Chapter 25 - Urinary System and Renal Physiology
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
prefix for kidneys
nephro-
sufix for kidneys
-uria
amount of fluid filtered from blood by kidneys every single day
200 liters
Function of the kidney
maintaining the composition of the body’s extracellular fluids by filtering the blood
Regulate total body water volume and concentration of solutes in water
Regulate concentration of ions in ECF
Acid-base balance
Remove toxins, metabolic wastes, & other foreign substances
Hormone production-EPO and renin
Location of kidneys
back
size of bar of soap
Each kidney lies between the parietal peritoneum and dorsal body wall
Kidney is what type of organ?
Retroperitoneal organ
no viseral peritoneum, just against bodywall
Medial portion of kidney is __
Concave
what enters renal hilum
ureters
renal blood vessels
lymphatics
Where is adrenal gland located
sits immediately superior to each kidney
Supporting external structures of the kidneys
Renal fascia
Perirenal fat capsule
Fibrous capsule
Renal fascia
Supporting external structure of the kidneys
dense connective tissue
Function: anchors kidneys to surrounding structures
Perirenal fat capsule
Supporting external structure of the kidneys
fat mass surrounding kidneys
Function: Cushions kidneys from physical trauma
still kidneys easily damaged
Fibrous capsule
Supporting external structure of the kidneys
thin, transparent capsule
Function: prevents disease from spreading to kidneys from other parts of body
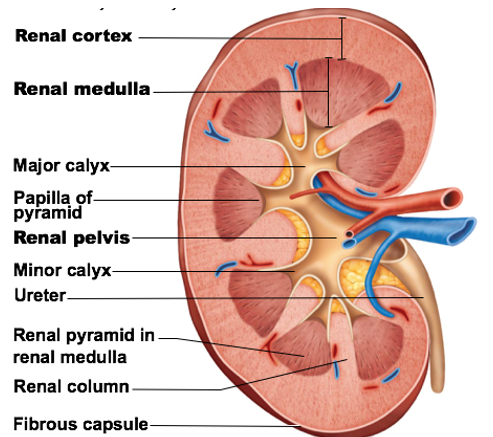
Major internal regions of kidneys:
Renal Cortex
Renal Medulla
Renal Pelvis
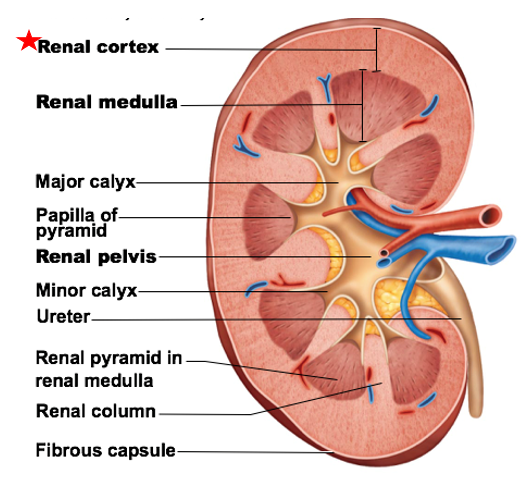
Renal Cortex
a major internal region of kidneys
outter most region
provides area for glomerular capillaries and blood vessel passage, EPO, & renin produced here
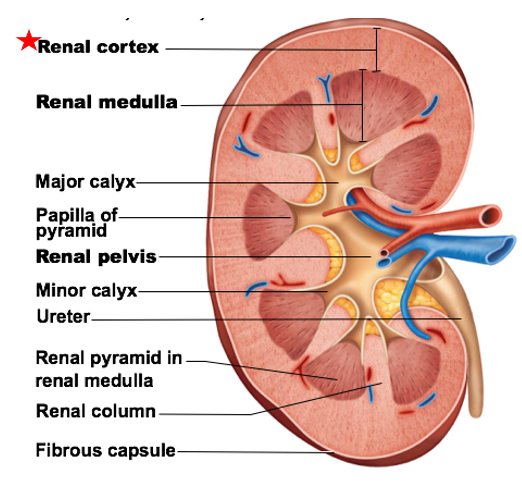
Renal Medulla
a major internal region of kidneys
Contain several renal pyramids → packed with capillaries & urine-collecting tubules
Function: allows for some water reabsorption, electrolyte balance, disposal of waste and H+ ions
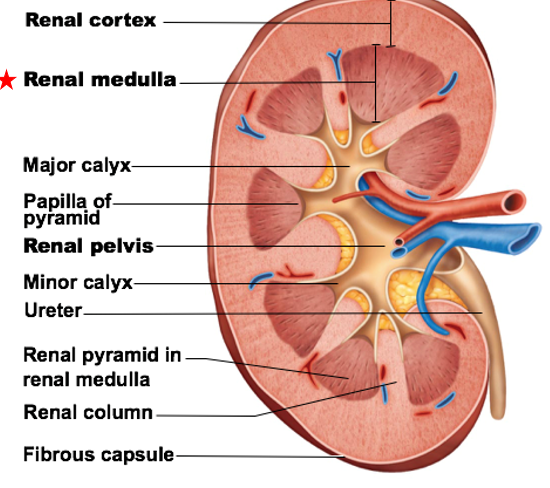
Renal Pelvis
a major internal region of kidneys
Open space (largest) in center of each kidney
Pelvis branches to form major calyces (calyx)
Major calyces lead into minor calyces at tip of each renal pyramid
Function of calyces and pelvis: urine collection from renal medulla
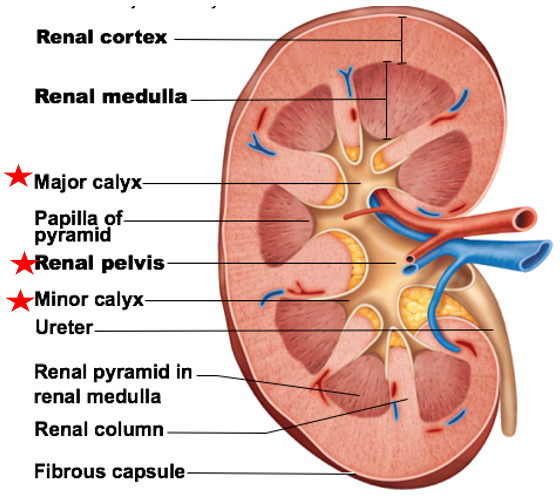
Pelvis branches to form
major calyces (calyx)
Major calyces lead into __ at tip of each renal pyramid
minor calyces
Function of calyces and pelvis
urine collection from renal medulla
what delivers blood to kidneys?
