exam 3 patho
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
HHS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
type 1 DM
autoimmune destruction of b-cells leading to insulin deficiency
type 2 DM
progressive insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion
DKA
acute metabolic complication of hyperglycemia, ketosis (fruity breath), and metabolic acidosis (low pH)
missed insulin dose, can lead to coma or death
hypoglycemia
<70 mg/dL, dizziness, sweating, confusion, and potential unconsciousness (give glucagon IM)
priority in pediatric diabetes
HbA1C
measures long-term blood glucose control over 2-3 months (long term control)
normal: below 5.7% pre diabetes: 5.7-6.4% diabetic: above 6.5%
diagnostic criteria for diabetes
fasting glucose >126 mg/dL, HbA1C >6.5%, 2-hour OGTT >200mg/dL, random glucose >200 mg/dL + symptoms (3p’s)
oral hypoglycemia
metformin: decreases glucose absorption, contraindicated with contrast dye, causes metallic taste
sulfonylureas (glipizide): stimulate insulin release but risk hypoglycemia
alpha-glucosidase inhibitors (acarbose): delays carbohydrate absorption
insulin
aspart (rapid): taken before meals; risk for hypoglycemia
regular: only IV insulin for DKA
GLP-1 agonists (semaglutide)
enhance insulin secretion, reduce glucagon, slow gastric emptying, increase satiety
chronic complications
peripheral neuropathy, cardiovascular disease, renal failure, infections
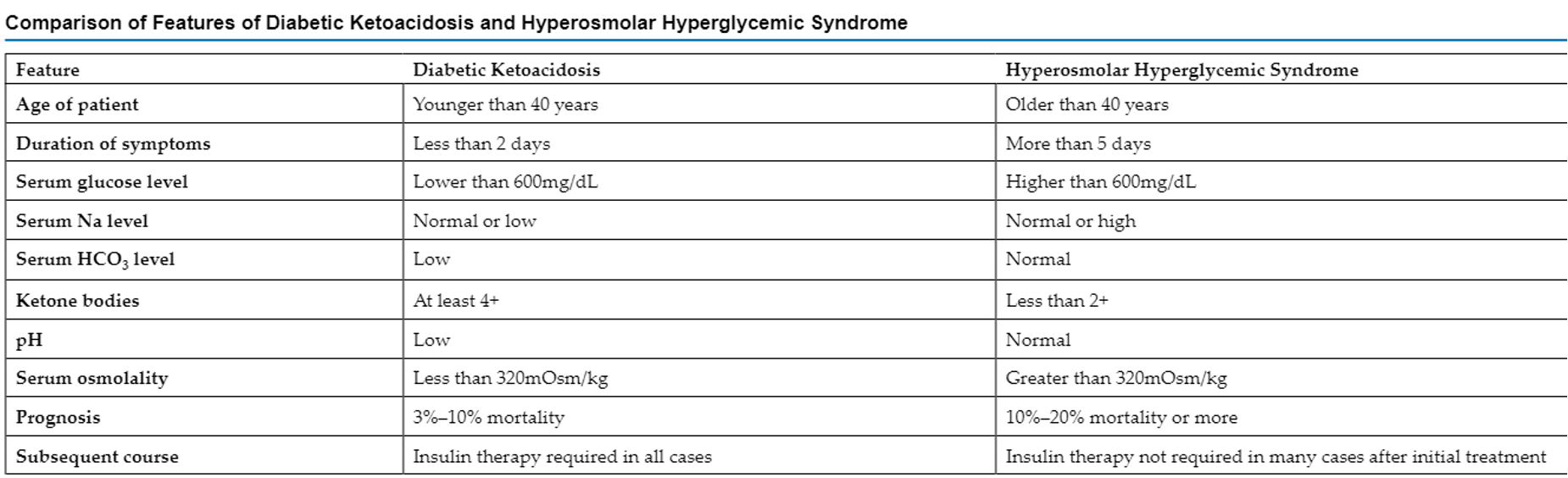
