THEORIES OF PERSONALITY
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
Personality
the unique and relatively stable ways in which people think, feel, and behave.
Character
value judgments of a person’s moral and ethical behavior.
Temperament
the enduring characteristics with which each person is born.
Four Perspectives in the Study of Personality
Psychodynamic
Behavioristic
Humanistic
Trait Perspectives
Psychodynamic
Emphasizes the importance of early childhood experiences and the unconscious mind.
Hidden in the unconscious could be revealed in a number of different ways, including through dreams, free association, and slips of the tongue.
Sigmund Freud
founder of the psychoanalytic movement in psychology
Psychoanalysis
Freud’s term for both the theory of personality and the therapy based on it
Behavioristic
includes social cognitive theory
Preconcious mind
level of the mind in which information is available but not currently conscious.
Conscious mind
the level of the mind that is aware of immediate surroundings and perceptions.
Unconscious mind
the level of the mind in which thoughts, feelings, memories, and other information are kept that are not easily or voluntarily brought into consciousness.
It can be revealed in dreams and Freudian
slips of the tongue.
Freud’s Theory: Parts of Personality
Id
Ego
Superego
Id
part of the personality present at birth and completely unconscious.
Ego
part of the personality that develops out of a need to deal with reality, mostly conscious, rational, and logical.
Superego
part of the personality that acts as a moral center.
Psychological defense mechanisms
are unconscious distortions of a person’s perception of reality that reduce stress and anxiety.
Denial
A psychological defense mechanism in which the
person refuses to acknowledge or recognize a threatening situation.
Repression
A psychological defense mechanism in which the person refuses to consciously remember a threatening or unacceptable event, instead pushing those events into the unconscious mind.
Rationalization
A psychological defense mechanism in which a person invents acceptable excuses for unacceptable behavior.
Projection
psychological defense mechanism in which unacceptable or threatening impulses or feelings are seen as originating with someone else, usually the target of the impulses or feelings
Reaction formation
psychological defense mechanism in which a person forms an opposite emotional or behavioral reaction to the way he or she really feels to keep those true feelings hidden from self and others.
Displacement
redirecting feelings from a threatening target to a less threatening one.
Regression
A psychological defense mechanism in which a person falls back on childlike patterns of responding in reaction to stressful situations.
Identification
A defense mechanism in which a person tries to become like someone else to deal with anxiety.
Compensation
A person makes up for inferiorities in one area by becoming superior in another area.
Sublimation
Channeling socially unacceptable impulses and urges into socially acceptable behavior
Freud’s Theory: Stages of Personality Development
Fixation
Psychosexual stages
Fixation
A Disorder in which the person does not fully resolve the conflict in a particular psychosexual stage, resulting in personality traits and behavior associated with that earlier stage.
Psychosexual stages
Five stages of personality development proposed by Freud and tied to the sexual development of the child.
Mnemonic: OAPhaLaGE
Oral Stage
Age: Birth to 1 or 1½ years old.
Focus of Pleasure: Oral activities (such
as sucking, feeding, and making noises
with the mouth).
Focus of Conflicts: Weaning.
Later Difficulties (affecting personality):
Ability to form interpersonal attachments.
Basic feelings about the world.
Tendency to use oral forms of aggression, such as sarcasm.
Optimism or pessimism.
Tendency to take charge or be passive.
Anal Stage
Age: 1 or 1½ to 3 years old
Focus of Pleasure: Bowel and bladder
control.
Focus of Conflicts: Toilet training.
Later Difficulties (affecting personality):
Sense of competence and control.
Stubbornness or willingness to go along with others.
Neatness or messiness.
Punctuality or tardiness.
Phallic Stage
Age: 3 to 6 years old.
Focus of Pleasure: Genitals.
Focus of Conflicts: Sexual awareness.
Later Difficulties (affecting personality):
Development of conscience through identification with same-sex parent.
Pride or humility.
Latency Stage
Age: 6 years old to puberty.
Focus of Pleasure: Social skills (such as
the ability to make friends) and intellectual
skills. This is also described as a dormant
period in terms of psychosexual
development.
Focus of Conflicts: School, play,
same-sex friendships.
Later Difficulties (affecting personality):
Ability to get along with others.
Genital Stage
Age: Puberty to death.
Focus of Pleasure: Sexual behavior.
Focus of Conflicts: Sexual relationship with partner.
Later Difficulties (affecting personality):
Immature love or indiscriminate hate.
Uncontrollable working or inability to work
Neo Freudians
Alfred Adler
Carl Jung
Karen Horney
Erik Erikson
Alfred Adler
Individual Psychology
Carl Jung
Analytical Psychology
Karen Horney
Psychoanalytical social theory
Erik Erikson
Ego
Psychology/Post-Freudian Psychology
Behaviorism and Personality
Emphasizes the importance of observational learning, self-efficacy, situational influences, and cognitive processes.
Behaviorists define personality as a set of learned responses or habits.
Habits
In behaviorism, sets of well-learned responses that have become automatic.
