Richter Scale, Moment-Magnitude Scale, Types of Waves, etc.
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Richter scale
-measures earthquake magnitude, which is the total amount of energy released by an earthquake at its source
-determined by the largest peak on a seismogram
Moment-Magnitude scale
-measures the magnitude of an earthquake by the seismic energy released, but uses newer technologies to produce a more accurate measurement
-geologists use this type of scale
Body waves
-waves that travel away from an earthquake and into the body of earth, then back to the surface
-P-waves & S-waves
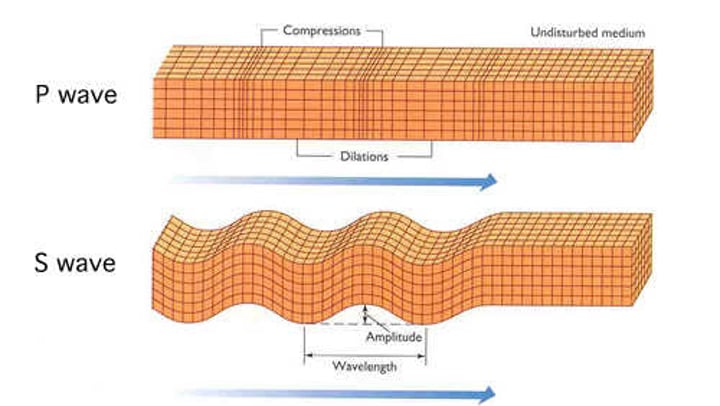
P-waves
-push and pull waves that travel left to right
-faster than S-waves
-vibration is parallel to the travel direction
(slinky)
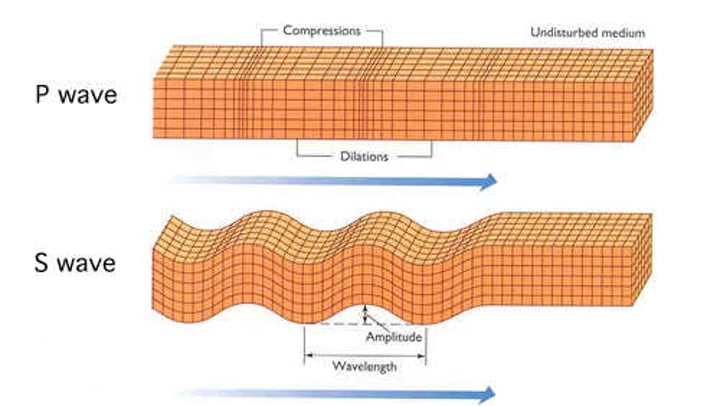
S-waves
-travel side to side and have a up and down motion
-slower than P-waves
-vibration is up and down
Surface waves
-waves leave the earthquake and stick to the surface
-rolling motion
-causes a lot of alarm
-L-waves
L-waves
-side to side, rolling motion
-causes horizontal shifting of the Earth
Epicenter
where the earthquake occured
What hazards are associated with earthquakes?
-ruptures
-landslides
-structural damage
-bridge failure
-tsunamis
-aftershocks
-fires