Integumentary System: Structure, Function, and Skin Chapter 5 Diseases
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is the integumentary system primarily composed of?
The integumentary system is primarily composed of the cutaneous membrane (skin) and accessory structures.
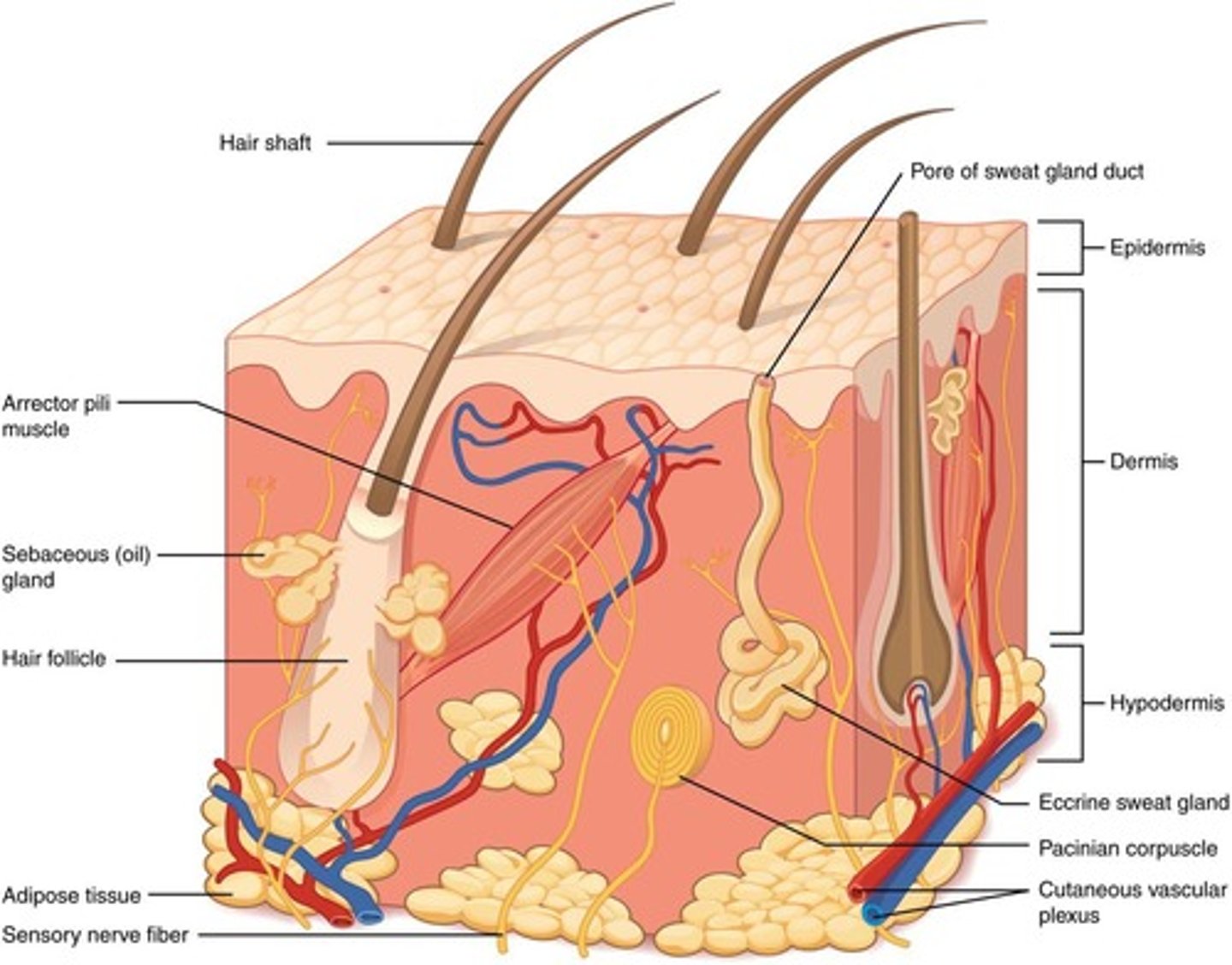
What are the main functions of the skin?
The skin protects underlying tissues, excretes wastes, maintains body temperature, synthesizes vitamin D3, regulates blood flow, and detects sensory stimuli.
What are the two main components of the cutaneous membrane?
The two main components are the outer epidermis (superficial epithelium) and the inner dermis (connective tissues).
