Bio 102 Exam 3 Richard Mccain
1/192
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I believe in person who finds this
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
193 Terms
Animal body size
Unicellular organisms get nutrients through diffusion
cell sized constrained by surface to area to volume ratio
larger organisms have more cells, not larger cells
Limits on body size
Gravity
drag
skeleton weight
surface area to volume ration in supporting skeletons and heat dissipation
Basal Metabolic Rate
Average amount of energy used by an organisms in a non-active state
Bioenergetics: Endotherms
Maintain relatively constant body temp
Metabolic rate
Amount of energy expended by an animal over a specific time
Size and BMR
Smaller endotherms have higher BMR and vice versa
Active animals have a higher BMR
Ectotherms have lower BMR
Evolution of tissues
Parazoa lack defined tissues and organs
ability to disaggregate and aggregate their cells
Eumetazoa have distinct and well defined tissues
haver irreversible differentiation for most cell types
possess unique tissues, absent in fungi and plants
Epithelial Tissue
Classified by number of layer and shape of the cell
Single layer(Simple)vsMultiple layers(Stratified)
Shape of epithelial tissue
Squamous - flat irregular round shape
Cuboidal - cube shaped, central nucleus
Columnar - tall, narrow, nuculeus toward base
Transitional - round, simple but appear stratified
Connective tissue
Consists of fibroblasts embedded in non-cellular matrix
matrix composed of ground substance
Connective tissue cont.
made up of living cells and non living substance.
Ground substance made up of organic and inorganic
principal cell is fibroblast
found in most connective tissues
motile, go through mitosis, synthesize connective tissue where needed
matrix gives tissue its density
