Gross Anatomy Module 5: Nerves and Vasculatures of The Upper Extremities
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
axilla location
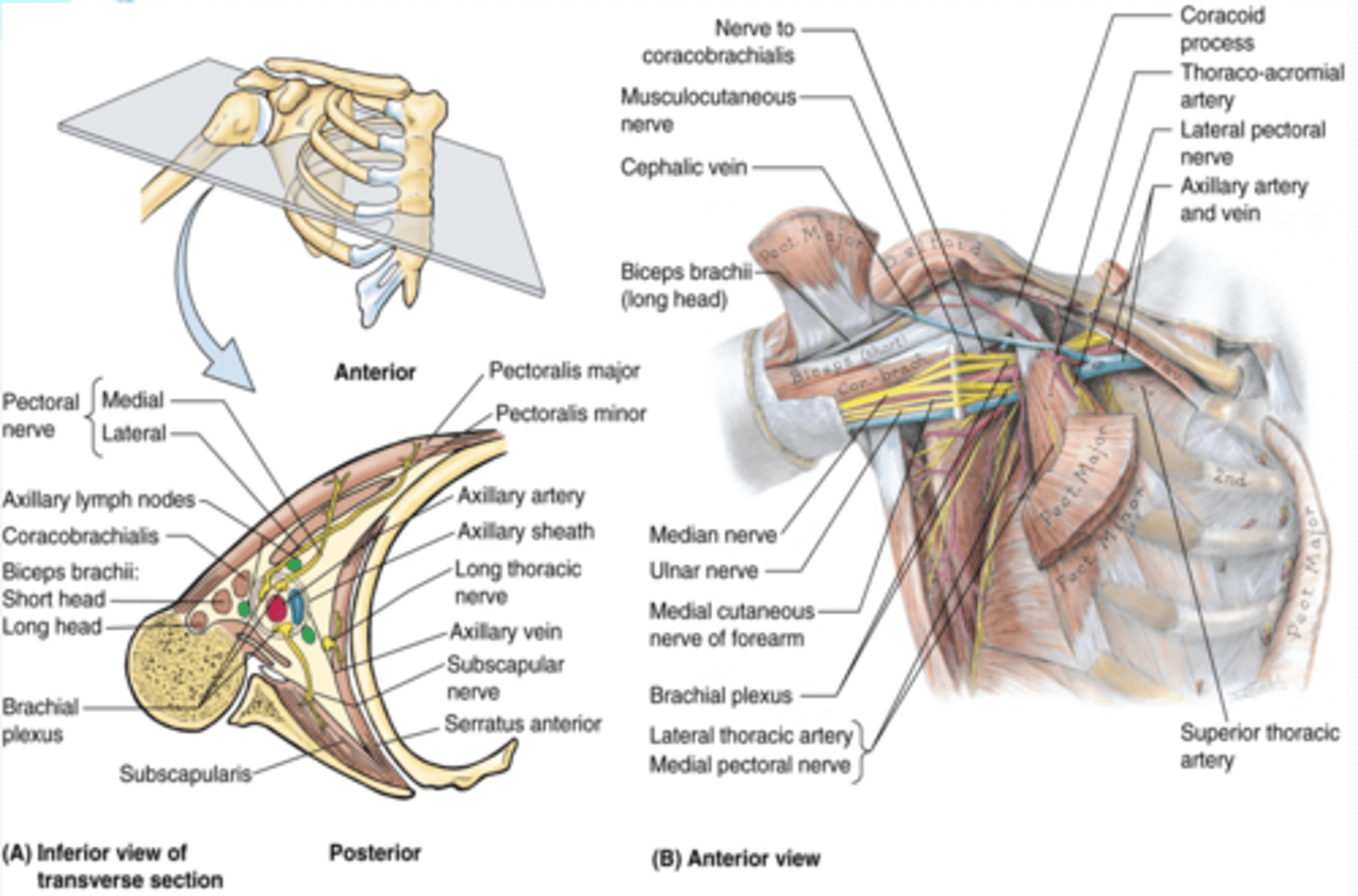
space inferior to the glenohumeral joint and superior to axillary fascia at the junction of UL and thorax
Axilla function
Provide protected passage for the neurovascular structures supplying the UL
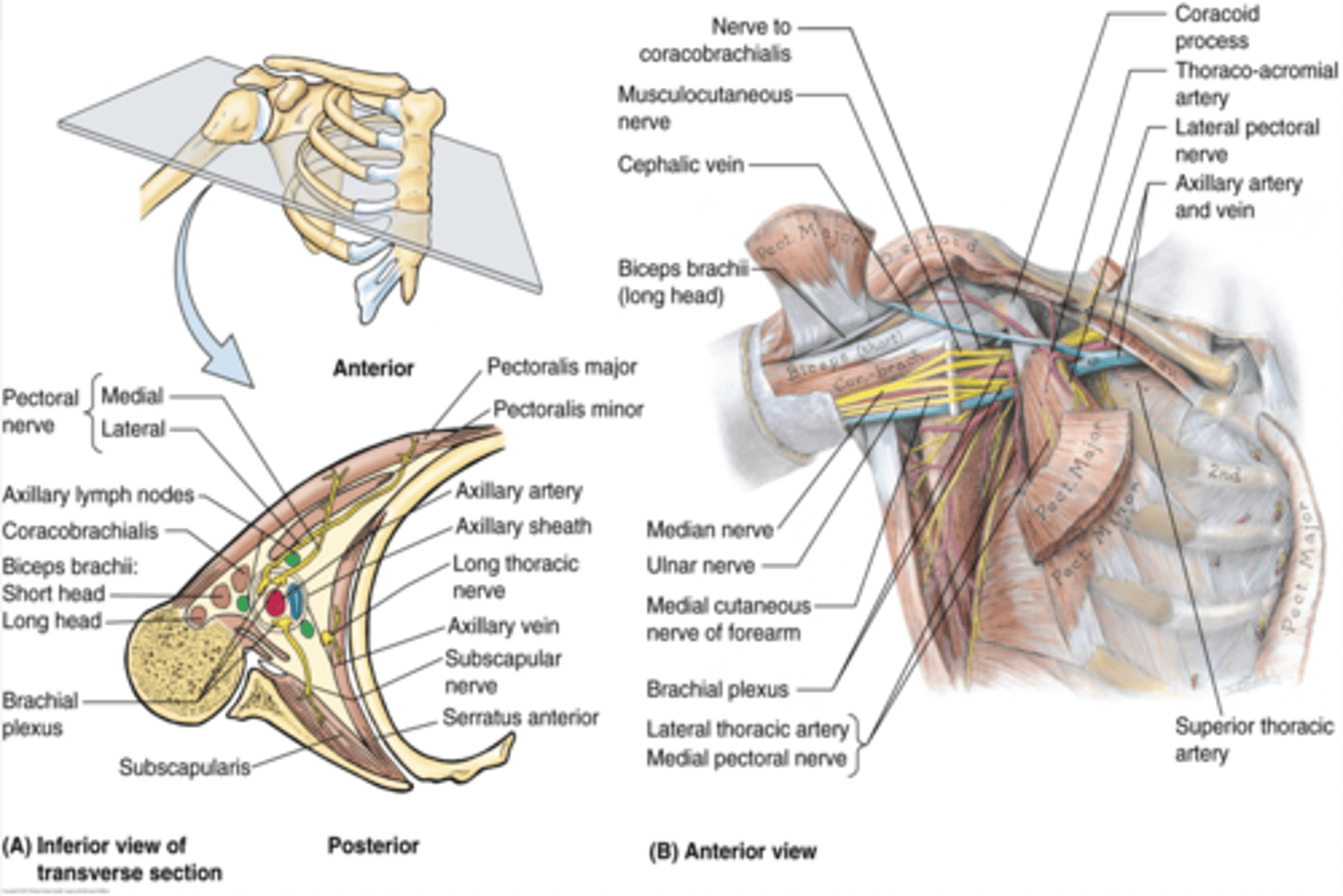
Axilla boundaries
Apex
Base (axillary fossa)
Anterior Wall
Posterior Wall
Medial Wall
Lateral Wall
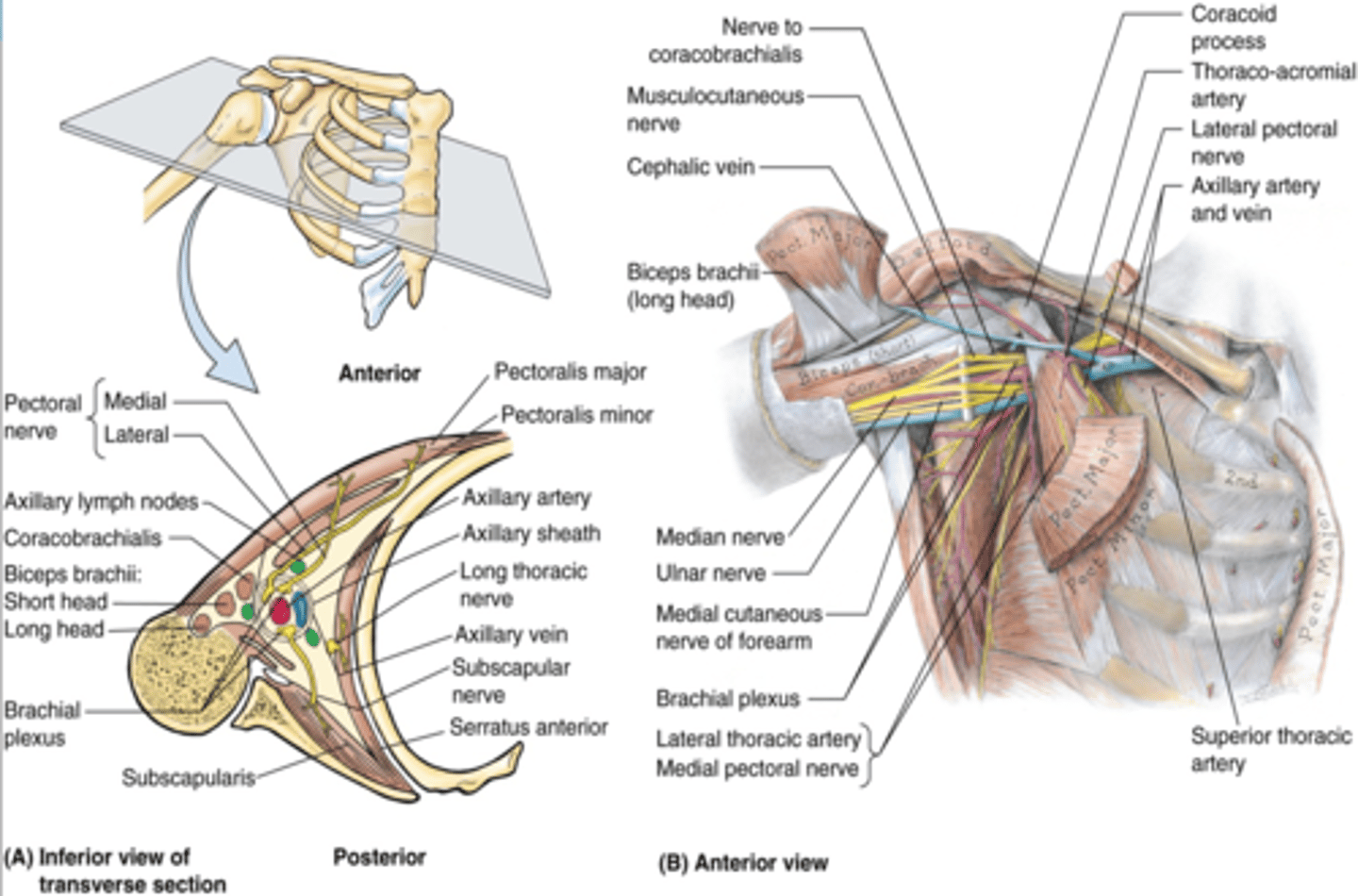
(Axilla boundaries:) Apex
-cervico-axillary canal
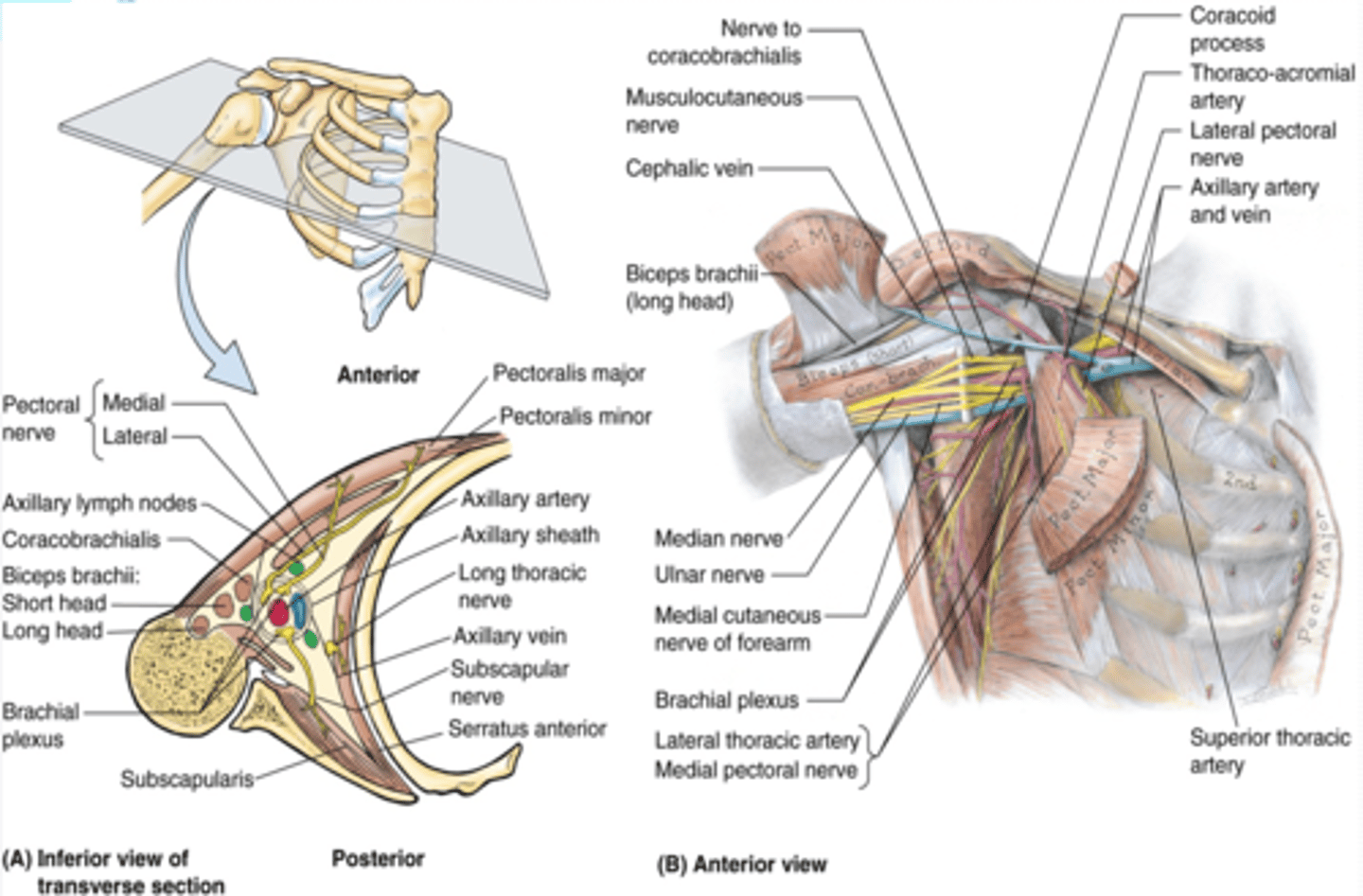
(Axilla boundaries:) Base (axillary fossa)
-skin, superficial and deep (axillary) fascia extending from the arm to the thorax
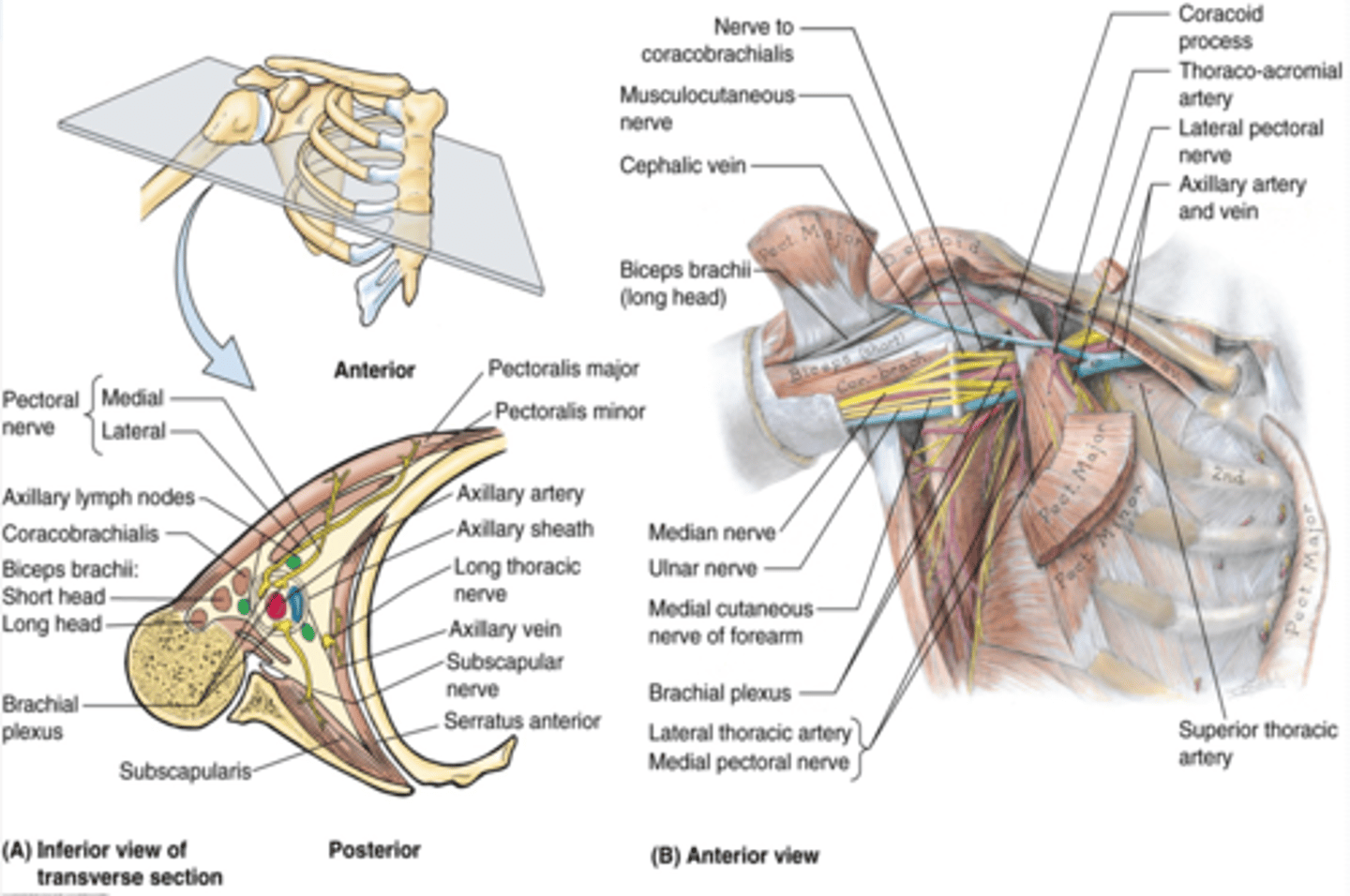
(Axilla boundaries:) Anterior wall
-pectoralis major and minor muscles and their associated fascias (pectoral and clavipectoral). Anterior axillary fold
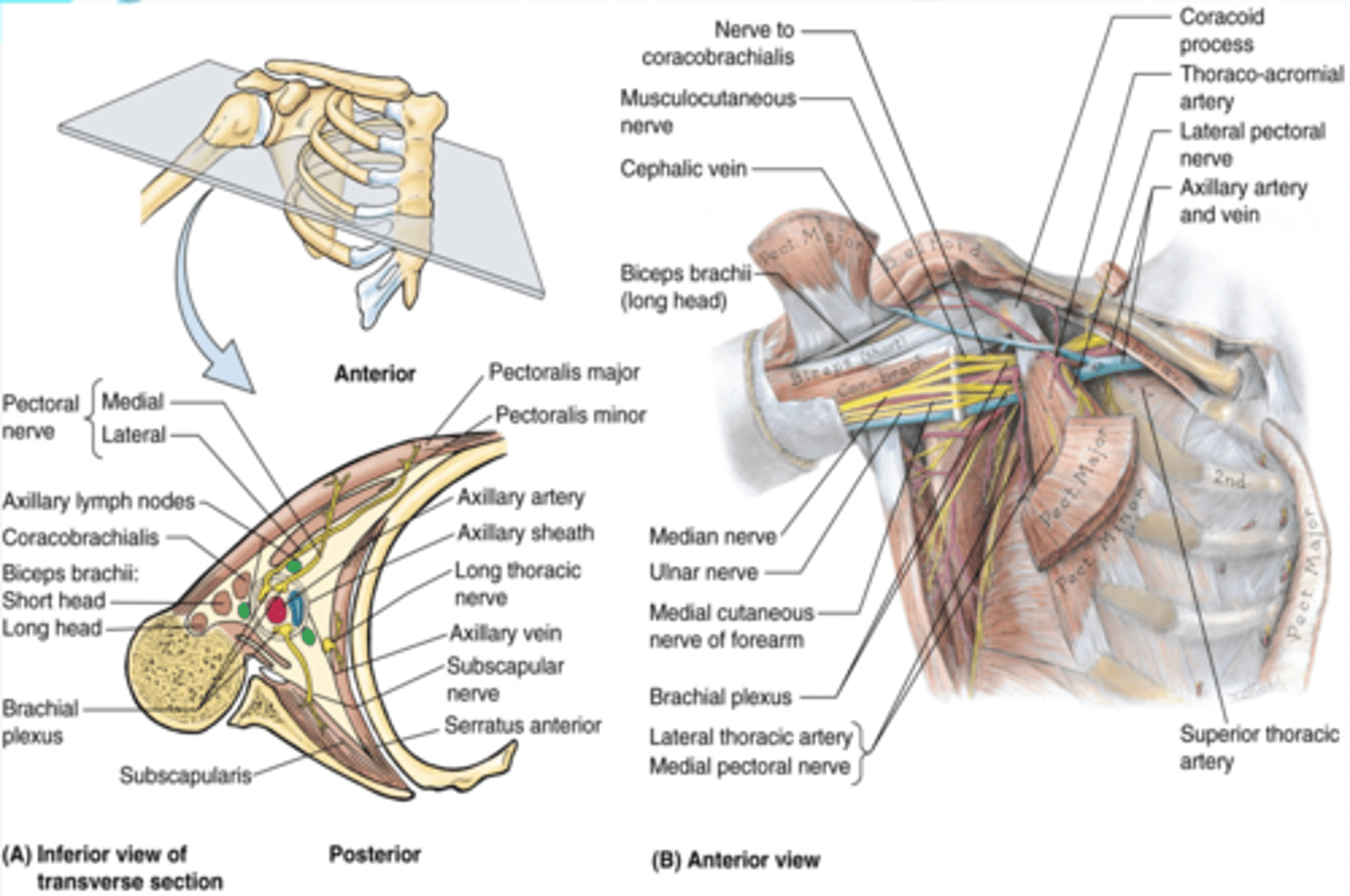
(Axilla boundaries:) Posterior wall
scapula and subscapularis muscle. Posterior axillary fold
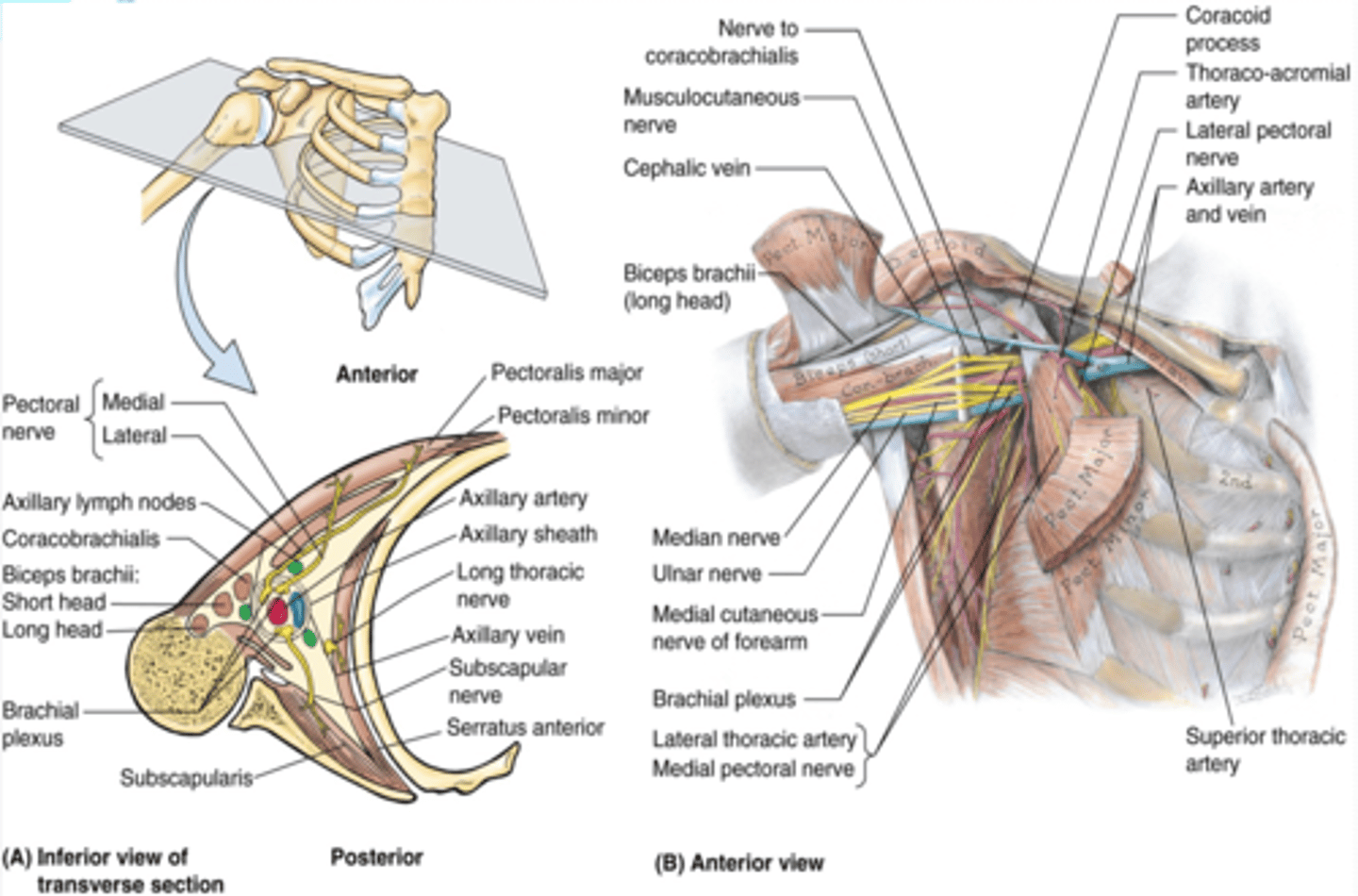
(Axilla boundaries:) Medial wall
thoracic wall and serratus anterior
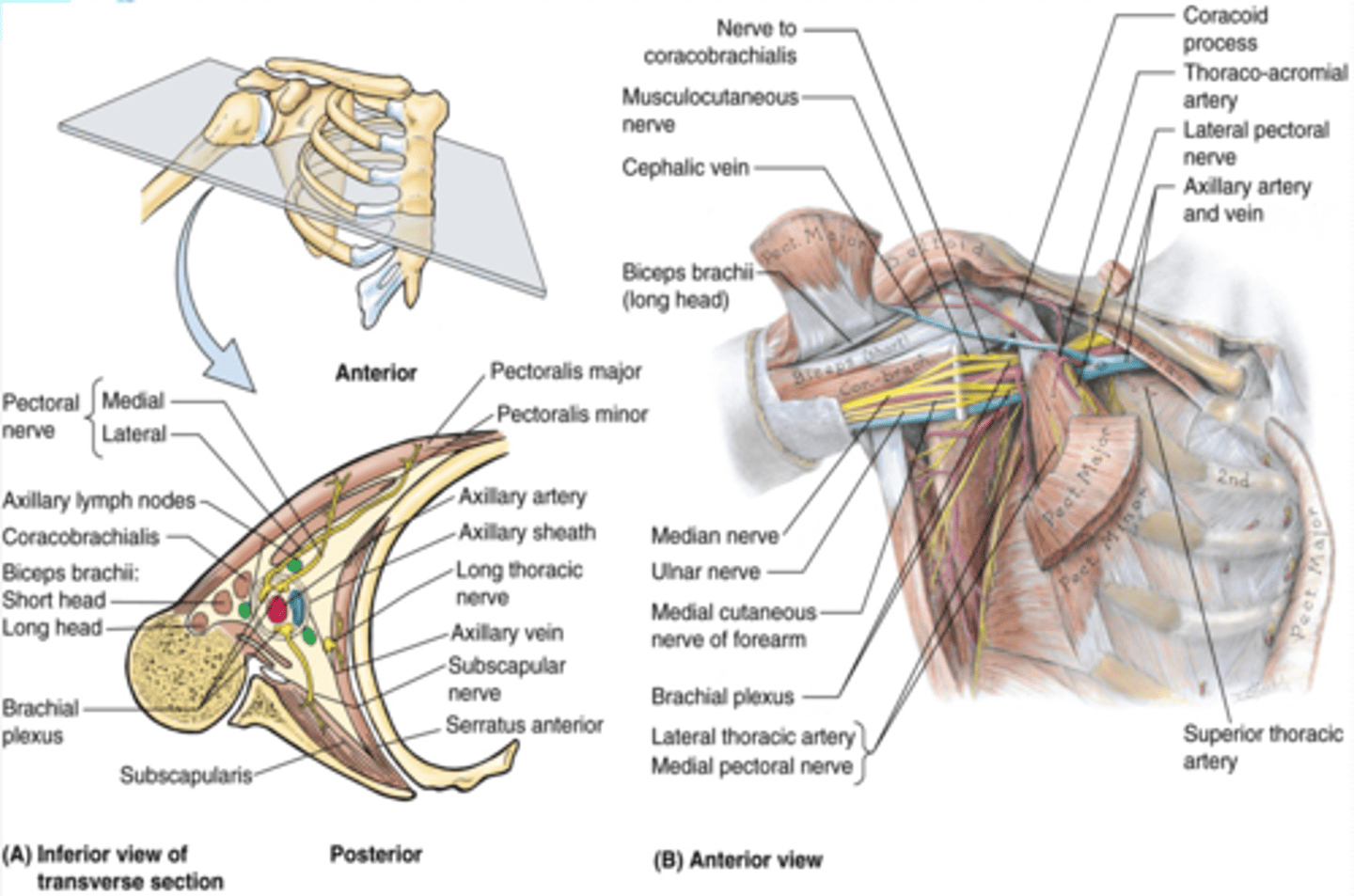
(Axilla boundaries:) Lateral wall
intertubercular groove of humerus
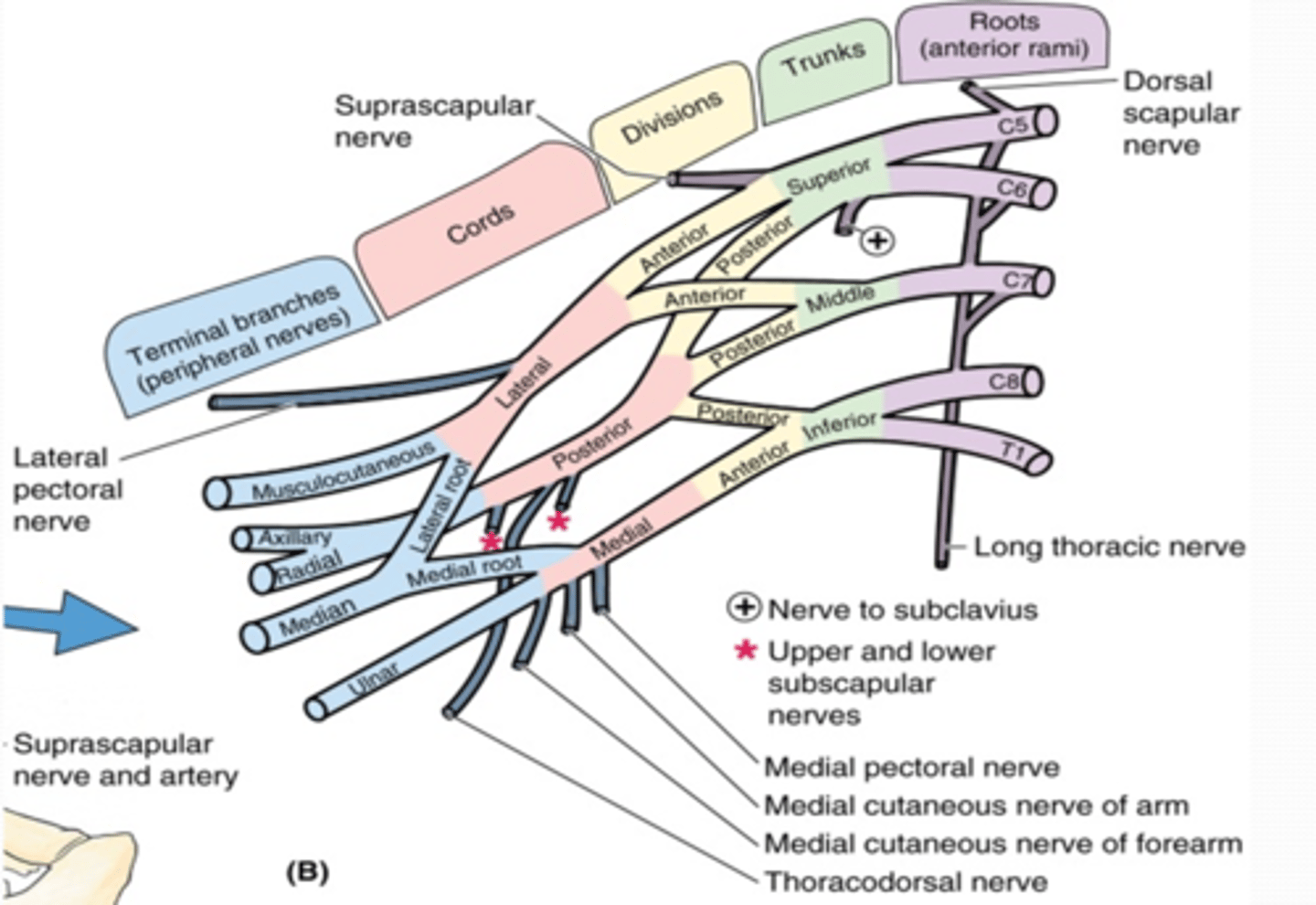
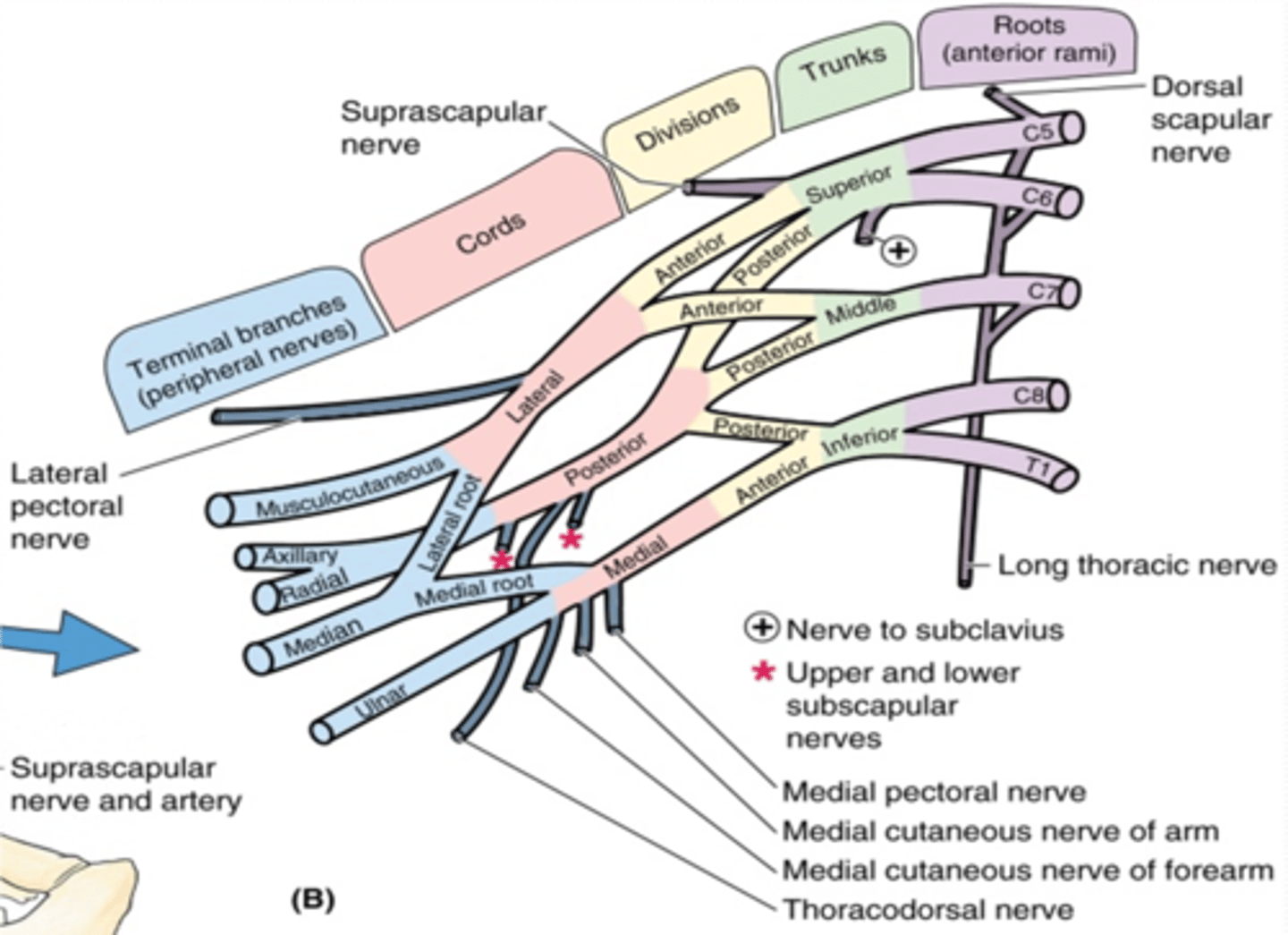
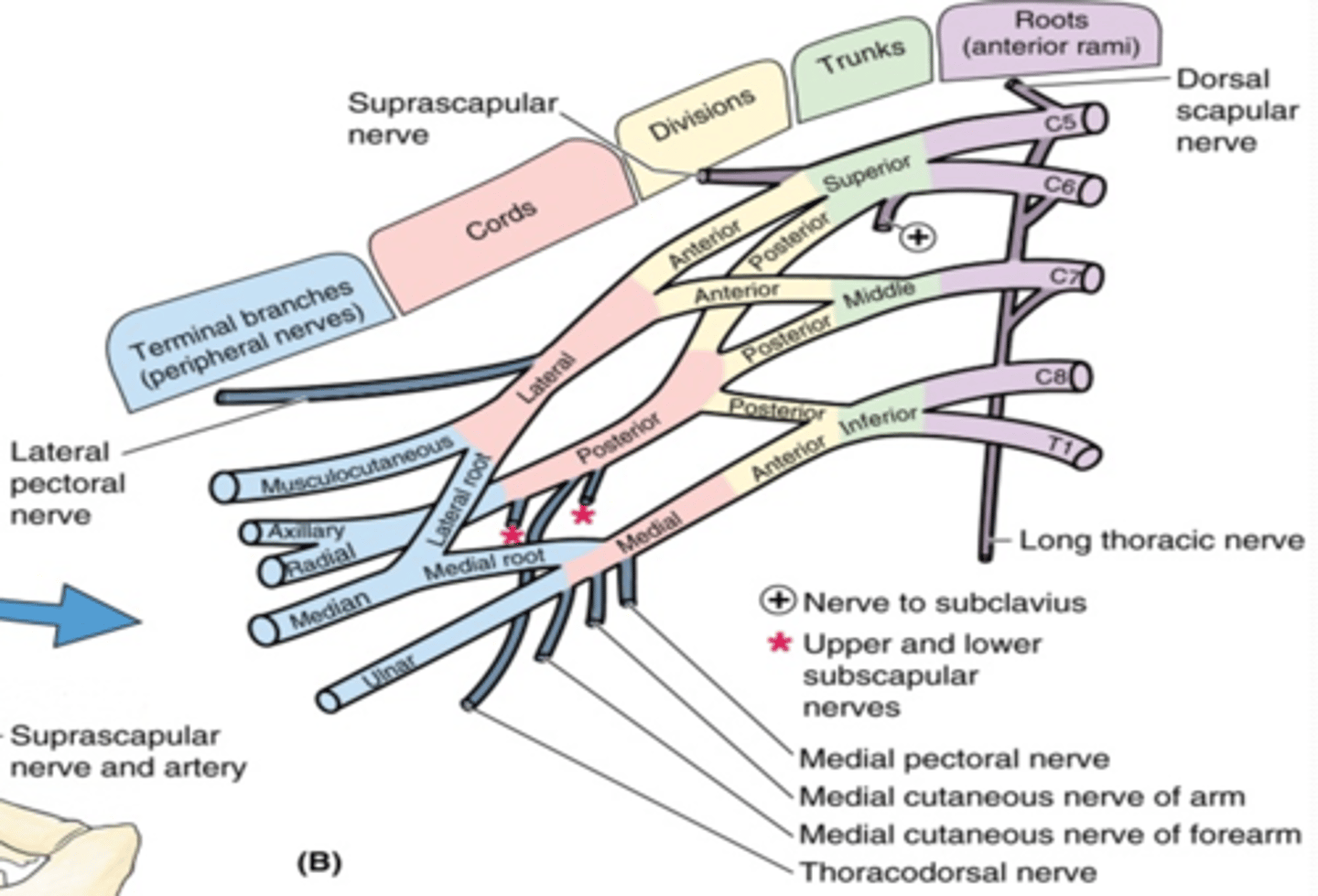
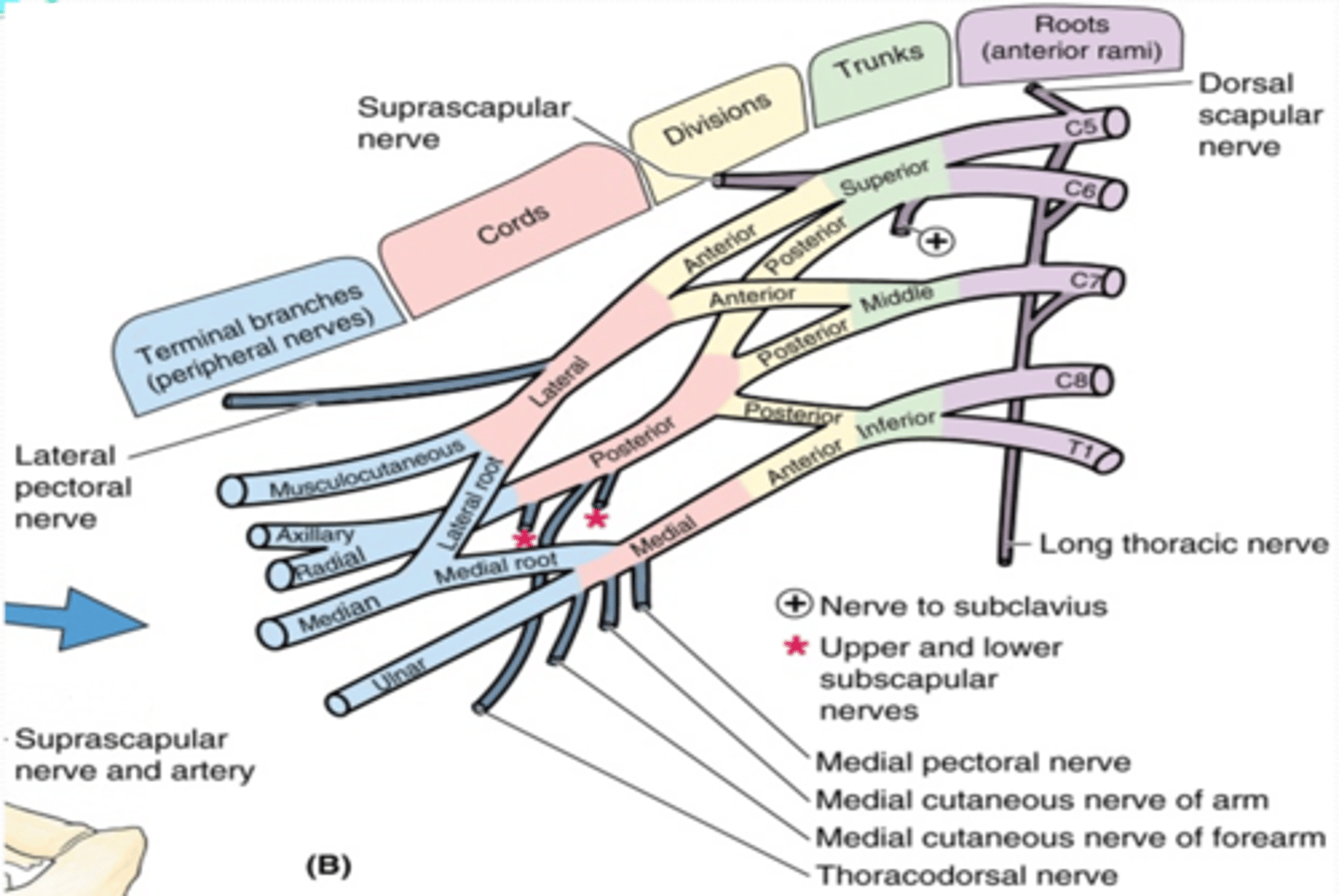
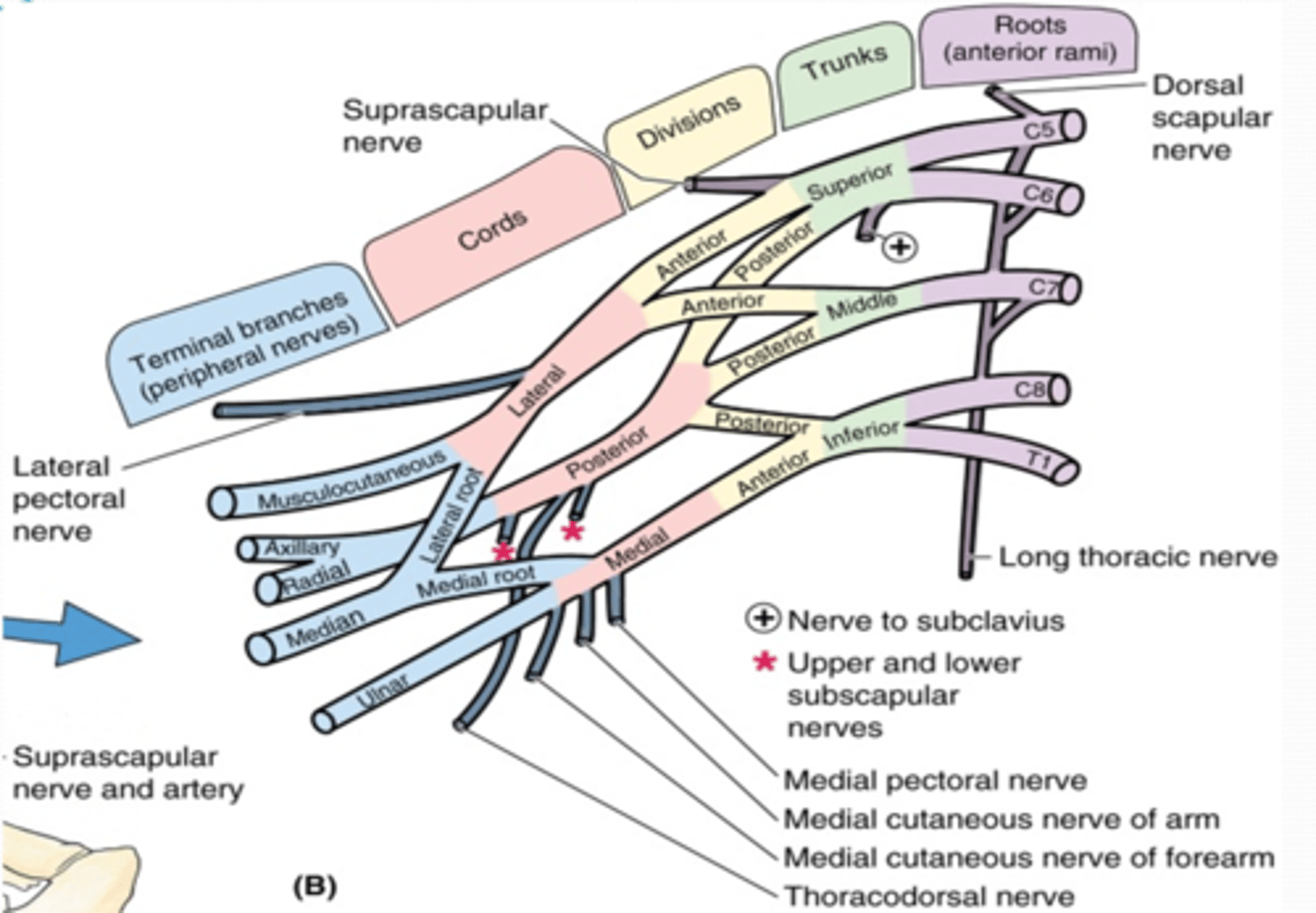
(Upper Limb Innervation:) Brachial plexus