Renal arteries deliver to kidneys → divide into smaller blood vessels to serve major regions of kidney
Renal arteries split into
Largest to smallest
Segmental arteries (5)
Interlobar arteries
Arcuate arteries
Cortical radiate arteries
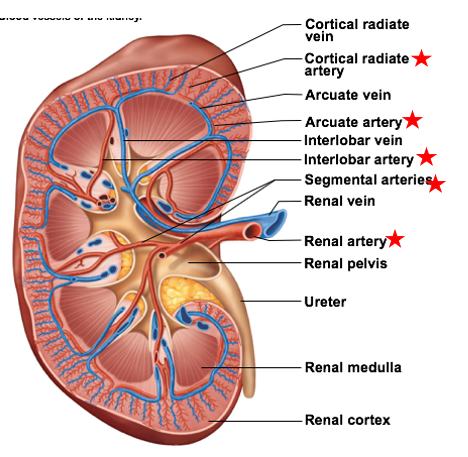
Segmental arteries
there are 5
the largest of the smaller blood vessels branching off the renal arteries
ensure blood reaches all branches
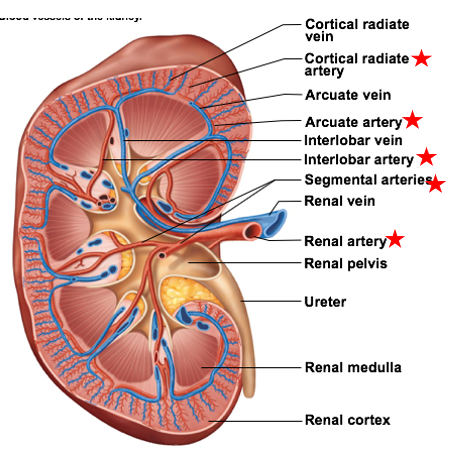
Interlobar arteries
the 2nd largest of the smaller blood vessels branching off the renal arteries
travel between renal pyramids
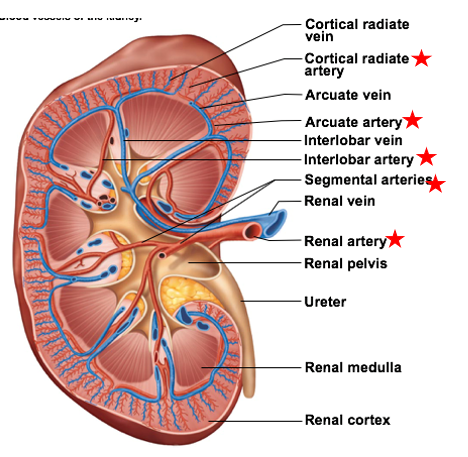
Arcuate Arteries
the 2nd smallest of the smaller blood vessels branching off the renal arteries
arc over bases of pyramids
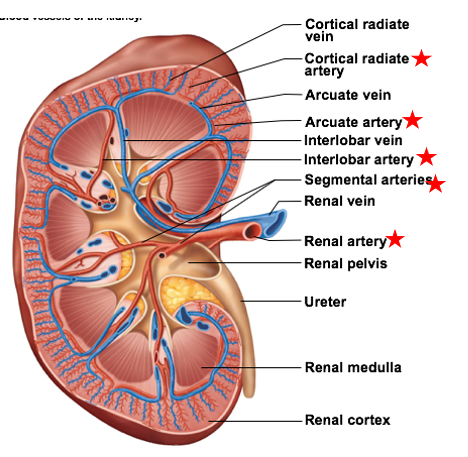
Cortical radiate arteries
the smallest of the smaller blood vessels branching off the renal arteries
supply renal cortex
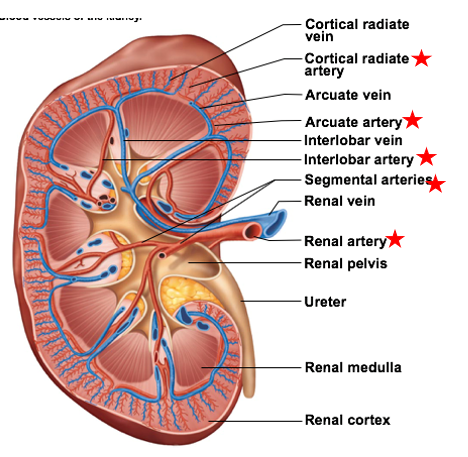
Veins of kidney
smallest to largest
Cortical radiate veins
Arcuate veins
Interlobar veins
Renal veins
Nerve Supply to the Kidneys
Renal plexus → autonomic nerve fibers & ganglia
Sympathetic vasomotor fibers regulate blood supply to each kidney
Function: Adjusts diameter of renal arterioles to adjust blood flow to glomeruli
Renal plexus
autonomic nerve fibers & ganglia of kidneys