DKA v Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS)
DKA: fruity breath, acidosis, ketonuria (breaks down ketones)
HHS: severe hyperglycemia without ketosis, normal pH
hyperthyroidism
graves’ disease; excess thyroid hormones; increased HR, heat intolerance
antithyroid drugs watch for low platelets
hypothyroidism
low thyroid hormones requiring replacement therapy; fatigue, drowsiness, constipation
goiter
thyroid enlargement d/t iodine deficiency or hormone imbalance
avoid iodine with thyroid cancer
elevated TSH levels
TSH and Free T4 Levels
directly monitors thyroid function and therapy
levothyroxine
treat hypothyroidism, take on empty stomach in morning, adjust dosage if s/s persist
emergency IV- 0.1 mg = 100 mcg
overdose s/s: palpitations, angina
methimazole
treats hyperthyroidism, effective if symptoms improve
overdose s/s: palpitations, angina
cushing’s syndrome
excess cortisol, leading to moon face, truncal obesity, and hypokalemia
s/s: high cortisol, hypokalemia, hypernatremia
osliodostat- synthesis inhibitor
addison’s disease
adrenal insufficiency requiring steroid replacement
s/s: hypotension, fatigue, hyperpigmentation
fludrocortisone + prednisone for treatment
corticosteroids
prednisone take in morning to reduce adrenal suppression, monitor for hyperglycemia and sodium retention, IV stress-dosed steroids
long term slows wound healing
SIADH
excessive ADH leading to concentrated urine and hypertension
DI treatment
decreased thirst
desmopressin effectiveness