•It is the network of nerves that innervates most of the UL
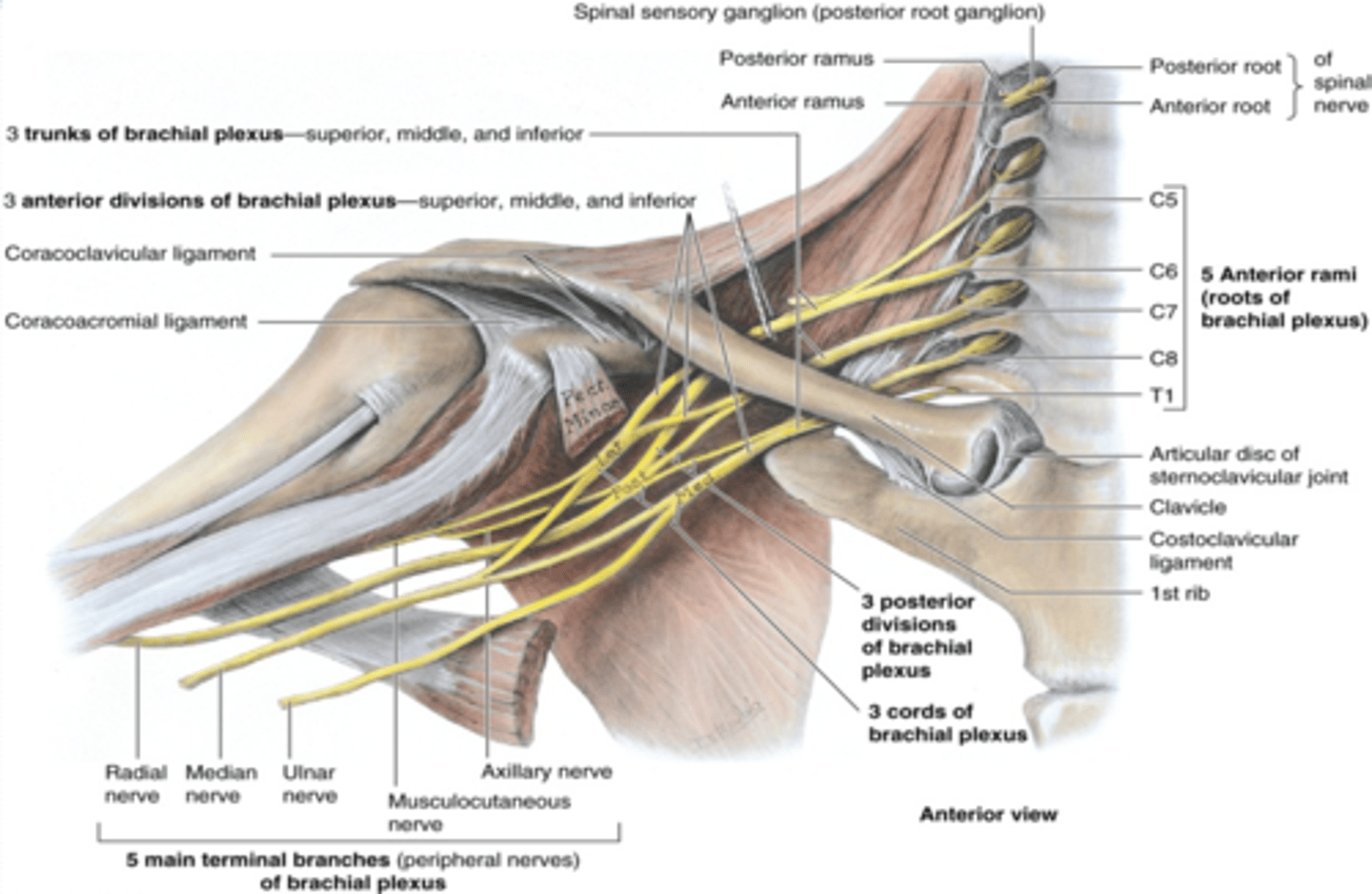
(Upper Limb Innervation:) Brachial plexus begins in
the neck and extends into the axilla
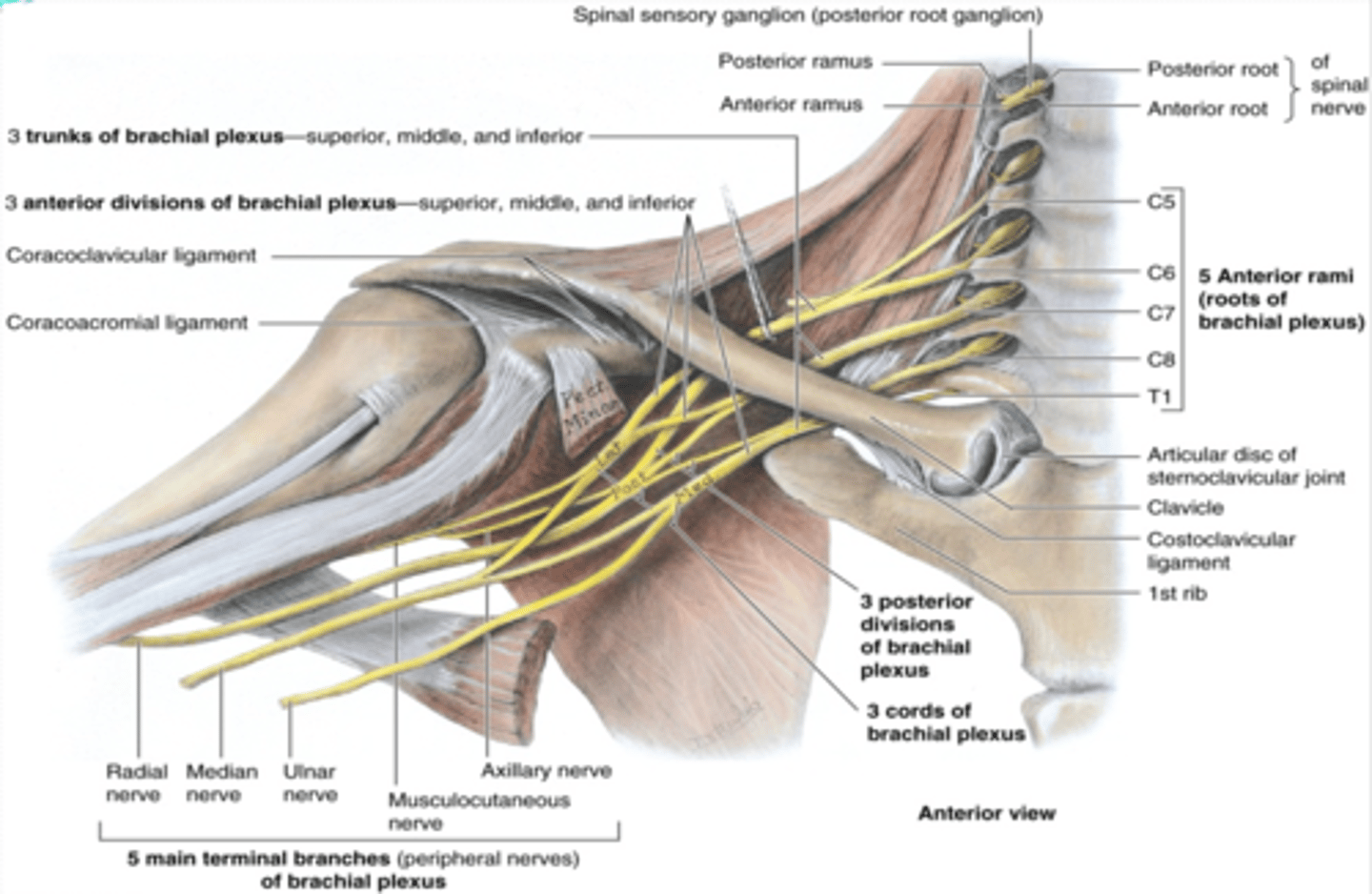
(Upper Limb Innervation:) Brachial plexus formed by
the anterior rami of C5 - T1
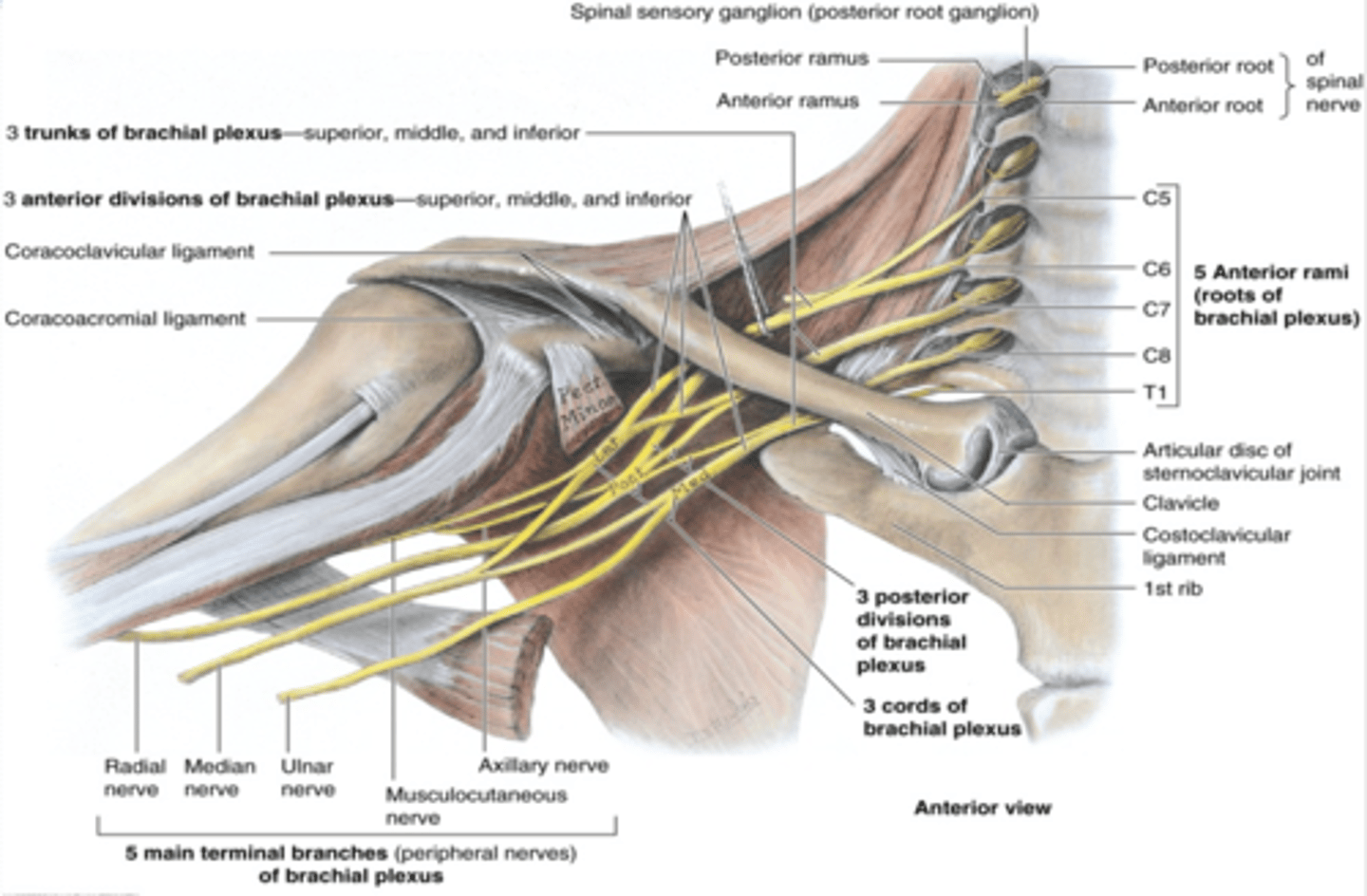
(Upper Limb Innervation:) Brachial plexus parts
-Roots
-Trunks
-Divisions
-Cords
-Branches
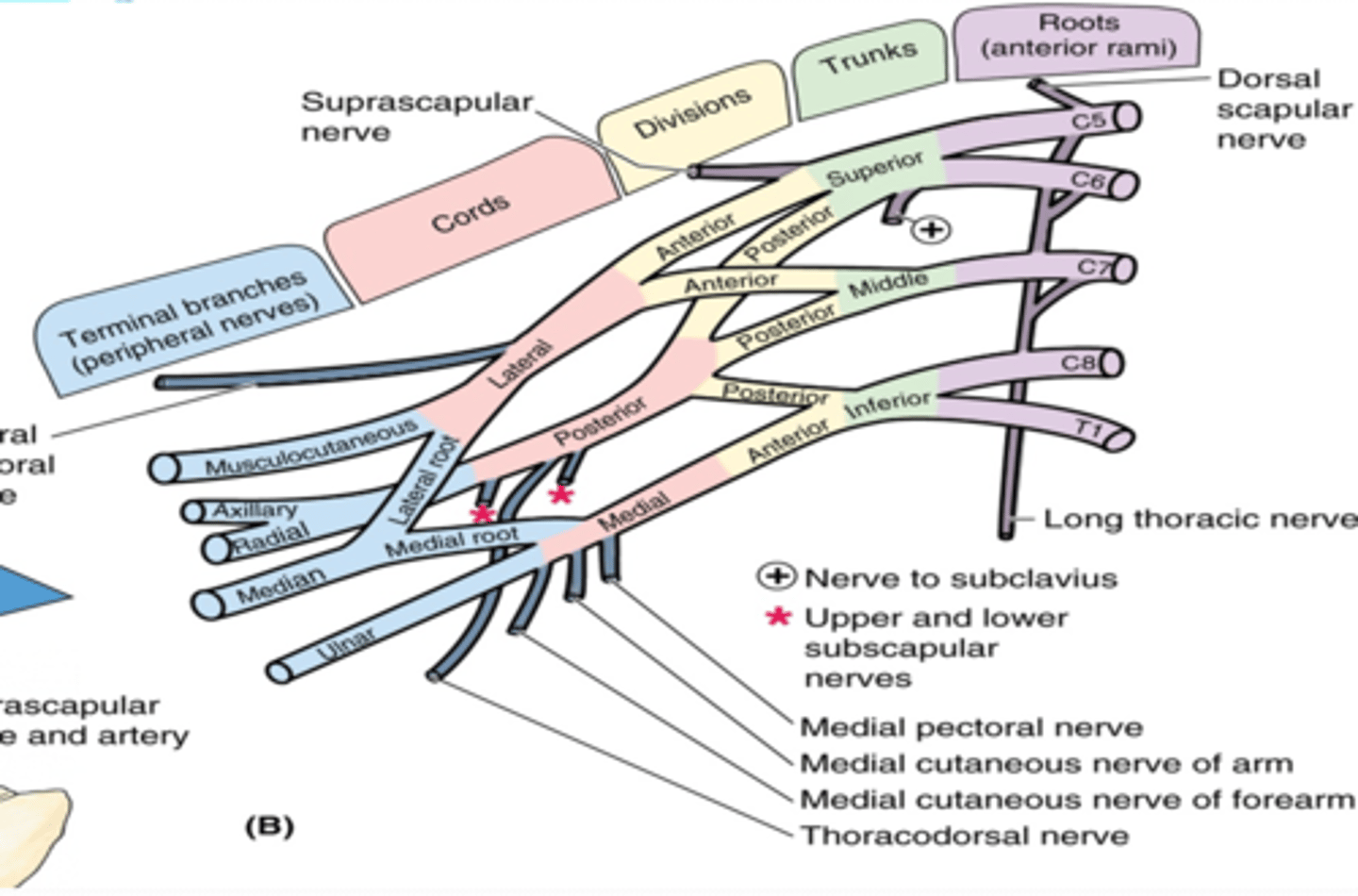
(Brachial plexus parts:) Roots
anterior rami of C5 - T1 that pass through anterior and middle scalene muscles.
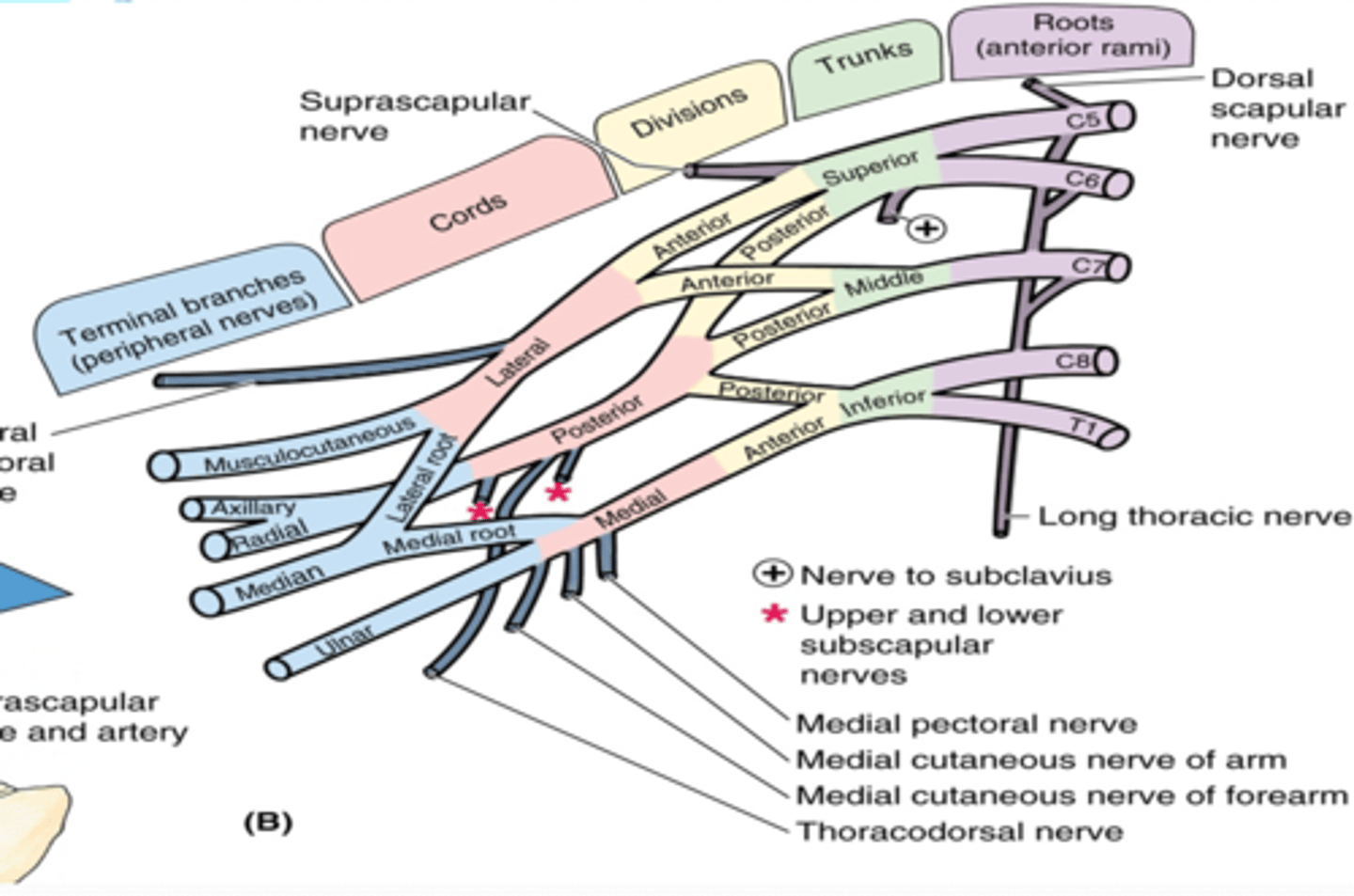
(Brachial plexus parts:) Trunks
union of the roots in the inferior part of the neck
-Superior: C5 + C6 roots
-Middle: continuation of C7 root
-Inferior: C8 + T1 roots
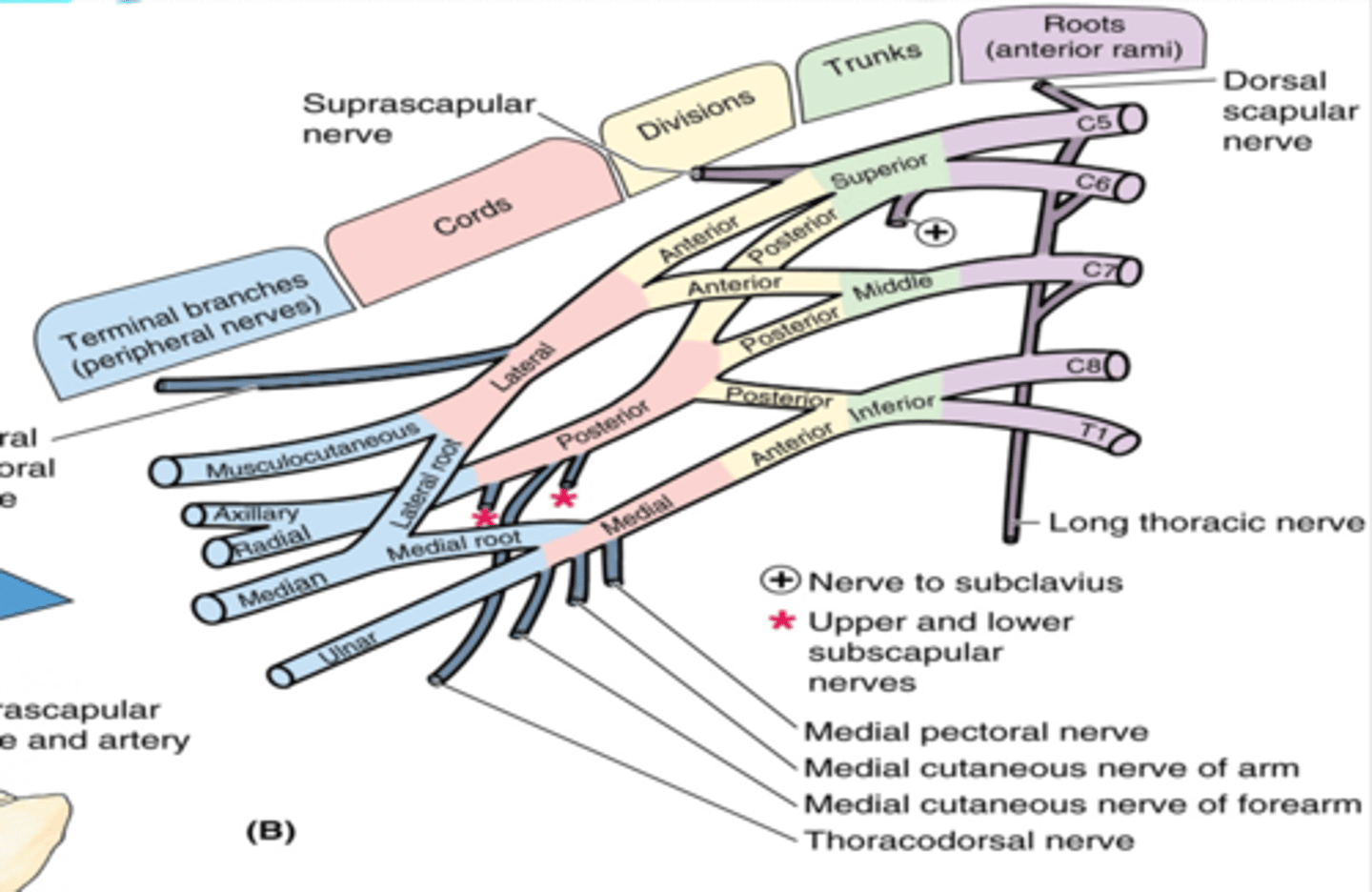
(Brachial plexus parts:) Divisions
separation of the trunks as they pass the cervico-axillary canal
-Anterior: supply anterior (flexors) compartments of the UL
-Posterior: supply posterior (extensor) compartments of the UL
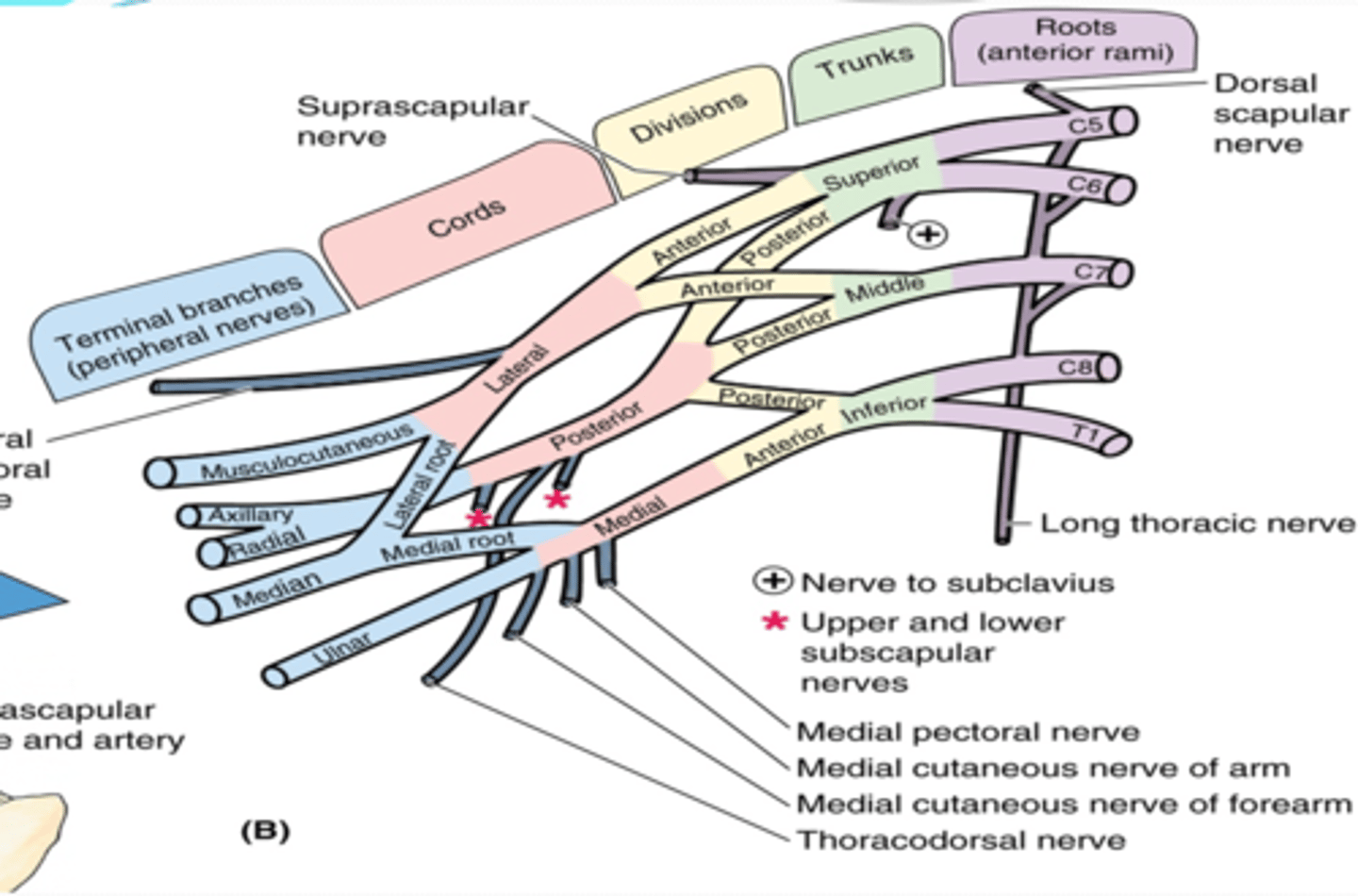
(Brachial plexus parts:) Cords
formed by the divisions of the trunks around axillary artery. at coracoid process. Cords are labeled in reference to their position around the axillary artery.
-Posterior: posterior division of all three cords
-Lateral: anterior divisions of superior and middle trunks
-Medial: anterior division of inferior trunk
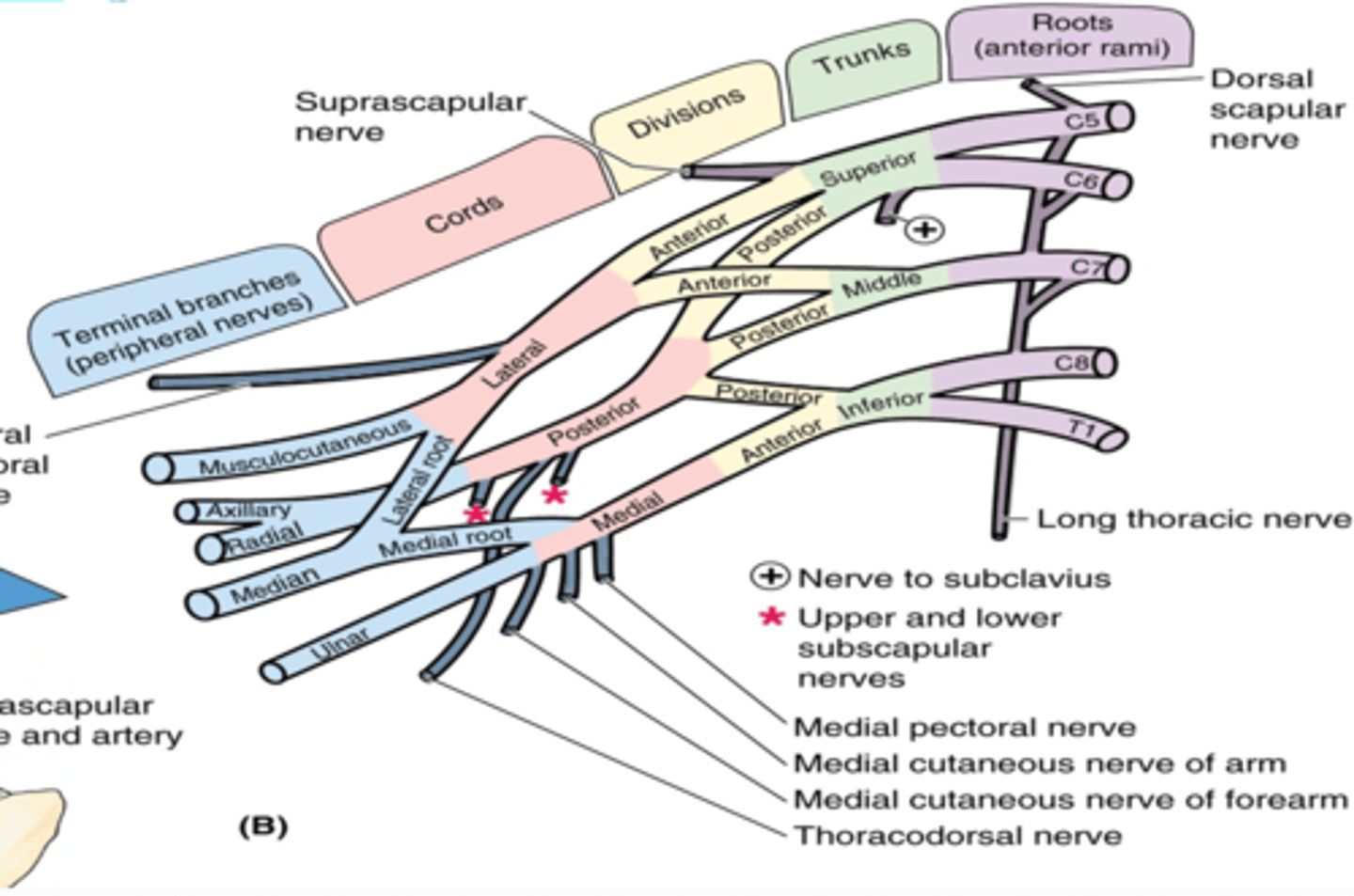
(Brachial plexus parts:) Branches
form 2-4 inches of the lateral border of pectoralis minor m.