_ regulate blood supply to each kidney
Sympathetic vasomotor fibers
nephron
is the functional unit of the kidney
Function: Responsible for forming filtrate and eventually urine in the kidneys
General structure of nephron
Each nephron contains a renal corpuscle and renal tubule
renal corpuscle
structure in the nephron
Located entirely within renal cortex
filters blood to form the filtrate
renal tubule
structure in the nephron
reabsorbs some substances from the filtrate & secretes other substances into the filtrate
Subdivisions of renal corpuscle
glomerulus
Glomerular capsule
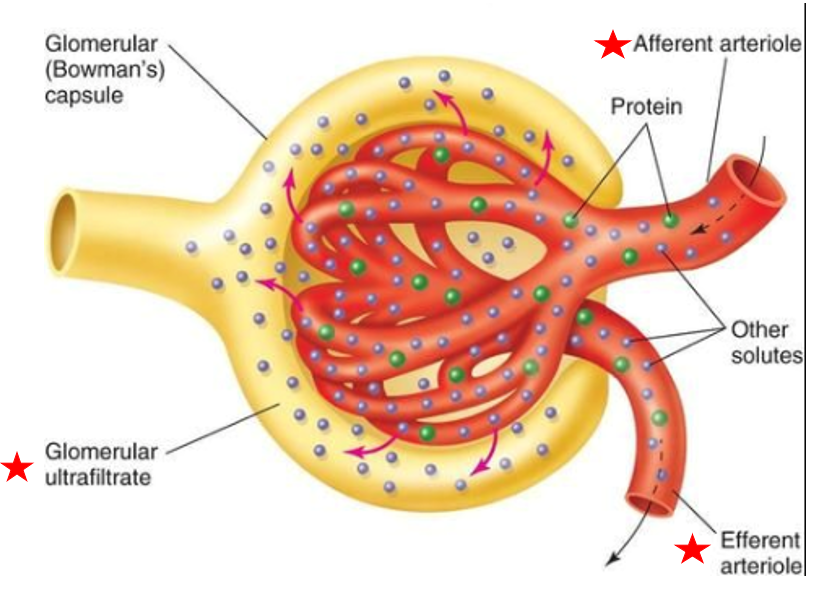
Glomerulus
Subdivision of renal corpuscle
cluster of capillaries
Blood enters glomerulus via afferent arteriole, leave via efferent arteriole
Capillaries are very porous → some fluid & substances in blood easily filtered out of capillary
Fluid is called filtrate
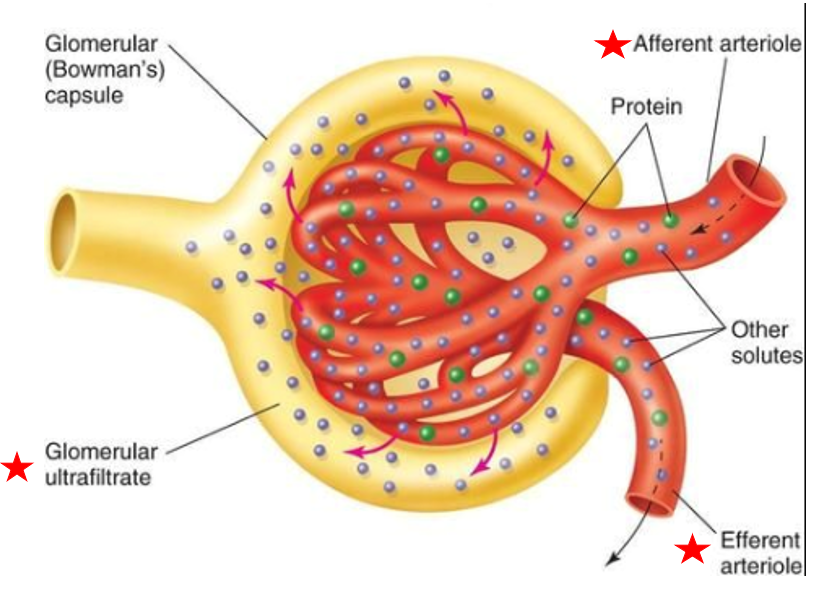
filtrate
some fluid in blood easily filtered out of capillary
raw material used to produce urine
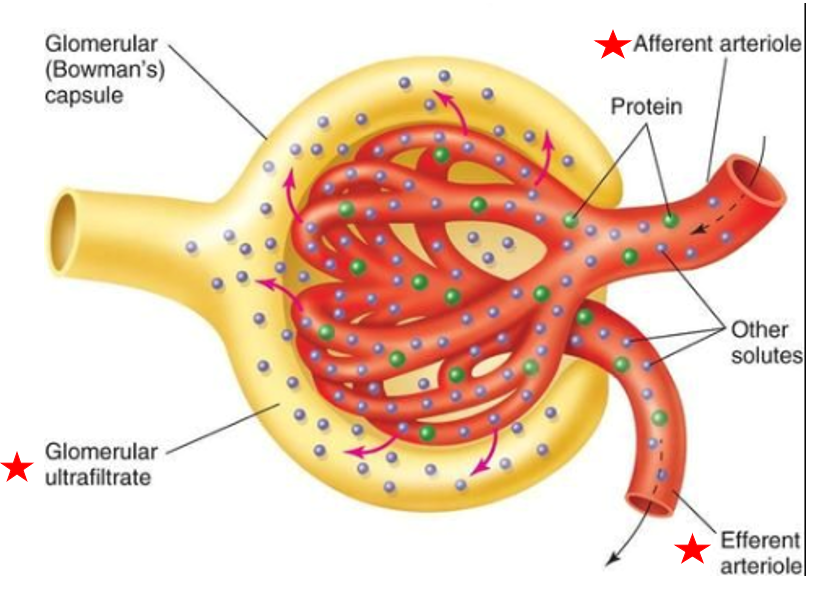
Blood enters glomerulus via
afferent arteriole
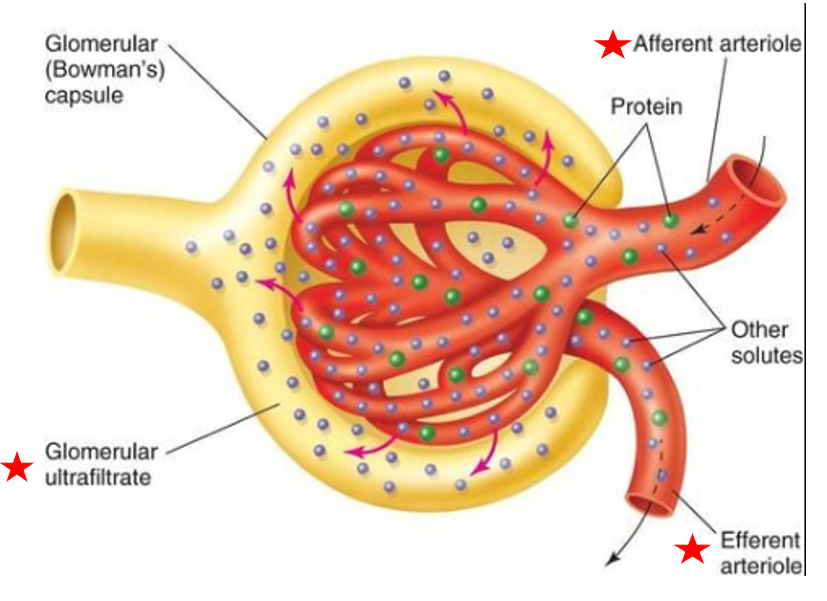
Blood leaves glomerulus via
efferent arteriole
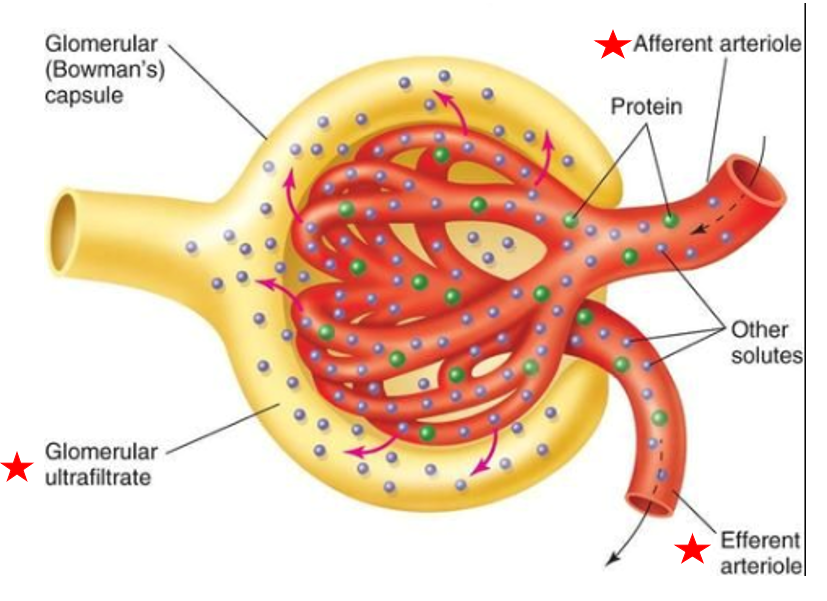
Glomerular capsule
Subdivision of renal corpuscle