increased urine concentration, decreased thirst
DDAVP: synthetic ADH used for DI
post-op respiratory risk
morphine induced apnea may lead to hypercapnia (excessive Co2 in blood)
pancreatitis and ARDS risk
severe hypoxemia, tachypnea
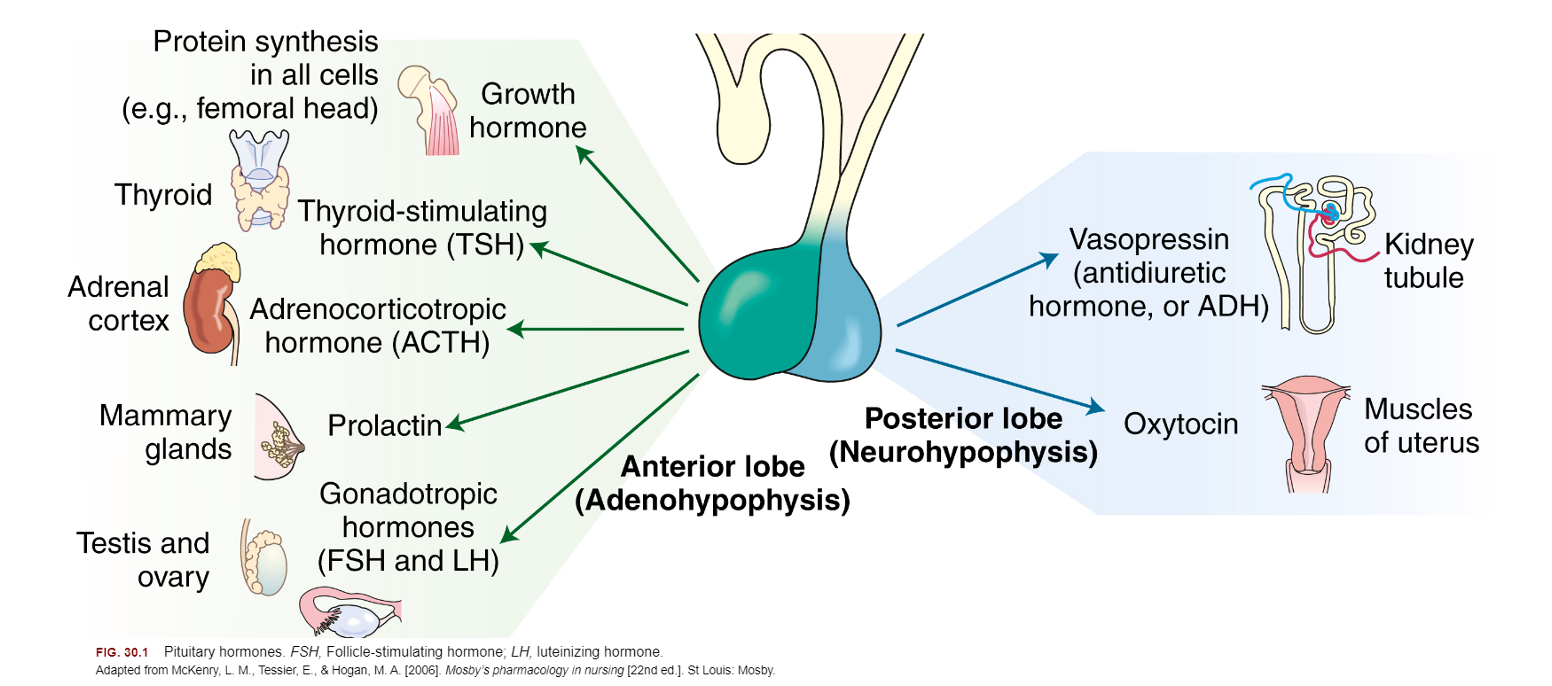
neuroendocrine system
CNS/hypothalamus controls pituitary gland
posterior: ADH, oxytocin
anterior: ACTH, FSH, GH, LH, PH, TSH
pituitary hormones visual
anterior drugs
cosyntropin- used in diagnosis of adrenocortical insufficiency
somatropin
octreotide
octreotide
alleviate s/s w/ carcinoid tumors from VIP secretion (diarrhea, flushing, hypotension), treats esophageal varices, may affect glucose reg. (severe hypoglycemia with type 1, hyperglycemia with type 2 or pt w/o diabetes), may enhance toxic effects of drugs that prolong QT interval
given IV/IM/SQ
may order EEG (AE of conduction abnormalities), baseline glucose levels, liver and kidney tests monitoring
somatropin
human GH produced by recombinant technology (hypopituitary dwarfism, wasting/weight loss with HIV)
important to not shake product, SQ or IM
monitor growth, motor skills, height, weight of pediatric pt
AE: headache, muscle pain, hyperglycemia, hypothyroidism, hypercalciuria, fluidlike syndrome
posterior drugs
vasopressin, desmopressin
both control polyuria, polydipsia, and dehydration in DI pt (deficiency of ADH), both can be given nasally
AE: high BP, fever, headache, abd cramps, nausea
desmopressin