What is the subcutaneous layer also known as?
The subcutaneous layer is also known as the superficial fascia or hypodermis.
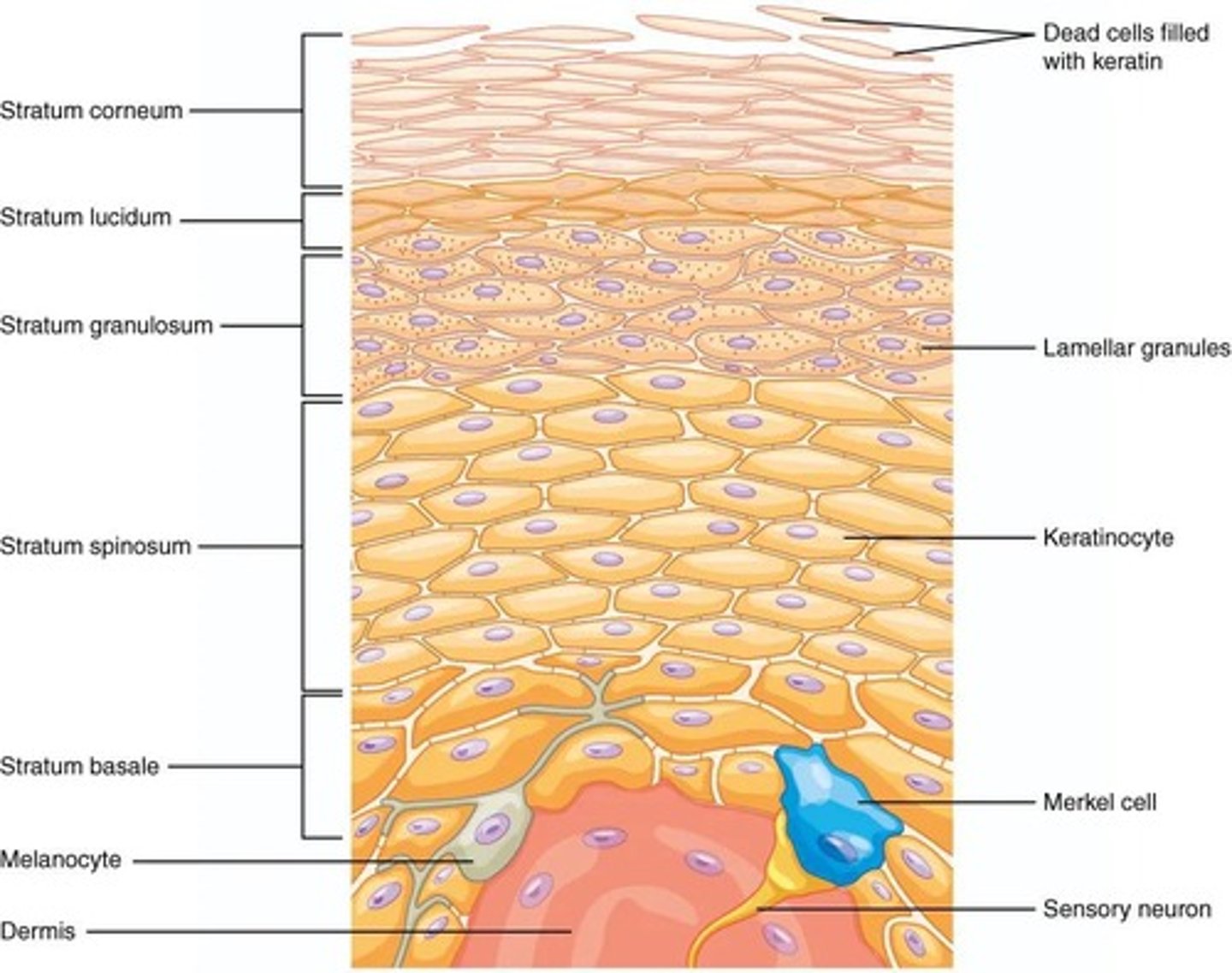
What type of epithelium is the epidermis made of?
The epidermis is made of avascular keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
What are keratinocytes?
Keratinocytes are the majority of epidermal cells. The primary type of cell found in the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin
What is the role of Langerhans cells in the epidermis?
Langerhans cells are macrophages that protect against toxins, microbes, and other pathogens. acting as the first line of immune defense
What is the function of melanocytes?
Melanocytes are responsible for producing pigment in the skin.