double-layered structure that completely surrounds glomerular capillaries
Inner layer has podocytes with foot processes
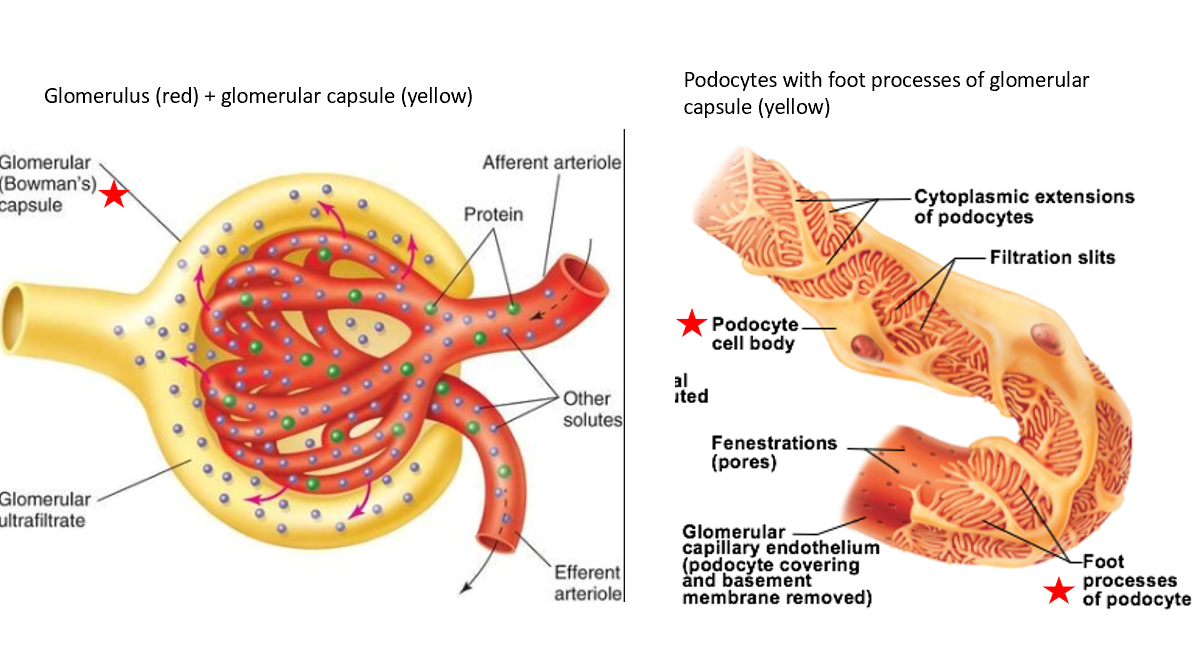
Inner layer of glomerular capsule has
podocytes with foot processes
Renal Tubules & Collecting Duct
Begins in renal cortex, extends into renal medulla, then returns to renal cortex
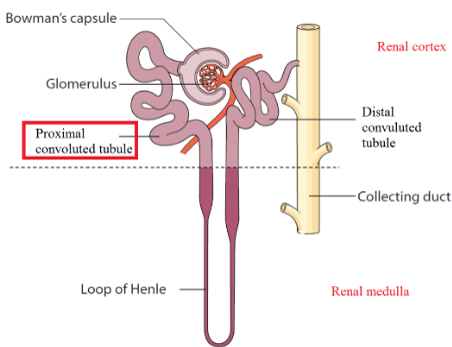
Subdivisions of renal tubules
Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
Nephron Loop
descending limb
ascending limb
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
leads immediately off from glomerulus
Located in renal cortex
Large cuboidal epithelial cells with dense microvilli
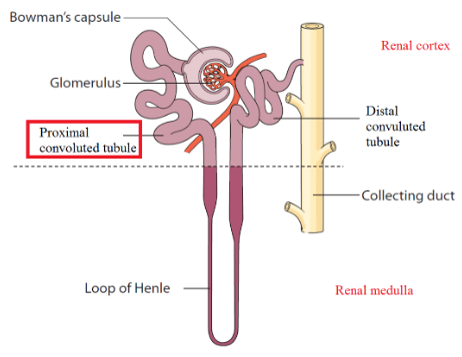
Nephron Loop
formerly Loop of Henle
Travel between renal cortex and renal medulla
Composed of
Descending limb
Ascending limb
Function: allows the kidneys to vary the concentration of urine according to how much water is reabsorbed at nephron loop
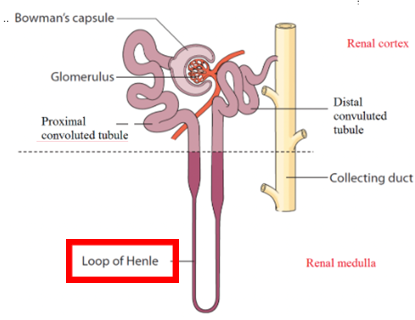
Descending limb Nephron Loop
Leads off from PCT
High permeability to H2O, impermeable to solutes
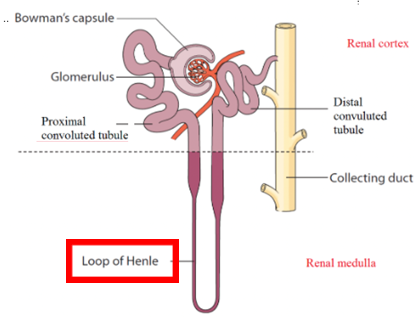
Ascending limb Nephron Loop
Continuous with DCT
High permeability to solutes, impermeable to H2O
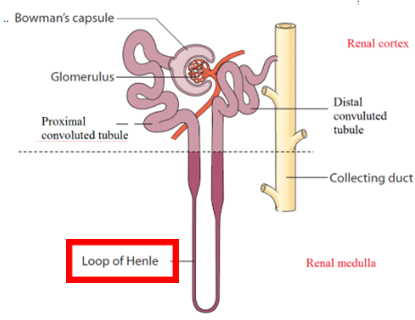
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Located in cortex, composed of small cuboidal epithelia
