Anatomy and Physiology Fall Semester Exam Review
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
175 Terms
Superior
Higher or above
Inferior
Lower or below
Anterior
Front of body
Posterior
lower or bellow (back)
Medial
Closer to midline of the body
Lateral
Farther from the midline
Proximal
Closer to point of attatchment
Distal
Farther from point of attachment
Superficial
Closer to the surface of the body
Deep
Farther from the surface of the body
Order from least to most complex
Chemical → cell → tissue → organ → organ system → organism
How organization levels work together to perform a task (nervous system)
Neurons form nervous tissue, which make sup organs like brain and spinal cord. These organs work together in the nervous system to help the organism respond to stimuli.
Homeostasis
The body’s ability to maintain a stable internal environment, vital for normal function.
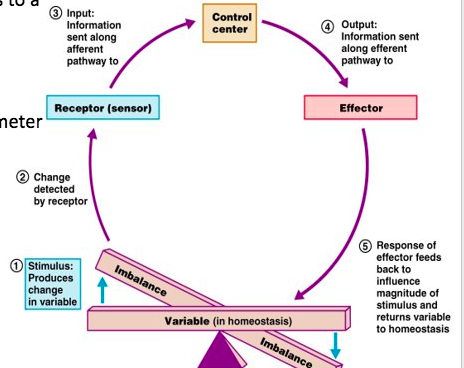
The process shown in the diagram is ___
Homeostasis
Negative Feedback Mechanism
Reduces of counteracts a change in the body, promoting stability and maintaining homeostasis such as temperature regulation
Positive feedback mechanism
Amplifies or increases a change, driving process to completion; such as during childbirth
Which type of feedback mechanism is most commonly used to maintain homeostasis
Negative feedback
Function and Organ(s) of: Simple Squamous Epithelium
Facilitates diffusion & filtration- found in air sacks of lungs, lining of blood vessels, & kidneys
Function and Organ(s) of: Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Protects underlying tissues from abrasion- found in skin, mouth, & esophagus
Function and Organ(s) of: Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Involved in secretion & absorption- found in kidney tubules and glandular ducts
