Procedures 1 & Image Analysis 1 CLASS 7 TEST (Toes, Foot, Calcaneus, and Ankle)
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Bone Cyst
Fluid-filled cyst with wall of fibrous tissue.
Gout
Hereditary form of arthritis in which uric acid is deposited in joints.
Dislocation
Displacement of a bone from the joint space.
Elongation
Image appears longer than actual object due to angled CR.
Foreshortening
Image appears shorter than actual object because part is not parallel with IR.
Osteoarthritis
Form of arthritis marked by progressive cartilage deterioration in joints and vertebrae.
Osteomyelitis
Inflammation of bone due to a pyogenic infection.
Osteopetrosis
Increased density of atypically soft bone.
Osteoporosis
Loss of bone density.
Rheumatoid arthritis
A chronic, systemic, inflammatory collagen disease.
Chondrosarcoma
Malignant tumor arising from cartilage cells.
Enchondroma
Benign tumor consisting of cartilage.
Ewing sarcoma
Malignant bone tumor arising in medullary tissue.
Osteosarcoma
Malignant, primary tumor of bone with bone or cartilage formation.
Metastasis
Transfer of a cancerous lesion from one area to another.
Congenital Clubfoot
Abnormal twisting of the foot, usually inward and downward.
Pott's fracture
Avulsion fracture of the medial malleolus with loss of the ankle mortise.
Jones Fracture
Avulsion fracture of the base of the fifth metatarsal.
Osgood-Schlatter disease
Incomplete separation or avulsion of the tibial tuberosity.
Osteomalacia/rickets
Softening of the bones due to a vitamin D deficiency.
Paget disease of bone
Chronic metabolic disease of bone marked by weakened, deformed and thickened bone that fractures easily.
Osteoclastoma
Lucent lesion in the metaphysis, usually at the distal femur.