-Trunk branches
-Root branches
-Lateral cord branches
-Medial cord branches
-posterior cord branches
-posterior cord terminal branches
-lateral cord terminal branches
-medial cord terminal branches
-medial and lateral cord branches
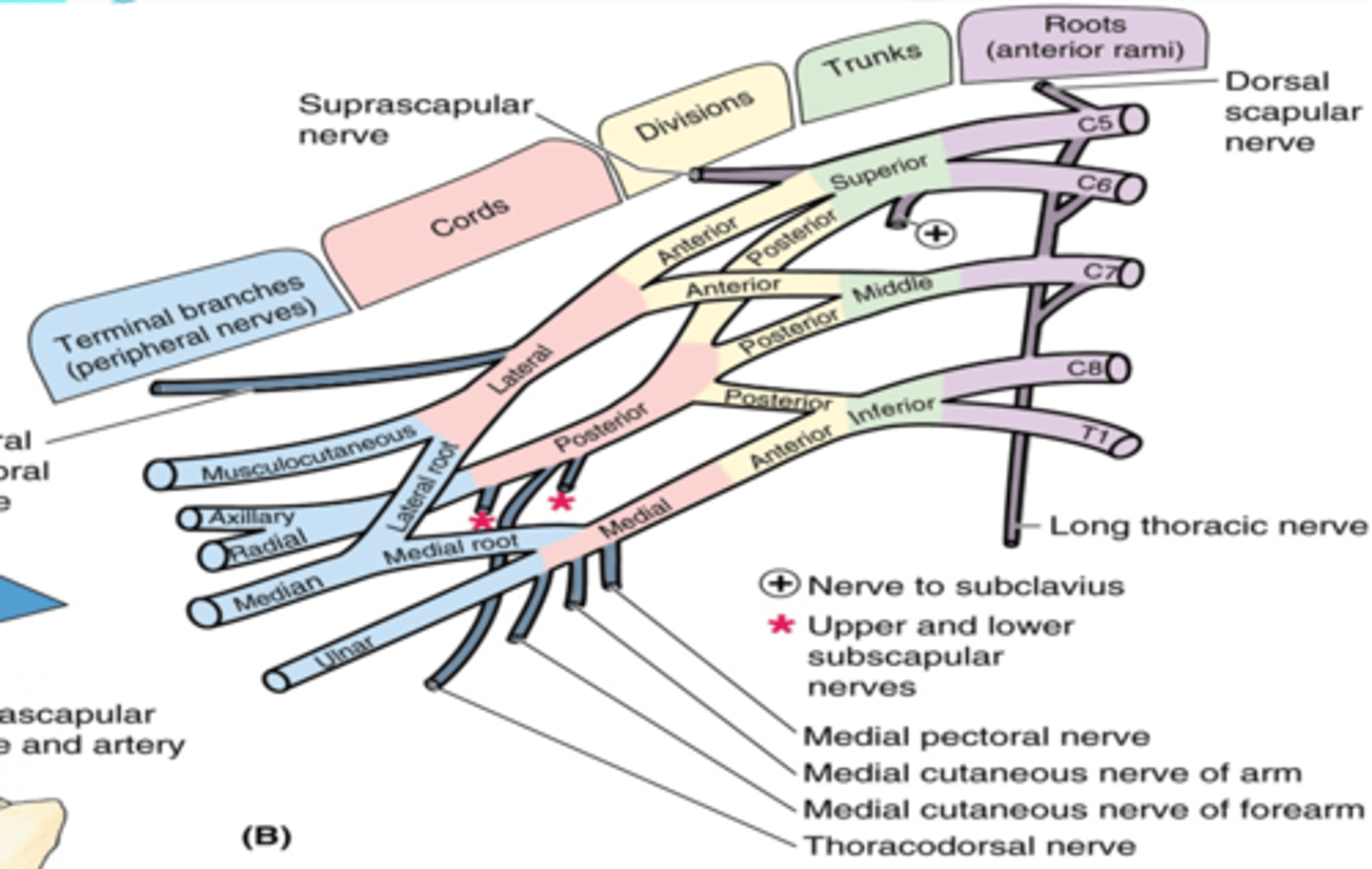
(Branches of the Brachial Plexus:) Root Branches
-Dorsal scapular n. (C4 - C5)
-Long thoracic n. (C5 - C7)
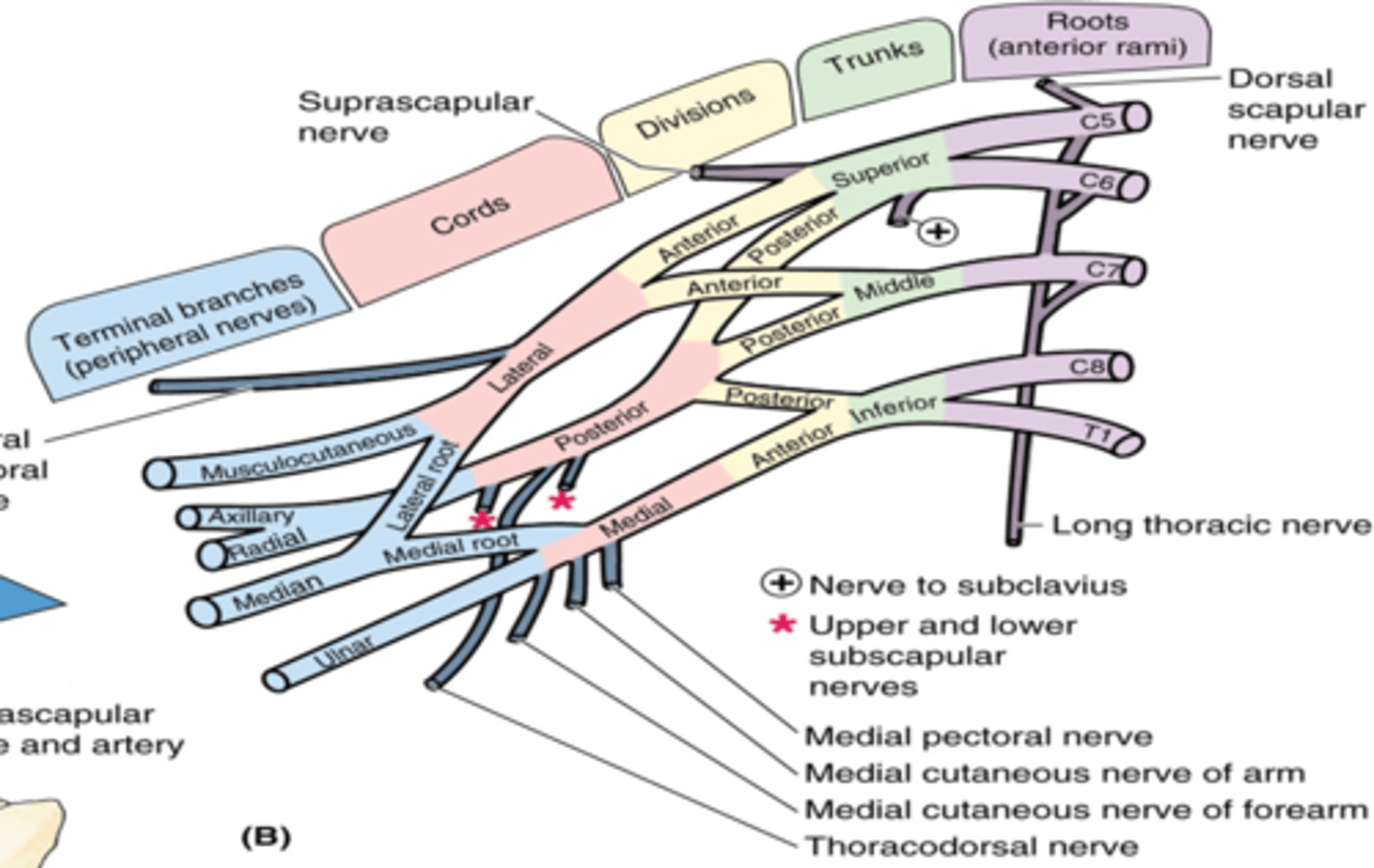
(Brachial Plexus Root Branches:) Dorsal scapular nerve. (C4 – C5)
-Course: pierces middle scalene and descends middle to levator scapulae and rhomboids
-Supply: rhomboids and levator scapulae
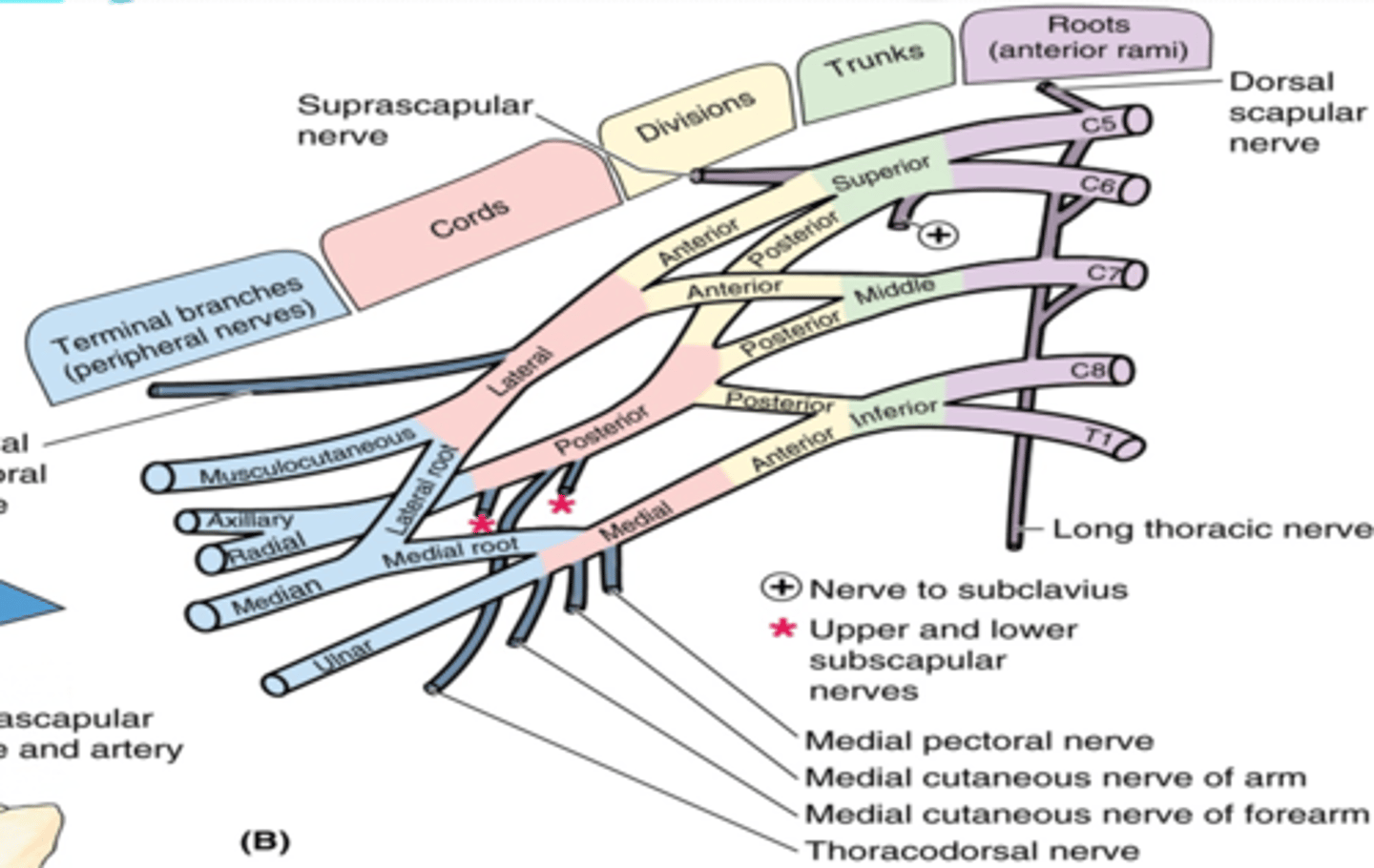
(Brachial Plexus Root Branches:) Long thoracic nerve. (C5 – C7)
-Course: passes through cervico-axillary canal à descends posterior to C8 and T1 roots of brachial plexus à runs on superficial surface of serratus anterior
-Supply: serratus anterior
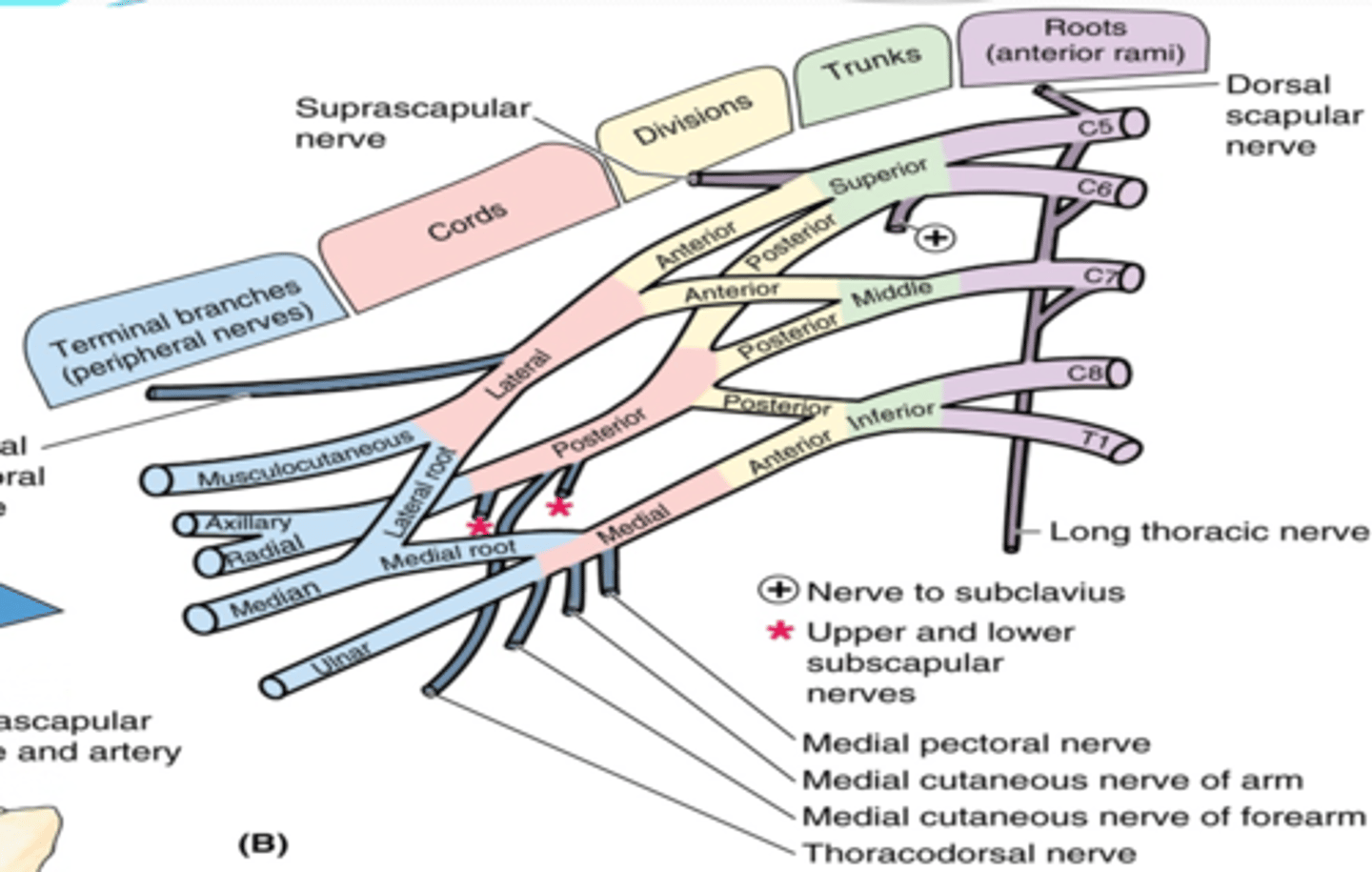
(Branches of the Brachial Plexus:) Trunk branches
-Suprascapular nerve (C5-C6)
-Subclavian nerve (C5-C6)
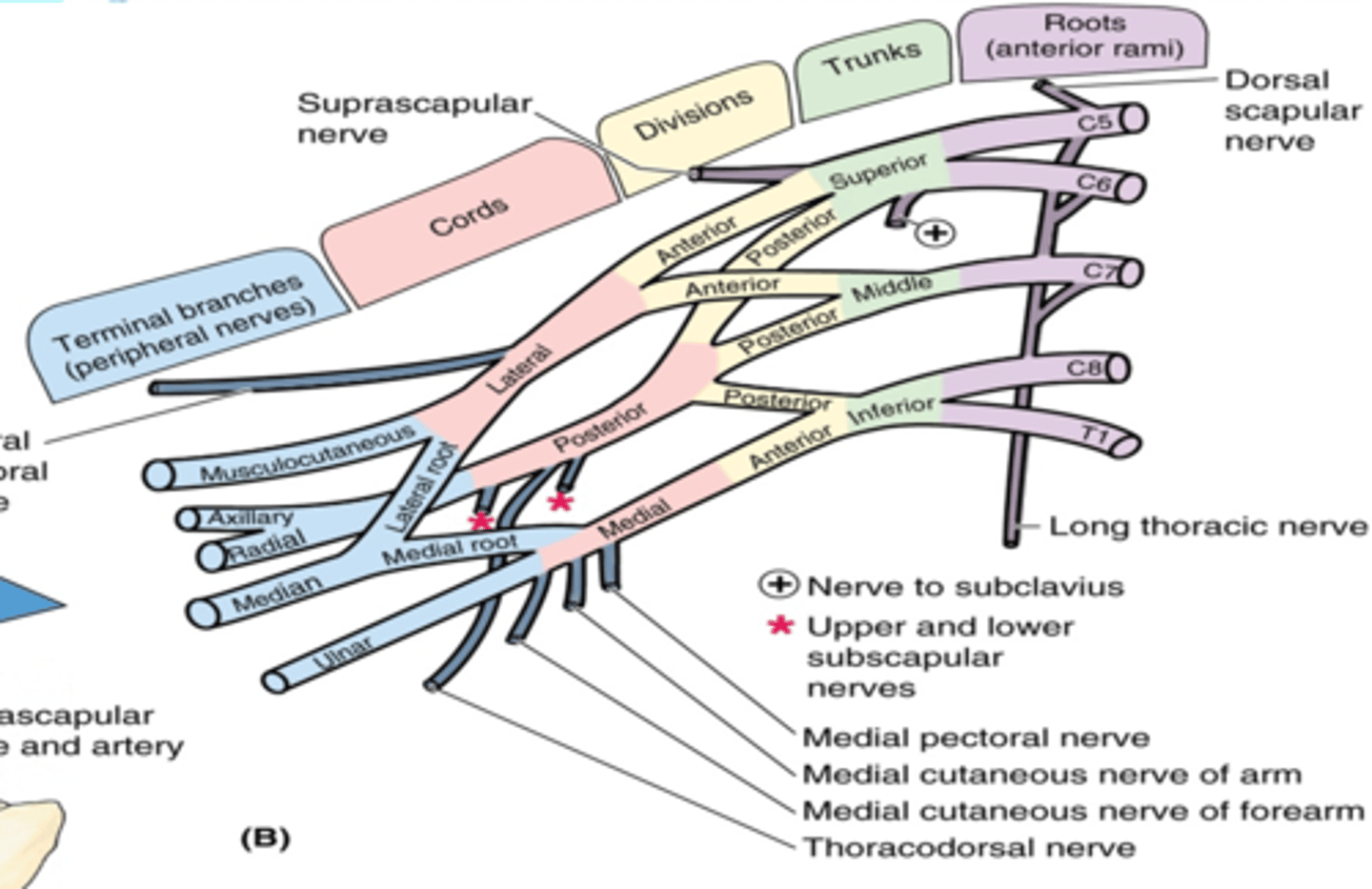
(Brachial Plexus Trunk branches:) Suprascapular nerve (C5-C6)
-Course: runs across lateral cervical region à through scapular notch
-Supply: supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles, glenohumeral joint
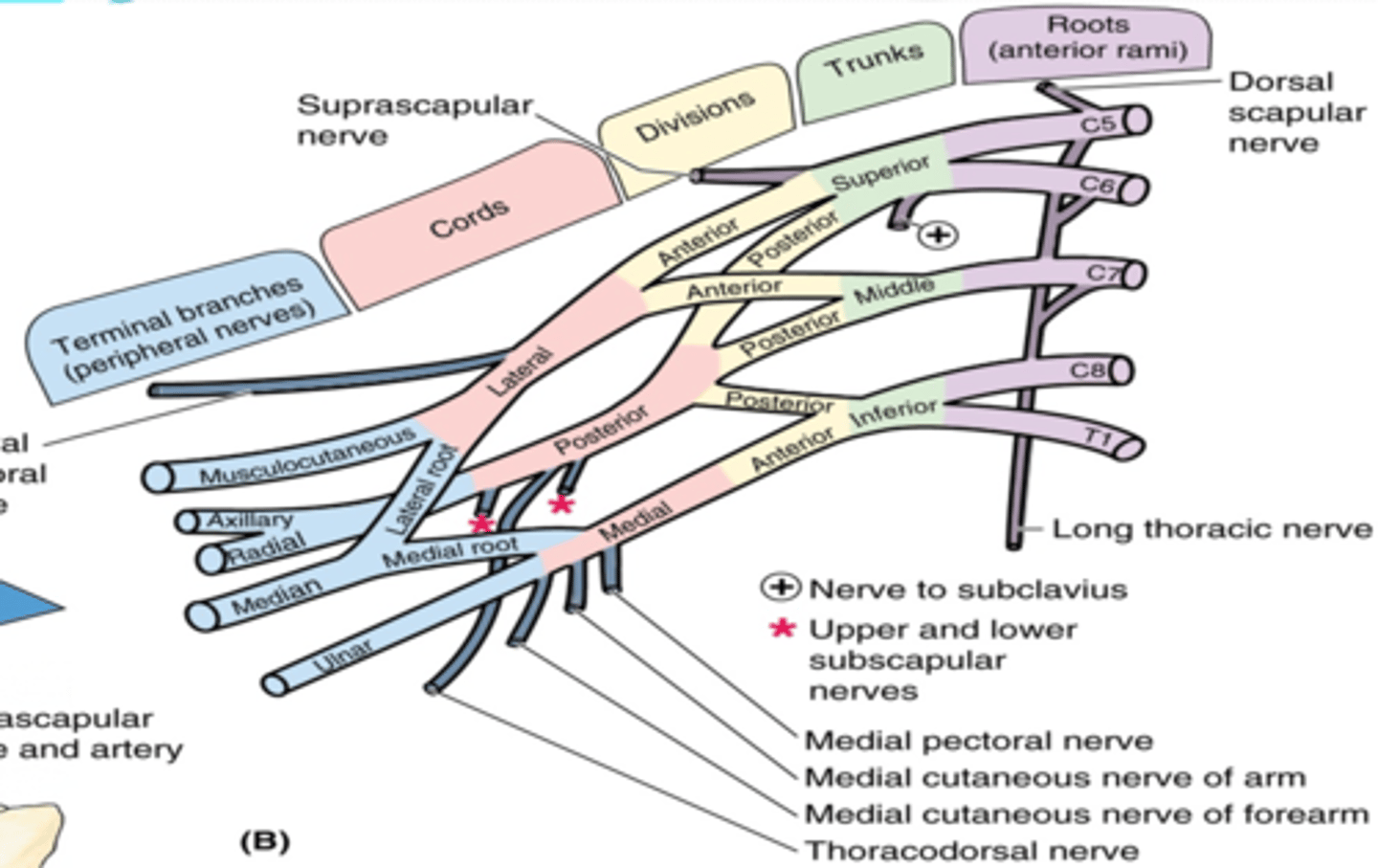
(Brachial Plexus Trunk branches:) Subclavian nerve (C5-C6)
Supply: subclavius muscle
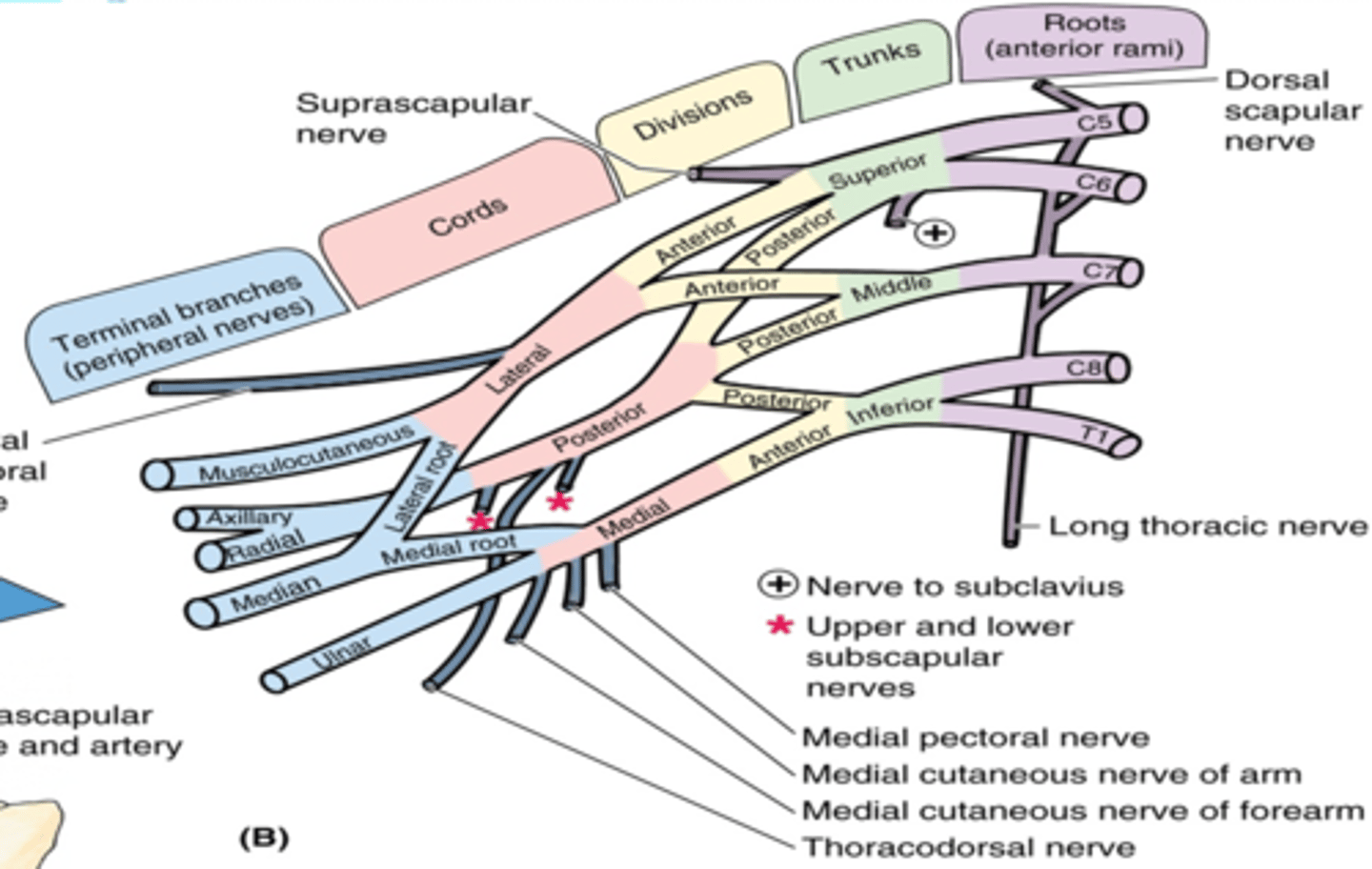
(Branches of the Brachial Plexus:) Lateral Cord Branches
Lateral pectoral n. (C5 – C7)
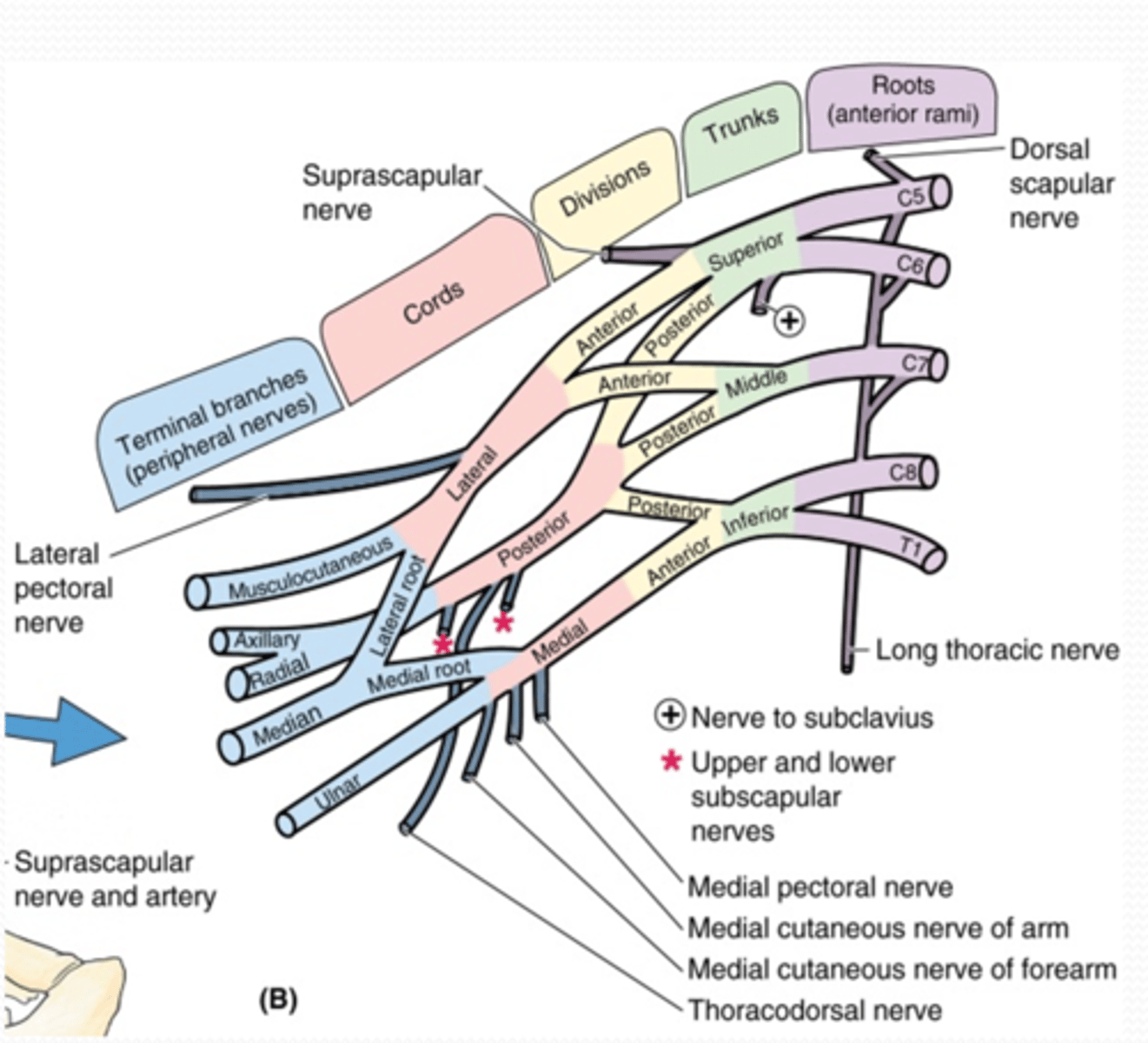
(Brachial Plexus Lateral Cord Branches:) Lateral pectoral n. (C5 – C7)
-Course: reaches pectoralis major m. on its deep surface
-Supply: pectoralis major m.
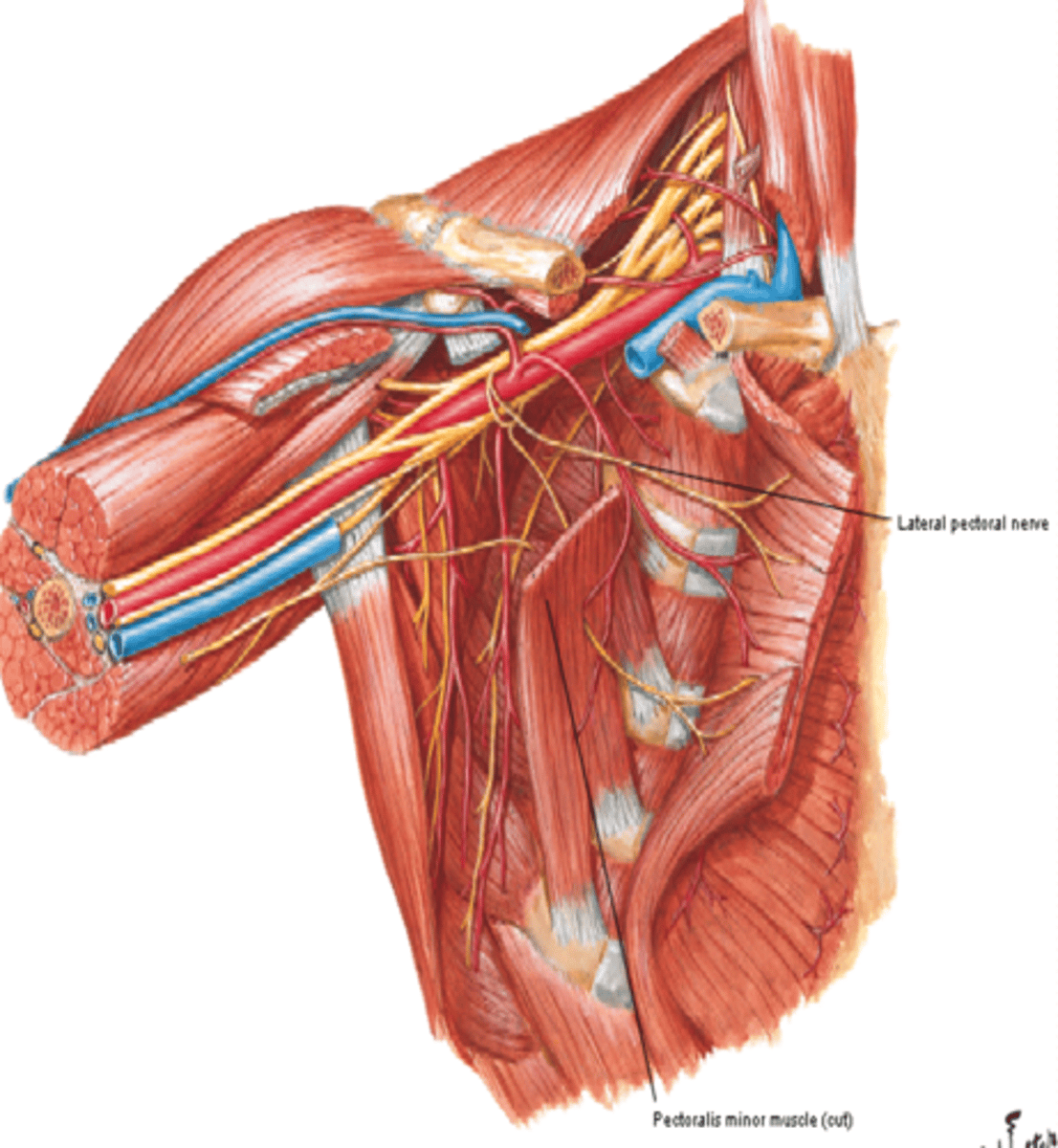
(Branches of the Brachial Plexus:) Medial Cord Branches
-Medial pectoral n. (C8 – T1)
-Medial cutaneous nerve of arm (C8 – T1)
-Medial cutaneous nerve of forearm (C8 – T1)
(Brachial Plexus Medial Cord Branches:) Medial pectoral n. (C8 – T1)
-Course: pierces pectoralis minor m. to get to deep surface of pectoralis major m.
-Supply: pectoralis minor and major muscles
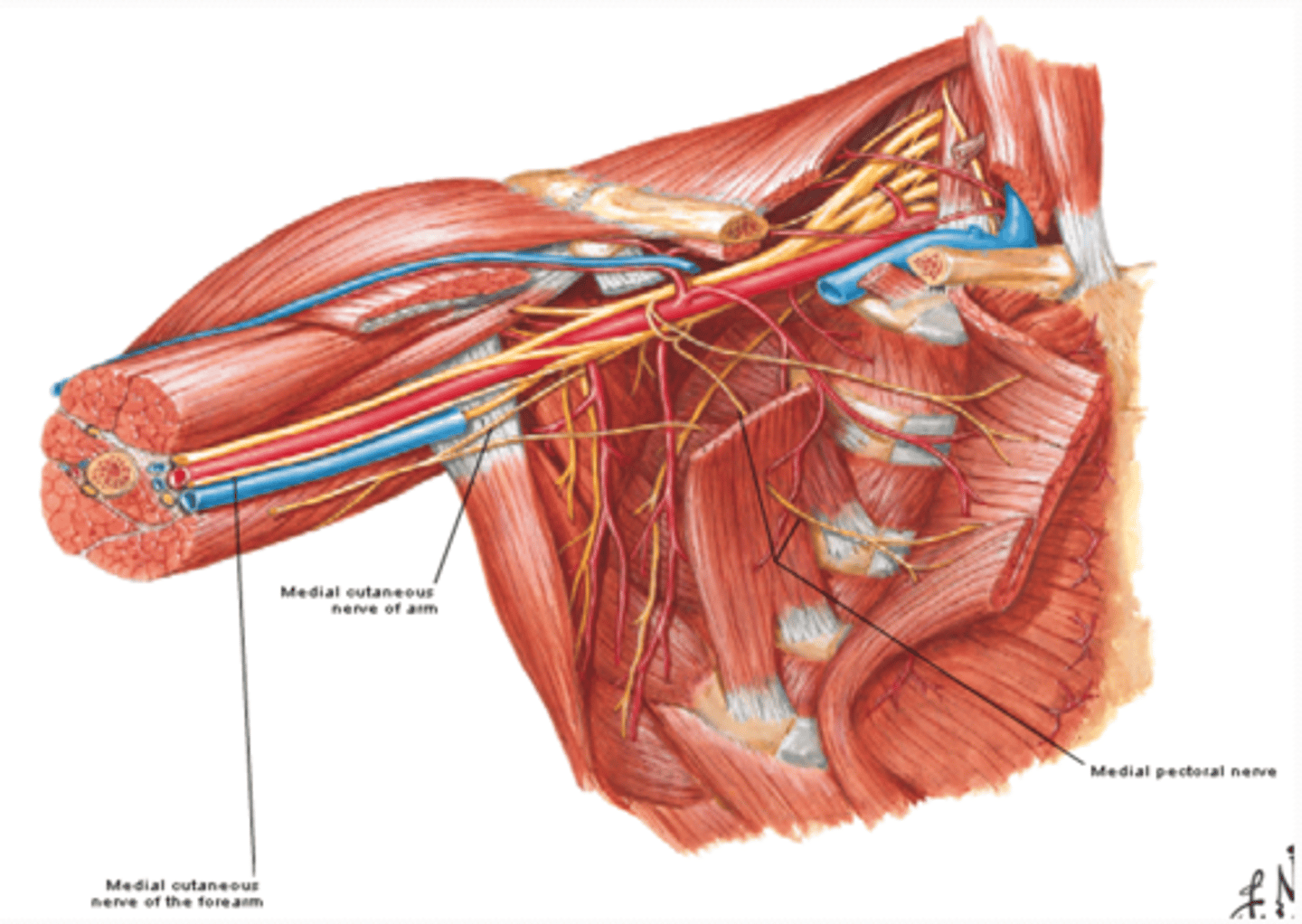
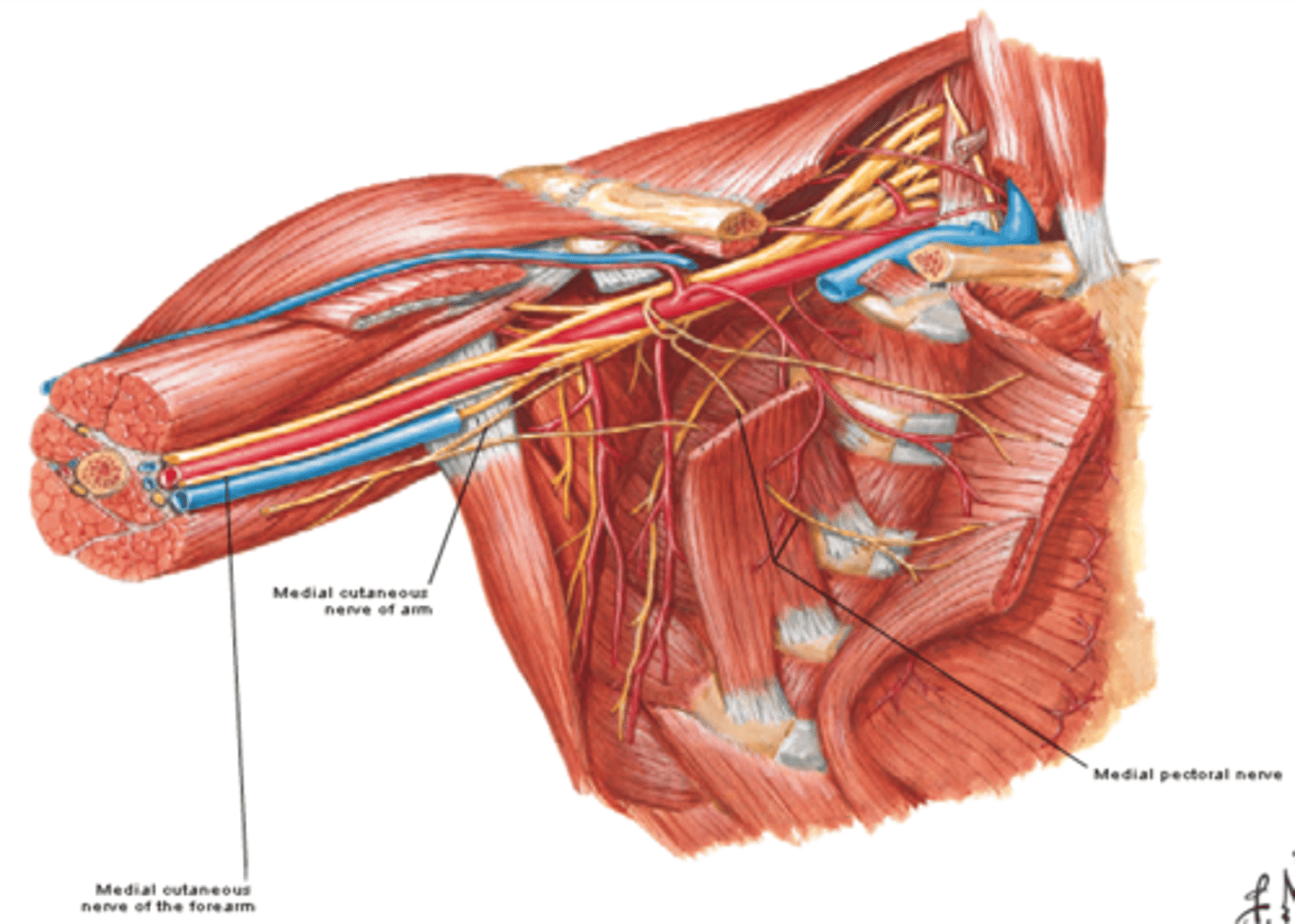
(Brachial Plexus Medial Cord Branches:) Medial cutaneous nerve of arm (C8 – T1)
-Course: runs along medial side of axillary and brachial veins
-Supply: skin on medial side of arm
-Communicates with intercostobrachial nerve (T2)
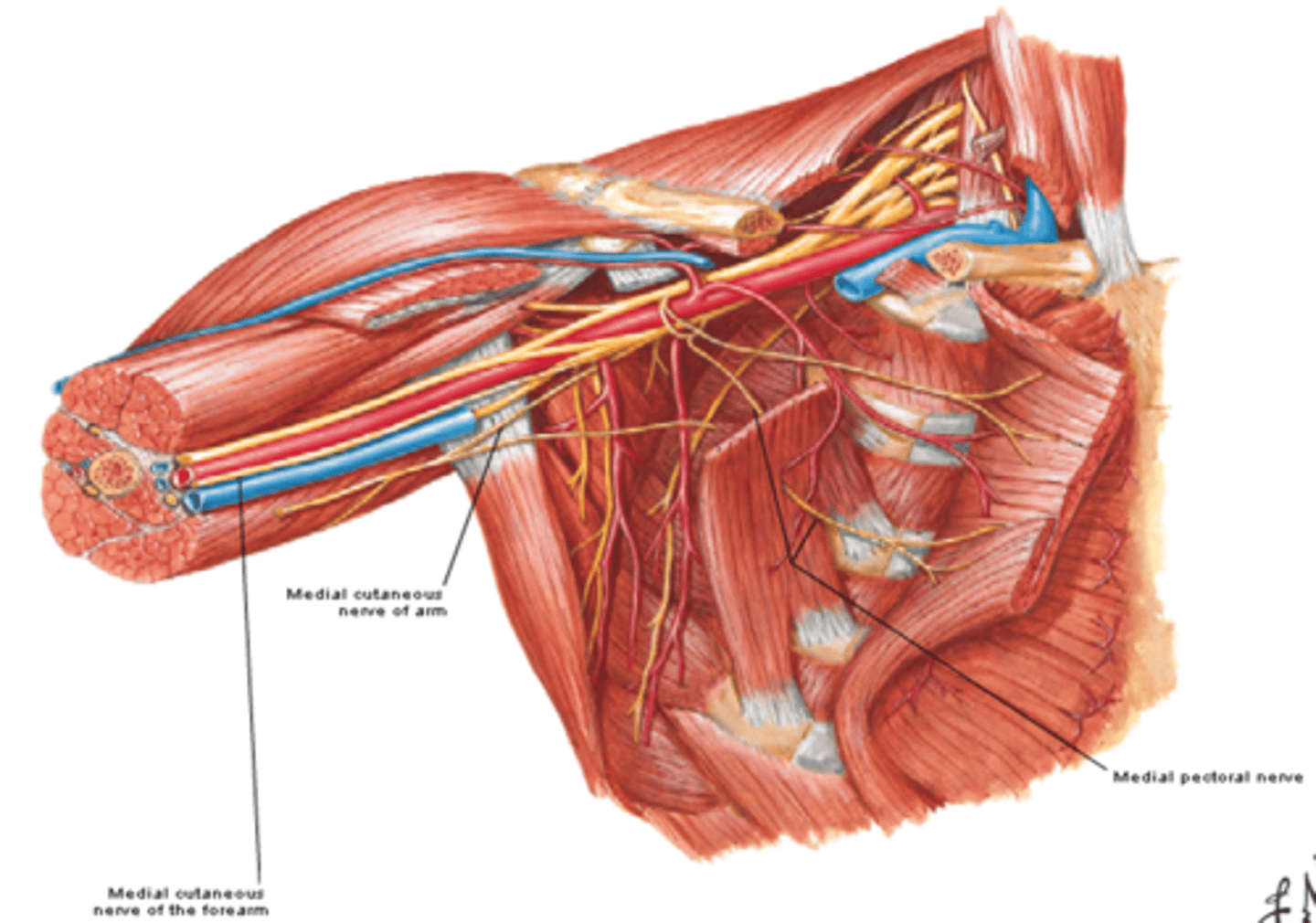
(Brachial Plexus Medial Cord Branches:) Medial cutaneous nerve of forearm (C8 – T1)
-Course: runs initially with ulnar nerve and pierces deep fascia to enter subcutaneous tissue
-Supply: skin on medial side of forearm
(Branches of the Brachial Plexus:) Posterior Cord Branches
-Upper subscapular n. (C5 – C6)
-Lower subscapular n. (C5 – C6)
-Thoracodorsal n. (C6 – C8)
(Brachial Plexus Posterior Cord Branches:) Upper subscapular n. (C5 – C6)
-Course: runs posteriorly towards the subscapularis m.
-Supply: subscapularis m.
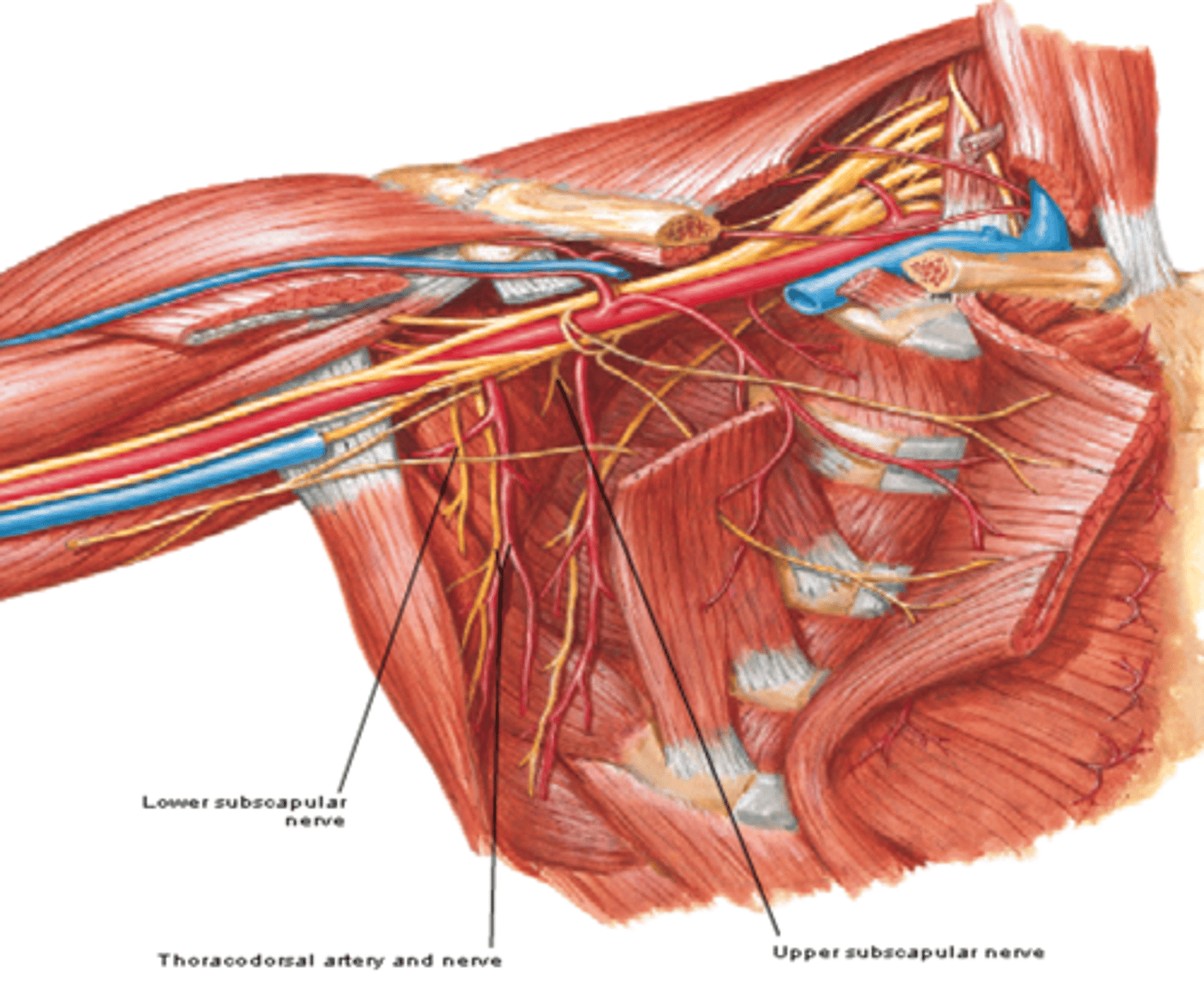
(Brachial Plexus Posterior Cord Branches:) Lower subscapular n. (C5 – C6)
-Course: runs inferolaterally towards subscapularis m.
-Supply: subscapularis m. & teres major m.
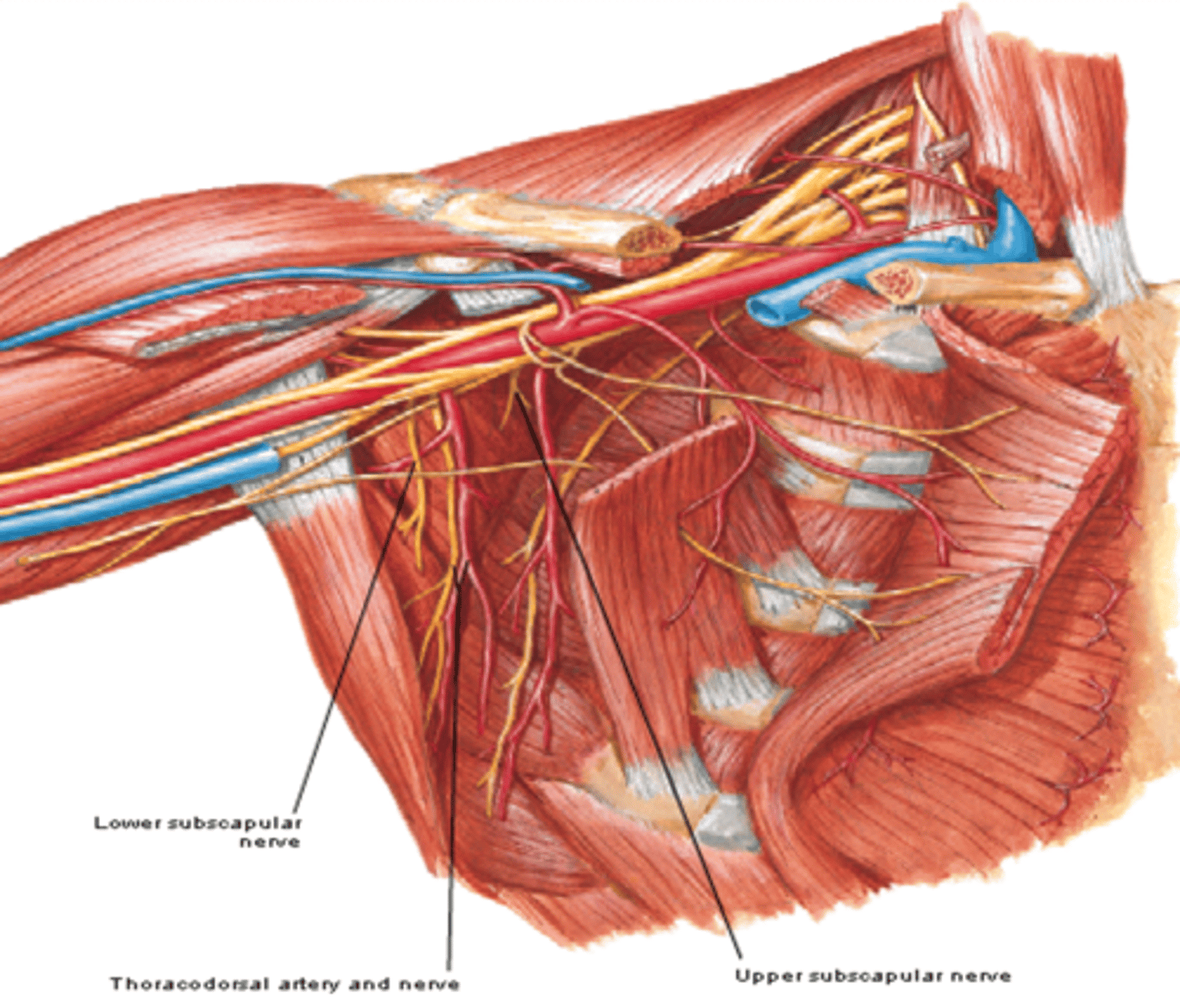
(Brachial Plexus Posterior Cord Branches:) Thoracodorsal n. (C6 – C8)
-Course: runs inferolaterally along posterior axillary wall
-Supply: latissimus dorsi m.
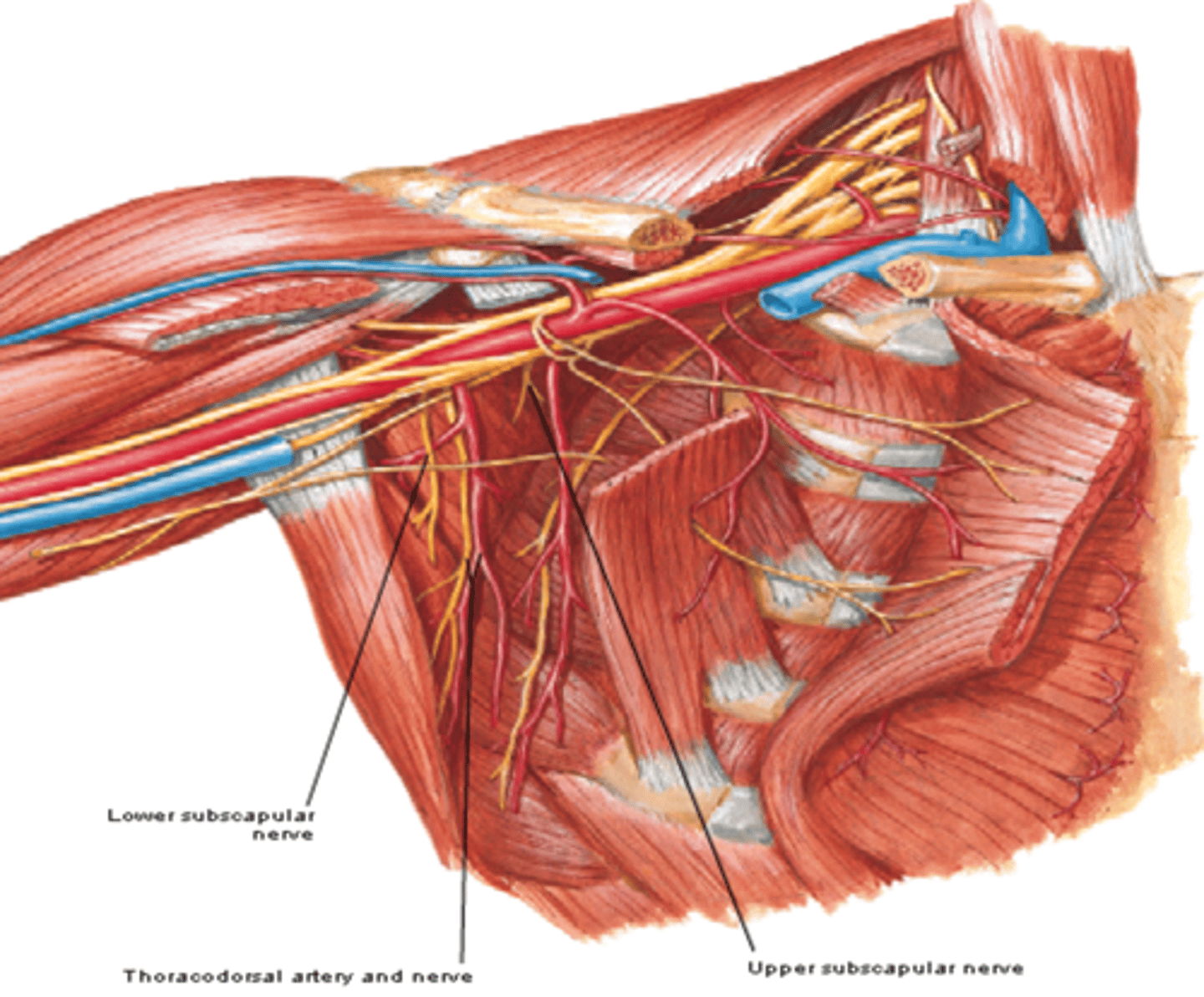
(Branches of the Brachial Plexus:) Posterior Cord Terminal Branches
Axillary n. (C5 - C6)
Radial n. (C5-T1)
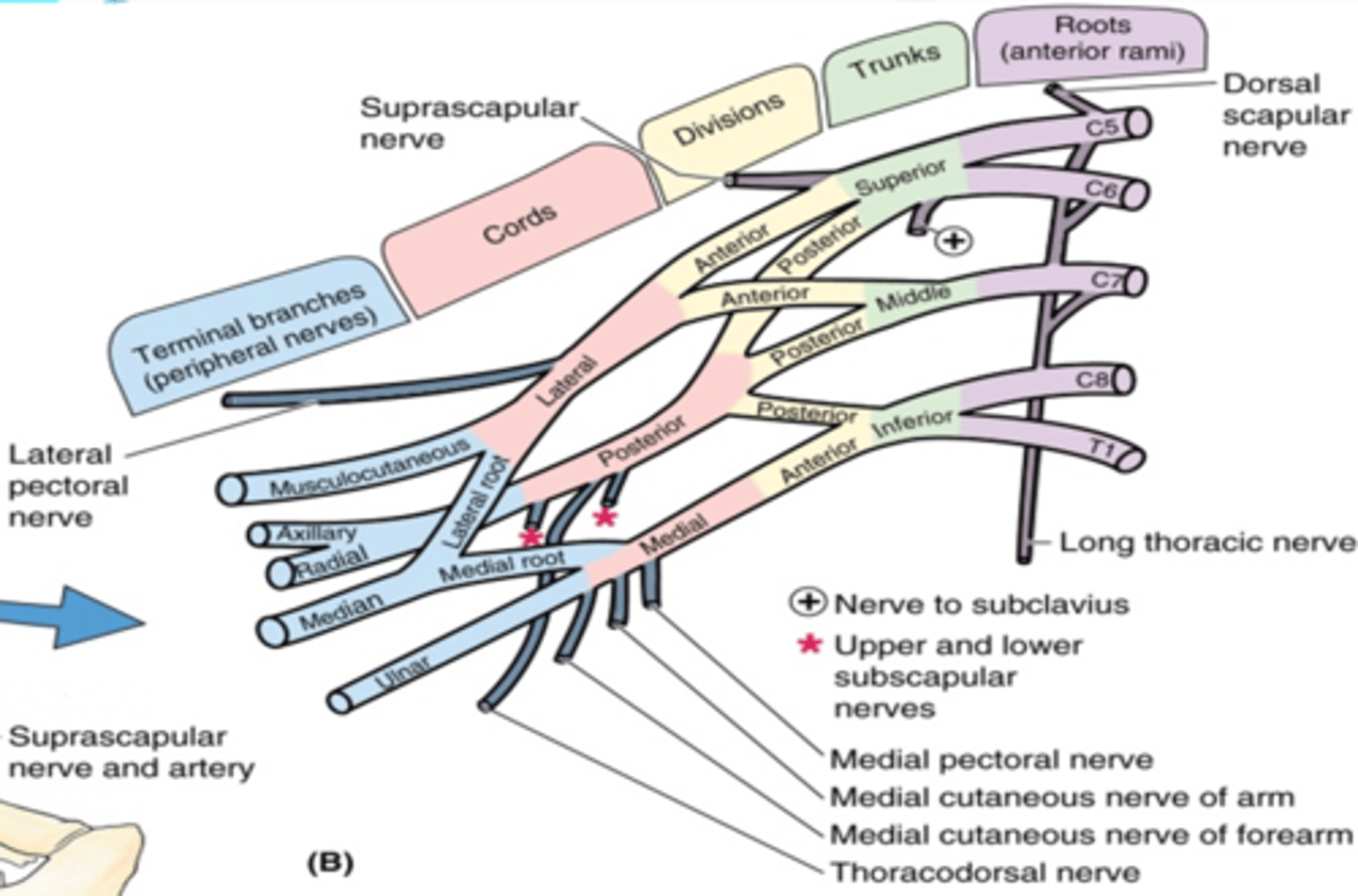
(Brachial Plexus Posterior Cord Terminal Branches:) Axillary n. (C5 – C6)
-Course: exits axillary fossa posteriorly and wraps around surgical neck of humerus deep to the deltoid m.