can treat bleeding (gastrointestinal hemorrhage), hemophilia A, & type I von willebrand disease (d/t clotting factors), + nocturnal enuresis, clotting factors
available as DDVAP rhinal tube, can be given IV (mix, may change nasal mucosa)
assess VS, hx of asthma, seizure, or cardiovascular disease, neuro status, breath sounds, heart sounds
AE:
vasopressin
controls pulsess arrest and vasodilatory shock (more for blood pressure), watch for s/s of infiltration
caution with seizure disorders, asthma, cardiovascular disease, renal disease
applies topically to nasal membranes (not inhaled), IM, IV (check clarity)
EEG monitoring, VS, invasive monitering (arterial lines, central venous pressure lines, ABGs)
AE: high BP, fever, nausea, abdominal cramping
pituitary drug assessment
weight, height, VS, pregnancy status, medication hx, allergies to prescriptions, OTC, supplements, and herbals
GH: baseline thyroid, glucose, calcium levels (potential hyperglycemia, hypothyroidism, hypercalcemia)
adrenal system
sits on top kidney, cortex (hormone driven; corticosteroids), adrenal medulla (hormone and peripheral autonomic nerve impulse driven; catecholamines)
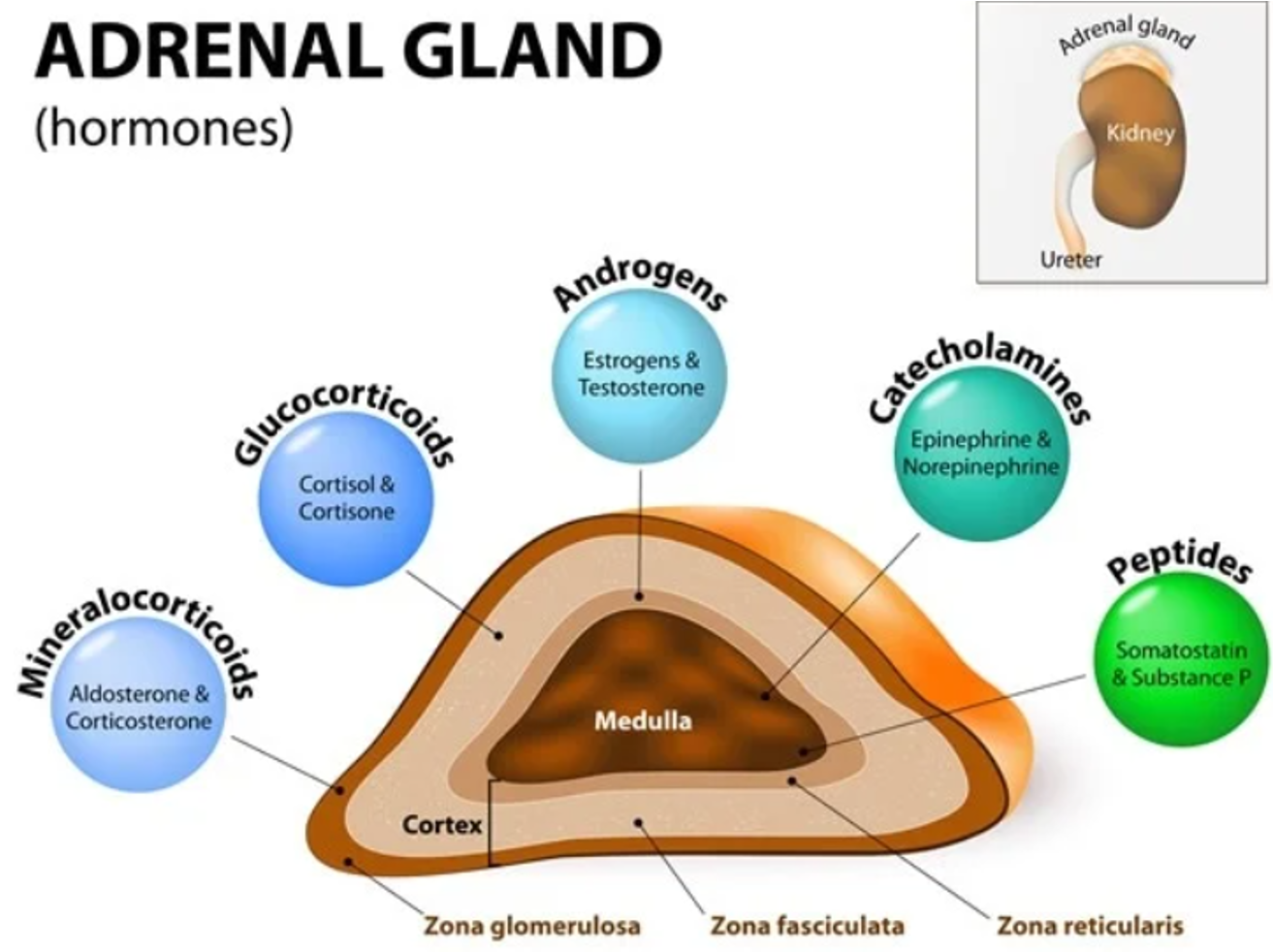
corticosteroids
not stored by body, synthesized as needed, reg. by HPA axis, negative feedback
cushings- fat in face, shoulders, trunk, and abd (moon face, humpback), hirsutism, ecchymoses, HTN, hypokalemia, abnormal glucose tolerance, muscle atrophy
addisons- decreased blood sodium and glucose, increase K, dehydration, weight loss
adrenal drugs
