Epithelial Tissue Histology
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Squamous
flat/scale-like

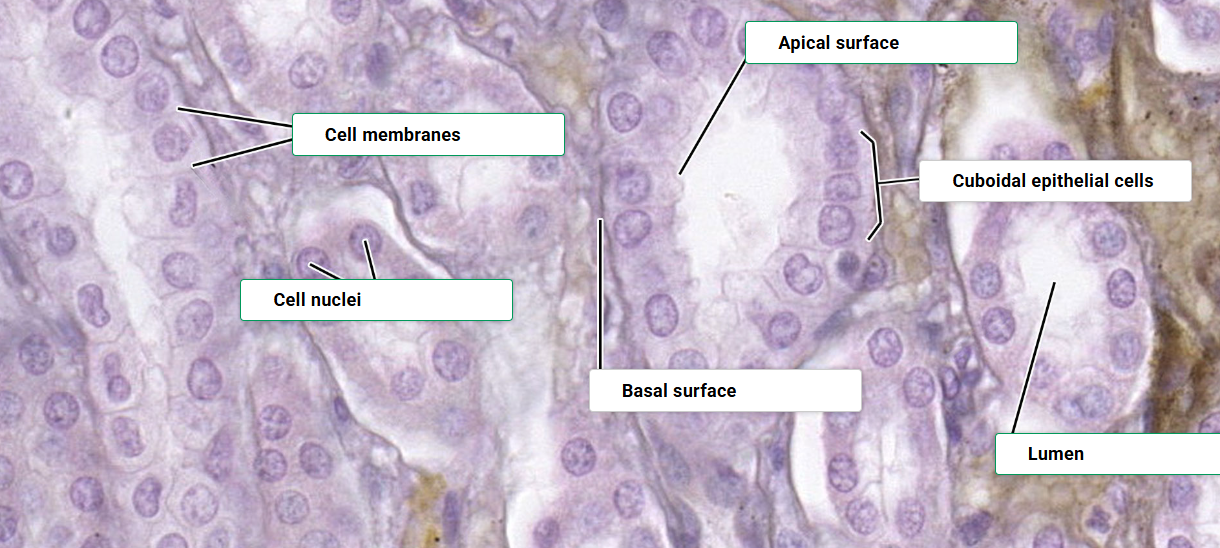
Cuboidal
cube shaped. as wide as it is tall

Columnar
column-like. taller than it is wide

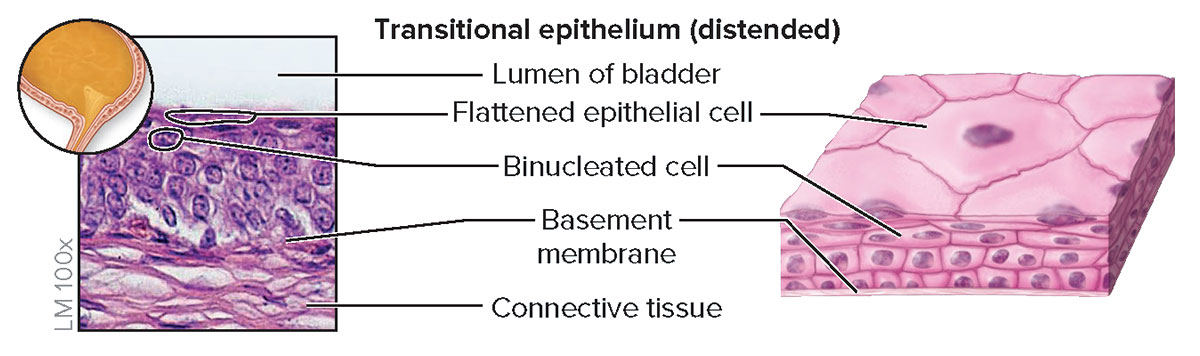
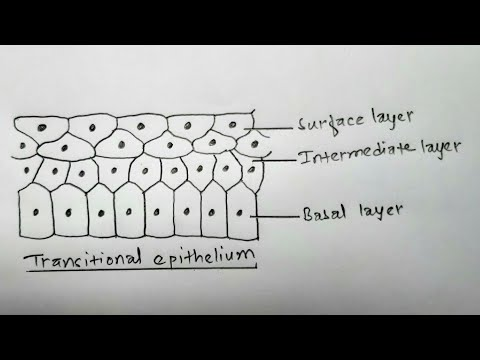
Transitional
a type of epithelial tissue that can change shape, typically found in the bladder, allowing it to stretch and accommodate fluctuating volumes of liquid.