-Supply: teres minor and deltoid muscles, glenohumeral joint, and skin on superolateral arm
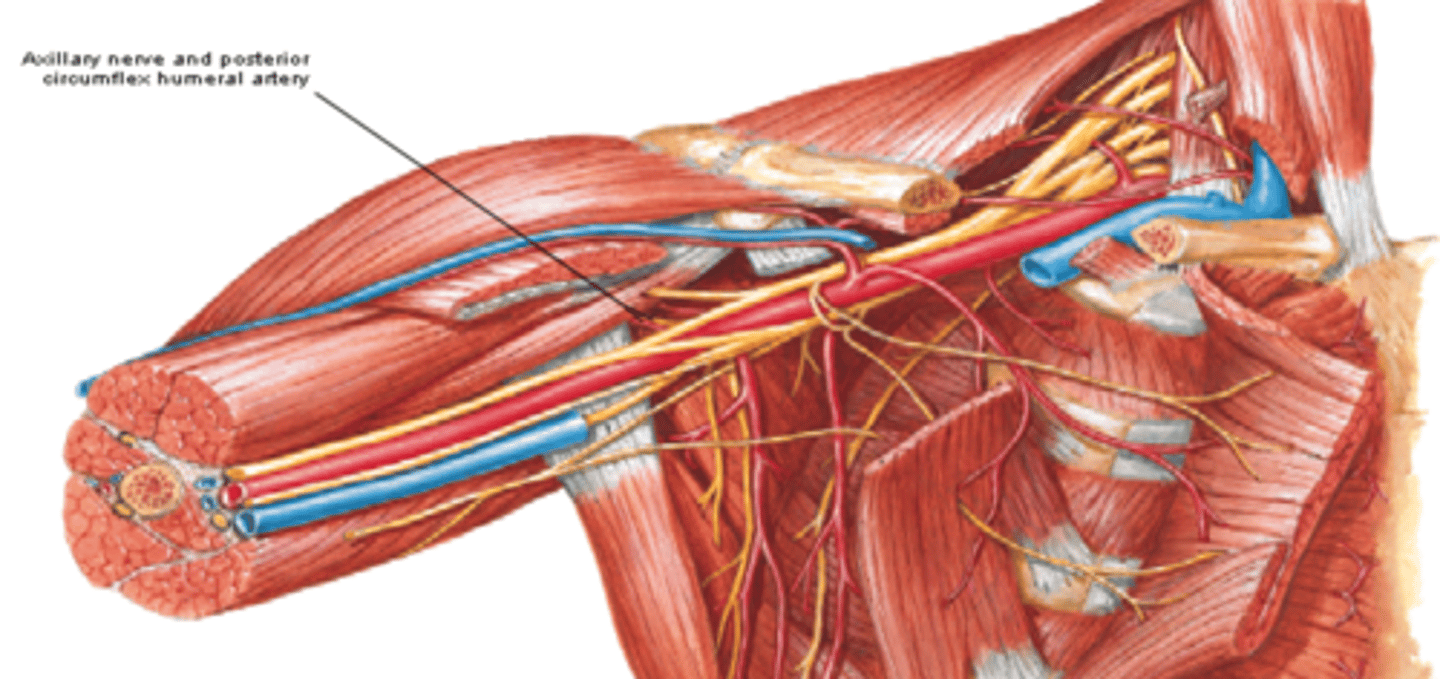
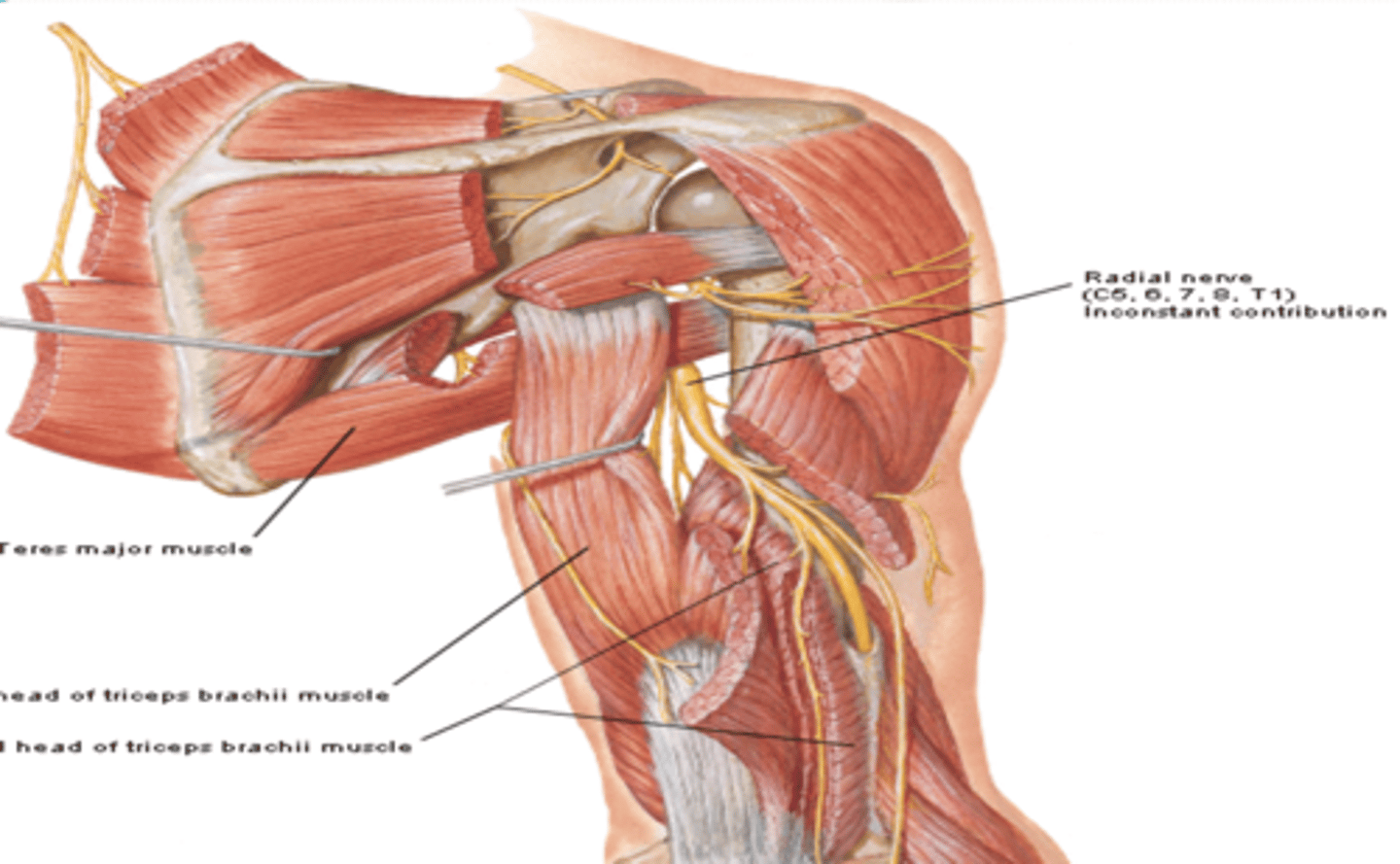
(Brachial Plexus Posterior Cord Terminal Branches:) Radial n. (C5-T1)
-Course: runs posterior to humerus in radial groove -> perforates lateral intermuscular septum -> enters cubita fossa
-Supply: all muscles of posterior compartments of the arm and forearm, and skin on posterior and inferolateral arm, posterior forearm, and dorsum of hand
(Branches of the Brachial Plexus:) Lateral Cord Terminal Branches
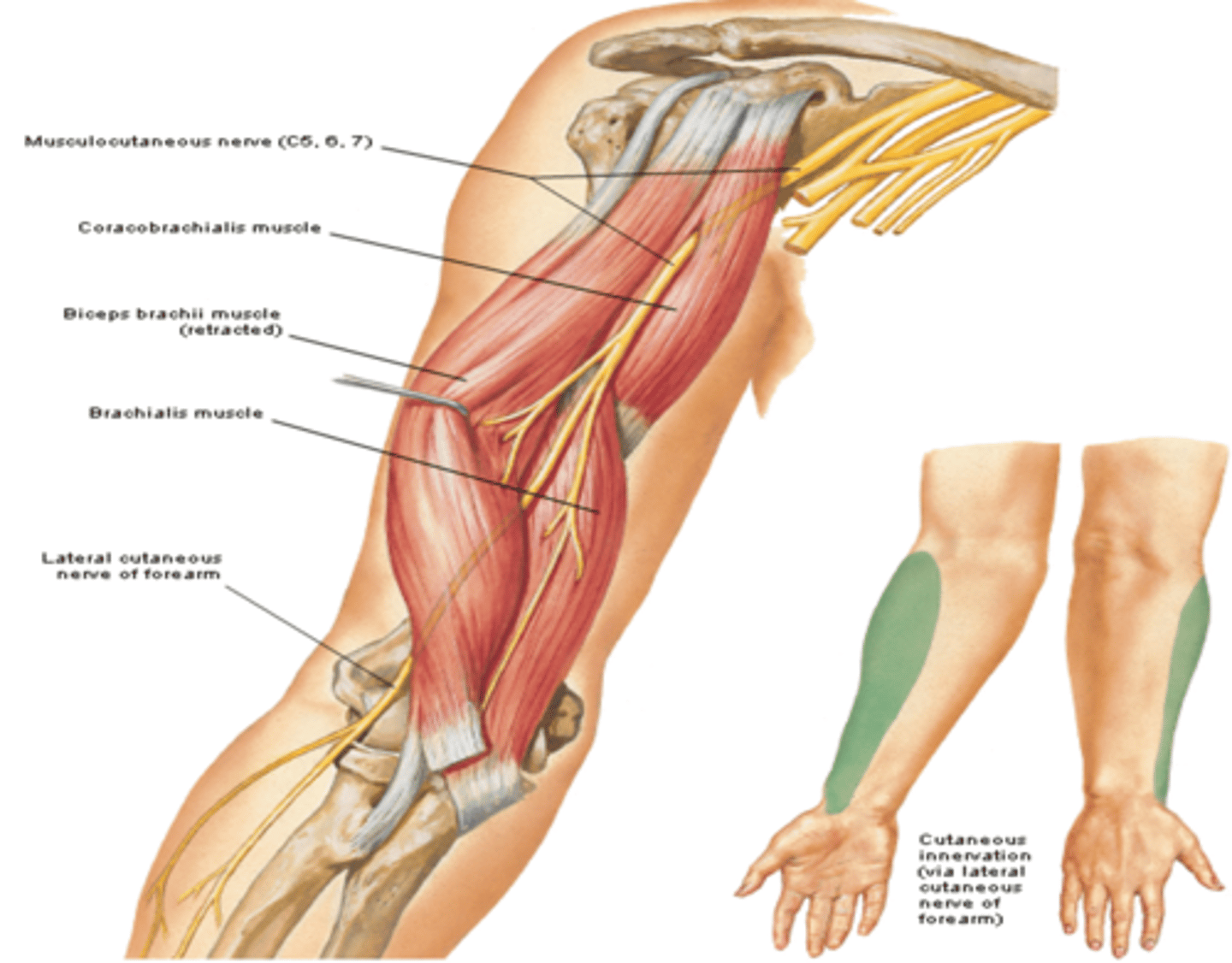
Musculocutaneous n. (C5 – C7)
(Brachial Plexus Lateral Cord Terminal Branches:) Musculocutaneous n. (C5 – C7)
-Course: exits axilla by piercing the coracobrachialis m. -> descends between biceps and brachialis muscles -> continues as lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm
-Supply: muscles in anterior compartment of arm, and skin on lateral forearm
(Branches of the Brachial Plexus:) Medial Cord Terminal Branches
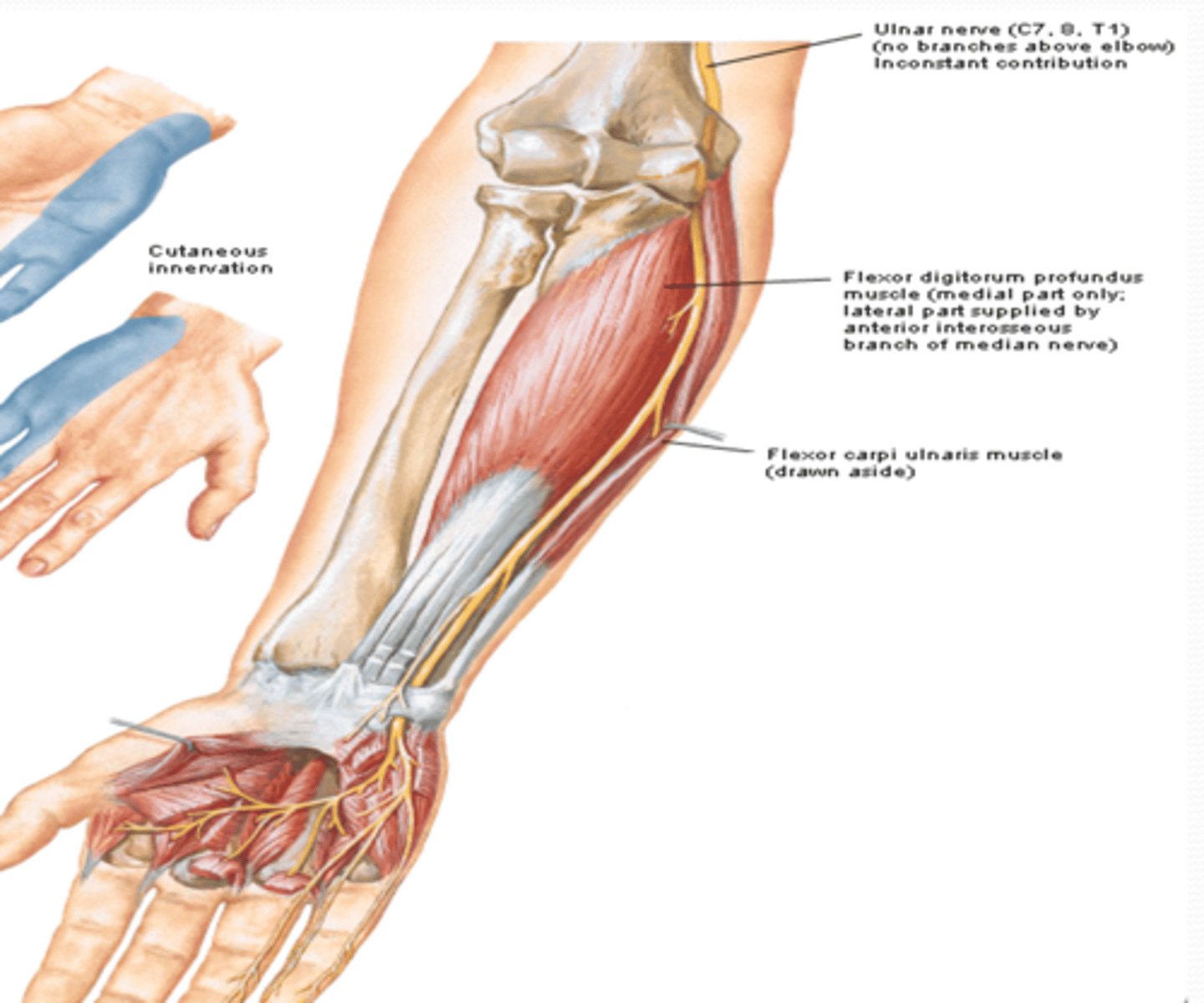
Ulnar n. (C7 – T1)
(Brachial Plexus Medial Cord Terminal Branches:) Ulnar n. (C7 – T1)
-Course: descends in arm passing posterior to medial epicondyle of humerus à descends on the ulnar aspect of forearm to the hand
-Supply: FCU, FDP, intrinsic muscles of hand, and skin on medial side of hand (5th digit and medial side of 4th digit)
(Branches of the Brachial Plexus:) Medial and Lateral Cords Terminal Branches
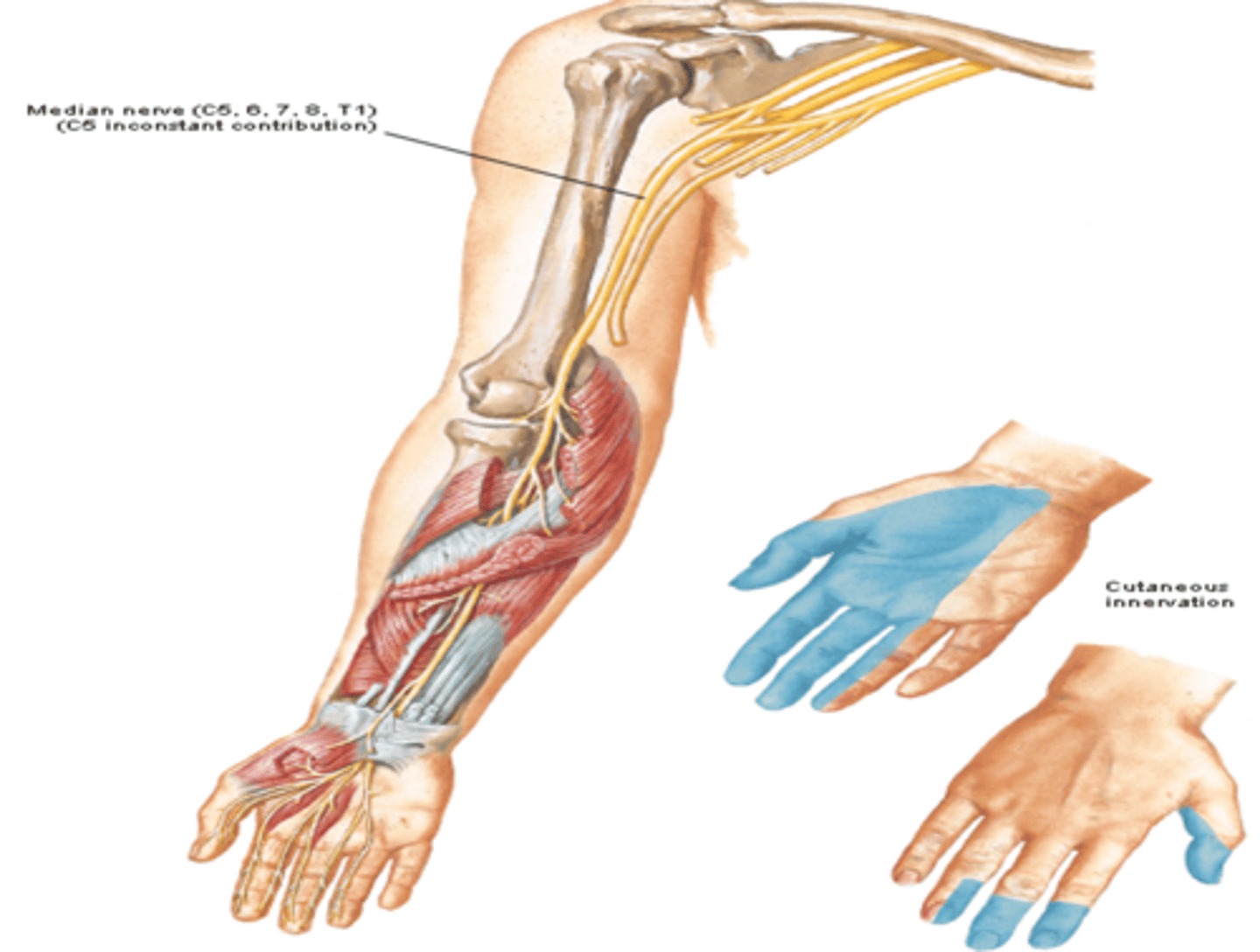
Median n. (C5 – T1)
(Brachial Plexus Medial and Lateral Cords Terminal Branches:) Median n. (C5 – T1)
-Course: descends through the arm next to the brachial a. -> crosses the elbow joint anterior to the medial epicondyle -> enters hand through the carpal tunnel
-Supply: muscles of anterior compartment of forearm (except FCU & part of FDP) and the thenar region, and skin over lateral side of hand
(Upper Limb Vasculature:) Subclavian Artery Branches
-Suprascapular a
-Dorsal scapular a.
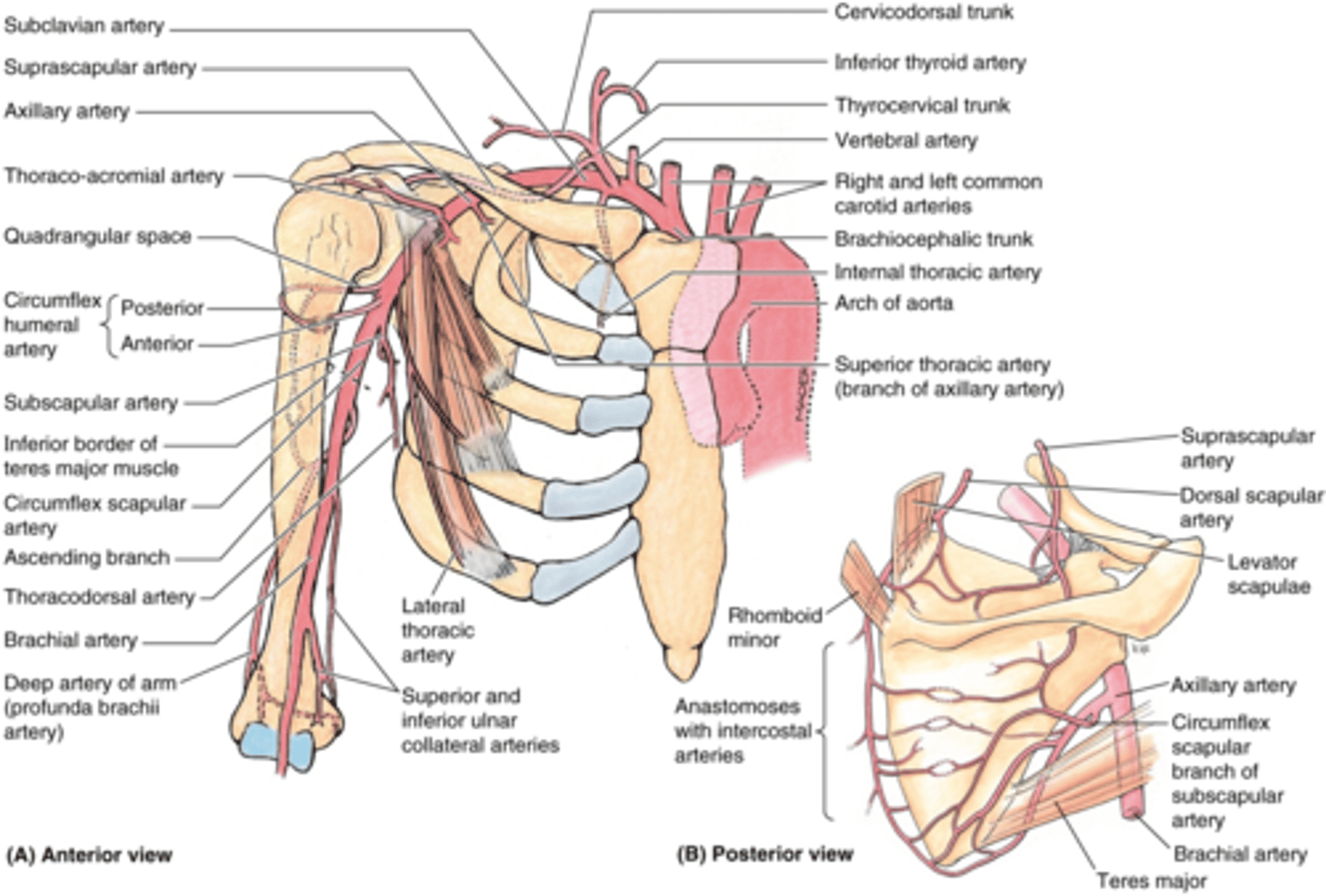
(Vasculature Subclavian Artery Branches:) Suprascapular artery
Supplies: lateral dorsal part of scapula and associated muscles
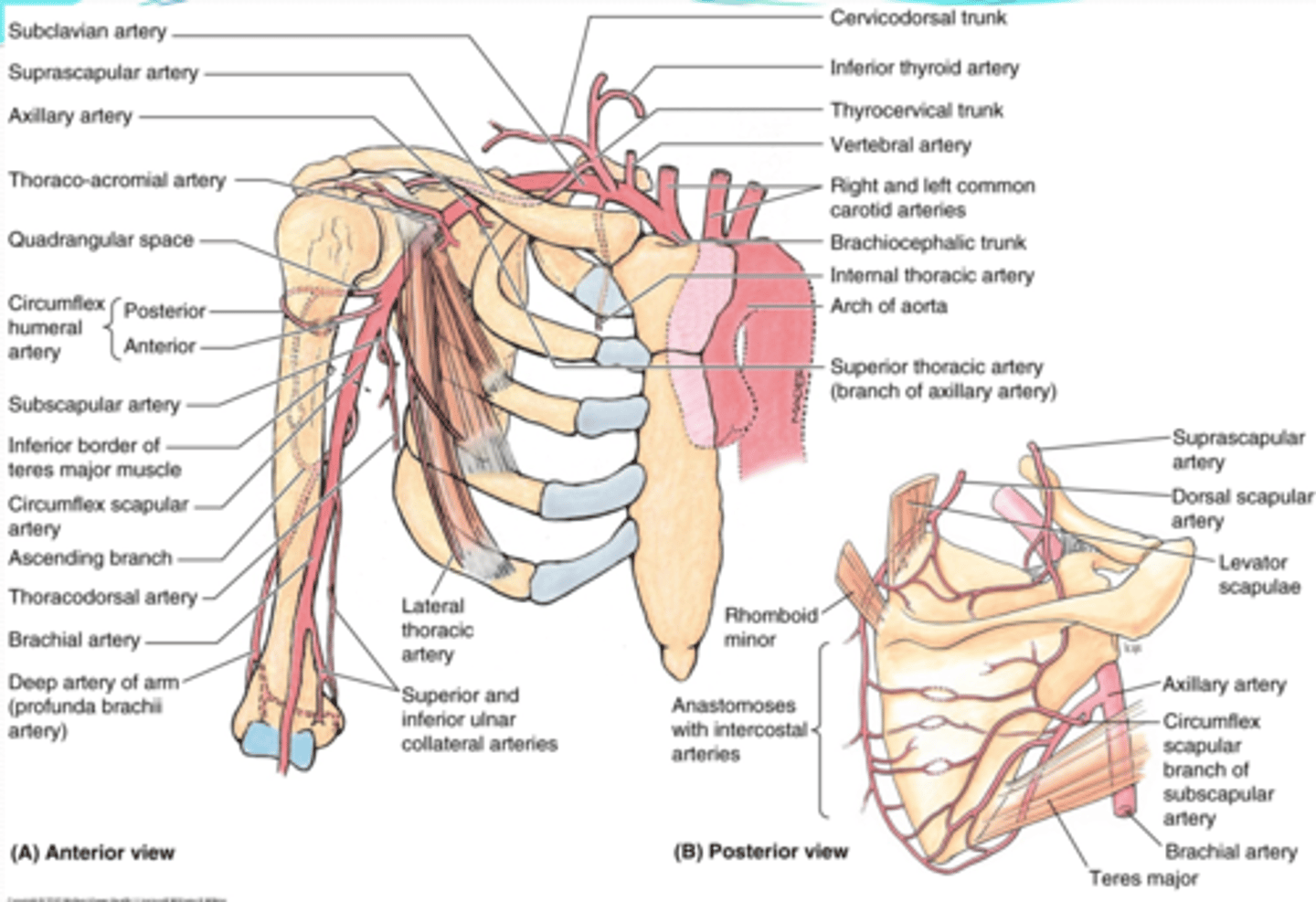
(Vasculature Subclavian Artery Branches:) Dorsal scapular artery
Supplies: medial dorsal region of scapula and associated muscles
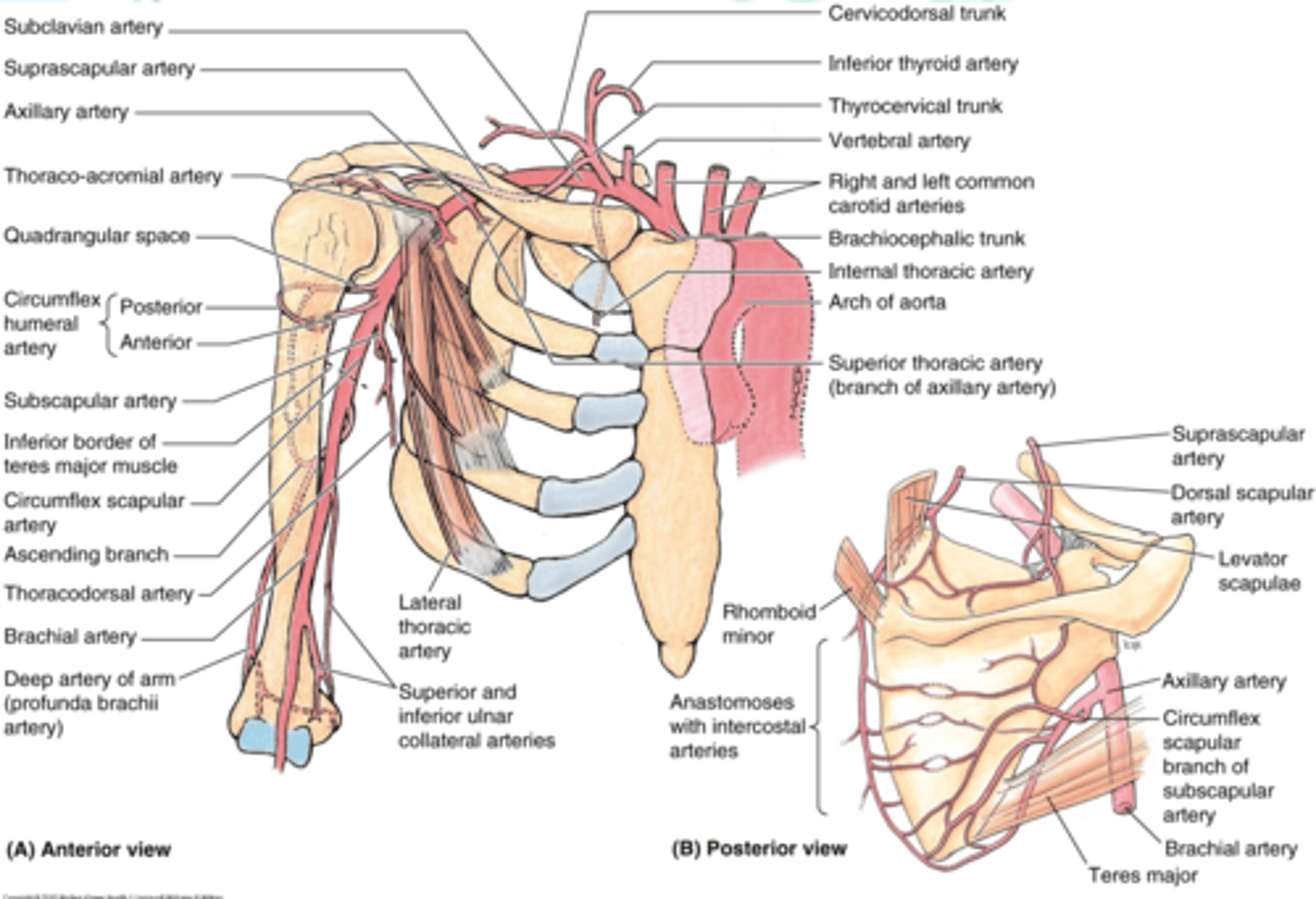
(Upper Limb Vasculature:) Axillary Artery Origin
Origin: begins at lateral border of 1st rib as a continuation of the subclavian a., passes posterior to the pectoralis minor m., and ends at the inferior border of the teres major m. (becomes brachial a.)
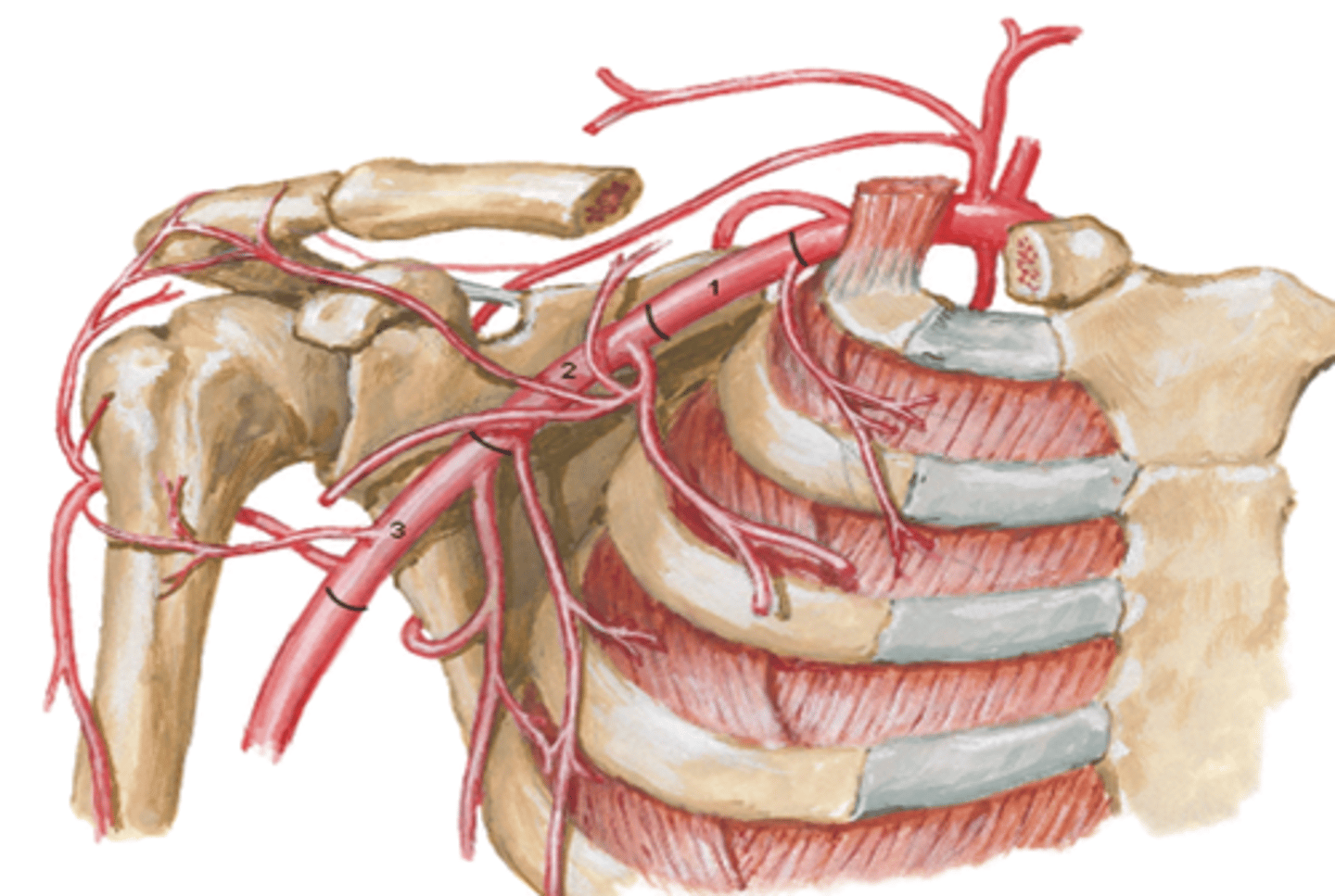
(Upper Limb Vasculature:) Axillary Artery Parts
Parts (in relationship to the pectoralis minor m.)
-1st part: between lateral border of 1st rib and medial border of pectoralis minor m.
-2nd part: posterior to pectoralis minor m.
-3rd part: between lateral border of pectoralis minor m. and inferior border of teres major m.
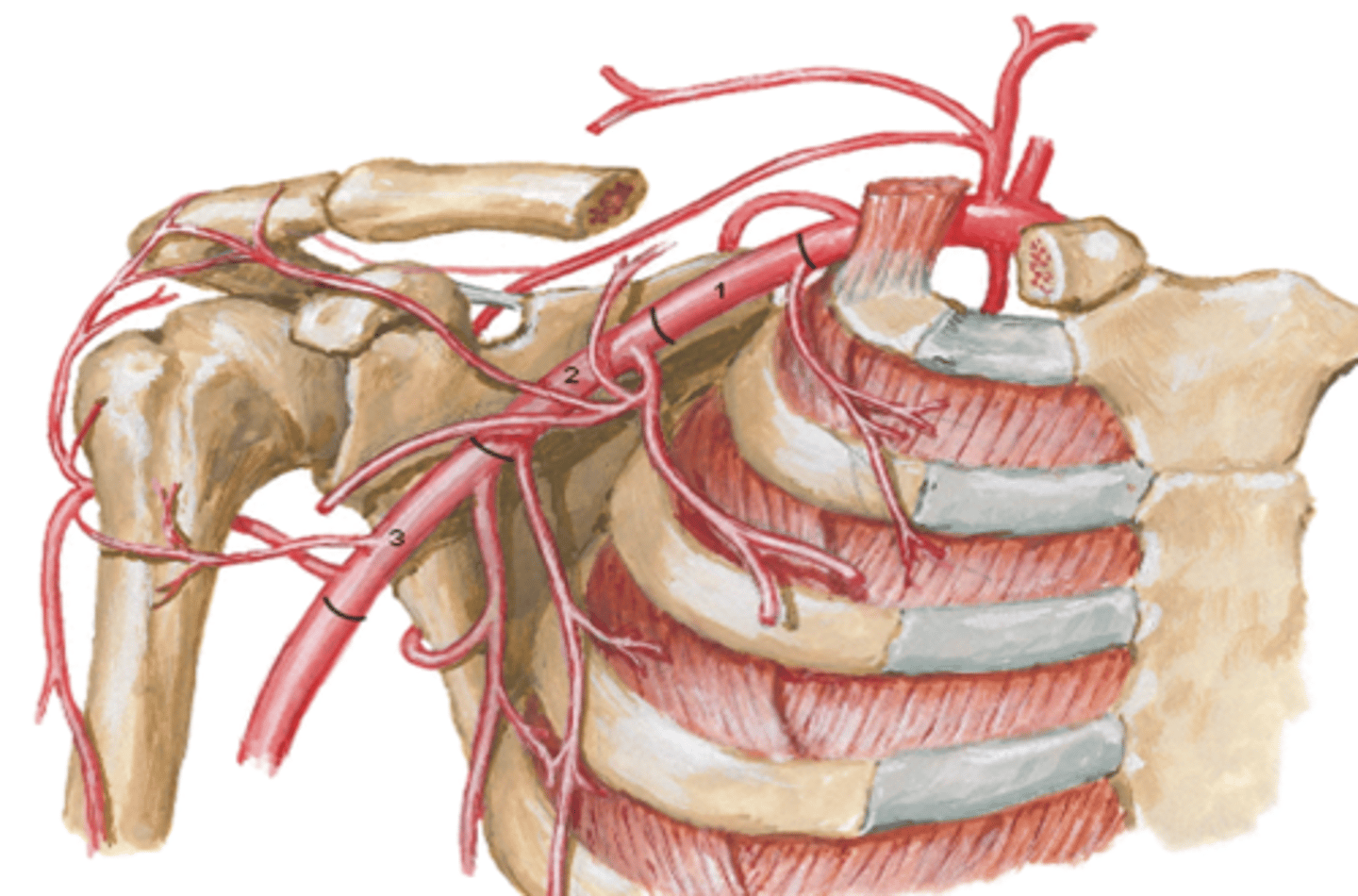
Axillary Artery Part 1
between lateral border of 1st rib and medial border of pectoralis minor m.
-Superior thoracic a.
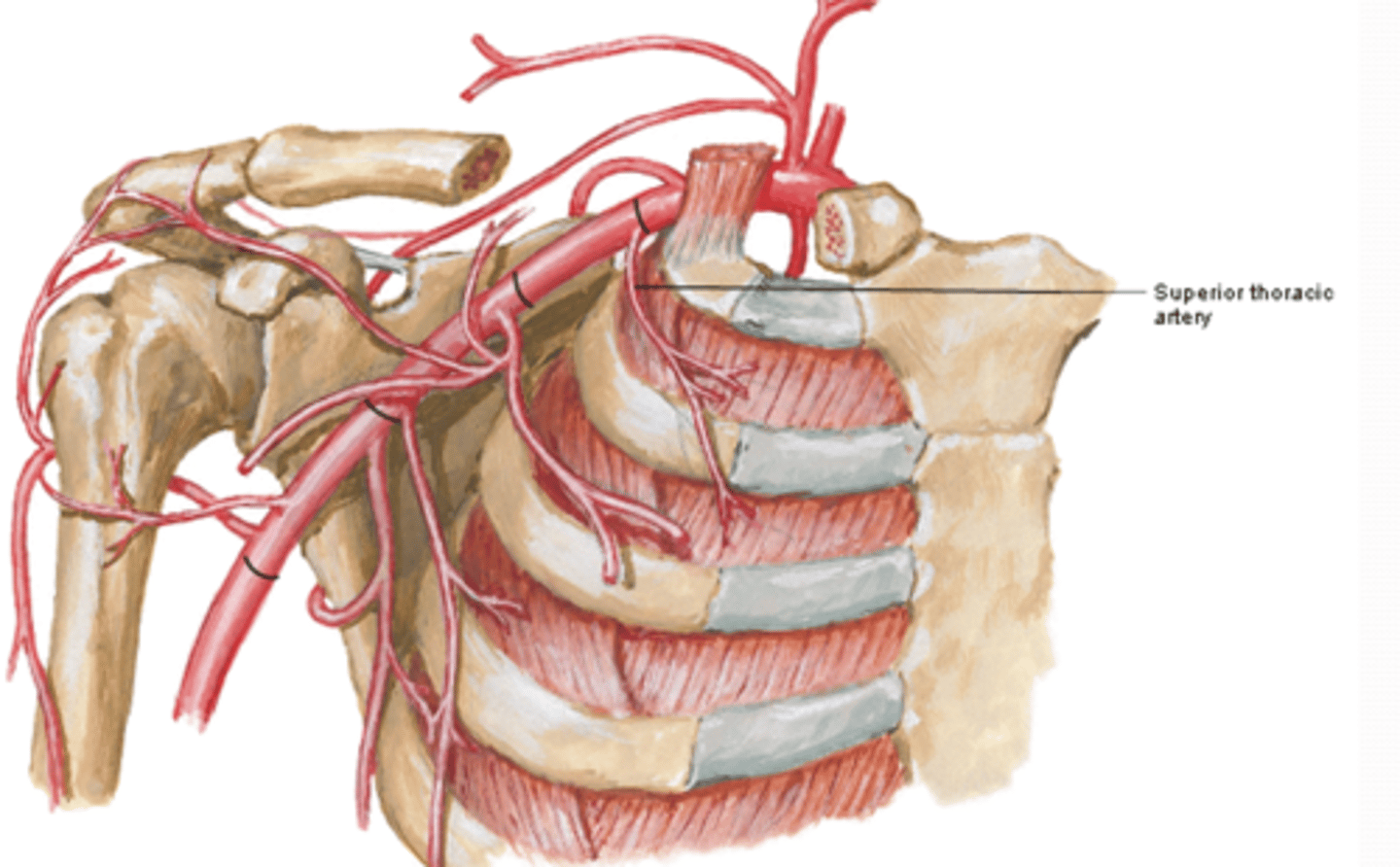
(Axillary Artery Part 1:) Superior Thoracic Artery
-Course: runs anteromedially along pectoralis minor m. à thoracic wall
-Supply: 1st and 2nd intercostal spaces and serratus anterior m.
Axillary Artery Part 2
posterior to pectoralis minor m.
