AP Human Geography AMSCO Unit 6
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
industrial revolution
series of improvements in industrial technology that transformed the process of manufacturing goods

imperialism
A policy of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy or military force.

assembly line
Production method that breaks down a complex job into a series of smaller tasks

Fordism
Form of mass production in which each worker is assigned one specific task to perform repeatedly.

substitution principle
replace one factor (part) of production with another to save costs; typically replace a worker with a machine

post-Fordism
increased automation on the assembly line requires workers who are not replaced to perform many jobs

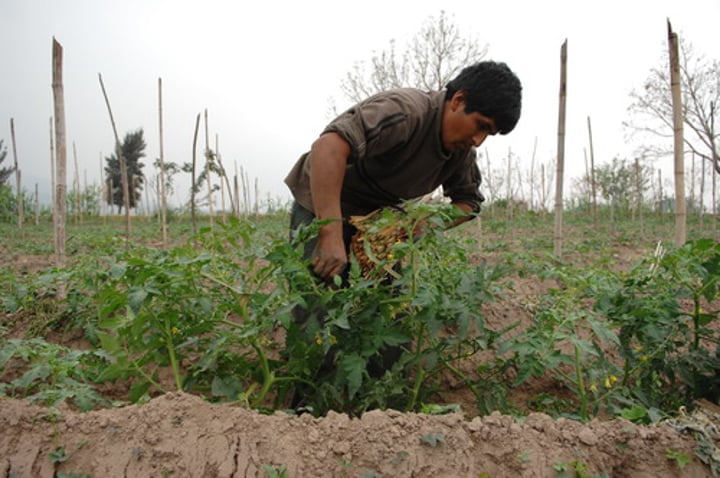
primary sector
the part of the economy that draws raw materials from the natural environment

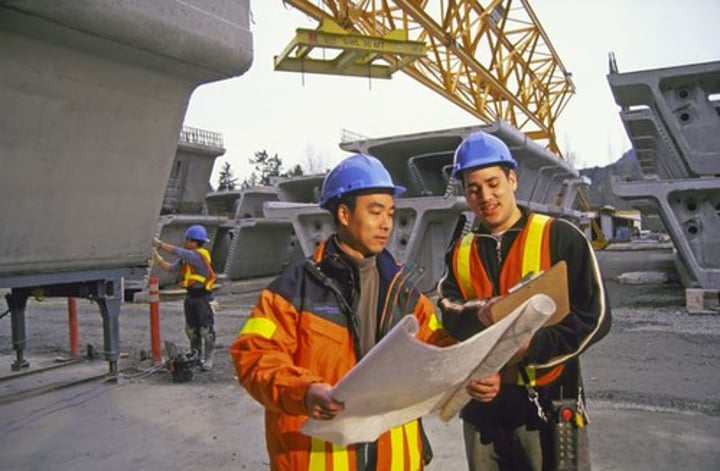
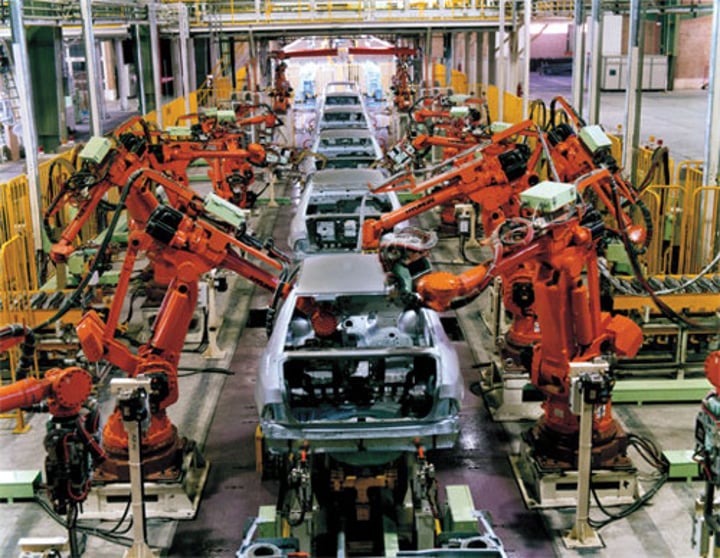
secondary sector
the part of the economy that transforms raw materials into manufactured goods