blood considered one because of matrix
Types of connective tissue
Loose/areolar
Dense, fibrous, connective tissue
cartilage
bone
adipose
blood
Muscle tissue
Skeletal - voluntary, striated
cardiac- involuntary, striated
smooth - involuntary, no striations
Nervous tissue
Consists of neurons and neuroglia
generate and transmit electrical impulse
Homeostasis/thermoregulation
Aims to keep internal conditions around set point(optimal point)
Set point can change in time
Acclimatization
changes in one organ system to maintain a set point in another organ system
Positive feedback loop
maintains or strengthens in response to stimulus
Negative feedback loop
stops and reverses whatever stimulus it is required to respond to
Thermoregulation
Controlled by hypothalamus
radiation
convection
conduction
evaporation
Obligate carnivores
must eat meat to survive
facultative carnivores
doesn’t have to eat meat but works best on it
Incomplete vs complete digestive tracts
Incomplete=single opening=gastrovascular
lacks specialized parts
in and out mouth
Complete=two openings=alimentary canal
food goes in mouth, out anus
Monogastric
one stomach
Avian digestion
stomachs have two chambers
proventriculus, gastric juioces digest food before the stomach
Diet adaptations
Herbivores
incisors for cliping
premolars and molars for grinding
Carnivores
pointed incisors and enlarged canines
shear off food
Human Digestion
Alimentary and extracellular
digestive enzymes secreted by wall of digestive tract and glands
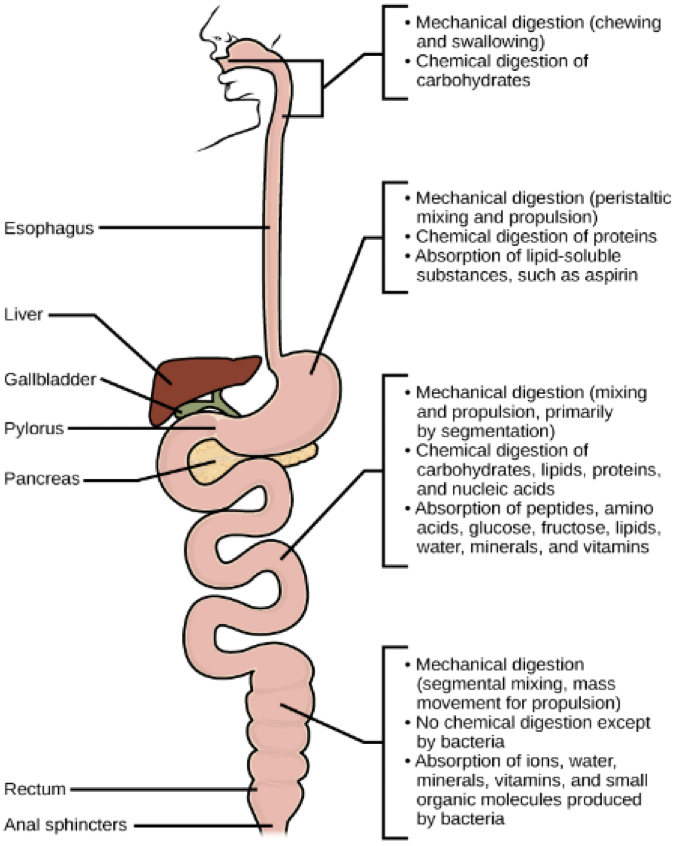
Mouth HDT
Salivary amylase starts starch digestion
tongue and chewing forms bolus
Pharynx
where digestive and respiratory passages come together
epiglottis stops food coming in air way
Esophagus HDT
food to stomach through peristalsis
Stomach HDT
