D.1.1 - DNA Replication
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Why does the production of DNA need to be accurate?
So new cells/organisms can carry out functions of life
What does DNA replication do?
Doubles the quantity of DNA
What is achieved by DNA replication?
Reproduction, growth & repair, tissue replacement
Introducing new bases to DNA
An experiment was done, introducing two new nitrogenous bases to the genetic code of bacteria. These bases were incorporated into the bacterial DNA code. This could be the basis for new medicines.
Why is it called semi-conservative replication?
Each strand in the DNA double helix acts as a template for the synthesis of a complementary strand
Each daughter DNA strand contains one old strand from the parental DNA and one new one
Hence the name semi-conservative
Helicase
The enzyme that unzips/unwinds the DNA double helix in the first step of DNA replication, breaks the hydrogen bonds joining organic bases.
DNA polymerase
Group of enzymes that join free-floating nucleotides onto single DNA strands to synthesise a parallel DNA double strand. (Uses the single DNA strand as a template), catalyses hydrogen bonds between the organic bases. Can only synthesise from 5’ to 3’ end.
Why are daughter strands from the same DNA strand synthesised in opposite directions?
Because DNA polymerase can only synthesise from the 5’ end (of the new strand) to the 3’ end. These are opposite in each strand because of DNA’s antiparallel structure (the two strands run in opposite directions.)
Outline DNA replication
DNA is unzipped by helicase
Two identical, complementary strands are formed
Free-floating nucleotides in the nucleoplasm join with the now-unpaired organic bases in the DNA single strand
These nucleotides form covalent bonds, catalysed by one of the DNA polymerase enzymes, which make up the DNA backbone
The two new DNA strands are synthesised in opposite directions, one towards the helicase, and one away from it.
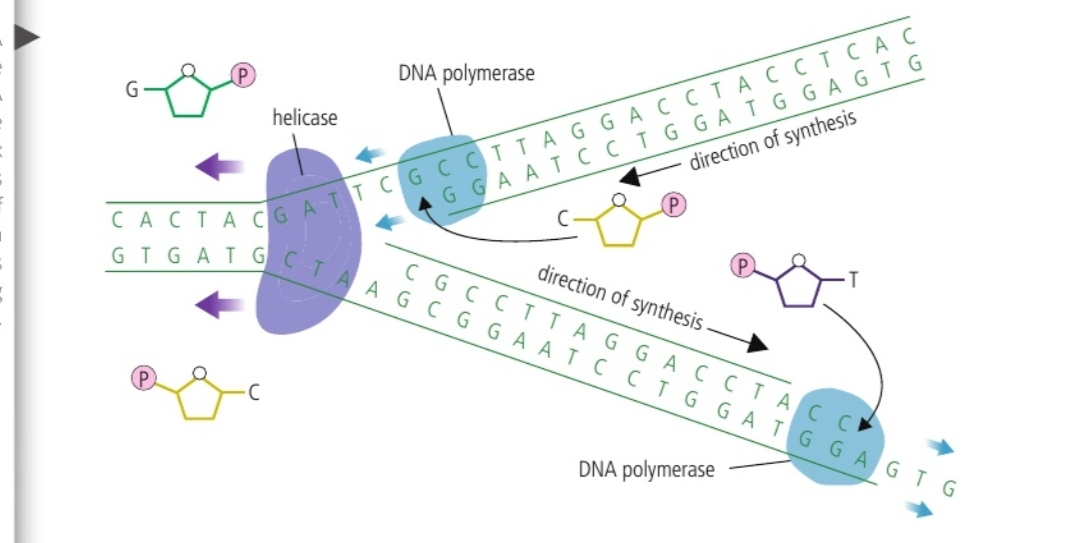
Summarise semi-conservative DNA replication
Helicase enzyme unzips a DNA double helix strand, allowing for two new, identical strands to be synthesised. Free-floating nucleotides are joined to the single strands by DNA polymerase enzymes
Why are the two daughter DNA strands synthesised from one DNA strand identical?
Because of the base pair rule
Replication fork
The shape of DNA during step one of replication: the double helix on one side of the moving helicase, the other side already separated by helicase, leaving 2 separated strands.
PCR
A thermocycler is used to take a small amount of DNA, then it copies all the nucleotides and can produce millions of copies of the DNA. PCR can only amplify a targeted section of DNA.
What is needed for PCR?
Primers
Taq polymerase (enzyme)
Free nucleotides
Helicase
PCR primers
Short, single-stranded polymers of nucleotides that are complementary to the nucleotides at one end of the target DNA. Neccessity: DNA polymerases can only attach new DNA nucleotides to existing polymers.
PCR process
Denaturation: 92-98°C, mixture is heated to break hydrogen bonds holding together the two DNA strands
Annealing: 50-65°C, allows primers to bind with nucleotides at the ends of target DNA
Elongation: 70-80°C, taq polymerase catalyses DNA replication by extending the primers.
Gel electrophoresis
Enzymes are used to fracture long DNA filaments into smaller particles of varying size. They are then placed in the wells of an electrophoresis chamber and exposed to an electric current. The largest, heaviest, and least charged particles move with great difficulty, while the smallest, least massive, and highly charged move with ease. This difference in speeds creates a banded pattern of DNA.
DNA profiling/fingerprinting
The process of comparing two different DNA samples to see if they correspond. Done using gel electrophoresis; if the patterns of DNA are identical, the DNA belongs to the same individual, if they are similar, the individuals are likely related. When little DNA is present, PCR is used to amplify the amount available for sampling.
Is DNA positively or negatively charged?
Negatively charged due to the phosphates
When is PCR used?
GMOs
Criminal investigations
Paternity testing
Testing for viral infection (PCR test)
Genetic diseases
Short tandem repeats
Repeated sequence of A-G-A-T, amount of repetitions varies per person. These create the band patterns made by gel electrophoresis.