Function and Organ(s) of: Simple Columnar Epithelium
Absorbs nutrients & Secrets mucus- found in lining of stomach & intestines
Function and Organ(s) of: Pseudo-stratified Ciliated Epithelium
Moves mucus and debris- found in respiratory tract
Function and Organ(s) of: Hyaline Cartilage
Provides support & flexibility- found in nose, trachea, & ends of long bones
Function and Organ(s) of: Bone (Osseous Tissue)
Supports the body, protects organs, and stores minerals- found in skeleton
Function and Organ(s) of: Adipose Tissue
Stores energy, insulates, & cushions organs- found beneath the skin & around the organs
Function and Organ(s) of: Blood
Transports gases, nutrients, and waste- found in blood vessels
Function and Organ(s) of: Cardiac Muscle
Contracts to pump blood through the heart- found in the heart
Function and Organ(s) of: Smooth Muscle
Moves substances through hollow organs & structures- found in walls of intestines, blood vessels, & the bladder
Function and Organ(s) of: Skeletal Muscle
Enables voluntary movement of the body- found attached to the bones
Function and Organ(s) of: Neurons
TRansmits electrical impulses for communication within the body- found i brain, spinal cord, & peripheral nerves
What is the major function of: Epithelial
Protects body surfaces, absorbs substances, secretes fluids, and facilitates diffusion
What is the major function of: Connective
Supports, connects, & protects organs & tissues, providing structure and flexibility
What is the major function of: Muscular
Enables movement through contraction, either voluntary or involuntary
What is the major function of: Nervous
Transmits electrical signals for communication between the brain, spinal cord, & rest of the body