Smaller diameter than PCT, contain no microvilli
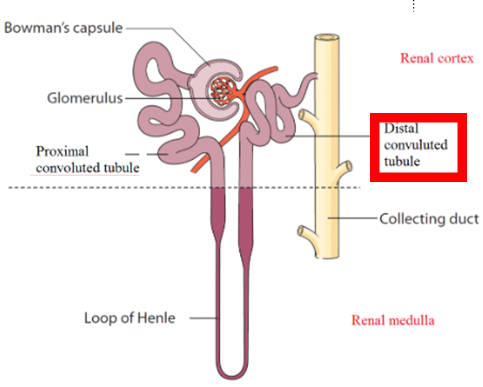
Collecting Ducts
Each collecting duct receives filtrate from tubules of multiple nephrons
Collecting ducts fuse together, dump urine into minor calyces
Important cell types in collecting ducts
Principal cells → maintain Na+ balance in body
Intercalated cells → help maintain acid-base balance
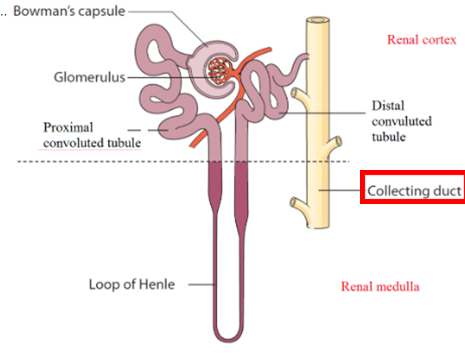
Types of Nephrons
Cortical Nephrons
Juxtamedullary Nephrons
have the same structures (previously described), BUT there are slight modifications to those structures
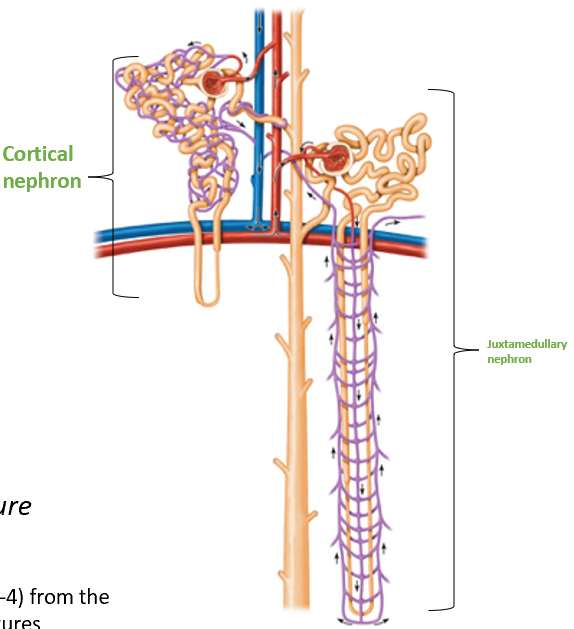
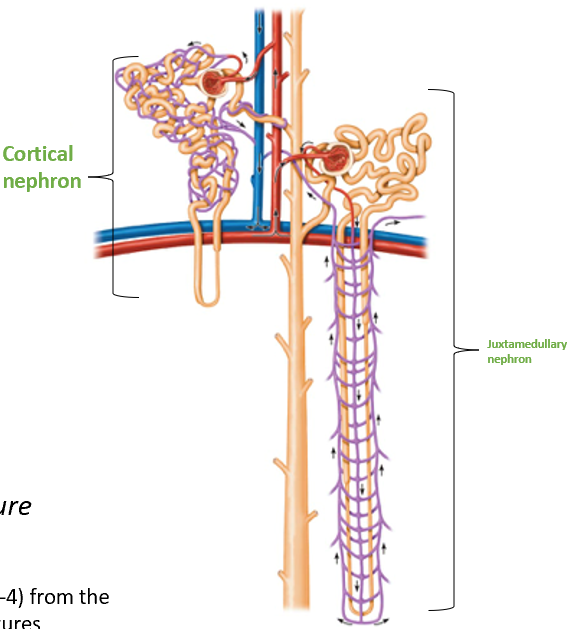
Cortical Nephrons
Located almost entirely in the cortex
Small portion of nephron loop found in renal medulla
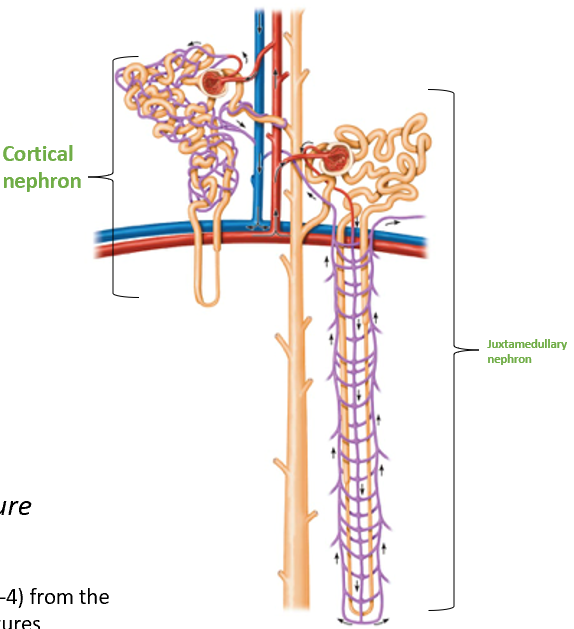
Juxtamedullary Nephrons
Nephron loops deeply invade renal medulla
Capillary Beds of Nephrons
Glomerulus Capillaries
Peritubular Capillaries
Vasa Recta
Glomerulus capillaries
Maintains high pressure to increase filtrate production
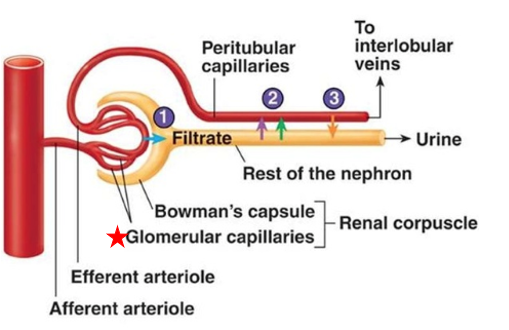
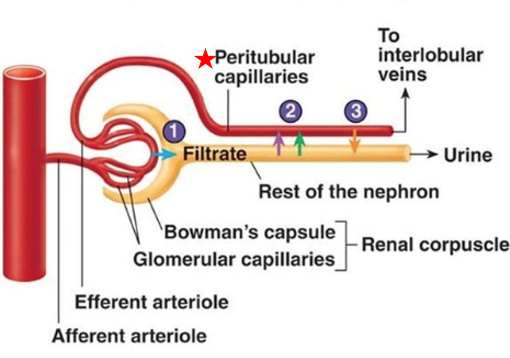
Peritubular Capillaries
Low pressure capillaries arising from efferent arteriole
Cling to proximal & distal tubules of cortical nephrons
