sq 11 - gene 2 transcription; dr reyes 🧬
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
X, Y
is 3x larger than the other xmosome
contains 55 genes only
Nucleus
Most dna is found in
Gene
is a length of DNA that directs the synthesis of a polypeptide or of a functional mRNA.
Replication
DNA copied to DNA
Transcription
DNA info copied to mRNA
Translation
proteins synthesized using mRNA info as a template
3, does not
Each of the estimated 30,000 genes in the human genome make an average of X proteins
97% of the human genome does/does not encode proteins “dark matter”
T
T/F The complexity of an organism does not relate to the amount of DNA in its genome
T
T/F?
Crick said it cant go backwards
Temin & Baltimore said you can use RNA template to enable DNA synth
Pro, Couple transcription translation, Euka, Nucleus, Cytoplasm
PRO VS EUKA?
can do simultaneous protein synthesis (translation) bc ribosomes are already there (doesnt need transcription to finish)
What is this process called
Trancscri & transla occur in different compartments
Transcri =
Transla =
Histones, introns
Prokaryotes do not have:
Aka non coding dna
Monocistronic, eukaryotes
MONOCISTRONIC vs POLYCISTRONIC 🤡
meaning a single gene produces a single protein. Has introns
Which organism?
Polycistronic, prokaryotes
MONOCISTRONIC vs POLYCISTRONIC
Meaning it comes from an operon, transcript is not modified and trimmed, and has NO introns.
Which organisms?
DNA, RNA polymerase, rRNA, tRNA, ncRNA
in TRANSCRIPTION…
RNA synthesis from a X template
Carried out by XX
Produces mRNA, X, Y, Z
Coding, sense; template, antisense; antisense; sense; antisense
Looking at. A gene.s equence…
The first strand is the DNA x strand, otherwise called the (sense/antisense?)
The second strand is the DNA y strand, otherwise called the (sense/antisense?)
Which strand is the mRNA complimentary to?
Which strand is the mRNA similar to, but instead of a T, has. uracil?
Which strand runs in the 3’ 5’ direction?
A, U
If the sense strand says T, then:
Antisense says: (normal pair)
mRNA says: (has uracil)
5’ and 3’ cap
In eukaryotes, the mrna isnt the mature form yet. It must first have a pre-mRNA before it becomes the mature form, whose hallmark is having the X&Y.
Initiation, elongation, termination
both rna & dna polymerases:
Involve general steps of X, Y, Z (5-3’ polarity)
Has polymerization complexes
Adheres to watson crick base pairs
Primers, RNAP, proofreading, portions
The difference of RNA POLYMERASE is that:
ni need for X to initiate transcription, bc they have Y that initiate synthesis de novo
No X (No 2’-5’ exonuclease activity)
Can transcribe/copy into RNA only X of the genome (DNA = whole)
Pro, mRNA
ID organism
Has 1 RNAPolymerase that transcribes DNA to all types of RNA
ribosomes bind to X while being transcribed thus translation can occur simultaneously
Eukaryote
ID organism:
Has 3 nuclear RNAP
Mitochondria has its own RNA polymerase to transcribe genes located in its own genome
Primary transcripts are modified and trimmed to produce mature RNA.
3’ to 5’
Step 1:
DNAtemplatestrandiscopiedinthe X-Y direction.
5′ to 3’
Step 2: Synthesis of the new RNA molecule occurs in the X-Y
direction.
ATP, CTPL GTP, UTP
Step 3:
Precursors include? 🥑 guacamole~
Ester, alpha, 5’
Step 5:
The polymerase forms an X bond between the X-phosphate on the ribose X′-hydroxyl of the nucleotide precursor (nasa baba) & the ribose 3′-hydroxyl at the end of the growing RNA chain.
Polymerization
Step 6:
The cleavage of a high-energy phosphate bond in the nucleotide triphosphate and release of pyrophosphate (from the β- and γ-phosphates) provides the energy for this X reaction.
Hairpin
The secondary structure of rna folds on itself like a ?
DNA template strand
In prokaryotes, hairpin formation can cause RNA polymerase to dissociate from ?
Mrna
What rna is protein coding
DNA, ribosomes, carboxy, 5
mrna:
Is transcribed from?
Is translated by x into specific proteins?
Exhibits amiNo terminal to C-terminus. What does C mean?