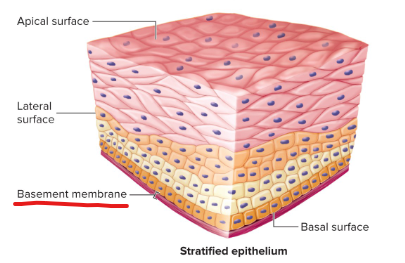
Apical surface
the surface of an epithelial cell facing the lumen or external environment
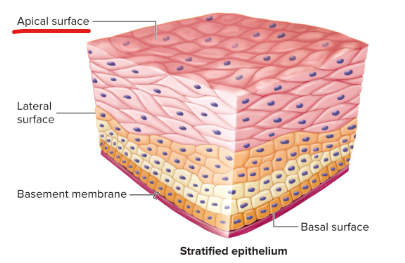
Basal surface
The surface of an epithelial cell facing the basement membrane.
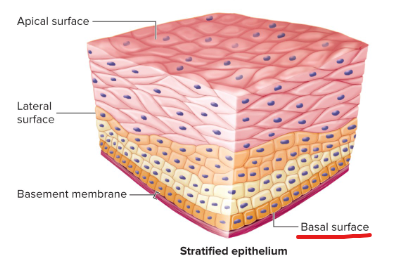
Basement membrane
Formed from the epithelial and underlying connective tissue layers. It aids in attachment of the epithelial tissue and as a selective molecular barrier to underlying connective tissue.
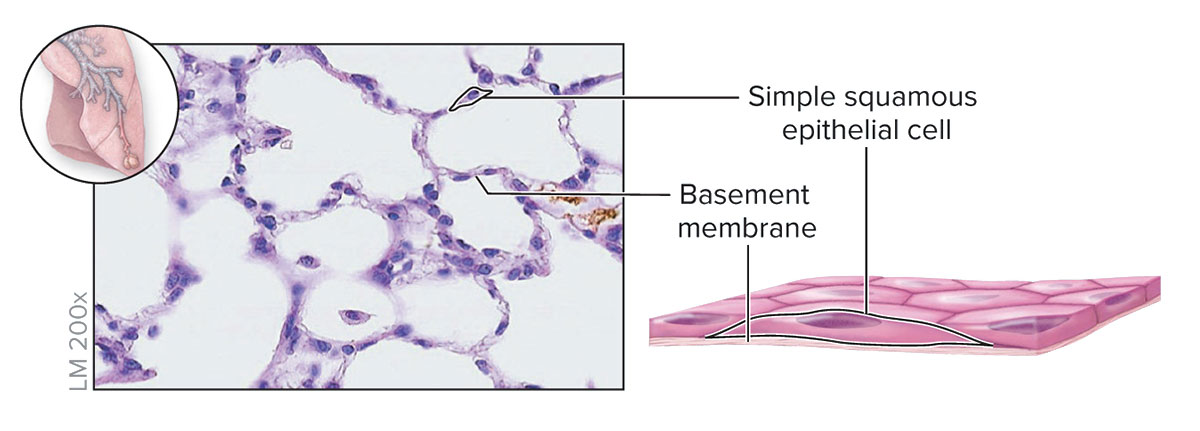
Simple squamous Epithelium
Structure
Single layer of thin, flat cells resembling irregular floor tiles; the single nucleus of each cell bulges at its center
Function
Thinnest possible barrier to allow for rapid diffusion and filtration; secretion in serous membranes
Location
Air sacs in lungs (alveoli); lining of lumen of blood vessels and lymph vessels (endothelium); serous membranes of body
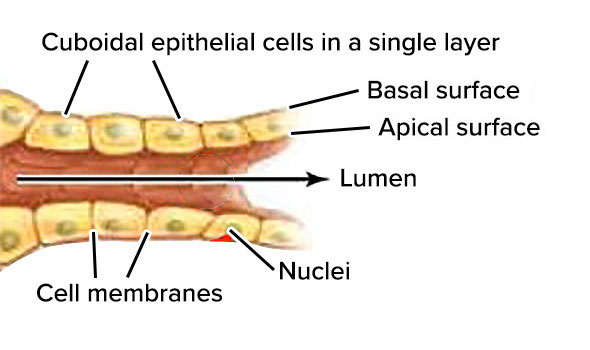
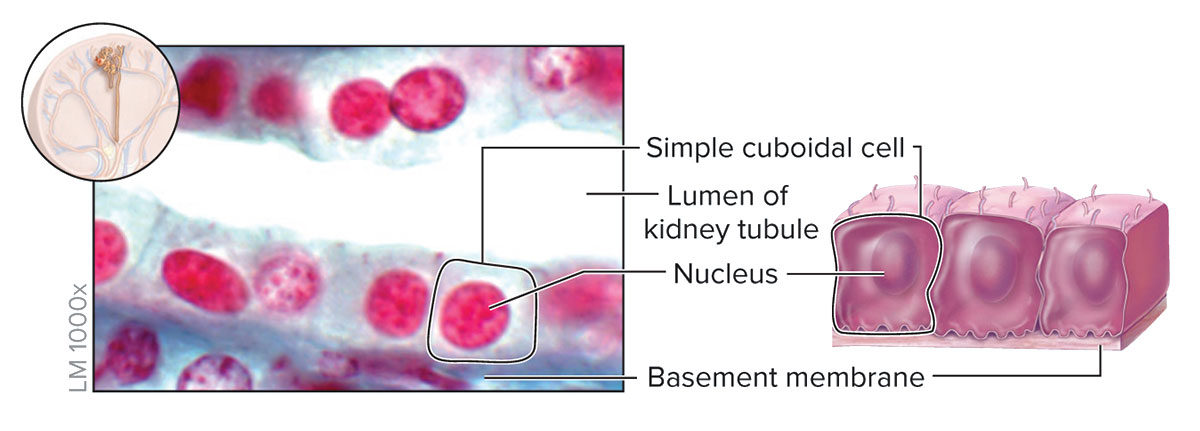
Simple cuboidal Epithelium
