Cardio Q1- didactic
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
what is a macule
small and flat
what is a patch
large and flat
what is a papule
small and raised
what is a plaque
large and raised
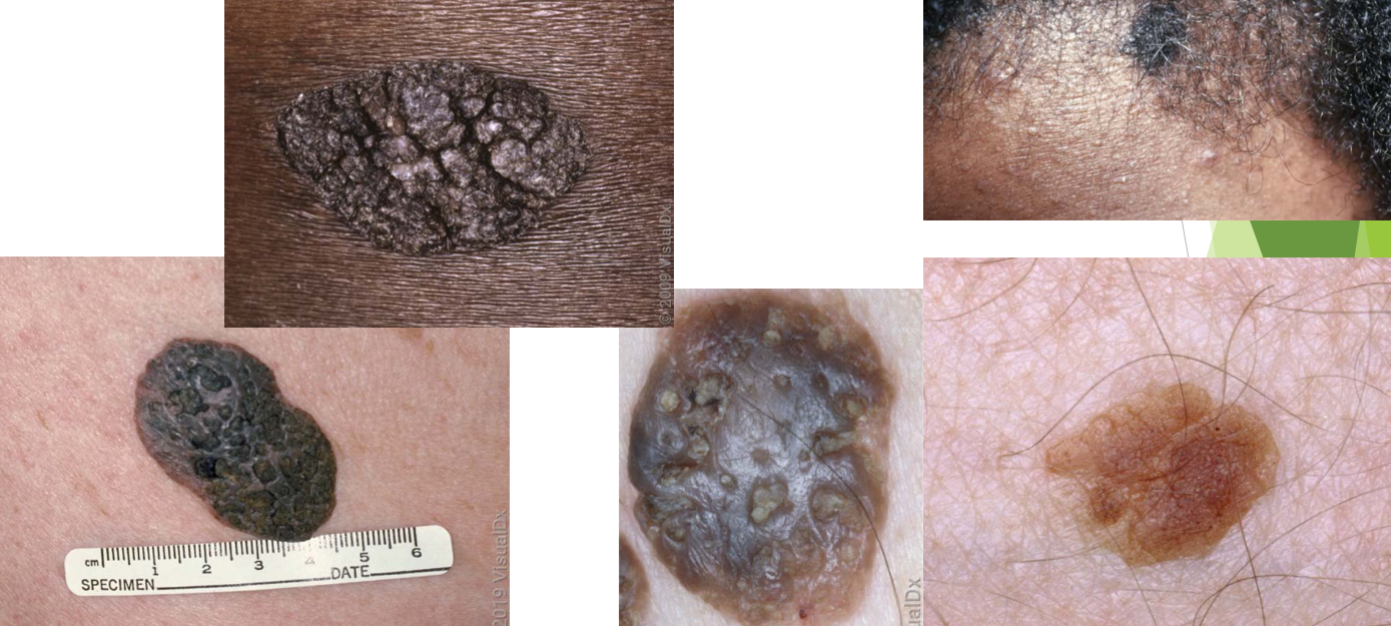
seborrheic keratosis (SK) characteristics
benign epidermal growth, “stuck-on” appearance, also known as “wisdom spot/barnacle”
when would you refer for a seborrheic keratosis skin lesion
if rapidly growing, symptomatic- pain, bleeding, itching, burning
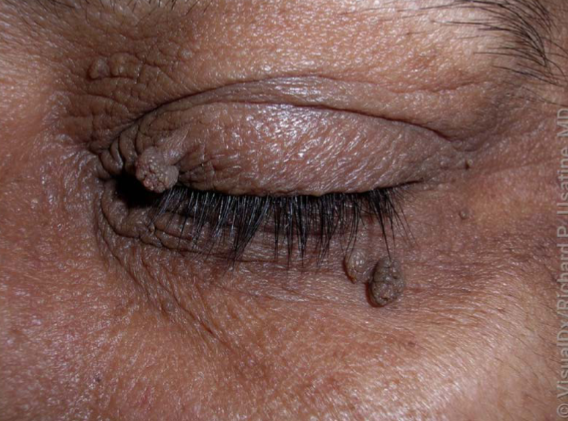
skin tag characteristics
benign epidermal growth, common on eyelids/neck/axillae, can become infarcted and necrose
skin tags are associated w
age, pregnancy, diabetes, obesity/metabolic syndrome
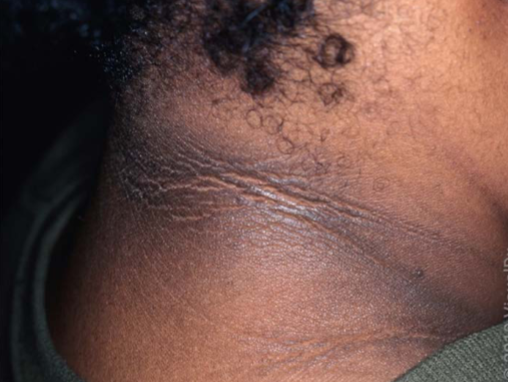
acanthosis nigricans characteristic
benign “velvety” and darkened skin
acanthosis nigricans is seen usually where on the body
on neck and armpits
acanthosis nigricans is more associated w
obesity, insulin resistance/metabolic syndrome
acanthosis nigricans is more commonly seen in what populations
black and indigenous populations
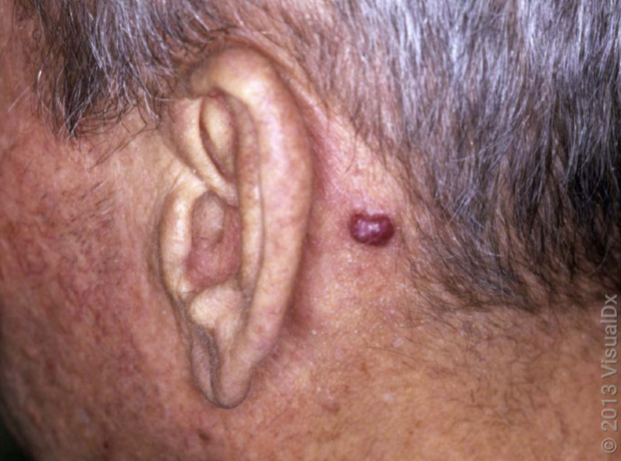
cherry angioma characteristics
benign vascular proliferation (thin-walled dilatated capillaries)
cherry angioma is more associated w
hormone status (e.g. pregnancy)
cherry angioma is seen usually where on the body
face, neck, trunk, extremities
what is diascopy
applying a glass slide onto the lesion w gentle but even pressure and watching the lesion flatten, should see blanching
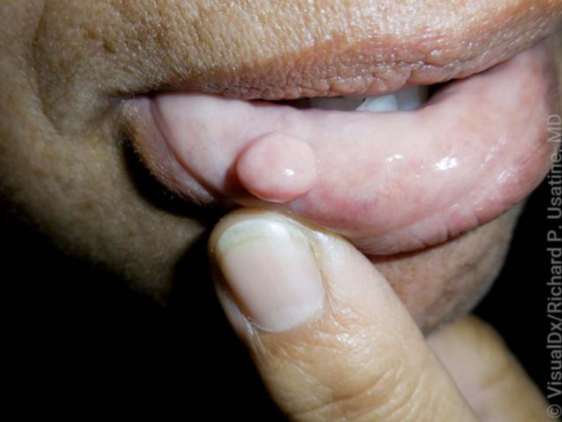
bite fibroma characteristics
chronic trauma (usually biting), painless and asymptomatic, may require biopsy for dx
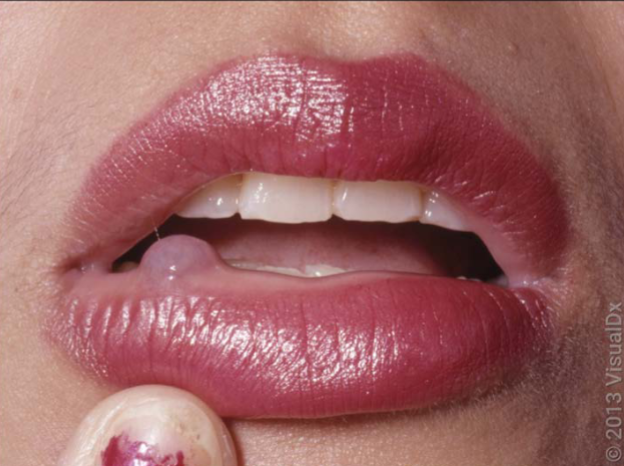
mucocele characteristics
rupture of minor salivary gland- mucin collection in soft tissue, swells and pops repeatedly, may fibrose over time, may require biopsy for dx
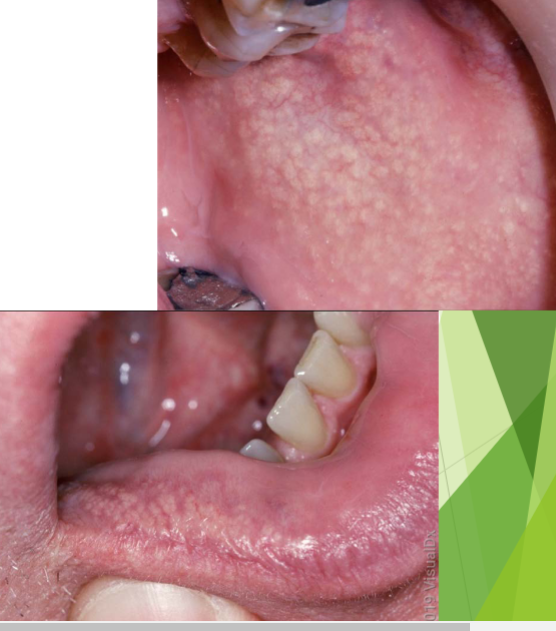
fordyce spots characteristics
