Gene Expression
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Topoisomerase enzyme (DNA rep)
relax’s/ relieves by reducing the degree of supercooling in the DNA strand
Helicase (DNA rep)
untwists and separates the 2 parental strands at the replication fork
RNA primer (DNA rep)
lays RNA so DNA nucleotide can be added to the 3’ end
DNA polymerase lll (DNA rep)
adds nucleotides to DNA templates
DNA polymerase l (DNA rep)
replaces RNA primer with DNA nucleotides. And fills the gaps between Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand.
Okazaki fragments (DNA rep)
fragments of DNA that conform on the lagging strand
leading strand (DNA rep)
synthesized continuously 5’ —> 3’ direction as strands unravel
lagging strand (DNA rep)
synthesized discontinuously, built away
Ligase (DNA rep)
acts as the glue that links okazaki fragments with primers
Single strand binding proteins (SSB’s)
help stabilize parental strands
Direction of template strand
3’ —> 5’
transfer RNA (tRNA)
is responsible for carrying amino acids to the ribosome during translation and transferring them on to the growing polypeptide (amino acid) chain.
messenger RNA (mRNA)
is an RNA copy of a gene that carries the instructions for producing a specific protein from the nucleus to the ribosome.
ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a structural component of ribosomes that assists with translation of messenger RNA .
Central Dogma
DNA-->RNA-->Protein
describes the flow of information
Transcription
process by which RNA polymerase synthesizes an mRNA copy of the target gene.
(Transcription) Step 1: Initiation
TF (transcription factors) recognize a key area within the promoter region. TATA box
TF mediate the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter
The assembly of the Transcription Initiation Complex (TIC) is complete
(Transcription) Step 2: Elongation
RNA polymerase pries DNA strands apart, reading the DNA template in a 3’ to 5’ direction
Transcription of the DNA template begins
RNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the 3’ end of a growing chain producing a transcription unit
(Transcription) Step 3: Termination
RNA polymerase transcribes the polyadenylation signal sequence
A short distance after transcribing AAUAAA, the pre-mRNA is cleaved and freedom from the DNA template
Prokaryotic transcription occurs in the ________
cytoplasm
don’t have introns (non-protein coding) sequences in their DNA, so prok mRNA is immediately available for translation by ribosomes.
Eukaryotic transcription occurs in the ______
nucleus
do have intron sequences in their DNA , so euk mRNA has to be processed before it can leave the nucleus to be translated.
splicing
is to prevent extra amino acids from being translated into the polypeptide, bc that would change the folding of the protein therefore, changing the function
(Translation) Step 1: Initiation
mRNA leaves the nucleus through nuclear pore and arrives at bound or unbound ribosome
Translation Initiation Complex (TIC) forms at P site from mRNA, 2 ribosomal subunits, and tRNA carrying methionine
(Translation) Step 2: Elongation
At site A a codon receives tRNA with anticodon
Enzymes help form peptide bond btw amino acids of tRNA molecules
tRNA at P-site rotates to E-site leaving an amino acid & detaching from ribosome
(Translation) Step 3: Termination
tRNA enters at A rotates to P —> E repeatedly until stop codon is reached
Release factor binds and molecules detach from one another. New protein is released into cell.
__________ couple transcription and translation
prokaryotes
___________ transcription and translation are separated because eukaryotes have nuclei.
eukaryotic
introns
extrons
RNA processing stages
Stage 1: Splicing
Stage 2: Alteration of ends
During stage 2 of RNA processing (alteration of ends), what is added to the 5’ end ?
guanine methyl cap
During stage 2 of RNA processing (alteration of ends), what is added to the 3’ end ?
poly A tail (200-250) adenine nucleotides
RNA processing sequence
snRNA base pair at specific sites along the intron
SnRNPs and other proteins form a molecular complex (spliceosome)
Pre-mRNA begins being spliced
RNA is cut - releasing intron while splicing exons together
Spliceosome comes apart, mRNA contains exons - now to be altered
5’ cap consisting of modified guanine nucleotide (GTP) is added to the 5’ end of pre-mRNA
string of (50-250) adenines are added to 3’ end to form poly A tail. pre-mRNA is called mature mRNA and may leave the nucleus safely.