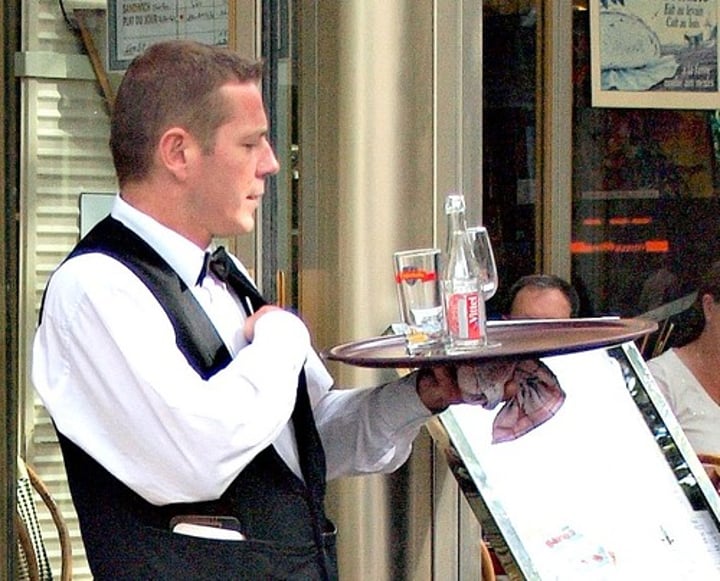
tertiary sector
the part of the economy that involves services rather than goods

quaternary sector
consists of information workers including information technology and scientific research
quinary sector
includes the highest levels of decision making in a society or economy

multiplier effect
expansion of economic activity caused by the growth or introduction of another economic activity
agglomeration economies
the benefits firms reap by locating in close geographical proximity to each other

isotropic plain
terrain is perfectly flat everywhere and equally well drained, so that any area of the land is equally suitable for any purpose

least cost theory
factories desire to minimize the cost of transportation, labor, and increase in agglomeration
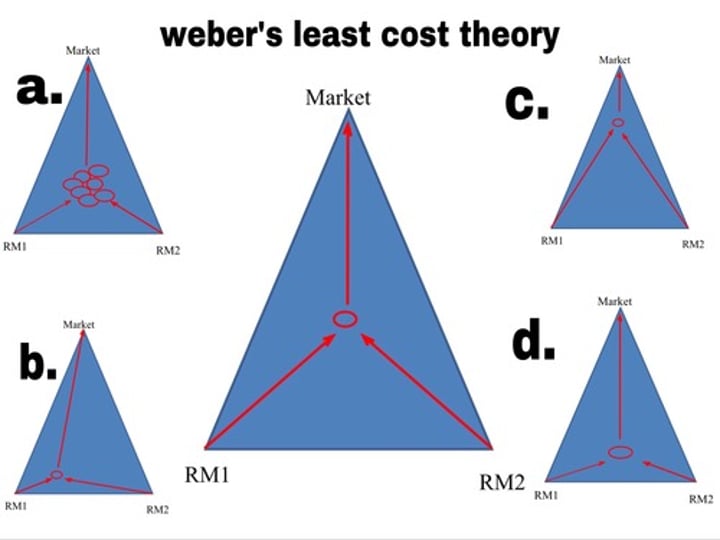
locational triangle
market for good at one end of triangle, two resources at other, factory located in the balance of costs for transportation
bulk-reducing industry
an industry in which the final product weighs less or comprises a lower volume than the inputs

bulk-gaining industry
an industry in which the final product weighs more or comprises a greater volume than the inputs

energy-oriented industry
energy demand for industry is high, so located near power source

labor-oriented industry
very specific skills needed to do work, industry located near universities or training centers ie. computer or engineering

locational interdependence
the influence on a firm's locational decision by locations chosen by its competitors
just-in-time delivery
shipment of parts and materials to arrive at a factory moments before they are needed

footloose
business that can pack up and move quickly, locational demands are minimal, can be done almost any where

front offices
high profile, high cost, for executives to allow them to interact with other execs, as small as able

back offices
cheaper office space, communicate using internet or phone to consumers
outsourcing clerical activities (e.g. payroll, call centers, etc.) to LDCs where labor is cheaper

offshoring
moving production or support processes to foreign countries

outsourcing
removes work from one company and sends it to another company (normally in a less developed country) that can complete it at a lower cost

barter
Exchange goods without involving money.