What is the significance of the stratum basale in the epidermis?
The stratum basale forms a strong bond between the epidermis and dermis and creates epidermal ridges. responsible for producing all other skin layers through continuous cell division
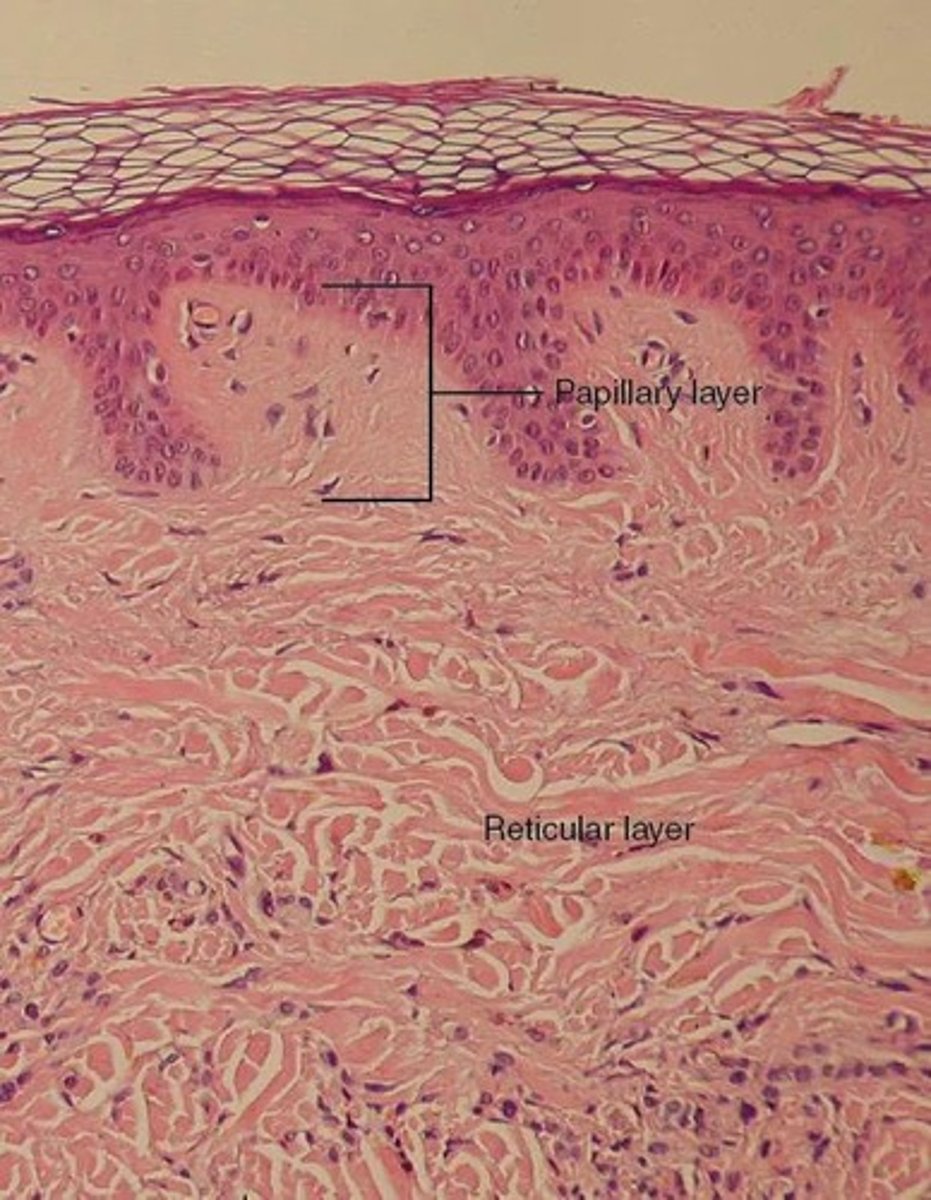
What are the two layers of the dermis?
The two layers of the dermis are the papillary layer (areolar tissue) and the reticular layer (dense irregular connective tissue).
What is melanin and what is its function?
Melanin is a pigment produced by melanocytes that gives skin its brown to black color and protects against UV light.
What causes cyanosis?
Cyanosis is caused by a severe reduction in blood flow or oxygenation, resulting in a bluish skin tint.
What is albinism?
Albinism is a defect in melanin production that results in little or no color in the skin, hair, and eyes.