Define Hemostasis and list stages
Process that prevents & stops bleeding, ensuring blood remains within the blood vessel stages: vascular spasm, platelet-plug formation, and consultation
Which integumentary structure is a vestigial feature which allows the hair to stand erect and produces goosebumps?
Arrector Pili Muscle
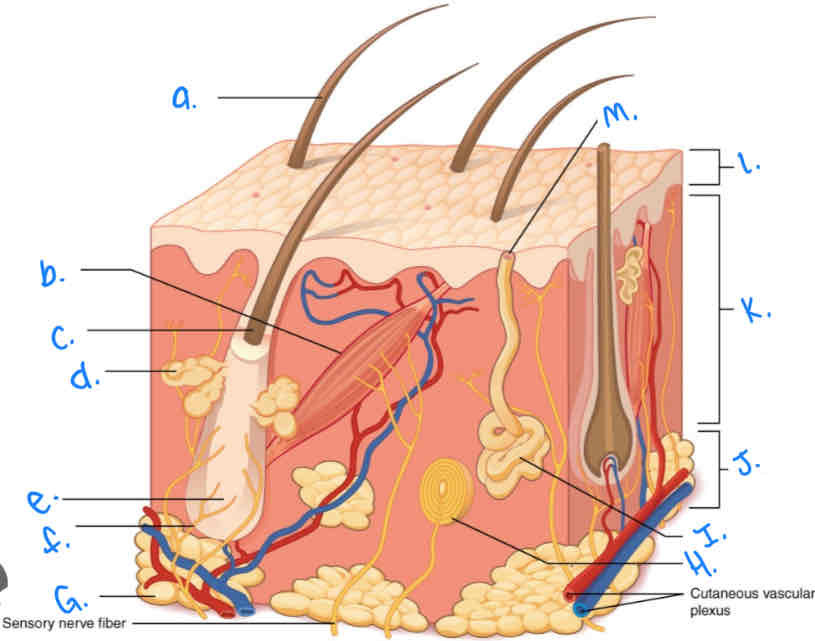
Label the skin diagram letter A
Hair Shaft
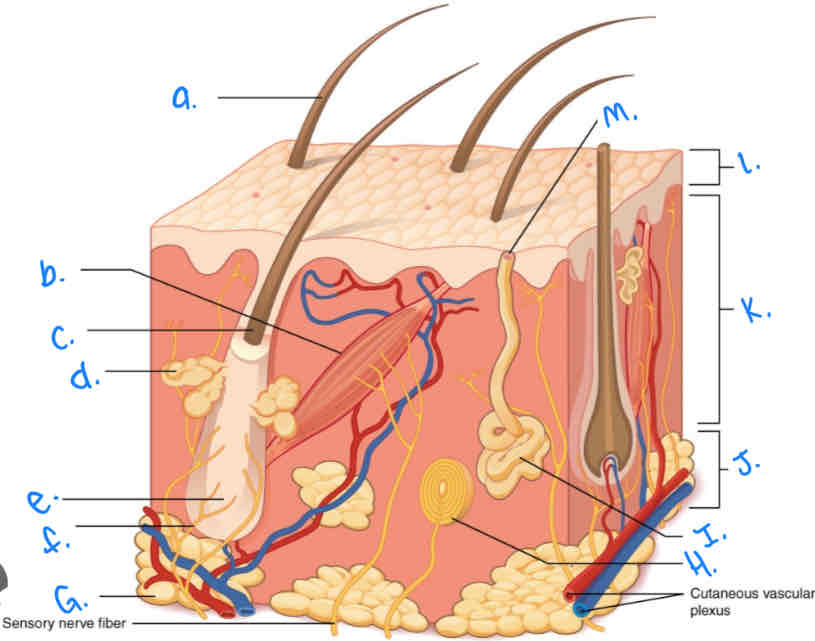
Label the skin diagram letter M
Pore of sweat gland duct
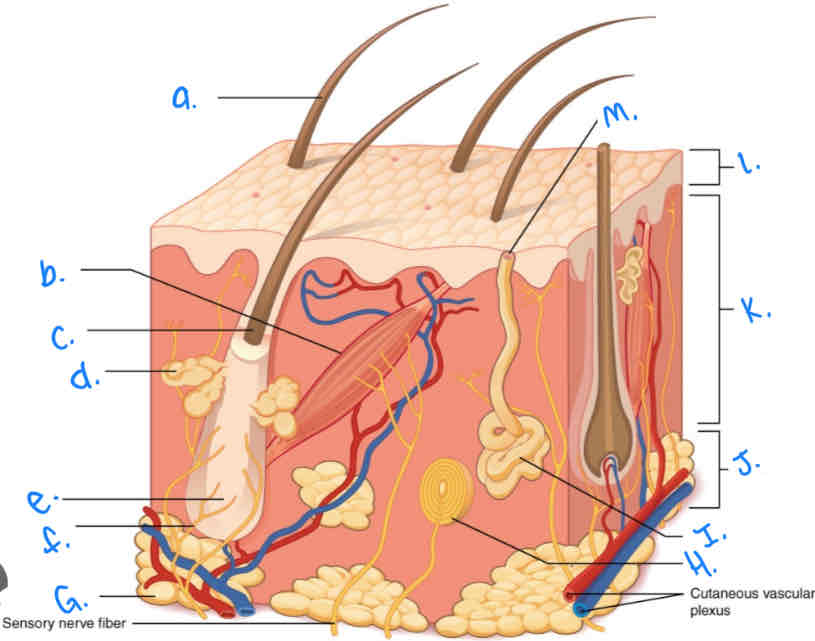
Label the skin diagram letter B
Arrector Pili Muscle
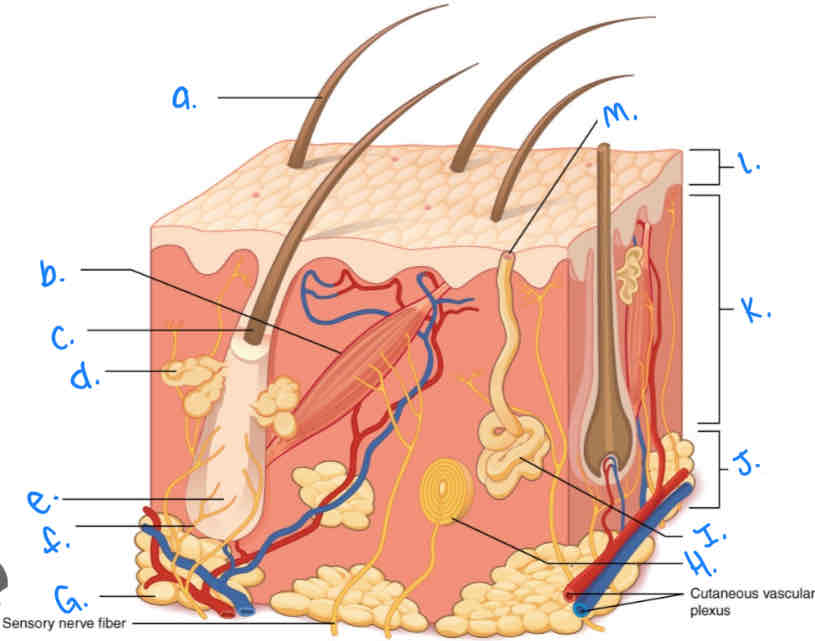
Label the skin diagram letter G
Adipose Tissue
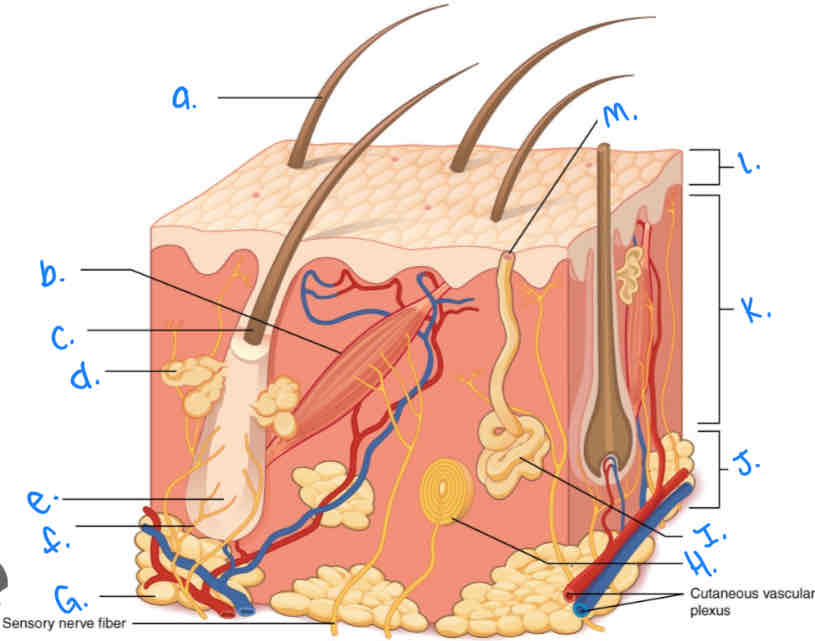
Label the skin diagram letter H
Pacinian Corpusde
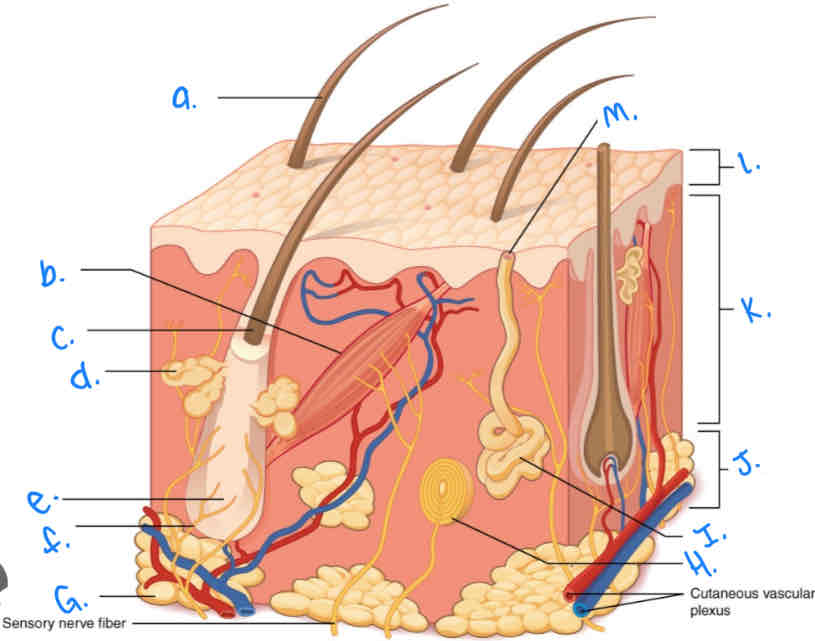
Label the skin diagram letter C
Hair Folicle
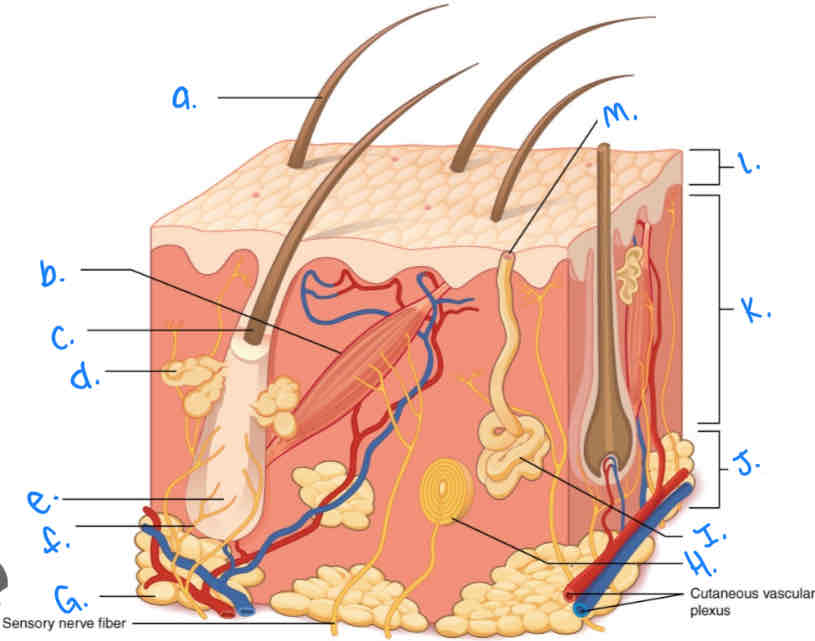
Label the skin diagram letter K
Dermis
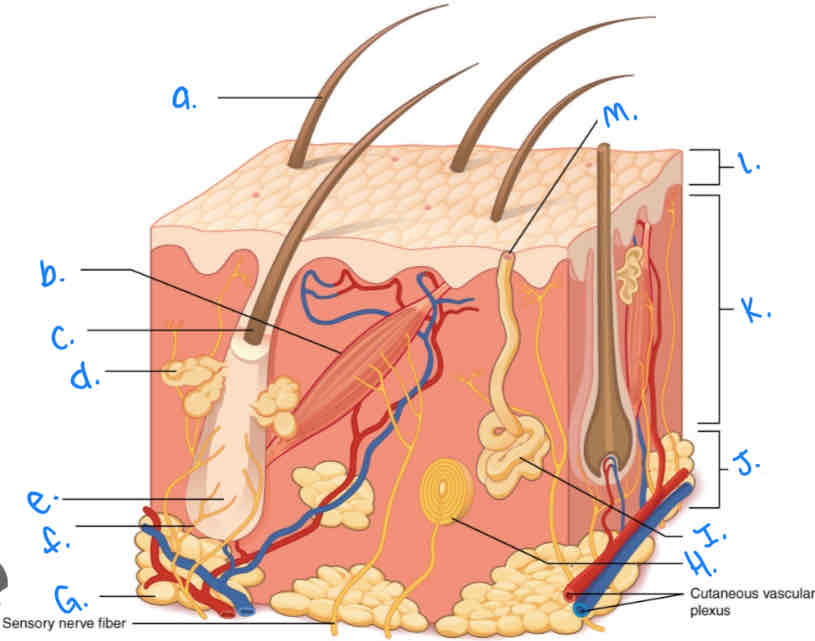
Label the skin diagram letter L
Epidermis
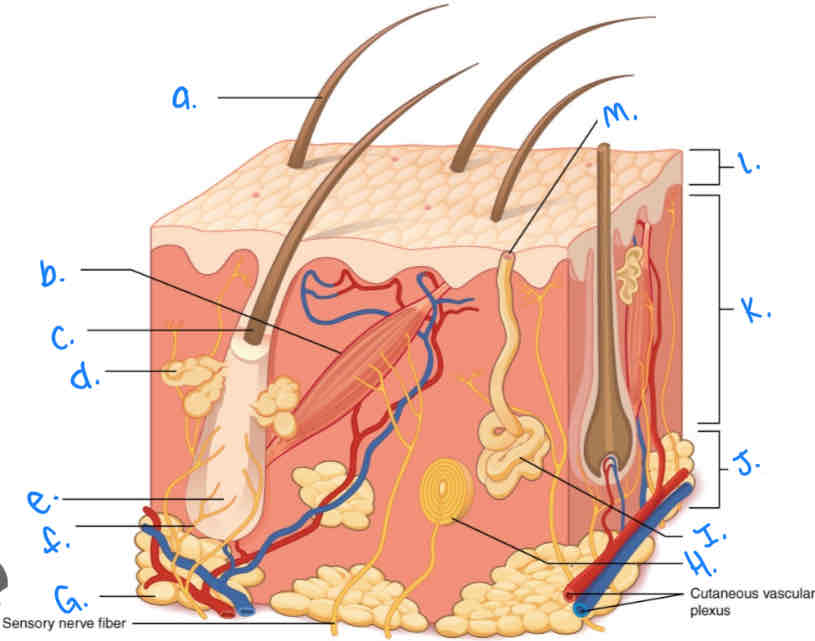
Label the skin diagram letter D
Sebaceous (oil) gland
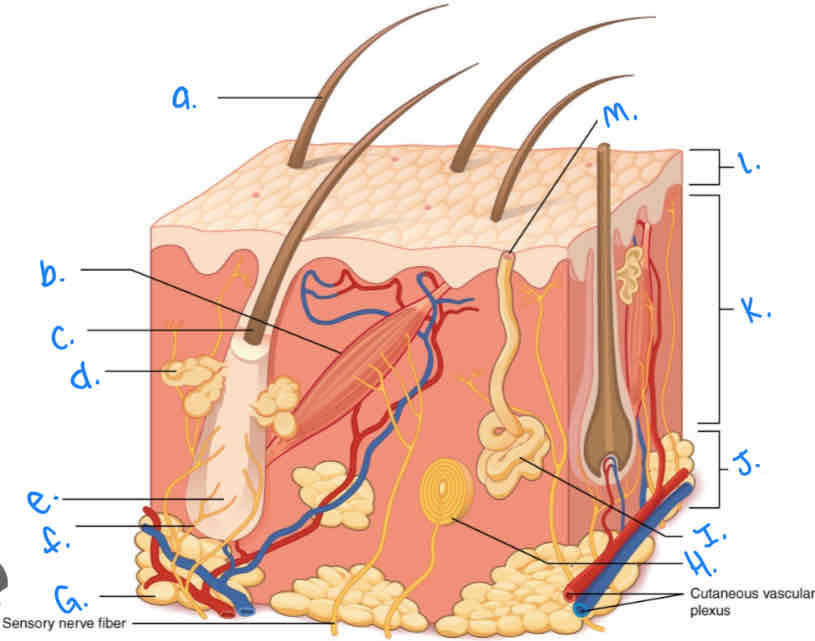
Label the skin diagram letter I
Eccrine Sweat Gland
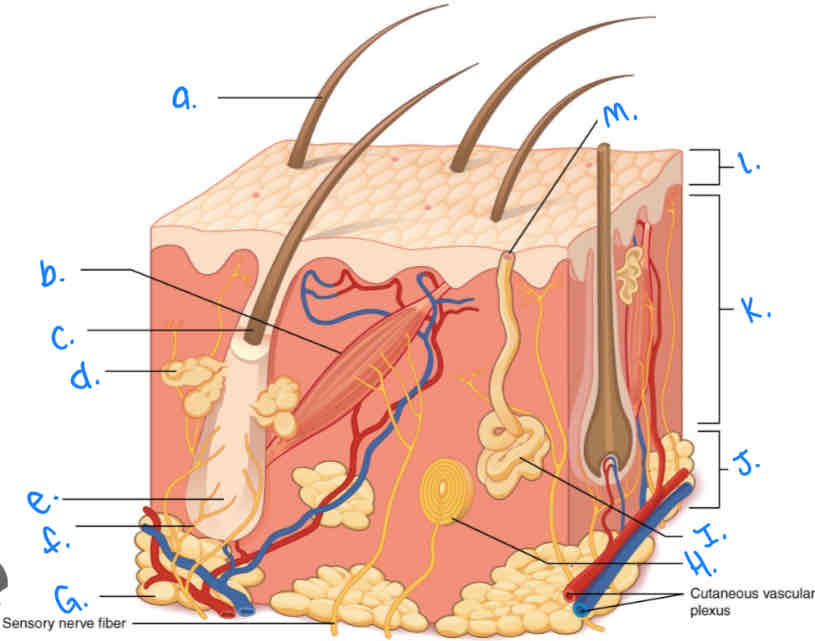
Label the skin diagram letter J
Hypodermis
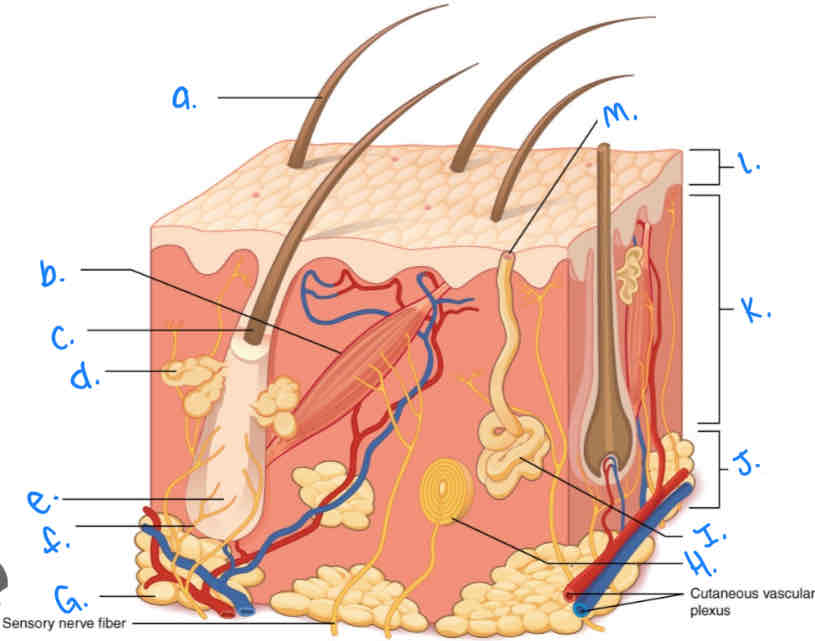
Label the skin diagram letter e
Hair Root
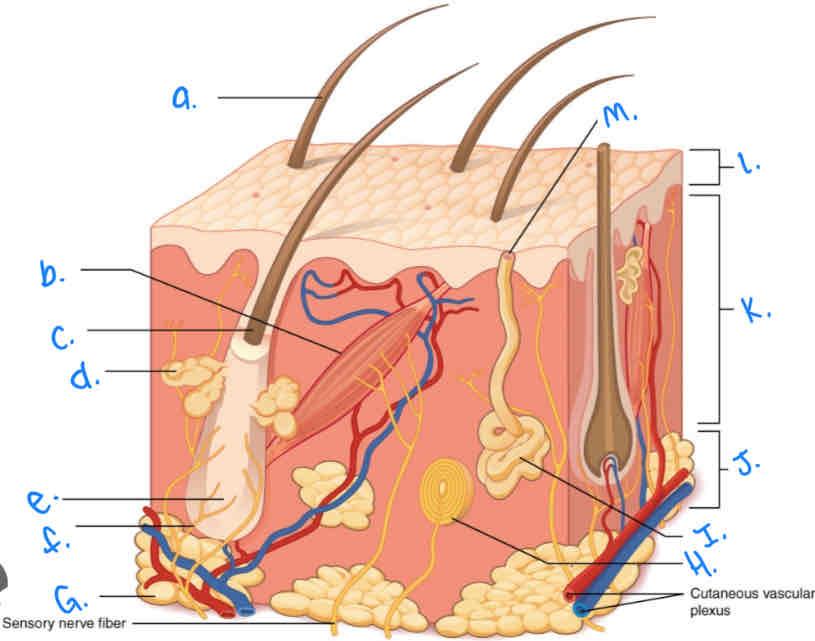
Label the skin diagram letter F
Hair Folicle Receptor
List 3-5 factors that can influence skin color
Melanin, Genetics, UV exposure, blood flow, & health conditions
Describe the Epidermis tissue
Composed of stratified squamous epithelial tissue, primarily keratinocytes, providing protective outer layers