complementarity
when two regions through an exchange of commodities can specifically satisfy each others demands
trading blocs
groups of countries agreeing to increase trade between them by lowering trade barriers
newly industrialized countries
A country that is undergoing or has recently undergone rapid industrialization and economic grown.
transnational corporations
corporations that operate worldwide

new international division of labor
a recent phenomenon in which the production process transcends international boundaries; selective transfer of some types of jobs (particularly low-paid, less skilled workers) from MDCs to LDCs

Export Processing Zone (EPZ)
Industrial parks for foreign companies to conduct export-oriented manufacturing.

maquiladoras
a factory in Mexico that assembles imported materials into finished goods for export

postindustrial
economy that emphasizes services and technology rather than industry and manufacturing

brownfields
property where reuse is complicated by the presence of hazardous substances from prior use
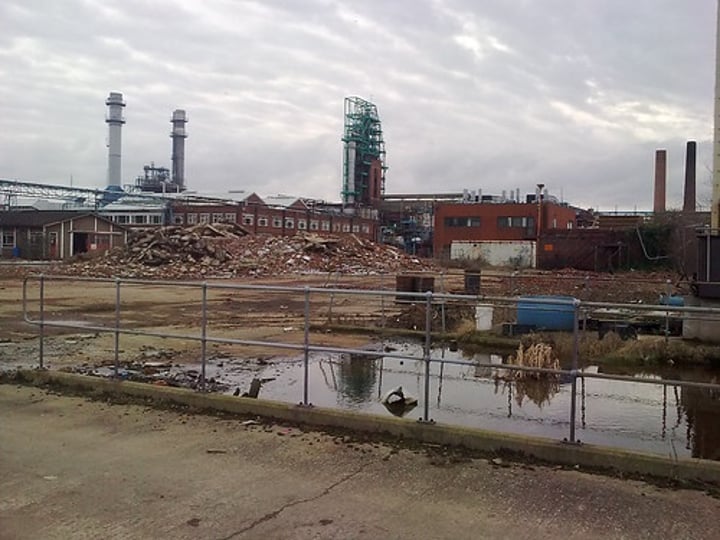

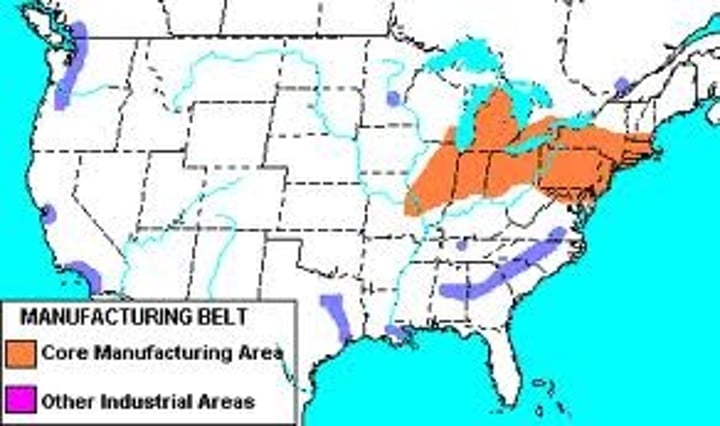
Rust Belt
the north central and northeastern states where major manufacturing centers were once dominant
corporate park or business park
A purpose build area of offices and warehouses, often at the edge of a city and on a main road.