Acidic and digests most of protein
has deep folds until filled up to one liter(max)
Small intestine HDT
Digestion and absorbtion continue here
Accesory glands HDT
add secretions that catabolize food into nutrients
Salivary glands
liver, bile, breakdown fatty stuff
pancreas, neutralize acidic chime, and digest protein and carbohydrates
gallblader stores and concentrates bile
Chyme
Gastric juices and food make chyme
Absorption
ridges, furrows, and villi increase absorptive area in small intestines
Carbs digestion
Starch & glycogen broken down by amylase and maltase
sucrase for sucrose
lactase for lactose
Protein digestion
mostly stomach through enzyme pepsin, into peptides which are 4-9 long amino acids
then absorbed in blood stream through small intestines
lipid digestion
begins in stomach
mostly in small intestine through lipase from pancreas, bile helps
Large intestine HDT
cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal
larger in diameter but shorter than small intestine
absorbs water, salts, and vitamins
too much water removed is constipation
too little is diarrhea
1/3 feces bacteria
Cephalic phase
neurons from food stimulus triggers salavation and secretion of gastric juices
Gastric phases
once food arrives in stomach, gastric acids and enzymes digest food, stimulated by
distension ins stomach
decrease in ph of stomach
presence of undigested material
Intestinal phase
chyme enters smalll intestine makes digestive secretions come out
Carbohydrates
Primary fuel
present in sugar, starch, fiber
Monosaccharides:
glucose
fructose
Disaccharides
lactose
sucrose
Glucose is preferred energy source in cells
Plants store glucose as starch
animals store as glycogen
Fiber
Undigestible carbohydrates
not a nutrient for humans
combines with bile acids and cholesterol in small intestine and doesn’t let them be absorbed