steroids, synthesizes specific proteins, most modify enzyme activity
glucocorticoids- inhibit inflam. response, lowers fever, stimulates WBC, increase glucose, protein break down, lipolysis, demineralization, mast cell stabilization
indications of adrenal drugs
nasal- rhinitis, prevents polyps
topical- inflam. management on skin
oral- most common prednisone, followed by dexamethasone
methylprednisolone- injectable glucocorticoid followed by hydrocortisone and dexamethasone
bethmethasone- accelerate fetal lung maturation (premature)
contraindications of adrenal drugs
glaucoma, peptic ulcer disease, mental health
caution with diabetes, infection, gastritis or reflux (gastric perforation risk), cardiac, renal, and/or liver disfunct. (alteration in elimination)
AE of adrenal drugs
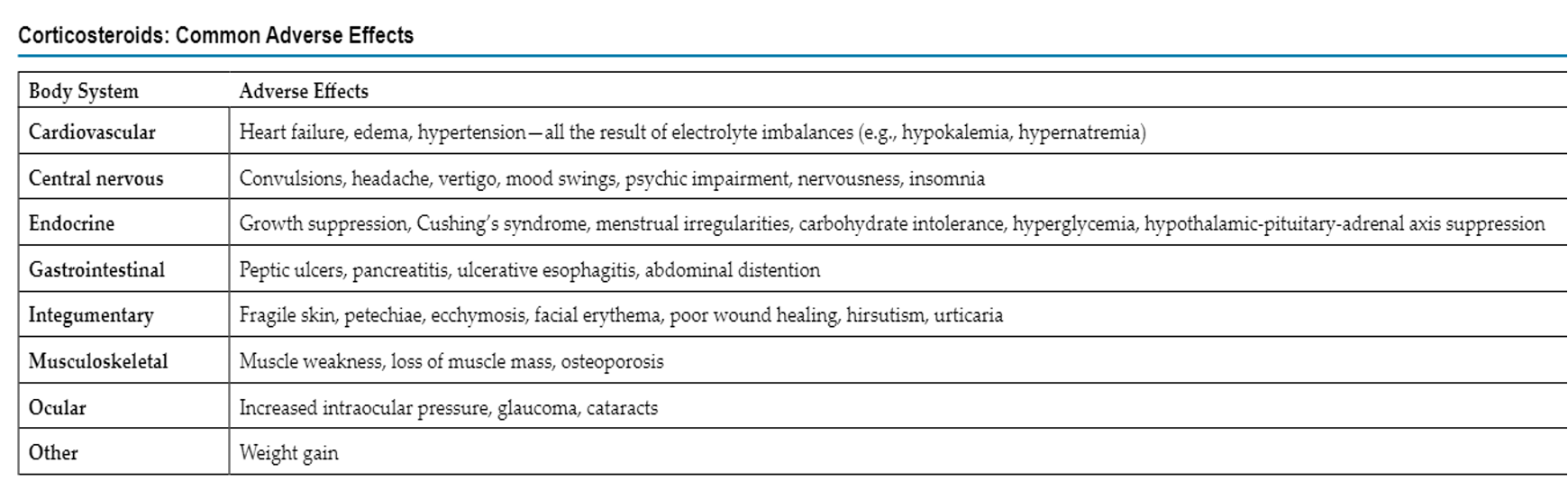
interactions of adrenal drugs
non-K sparing diuretics (thiazides, loop), aspirin + NSAIDs, anticholinesterase
adrenal drugs ADPIE
asses nutrition, hydration, immune status, baseline weight and labs, I/O, VS, skin
implement early (6-9a), avoid infection, monitor assessments ^, call HCP for edema, SOB, joint paint, fever, mood swings, prednisone + fludrocortisone orally w. snack, avoid abrupt withdrawal, inhaled risk of fungal infection
AE: weight gain, HTN, Na increase, K loss, MS changes, abd distention, ulcer s/s, vision changes
thyroid
T4, T3 (needs iodine from diet, released by TSH), calcitonin
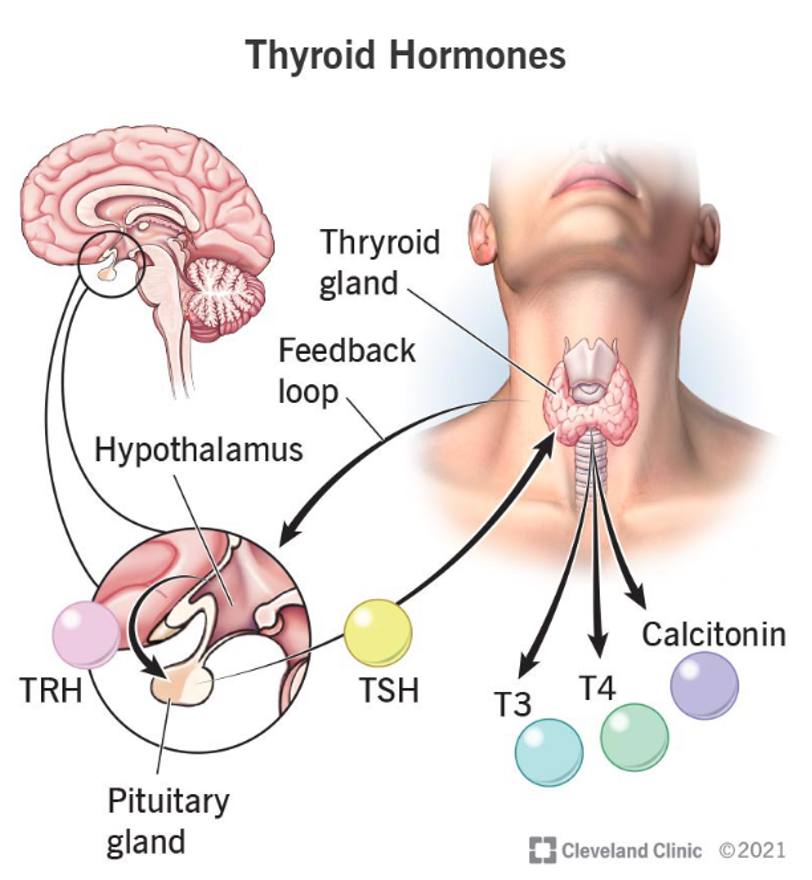
parathyroid