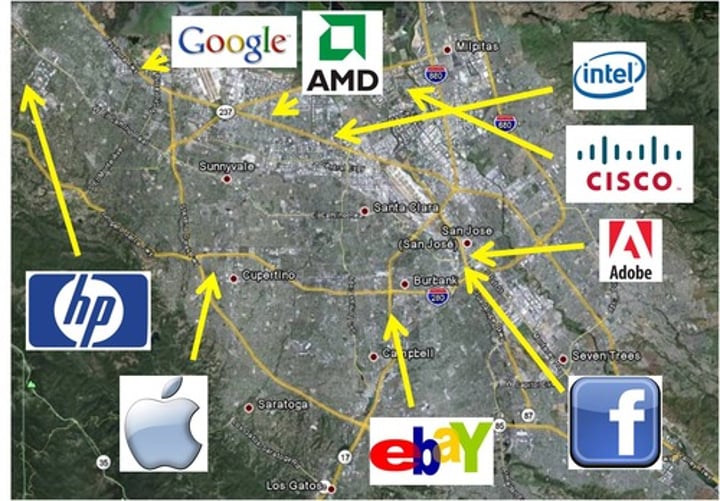
technopoles
A center of high-tech manufacturing and information based industry

growth poles or growth centers
economic activities that are deliberately organized around one or more high-growth industries.
spin-off benefits
extra positive outcomes in addition to the main outcome - can be far or near to growth pole

backwash effects
the negative impacts on a region of the economic growth of some other region.
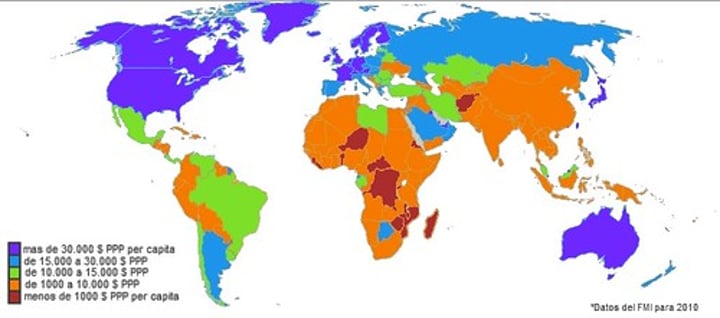
per capita
per person basis; total divided by population
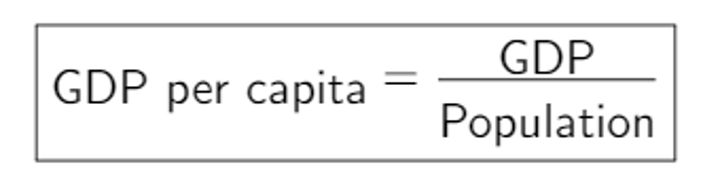
Gross National Product (GNP) per capita
Is the total value of all the goods and services produced by a state in a single year.

Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita
The total value of a state's goods and services produced inside of the country divided by its population.
Gross National Income (GNI) per capita
measures the total annual income received by residents of a nation divided by its population.
purchasing power parity (PPP)
the amount of money needed in one country to purchase the same goods and services in another country

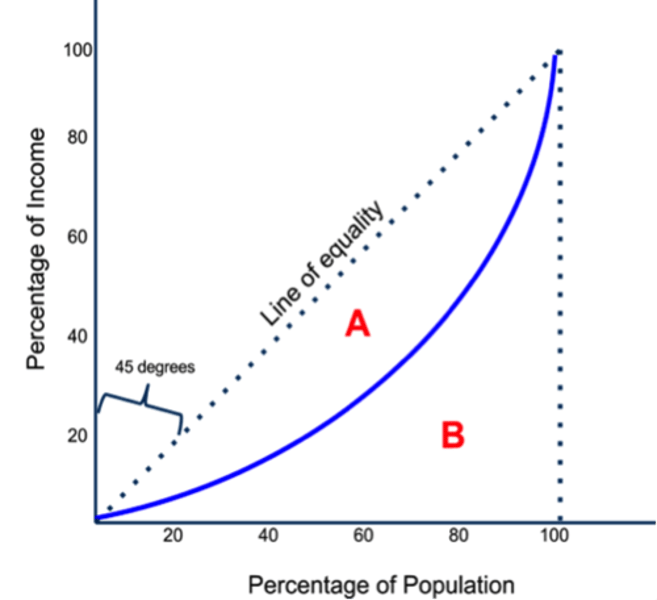
Gini index
a mathematical formula that measures the amount of economic inequality in a society
gender gap
the discrepancy in opportunities, status, attitudes, etc., between men and women.