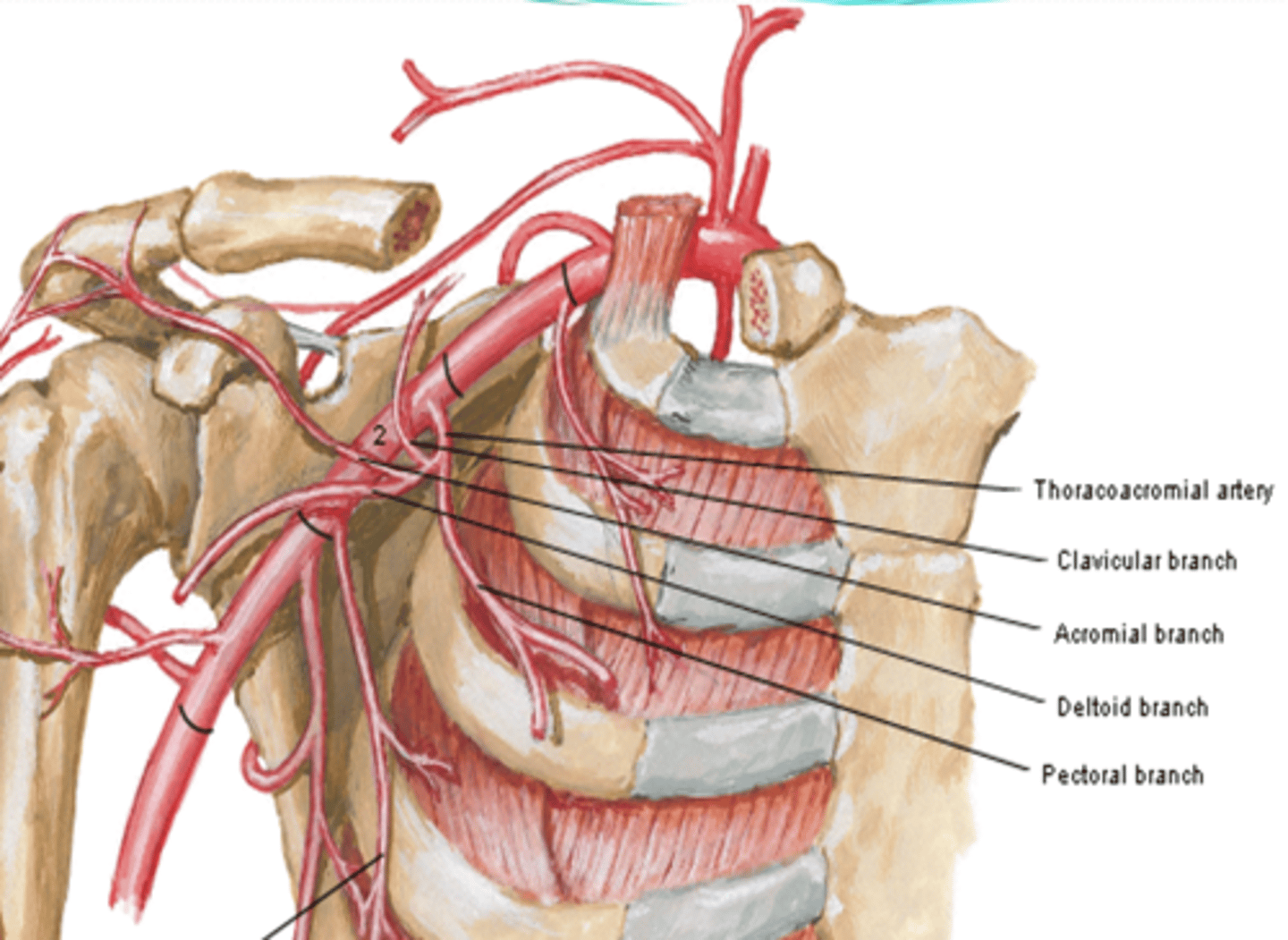
-Thoracoacromial a
-Lateral thoracic a.
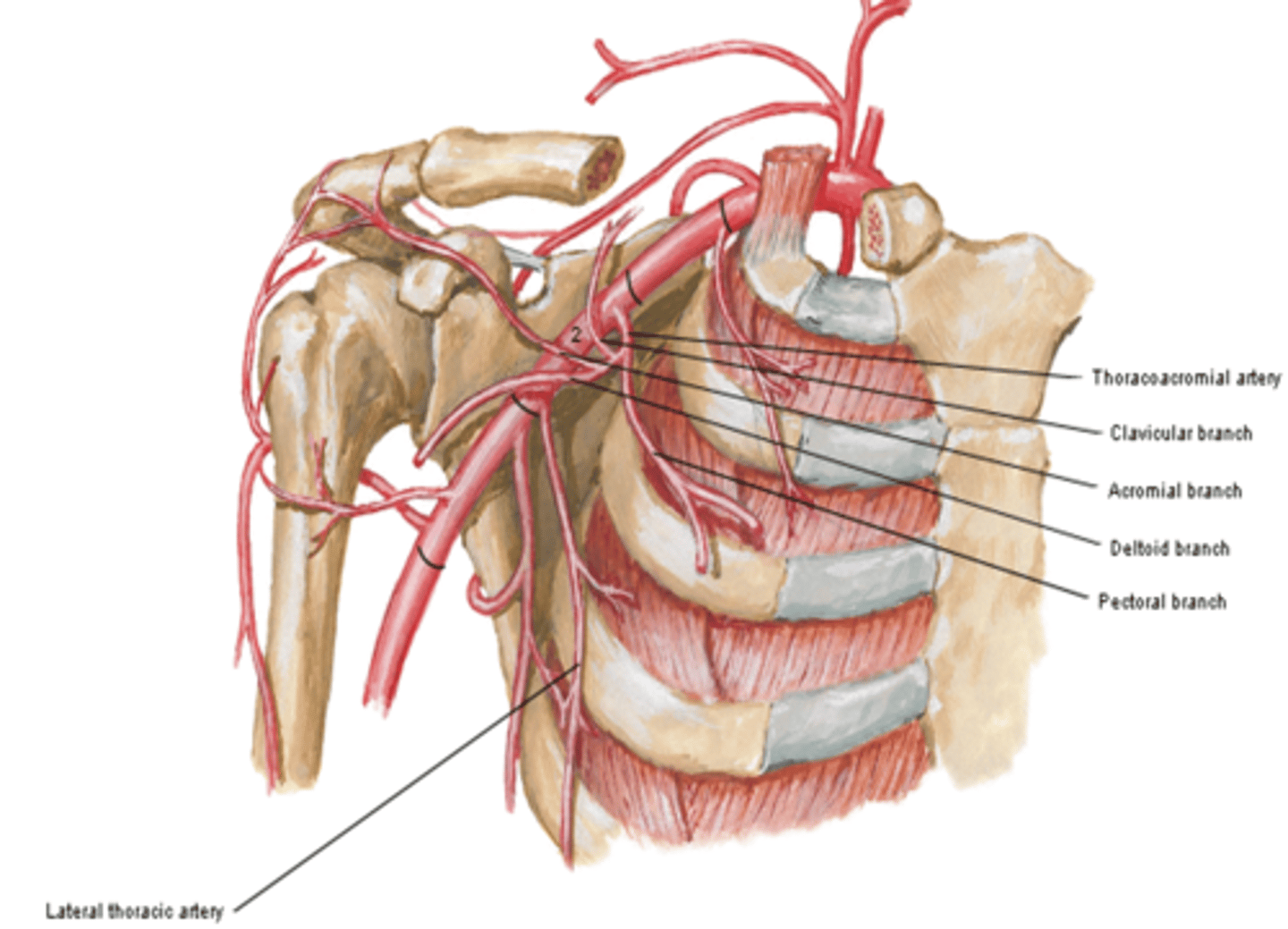
(Axillary Artery Part 2:) Thoracoacromial a
trunk providing the chest and shoulder regions
Branches
-Clavicular: clavicular area
-Acromial: major supplier of rotator cuff
-Deltoid: deltoid muscle and area
-Pectoral: pectoralis major and minor muscles
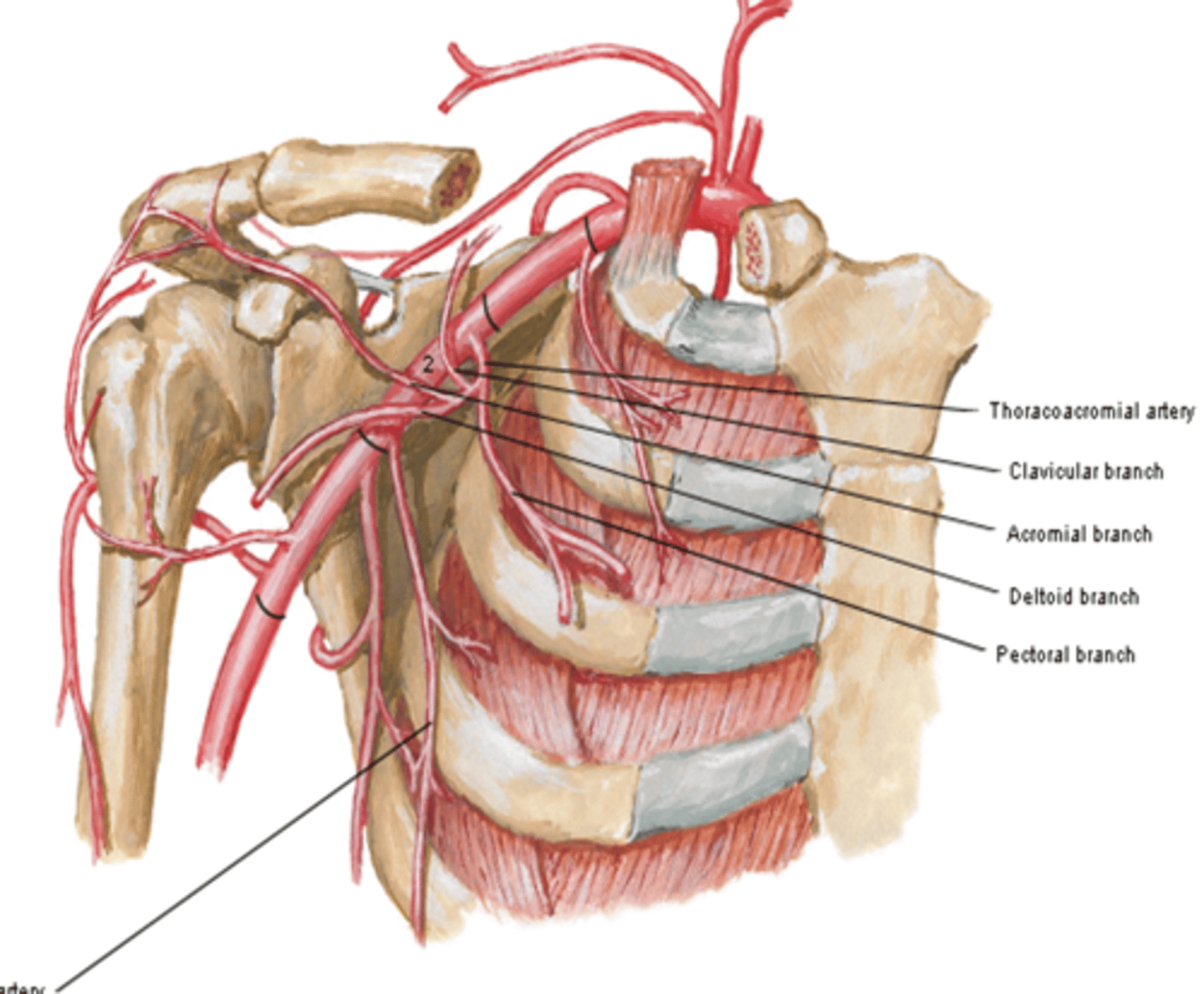
(Axillary Artery Part 2:) Thoracoacromial artery branches
-Clavicular: clavicular area
-Acromial: major supplier of rotator cuff
-Deltoid: deltoid muscle and area
-Pectoral: pectoralis major and minor muscles
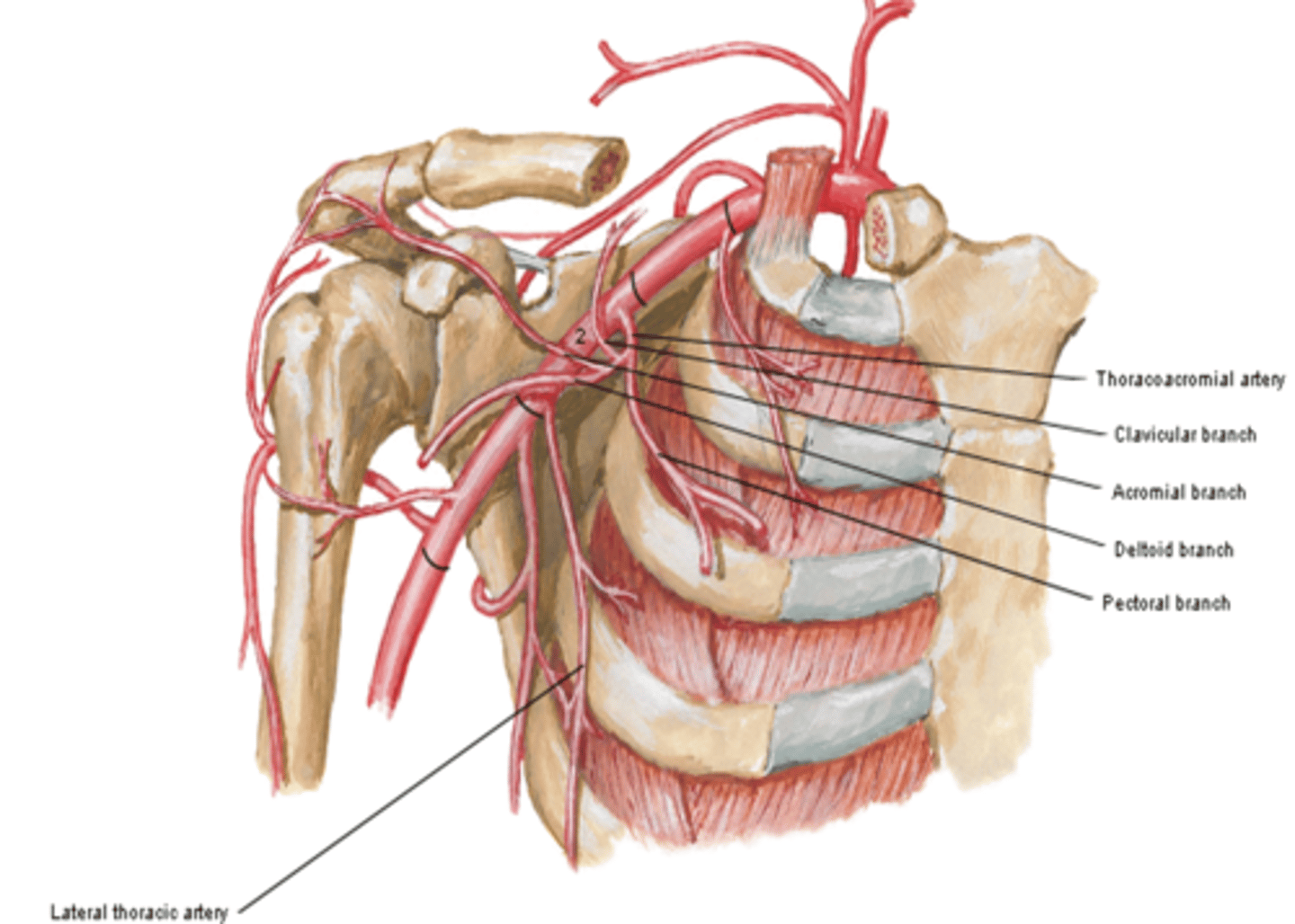
(Thoracoacromial artery branches) Clavicular:
clavicular area
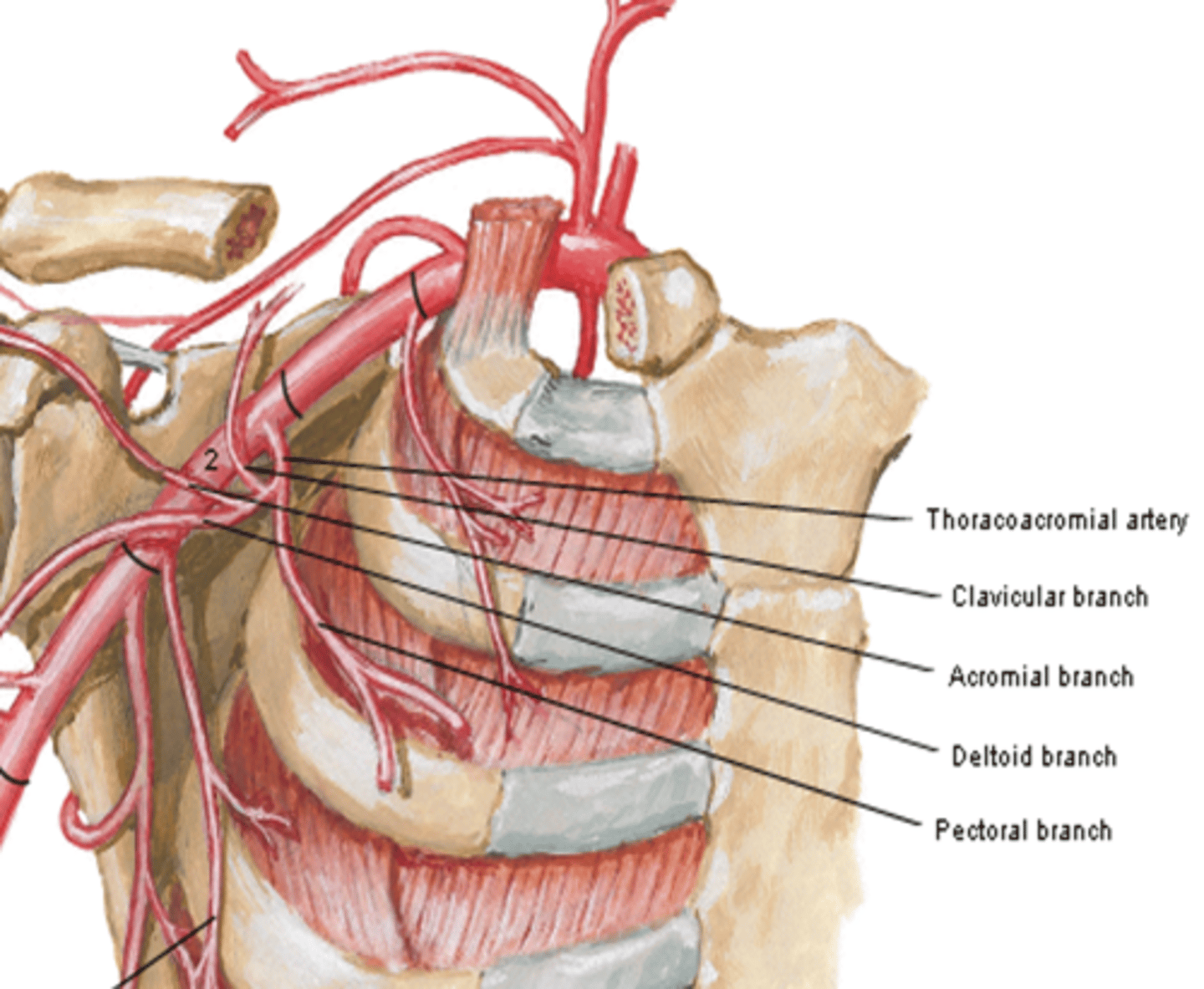
(Thoracoacromial artery branches) Acromial:
major supplier of rotator cuff
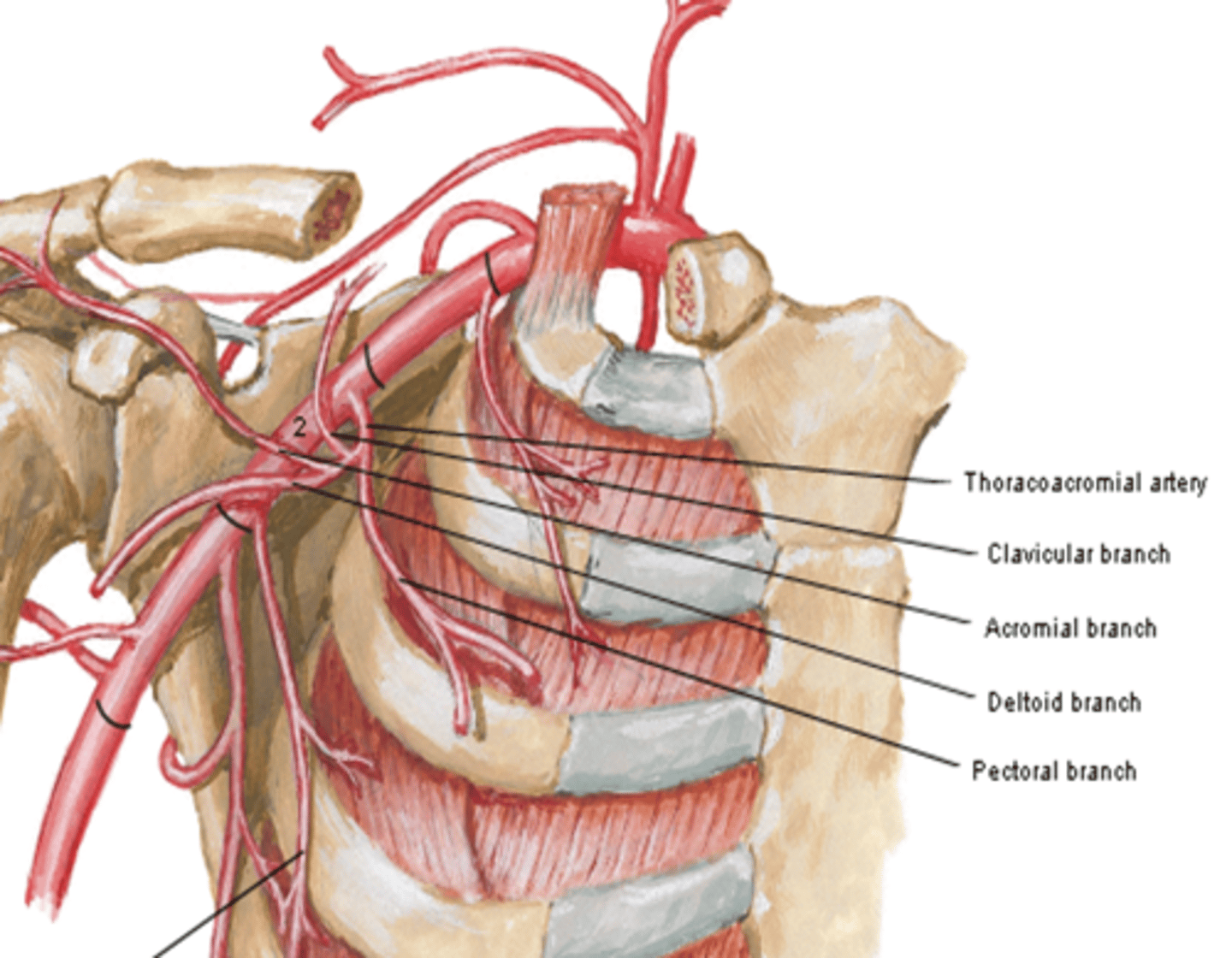
(Thoracoacromial artery branches) Deltoid:
deltoid muscle and area
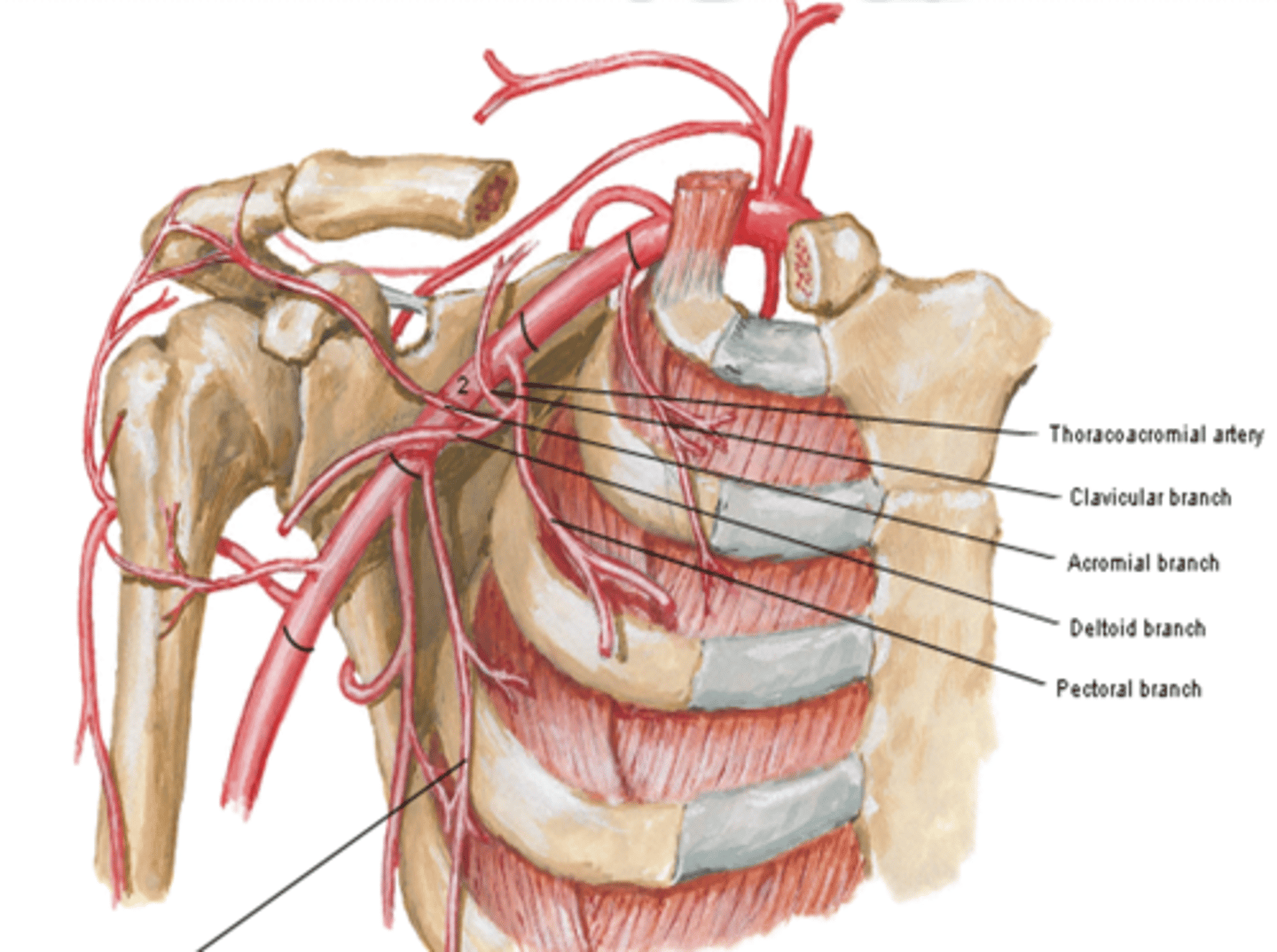
(Thoracoacromial artery branches) Pectoral:
pectoralis major and minor muscles
(Axillary Artery Part 2:) Lateral thoracic a.
-Course: descends along lateral border of pectoralis minor m. to the thoracic wall
-Supply: serratus anterior m. and lateral aspect of breast
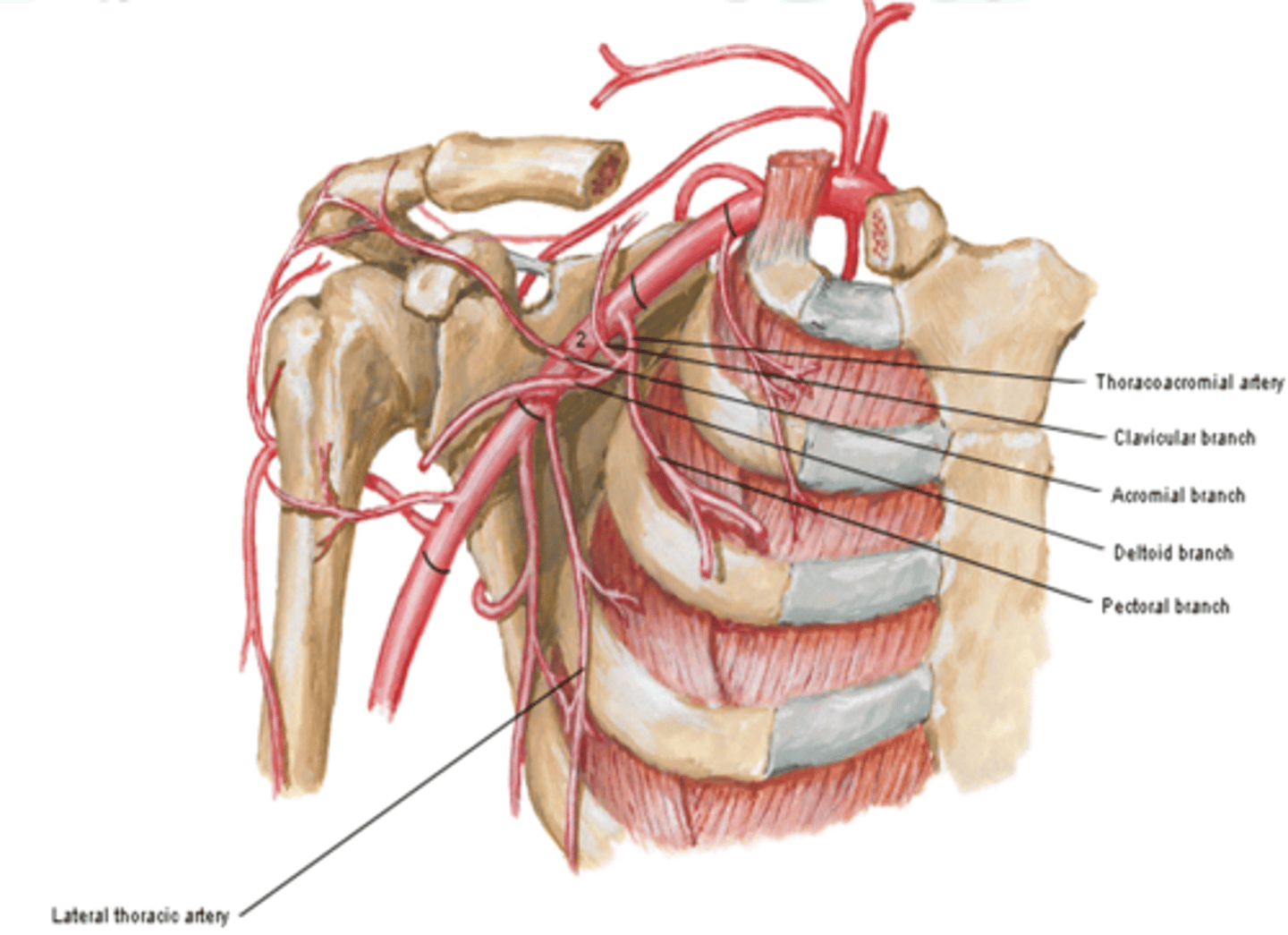
Axillary Artery Part 3
between lateral border of pectoralis minor m. and inferior border of teres major m.
-Subscapular a.
-Anterior & Posterior circumflex aa.
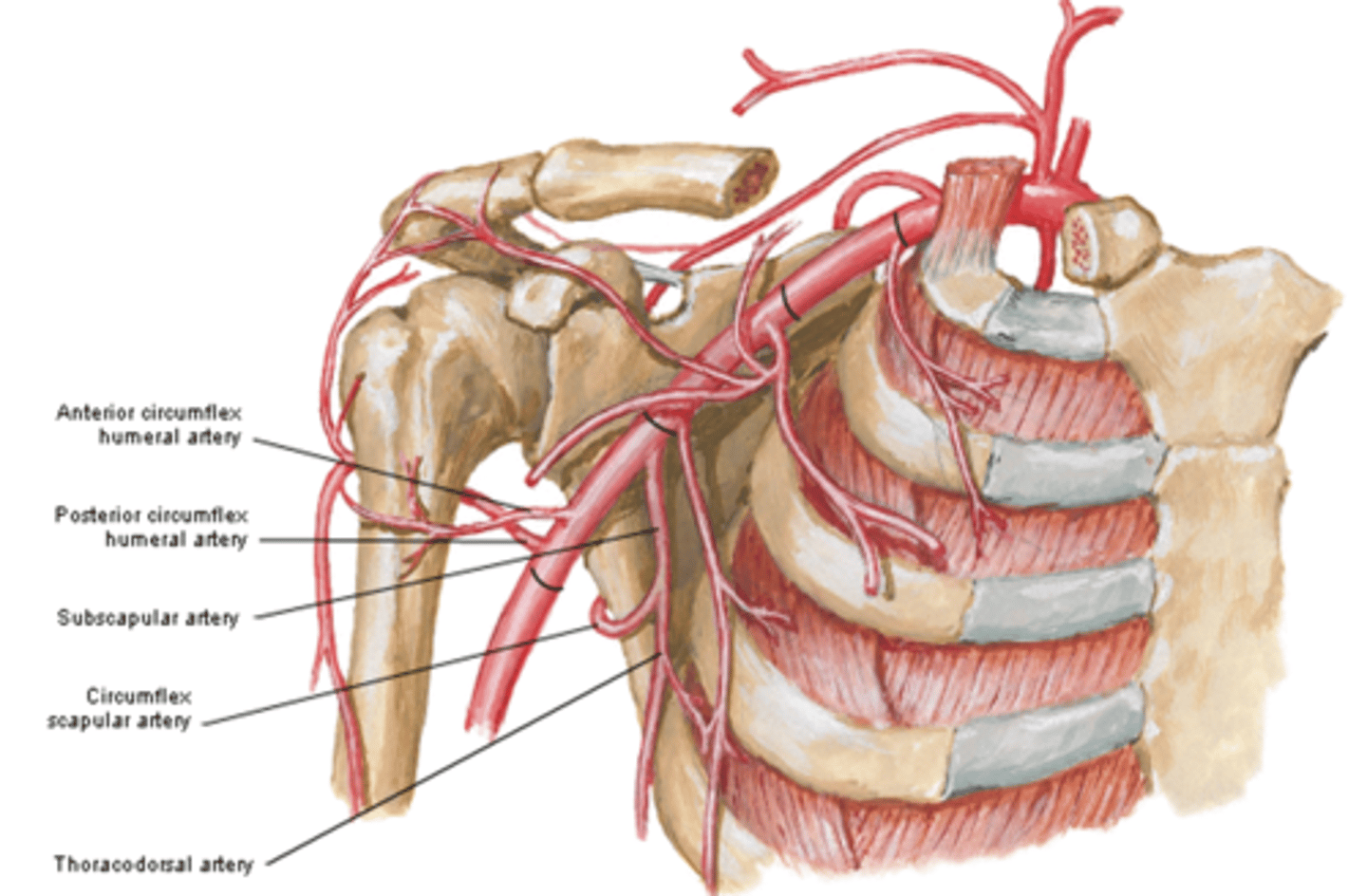
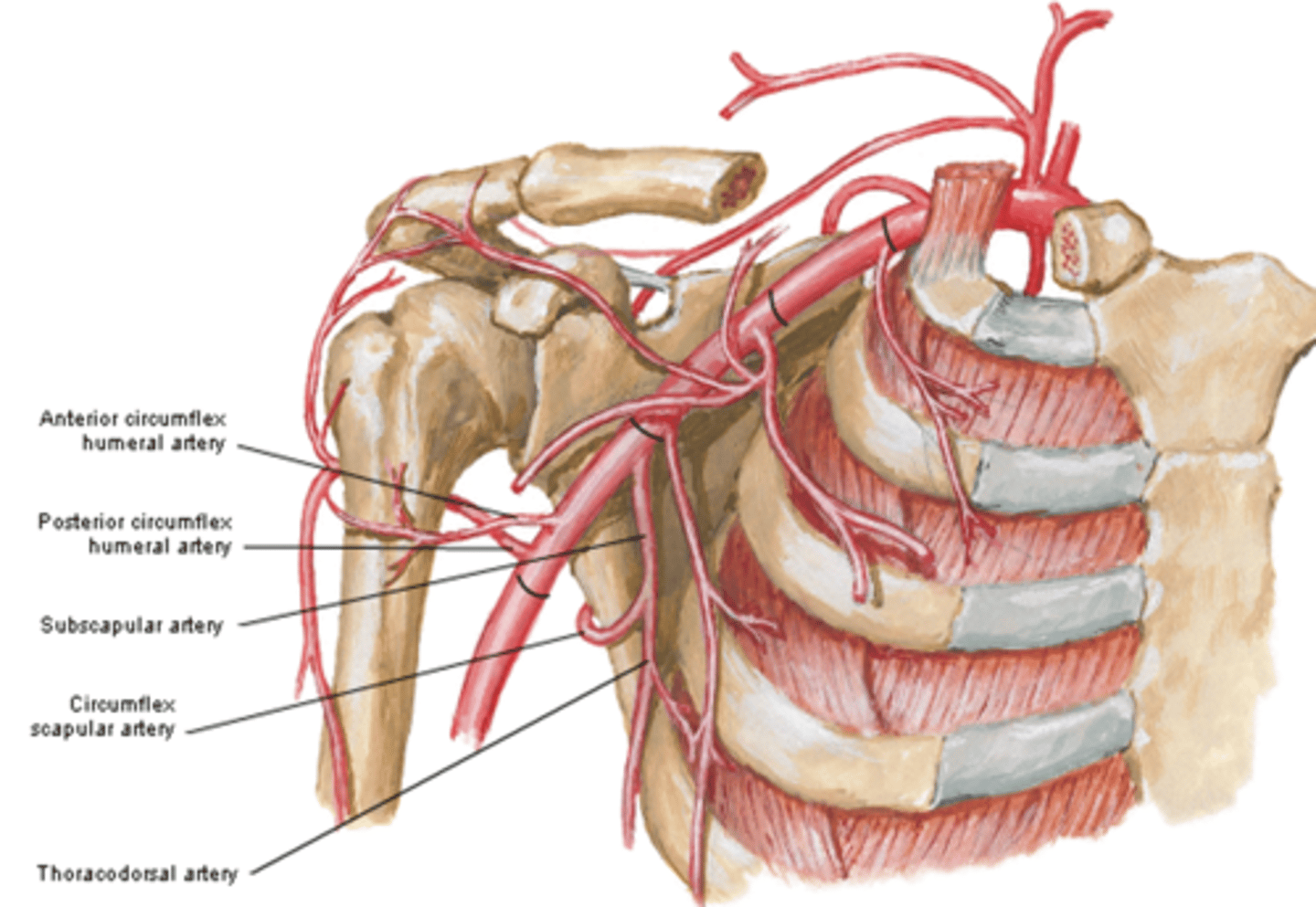
(Axillary Artery Part 3:) Subscapular artery
-Course: largest branch of axillary a. that descends along lateral border of the subscapularis muscle
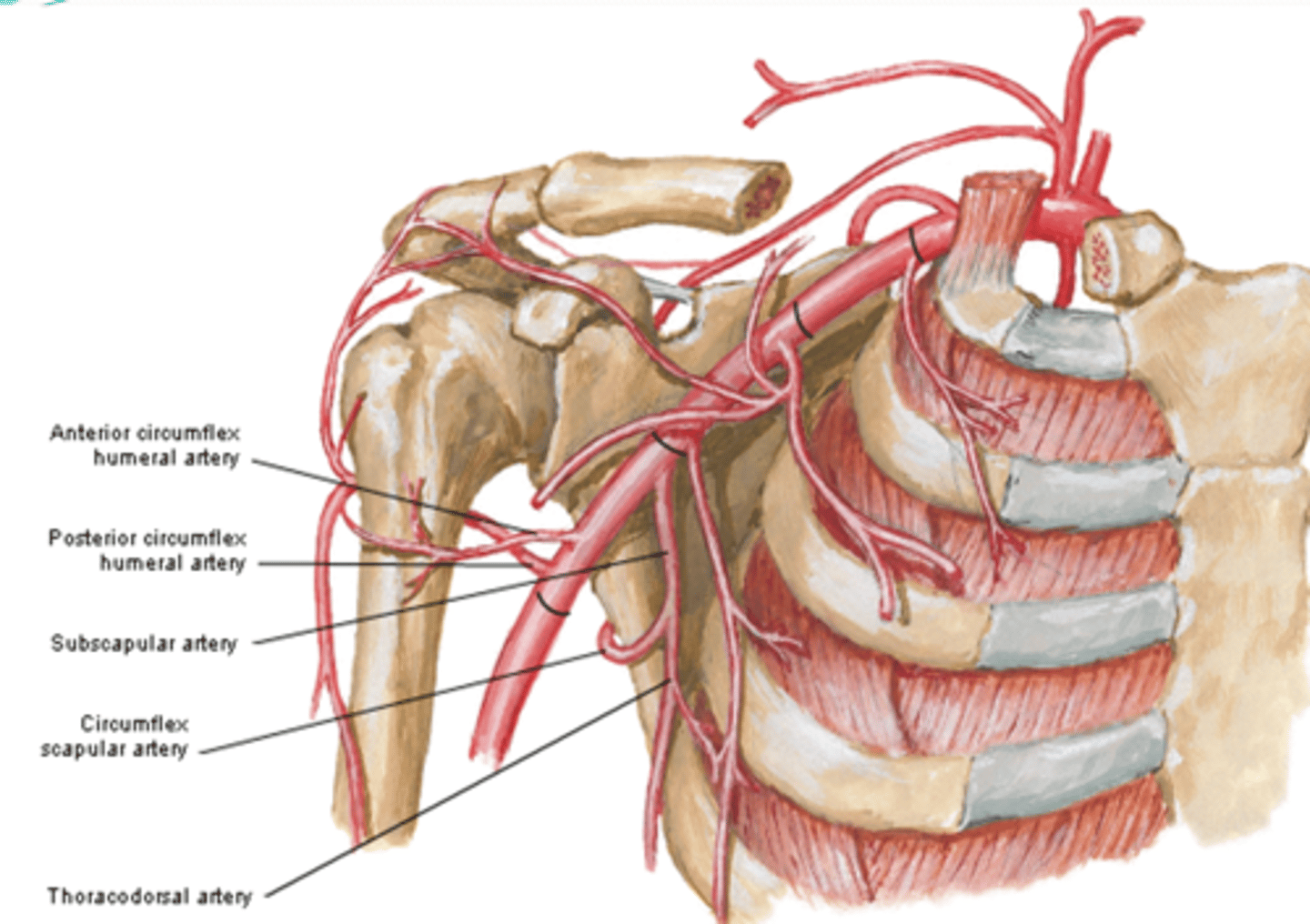
(Axillary Artery Part 3:) Subscapular artery branches
Circumflex scapular a.: curves posteriorly around lateral border of scapula and supplies muscles on dorsum of scapula
Thoracodorsal a.: descends to the inferior angle of the scapula supplying muscles in the region, particularly the latissimus dorsi
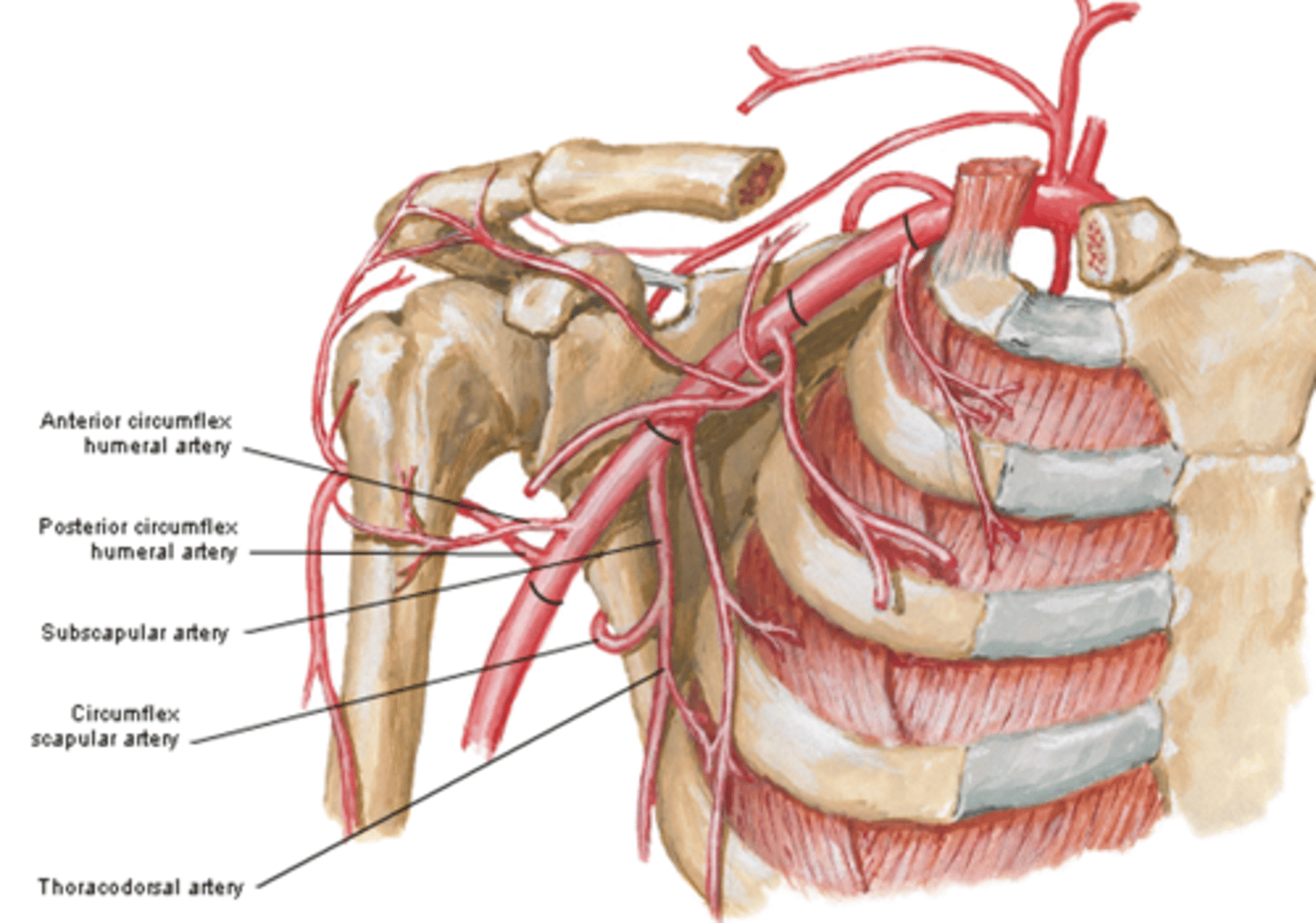
(Subscapular artery branches:) Circumflex scapular a.
curves posteriorly around lateral border of scapula and supplies muscles on dorsum of scapula
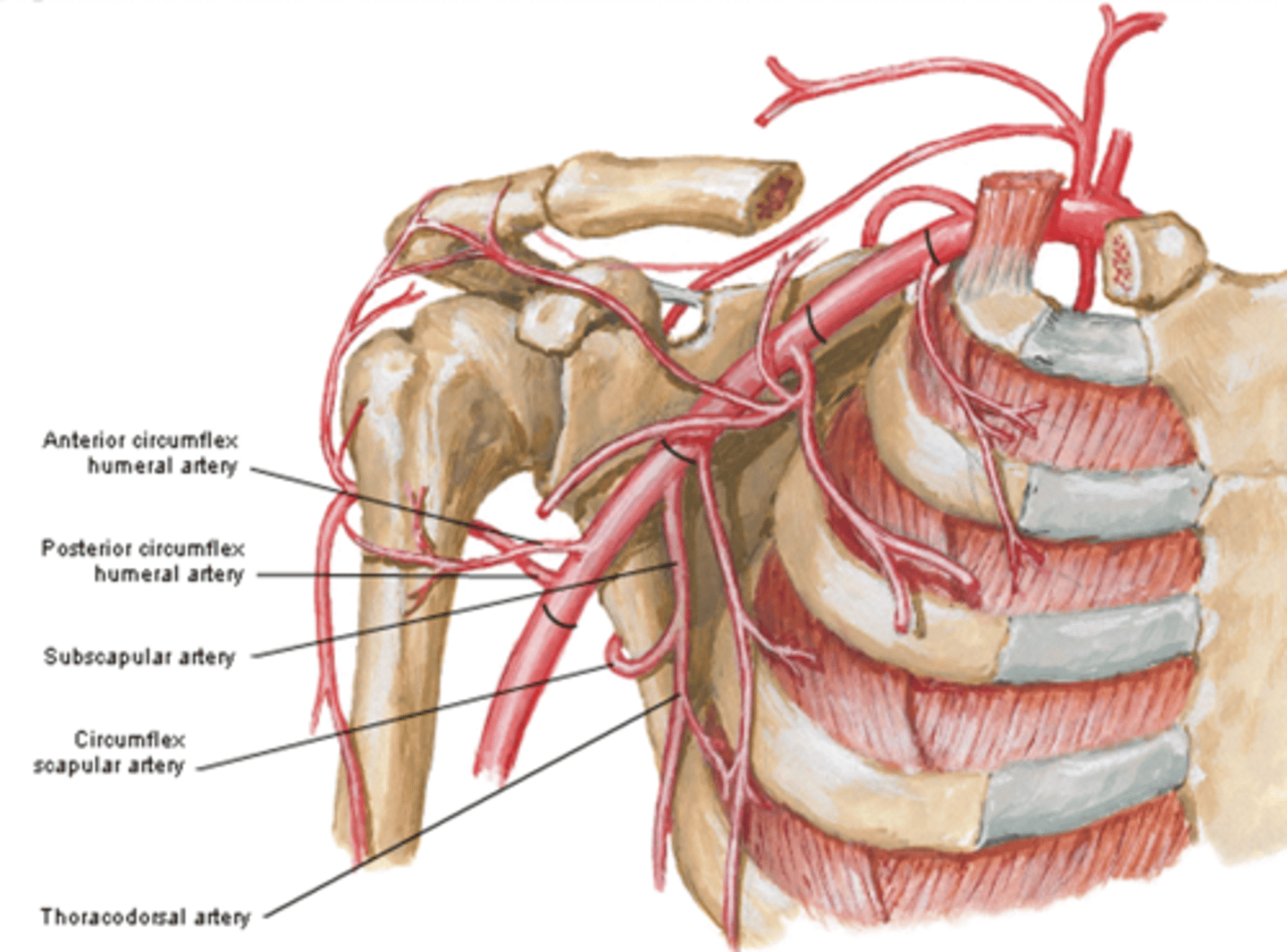
(Subscapular artery branches:) Thoracodorsal a.
descends to the inferior angle of the scapula supplying muscles in the region, particularly the latissimus dorsi
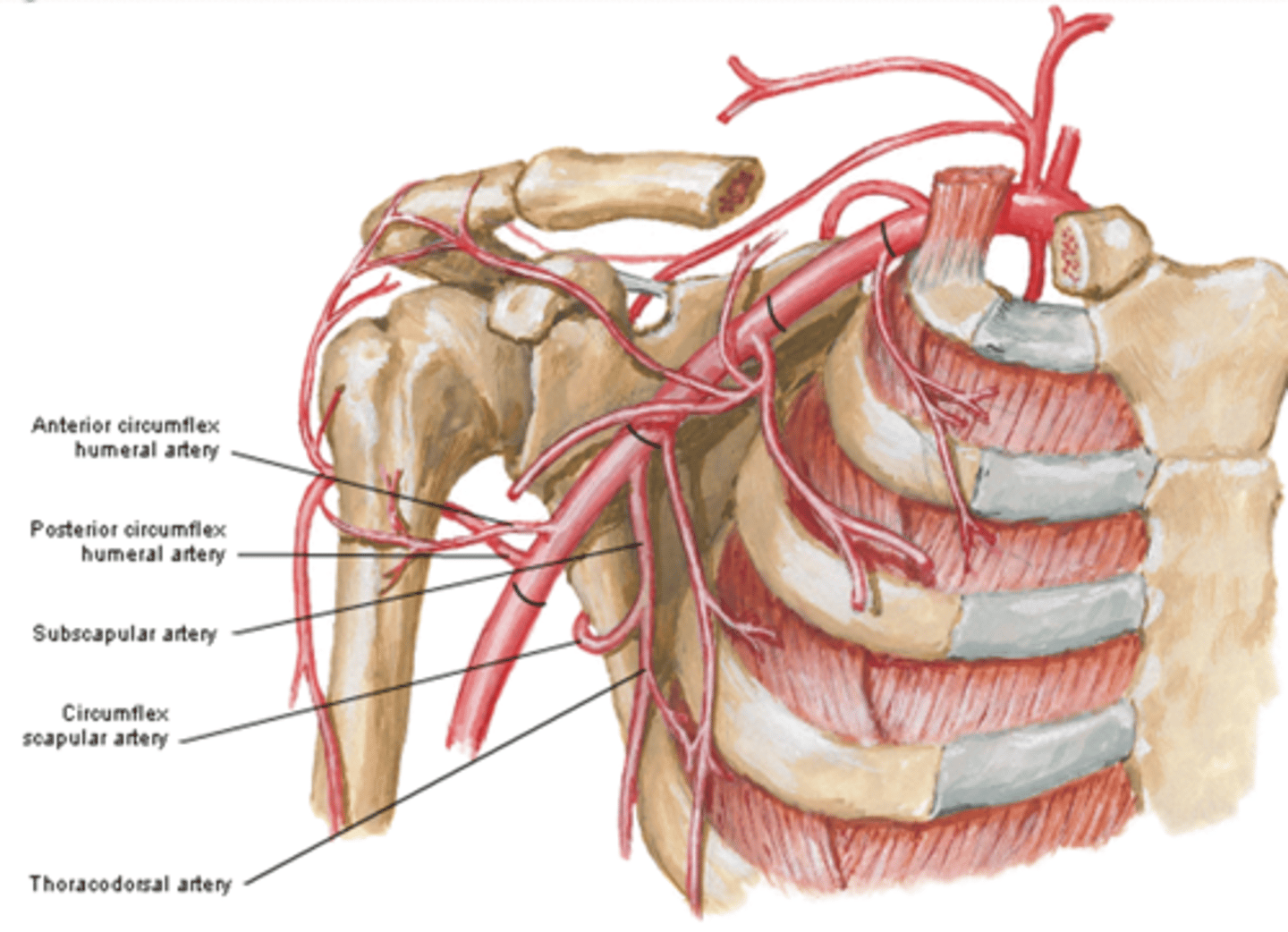
(Axillary Artery Part 3:) Anterior & Posterior circumflex aa.