Function: Reabsorb water & solutes from tubule cells
Empty into cortical radiate veins → filtered blood returns to circulation
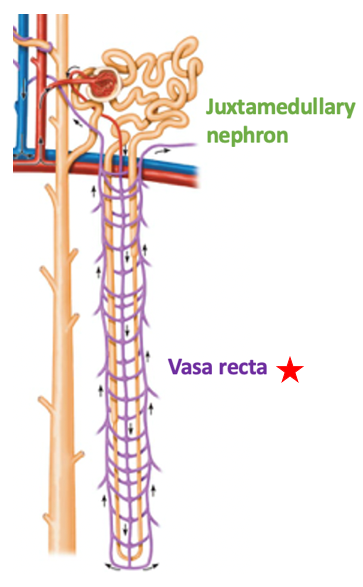
Vasa Recta
Found only on juxtamedullary nephrons
Run parallel to long nephron loop
Help form concentrated urine
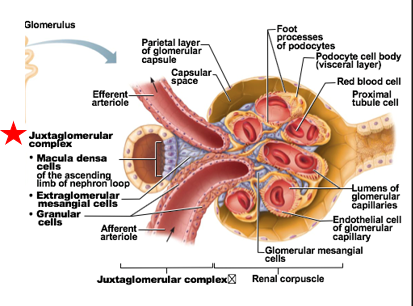
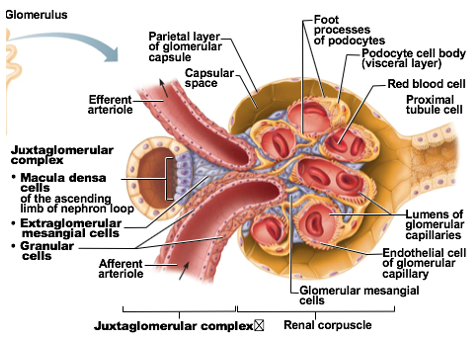
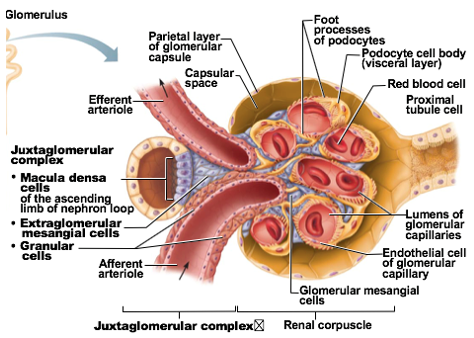
Juxtaglomerular complex
portion of nephron where portion of ascending limb lies against afferent & efferent arterioles
Overall function: Regulate blood pressure & filtration rate of the glomerulus
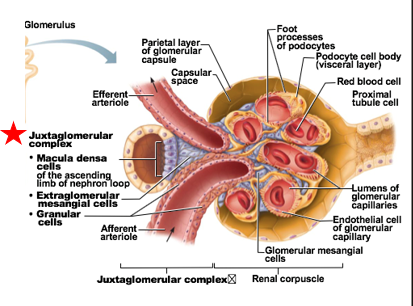
cellular modifications at Juxtaglomerular complex
Macula densa
Granular cells (Juxtaglomerular cells)
Extraglomerular mesangial cells
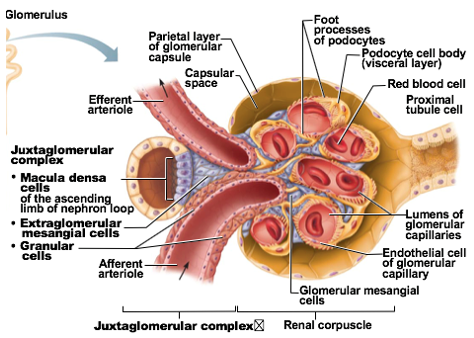
Macula densa
1 of the cellular modifications at Juxtaglomerular complex
chemoreceptor cells
Function: Monitor NaCl content of filtrate entering distal convoluted tubule
Granular cells
aka: Juxtaglomerular cells
1 of the cellular modifications at Juxtaglomerular complex
specialized smooth muscle cells cells
Found in arteriolar walls of afferent arteriole
Can sense blood pressure in afferent arteriole
Also stimulated by macula densa cells
The granules in granular cells _
secrete renin
Renin mostly affects the efferent arteriole!