Gender Inequality Index (GII)
A means of measuring the differences in the distribution of achievements between men and women.

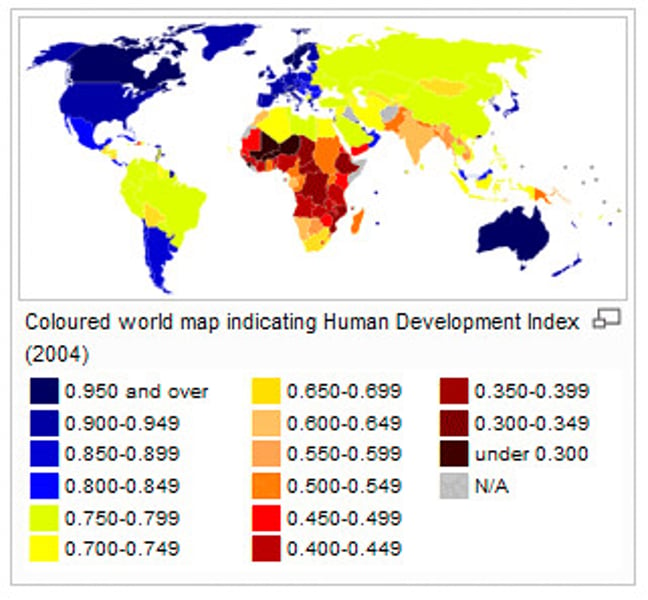
Human Development Index (HDI)
Measurement held by the UN that calculates the level of development in terms of human welfare
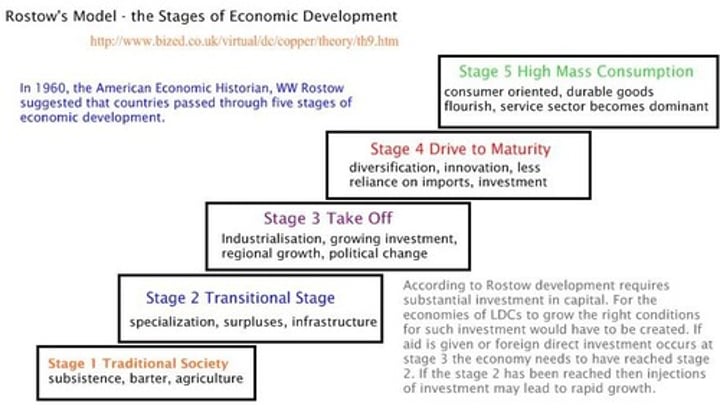
Rostow
developed the "Stages of Growth" model of economic development; all countries want to develop but will do so at different paces