ectopic sebaceous glands, no tx, asymptomatic, any age affected
fordyce spots are seen where in the body
vermillion border, buccal mucosa
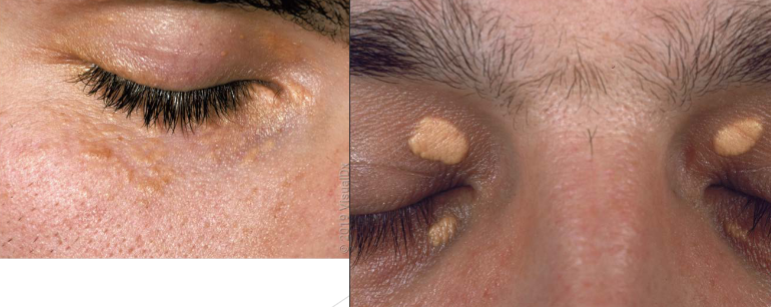
xanthelasma
type of plane xanthoma, 50% have underlying hyperlipidemia
what is hyperlipidemia
high levels of lipids (fats) in the blood
xanthelasma is more common in…
women (3x more than men)
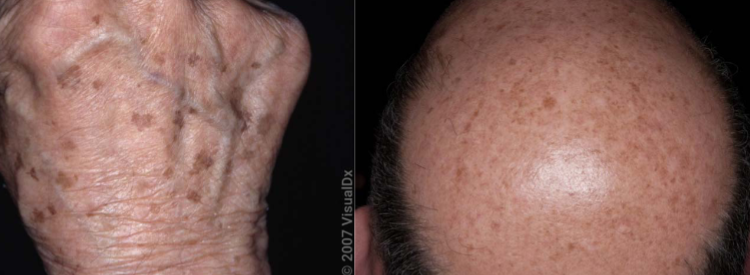
solar lentigo characteristics
benign epidermal growth, marker of ultraviolet radiation exposure
types of skin cancer
basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma
what is the most common type of skin cancer and least concerning
basal cell carcinoma
risk factors for basal cell carcinoma
UV exposure, radiation, light skin, age
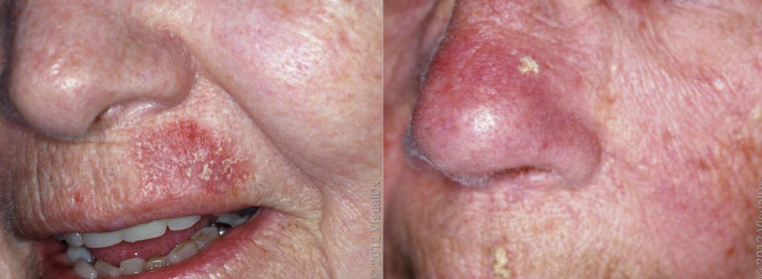
actinic keratosis characteristics
precancerous lesion, marker of actinic damage (and skin cancer risk), sandpaper texture, flakes off and comes back
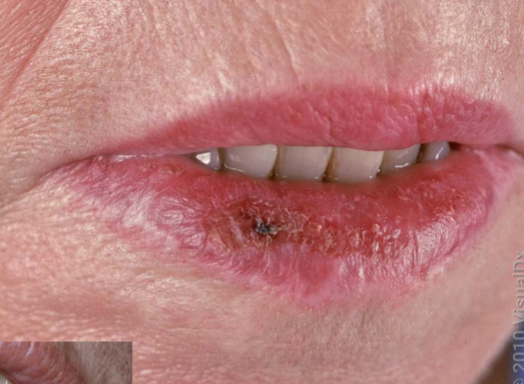
actinic cheilitis characteristics
usually lower lip (AK of lip), can see dryness, cracking, white color
is actinic keratosis or actinic cheilitis at higher risk of transformation to SCC
cheilitis > keratosis
squamous cell carcinoma in-situ is also referred to as
bowen’s disease
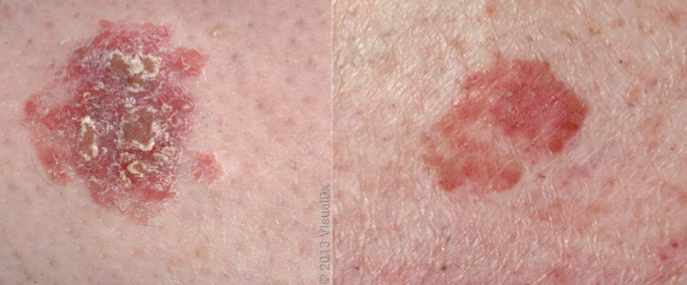
squamous cell carcinoma in-situ appearance characteristics
full thickness epidermal involvement w/o invasion into dermis
what is the second most common skin cancer and has a low risk of metastasis
squamous cell carcinoma
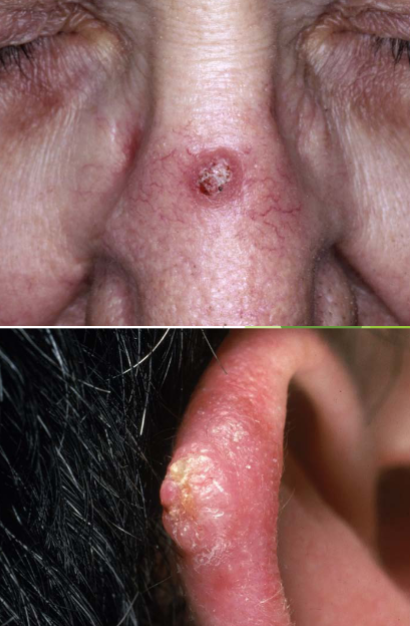
risk factors for squamous cell carcinoma
UV, radiation, transplant, tobacco use, light skin, age, chronic non-healing wounds
which skin cancer is the most aggressive of the common skin cancers and has a higher risk of metastasis
melanoma
risk factors for melanoma
fair skin, red hair, >50-100 moles, >5 atypical moles, UV exposure, family history
ABCDE stands for
Asymmetry, Borders, Color, Diameter, Evolving
