BIOL 355: Ecology - Competition, Predation, & Herbivory
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Exploitative competition
competition in which individuals consume or acquire a resource and thus deprive others of using it (indirect competition)
Interference competition
when individuals prevent access to a resource through aggressive or exclusionary methods (direct competition)
Allelopathy
a type of interference competition that occurs when organisms use chemicals to harm their competitors
Apparent competition
when two species have a negative effect on each other through an enemy—including a predator, parasite, or herbivore
Leibig’s law of the minimum
law stating that a population increases until the supply of the most limiting resource prevents it from increasing further
Competitive exclusion principle
two species that are limited by the same resources cannot coexist indefinitely in the same community
Logistic growth model with competition equation
see pic
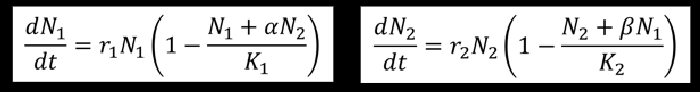
Zero population growth isocline
population sizes at which a population experiences zero growth
If a population (species 2) is below the isocline, is it increasing or decreasing?
increasing
If the population (species 2) is above the isocline, is it increasing or decreasing?
decreasing
If a population (species 1) is to the left of the isocline, is it increasing or decreasing?
increasing
If a population (species 1) is to the right of the isocline, is it increasing or decreasing?
decreasing
Mesopredator
relatively small carnivores that consume herbivores
Top predators
predators that typically consume both herbivores and predators (e.g., mountain lions, wolves, sharks)
Crypsis
camouflage that either allows an individual to match its environment or breaks up the outline of an individual to blend in better with the background
Warning coloration (aposematism)
a strategy where distastefulness (or being “dangerous”) evolves in association with very conspicuous colors and patterns
Batesian mimicry
when palatable species evolve warning coloration that resembles unpalatable species (e.g., hover flies and hornet clearwings resemble the common wasp)
Müllerian mimicry
when several unpalatable species evolve a similar pattern of warning coloration (e.g., several species of poison dart frogs have evolved similar warning coloration)