Stages of Economic Growth Model
traditional society - pre-condition for take off - take off - drive to maturity - high mass consumption
modernization model
model of economic development maintains that all countries go through five stages of development
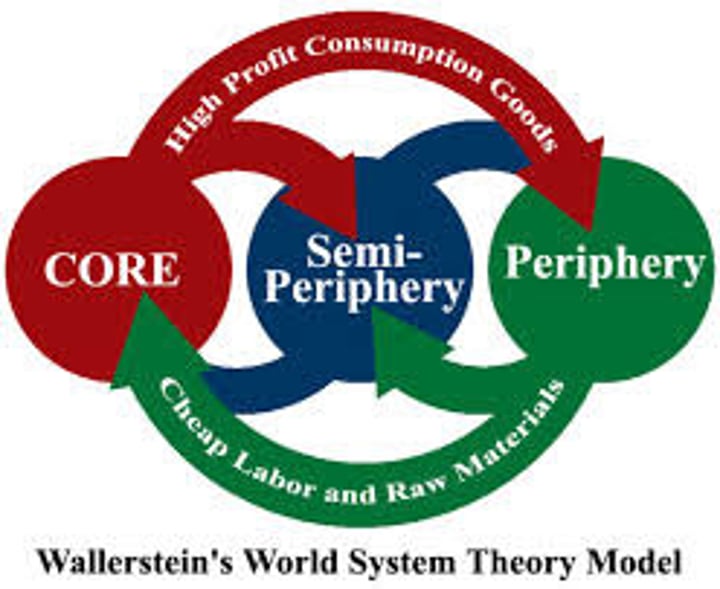
Wallerstein
Suggest that MDCs are keeping LDCs poor to keep power and wealth.; created World Systems Theory
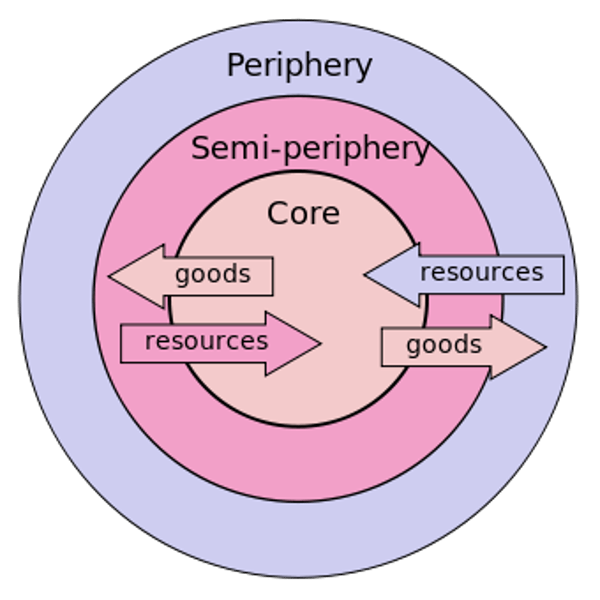
World Systems Theory
economic and political connections that tie the world's countries together
dependency model
countries do not exist in isolation but are part of an intertwined world system in which all countries are dependent on each other
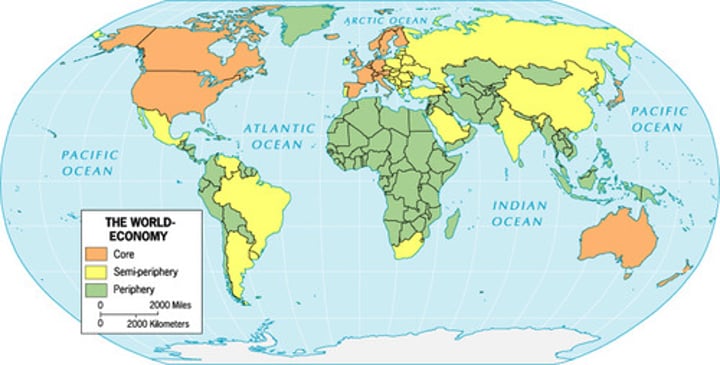
Core-Periphery Model
The way of classifying countries as core, semiperiphery, and periphery
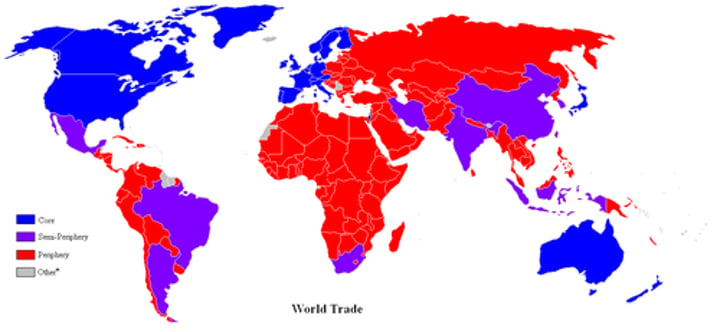
core
economically advantaged countries, high skill jobs, benefits greatly from international trade, dominates periphery and semiperiphery countries
periphery
least developed countries, mostly low skill jobs, labor intensive, provides core and semiperiphery with inexpensive raw materials
semiperiphery
structural position in the world system intermediate between core and periphery
sustainable development
conducting business in a way that protects the natural environment while making economic progress

NGOs
non-governmental organizations; groups not affiliated with any government; groups who were concerned about social movements

microcredit
the lending of small amounts of money at low interest to new businesses in the developing world.
