a 10-fold change in [H+] or [OH-].
If [H+] = 10^-11 M, what is the pH?
pH = 11.
If pH = 3, what is [H+]?
[H+] = 10^-3 M.
What is the relationship between pH and pOH?
pH + pOH = 14.
What does a solution of pH 2 indicate compared to pH 11?
A solution of pH 2 has a greater concentration of H+ ions than a solution of pH 11.
How does a buffer function?
Buffers absorb or release H+ or OH- to maintain a constant pH.
What is a common buffer in biological systems?
Bicarbonate buffer.
What is the pKa of a buffer?
The pKa is the pH at which the buffer is half ionized, indicating its effectiveness.
What happens to amino acids at low pH (< 2)?
They are fully protonated and have a net positive charge.
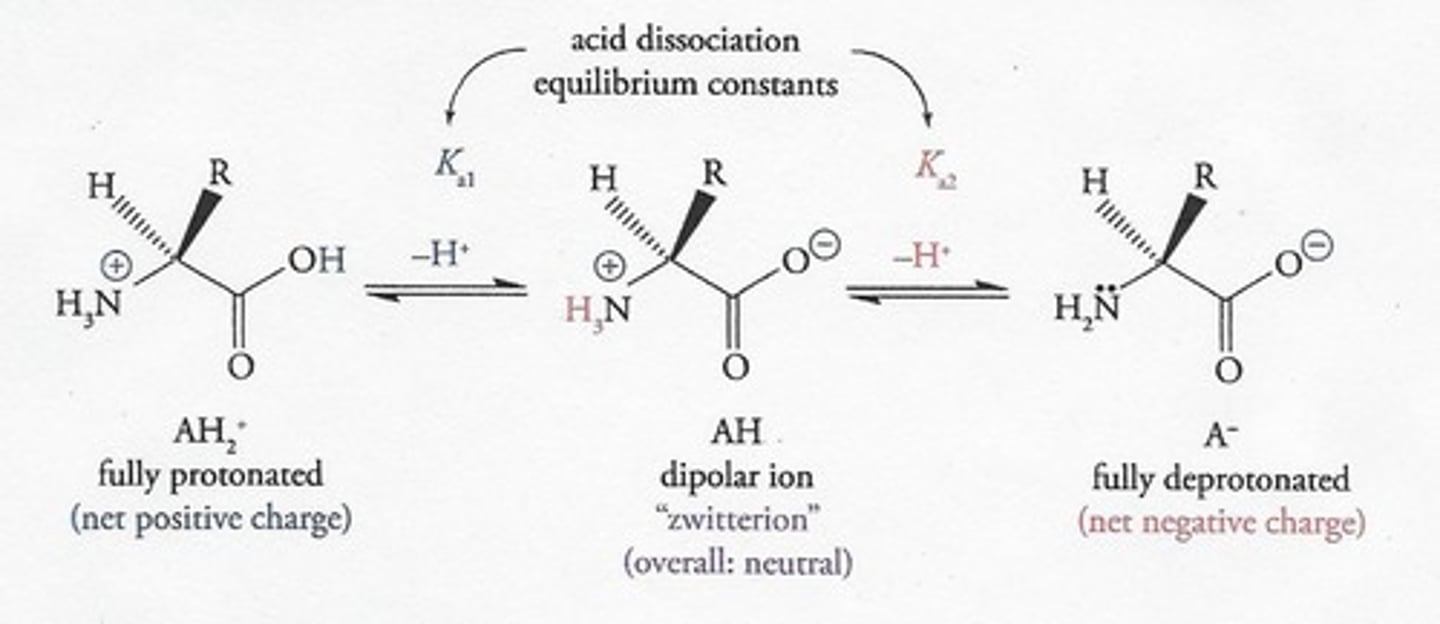
What is the ionization state of amino acids at neutral pH (~ 7)?
They exist as zwitterions, overall neutral but with both positive and negative charges.