bone mass is dynamic, what does this mean
it changes according to loading
bone remodeling allows for…
bone adaption to load and repair of damage
what is the cellular “renovation” team
osteo-cytes, clasts, blasts
what are osteocytes
start/stimulate bone formation/resorption dynamic
what are osteoclasts
resorb bone
what are osteoblasts
build bone
what is the osteocyte network
osteocytes extend plasma membrane projections through canaliculi where neighboring osteocytes are connected by gap junxs that allow sharing of intracellular material and signaling molecule
what is the purpose of the osteocyte network
so mechanical forces experiences by one osteocyte can produce a response in all of its neighbor
what are the phases of remodeling bone
activation→ resorption → reversal → formation → quiescence
what cell is responsible to initiate remodeling by inc RANKL secretion
osteocytes
activation phase of bone remodeling
osteocytes (and osteoblasts) secrete RANKL that stimulates clasts differentiation and osteoprotegerin (OPG) that will supress osteoclast differentiation
what is osteopetrosis- “marble bone disease”
a disorder of impaired osteoclast activation
what are osteoclasts doing during the resorption stage of bone remodeling
mature clasts form tight attachments on the bone surface to form resorptive space
what enzymes are used in the resorption stage of bone remodeling, that osteoclasts use to produce and pump acid into the resorption space
carbonic anhydrase, vacuolar ATPase
what components are released into the cellular space during resorption of bone remodeling
acidic pH and secreted proteases digest the mineral and protein components of bone and these are released
reversal stage of bone remodeling
osteoclasts are resorbing and secreting factors that stimulate -blast differentiation/activity
the reversal stage of bone remodeling is marked by…
reduction in number of -clasts and recruitment of -blast precursors
formation stage of bone remodeling