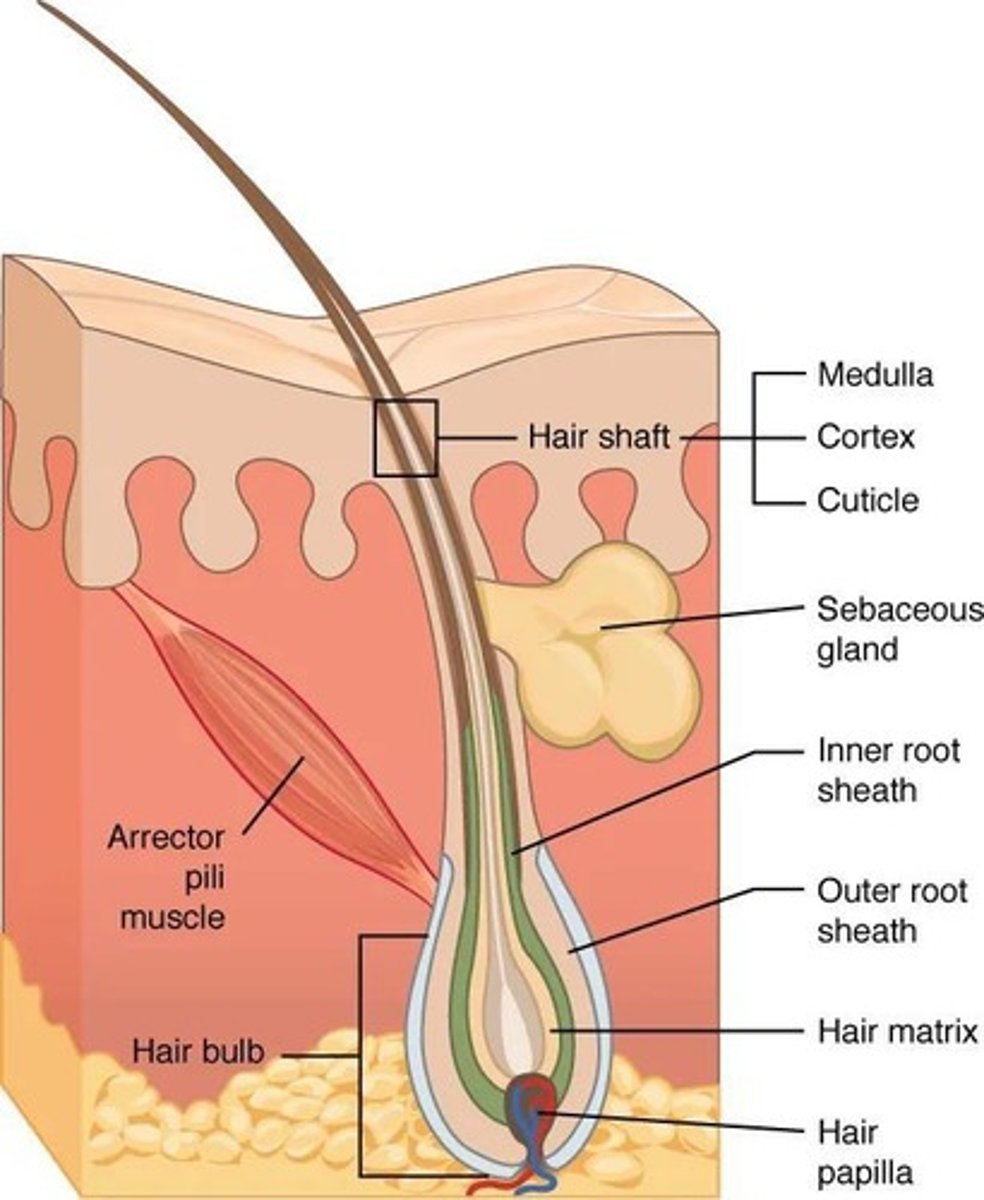
What are the functions of hair?
Hair protects and insulates, guards openings against particles and insects, and is sensitive to light touch.
What is the role of sebaceous glands?
Sebaceous glands secrete sebum (oily substance), which lubricates and protects the epidermis and inhibits bacteria.