Low NaCl concentration = increased renin release
Low pressure in arteriole = increased renin release
Extraglomerular mesangial cells
1 of the cellular modifications at Juxtaglomerular complex
Packed between tubule and arterioles
function: provide structural support and regulate blood flow within the glomerulus.
Diuresis
Urine formation
Urine Formation Steps
Glomerular Filtration
Reabsorption
Secretion
Glomerular filtration (Urine Formation Step)
production of a cell and protein-free filtrate that serves as the raw material for urine
How does Glomerular filtration work?
Pressure forces fluid out of glomerular capillary & into glomerular capsule
The filtration membrane allows passage of water, small solutes into glomerular capsule
aided by foot processes of podocytes
what do foot processes of podocytes in glomerular filtration
foot processes create filtration slits
Slits prevent passage of macromolecules/large-sized materials into filtrate
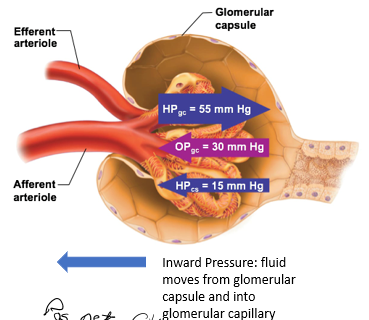
Filtration Pressures
pressures that force fluid into or out of glomerulus
Outward Filtration Pressure
force fluid out of glomerulus
promotes filtrate formation
outward pressure here is always HIGH
composed of: Hydrostatic pressure in glomerular capillaries (HPgc)
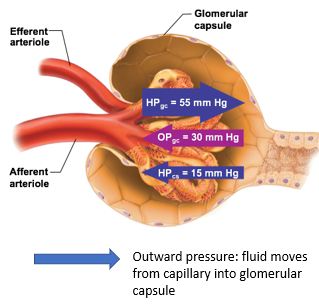
Hydrostatic pressure in glomerular capillaries (HPgc)
blood pressure of the glomerular capillaries that forces fluid out of glomerulus and into the space of the glomerular capsule
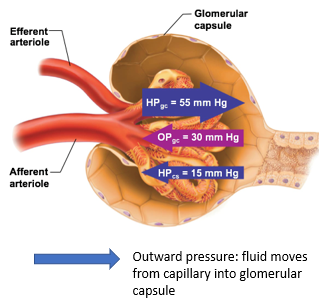
Inward Filtration Pressure
oppose filtrate formation
composed of
Hydrostatic pressure in capsular space (HPcs)
Colloid osmotic pressure in glomerular capillaries (OPgc)
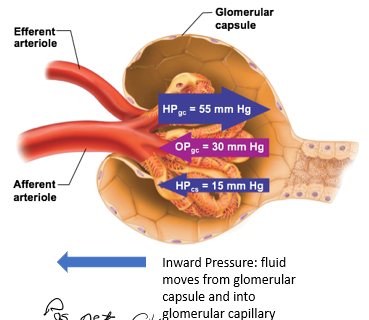
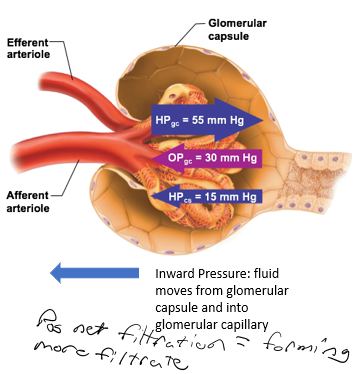
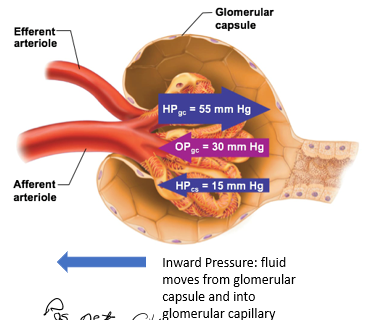
Is the net filtration pos or neg?
positive
means forming more filtrate
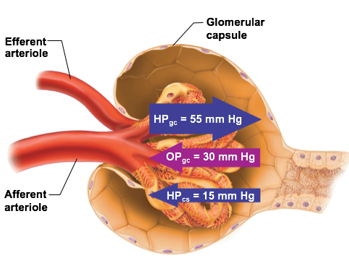
Hydrostatic pressure in capsular space (HPcs)
part of the inward filtration pressure
pressure exerted by filtrate that is already in the glomerular capsule
Colloid osmotic pressure in glomerular capillaries (OPgc)
part of the inward filtration pressure
proteins that are still in capillaries will “pull” water back in
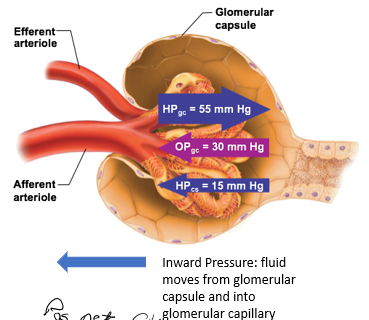
Which is smaller, Hydrostatic pressure in capsular space (HPcs) or Colloid osmotic pressure in glomerular capillaries (OPgc)?
