Unit 1 Lesson 3 - Community Ecology
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is a community?
Interactions between populations within a specific location.
What type of factors (biotic or abiotic) is in a community?
Biotic factors
What are living things made up of?
Cell(s)
What do cells require to function?
Energy
What is the currency of energy?
ATP/Solar Enrgy
True or False? Solar Energy is chemical energy.
False
What are 2 biochemical reactions needed to turn solar energy into ATP
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
List all reactants of photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide (CO2), Water (H2O), and light
List all products of photsynthesis
Glucose(C6H12O6) and Oxygen (O2)
An organism that can do photosynthesis is called what?
A producer or autotroph
True or False? Glucose is the same as ATP
False
What is glucose?
It is stored potential energy used to make ATP. It is like unused batter.
What is cellular respiration?
A multistep process in which the stored energy in glucose is released in the form of ATP.
Organisms that are not producers are called what?
Consumers or Herotrophs
What are the reactants for cellular respiration?
Glucose (C6H12O6) + Oxygen (O2)
What are the products for cellular respiration?
ATP + Carbon Dioxide(CO2) + Water(H2O)
What are Herbivores?
Organisms that eat plants.
What are Omnivores?
Organisms that eat plants and animals.
What are Carnivores
Organisms that eat animals.
What are Detritivores?
Organisms that feed on dead material.
What are Decomposers?
Organisms that chemically break down dead material.
True or False? All life on Earth depends on organisms that can do photosynthesis.
True
What type of organism is first in a food chain?
Producers
What type of organism has 100% of energy available in a food chain?
Producers
True or False? Decomposers obtain 100% of their energy from all trophic levels upon death.
True
Why are decomposers important?
Decomposers help recycle matter and nutrients.
What is a food chain?
A representation of the linear energy transfer from the producer to the apex predator.
Why do food chains have to be longer than 4-5 organisms?
Energy runs out FAST from trophic level to level.
What is the second law of thermodynamics?
When energy is transferred, some of it is lost as heat, increasing entropy. In the context of food chains, this means that as energy moves from one trophic level to the next (for example, from plants to herbivores to carnivores), a large portion of the energy is lost as heat and cannot be fully passed on.
What is the 10% rule?
There is only a 10% gain of energy from one trophic level to trophic level. To calculate this quickly, simply move the decimal to the “left to the left”.
What percent of heat is lost into the environment?
90%
What is a food web?
A more realistic, interlinked set of food chains that is more complex.
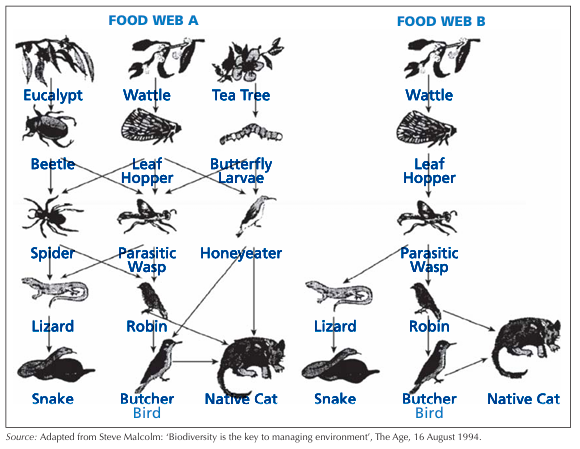
Which food web is healthier?
Food Web A is healthier due to more biodiversity. This community is more resistant to disruptions in the food web.