Social cognitive learning theorists
Theorists who emphasize the importance of both the influences of other people’s behavior and of a person’s own expectancies on learning
Social Cognitive view
Learning theory that includes cognitive processes such as anticipating, judging, memory, and imitation of models.
Reciprocal determinism
Bandura’s explanation of how the factors of environment, personal characteristics, and behavior can interact to determine future behavior.
Self-efficacy
Individual’s perception of how effective a behavior will be in any particular circumstance (NOT the same as self-esteem)
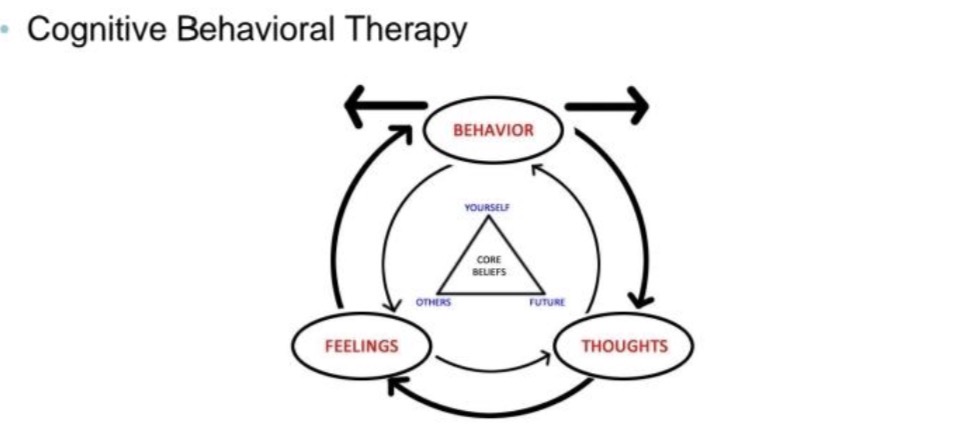
Counseling and Therapy
The first thing that we need to know is to
identify the cognitive distortion. After that,
we have some behavioural therapy na
ginagawa such as systematic
desensitization. Common in addressing
different psychological disorders
especially phobia, ptsd, anxiety.
Behaviorist Theorists
Albert Bandura
Ivan Pavlov
B.F. Skinner
Albert Bandura
Social Learning Theory
Ivan Pavlov
Classical Conditioning
B.F Skinner
Operant Conditioning
Roger’s Theory of Personality
Self-actualizing tendency
Self-concept
Self (Archetype)
Real self
Ideal self
Positive regard
Unconditional positive regard
Conditional positive regard
Fully functioning person
Self-actualizing tendency
The striving to fulfill one’s innate
capacities and capabilities.
Self-concept
The image of oneself that develops
from interactions with important,
significant people in one’s life.
Self (Archetype)
Works with the ego to manage
other archetypes and balance the
personality.
Real self
One’s perception of actual
characteristics, traits, and abilities.
Ideal self
One’s perception of who one
should be or would like to be
Positive regard
Warmth, affection, love, and
respect that come from significant
others in one’s life.
Your real self and ideal self should be
congruent. If they're not congruent,
sometimes, nagkakaroon ng mismatch,
and nagpo-proceed into different types of
anxiety.

Unconditional positive regard
Positive regard that is given without conditions or strings attached.
Conditional positive regard
Positive regard is given only when the person is doing what the providers of positive regard wish.
Fully functioning person
A person who is in touch with and
trusting of the deepest, innermost
urges and feelings
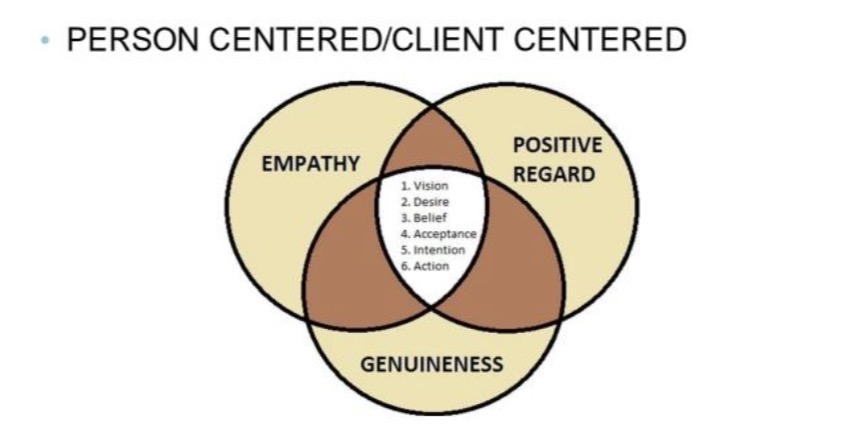
This is for the growth, for the psychological growth. What we need is to have this positive regard, the empathy, and genuineness. Basically, the positive regard may be in line with unconditional. We need to be more emphatic. We need to try to understand, and feel ‘yung nararamdaman niya. Yung genuineness (pagpapakatotoo) sa kaniya. Hindi natin siya tini-treat bilang patient, but as a
Victor Frankl
Logotherapy
Logotherapy
It talks about meaning in life, about the
freedom of will. In short, we need to find
our purpose in life. Sometimes, ginagamit
din sa therapeutic techniques, and it's also
in line with humanistic existentialism.