-Course: they encircle the surgical neck of the humerus, anastomosing laterally with each other
-Supply: glenohumeral joint and surrounding muscles
(Upper Limb Vasculature:) Brachial Artery
-Provides main arterial supply to the arm
-Course: continuation of the axillary a. that begins at the inferior border of teres major àruns in the arm medial to the humerus, and enters the forearm lateral to the median n. and deep to the bicipital aponeurosis to end in the cubital fossa, as it divides into the radial and ulnar aa.
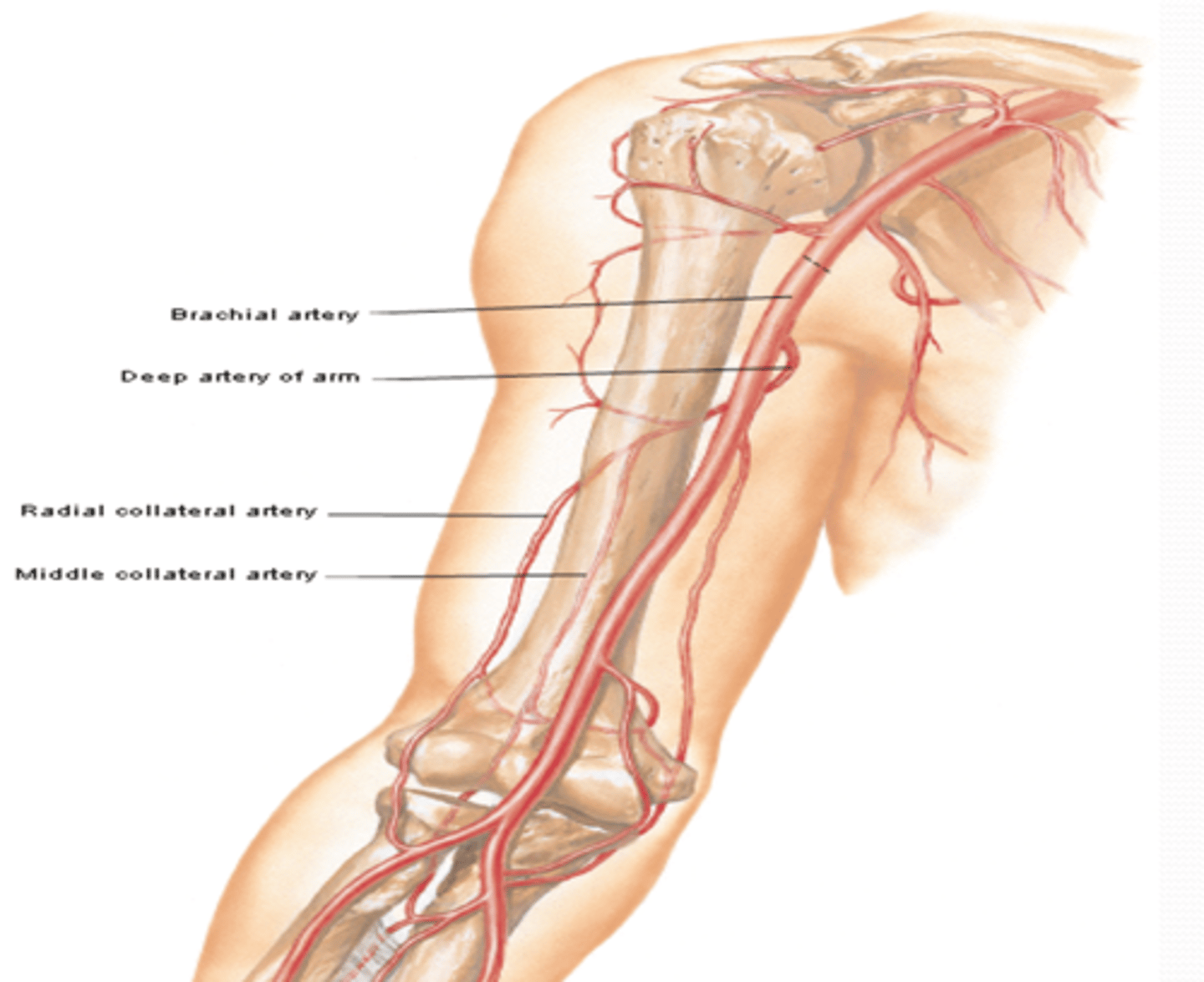
(Upper Limb Vasculature:) Brachial Artery Branches
-Deep artery of arm: Middle and radial collateral aa
-Humeral nutrient a.
-Superior ulnar collateral a.
-Inferior ulnar collateral a.
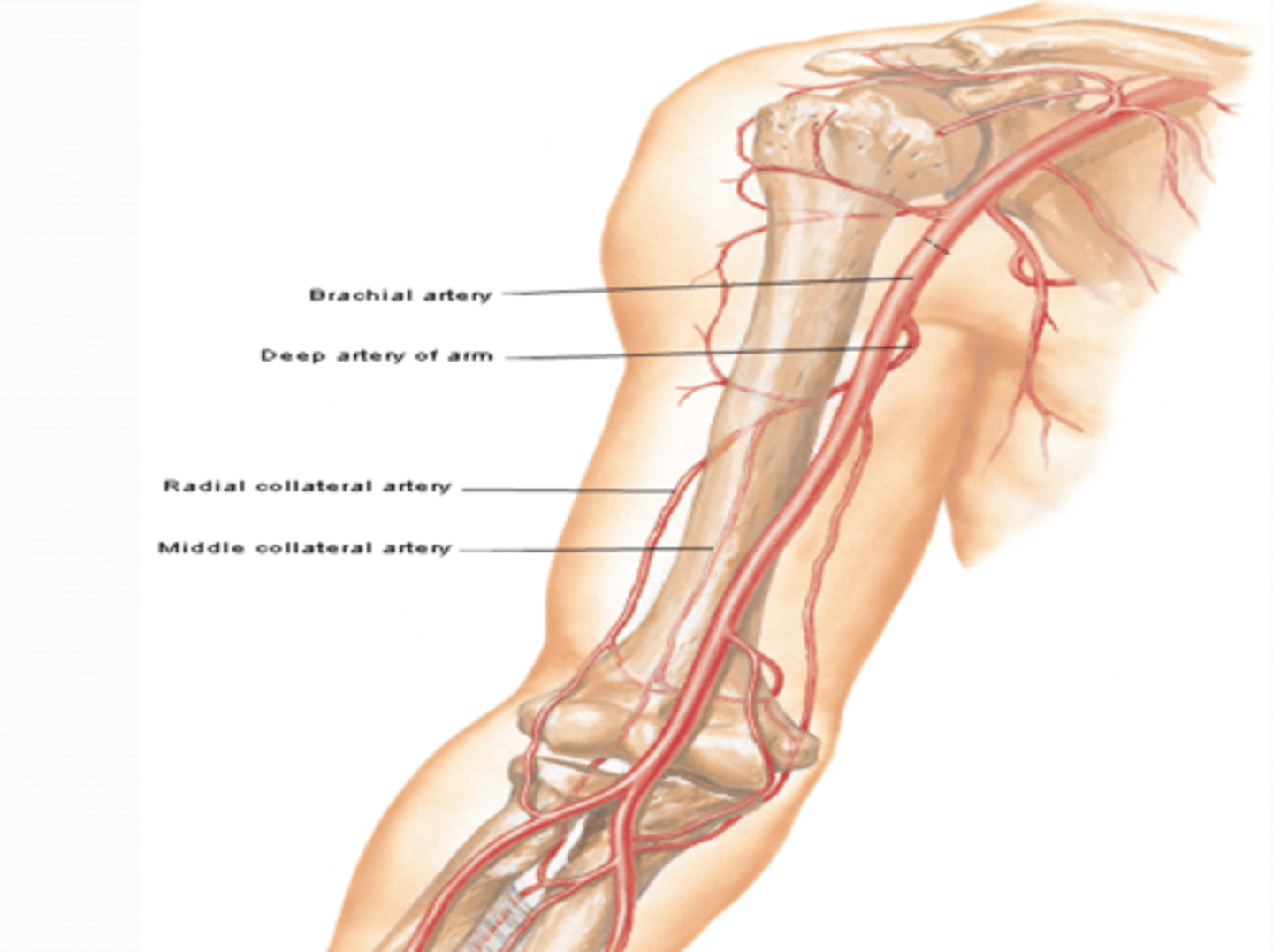
(Brachial Artery Branches: Deep artery of arm: ) Middle and radial collateral arteries
Course: most superior and largest branch of brachial a. à runs with radial n. in radial groove
Branches
-Middle and radial collateral aa.: participate in arterial anastomose around elbow
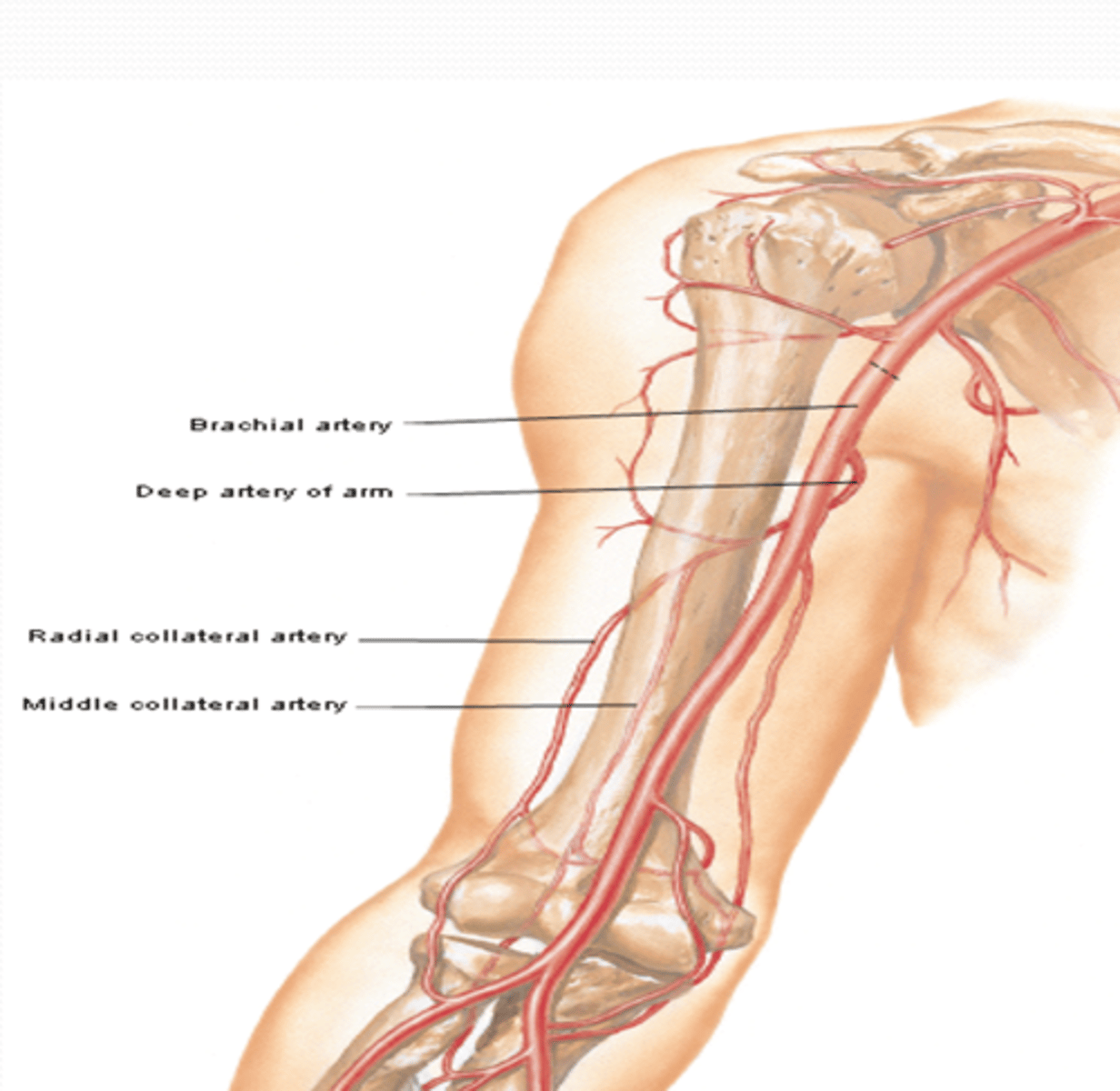
(Brachial Artery Branches:) Humeral nutrient artery
Course: arises around middle of arm -> enters nutrient canal on humerus and supplies the bone marrow
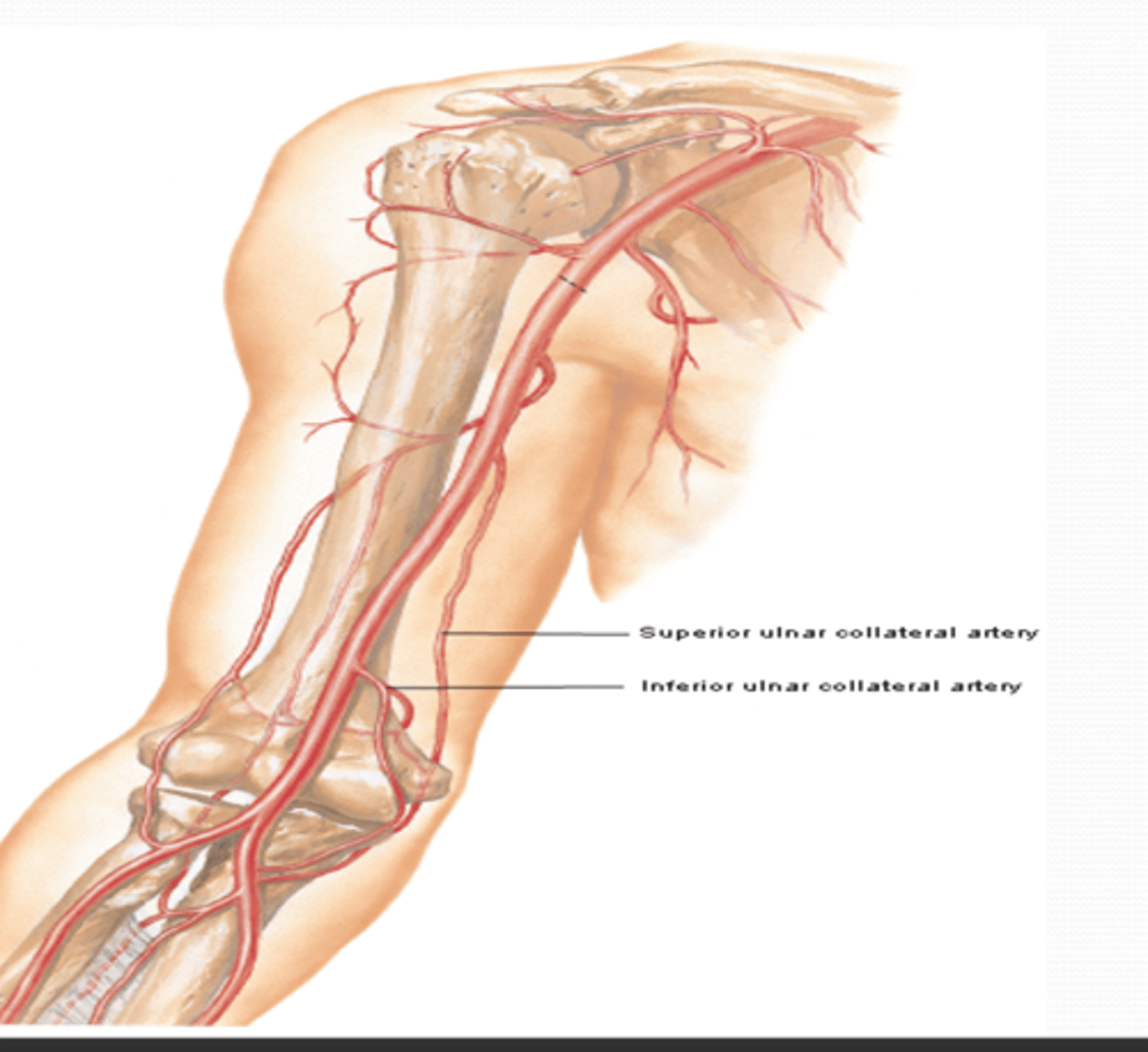
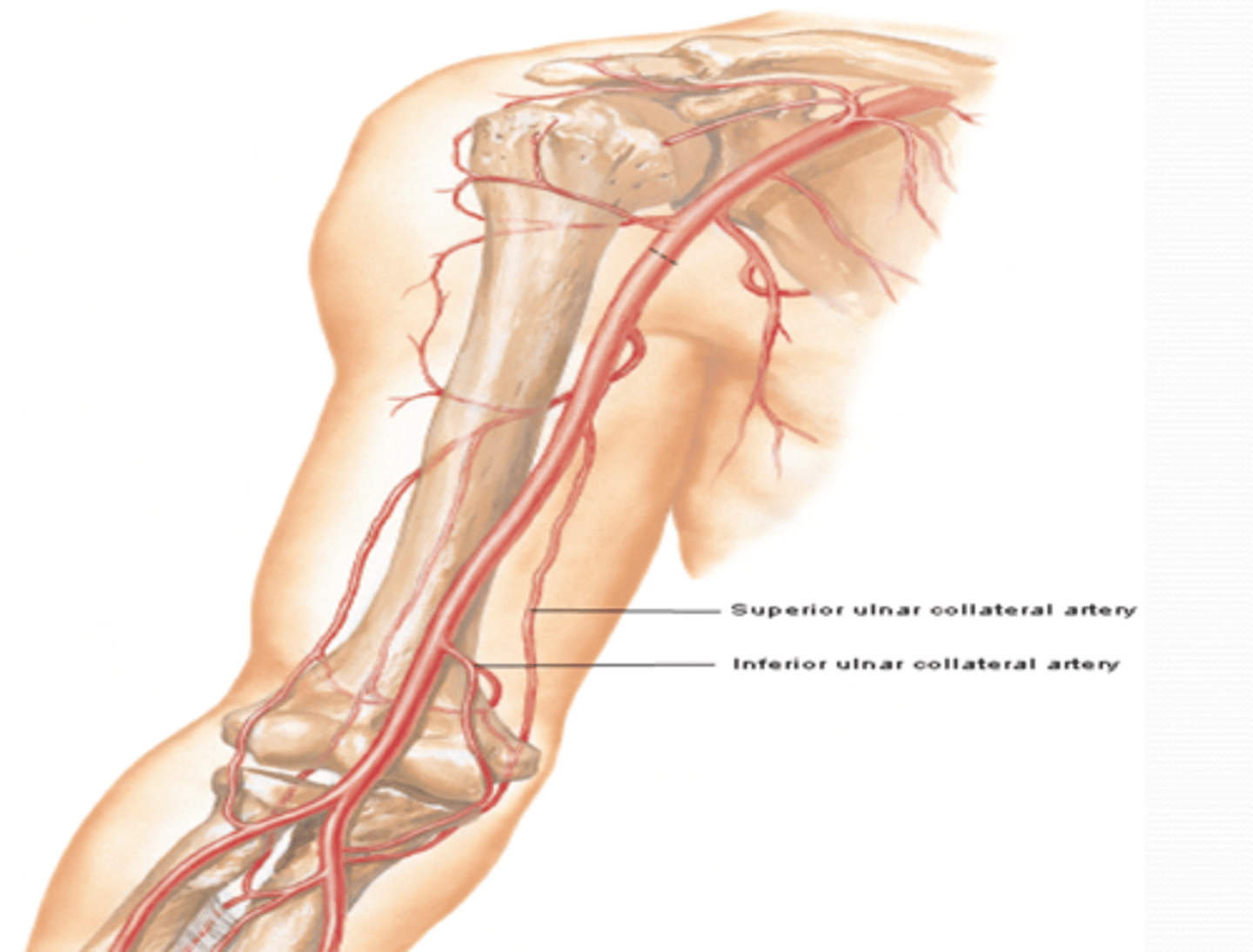
(Brachial Artery Branches:) Superior Ulnar Collateral Artery
-Course: descends in the arm towards the elbow, accompanying the ulnar n. posterior to medial epicondyle
-Supply: participates in arterial anastomose around elbow
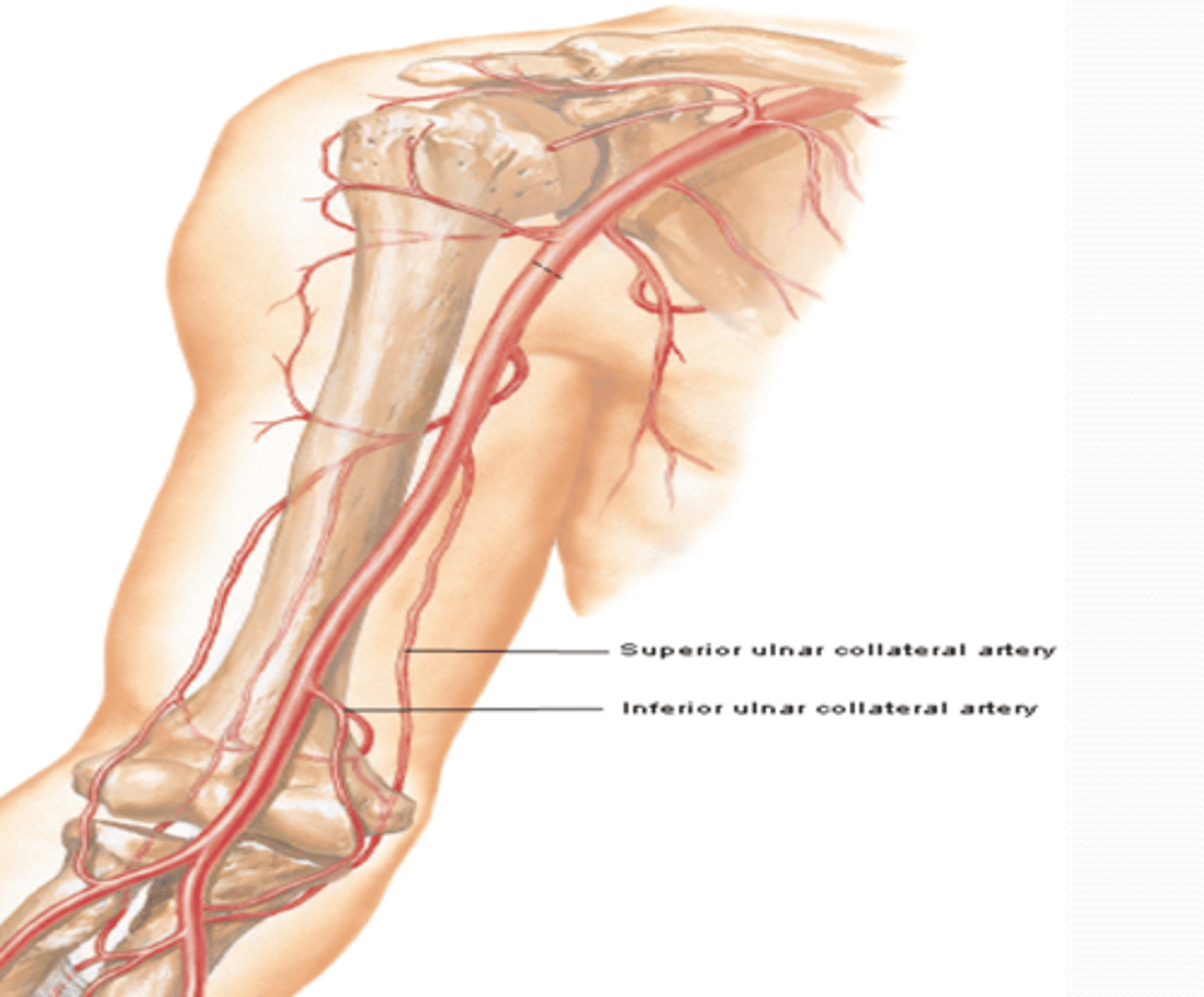
(Brachial Artery Branches:) Inferior ulnar collateral artery
-Course: descends in the arm towards the elbow anterior to medial epicondyle
-Supply: participates in arterial anastomose around elbow
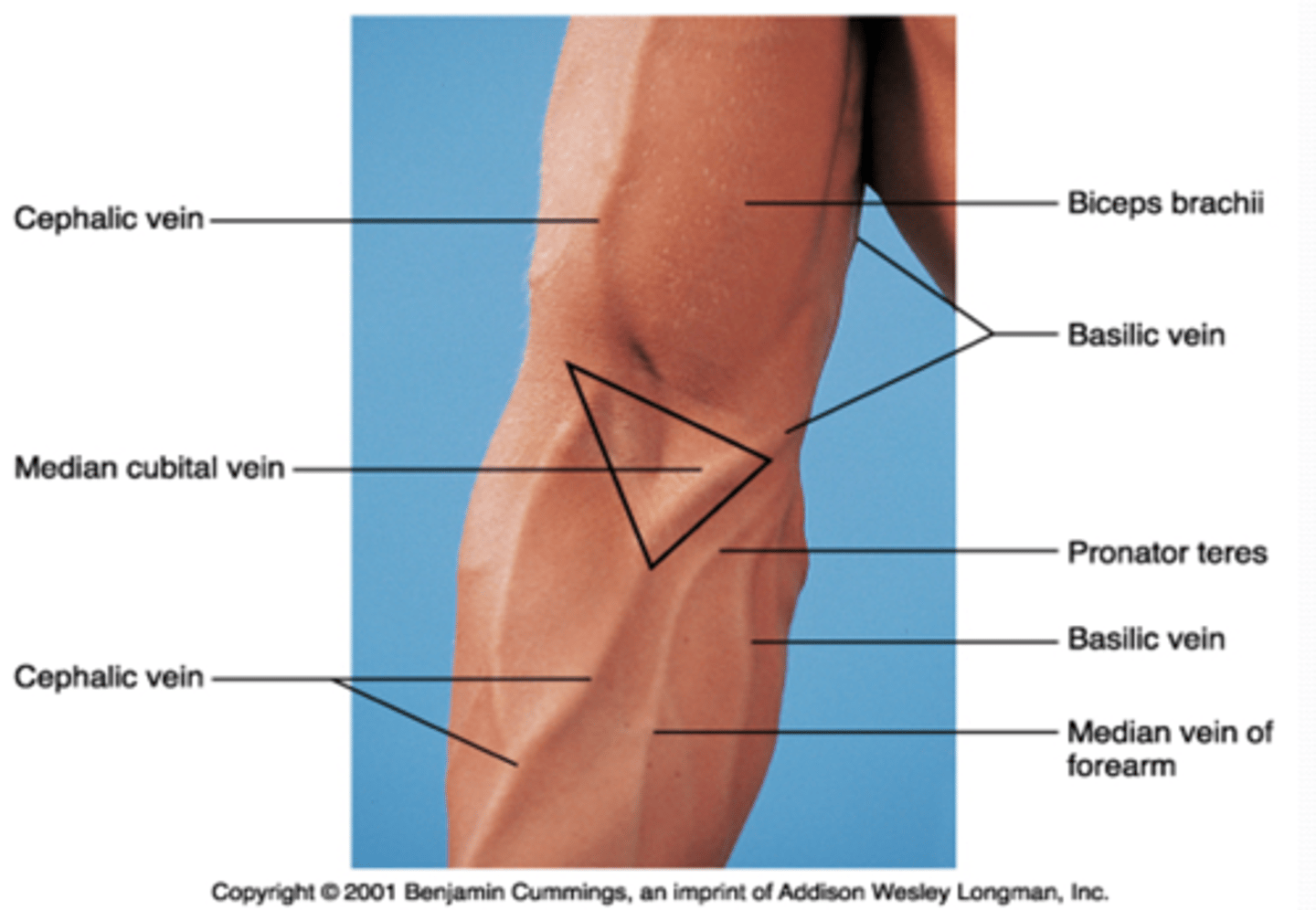
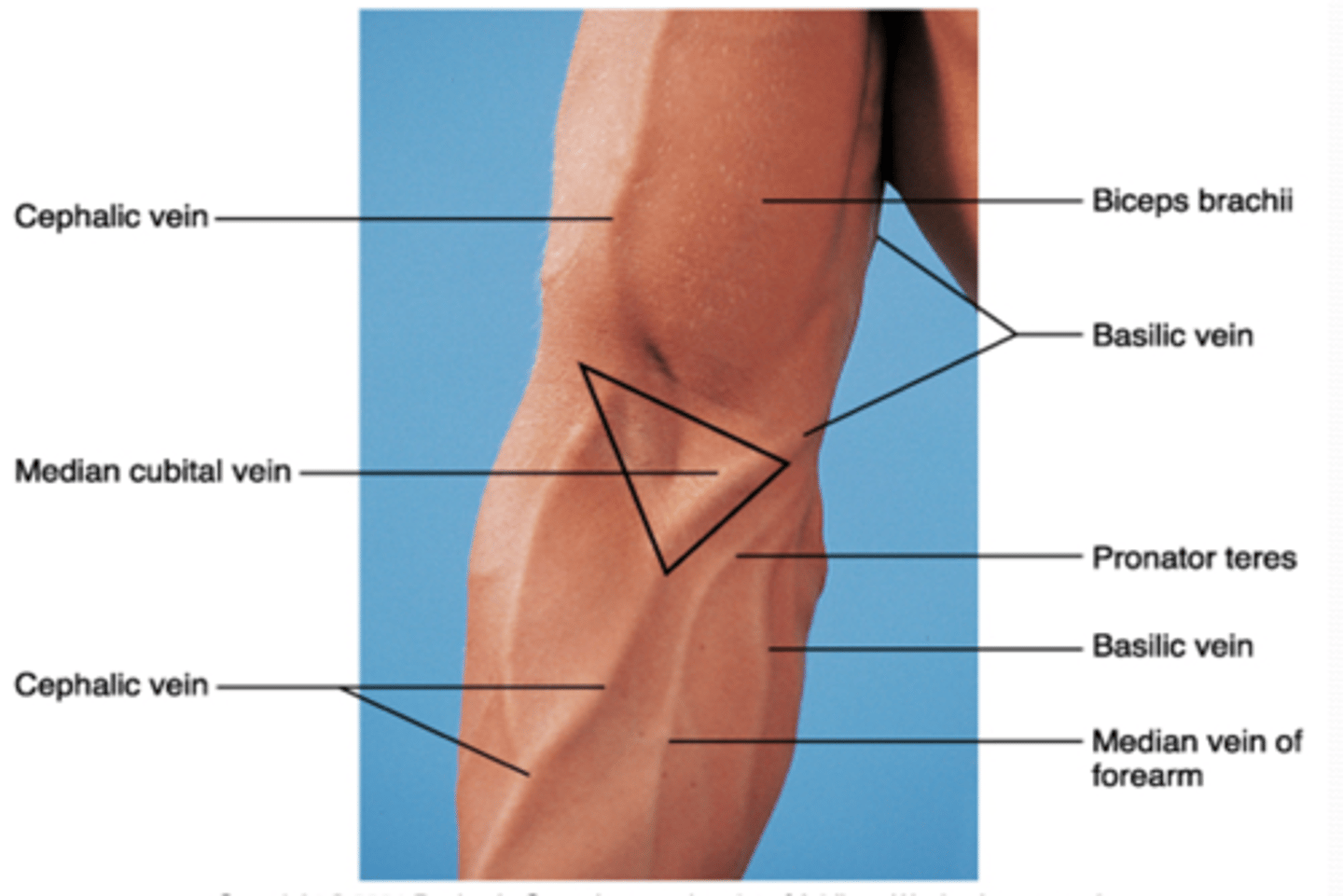
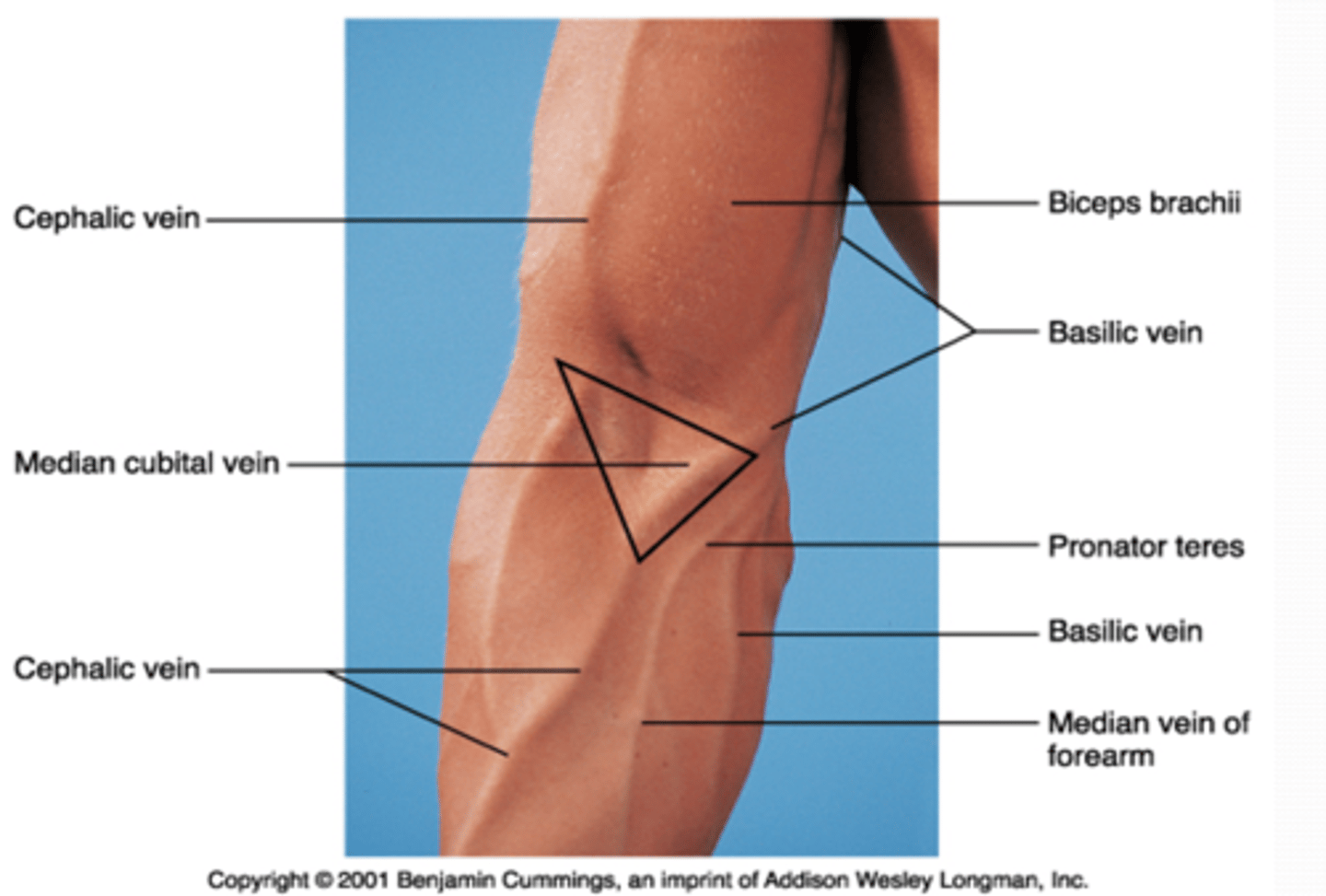
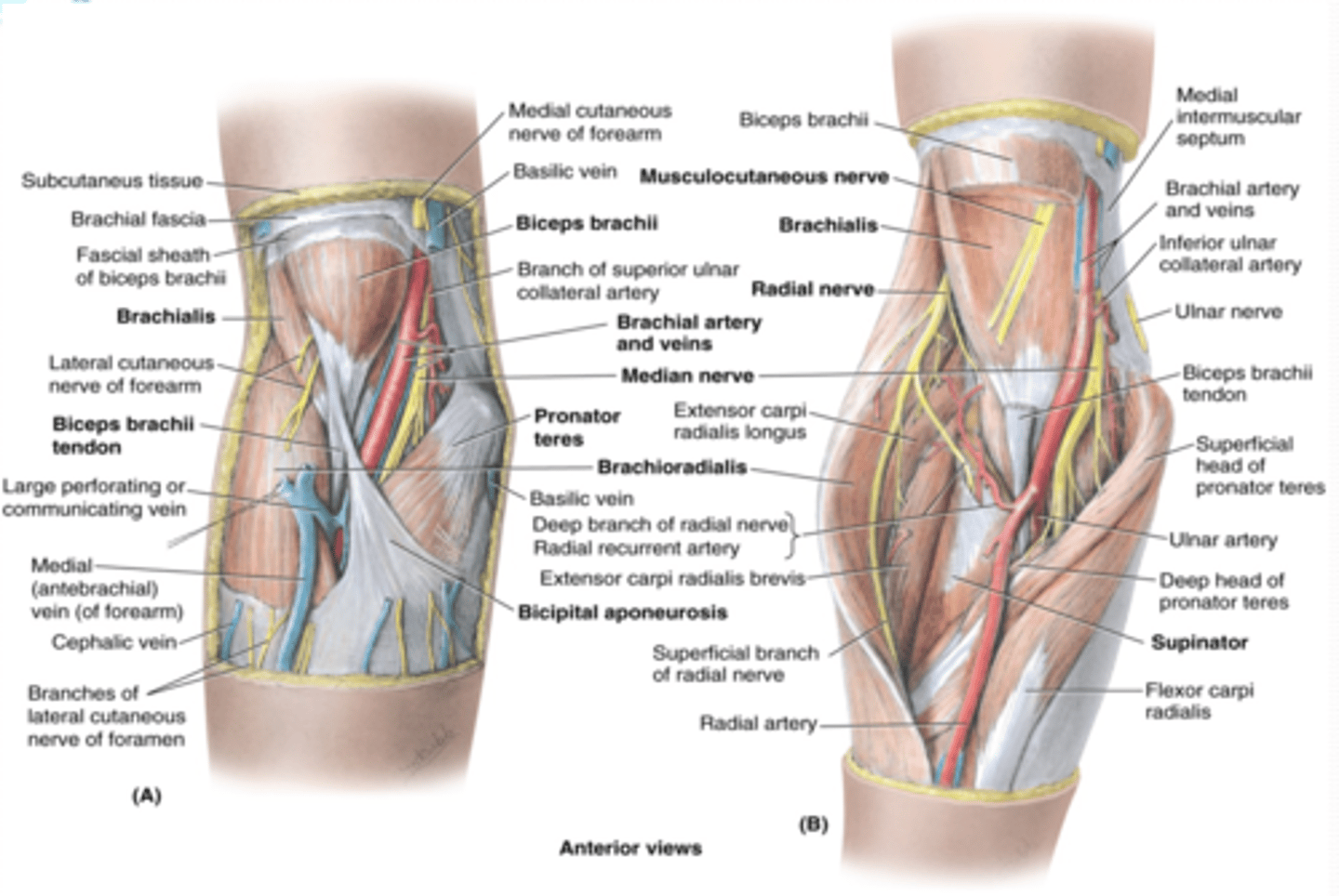
(Upper Limb Vasculature:) Cubital Fossa Location
triangular space on anterior aspect of elbow
(Upper Limb Vasculature:) Cubital Fossa Boundaries
-Superior
-Medial
-Lateral
-Floor
-Roof
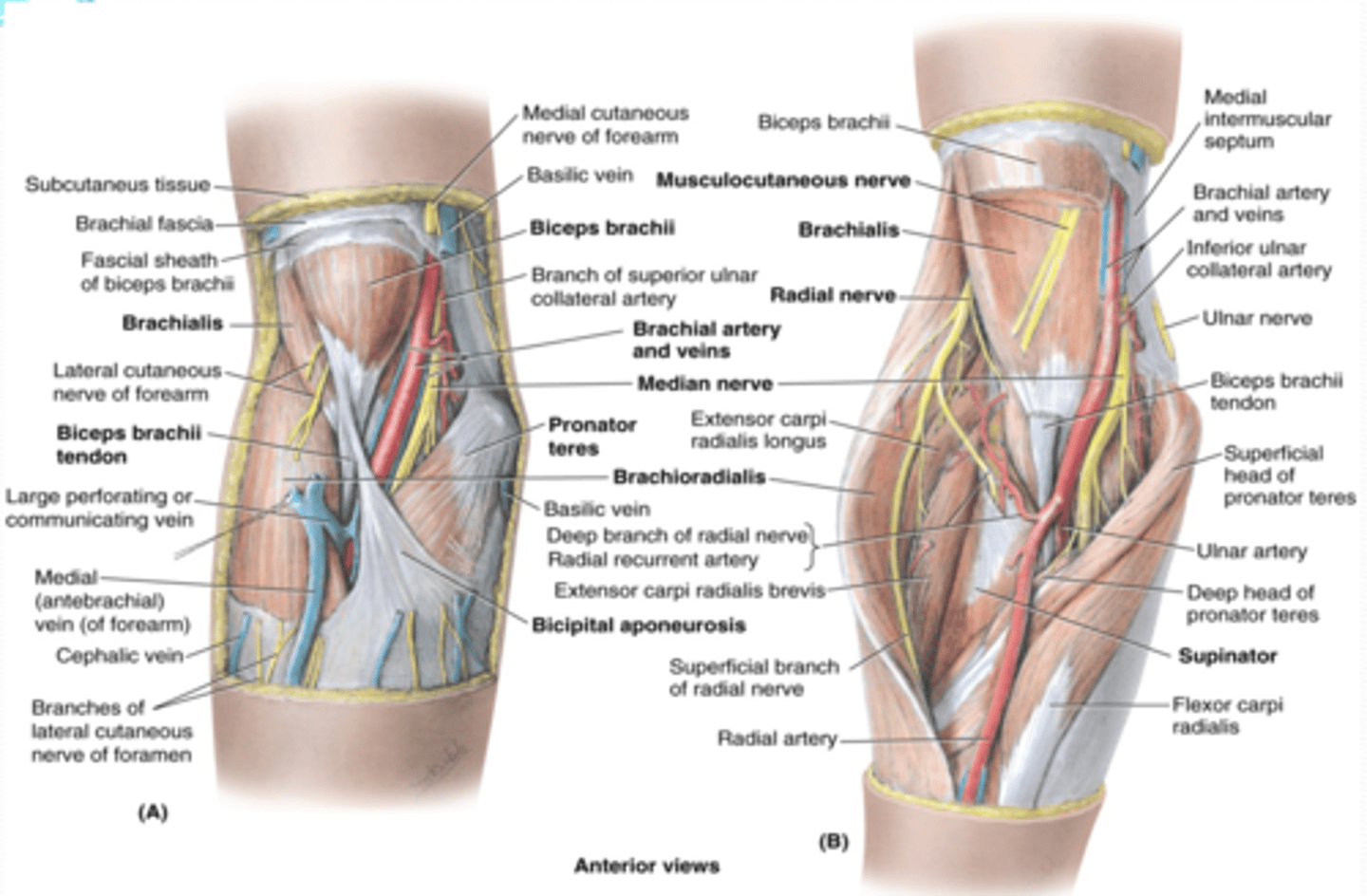
(Cubital Fossa Boundaries:) Superior
imaginary line connecting medial and lateral epicondyles
(Cubital Fossa Boundaries:) Medial
flexors (pronator teres m.)