Structure
Single layer of cells about as tall as they are wide; spherical and centrally located nucleus
Function
Absorption and secretion; forms secretory tissue of most glands and small ducts
Location
Kidney tubules, thyroid gland follicles; surface of ovary; secretory regions and ducts of most glands
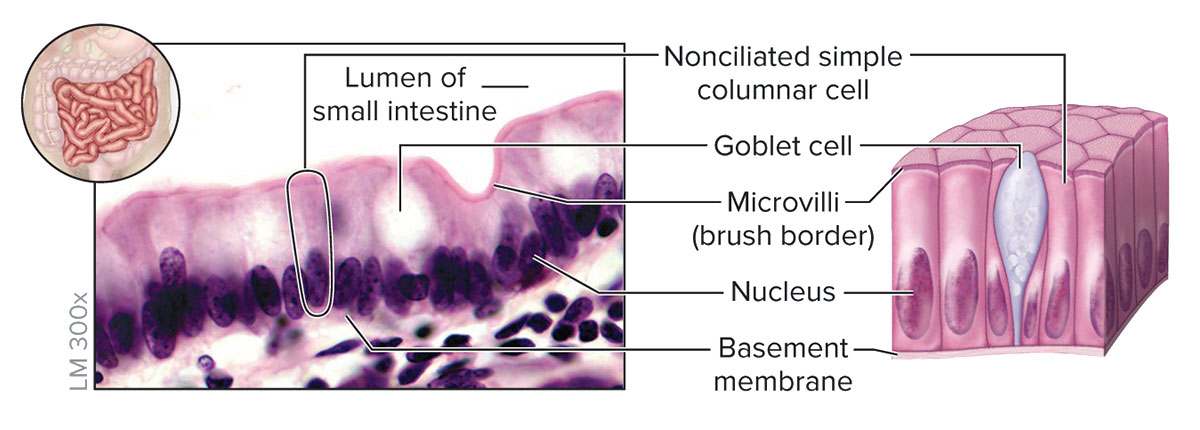
Simple columnar Epithelium
Structure
Single layer of cells taller than they are wide; oval-shaped nucleus oriented lengthwise in basal region of cell; apical regions of cell may have microvilli; may contain goblet cells that secrete mucin
Function
Absorption and secretion; secretion of mucin
Location
Inner lining of most digestive tract (stomach, small intestine, and large intestine)
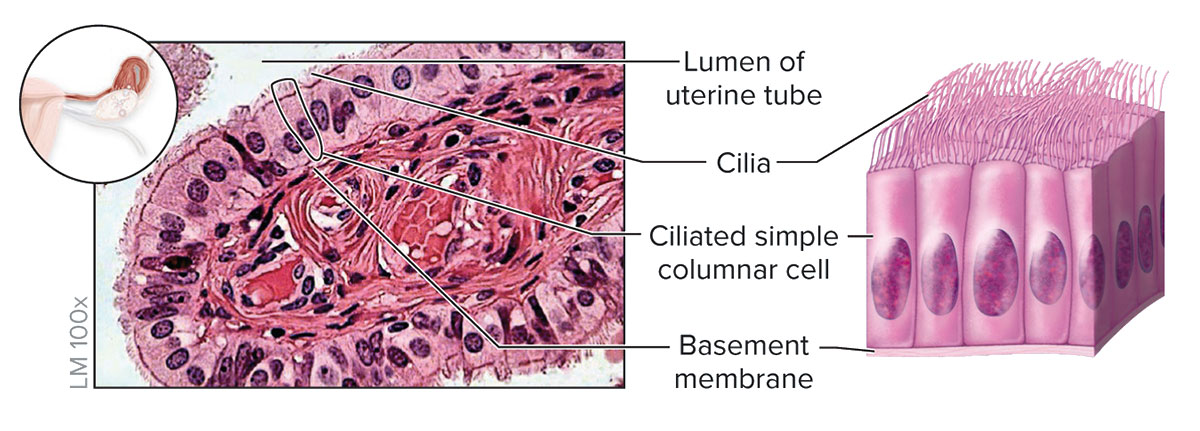
Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium
Structure
Single layer of ciliated cells taller than they are wide; oval-shaped nucleus oriented lengthwise in basal region of cell; may contain goblet cells
Function