Proteins
Protein formation requires 20 different types of amino acids
adults require 8 amino acids from their diet, while children require 9
meat milk eggs, have all 20
vegetables are usually lacking in one
Essential amino acids
Methionine
Valine
Threonine
Phenylalanine
Leucine
Isoleucine
Tryptophan
Lysin
Arginine for children
Lipids
Fats, oils, cholesterol
need for vitamins ADEK
fat storage needed to protect organs and insulation
saturated fats (solid at room temp)
butter meat got them
palm and coconut oil got them too
Vitamins
Compounds we cant make, but we need them
Vitamin A
fat
promotes eye health, healthy skin, teeth, and bones
Vitamin D
fat
calcium absorption, strong bones
Vitamin E
Fat
Antioxidant, boost immune function
Vitamin K
Fat
blood clotting
Vitamin B
Water
helps body with energy, growth and development
Vitamin C
Water
Immune function,fights aging skim, antioxidant
Minerals
Calcium, Phosphorus, Sodium, Chlorine, Potassium, Magnesium, iodine, iron
Asexual reproduction(animals
Hydras bud
flatworms split in half
sponges, annelids, and echinoderms regenerate from fragments
Parthogensis is a type where unfertilized egg creates an organism
Internal fertilization
PRotects eg from dehydration
limites predation on young
enhances the fertilization of eggs by specific male
fewer offspring, higher survival rate
External fertilization
Broadcast spawing - greater mix of genes in a group and greater chance of survival in hostile environment
for sessile organims, only way to spread
makes predation easier
offspring must mature rapidly
survival rate low
Sexual reproduction
most animals dioecious- useful to high mobility anim
some monoecious - useful to little mobility anims
Invertebrates
Insect eggs made in ovaries
yolk is stored food
some go through metamorphosis
