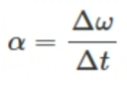Understanding Translational and Rotational Motion
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
distance
how much ground an object has covered, regardless of direction
displacement
measures how far and in what direction an object is from its start point
velocity
a vector because it tells you how fast and in which direction something moves
scalar
magnitude only
does not have direction
specified by a number and a unit
represented by quantity symbol
vector
has both magnitude and direction
has direction
also specified by a number along with the direction and unit
represented by quantity symbol in bold or with the arrow sign above
meter (m)
the si unit for both distance and displacement
acceleration
the rate at which an objects velocity changes over time
centripetal acceleration
the idea that any object moving in a circle, in something called circular motion, willl have an acceleration vector pointed towards the center of that circle
motion
one of the very first things people noticed in the world around them
translational motion
how an object moves in a straight line or across a flat surface
all parts of the object move the same distance, in the same direction, and at the same time
rotational motion
how an object turns or spins around an axis
linear displacement
refers to the change of position of an object
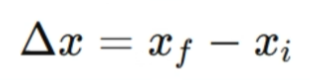
linear velocity
refers to the rate at which an object changes its position
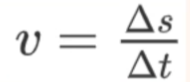
linear acceleration
refers to the rate at which an object’s velocity changes with respect to time
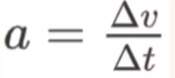
angular displacement
refers to the angle made by a body while moving in a circular path
angular velocity
refers to how fast an object rotates ir revolves relative to another point
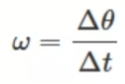
angular acceleration
refers to the rate with which angular velocity changes with time