-blasts produce a (primarily) type I collagen matrix- osteoid- and secrete -blast stimulating factors that embed within the matrix for future remodeling
in bone formation, what does mineralization look like starting from a mesenchymal stem cell
preosteoblast → osteoblast → osteoid osteoblast → mineralizing osteocyte → osteocyte
quiescence stage of bone remodeling
-cytes of newly formed bone secrete variety of -clasts and -blast inhibitory factors to suppress resorption and formation
what is the major -blast inhibitor
sclerostin
as -blasts become -cytes, their expression of sclerostin __________ (inc/dec)
inc
the bone will remain __________ until more stress or damage is detected
quiescent
a disease caused by loss of sclerostin
sclerosteosis
sclerosteosis is characterized by
global progressive inc in bone density, possible hearing, sight, or smell due to CN compression, sudden death due to brain stem compression
sclerosteosis is what mode of inheritance
autosomal recessive inheritance pattern
when you zoom into muscle, you will see
muscle fibers
when you zoom into muscle fibers, you see
myofibrils
when you zoom into myofibrils, you will see
sarcomeres
when you zoom into a sarcomere, you see
G/F actin filaments
when you zoom into actin filaments, you see
myosin filaments
myofibril sarcomeres are made up of
thick and thin filaments interdigitated
what drives filament sliding of the sarcomere
interactions between the thick and thin filaments
thick filaments are made up of
myosin heads
what primarily makes up the thin filaments
actin
lever-arm rotation is coupled to…
ATP hydrolysis
what cycle drives all of muscle contraction in all life
Myosin’s chemo-mechanical cycle
what is rigor mortis
when muscles get stiff and cannot be manipulated
why does rigor mortis happen
myosin gets stuck in the myosin-actin state “waiting” for next ATP to come
What neurotransmitter triggers muscle contraction
acetylcholine
what role does calcium play in muscle contraction