Some have larval stage where they have dif diet than adults
Vertebrates
Reptiles and birds oviparous
mammals viviparous
placenta eliminates need for shelled
Ovoviviparous
retain eggs and release young when they can fend for themselves, no direct nourishment from parent
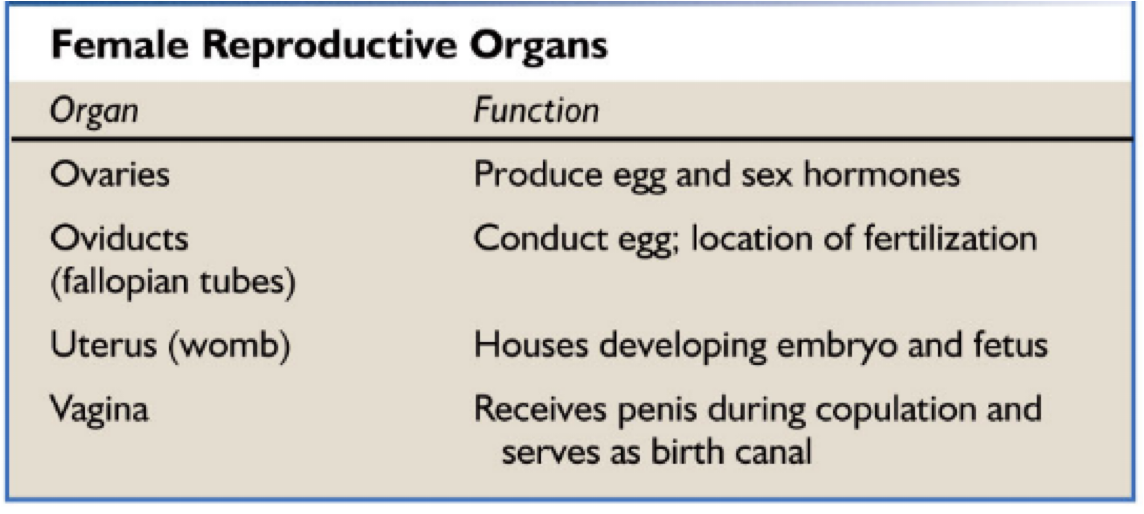
Male reproduvtive system
Seminiferous tubules make sperm in testes
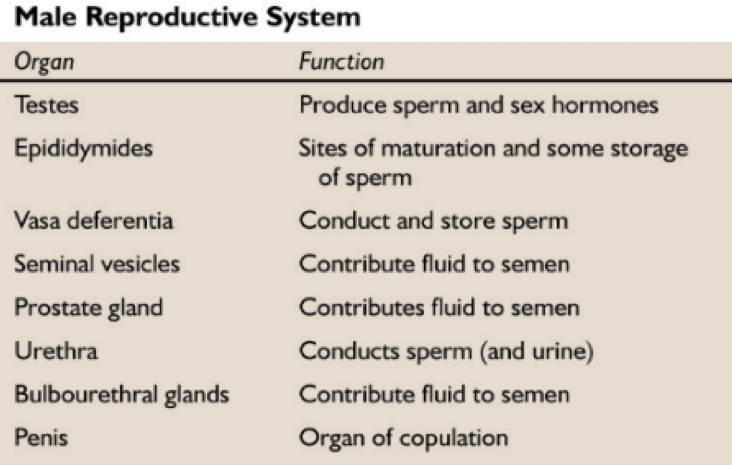
Female reproductive system
Ovarian cycle
Follicular phase
FSH promotes follicle development
follicle secretes estrogens
Ovulation
release oocyte from vesicular follicle
follicle develops into corpus luteum]
degenerates if no pregnancy
Luteal phase
LH promotes development of corpus luteum
corpus luteum secretes progesterone
Hormones in guys
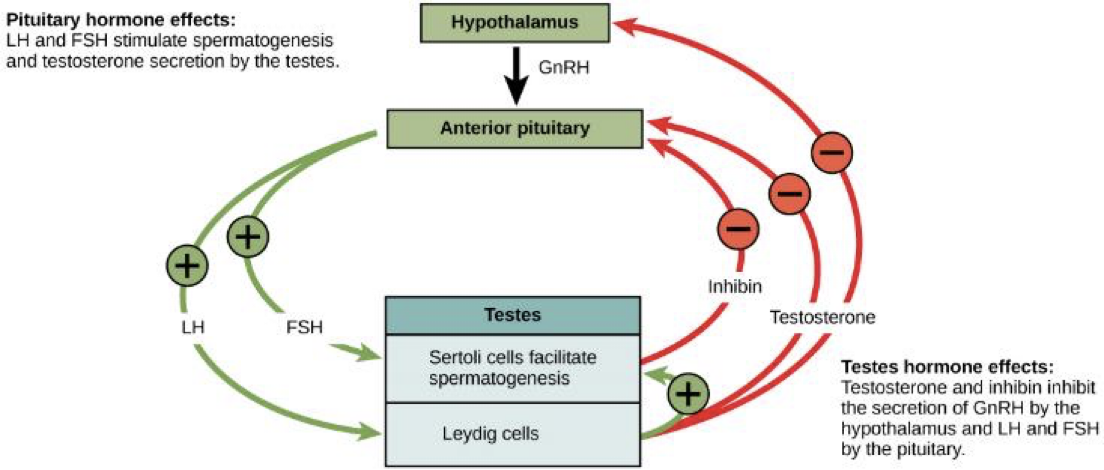
Hormones in girls

Uterin cycle
Sex hormones produced in ovarian cycle affect endometrium
Days 1–5: Menstruation
Endometrium disintegrates
Menses pass out vagina during menstruation (periods)
Days 6–13: Proliferative phase
Endometrium thickens
Ovulation usually occurs on 14th day
Days 15–28: Secretory phase
Endometrium doubles in thickness
Infertility
inability to have kid after year of unprotected, regular sex
even split between men and women
Common causes
female - endometriosis
male - low sperm count
Assisted reproductive tech
IVF
Articial insemination
Gamete Intrafallopian transfer
intracytoplasmic sperm injection
Hormones
Regulagtory chemical secreted into extracellular fluid thats carried by the blood
need these for homeostasis
attachment of hormone to receptor induces cellular response
Classifying hormones
lipid-derived hormones
amino acid derived
peptide
Lipid derived hormones
diffuse through plasma membranes
Amino acid derived hormones
many neurotransmitters
Peptide Hormones
much larger than other hormones