Describe the tissues in the dermis
Dense irregular connective tissue, with collagen, elastic fiber, blood vessels, nerves, & glands for support and nourishment
Describe the tissues in the hypodermis
Loose connective tissue & adipose tissue, providing insulation, cushioning, and energy storage
Describe the skin cancer: Basal Cell Carcinoma
Least aggressive skin cancer, pearly flesh-colored caused by sun exposure
Describe the skin cancer: Squamous Cell Carcinoma
More aggressive, scaly, red pattern, non-healing sore linked to UV damage
Describe the skin cancer: Malignant Melanoma
Most dangerous, irregular darkly pigmented moles that can spread rapidly
Describe this type of burn and its consequences: 1st Degree
Only epidermis, causes redness and pain- consequences are only redness
Describe this type of burn and its consequences: 2nd Degree
Extends to dermis, blistering & severe pain- may leave scars; consequences are scarring
Describe this type of burn and its consequences: 3rd Degree
Destroys all layers of skin- painless form nerve damage; consequences include risk of infection and deep scarring
List and describe 6 functions of skeletal system
Support: framework for body, Protection: Shield vital organs, Movement: works with muscles to facilitate body movement, Mineral storage: stores minerals, Blood Cell Production: provides blood cells in brown marrow, Fat Storage: Store energy
Describe the role of parathyroid hormone
Increases blood calcium by stimulating bone breakdown
Describe osteoclasts
Break down bone tissue for remodeling and calcium release
Describe calcitonin
Lowers blood calcium by promoting calcium storage in bones
Describe osteoblasts
Build new bone tissue for growth & repair
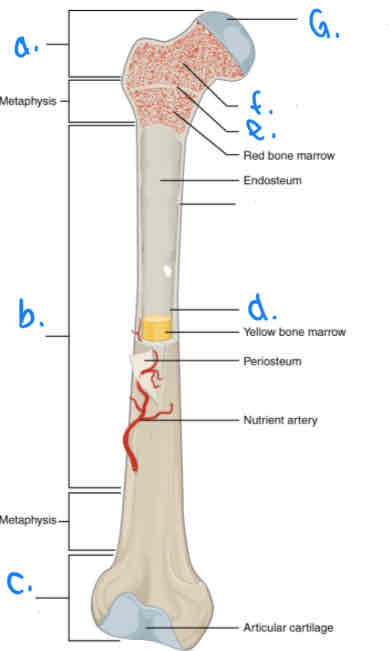
What is B?