Osteoid Osteoma
Benign lesion of cortical bone.
Which projection of the foot will show the cuboid in profile?
AP oblique, medial rotation
How many degrees are the lower leg and foot rotated for the AP oblique projection of the toes in medial rotation?
30 to 45
For an axial projection of the calcaneus, the ankle should be dorsiflexed so the plantar surface of the foot is:
90 degrees from the plane of the IR
How many degrees of angulation are needed to open the IP joint spaces on an AP axial projection of the toes?
15
Which of the following will clearly demonstrate the cuboid?
AP oblique, medial rotation
Which of the following is not clearly demonstrated on an AP projection of the ankle?
ankle mortise
To demonstrate the ankle mortise, the leg and foot should be rotated medially how many degrees?
15-20
What is the central-ray angulation for the axial (plantodorsal) projection of the calcaneus?
40 degrees
For an AP oblique projection of the foot with medial rotation, the plantar surface of the foot should form an angle of _____ degrees.
30
Which projections of the ankle are performed on a patient following an inversion or eversion injury?
AP stress studies
Tangential Sesamoid Projection (Lewis Method)
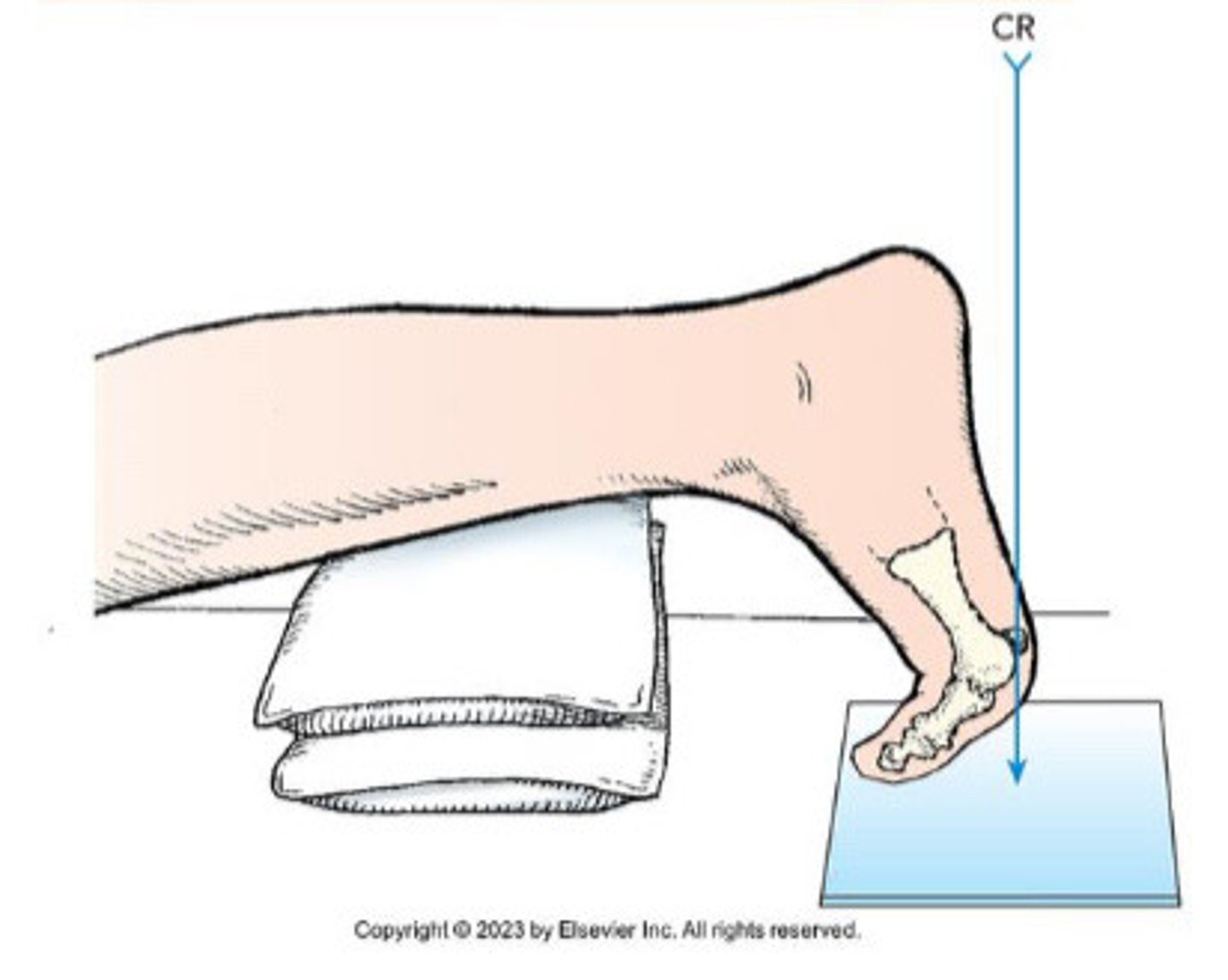
Tangential Sesamoid Projection (Holly Method)
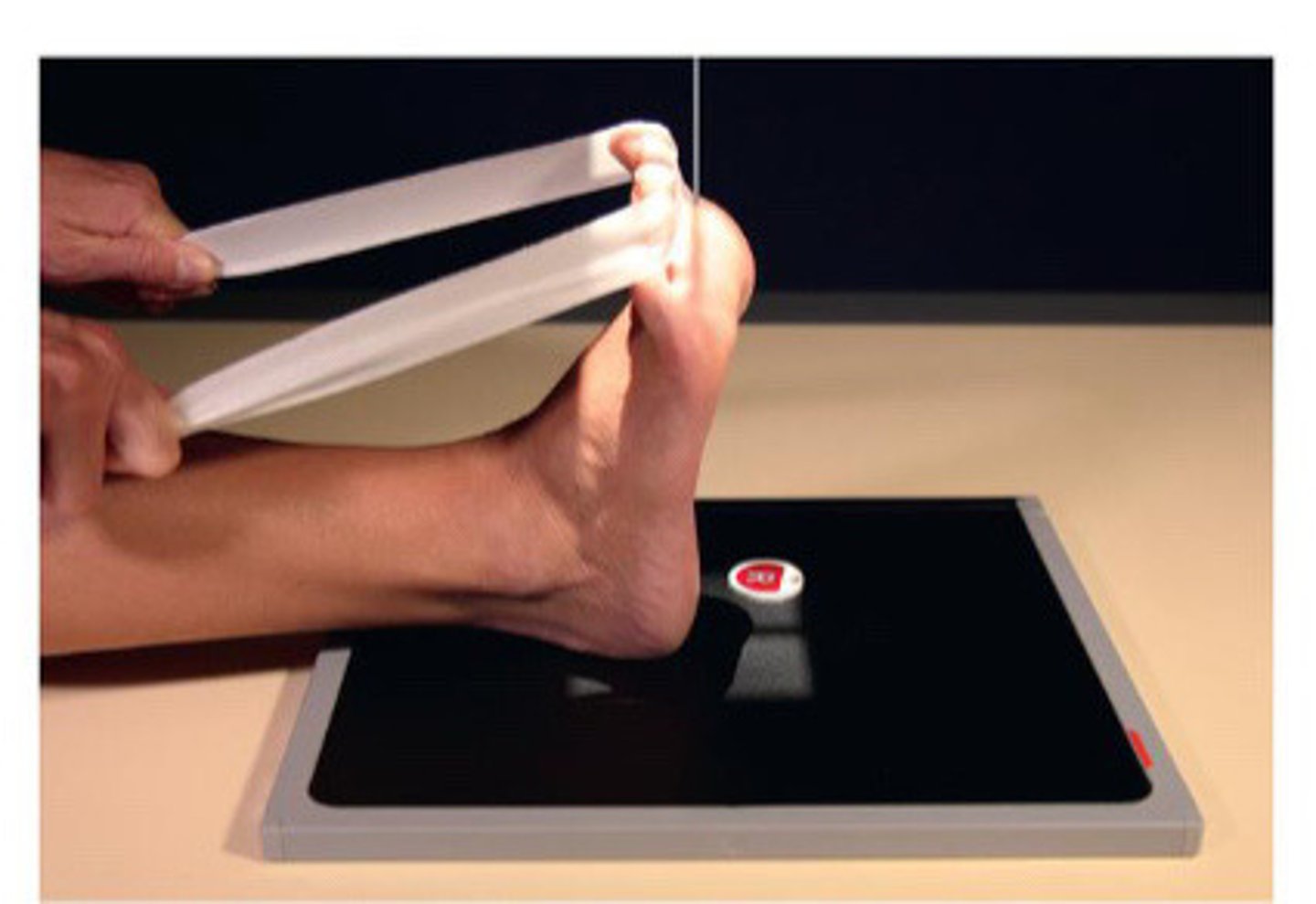

Why should an AP oblique ankle be dorsiflexed?
An AP oblique ankle does not need to be dorsiflexed
To prevent the SI of the lateral malleolus and the calcaneus
To keep the ankle in the medial oblique postion
To prevent the SI of the cuniforms
To prevent the SI of the lateral malleolus and the calcaneus
What exam is done to evaluate the longitudinal arch of the foot?