Neuro vs endocrine
millisecond response vs longer response, secs to days
specific effects vs widespread effects
adapts quickly vs slowly adapting
Hormone regulation
work through negative feedback (usually)
MoHr(mechanisms of hormonal release) respond to
Humoral stimuli : changes in extracellular fluid levels or ion levels
Hormonal stimuli: hormones from other glands
Neural stimuli: neurons telling it to
How Hormones work
need specific receptor
Number can change due to
up-regulation
down- regulation
Receptors found within cell or on membranes
Intracellular Hormone Receptors Lipid-derived hormones
bind to transport proteins
release from protein when at cell and bind within cell by passing through membrane
lipophillic - cross membrane and bind to intra-cellular receptor
hormone/receptor complex regulates transcription by changing synthesis of mRNA
Intracellular Hormone Receptors
bind to transport proteins
pass through plasma membrane
bind within cell with target
Hormone receptor complex regulates transcription
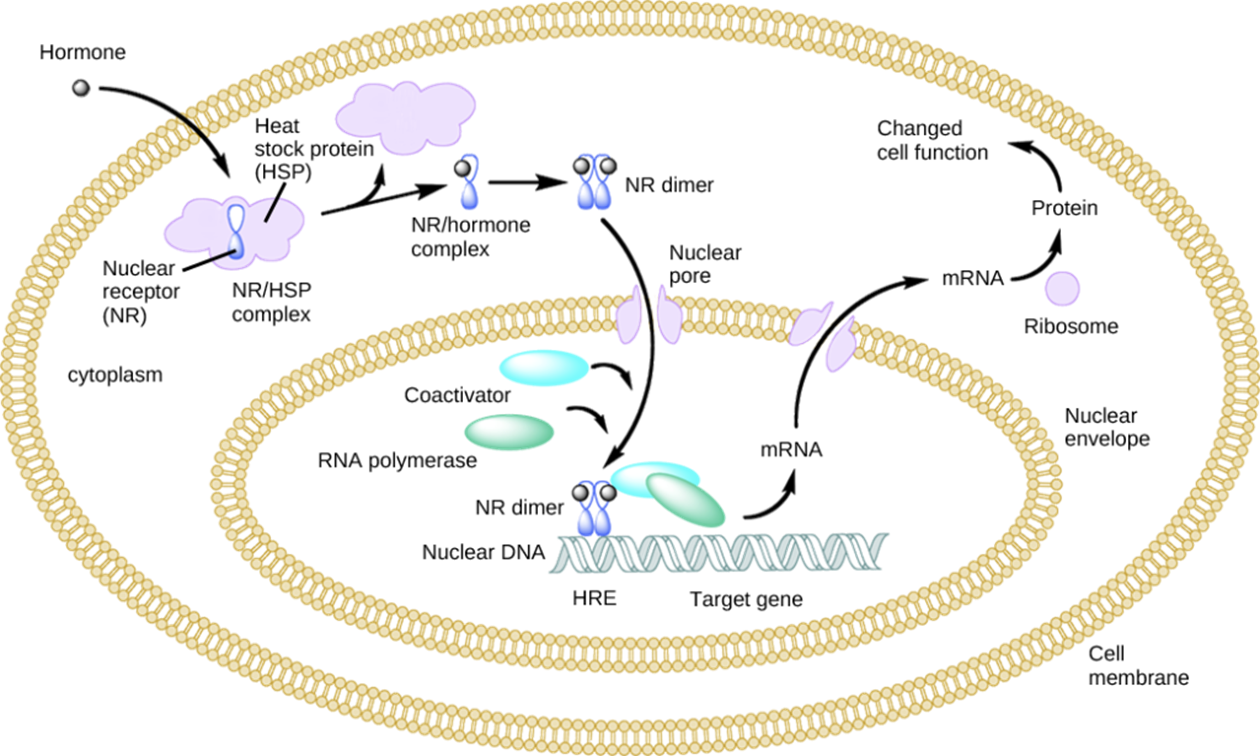
Excretory system
maintains water balance
ADH(Antidiuretic hormone)
regulates amounts of water excreted by kidney
released when water levels low in blood
made in Hypothalmus
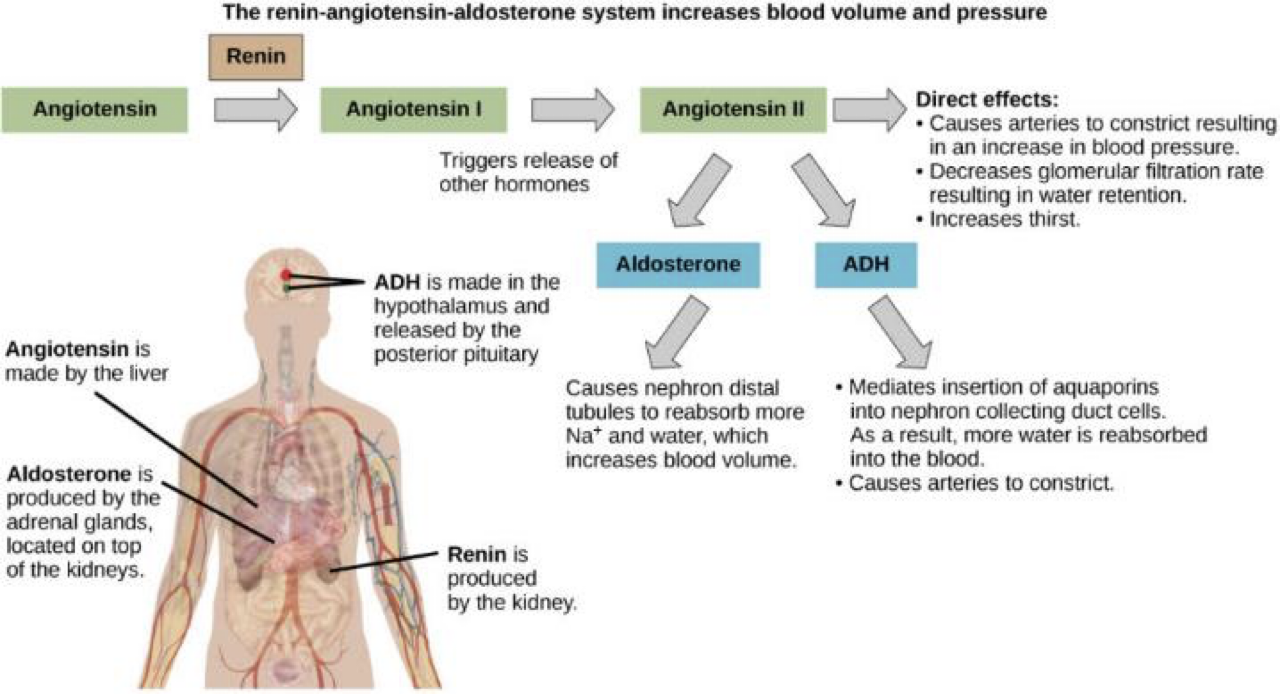
Aldosterone
made by adrenal cortex
main regulator of water and electrolytes
promotes reabsorption of water
released due to renin angiotensin system, while ADH is released with osmo-receptors
Reproductive system
FSH(follicle stimulating hormone
males: make sperm
females: make eggs
LH (luteinizing hormone)
males: make testosterone
females: lots of it causes ovulation
Oxytocin
stimulates contraction in birth
Metabolism
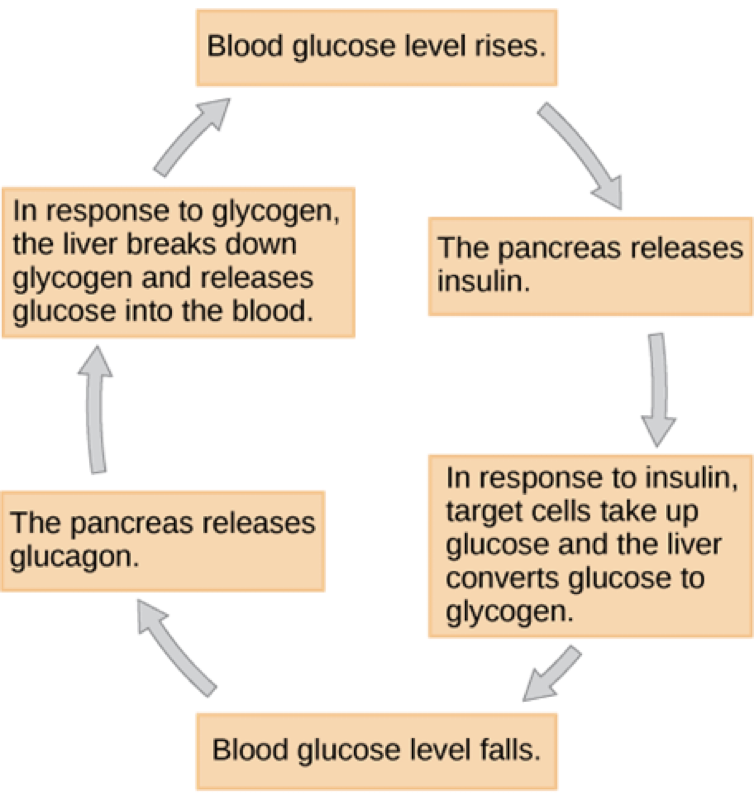
Insulin
produced by beta cells pancreas
lowers blood sugar by making cells take up more