Diaphysis
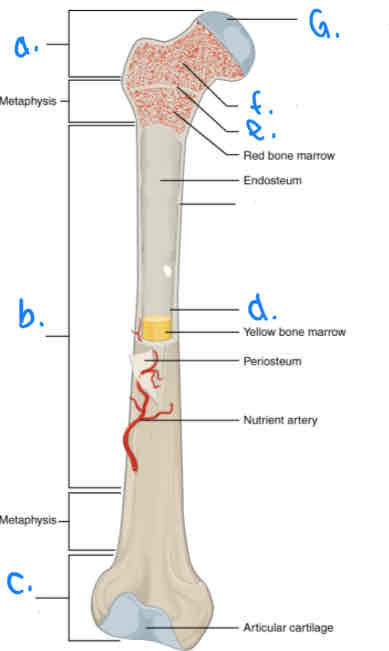
What is D?
Medular Cavity
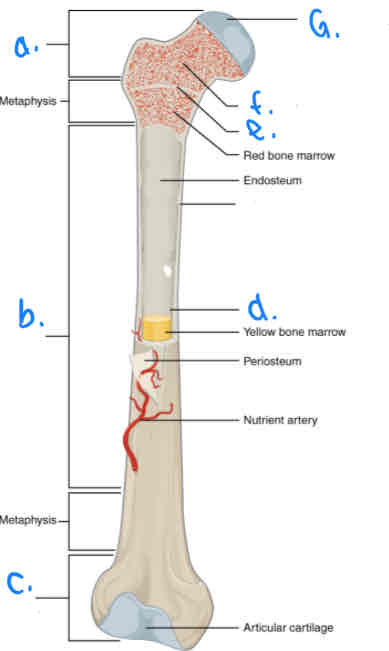
What is E?
Epiphyseal Line
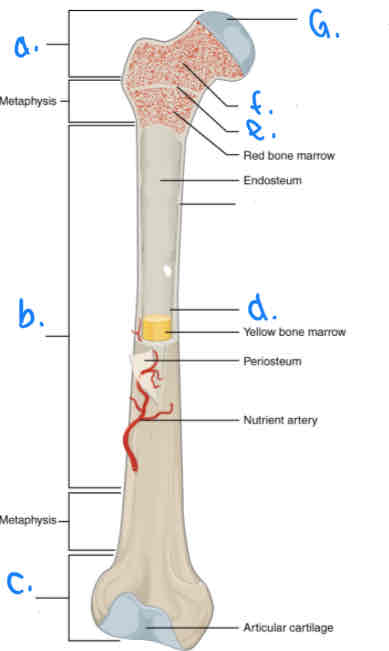
What is G?
Articular Cartilage
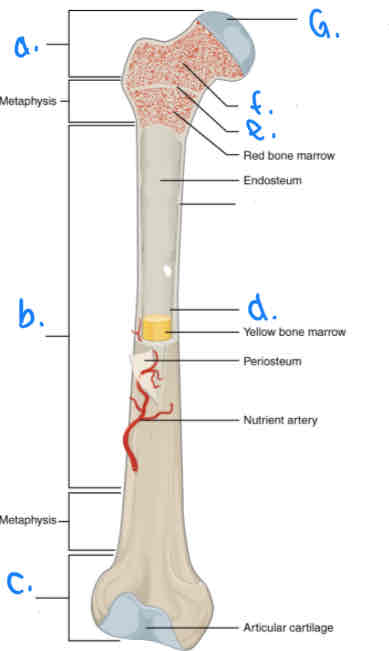
What is F?
Spongy Bone
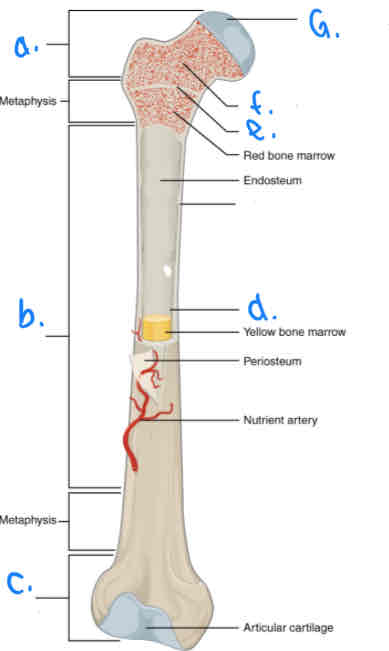
What is a?
Proximal Epiphysis
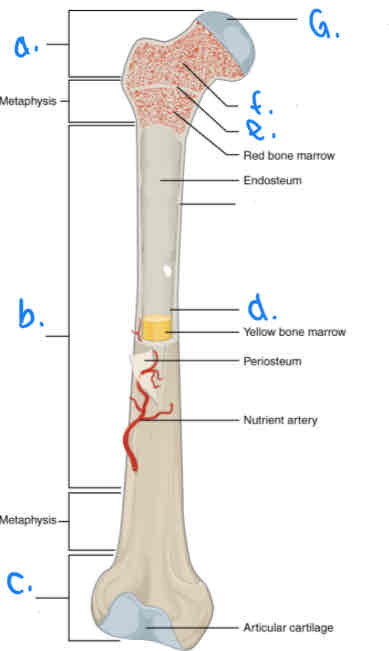
What is C?
Distal Epiphysis
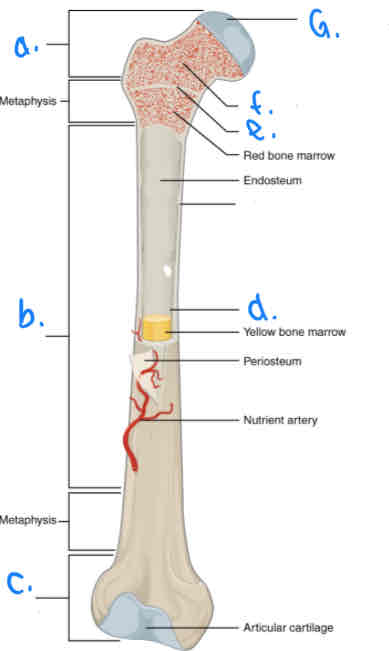
What is the part under the endosteum?