HPcs is smaller than OPgc, usually at 15mmHg
OPgc has more influence on the inward pressure
Glomerular Filtration Rate
the total volume of filtrate formed per minute for all nephrons in the kidneys
highly regulated
ideal is 125mL/min for men
What part of the glomerular capillary does filtration occur
Filtration occurs along the entire length of a glomerular capillary
Factors affecting GFR
Net Filtration Pressure (NFP)
Surface area of capillaries
increased area increases rate
Filtration membrane permeability
Regulation of GFR
Tightly regulated for two reasons:
Kidneys need constant GFR to make filtrate and maintain extracellular homeostasis
Regulating GFR regulates blood pressure in entire body
Ex: decreasing GFR will decrease urine output
bc blood volume
Primary variable controlled to regulation GFR
HPgc
When HPgc increases → NFP & GFR also increase
When HPgc decreases → NFP & GFR decrease
Control of HPgc can be
intrinsic (renal)
extrinsic (CNS)
Renal autoregulation of GFR
intrinsic
kidneys adjust resistance to blood flow
Intrinsic controls can maintain GFR for blood pressures ranging 80-180 mm Hg
Myogenic mechanism
Tubuloglomerular Feedback Mechanism
Myogenic mechanism
Renal autoregulation of GFR
Rising systemic blood pressure stretches afferent arteriole
In response to stretch, the afferent arteriole's smooth muscle cells contract, causing the arteriole to constrict
Blood flow into glomerulus restricted to maintain GFR at desirable rate
Tubuloglomerular Feedback Mechanism
Renal autoregulation of GFR
controlled by macula densa
Remember: macula densa monitor NaCl concentrations
Increasing GFR = decrease in reabsorption rate
Response: Macula densa cause vasoconstriction of afferent arteriole → decreases blood flow into glomerulus → decreases GFR
Neural Mechanisms of GFR regulation
Extrinsic
The sympathetic nervous system will override renal autoregulation
happens during stressful situations, exercise, or when blood pressure drops significantly
fast
Norepinephrine released by sympathetic system in response to low blood pressure
Vascular smooth muscle contracts
afferent arterioles contract
Hormonal Mechanisms of GFR regulation
Extrinsic
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone mechanism → overall effect is to increase BP
Granular cells of JGC stimulated to release renin
Activation of granular cells to release renin can involve
Stimulation by sympathetic nervous system
Activated macula densa cells
Macula densa sense low NaCl concentrations due to decreased GFR
Reduced stretch of arteriole walls
Decreased stretch of arteriole walls = low blood flow/pressure in afferent arteriole
Reabsorption (Urine Formation Step)
selectively moving substances from the filtrate back into the blood
99% of filtrate is reabsorbed by the body
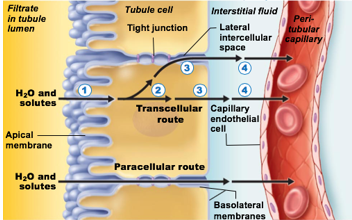
Substances can either move in between kidney tubule cells (paracellular) or through kidney tubule cells (transcellular)
includes rebsorption of
Na+
Nutrients and ions
Water
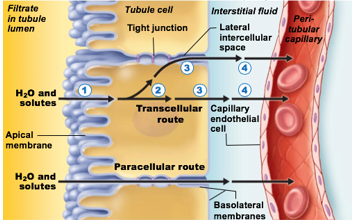
paracellular (in terms of reabsorption)
Substances move in between kidney tubule cells
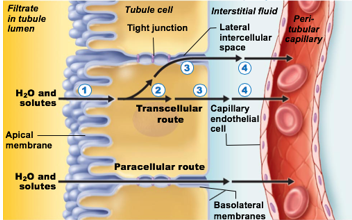
Transcellular (in terms of reabsorption)
Substances move through kidney tubule cells
What type of process is reabsorption of Na+
transcellular, active process
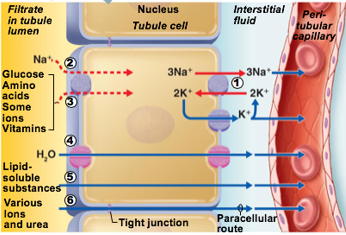
What type of process is Reabsorption of nutrients & ions
Can be transcellular or paracellular
Nutrients are co-transported with Na+ via transcellular route
Ions can be transcellular or paracellular
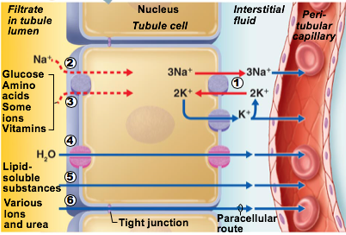
What type of process is Reabsorption of water
Passive
Some H20 absorbed via paracellular route
Transmembrane protein aquaporin allows water to cross plasma membrane of tubule cell
PCT has many aquaporins → water is always absorbed here
Collecting ducts have no aquaporins until antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is present
Number 4 in pic
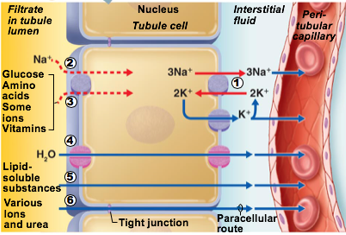
aquaporin
transmembrane protein
allows water to cross plasma membrane of tubule cell
in PCT
in Collecting duct only when antidiuretic hormone is present
Collecting ducts have no aquaporins until antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is present
Any pathway using a transport protein has a
transport maximum (Tm)
based on the number of binding sites
The more transport proteins for a specific molecule, the higher the amount absorbed
What happens when all the transport proteins for a particular substance are bound?
in diabetes mellitus this leads of glucosuria
Reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
Contain villi and microvilli
All glucose, amino acids, most nutrients reabsorbed here
Most water and Na+ also reabsorbed here (~65%)
Most electrolytes reabsorbed here
Uric acid and urea also reabsorbed here
Reabsorption in the nephron loop
Water reabsorption is not coupled to solute reabsorption here
Water can leave the descending limb, but not the ascending limb
Solutes can leave the ascending limb, but not the descending limb
Importance: the difference in permeability between the ascending limb and descending limb allows the nephron to form dilute or concentrated urine
Reabsorption in the DCT & Collecting Duct
Most water and solutes have already been reabsorbed by PCT and nephron loop
Hormonally controlled
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Aldosterone
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
inhibits urine formation by increasing water reabsorption to blood
If water is returned to blood → it will not be put in urine
Aquaporins inserted into collecting ducts
Amount of ADH is directly proportional to number of aquaporins inserted