Comprise only X% of total rna
PolyCisTronic, monocistronic
If your mrna:
carrying information from more than one gene is? (prokaryotes, mitochondria, some viruses, and in chloroplast in plants)
carrying information from only one gene is? (eukaryotes)
Poly-A tail, 5
Special structural characteristics of eukaryotic mRNA:
Long sequence of adenine nucleotides aka? On the end of rna
Cap on the X’ end consisting of a molecule of 7-methyl guanosine, attached through an unusual 5’ - 5’ untranslated region
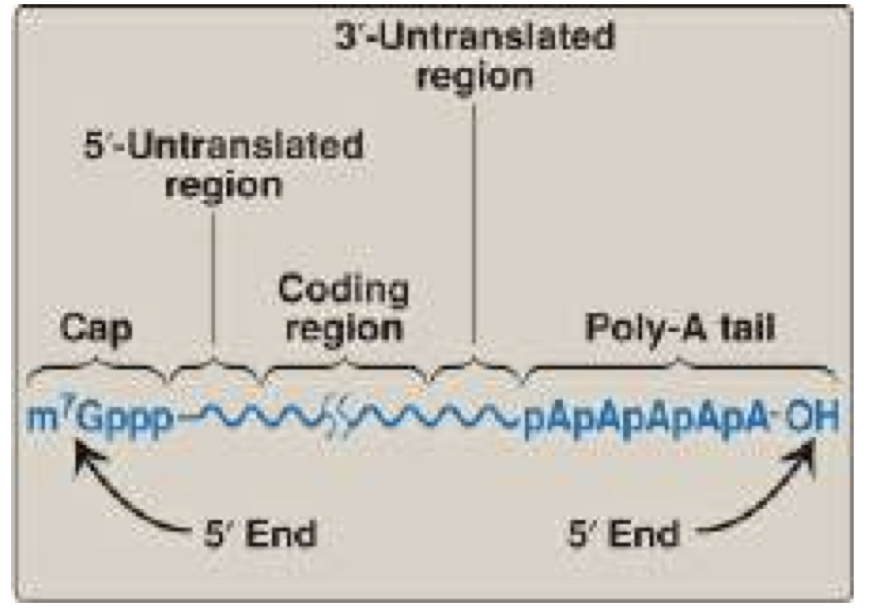
Poly-A tail
This mrna special structure:
Req for initiation of protein synthesis after producing mature mrna transcript.
Maintains intracelllular stability by preventing 3-exoribonuclease attacks
Methyl cap
Prevents attack of 5’ exoribonuclease
Folding, complimentarity, smallest, 15, 3’ terminus
Trna is:
Adapters for translation of information
They have a primary structure allowing extensive X and intrastrand Y to generate a cloverleaf struc
Size-est?
Make up X%
Attachment site?
Nucleus and mitochondria
Trna is encoded in the chromosomes of where?
Mrna
The anticodon loop of trna pairs with codon on the X during protein synth
UAC
Mrna to trna:
AUG =?
45S, 5S, 5S, 5.8S. 18S. 28S
rRNAs:
SinGle precursor of X except the Y rRNa
In eukaryotes, they have the 4 nuclear rRNAS?
and 2 rRNAs (12S & 16S)
They make up 80% of total rna.
snRNA, U3, U7
Rna that is involved in rRNA & mRNA processing & gene regulation
all U’s are involved in intron removal & processing of mrna precursors, EXCEPT?
The Ux snRNA is involved in prod of correct 3’ ends of histone mRNA
Nucleolus,rRNA; cytoplasm, mRNA; nucleus, tRNA
RNA FORMS : location : MAJOR PD
RNAP I : x : x
RNAP II : x : x + microrna
RNAP III : x : x + noncoding
congratulations, rmt ka na!
Sigma, no,
PROKARYOTES…
specialfactor to become a complex / rnap can be recognized
does it need transcription factors?
-35, -10, a & t, -25
RNAP needs to bind to:
X upstream
and TATA box, Y upstream (promoter region)
Rich in,? Containing hydrogen bonds kaya easy to melt
But in eukaryotes, tata box is located
Introns
What contains non coding sequences? Exons or introns?
Introns
What contains foxed invariant dna control sequences
Promoter proximal elements
High rates of trasncription of genes is credited to
Lac operon
Bacterial operon that responds to favorable amounts og glucose or lactose in yeast cell
-35 sequence, -10
Initial contact point for closed complex
Holoenzyme moves and covers the X sequence for initial melting
Elongation, nusa
What process?
Sigma subunit is replaced by? To signal dissociation / termination
sinu sha elon….. 🤨😢😔😣
Rho protein, RAT
specialized helicase that uses energy from ATP to unwind a DNA/RNA hybrid double helix
Activated by a recognition site called X sequence
ubf1, SL1, cg rich region, T1F1A
Eukaryotic RNAP I:
When it binds to rrna, it requires these to be recognized by the promoter region:
Upstream binding factor aka
And selectivity factor
The promoter region, instead of tata box, is:
Needs what TF?
Rnap 3, internal promoter, downstream, TF3C
tRNA transcription is:
Done by what rnap
Using an?
Its promoter elements is located up or downstraem?
Needs what TF? To create tf3b
Tf3b contains tbp
Tbp, TFIID, tfiiA, tfiiB, tHiiF
All of this is bc RNAP 2 binds to the promoter region.
Trans factors:
Binds to tata box, part of TFIID
recognizes pol II specific promoter
Binds UPstream of tata
binds DOWNstream of tata
Bodyguard, accompanies rnap 2 upon binding to promoter
Nelf, DSIF, p-TEFb
RNAP II can pause by:
Drb sensitivity inducing factor
RNAP II can continue in the presence of? Positive transcription elongation factor by phosphorylating those inhibitors
Enhancers
can be located upsteeam or downstream
Cobalamin & folic acid
Vitamin deficiency affecting mrna
Hairpin, chain growth
Important in termination of signal is when the rna forms a?
Rifampin binds to RNAP to prevent ? Aka elongation.