Compact Bone
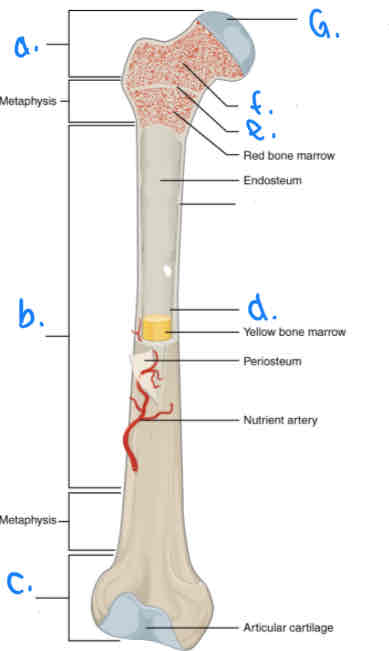
What is the thin outer lining of the bone?
Periosteum
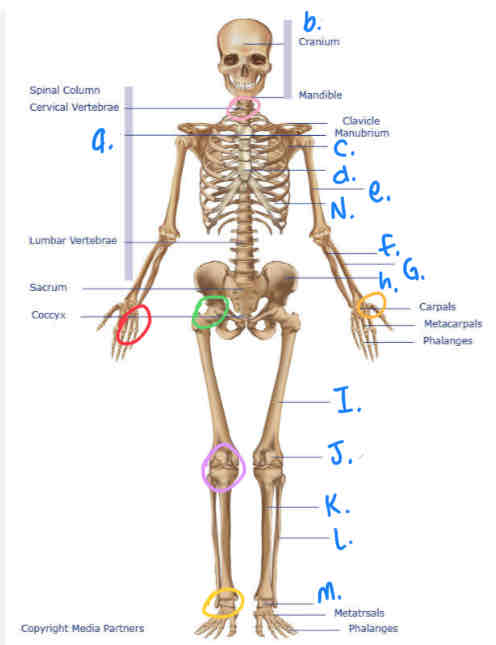
What is b?
Cranium
What is I?
Femur
What is M?
Tarsals
What is K?
Tibula
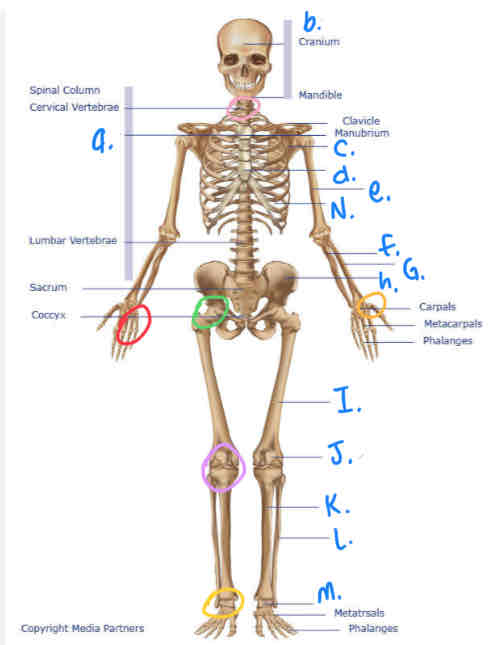
What is L?
Fibula
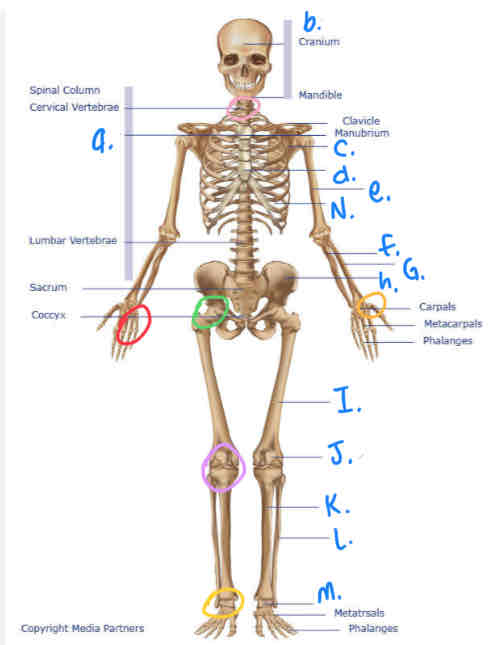
What is J?
Patella
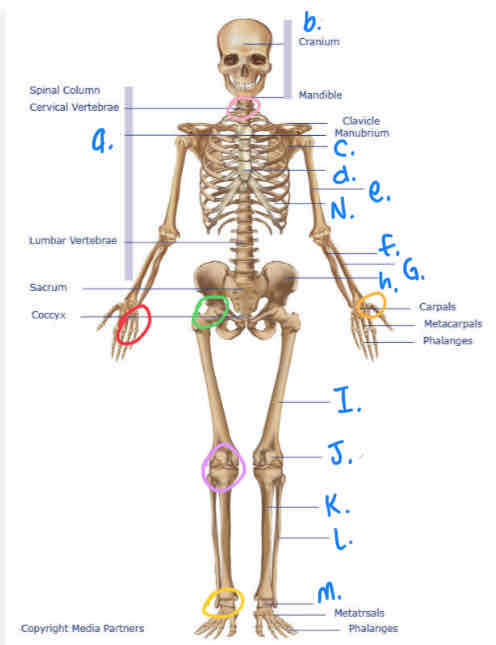
What is H?
Pelvis
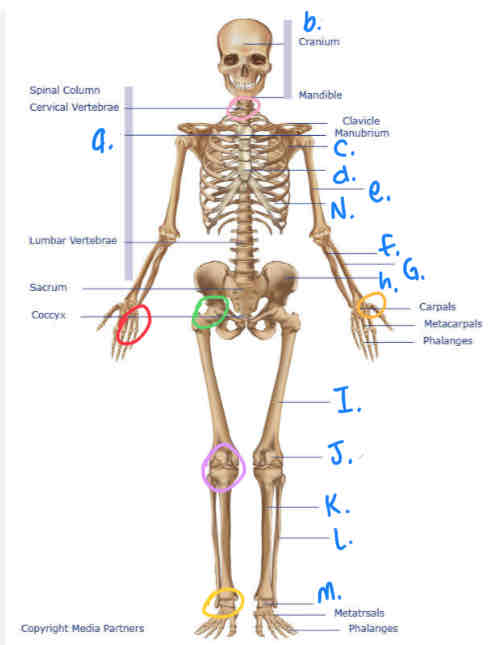
What is A?