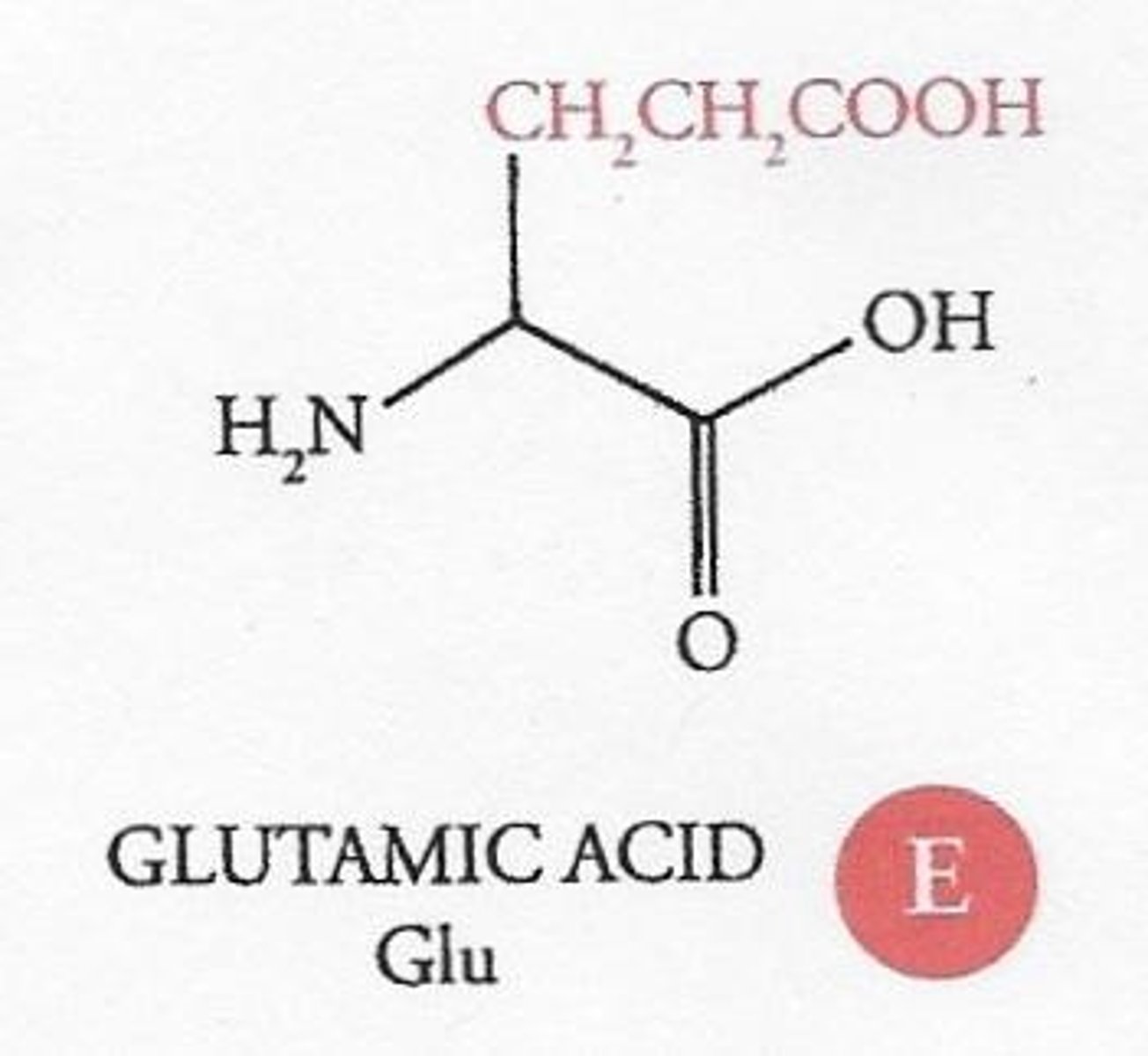
What characterizes acidic amino acids?
They have an additional carboxyl group in their R group, resulting in a net negative charge when fully ionized.