AP axial foot
AP lateral foot
AP medial oblique foot
Weight-bearing lateral foot
Weight-bearing lateral foot
What is the method name for the projections of congenital club foot?
Lawerence method
Pearson method
Kite method
Grashey method
Kite method
Which of the following is osteoporosis?
avulsion FX, base of the 5th metatarsal
loss of bone density
avulsion FX, medial malleolus
inflammation of bone due to pyogenic infection
loss of bone density
Which of the following is osteomyelitis?
avulsion FX, base of the 5th metatarsal
loss of bone density
avulsion FX, medial malleolus
inflammation of bone due to pyogenic infection
inflammation of bone due to pyogenic infection
What is the superior or top surface of the foot called?
dorsum
What type of injury is demonstrated by a stress study of the ankle?
Torn ligament
Torn tendon
Stress fracture of the ankle
Torn muscle
Torn ligament
Which of the following is a Jones' fracture?
avulsion FX, base of the 5th metatarsal
loss of bone density
avulsion FX, medial malleolus
inflammation of bone due to pyogenic infection
avulsion FX, base of the 5th metatarsal
When positioning for an axial projection of the calcaneus, the plantar surface of the foot should be _________ to the IR.
perpendicular
Which of the following is a Pott's fracture?
avulsion FX, base of the 5th metatarsal
loss of bone density
avulsion FX, medial malleolus
inflammation of bone due to pyogenic infection
avulsion FX, medial malleolus
Which projection of the ankle best demonstrates the distal tibiofibular articulation?
AP ankle
Lateral ankle
AP oblique ankle, 15-20 degrees medial rotation
AP oblique ankle, 45 degrees medial rotation
AP oblique ankle, 45 degrees medial rotation