Purpose of translation
make protein
(Translation) When mRNA leaves the nucleus goes to
a ribosome
(Translation) Bound ribosome
attached to ER, used if protein is outside of a cell
(Translation) Unbound ribosome
freely in cytoplasm, used if protein is inside the cell
(Translation) trucks in amino acids in translation
tRNA
(Translation) 2 attachment site on tRNA
(Translation) Specifies the sequence in which tRNA lands on the mRNA
codon
The ____ of the mRNA binds to the _____ on the tRNA
codon
anticodon
Determines the ultimate shape and function of a protein
sequence of amino acids
Point mutations
only affect one gene
Occur during DNA synthesis
2 types: substitution or frameshift
Chromosomal mutations
affect big sections
More detrimental
Occurs during meiosis
Substitution mutation
Type of mutation where the original nucleotide is replaced by a different nucleotide
3 types:
silent
missense
nonsense
Silent substitution mutation
A change in a single nucleotide that doesn’t result in a change in amino acid sequence (neutral)
Missense mutation
A change in single nucleotide that results in a change in a single amino acid sequence
Nonsense mutation
A change in a single nucleotide that results in a premature stop-codon in the mRNA sequence
negative impact on protein
Won’t fold or function properly bc lack of amino acids
Frameshift mutation
Mutation where the addition or removal of a single nucleotide changes the reading frame for the protein. Always negative effect
2 types:
insertion
deletion
Insertion mutation
Mutation where an insertion of a single nucleotide into the DNA sequence changes entire amino acid sequence. Protein won’t fold or function properly
Deletion mutation
Mutation where a deletion of a single nucleotide into the DNA sequence changes entire amino acid sequence. Protein won’t fold or function properly
Sickle Cell Anemia
caused my missense mutation in hemoglobin gene
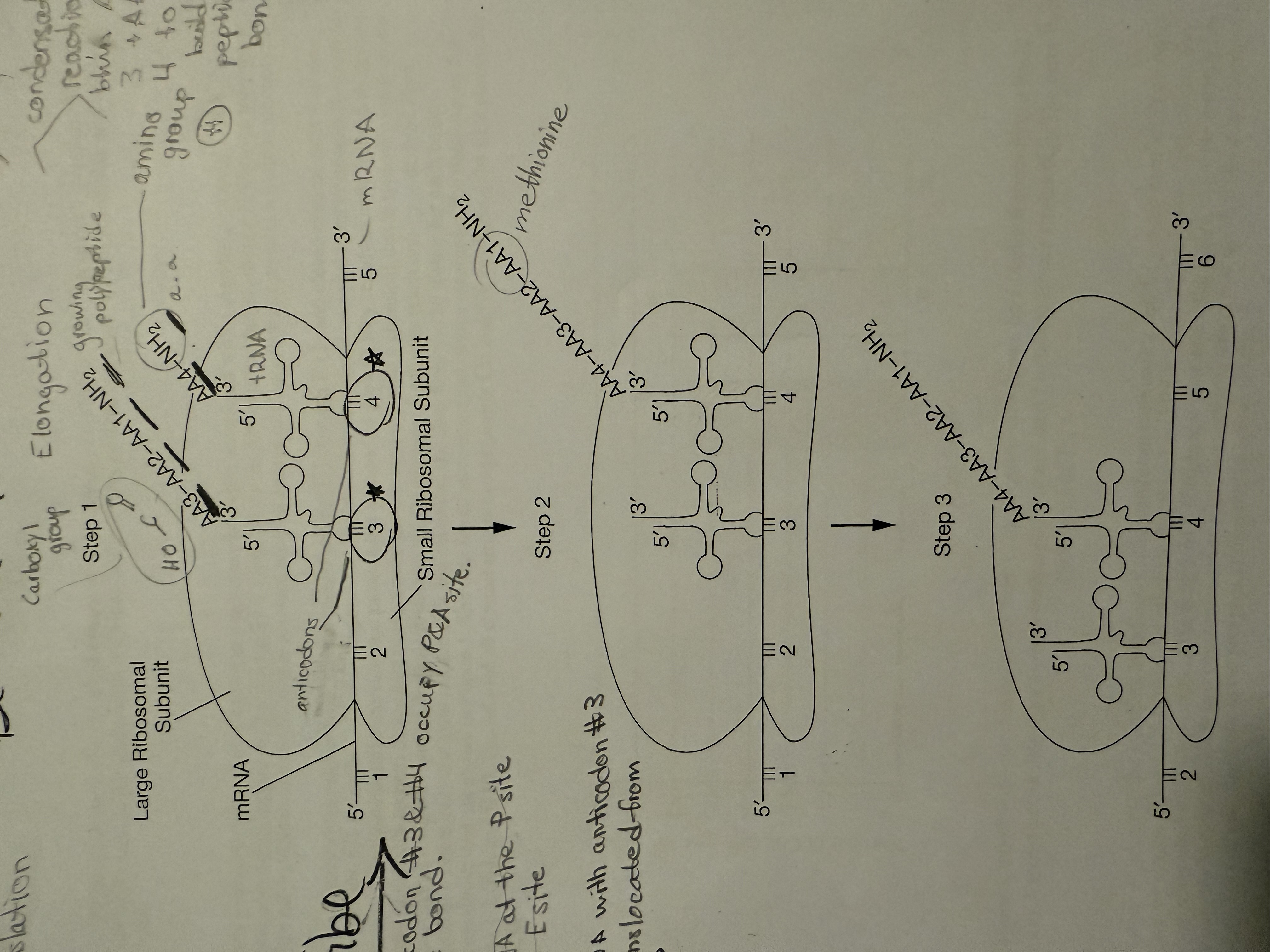
Practice FRQ: Describe what happening between steps 1 & 2?
tRNA anticodon #3 and #4 occupy the P and A site. There is a condensation reaction between amino acid 3 and amino acid 4 to build a peptide bond.