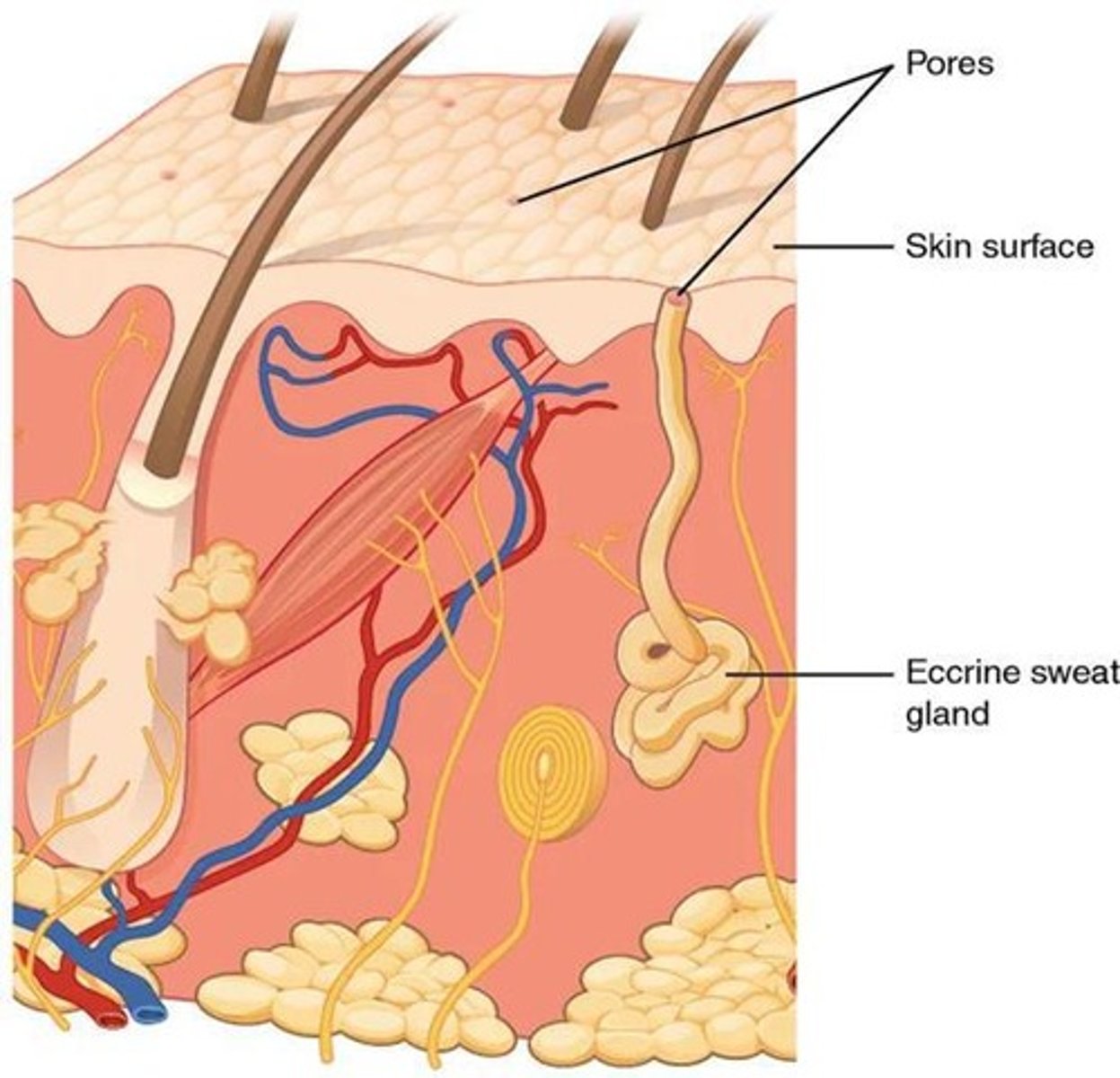
What are the two types of sweat glands?
The two types of sweat glands are apocrine sweat glands and merocrine (eccrine) sweat glands.
What is the primary function of merocrine sweat glands?
Merocrine sweat glands cool the skin, excrete water and electrolytes, and flush microorganisms from the skin.