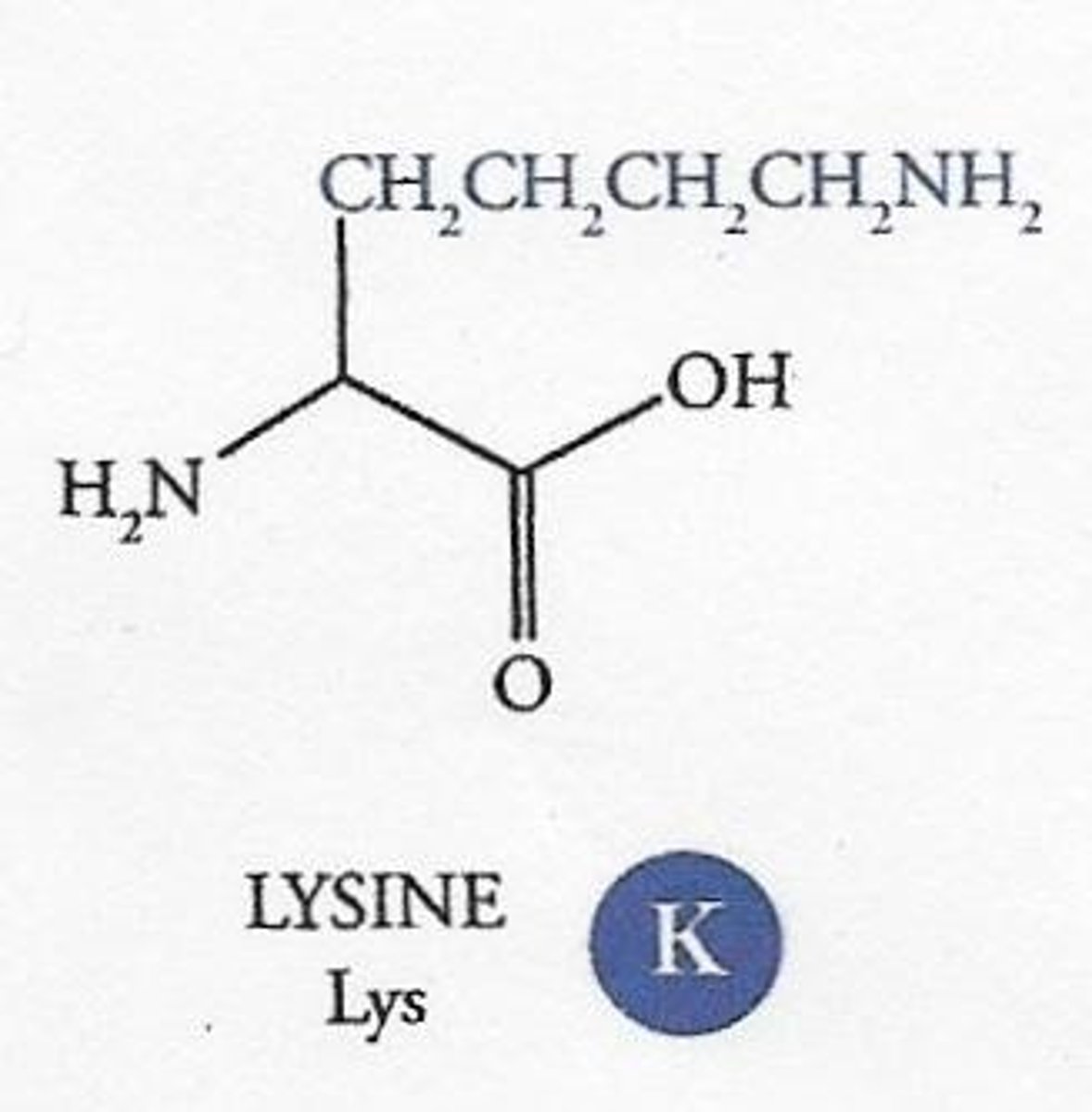
What characterizes basic amino acids?
They have an additional amine group in their R group, resulting in a net positive charge when fully ionized.
What is the effect of a decrease in pH from 7 to 6?
It represents a 10-fold increase in [H+].
If pOH = 5, what is [OH-]?
[OH-] = 10^-5 M.
What is the effect of buffers on pH?
Buffers help maintain a stable pH by absorbing or releasing H+ or OH-.
What is the significance of the coordinate bond in amino acids?
It allows the amine group to absorb H+ ions, affecting the pH of the solution.
What occurs at high pH (> 9) for amino acids?
They are fully deprotonated and have a net negative charge.
What is the effective pH range of Tris buffer?
Tris buffer has an effective pH range between 7.0 and 9.2.