Chordates
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Chordates are the ________ largest group of animals on Earth (though pale in comparison to arthropods and nematodes).
Fourth
What groups are chordates broadly divided into? (Hint: there are 3).
Cephalochordates, Urochordates, and Vertebrates.
What is the evolutionary line that chordata follows?
Eumetazoa ("true tissue") --> Bilatera (has left and right compared to radial symmetry) --> Deuterostome (blastopore = anus)
What is the difference between deuterostome and protostome?
Deuterostome's blastopore develops into the anus. Protosome blastopore develops into the mouth.
In at least one part of their life cycle, chordates have the following characteristics:
- Notochord
- Pharyngeal slits
- Endostyle
- Dorsal hollow nerve cord
- Postanal tail
What is a notochord?
A thin, flexible rod dorsal to coelom. It's primary function is to permit swimming motion.
Do humans have a notochord?
Humans have a notochord, but only during the embryonic stages.
Most notochords serves as the template for development of what?
It serves as the template for development of the vertebral column.
Notochords are retained in the adult stages within:
Amphioxus, hagfish, and lamprey
What is the notochord made of?
Superficial layer of dense, tough connective tissue and collagen. Its core is composed of cells within large fluid-filled vacuoles. Its rigidity is more a function of hydrostatic pressure (if the fluid from the core is released, the notochord collapses).
What are pharyngeal slits?
They play no role in respiration nor do gills develop from them in embryo. It is part of the pharynx, which is part of the digestive system. It is similar to the notochord, as it is rarely in adult stages.
What does the pharyngeal slits become in humans?
During embryonic development, it will eventually become the lower jaw, a portion of the inner ear, and auditory tube.
What is the endostyle?
An endocrine gland involved in iodine metabolism. It is primarily observed in embryonic/larval stages. It becomes the thyroid gland in adults.
What is the dorsal hollow nerve cord?
It develops into central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). Opposed to ventral nerve cord often observed in invertebrates.
What does the dorsal hollow nerve cord forms into during embryonic development and what can occur with an incomplete development?
It forms the endoderm and Spina bifida occurs due to incomplete development
In most invertebrates, the anus terminates at most posterior location. In chordates, the anus terminates prior to tail. This forms the characteristic of...
Postanal tail
Again, the human tail is most predominant during embryonic stages, which is significantly reduced in adults. What does the postanal tail develop into?
Coccyx
Cephalochordates have 32 extant species in 3 genera (referred to as lancelets). What are the three genera and some key charactersitics?
- Asymmetron (asymmetrical and tropical)
- Branchiostoma (symmetrical and temperate)
- Epigonichthys (asymmetrical and tropical and temperate)
There are not a lot of fossils of cephalochordates. What are some famous ones found?
Pikaia and Yunnanozoon
There are several anatomical features in extant species that can be observed in Cephalochordates. What are some of them?
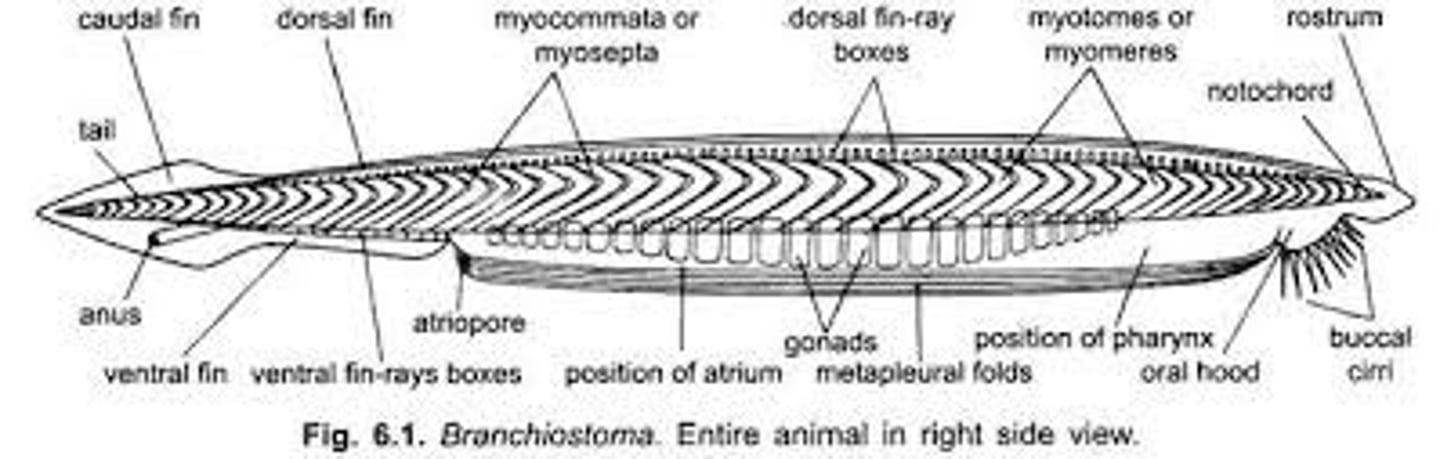
Cephalochordates are what type of feeders and where are they found?
They are filter feeders that burrow into the substrate.
What is the feeding process of the cephalochordates?
The wheel organ creates a water current. The pharyngeal slits are used for filter feeding by trapping food particles in mucous. They have a very simple digestive system, where the hepatic cecum performs both digestion and functions similar to our liver.
What are urochordates?
Urochordates (or tunicates or sea squirts) and sessile as adults and resemble a small sponge. Though some, like salps, are free-floating and can create large colonies.
How do Urochordates feed?
They are filter feeders. Water pulled in through oral siphon (branchial siphon) by action of cilia lining slits in the branchial basket (pharyngeal basket).
Do urochordates have a brain? Do they have a digestive system and do they have a circulatory system?
They have a "brain", where is a nerve ganglion. They have a more developed digestive system, have a heart and a basic circulatory system for nutrient transport.
What do urochordates miss in their adult stage?
postanal tail, notochord, and a dorsal hollow nerve cord. However, all of this is found in the larva.
How do urochordates reproduce?
Sexual reproduction most common but can reproduce asexually.