Thoracic Vertebrae
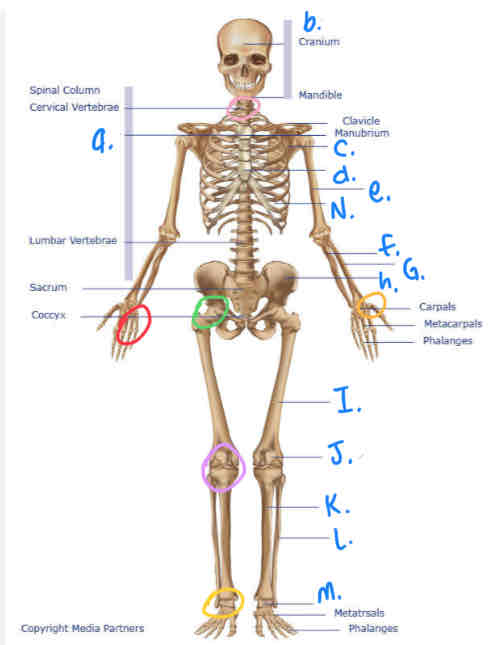
What is N?
Ribs
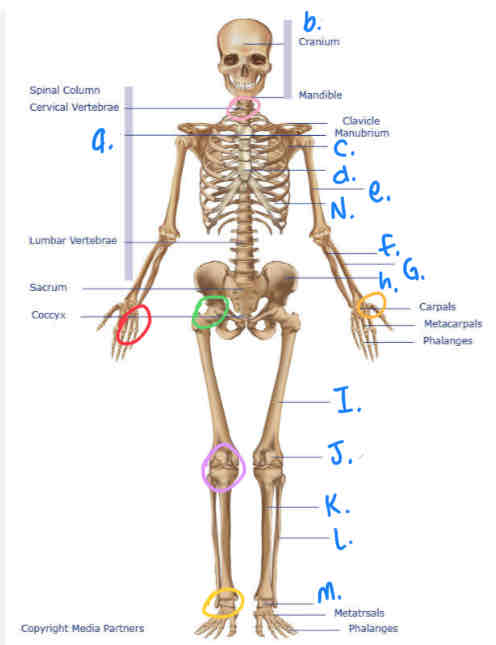
What is D?
Sternum
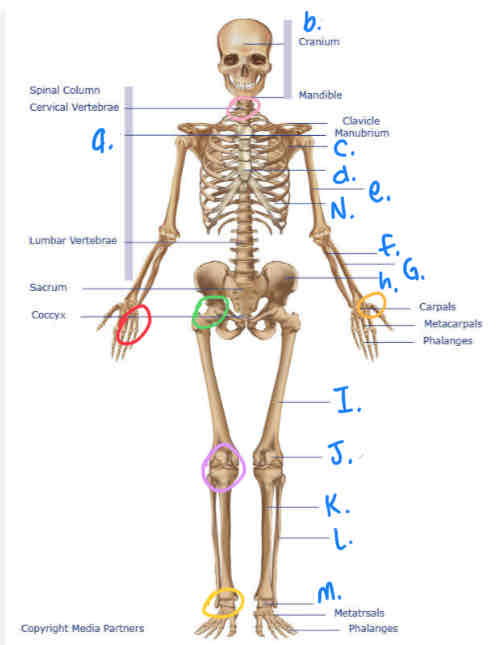
What is e?
Humerus
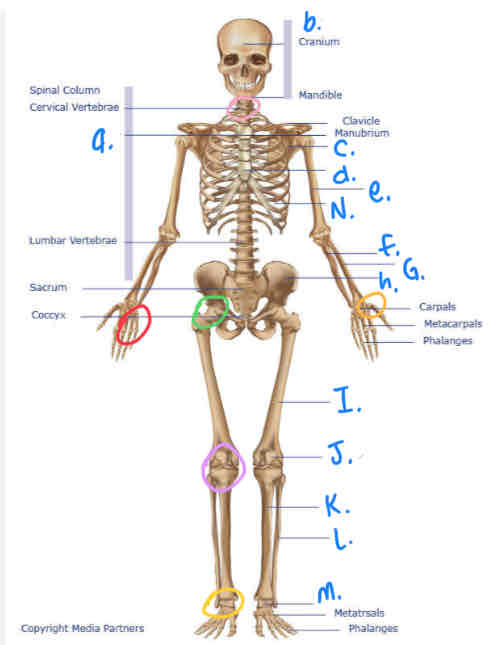
What is C?
Scapula
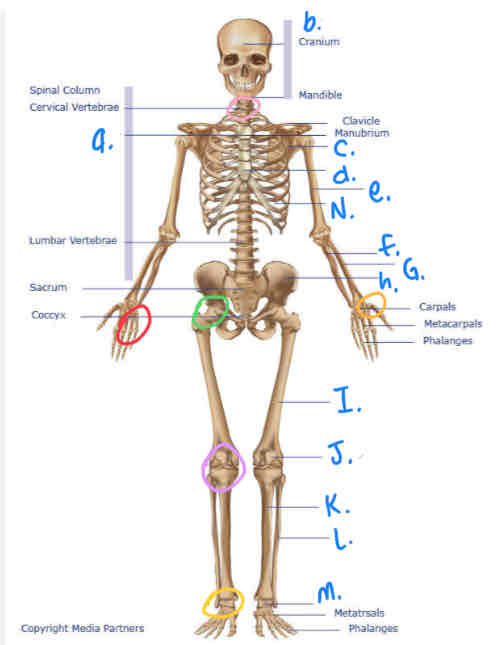
What is F?
Ulna
What is G?
Radius
What is the yellow circle?
Plane Joints
What is the red circle?
Hinge Joint
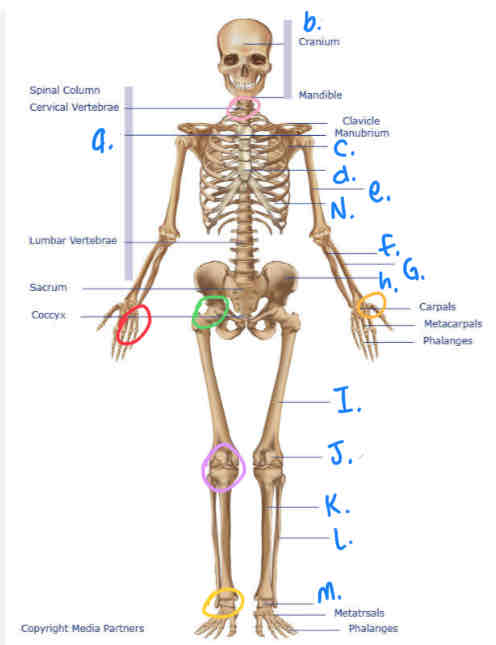
What is the pink circle?
Atlantoaxial Joint
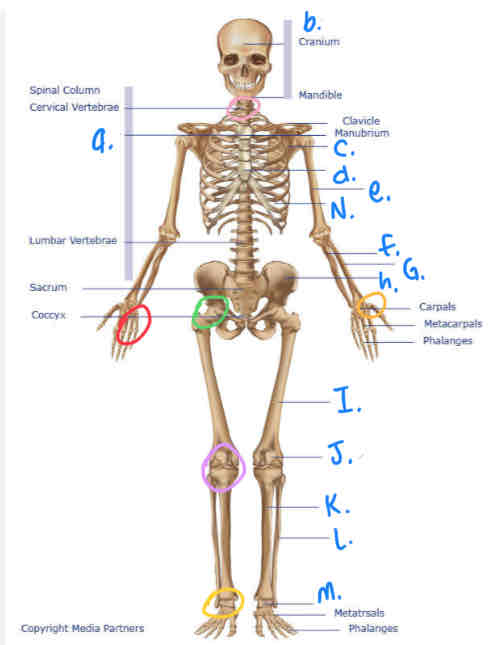
What is green circle?