maintain calcium in ECF
hypothyroidism
s/s: cold intolerance, weight gain, depression, dry brittle hair and nails, fatigue
primary most common, hyposecretion can lead to cretinism (youth) or myxedema (adult)
amiodarone can cause
thyroid replacement drugs
levothyroxine (T4; most preffered), lipothyronine (T3), liotrix (T4 + T3; 4:1 ratio)
monitor serum TSH and free thyroid hormone levels for dosing
increase O2 consumption, body temp. blood vol, cell growth/differentiation, stimulate cardiovascular, increase renal blood flood
thyroid contraindications and AE
recent MI, adrenal insufficiency, hyperthyroidism
interacts with warfarin (increases activity)
take on empty stomach in morning
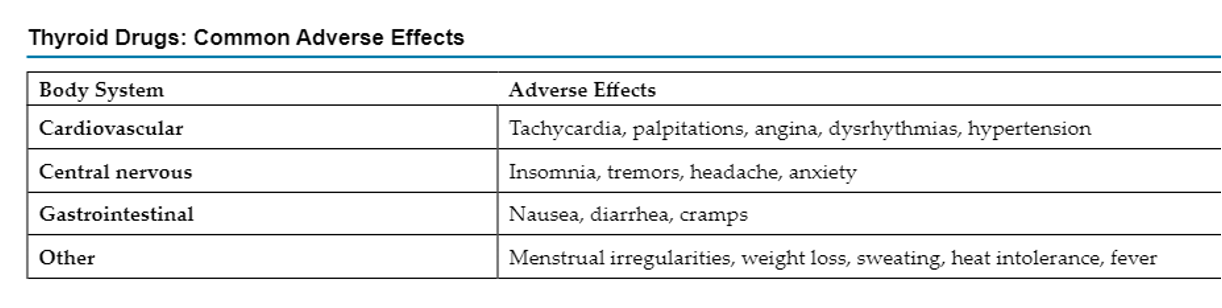
levothyroxine
stick to same brand, dosed in micrograms (question doses >200mcg), IV
baseline VS, medication hx, allergies
avoid iodized salt
antithyroid drugs
treat hyperthyroidism, inhibit precursors to make T3 and T4, prevent surges in hormone after surgery or radioactive treatment, graves’ disease, and thyroidectomy
methimazole, propylthiouracil (PTU), or radioactive iodine, sometimes potassium iodide
antithyroid contraindications
allergies, use in pregnancy (PTU in first trimester)
effects liver and bone marrow, additive leukopenic effects w/ bone marrow suppressants, increase oral anticoagulant
asses VS, thyroid crises s/s
take w/ meals, monitor liver test and CBC, avoid iodized salt, monitor for hypoparathyroidism
pancreas