Secretion of mucin and movement of mucus along apical surface of epithelium by cilia; oocyte movement through uterine tube
Location
Lining of the larger bronchioles (air passageways) of the lung and the uterine tubes
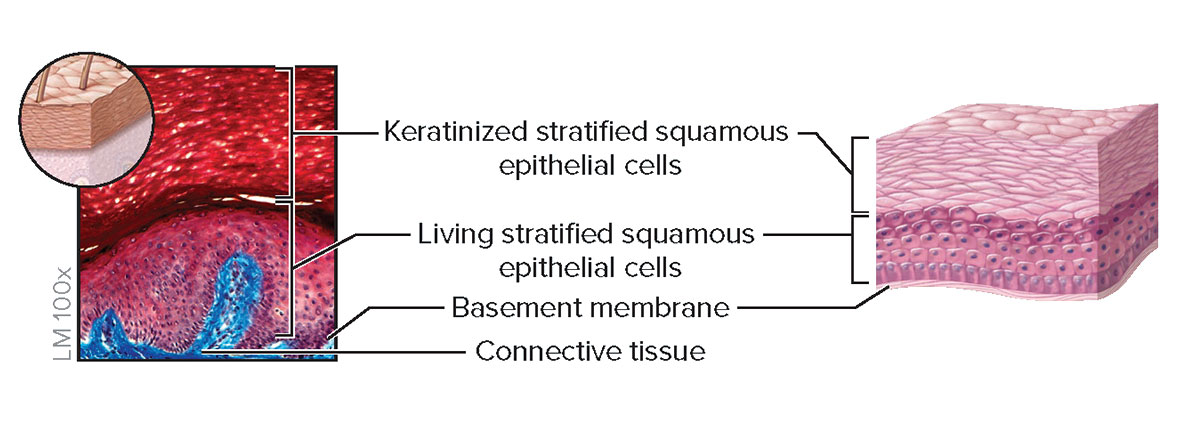
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Structure
Multiple cell layers; basal cells are cuboidal or polyhedral, whereas apical cells are squamous; apical cells are dead and filled with the protein keratin
Function
Protection of underlying tissue from abrasion
Location
Epidermis of skin
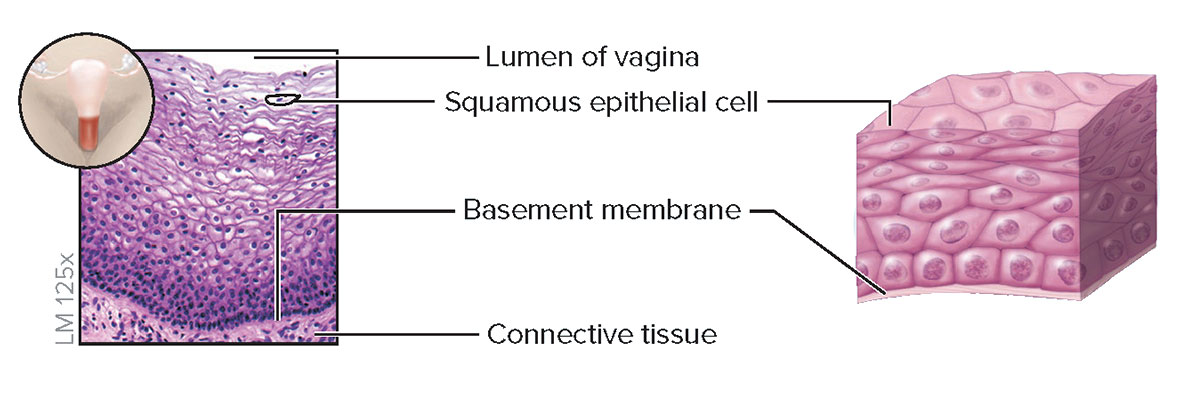
Nonkeratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Structure
Multiple cell layers; basal cells are cuboidal or polyhedral, whereas apical (superficial) cells are squamous; cells lack keratin; superficial cells are alive and kept moist
Function
Protection of underlying tissue from abrasion
Location
Lining of oral cavity, part of pharynx, part of larynx, esophagus, lining of vagina, and anus
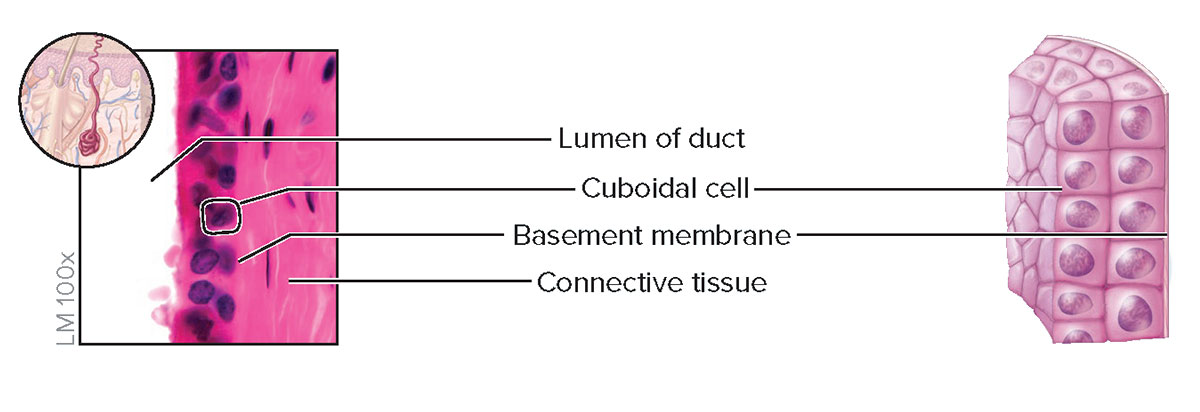
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Structure