Ball & Socket Joint
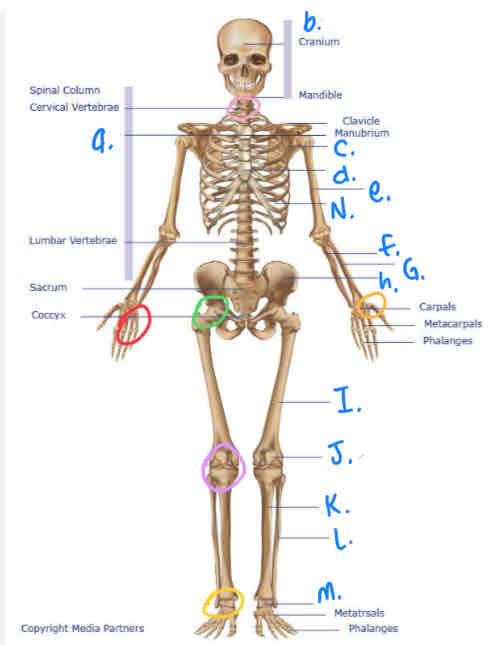
What is purple circle?
Hinge Joint (inferior)
Define a simple fracture
Bone breaks but doesn’t pierce the skin
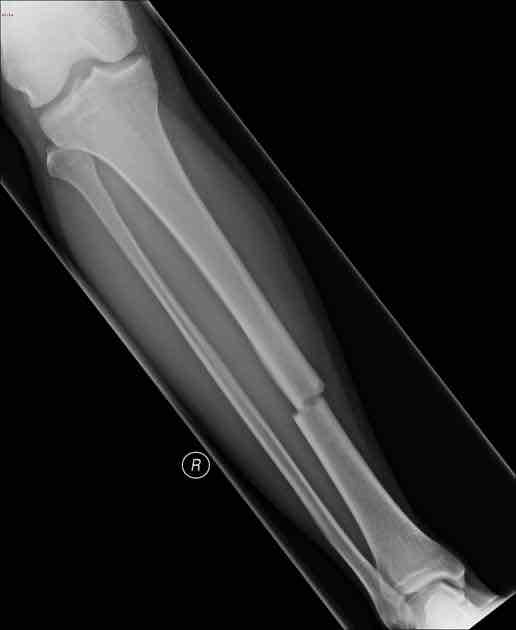
Define Compound Fracture
Bone Breaks & pierces through the skin
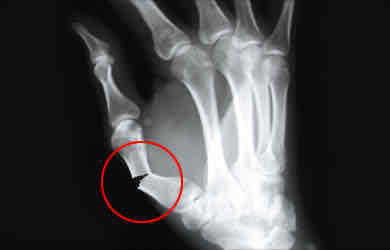
Define Comminuted Fracture
Bone shatters into multiple pieces
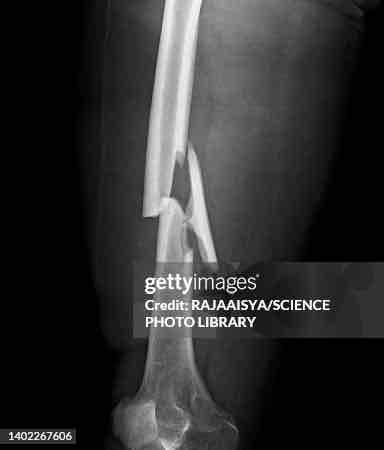
Define Greenstick fracture
Bone bends & cracks, often seen in children to more flexible bones
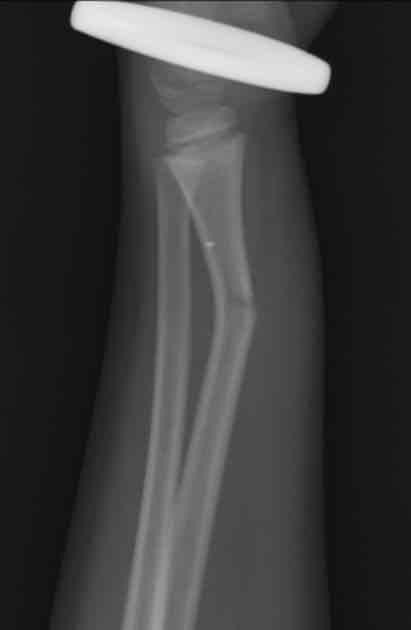
Define Spiral Fracture
Bone twisted apart due to rotational force
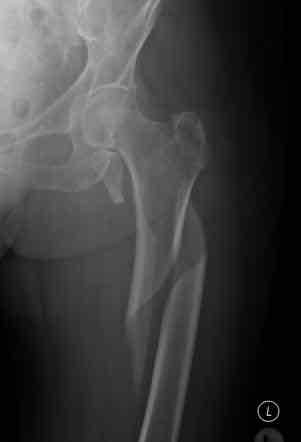
Define Transverse Fracture
Bone breaks straight across, typically at a right angle to the bones axis
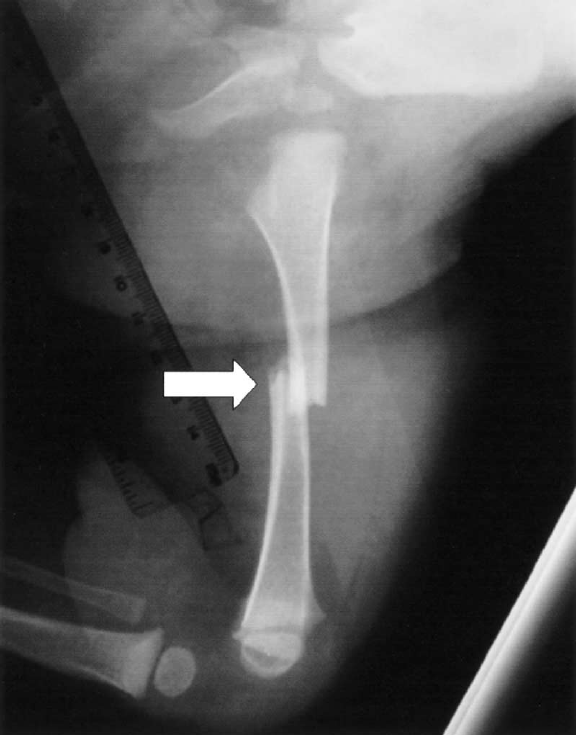
Define Scoliosis
Abnormal Lateral curvature of the spine, often forming a “s” or “c” shape
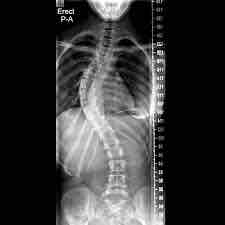
Define Lordosis
Excessive inward curvature of the lower back, often causing a “swayed appearance”