exocrine- secretes from duct, endocrine- secretes into bloodstream, insulin + glucagon
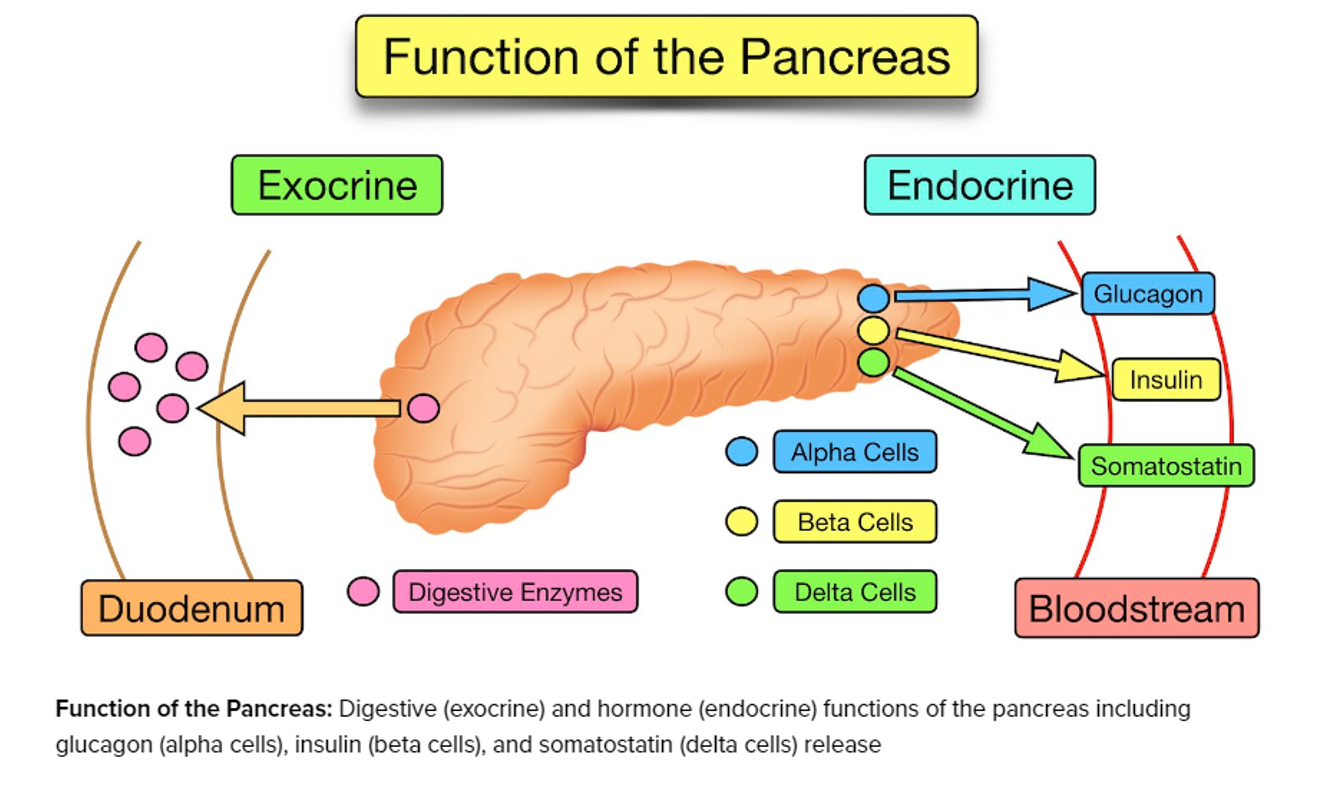
hyperglycemia complications
macrovascular: plaque effecting central and peripheral circulation
microvascular: damages eyes and kidneys, nerve damage
rapid acting
lispro, aspart, glulisine (LAG, NAH)
15 min
short acting
regular insulin, used in DKA or coma w/ type 1
30-60 min
intermediate acting
NPH
1-2hr
long acting
glargline, detemir, degludec (DDG, LLT)
glargine (lantus): blood levels do not rise or fall, clear, dosed 1-2 daily, sometimes referred as basal insulin
1-2hr
basal bolus
preferred tx for hospitalized pt, basal given to mimic pancreas then bolus mimics response to increase in blood glucose levels, NPO pt not good candidates (risk of hypoglycemia)
non insulin drugs
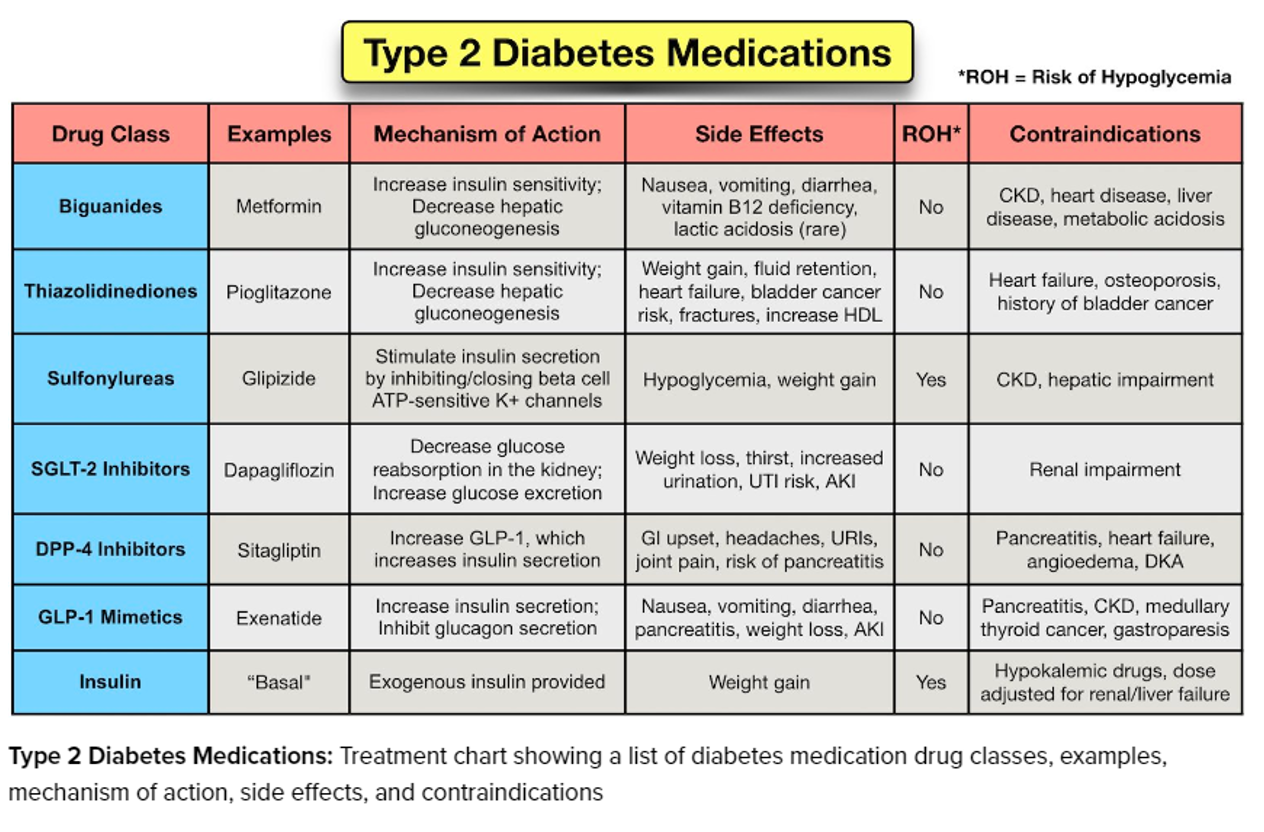
biguanides
first line drug for type 2, decreases glucose production, metformin initially, can cause weight loss
contraindicated with renal disease/function (creatine clearance of >30 mL/min), can accumulate and cause lactic acidosis
AE: lactic acidosis (hyperventilation, clammy skin, muscle pain, abd pain, dizziness, irregular heart beat)
sulfonylureas
bind to beta cells to release insulin, glipizide, glyburide, glimepiride, must have some functioning beta cells in pancreas, should not be used in advanced diabetes dependent on insulin
contraindicated in hypoglycemia, NPO, or advanced age
can cross-allergy with atbs, AE- hypoglycemia, weight gain
glinides