Two or more layers of cells; cells at the apical surface are about as tall as they are wide
Function
Protection and secretion
Location
Ducts of most exocrine glands and ovarian follicles
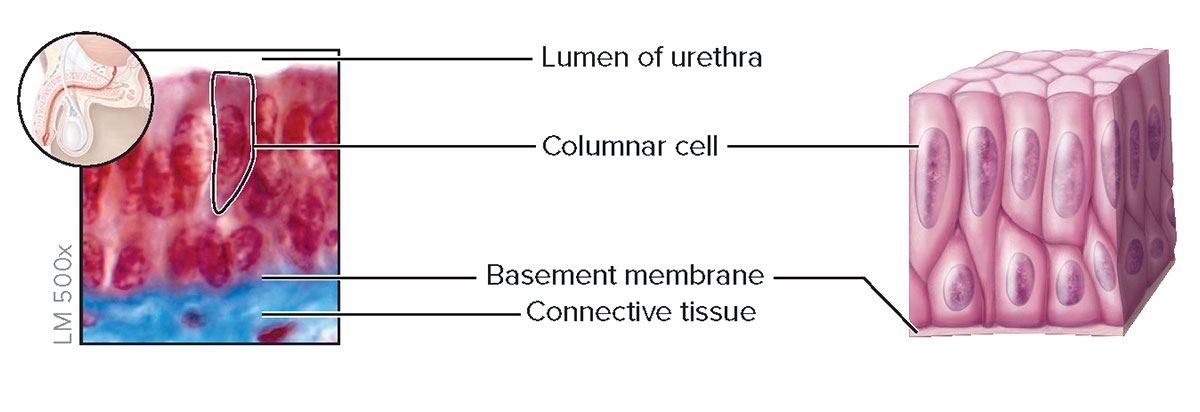
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Structure
Two or more layers of cells; cells at the apical surface are taller than they are wide
Function
Protection and secretion
Location
Large ducts of salivary glands, conjunctiva covering the eye, and membranous part of male urethra
Transitional
Structure
Epithelial appearance varies, depending upon whether tissue is relaxed or distended (stretched); relaxed epithelium (top) has cuboidal or polyhedral cells and the apical cells are large and rounded, whereas distended epithelium (bottom) has flattened cells at the apical surface; some cells are binucleated
Function
Accomodates urine volume changes (by distending or relaxing) in the urinary bladder, ureters, and part of urethra
Location
Lining of urinary bladder, ureters, and part of urethra