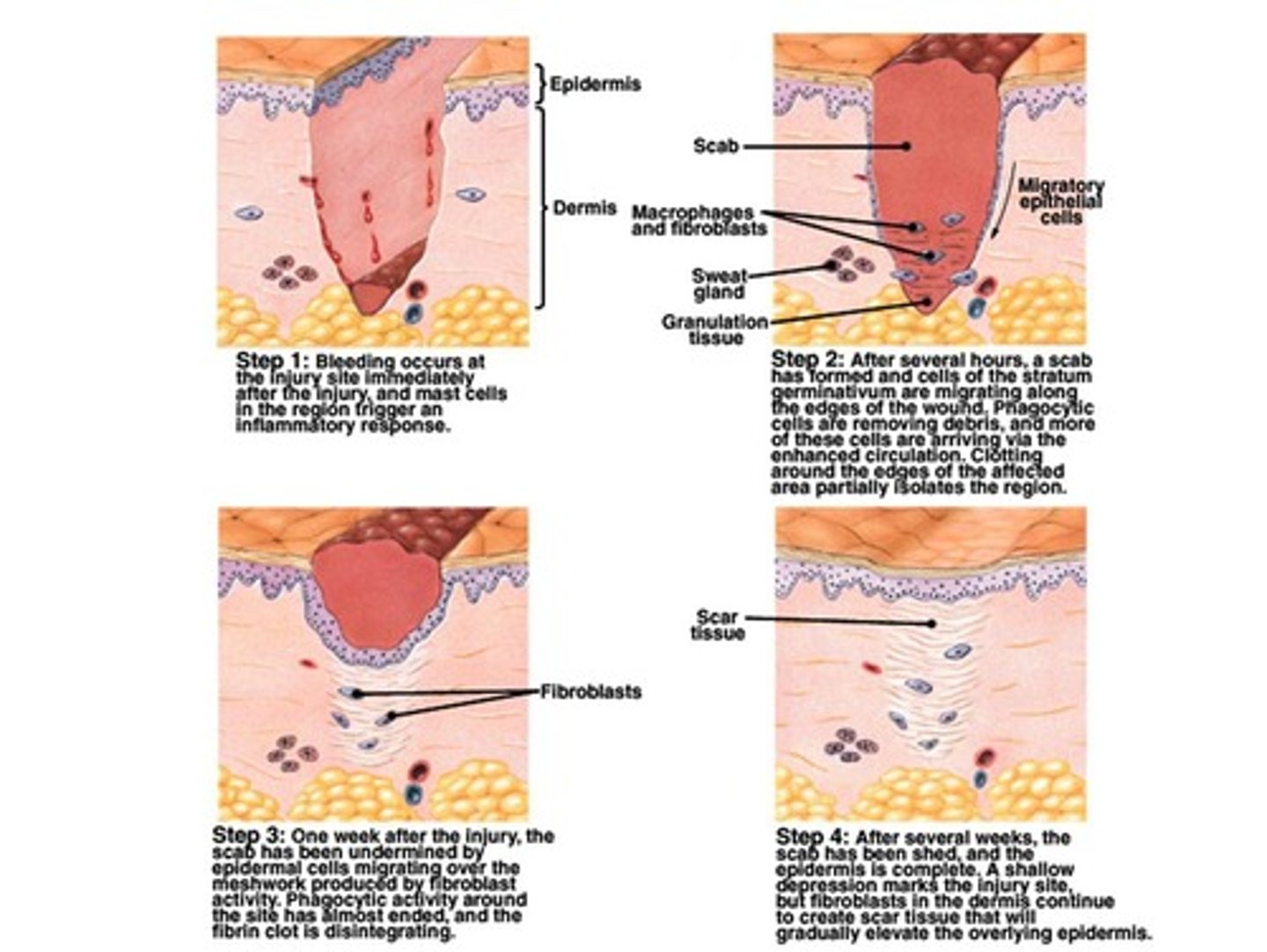
What is the process of wound healing?
Wound healing involves inflammation, migration phase, proliferative phase, and maturation phase.
What are the three major types of skin cancer?
The three major types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
What is the most common type of skin cancer?
Basal cell carcinoma is the least malignant and most common skin cancer.
What characterizes melanoma?
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer due to its high metastasis and resistance to chemotherapy.
What are the characteristics of a first-degree burn?
A first-degree burn damages the epidermis, causing localized redness, swelling, and pain.
What distinguishes a second-degree burn from a first-degree burn?
A second-degree burn destroys the epidermis and part of the dermis, causing redness, swelling, pain, and blisters.
What is a third-degree burn?
A third-degree burn destroys the epidermis and entire dermis, resulting in gray-white, cherry red, or black skin with no pain.
What are the dangers associated with second and third-degree burns?
Dangers include loss of fluid and electrolytes, impaired thermoregulation, and increased risk of infection.