repaglinide, nateglinide, similar function as sulfonylureas (increase insulin; but not combined), shorter action + given with meal, treats type 2
thiazolidinediones (glitazones)
insulin-sensitizing drugs (decrease insulin resistance by enhancing insulin receptor sensitivity), pioglitazone, can be combined with metformin and sulfonylurea
contraindicated with NY heart association class 3-4 heart failure
BB: can exacerbate HF, not recommended w. symptomatic HF
alpha-glucosidase inhbitor
acarbose, miglitol, reversely inhibit in small intestine, timing important + take with food, lowers glucose spike from food
contraindicated with inflam. bowel disease, malabsorption, or obstruction
AE: flatulence, diarrhea, abd pain
DPP-IV inhibitor
-gliptin, combination drugs, delay breakdown of incretin, reduce glucose concentrations, used w/ diet and exercise to control glycemic levels, sitagliptin may increase digoxin levels
GLP-1 agonist
acts on endogenous hormone incretin (secretes insulin, reduce glucagon production, slow emptying, increase satiety), -tide, semaglutide (ozempic), only for type 2 that are unable to control glucose w/ metformin, sulfonylurea, or glitazone
BB: thyroid C-cell tumor
amylin agonist
secreted with insulin, SQ injections during mealtime if insulin not optimal, pramlintide, take 1hr before other drugs
Sglt2 inhbitors
oral drug, inhibit glucose reabsorption in proximal renal tubules
glucose elvating drugs
below 70mg/dL, D50W, oral tablets, glucagon for unconscious pt