(Cubital Fossa Boundaries:) Lateral
extensors (brachioradialis m.)
(Cubital Fossa Boundaries:) Flood
supinator m.
(Cubital Fossa Boundaries:) Roof
bicipital aponeurosis
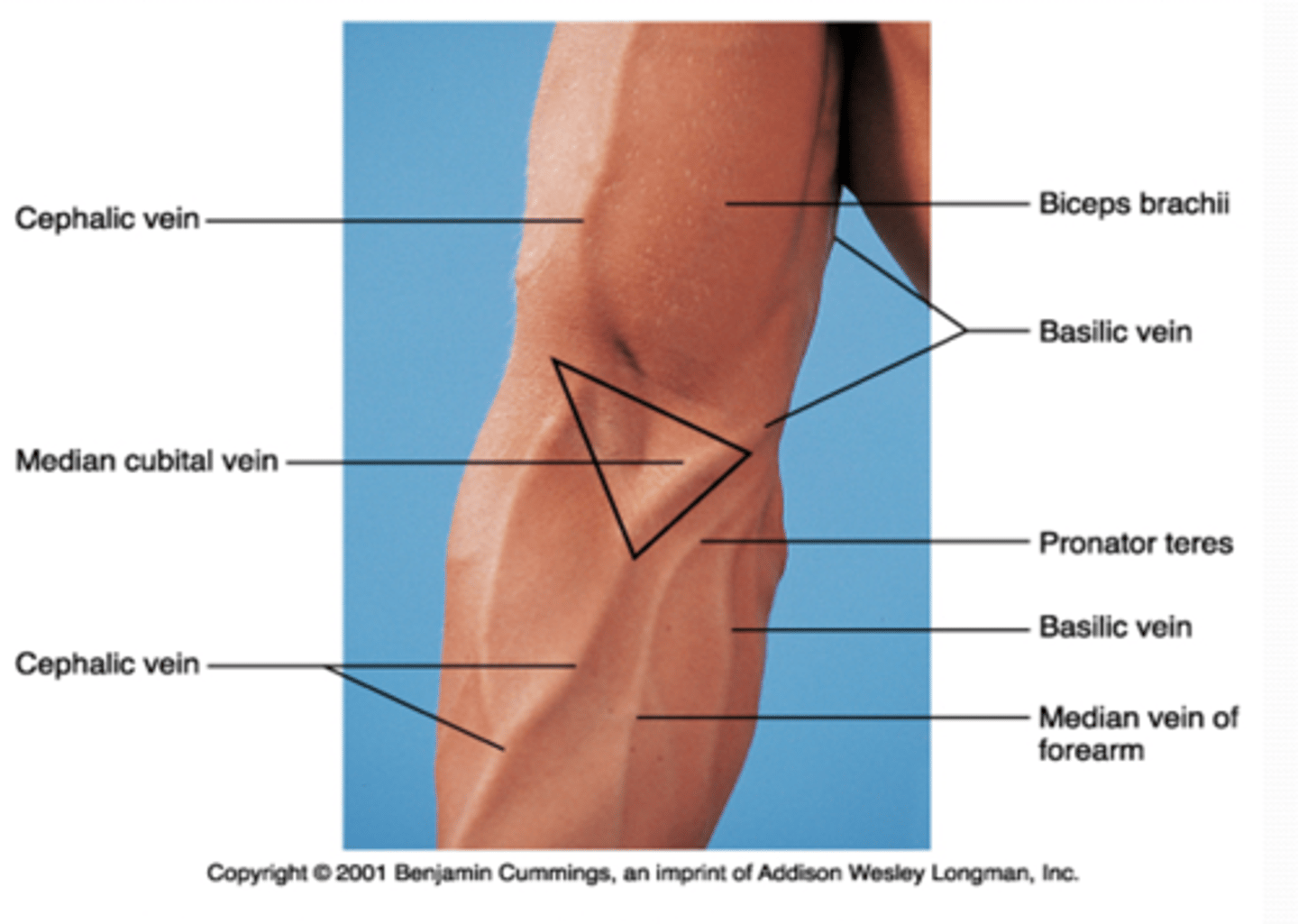
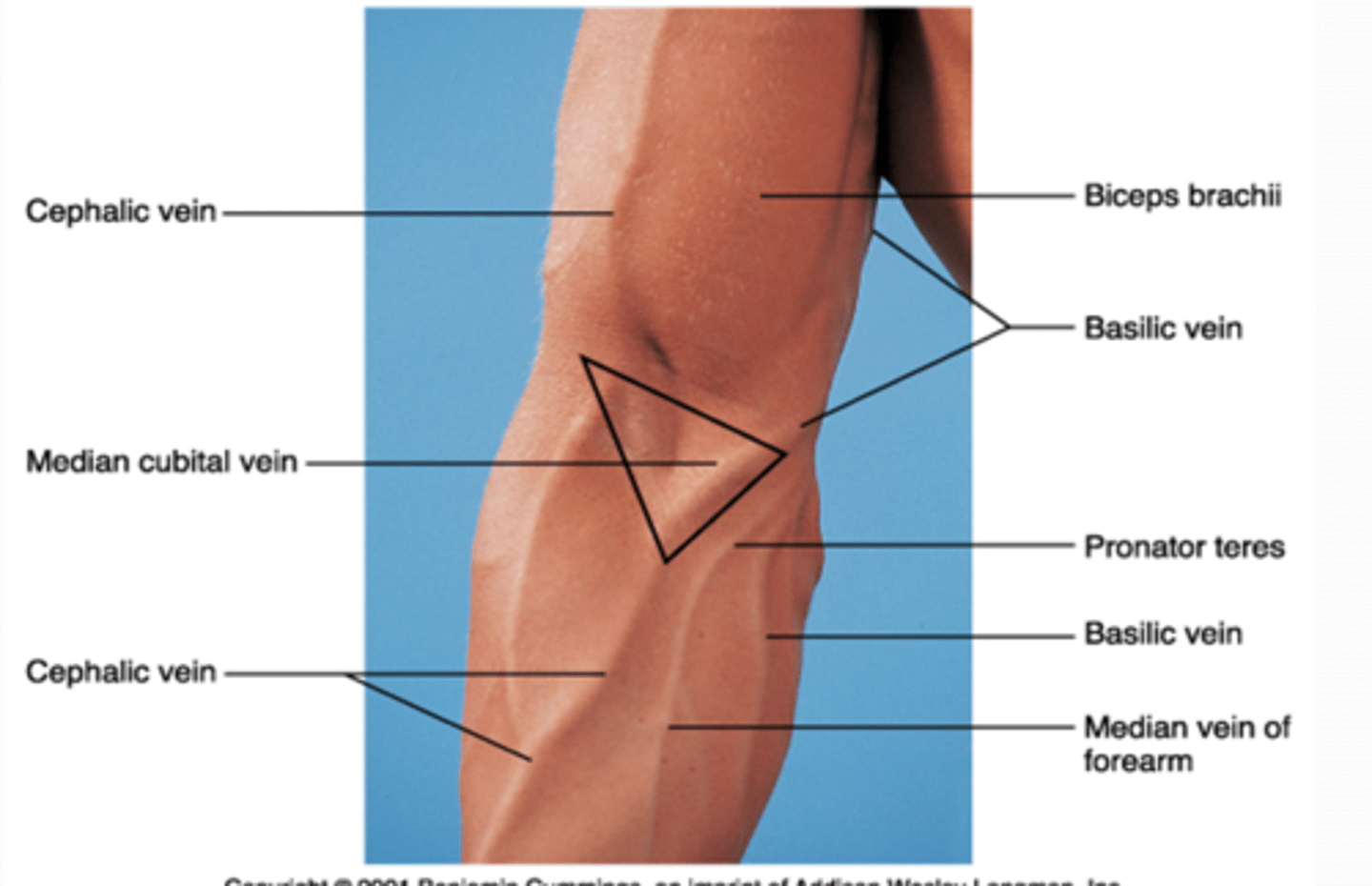
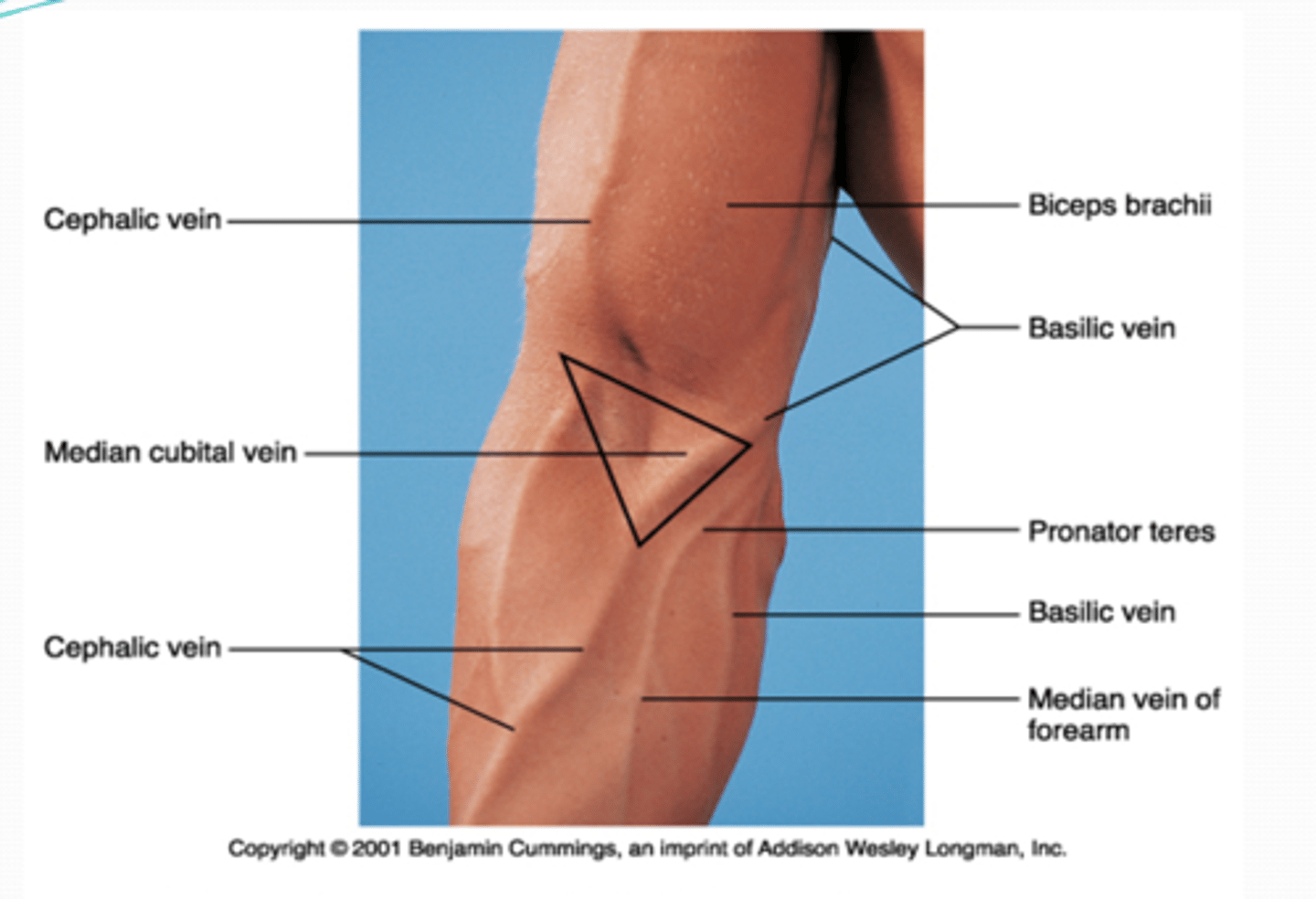
(Upper Limb Vasculature:) Cubital Fossa Content
-Brachial a. dividing into radial and ulnar aa.
-Deep veins accompanying the arteries
-Median nerve
-Radial nerve (deep between extensor muscles forming lateral boundary of fossa)
-Biceps brachii tendon
-Overlying the fossa is the median cubital vein
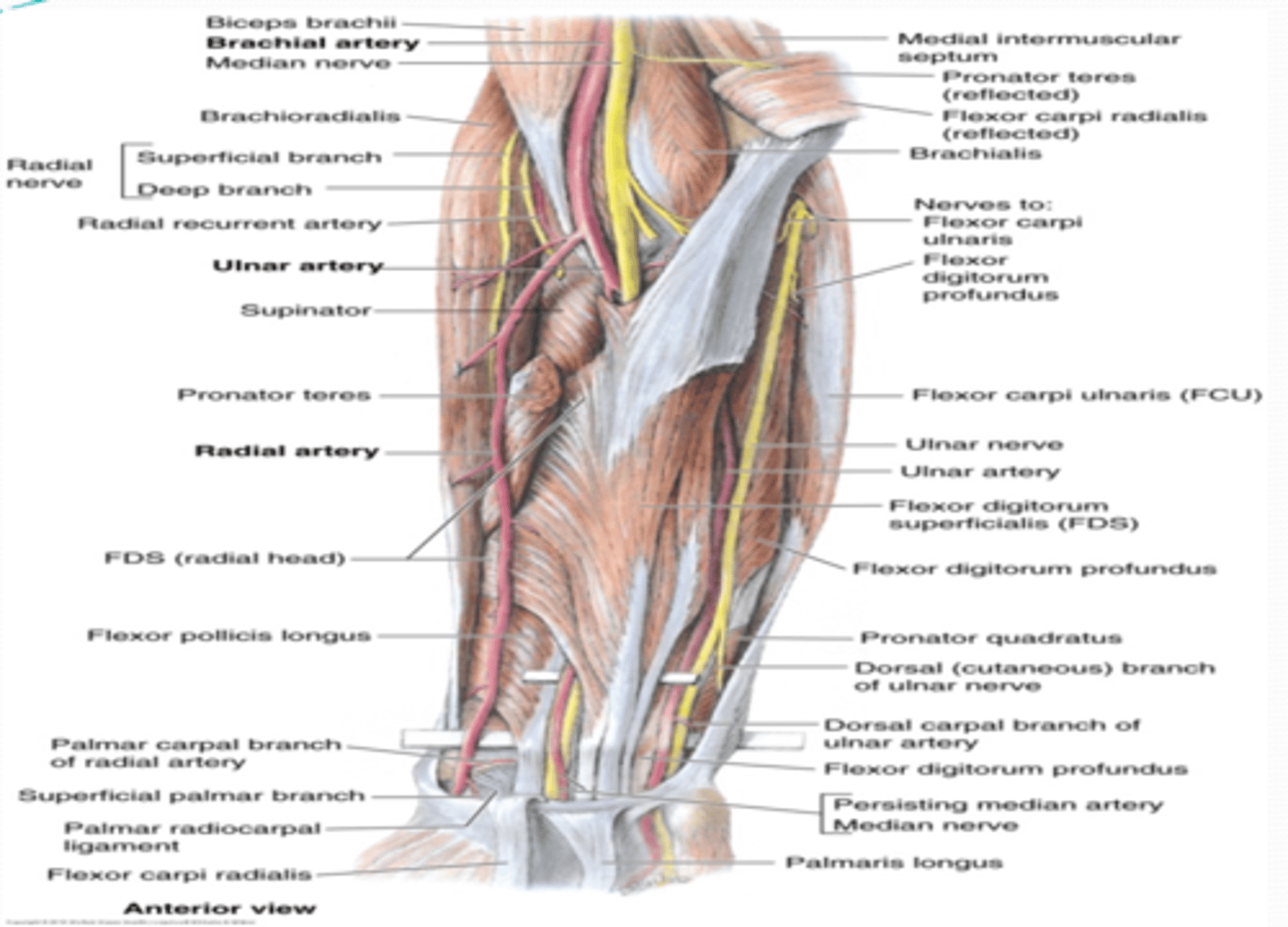
(Upper limb vasculature:) Ulnar artery
Course: largest terminal branch of the brachial a. that arises opposite to the neck of the radius in the inferior part of cubital fossa -> runs inferiorly lateral to the ulnar n. -> and it is superficial to flexor retinaculum when it enters the hand
(Upper limb vasculature Ulnar artery:) Branches
-Anterior and posterior ulnar recurrent aa.
-Common interosseous a.
-Palmar carpal branch
-Dorsal carpal branch
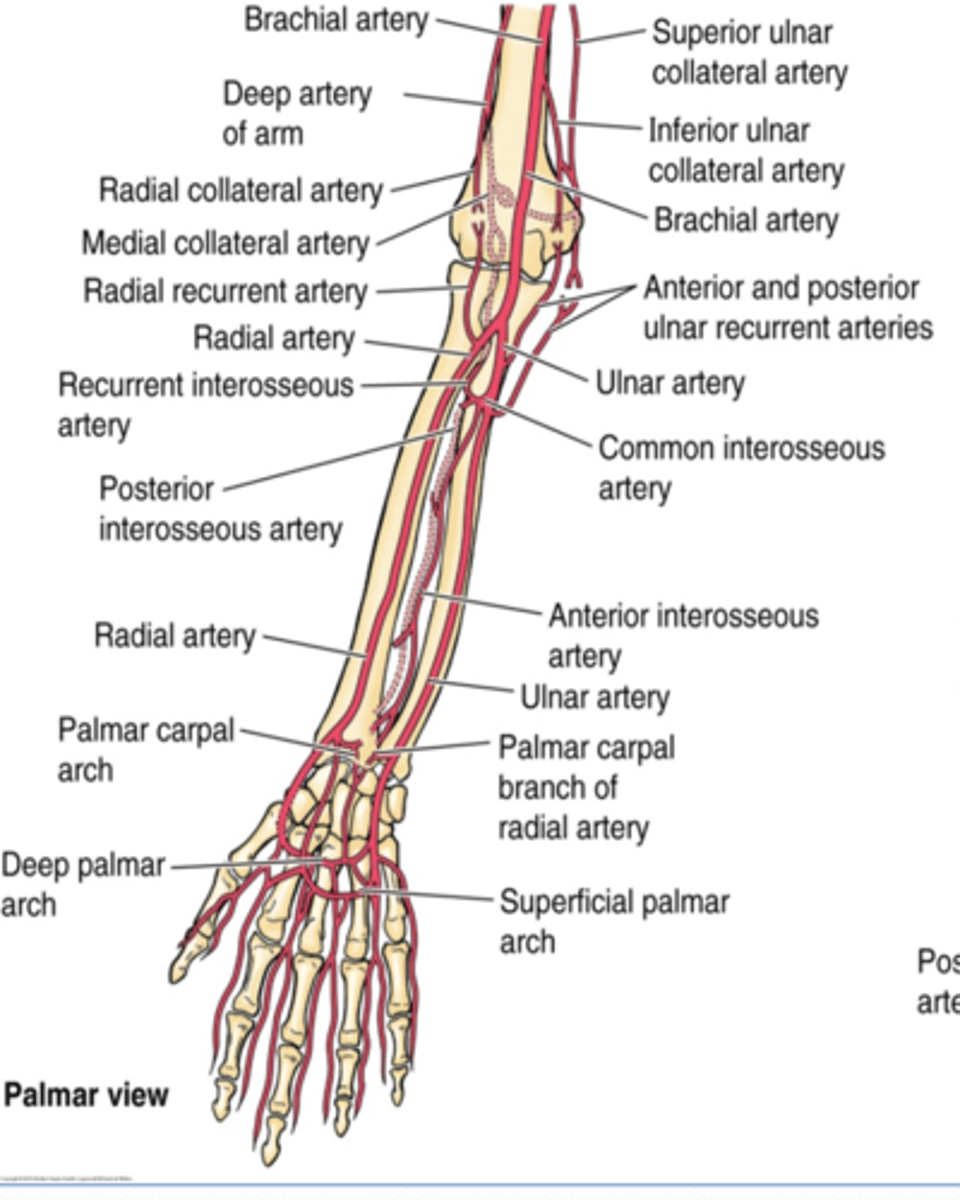
(Ulnar artery Branches:) Anterior and posterior ulnar recurrent aa.
Supply: participate in arterial anastomose around elbow
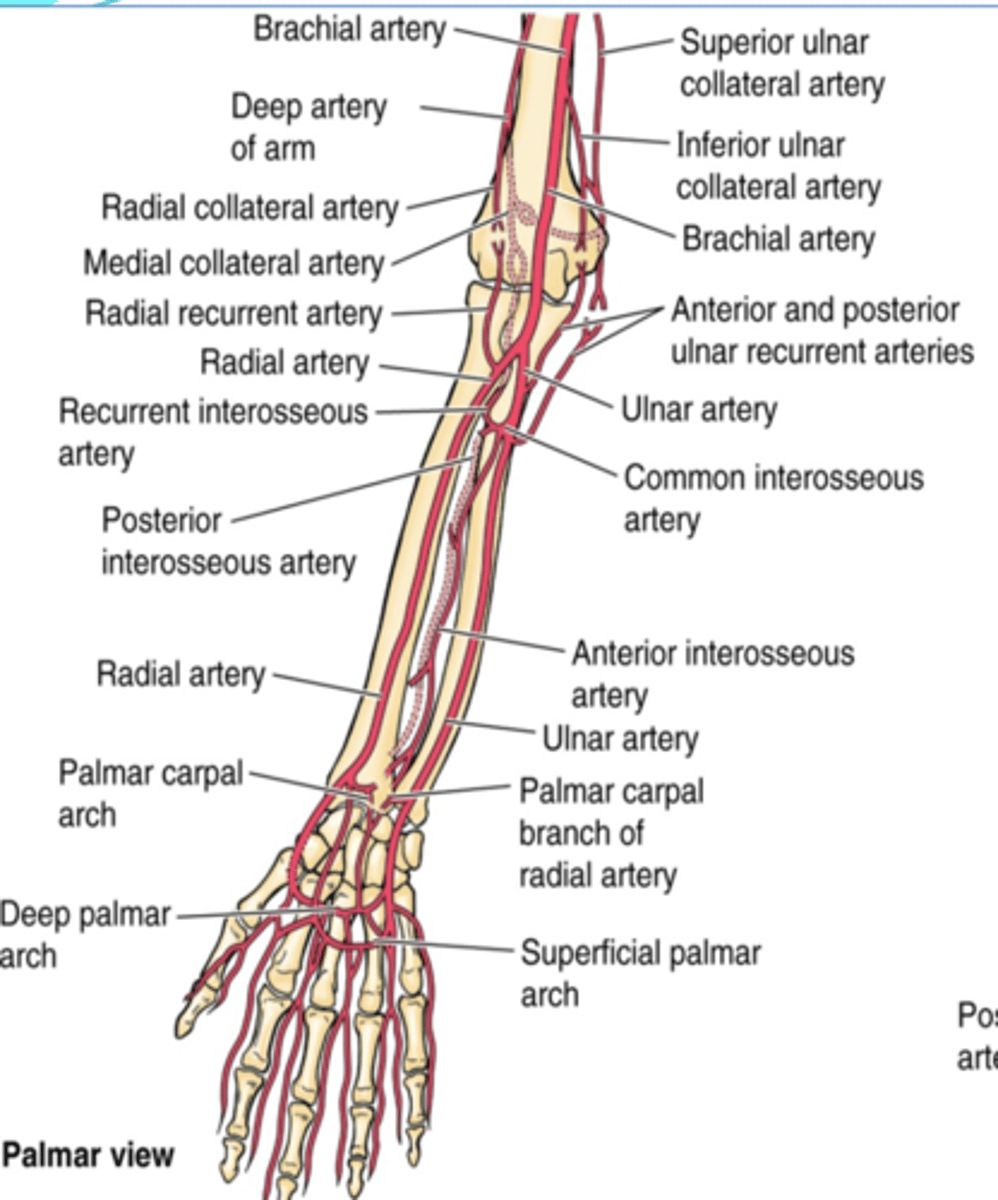
(Ulnar artery Branches:) Common interosseous a.
Course: runs laterally and deeply, and quickly divides
Branches
-Anterior interosseous a.
-Posterior interosseous a.
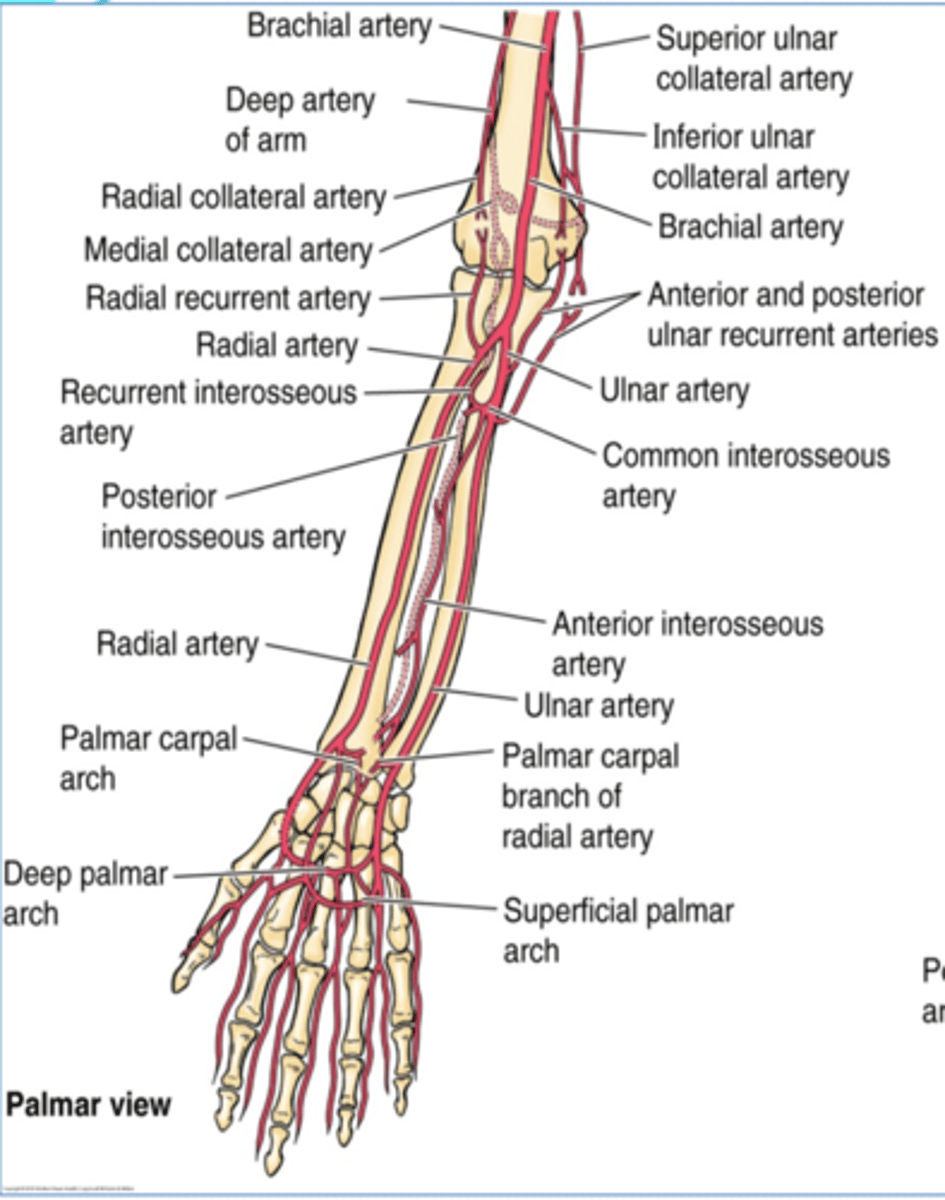
(Ulnar artery: Common interosseous artery's Branches:) Anterior interosseous a.
runs on anterior aspect of interosseous membrane -> pierces the membrane distally to pass posteriorly and join the dorsal carpal arch
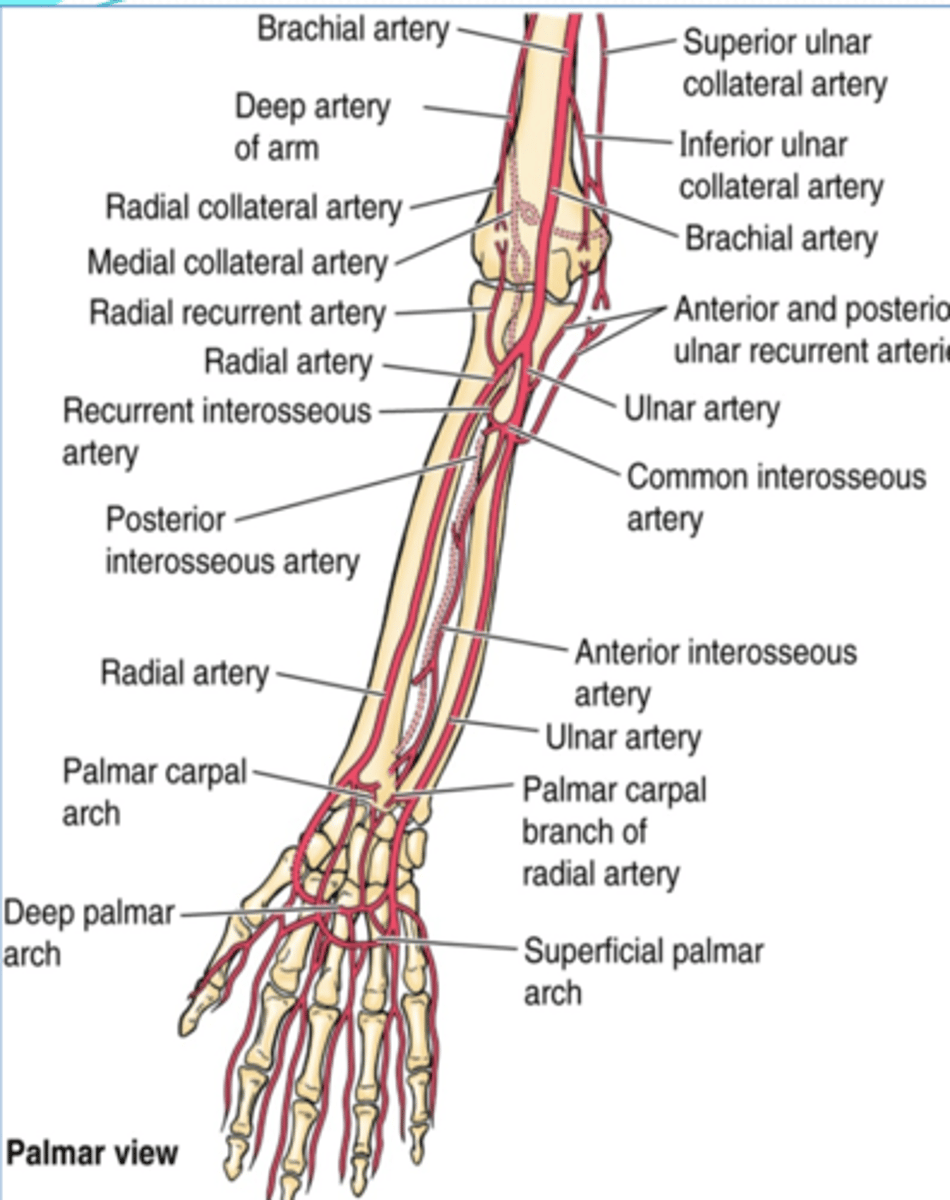
(Ulnar artery: Common interosseous artery's Branches:) Posterior interosseous a.
runs on posterior aspect of interosseous membrane -> it's replaced distally by the anterior interosseous a.
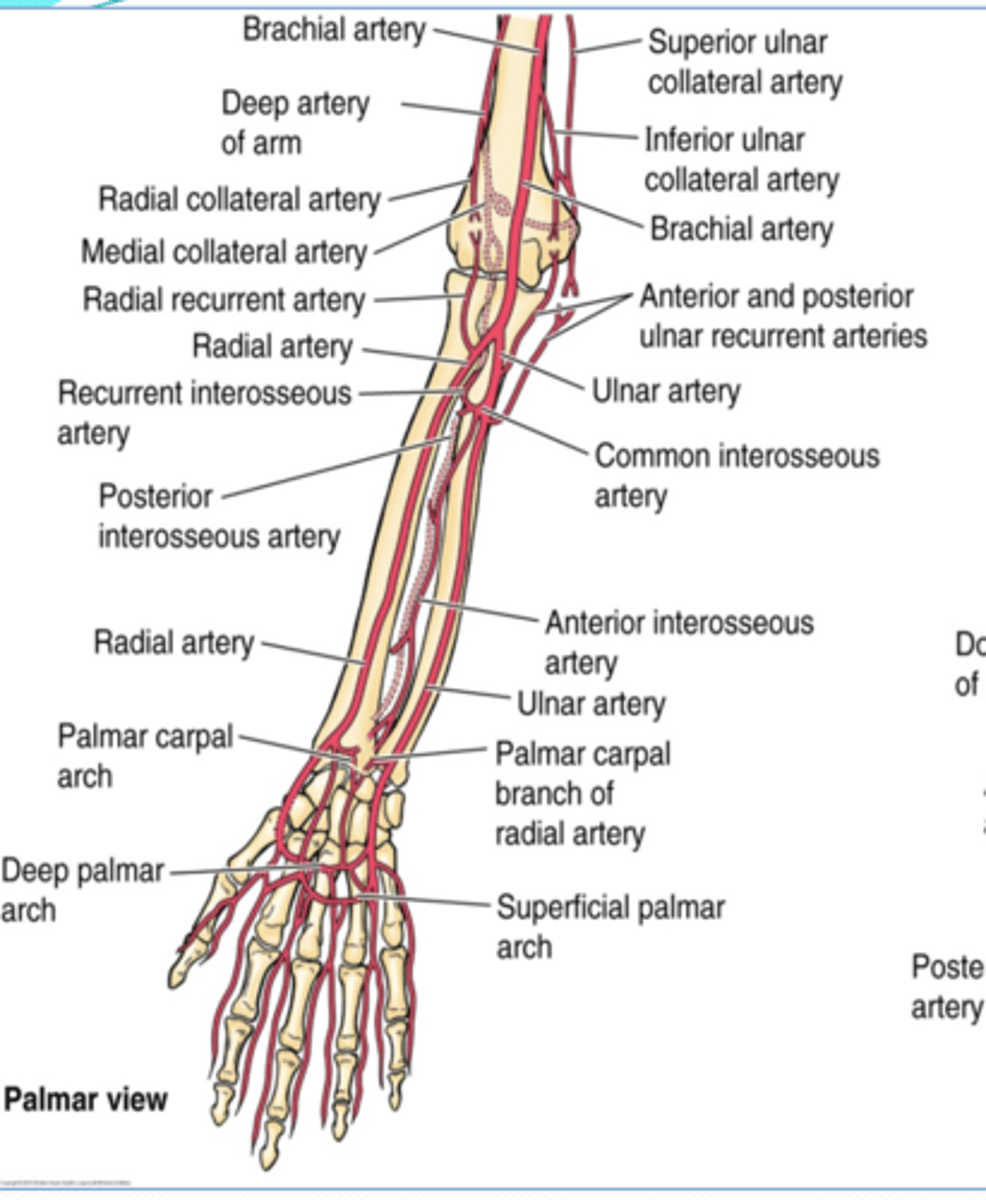
(Ulnar artery Branches:) Palmar carpal branch
Course: runs across anterior aspect of wrist to anastomose with palmar carpal branch of radial a. to form the palmar carpal arch
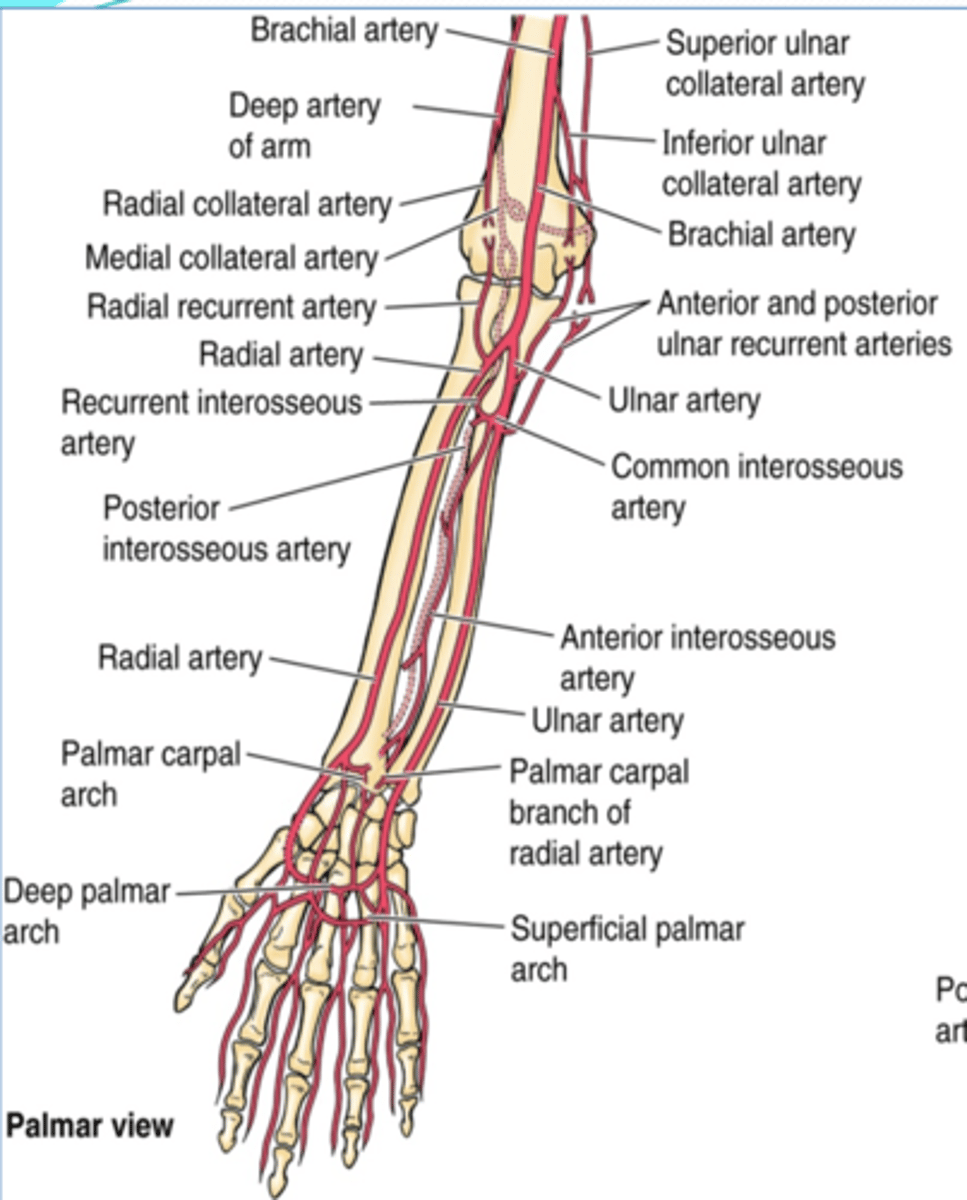
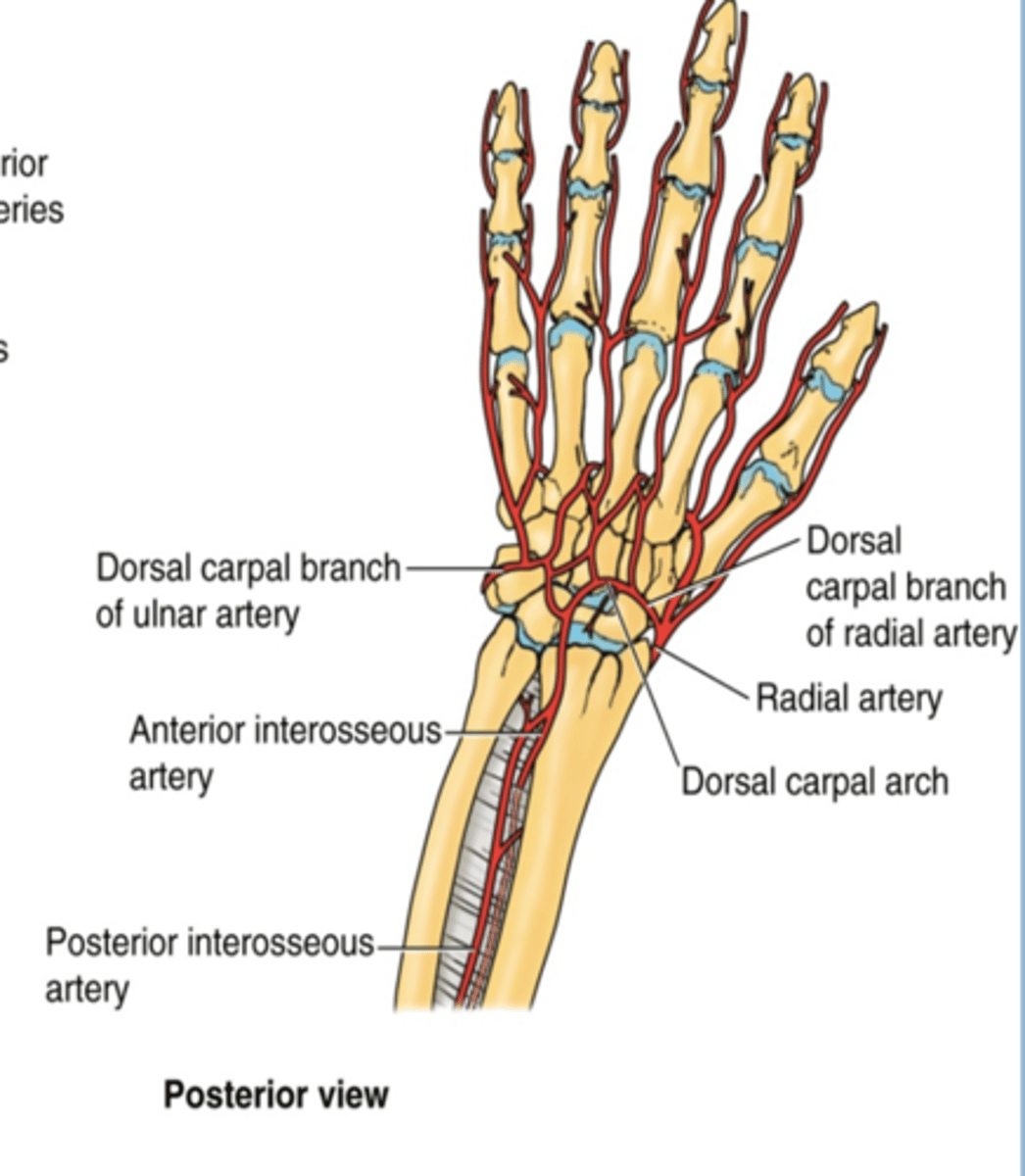
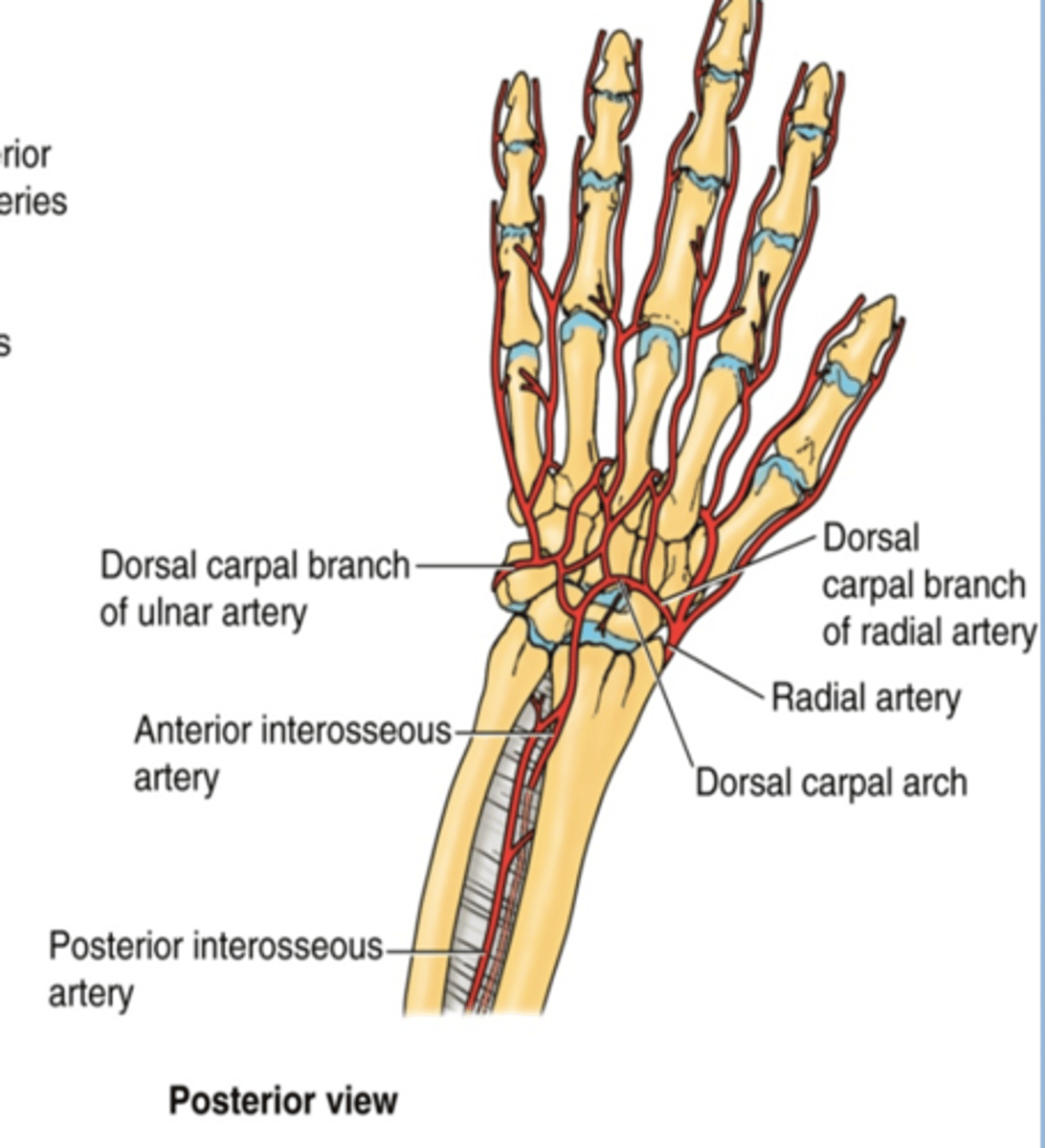
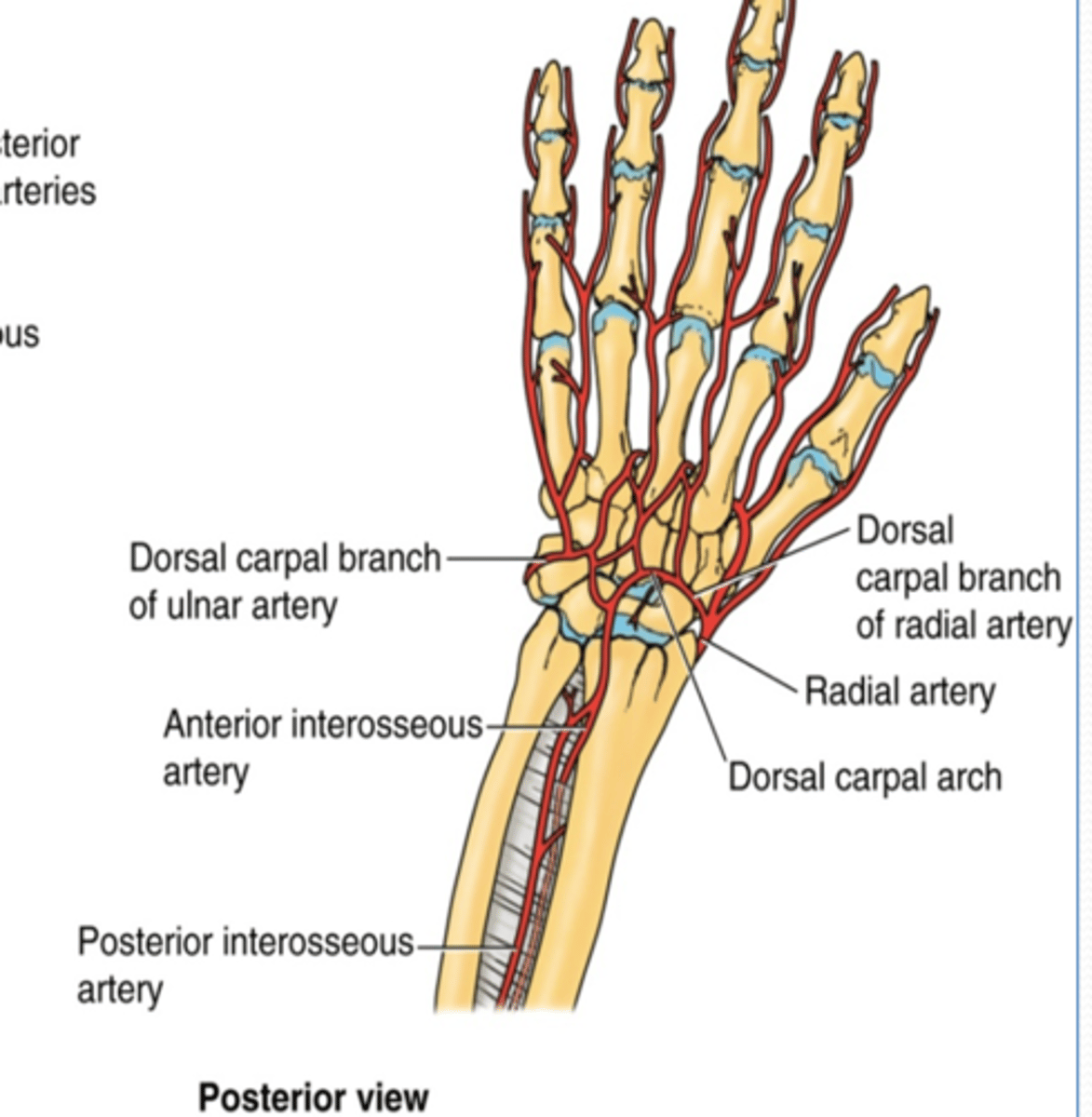
(Ulnar artery Branches:) Dorsal carpal branch
Course: runs across dorsal aspect of wrist to anastomose with dorsal carpal branch of radial a. to form the dorsal carpal arch
(Upper limb Vasculature:) Radial artery
Course: smallest terminal branch of the brachial a. that arises opposite the neck of the radius in the inferior part of cubital fossa -> runs inferiorly and on distal part lies on top of radius (making it easy to check the radial pulse)
(Upper limb Vasculature:) Radial artery branches
-Radial recurrent a.