Trait Theories of Personality
Centered on identifying, describing, and
measuring the specific traits that make up
human personality
Trait theories
Theories that endeavor to describe the characteristics that make up human personality in an effort to predict future behavior.
Allport first developed a list of about 200 traits and believed that these traits were part of the nervous system.
Cattell reduced the number of traits to between 16 and 23 with a computer method called factor analysis.
Trait
A consistent, enduring way
of thinking, feeling, or behaving
Surface traits
Aspects of personality that can easily be seen by other people in the outward actions of a person
The big five theory
Openness
Conscientiousness
Extraversion
Agreeableness
Neuroticism
Five-factor model (Big Five)
A Model of personality traits that describes five basic trait dimensions
Openness
High Scorer Characteristics: Creative, artistic, curious, imaginative, nonconforming.
Low Scorer Characteristics: Conventional, down-to-earth, uncreative.
Conscientiousness
High Scorer Characteristics: Organized, reliable, neat, and ambitious.
Low Scorer Characteristics: Unreliable, lazy, careless, negligent, spontaneous.
Extraversion
High Scorer Characteristics: Talkative, optimistic, sociable, and affectionate.
Low Scorer Characteristics: Reserved, comfortable being alone, stays in the background.
Agreeableness
High Scorer Characteristics: Good-natured, trusting, helpful.
Low Scorer Characteristics: Rude, uncooperative, irritable, aggressive,
competitive.
Neuroticism
High Scorer Characteristics: Worrying, insecure, anxious, temperamental.
Low Scorer Characteristics: Calm, secure, relaxed, stable
Cultural Personality
Four basic dimensions of personality along which
cultures may vary:
1. Individualism/collectivism
2. Power distance
3. Masculinity/femininity
4. Uncertainty avoidance
Measuring Personality: Interviews
Interview
Halo Effect
Interview
A Method of personality assessment in which the professional asks questions of the client and allows the client to answer, either in a structured or unstructured fashion.
Halo effect
Tendency of an interviewer to allow positive characteristics of a client to influence the assessments of the client’s behavior and statements.
Measuring Personality: Projective Tests
Projection
Protective Tests
Rorschach inkblot test
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
Projection (Defense Mechanism)
Placing, or "projecting," one’s own unacceptable thoughts onto others, as if the thoughts actually belonged to those others and not to oneself.
Projective tests
Personality assessments that present ambiguous visual stimuli to the client and ask the client to respond with whatever comes to mind.
Rorschach inkblot test
A projective test that uses 10 inkblots as the ambiguous stimuli.
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
A projective test that uses 20 pictures of people in ambiguous situations as the visual stimuli.
Subjective
Concepts and impressions that are only valid within a particular person’s perception and may be influenced by biases, prejudice, and personal experiences. This is a problem with projective tests.
Measuring Personality: Behavioral Measures
Direct Observation
Rating scale
Frequency count
Direct observation
Assessment in which the professional observes the client engaged in ordinary, day-to-day behavior in either a clinical or natural setting.
Rating scale
An Assessment in which a numerical value is assigned to specific behavior that is listed in the scale.
Frequency count
Assessment in which the frequency of a particular behavior is counted.
Measuring Personality: Personality Inventory
Personality Inventory
Paper-and-pencil or computerized test that consists of statements that require a specific,standardized response from the person taking the test.
NEO-PI: Based on the five-factor
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator: Based on Jung’s theory of personality types.
MMPI-2: Designed to detect abnormal personality
Personality Tests and the Internet
Numerous personality tests are available on the Internet. Not all are equal in quality, reliability, or validity. There is a lack of professional interpretation of the results of such tests
Early Explanations of Mental Illness
In ancient times, holes were cut in an ill person’s head to let out evil spirits in a process called trepanning.
Hippocrates believed that mental illness came from an imbalance in the body.
In the Middle Ages, the mentally ill were labeled as witches
Psychopathology
The study of abnormal behavior.
Psychological disorders
Any pattern of behavior that causes people significant distress, causes them to harm others, or harms their ability to function in daily life.
A ______ is often statistically rare.
A ______ is often deviant from social norms.
Situational context:
The social or environmental setting of a person’s behavior.
Subjective discomfort
emotional distress or emotional pain
Maladaptive
Anything that does not allow a person to function within or adapt to the stresses and everyday demands of life
Five D’s
Deviant - Kakaiba ang kinikilos
Dysfunction - Impaired (doesn't function)
Distress - Intense worry that causes to harm others
Danger - Delikado ka na, and your surroundings
Duration - How long has this been going on
Sociocultural Perspective
Cultural Relativity
Culture-Bound Syndromes