Glucagon
Antagonist to insulin
produced by alpha cells pancreas
raises blood sugar by breaking down glycogen in liver
Regulation of Metabolism, Thyroid
BML is determine by T4 (Thyroxine) and T3 (Triiodothyronine)
released from thyroid after TSH(Thyroid Stimulating Hormone)
hyperthyroidism = high Metabolism
weight loss, irritability, increased bpm
Hypothyroidism = low metabolism
Weight gain, sensitivity to cold, lethargy
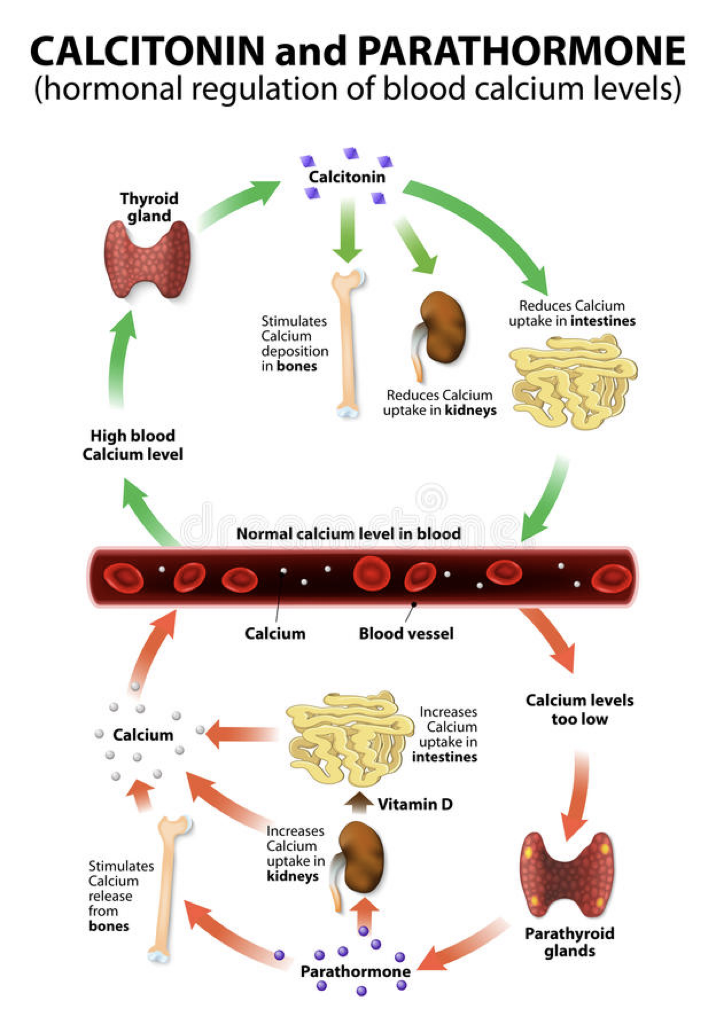
Hormonal control of blood calcium
PTH(parathyroid hormone)
released when low blood calcium
antagonist is calcitonin(made by thyroid)
growth control with hormones
Regulated by GH(growth hormone)
stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regen
increase of protein synthesis
glucose sparing
regulated by growth hormone stimulating other hormones
Hormonal control of stress
Short term stress
epinephrine(adrenal gland)
Long term
cortisol(Adrenal gland)
Anti-inflammatory
Hypothalmus
intergrates endocrine and nervous system
makes regulatory hormones that control the cells in the anterior pituitary
Pituitary gland
hypophysis
hang from hypothalamus
anterior pituitary(adenohypophysis)
appears glandular
not brain part
regulated by neurohormones from hypothalamus which can stop or start tropic hormones
Posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)
appears fibrous
part of brain
ADH and oxytocin
Anterior Pituitary
7 essential hormones
Peptide Hormones
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) - adrenal gland to make cortisol
Melanin-stimulating hormone(MSH)-dispersion of color
Protein hormones
GH
Prolactin (PL) stimulates mammary glands
Glycoprotein Hormones
TSH
LH
FSH
Adrenal glands
right above kidneys
Adrenal cortex
Glucocorticoids(Cortisol, Stress)
Mineralocorticoid (Aldosterone, ion uptake)