-Palmar carpal branch
-Dorsal carpal branch
(Radial artery branches:) Radial recurrent artery
Supply: participate in arterial anastomose around elbow
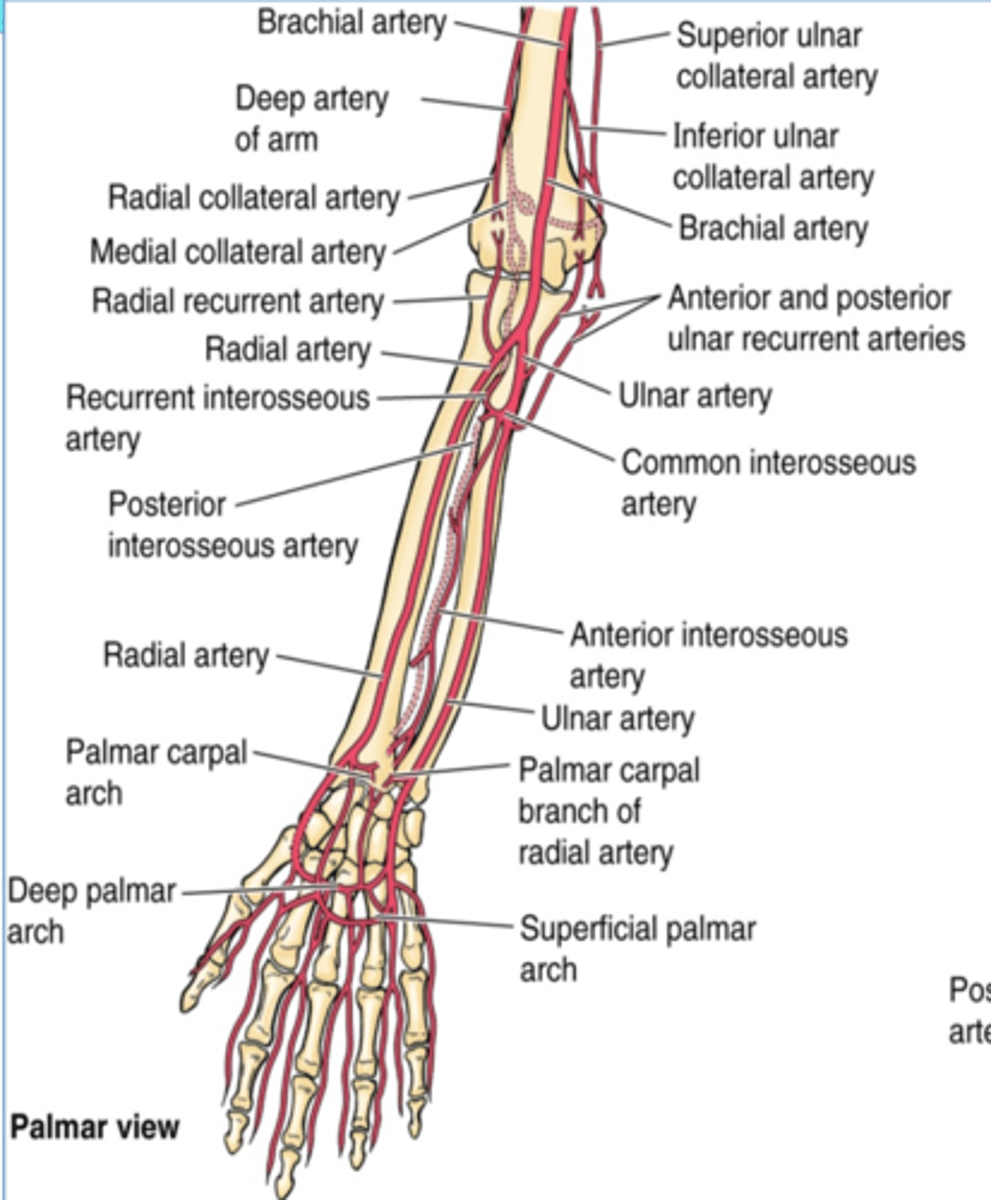
(Radial artery branches:) Palmar carpal branch
Course: runs across anterior aspect of wrist to anastomose with palmar carpal branch of ulnar a. to form the palmar carpal arch
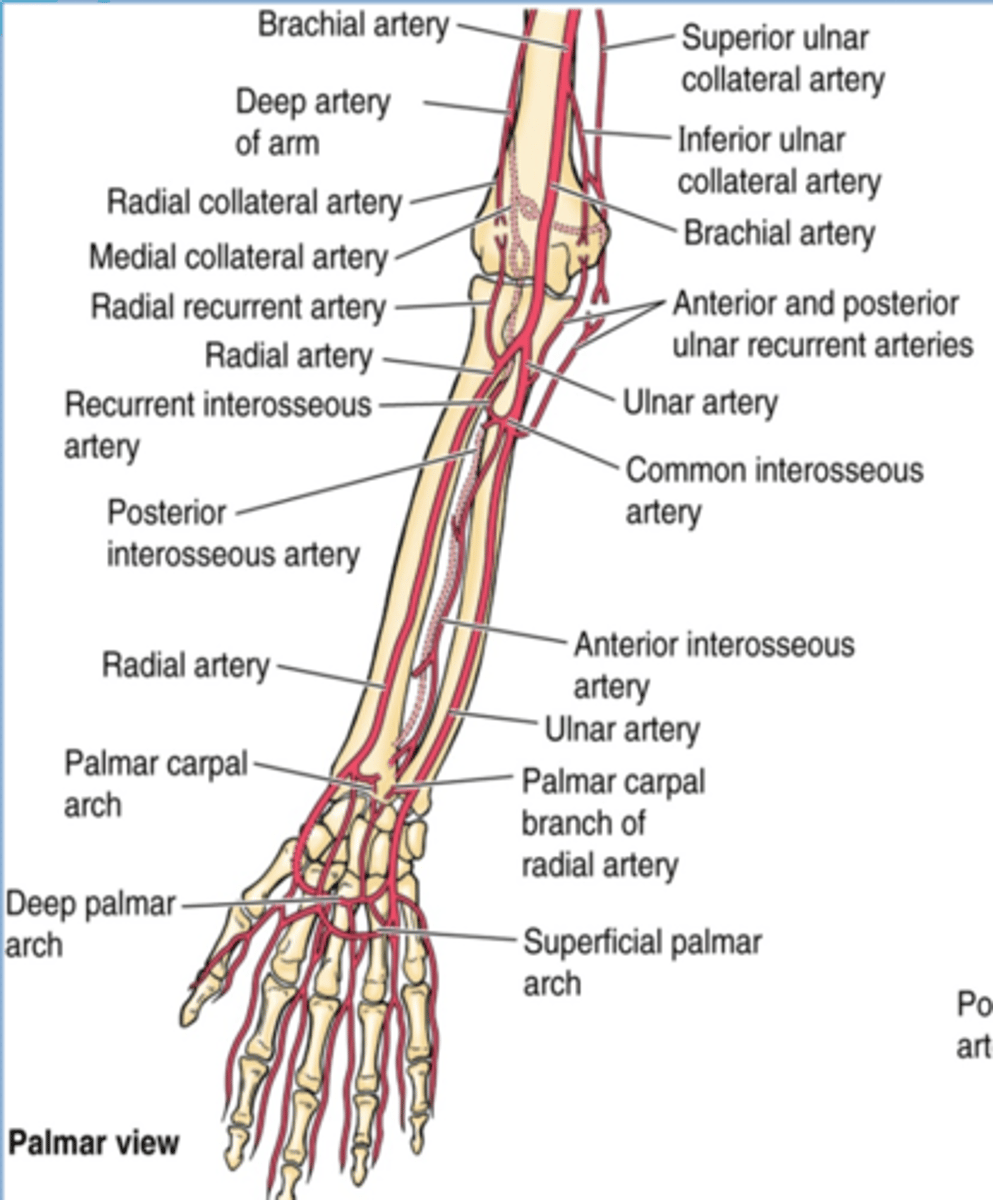
(Radial artery branches:) Dorsal carpal branch
Course: runs across dorsal aspect of wrist to anastomose with dorsal carpal branch of ulnar a. to form the dorsal carpal arch -> dorsal metacarpal aa.
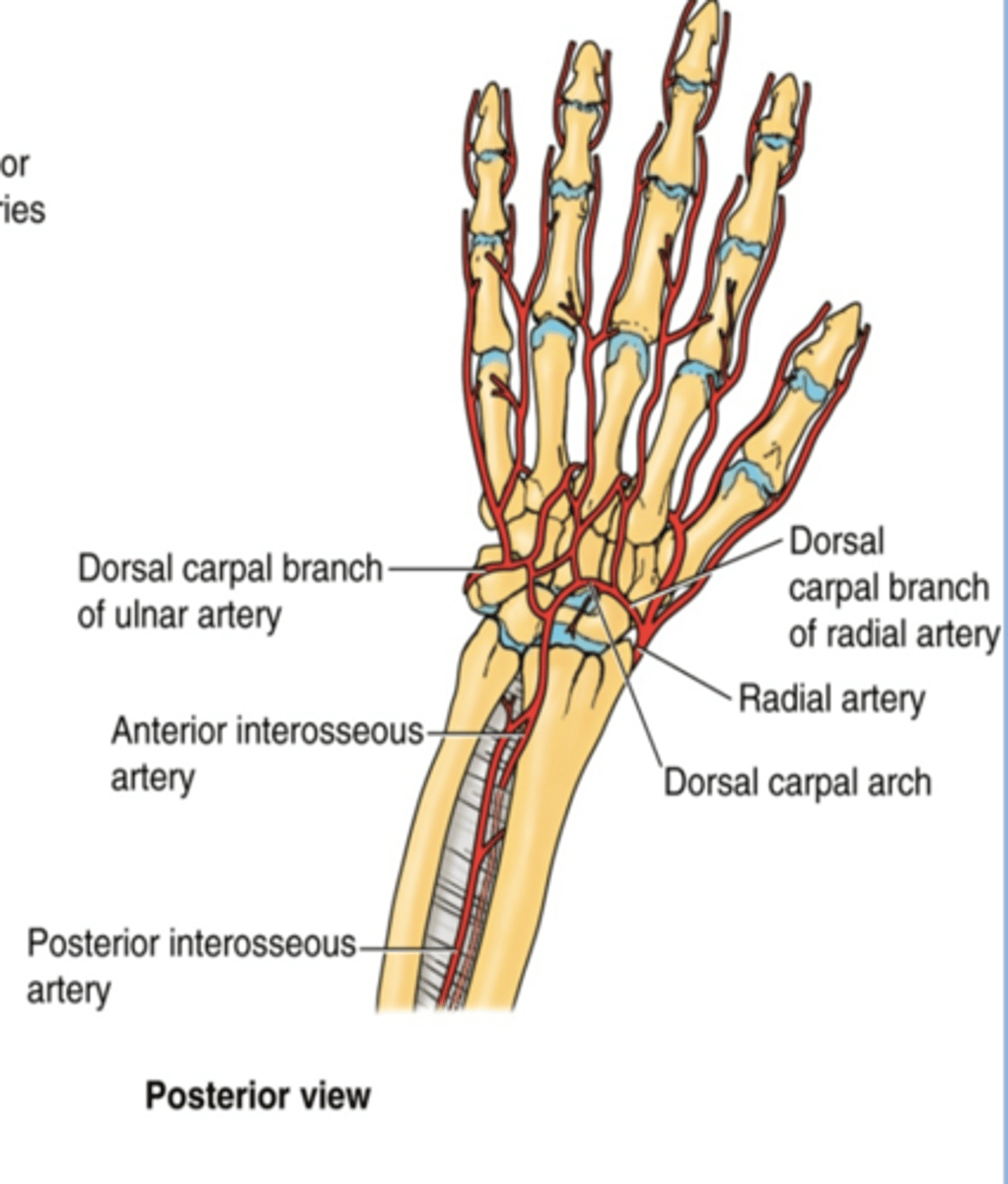
(Upper Limbs Vasculature:) Termination of ulnar and radial arteries in the hand
-Ulnar branches
-Radial branch
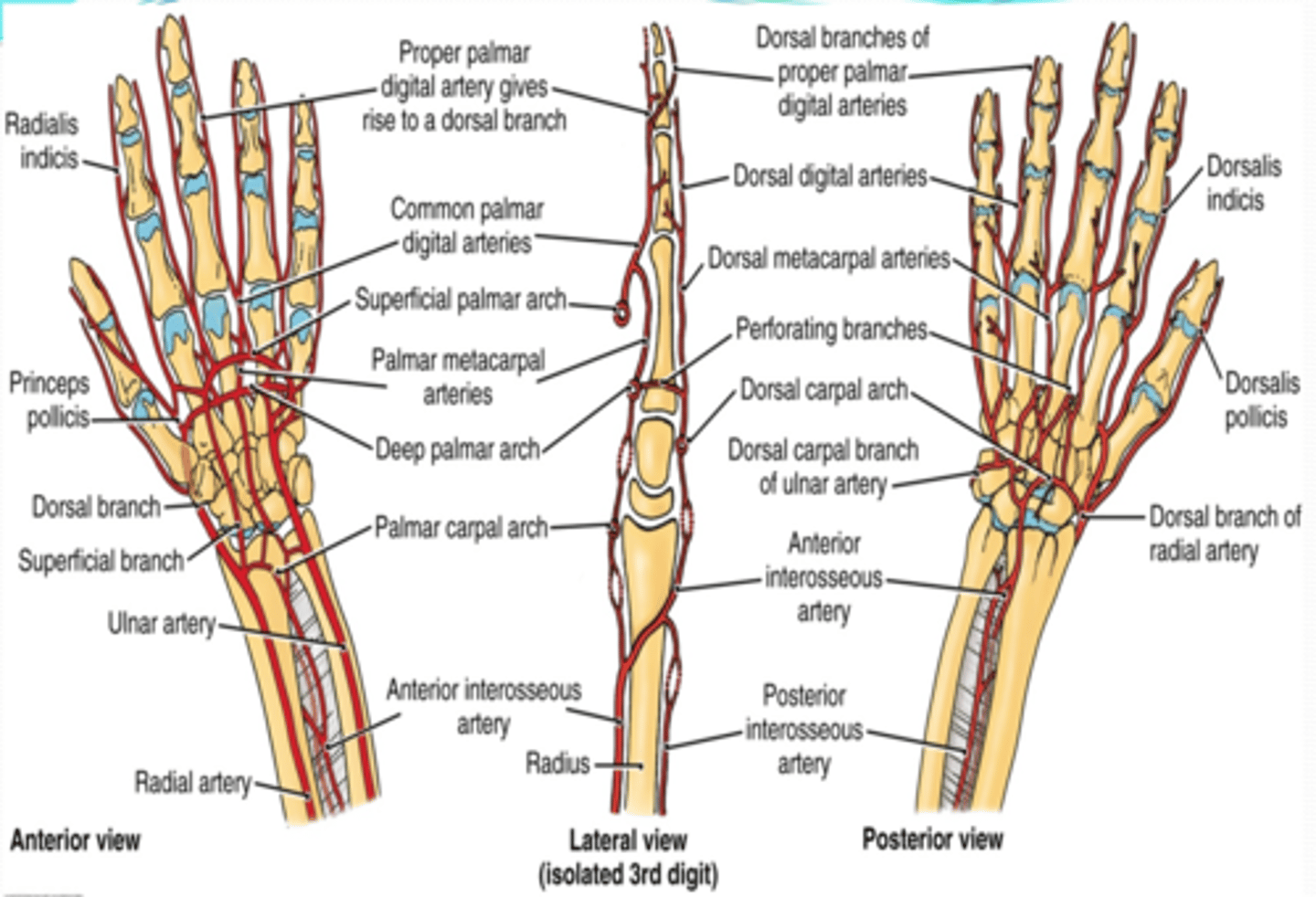
(Termination of ulnar and radial aa. in the hand:) Ulnar branches
Superficial palmar branch
Deep palmar branch
Superficial palmar arch -> palmar digital aa.
Deep palmar arch -> palmar metacarpal aa
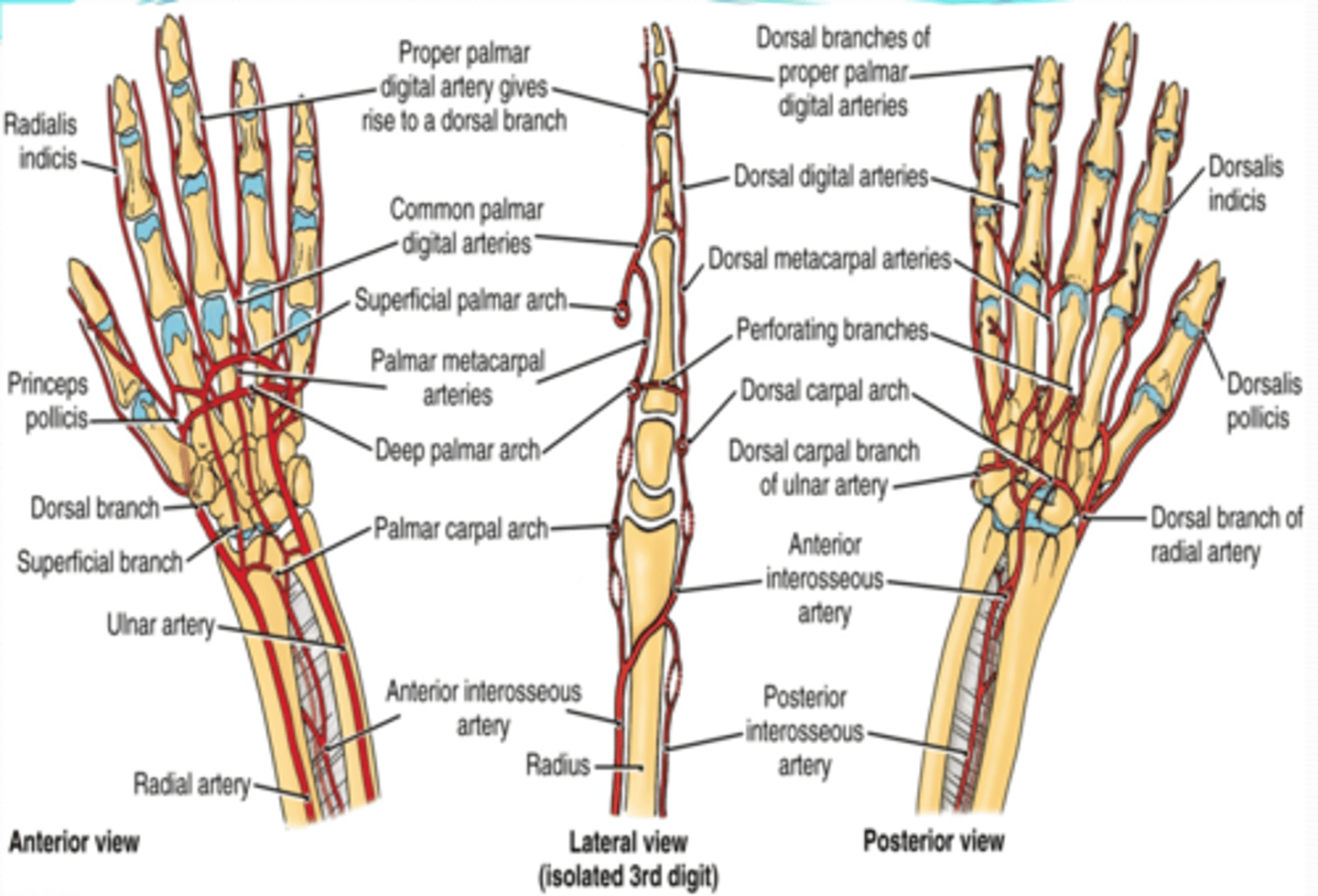
(Ulnar A branches/termination:) Superficial palmar branch
Main termination of ulnar a. that forms the superficial palmar arch
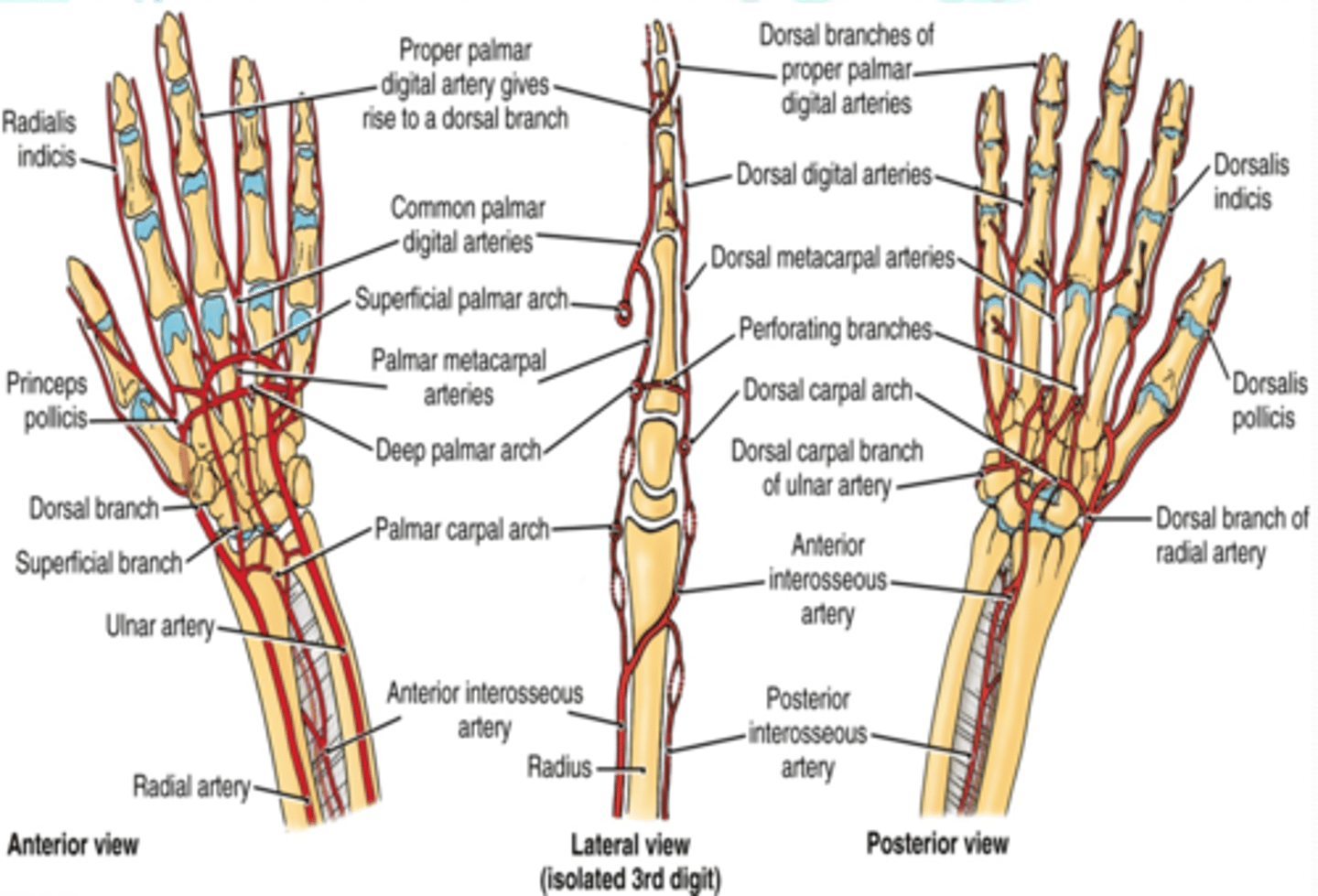
(Ulnar A branches/termination:) Deep palmar branch
Course: anastomose with the deep palmar arch of the radial a.
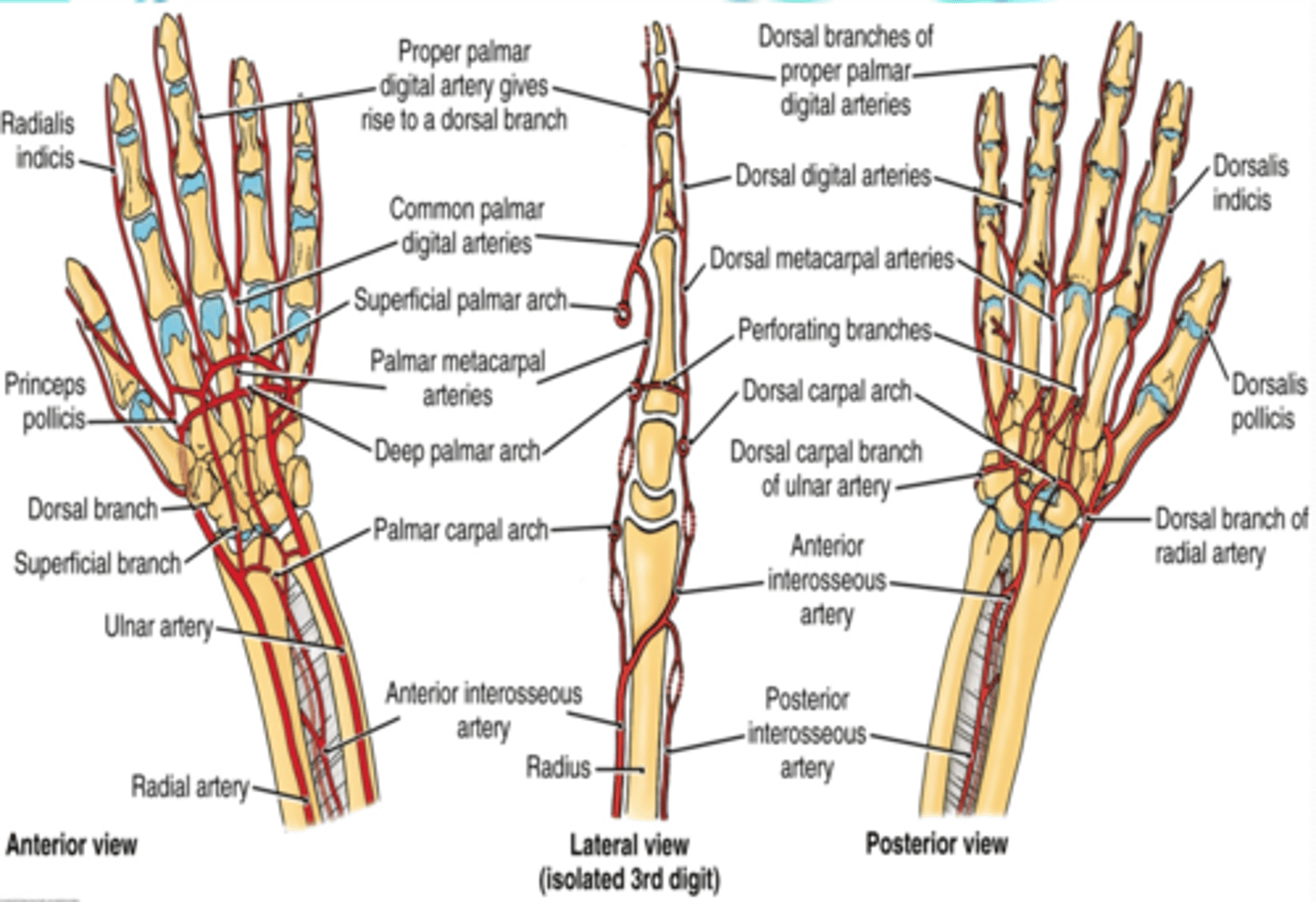
(Termination of ulnar and radial aa. in the hand:) Radial branch
Superficial palmar branch
Deep palmar branch
(Radial branches/termination:) Superficial palmar branch
Main termination of radial a. that forms the superficial palmar arch
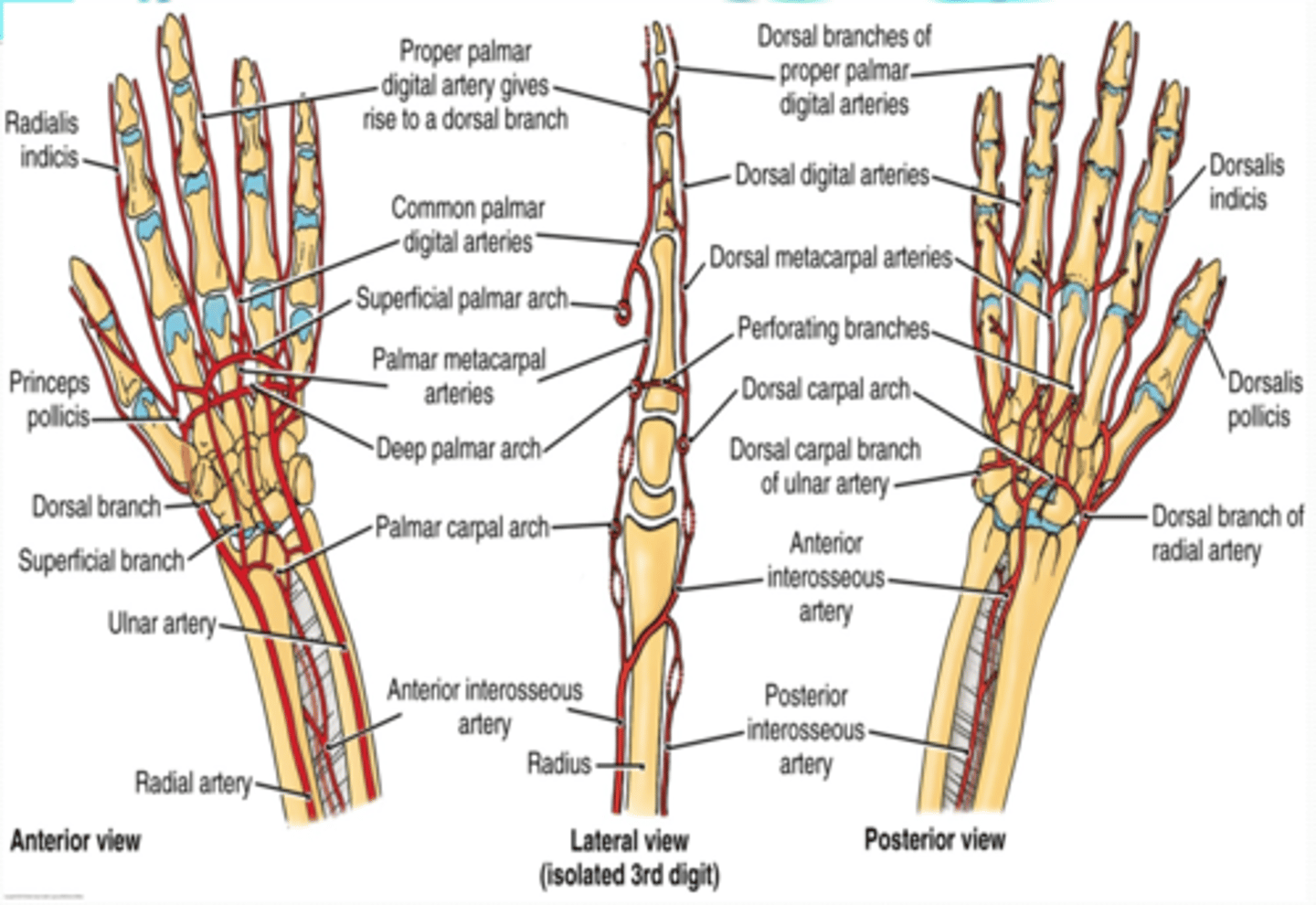
(Radial branches/termination:) Deep palmar branch
Termination of radial a. that forms deep palmar arch
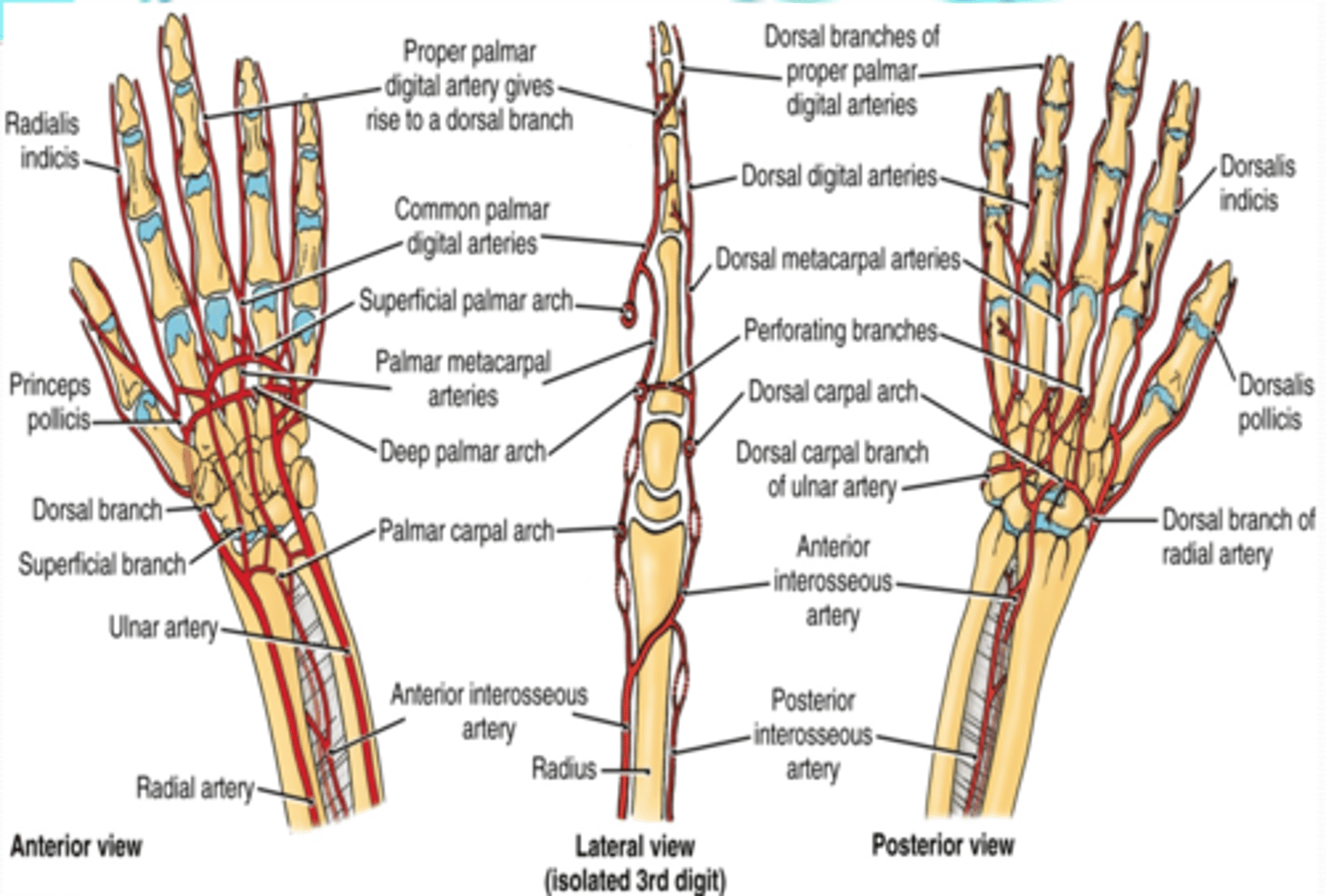
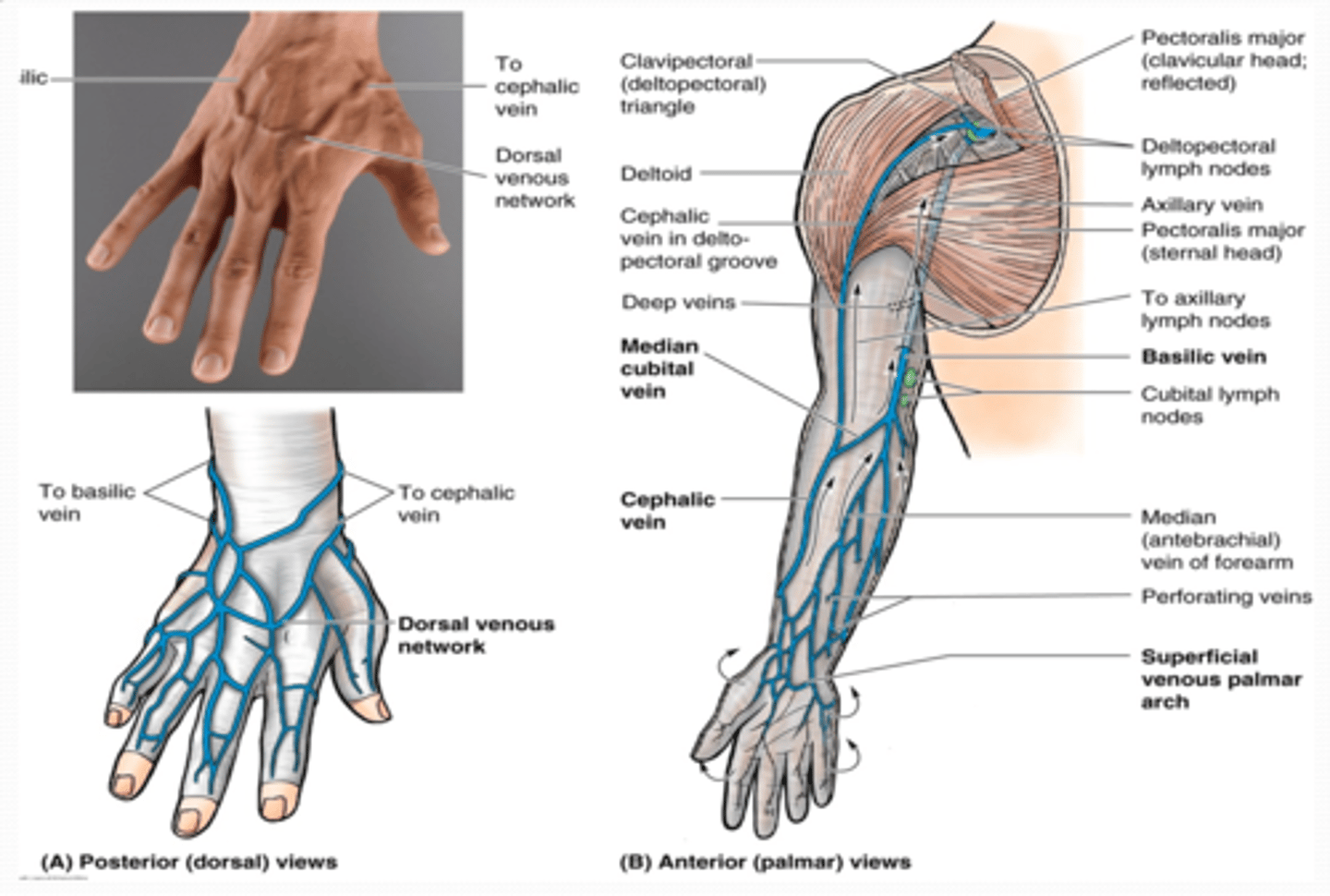
Deep venous drainage
•Lie internal to deep fascia
•Travel with and bear the same name as the major arteries of the UL
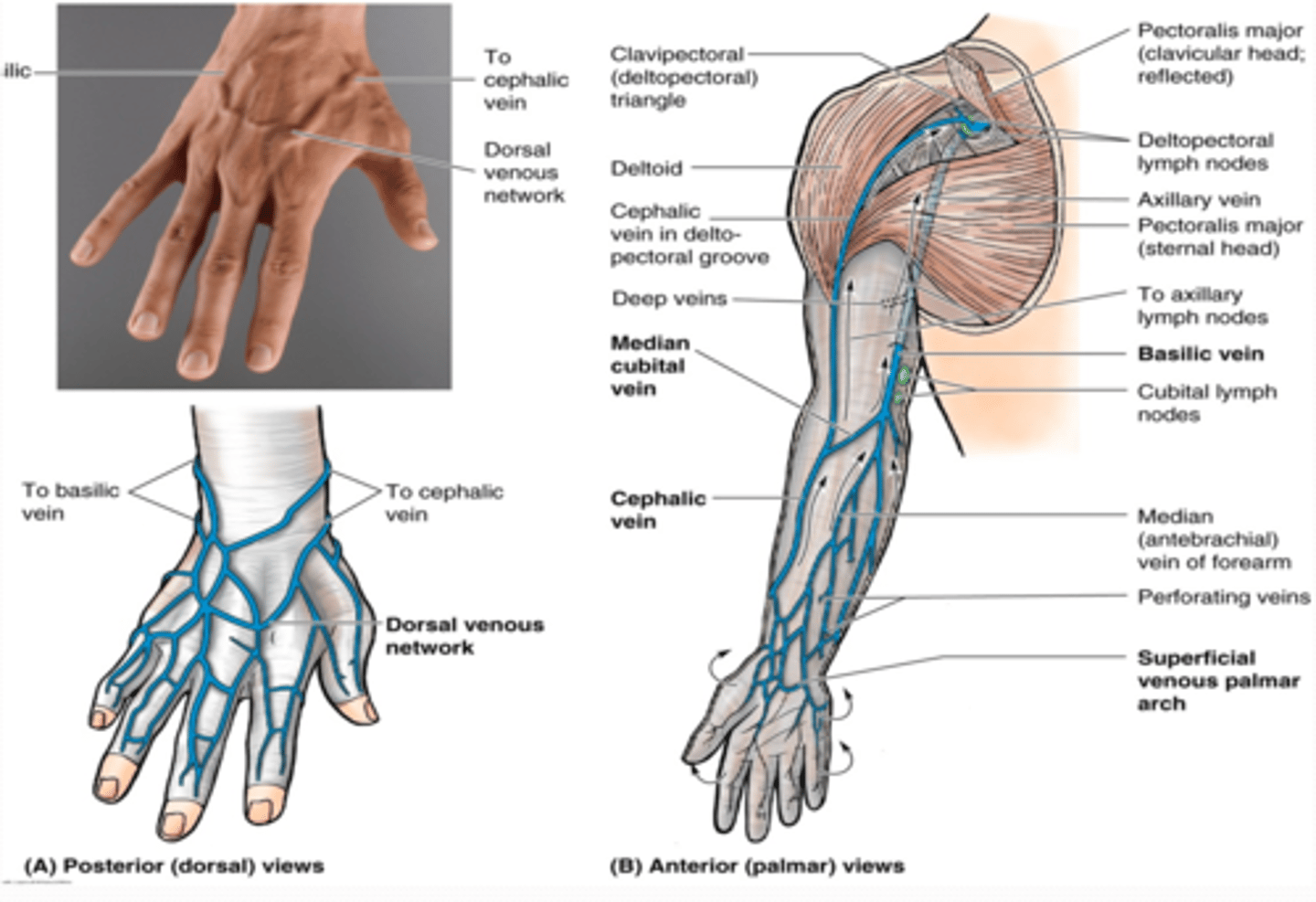
Superficial venous drainage
•Dorsal venous network
Formed on the dorsum of hand from digital and metacarpal veins