when ca channels are open, ca “bathes” sarcomeres and binds to the thin filaments
What does the sarcoplasmic reticulum store
calcium
what are the two divisions or the circulatory system
cardiovascular and lymphatic
what does the cardiovascular system include
blood vessels and heart, plus the blood they carry
what does the lymphatic system include
lymph vessels plus the lymph they carry
the vessels of the circulatory system include
arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and viens
what is an artery
conducting/distributing vessel
what is an arteriole
resistance vessel- major determinant of systemic bp
what is a capillary
gas/nutrient exchange vessel
what is a venule
exchange vessel- inc permeability during inflammation
what is a vein
conducting/reservoir vessel
is there a higher pressure in the arterial or venous system
arterial
most of the time, there is more blood on the venous or arterial side
venous
blood pressure will start to decrease when going from arteries to _________ and will continue to decrease until you pump the blood back out of the heart
arterioles
tissue perfusion
in the capillaries, maintains homeostasis of the tissue fluid by exchanging stuff (e.g. water, nutrients, gases, metabolites, ions, hormones, etc)
there are more __________ than any other blood vessel in the body
capillaries
the flow rate is lowest at _________ bc…
capillary beds; give time for exchanges
a neurovascular bundle contains…
an artery, vein, lymph vessel, nerve
what are the three main capillary types
continuous, fenestrated, discontinuous
continuous capillary characteristics
most common type, cells are tightly packed
fenestrated capillary type characteristics
rapid exchange between tissue and blood- have thinner spots within cell for shorter exchange
discontinuous capillary type characteristics
sinusoids- only found in 3 places in the body: bone marrow, liver, spleen
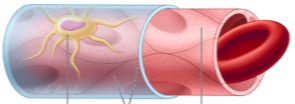
capillary type
continuous