Sex hormones
Adrenal Medulla
Epinephrine(fight
Norepinephrine(flight
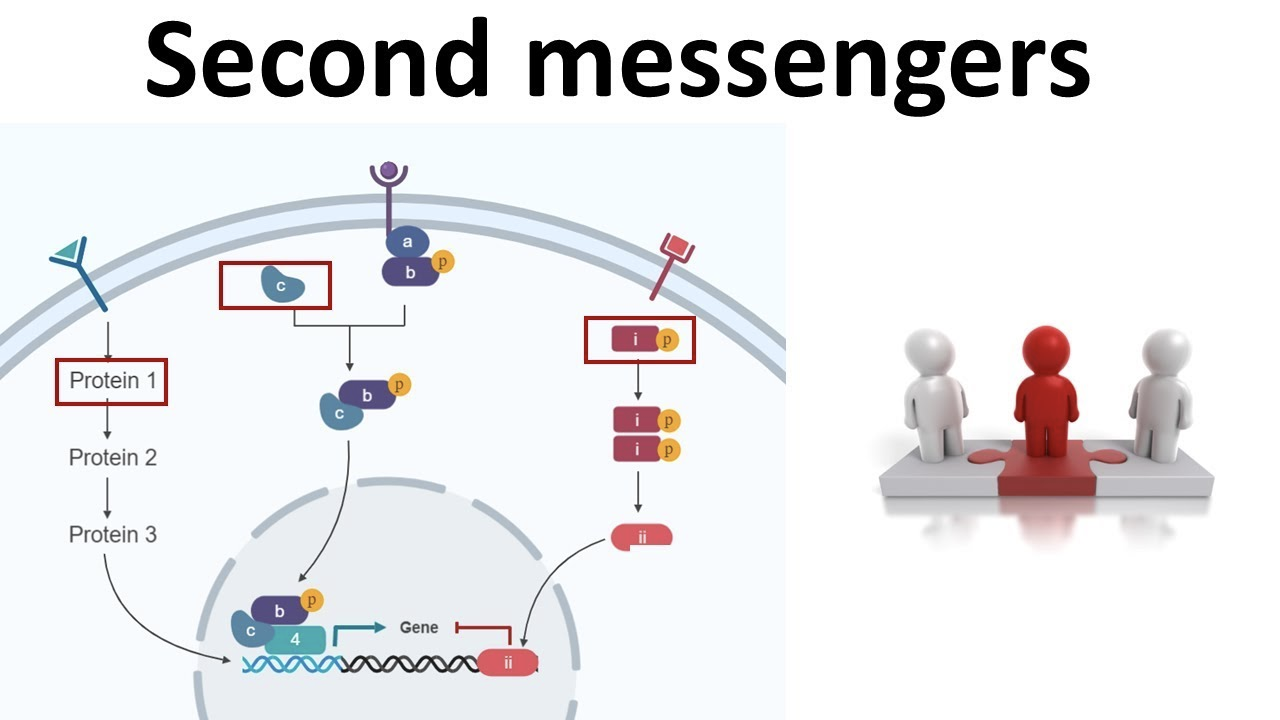
Plasma membrane hormone receptors
Amino acid derived hormones and peptides cannot pass through
bind to receptors on outer surface of membrane and initiates 2nd messenger system
Invert Nervous system
Hydras
nerve net
Planarians
ladder-like nervous system
cephalization
Annelids, Arthropods, and Mollusks
true nervous systems
HNS
CNS- brain spinal cord
PNS- somatic, autonomic
three specific functions
receiving sensory input
performing intergration
generating motor input
Neurons
i know this shit
they got regular organelles as well as the cool shit
Types of neurons (Function)
motor neurons
accept nerve impulses from CNS
transmit to muscles, or glands
Sensory Neurons
Accept from sensory receptors
transmit to CNS
Interneurons(Relay)
Convey neve pulses in CNS
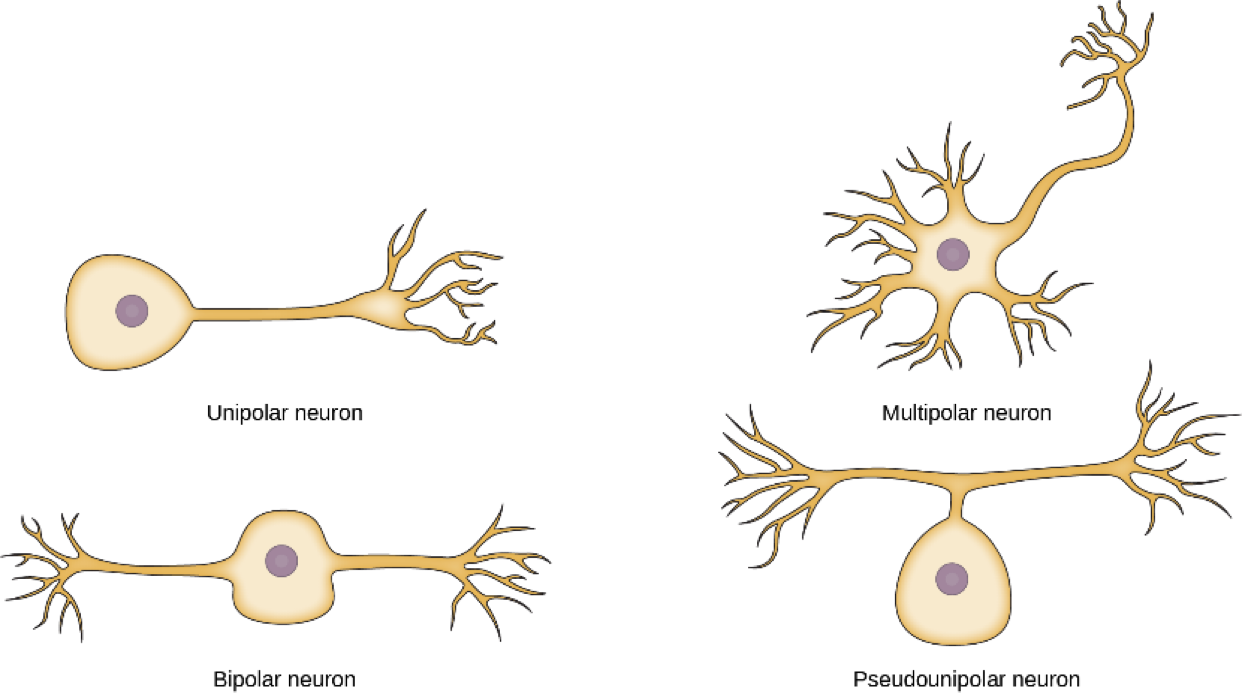
Types of Neurons (Shape)
unipolar
bipolar
pseudounipolar
multipolar(most common)
Glial Cells
Support, protect, and nourish neurons
10 to 1 in brain with neurons
most brain tumors glia
what glial cells where
CNS:
oligodendrocytes: form myelin sheath
Astrocytes: nutrients and structural support
Ependymal cells: produce cerebrospinal fluid
microglia: scavenges pathogens and dead cells
PNS:
Schwann cells: form myelin sheath
Satellite cells: nutrients and structural support
Neuron Comminication
Signals sent with charged cellular membrane( voltage difference between ecto and endo
Charged membranes
Voltage-gated ion channels regulate concentraions of different ions
difference in total charge between inside and outside of cell is called membrane potential
Resting membrane potential
usually around -70mV
negative charge in cell is because cell membrane dont let sodium move as easy as potassium